Excitement Brewing for Gateshead FC Away At Wembley
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item on Lumo.
This is the sub-heading.
Lumo, the Open Access rail operator, has teamed up with local Gateshead brewery Black Storm to offer Gateshead FC fans a special commemorative beer onboard its trains.
These first two paragraphs add a few more details.
Hot on the heels of Tyneside based Lumo, the Open Access rail operator, announcing an extra train on Saturday 11th May to get Gateshead FC fans back from London as part of the club’s huge achievement of a second Wembley FA cup final in as many years, they’ve teamed up with local Gateshead brewery Black Storm to offer fans and travellers a special commemorative beer onboard its trains.
The appropriately named’ Whistle Stop’ is a 5% ABV Helles Lager featuring special commemorative Gateshead FC Wembley 2024 and Lumo branding on the can and will be available to purchase on the LumoEats at seat trolley service on all Lumo trains from this week, including on its specially named ‘Heed Army Express’ trains on Saturday 11th (running from Newcastle to London at 07:12 and 10:22, and returning at 20:26).
Surely, rail companies should do more deals like this to support local teams and suppliers.
Feadship Ushers In The Fuel-Cell Era With The Launch Of118.80-metre Project 821
The title of this post, is the same as this press release from Feadship.
This picture from Feadship shows project 821.
These are the first two paragraphs of the press release.
When the drydock doors slid open on 4 May at Feadship’s Amsterdam shipyard, the yachting
world was forever changed. Say hello to Project 821, the world’s first hydrogen fuel-cell
superyacht. Five years in the making, innovation-packed Feadship Project 821 is the answer to
a fundamental question: “How far can we push green technology on superyachts?”Designed by RWD and with owners representation by Edmiston, Feadship’s bold response was
a multi-faceted, zero-diesel approach designed to cruise between harbours or anchorages and
to operate the yacht’s hotel load and amenities with emission-free power from green hydrogen.
“The aim has been to develop a new, clean technology not just for this project, but for the
world,” said Jan-Bart Verkuyl, Feadship Director / CEO Royal Van Lent Shipyard. The size of
the proposed yacht – 100-metres-plus – made it a good candidate to explore pure green
hydrogen as the fuel-cell source. For those captivated by cutting-edge innovations, this yacht
presents an opportunity for potential acquisition as it showcases the pinnacle of modern
technological advancements.
As the superyacht is 118.8 metres long, I can see a lot of ships of this size being powered by hydrogen.
Klaipėda – Kyiv Rail Freight Plan
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
These two paragraphs give more details.
Lithuania’s national train operator LTG Group and Ukrainian Railways have signed a memorandum of understanding to develop an intermodal freight service from the Baltic port of Klaipėda to Kyiv via Poland.
Test runs are planned for this year, ahead of regular services.
I have some thoughts.
The Route
This Google Map shows the route.
Note.
- Russia is in the North-East corner of the map, with Moscow clearly marked.
- Lithuania is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Klaipėda is on the Lithuanian coast.
- South-West of Lithuania is the Kaliningrad enclave, which is part of Russia.
- South of the Kaliningrad enclave is Poland, where Gdansk, Warsaw and Krakow are clearly marked.
- Belarus is in the middle of the map, with Minsk clearly marked.
- Ukraine is South of Russia and Belarus and East of Poland.
- Dnipro, Kharkiv, Kyiv and Lyiv in Ukraine are clearly marked.
It looks to me, that a possible route would be along the Eastern Polish Border avoiding both Belarus and the Kaliningrad enclave.
The Gauges
This Google Map shows the gauges between Klaipėda and Kyiv.
Note.
- Black tracks are Standard gauge of 1435 mm.
- Red tracks are Russian gauge of 1520 mm.
- Klaipėda is on the Lithuanian coast in the North-West corner of the map.
- Kviv is in the South-East corner of the map.
It looks to me, that although Lithuania and Ukraine are Russian gauge, the routes through Poland could be standard gauge.
So there may be a need for some rolling stock, that can run on both Russian and Polish gauges.
This article on Railway Gazette is entitled Ukrainian Railways Produces Cross-Border Grain Wagon.
These two paragraphs describe the wagons.
National railway Ukrzaliznytsia has used mostly domestic components to produce a grain hopper wagon which can operate on both the former USSR’s 1 520 mm broad gauge and the 1 435 mm standard gauge of neighbouring EU countries.
The Type 19-8005-U wagon has a capacity of 70 tonnes and 104 m3, with five loading and six unloading hatches. It is designed for operation at up to 120 km/h.
The wagon certainly looks professional in the pictures.
I don’t think that dual-gauge wagons for containers will be a serious engineering problem for the Ukrainians.
Rail Baltica
The Wikipedia entry for Rail Baltica has this introduction.
Rail Baltica is an under-construction rail infrastructure project that is intended to integrate the Baltic states in the European rail network. Its purpose is to provide passenger and freight service between participating countries and improve rail connections between Central and Northern Europe, specifically the area southeast of the Baltic Sea.
Note.
- As it is an EU-funded project, it is being built as standard gauge.
- It is being built with operating speeds of 145 mph for passengers and 75 mph for freight trains.
- There will be comprehensive connections to airports, freight terminals and major conurbations.
This page on the Rail Baltica web site has an interactive map of Rail Baltica.
It is thought that Putin is not pleased about Rail Baltica, as his extensive fleet of rail transporters for tanks and other military vehicles, are now built for the wrong gauge to invade the Baltic States.
Putin And Dual-Gauge Tracks And Wagons
As they could be used to bring war-related imports to Kyiv, I suspect Vlad the Genocider is against them.
How Will Ukraine Protect The Trains?
Consider.
- Being West of Kyiv will help.
- I suspect the UK have a few ideas for camouflage.
- Will a few brave Ukrainians ride the trains, with a sophisticated train protection missile?
- Drones probably won’t be as effective as ground attack aircraft at attacking trains.
I do suspect though that the Ukrainians have a plan.
Conclusion
This is going to be an interesting development.
250,000 Seats A Day On The WCML?
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Engineer.
These are the first three paragraphs.
In the Parliamentary debate on the cancellation of HS2 phase 2, Transport Minister Mark Harper claimed that what remains of HS2 will deliver “a massive increase in capacity to the West Coast Main Line (WCML)” by providing 250,000 seats a day. This figure was subsequently repeated by the Prime Minister and Rail Minister who advised that it applies “across the primary long-distance operator on the West Coast.”
Yet without HS2 phase 2a, there is to be no WCML capacity increase north of Lichfield. Furthermore, with no HS2 station in Manchester it will not be possible to run the planned two-unit 400-metre HS2 trains to the city. Instead, there can only be single 200-metre unit HS2 trains which are shorter than the current 265-metre Pendolino trains.
Furthermore, 250,000 seats a day is equivalent to running 17 x 605-seat Pendolinos an hour, 24 hours a day. This is clearly not credible.
Note.
- The writer’s assumptions about Manchester are correct.
- Liverpool Lime Street is already is already HS2-ready for trains between Crewe and London, after the recent upgrade.
- Liverpool Lime Street will certainly be able to take two London trains per hour (tph), which can only be single 200-metre unit HS2 trains.
- Liverpool Lime Street may be able to take a third London train per hour.
These are my thoughts.
Current Services
Current services include.
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Blackpool North via Birmingham New Street – 2 trains per day (tpd)
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Glasgow Central via Birmingham New Street – 5 tpd
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Edinburgh Waverley via Birmingham New Street – 7 tpd
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Birmingham New Street – 1 tph
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Holyhead – 10 tpd
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street – 1 tph – Increasing to 2 tph.
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly via Stoke-on-Trent, Macclesfield and Stockport – 1 tph
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly via Stoke-on-Trent and Stockport – 1 tph
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly via Crewe, Wilmslow and Stockport – 1 tph
- Avanti West Coast – London Euston and Glasgow Central – 1 tph.
- West Midlands Trains – London and Birmingham New Street – 2 tph
- West Midlands Trains – London and Crewe – 1 tph
- West Midlands Trains – Birmingham New Street and Liverpool Lime Street – 1 tph
It looks like there are eight Avanti West Coast tph and two West Midlands Trains tph between Stafford and Crewe.
High Speed Two Services
This diagram shows High Speed Two services, as they were originally envisaged before Phase 2 was discontinued.
Note.
- Trains to the left of the vertical black line are Phase 1 and those to the right are Phase 2.
- Full-Size trains are shown in blue.
- Classic-Compatible trains are shown in yellow.
- The dotted circles are where trains split and join.
- In the red boxes routes alternate every hour.
- Was Lancaster chosen as it’s close to the new Eden Project Morecambe?
Click on the diagram to enlarge it.
The Author’s Assumption
The author has made these assumptions.
- Current West Coast Main Line capacity North of Lichfield; Avanti West Coast – 8 tph, West Midlands – 1 tph and freight trains – 4 tph
- HS2 offers no extra capacity North of Lichfield.
- Max capacity ; Old Oak Common – 8 tph and London Euston – 10 tph.
- 400-metre long trains North of Birmingham ; Min – 1 tph to Edinburgh/Glasgow
- 400-metre long trains North of Birmingham ; Max – plus 3 tph to Liverpool/Manchester
- Trains operate a maximum of 14 hours per day.
I would add.
- All pairs of 200-metre long trains split and join at Crewe.
- Birmingham Curzon Street has seven platforms.
- Lancaster and Macclesfield have long bay platforms, that can handle 200-metre trains
- Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly have two platforms, that can handle 200-metre trains.
- I suspect
- Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly could both handle four 200-metre trains tph hour – Three for London and one for Birmingham.
There is a surprising amount of capacity in the North.
The Author’s Minimum Plan For HS1 – Phase 1
I think his minimum plan is as follows.
- Old Oak Common and Birmingham Curzon Street – 400-metre long trains – 3 tph
- Old Oak Common and Liverpool Lime Street/Lancaster – 400-metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- Old Oak Common and Liverpool Lime Street – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Old Oak Common and Macclesfield via Stafford and Stoke-on-Trent – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Old Oak Common and Manchester Piccadilly – 200-metre long trains – 2 tph
- Old Oak Common and Edinburgh Waverley/Glasgow Central – 400-metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
Note.
- 400-metre long trains are a pair of 200-metre long trains, that can split and join.
- This fulfils all the requirements of the original HS2 timetable for Phase 1.
- The total is nine tph and Old Oak Common can only handle 8 tph.
- Perhaps, the Liverpool Lime Street service could be a Liverpool Lime Street/Manchester Piccadilly service, that splits at Crewe?
I think it could work with London having the following services.
- Birmingham Curzon Street – 400-metre long trains – 3 tph
- Birmingham International – 400-metre long trains – 4 tph
- Carlisle – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Crewe – 400-metre long trains – 3 tph
- Edinburgh Waverley – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Glasgow Central – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Lancaster – 200 metre long trains – 1 tph
- Liverpool Lime Street – 200-metre long trains – 2 tph
- Macclesfield – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Manchester Piccadilly – 200-metre long trains – 2/3 tph
- Preston – 200-metre long trains – 2 tph
- Stafford – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Stoke-on-Trent – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Warrington Bank Quay – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- Wigan North Western – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
Services care as good or better than the current services.
The Author’s Maximum Plan For HS1 – Phase 1
I think his maximum plan is as follows.
- London Euston and Birmingham Curzon Street – 400-metre long trains – 3 tph
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street/Lancaster – 400-metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street/Manchester Piccadilly – 400-metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Macclesfield via Stafford and Stoke-on-Trent – 200-metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly – 200-metre long trains – 2 tph
- London Euston and Edinburgh Waverley/Glasgow Central – 400-metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
Note.
- 400-metre long trains are a pair of 200-metre long trains, that can split and join.
- This fulfils all the requirements of the original HS2 timetable for Phase 1.
- That is nine tph and London Euston can handle 10 tph.
- Perhaps, a tenth train could serve Edinburgh Waverley/Glasgow Central with a split at Crewe.
It should work.
Could High Speed Birmingham Curzon Street and Liverpool Lime Street And Manchester Piccadilly Services Be Provided With A Reverse At Birmingham Curzon Street?
A train would take this route.
- A 400 metre long train would leave London and go to Birmingham Curzon Street.
- At Birmingham Curzon Street the train would reverse and travel to Crewe.
- At Crewe the train would split with separate trains going to Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly.
Note.
- Automation could be used extensively to do the joining and splitting.
- The train would have an onboard team of drivers, so all joins, reverses and splits are performed as fast as possible.
- A local service could be paired with each train, so that intermediate stations on the Liverpool and Manchester branches had excellent connections to Birmingham and the South.
Suppose the maximum plan is now as follows.
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street/Manchester Piccadilly via Birmingham Curzon Street – 400 metre long trains – 3 tph – Reverses at Birmingham Curzon Street – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Birmingham Curzon Street – 400 metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Lancaster – 200 metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street – 200 metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Macclesfield via Stafford and Stoke-on-Trent – 200 metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly – 200 metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Edinburgh Waverley/Glasgow Central – 400 metre long trains – 2 tph – Splits at Crewe.
Note.
- Birmingham Curzon Street, Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly would all get four tph to and from London.
- Birmingham Curzon Street, Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly would all get one tph to and from London, that could be non-stop and didn’t join, reverse or split.
- Birmingham Curzon Street and Liverpool Lime Street would have a three tph service.
- Birmingham Curzon Street and Manchester Piccadilly would have a three tph service.
- Lancaster, Edinburgh Waverley, Glasgow Central and other stations would get the originally-promised service to and from London.
- That is ten tph to and from London Euston and the station can handle that number of trains.
It should work.
Could High Speed Birmingham Curzon Street and Edinburgh Waverley and Glasgow Central Services Be Provided With A Reverse At Birmingham Curzon Street?
In the previous section, I showed how, three tph between London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street/Manchester Piccadilly could be provided with a reverse at Birmingham Curzon Street.
So could the fourth train between London and Birmingham Curzon Street take this route?
- A 400 metre long train would leave London and go to Birmingham Curzon Street.
- At Birmingham Curzon Street the train would reverse and travel to Crewe, or another station, where the split can be performed.
- The train would split with separate trains going to Edinburgh Waverley and Glasgow Central.
Note.
- They would use the current paths used by Avanti West Coast Birmingham and Scotland services along the West Coast Main Line.
- This would give a third train to both Edinburgh Waverley and Glasgow Central.
It certainly appears that by using a reverse at Birmingham Curzon Street, more capacity can be created on the West Coast Main Line/HS2 route.
Could High Speed Two Serve North Wales?
It finally looks like the North Wales Coast Lines will finally be electrified.
- Would this allow a 200 metre long train to run all the way to Holyhead for the boats to Ireland?
- There could be a join and split at Crewe with another train.
- Chester would also be served by HS2.
It would create a zero-carbon route to Ireland.
What Would Be The Daily Number Of Passengers Carried?
The maximum plan could now be as follows.
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street/Manchester Piccadilly via Birmingham Curzon Street – 400 metre long trains – 3 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Edinburgh Waverley/Glasgow Central via Birmingham Curzon Street – 400 metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street/Lancaster – 400 metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Macclesfield via Stafford and Stoke-on-Trent – 200 metre long trains – 1 tph
- London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly/Holyhead – 400 metre long trains – 1 tph – Splits at Crewe.
- London Euston and Edinburgh Waverley/Glasgow Central – 400 metre long trains – 2 tph – Splits at Crewe.
Note.
- There are eight 400 metre long trains and one 200 metre long trains in both directions.
- A 200 metre long train hold 550 passengers.
- There are seventeen 200 metre long tph in both directions.
- Trains operate a maximum of 14 hours per day.
The number of passengers per day is 261,800.
Minding The Gap: ‘It’s A Scandal, It’s A Death Trap’
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
The announcement “mind the gap” is almost as much a part of travelling in London as the Tube sign or a red bus. But when is the gap between the train and the platform too far and too dangerous?
These are the first two paragraphs.
Eric Leach thinks he has the answer to that, and it is 30cm, or 12 inches. He knows this because while lying on the platform in agony having fallen over while getting off a train, he had time to look at the vertical drop between the train and the platform.
In February, at Ealing Broadway station in west London, he stepped off an Elizabeth line train onto the platform. Such was the force from the drop, that he broke a bone in his foot. He collapsed on the platform.
I went to Ealing Broadway station and took these pictures.
The gap is quite large, but not larger than many of the suburban trains in London.
These pictures are from Greater Anglia and Merseyrail.
Note the gap-fillers below the door.
Conclusion
The Elizabeth Line can do better.
Could London Drivers Be Charged On A Cost Per Mile Basis?
This article on CarWow is entitled Transport for London Investing £150 million In Technology Capable Of Enforcing Pay-Per-Mile Road Charging.
These reasons are given for the new system.
- Transport for London developing new ANPR technology
- Set to be used for Ulez and congestion charging for now
- Could be expanded in the future to include pay-per-mile road charging
- Estimated project cost of £150 million
In addition, this paragraph gives another reason.
A new platform for existing road user charging schemes, such as Ulez and the Congestion Charge, is being developed by Transport for London to replace the outsourced system currently in place as the contract is due to expire in 2026.
I can understand, that if it is brought in house, that this might create more jobs in London, rather than somewhere far away.
Speeding
If you read the article on CarWow, nothing is said about speeding.
But surely, if a sophisticated computer system knew you were at A and B at certain times, it could calculate your speed.
Coupled with a 20 mph speed limit, it could be a big money earner.
It also gets Sadiq Khan off the hook with pay-per-mile charging. He just introduces fines for people, who break the law by speeding.
Conclusion
I don’t drive, so it doesn’t bother me.
But I would advise anyone, who does, to think long and hard about who they vote for.
Rail Minister Marks Completion Of £150m Hope Valley Railway Upgrade
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Rail Magazine.
These first two paragraphs summarise the work.
More reliable journeys are promised on the Hope Valley line between Manchester and Sheffield after a £150 million upgrade was completed in early April.
Over the last three years, the existing platform at Dore & Totley station on the south side of Sheffield has been extended to cope with six-coach trains. Meanwhile the second platform has been rebuilt and commissioned (after it was removed in the 1980s), two mechanical signal boxes have been abolished and a new one-kilometre freight loop laid in the Peak District. At Hathersage, a pedestrian crossing has also been removed and replaced with a footbridge.
These are my thoughts.
Dore And Totley Station
The Rail Magazine article says this about the improvements at Dore and Totley station.
Replacing two tracks through Dore & Totley removes a single-track bottleneck that often saw Sheffield to Manchester express services held up by slower stopping services and cement trains destined for Earles Sidings. A nine-day shutdown of the route in March was needed to finish the work.
The new platform sits between the Midland Main Line and the Hope Valley line, so can only be reached via the new footbridge or lifts. As well as the usual ‘blister paving’ slabs marking the edge of the platform, other tactile paving has been laid to help people with visual impairments find their way around the station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the new layout of tracks at Dore and Totley station.
Note.
- The four tracks at the North of the map go to Sheffield station.
- The Eastern pair of tracks are the Midland Main Line and they go to the South-East corner of the map for Chesterfield and the South.
- The Western pair of tracks are the Hope Valley Line and they go to the South-West corner of the map for Manchester.
- The blue lettering in the middle of the map indicates Dore and Totley station.
- There is a single track curve between the Midland Main Line and the Hope Valley Line, which is mainly used by freight trains.
This secondOpenRailwayMap shows Dore and Totley station in greater detail.
The big improvement is that the Hope Valley Line is now double instead of single track, which must eliminate a lot of delays.
These pictures show the station in July 2020.
The pictures clearly show the single track and platform at Dore and Totley station.
Dore South Curve
Dore South Curve links the Southbound Midland Main Line with the Westbound Hope Valley Line.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the curve.
There is a crossover in the South-West corner of the map, so with careful signalling, trains can use the Dore South Curve in both directions.
Bamford Loop
This is a freight loop between Bamford and Hathersage stations.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the loop.
Note.
- The Hope Valley Line goes diagonally across the map.
- Manchester is to the North-West.
- Sheffield is to the South-East.
- Bamford station is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Hathersage station is just off the South-East corner of the map.
- The loop is on the Northern side of the Hope Valley Line.
The loop will most likely be used by trains going to Sheffield or Chesterfield.
Hathersage Footbridge
This Google Map shows Hathersage station.
Note.
- Dore Lane and the B 6001 appear to pass under the railway.
- There appears to be what could be foundations just to the West of the platforms at Hathersage station.
- From pictures found by Google the bridge appears to be a simple steel structure.
I shall have to go and take pictures.
Fast Trains Between Manchester And Nottingham
In the Wikipedia entry for the Hope Valley Line, this is said.
Nottinghamshire County Council and the Department for Transport have investigated the possibility of adding another service that does not call at Sheffield in order to improve the journey time between Nottingham and Manchester. Stopping (and changing direction) in Sheffield, the fastest journey is 110 minutes (in 2019), but the council has estimated bypassing Sheffield would cut the time to 85 minutes. Suggested improvements on a 2+1⁄2-mile (4 km) stretch near Stockport may reduce journey times by 2–3 minutes.
Consider.
- According to Google, the driving time between the two cities is 128 minutes and the motorway route is via the M1 and M62.
- If nearly half-an-hour could be saved between Manchester and Nottingham could be a big saving in journey time.
- Manchester Piccadilly is likely to be rebuilt for High Speed Two and a fast route via Nottingham could be a viable alternative.
- Both Manchester and Nottingham have good local tram and train networks.
- As the electrification of the Midland Main Line progresses, the route will be increasingly suitable for 100 mph battery-electric trains.
A Manchester and Nottingham express service looks to be an easy service to implement after the Hope Valley Line has been improved.
Hourly Stopping Trains Between Manchester And Sheffield
The Wikipedia entry for the Hope Valley Line gives these details for the stopping service between Manchester Piccadilly and Sheffield.
- Trains are hourly.
- Trains call at Reddish North, Brinnington, Bredbury, Romiley, Marple, New Mills Central, Chinley, Edale, Hope, Bamford, Hathersage, Grindleford and Dore & Totley.
- But some services do not call at some or all of Edale, Bamford, Hathersage, Grindleford and Dore & Totley giving some 2-hour gaps between services at these stations.
Let’s hope that some of the extra capacity is used to provide a regular service at all stations on the Hope Valley Line.
As in a few years, it will have electrification at both ends, this route could be very suitable for battery-electric trains.
Completion Date
It appears that the first day, when passengers will be able to use the new upgraded tracks and stations will be Thursday, the 2nd of May.
Conclusion
The improvements, certainly seem to allow extra and improved services through on the Hope Valley Line.
I also feel that in a few years, services will be run by battery-electric trains.
Very Light Rail Trial For Heathfield Branch?
The title of this post, is the same as that of an article in the May 2024 Edition of Modern Railways.
This is the first four paragraphs.
Investigations are ongoing as to whether the disused Heathfield branch line in Devon could be used as a test route for the Revolution Very Light Rail (RVLR) vehicle.
Heathfield Rail Link Association (HRLA) says a survey has been completed along the four-mile line from Newton Abbot, which was last used by timber trains in 2017 and hasn’t seen a regular passenger service since 1959.
The work, by Lampitt Rail, has been completed for Eversholt Rail, one of the firms behind RVLR, a hybrid vehicle, which aims to help reduce costs on existing branch lines and those earmarked for reopening.
A spokesman for Eversholt said the line is one of more than 200 potential opportunities for RVLR ahead for 2026, when it’s hoped tests will start on branch lines around the country using three new battery prototypes.
These are my thoughts and observations.
The Heathfield Branch
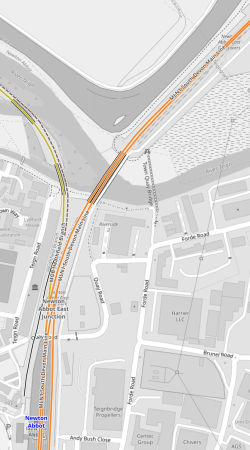
This OpenRailwayMap shows the Heathfield branch.
Note.
- The former site of Heathfield station is indicated by the blue arrow.
- The yellow track is the Heathfield branch.
- The orange track is the Cornwall Main Line, that goes through Newton Abbot station to Plymouth and Penzance stations.
This second OpenRailwayMap shows the track layout Newton Abbot station.
As there are three platforms, I suspect that matters can be arranged to turn an occasional train from the branch.
How Will The Revolution VLR Be Charged?
The Modern Railways article says this about charging.
Eversholt Rail and partner firm Transport Design International have stated they will build three new battery-powered vehicles for the 2026 tests, which will need rapid charging points, made up of two rails in-between the running lines which would contact a shoe hanging from the train. HRLA is working with UK Power Networks to find locations for these chargers, including at Newton Abbot.
It sounds very much like the Vivarail/GWR Fast Charge equipment.
What Will Be The Range Of The Revolution VLR?
The range of the Revolution VLR has not been stated.
But this is stated in the Modern Railways article.
Heathfield Rail Link Association (HRLA) says a survey has been completed along the four-mile line from Newton Abbot.
So will the train be able to do a round trip on one charge or just a single journey?
Or could this route be a strong possibility, as the Revolution VLR has the range to do a round trip on one charge?
Sekisui’s FFU: Newark Flat Crossing Four Years On
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Engineer.
These two paragraphs introduce the article.
Sekisui manufactures synthetic wood baulks made from Fibre-reinforced Foamed Urethane (FFU). Network Rail engineers installed the first FFU baulks and sleepers as replacements for traditional hardwood on military canal bridges in Kent during 2014. The FFU product was first introduced on Japanese Railways in 1980 and early installations are still performing to specification. FFU is now widely used on railway infrastructure in 33 countries to support track on bridges, decking for level crossings, plain line sleepers, and switch and crossing (S&C) bearers.
Newark flat crossing is an example of a unique and large application of FFU technology on Network Rail infrastructure which required the development of the long FFU synthetic bearers forming a lattice track support 16 by 16 metres. Sekisui holds full Network Rail Product Acceptance Certification PA05/07176 for this project which became operational following complete track renewal in August 2019. The FFU was used to replace the traditional hardwood to support the track.
The article is a fascinating insight into the use of FFU.
Fabricated To Requirement
The article describes how the FFU technology was fabricated to create a replacement for all the timber in a factory in Nottingham.
This paragraph describes the advantages of FFU.
Key benefits over hardwood include longevity with over 50 years’ service life. FFU is form retentive, not prone to splitting or absorption of water, and does not rot or deteriorate in sunlight so it contributes significantly to ‘whole life cycle cost reduction’ by reducing track maintenance and renewal interventions. The product does not require maintenance inspectors to complete micro-drilling during service life and is fully recyclable.
This paragraph details a problem, that Network Rail were having with the maintenance.
Prior to the 2019 renewal, the supporting lattice that holds the cast crossings into position was made up from hardwood and typically required replacement every 15 years. The last renewal occurred in 2003. Network Rail found that procuring suitable hardwood timbers of 16 metres for a further renewal proved problematic.
This reminds me of the problems, Brunel’s successors had with his timber viaducts. They just couldn’t get the quality of timber he had been able to source.
It appears from the two pictures in the article, that FFU can be worked like hardwood.
Maintenance Comparison After Four Years
This paragraph introduces this section.
Over four years after the renewal of Newark Flat Crossing utilising FFU, Network Rail Track Maintenance Engineers (TME) in Doncaster report significant reduction in maintenance requirements.
These paragraphs compare four years of use of both systems.
2003-2007 hardwood timber renewal – track geometry deterioration, ride quality issues, splitting of timbers, failure of screws, several rail management interventions to cast crossings, including cracking of castings leading to early replacement of ironwork.
2019-2023 FFU renewal – stable track geometry with no ride quality issues reported, no screw failures, no deterioration in the FFU material, reduced rail management intervention and no cracking or premature replacement of cast crossings.It looks to me, that the FFU is a long-term cost saver.
This paragraph indicates the maintenance savings.
In terms of rail management, since the introduction of FFU, Network Rail’s TMEs have reduced the cyclical inspection and maintenance requirements from four-weekly to eight-weekly. There is now only minimal crossing nose profile grinding required and two small casting weld repairs have been done to date.
That looks like a fifty percent saving.
Other Uses Of FFU
In my 76 years, I’ve came across various uses of large timbers.
- At ICI in the late 1960s, some of the plants, I visited at Winnington, had been built from massive oak beams in the early 19th Century.
- With one plant, that ICI demolished, the oak beams were sold for a surprising amount of money.
- I’ve lived in two early 19th Century houses, that were built with oak beams.
- An architect designed a replacement barn for me, that was made of large timbers. Sadly, the new owners of the house demolished it and I don’t have any pictures.
For these reasons, I’m certain, that architects, builders and restorers can find all sorts of uses for FFU.
This is the product page.
Conclusion
This looks like a success story and the Rail Engineer article should be read in full.
It might give you very good ideas.