Wales Puts Another Pumped Storage Hydroelectric Power Station Into Play
This page on World Energy is entitled Fortune Hydro AG and Voith Acquire 450 MW Dorothea Lakes Pump Storage.
This paragraph introduced the article.
Fortune Hydro AG, in collaboration with Voith Small Hydro, has acquired the 450 MW Dorothea Lakes Pump Storage project as part of an £800 million (US$1 billion) strategic investment in renewable energy in the UK.
It looks to me that this was a good buy in July 2023, as after last week, when I wrote Price Framework Paves Way For Vast Electricity Storage Scheme, in response to a UK Government announcement about funding pumped storage hydroelectricity.
These two paragraphs give more details of the project.
Located in Snowdonia, Northern Wales, this green storage facility presents a unique opportunity to integrate wind, solar and hydroelectric power, Fortune Hydro said. The Dorothea Lakes site was one of the largest slate quarries in Europe and the largest in North Wales.
Electricity produced by solar and wind during low demand can be stored until demand is there. This storage allows balancing of the production cycle in the large solar and wind farms in the north against the demand cycle of consumers and businesses in central and southern UK. It will generate up to 600 jobs and bring economic development and new business opportunities to the local community, the company said.
This map shows the location of Dorothea Lakes.
Note.
- Dorothea Lakes is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Menai Strait between Bangor and Caernarfon is at the top of the map.
- It is certainly in a convenient place, with all the wind farms off the North Wales Coast.
At 450 MW, it’s about a third the size of Electric Mountain, so I suspect it could hold about 3 GWh of electricity.
Leisure Market Boom? GWR’s Vision For Direct Bristol-Oxford Services
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Magazine.
This is the first paragraph.
Great Western Railway has hopes on running direct services between Bristol Temple Meads and Oxford from September 14, subject to approval of its new trial proposal by the Department for Transport and Network Rail. The move is a test of growth in demand for leisure travel by train.
It is an interesting idea.
These are some points about the service, given in the article.
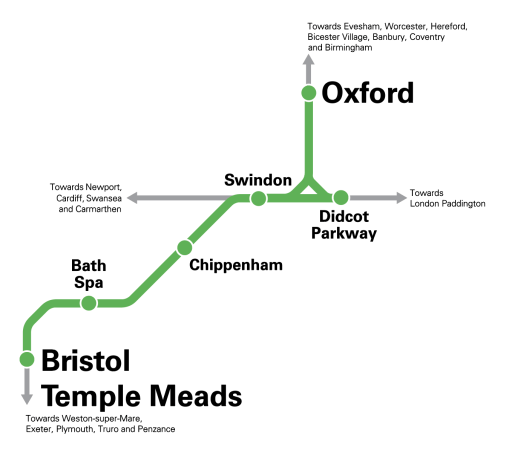
- The route will be via Swindon, Chippenham and Bath Spa.
- Fastest journey time would be 71 minutes.
- The route will be aimed at the leisure market.
- There will be two trains per day (tpd) in each direction on Saturdays.
This is GWR’s handy route map.
These are my thoughts.
Will The Trains Call At Didcot Parkway?
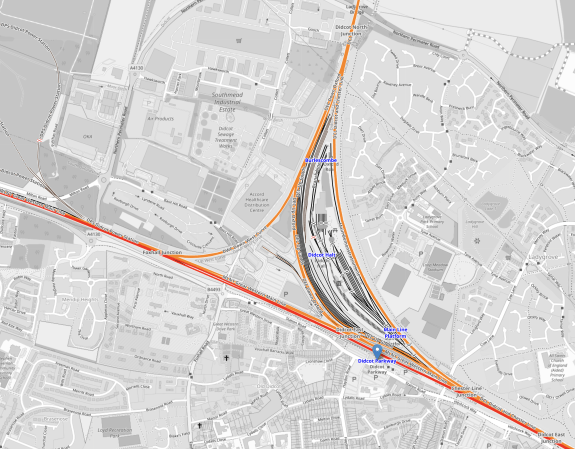
This OpenRailwayMap shows Didcot Parkway station and the large triangular junction, that connects Oxford to the Great Western Main Line.
Note.
- The red tracks are the Great Western Main Line.
- The blue arrow indicates Didcot Parkway station.
- Oxford station is about ten miles to the North.
- Chords in the junction allow trains to go between Oxford and Paddington and Oxford and Swindon, with or without a stop at Didcot Parkway station.
The article says that GWR has asked to run the following services.
- 1018 Bristol Temple Meads-Oxford – Would arrive at Oxford at 1129.
- 1155 Oxford-Bristol Temple Meads (via Didcot) – Would arrive at Bristol Temple Meads at 1306.
- 1518 Bristol Temple Meads-Oxford – Would arrive at Oxford at 1629.
- 1712 Oxford-Bristol Temple Meads – Would arrive at Bristol Temple Meads at 1823.
Note.
- I suspect that the 1155 will reverse at Didcot Parkway station.
- There is a two train per hour (tph) service between Didcot Parkway and London Paddington stations.
- It looks like the four services could be run by a single train shuttling up the Great Western Main Line.
Would it be sensible if all Oxford and Bristol trains called at Didcot Parkway station, so that travellers could use the London service to their advantage?
But, calling at Didcot Parkway station would slow the service as there would need to be a reverse.
What Class Of Train Would Be Used?
Consider.
- A Bristol and Didcot Parkway via Bath Spa service takes 55 minutes.
- This is an average speed of 71.1 mph over a distance of 65.2 miles.
- 24.4 miles at the Bristol end of the route is not electrified.
- 10.3 miles at the Oxford end of the route is not electrified.
- The four services can be run by a single train shuttling up the Great Western Main Line.
It looks to me, that a bi-mode train with good performance is needed.
So I suspect that a five-car Class 800 or Class 802 train will be used.
Will The Train Be Battery-Electric Powered?
This is an interesting possibility.
- An ideal route for a battery electric train, is surely one with a long electrified section in the middle, which can be used to fully charge the train’s batteries.
- The train would have to run for 48.8 miles on its own power at the Bristol end of the route.
- The train would have to run for 20.6 miles on its own power at the Oxford end of the route.
The data sheet for a battery-electric Class 800/802 train can be downloaded from this page on the Hitachi web site.
In a section on the page, which is entitled Intercity Battery Trains, this is said.
A quick and easy application of battery technology is to install it on existing or future Hitachi intercity trains. Adding just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%.
Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance. Hitachi Rail’s modular design means this can be done without the need to re-engineer or rebuild the train and return them to service as quickly as possible for passengers.
The range of 70 km is 43.5 miles, which would appear to be a little bit short to go from the end of the electrification at Chippenham to Bristol Temple Meads and back.
But various measures could be taken to make sure the train can handle the route.
- The regenerative braking strategy could be used to conserve battery power.
- A second battery could be added to the train.
- Methods to charge the train at Bristol Temple Meads could be installed.
As London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads is an important route, I suspect that Hitachi and Great Western Railway have a strategy to handle trains from Chippenham and sending them back.
Could This Route Be A Trial Route For Battery-Electric Trains?
Consider.
- Hitachi and Great Western Railway wouldn’t want to introduce an unreliable train without full full testing.
- Trains can probably limp to either Stoke Gifford or Reading depots, after a battery failure.
- Great Western Railway could test a new route.
- A full test only needs one train.
- Passenger reaction to a battery-electric train can be assessed.
- Staff need to be trained.
- The route can be run by a standard bi-mode if required.
- It could be the world’s first high-speed battery-electric train.
- Enthusiasts would flock to have a ride.
Could this be a trial service to make sure everything goes right?