Travelling Between Heathrow Airport And Staines Station
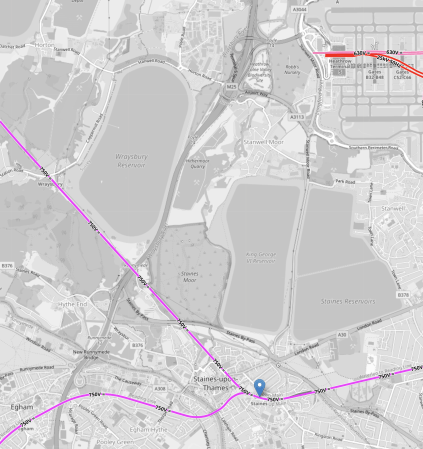
Staines Station and Heathrow Airport are not far apart, as this OpenRailwayMap shows.
Note.
- The mauve lines in the bottom half of the map are South West Trains services out of Waterloo.
- Waterloo via Feltham, Twickenham and Richmond to name but three stations , is to the East.
- Reading is to the South-West
- Windsor is to the North-West.
- The blue arrow indicates Staines station.
- Heathrow Terminal 5 is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The pink tracks are the Piccadilly Lines
- The red tracks are for the Elizabeth Line and Heathrow Express.
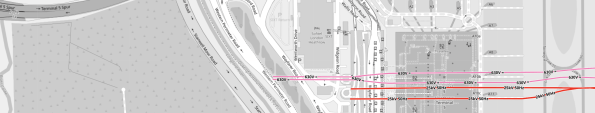
- This OpenRailwayMap shows Terminal 5 to a larger scale.
Note.
- The pink tracks are the Piccadilly Line.
- The red tracks are for the Elizabeth Line and Heathrow Express.
- In front of the red tracks is what looks like a circular walkway or emergency exit, with a rectangular block to its West.
- The rectangular block is the lift tower to get from the railway station to the Departures and Arrivals floors of Terminal 5.
I asked Google AI if it would it be possible in the future to extend the Elizabeth Line to the West out of the Western end of Terminal 5 and received this reply.
Extending the Elizabeth line west from Terminal 5 is technically possible and has been proposed, notably as part of a potential westward rail link to Staines or to support airport expansion, but it is not currently funded. Terminal 5 was designed with future expansion in mind, potentially allowing a connection to Staines to create a “southern rail link” for better connections.
Perhaps there are two tunnels under the lift shafts?
How many trains per hour (tph) terminate in those two platforms?
- 4 tph – Heathrow Express
- 2 tph – Elizabeth Line to Shenfield.
Note.
- Only six trains in two platforms is easily managed.
- Because, Heathrow Express services appear to use both platforms, when I visited yesterday, the system seems to confuse passengers.
- The services surely need to be evened up, so that there are four tph of each service, with each service having a dedicated platform.
- But terminating eight trains in two platforms could be troublesome.
- Platforms are numbered 1 to 6 from the South.
- Platforms 1 and 2 have not been built yet.
Although four tph for Heathrow Express in one platform, should be easy with digital signalling, as you see it every day in London, it may be difficult on two platforms, at the same time.
In Is More Capacity Between Heathrow Airport And Central London, Needed On The Elizabeth Line?, I said this.
Currently, the Elizabeth line provides up to 12 trains per hour (including Elizabeth line and Heathrow Express) on the relief lines, making it nearly at capacity.
Note.
- When I use the Elizabeth Line, I deliberately avoid trains going to and from Heathrow, unless I’m going that way, as they are too crowded with passengers and their oversized cases.
- High Speed Two, the West London Orbital Railway and the North London Line will bring passengers for Heathrow Airport to Old Oak Common station.
- Surely, as Heathrow Airport gets bigger and increases its passenger numbers. the Elizabeth Line will need to be increased in capacity.
I believe Elizabeth Line capacity needs to be increased soon.
The only feasible plan I’ve seen is Heathrow Southern Railways plan, which included.
- Construction of a bay platform 0 at Staines alongside the Staines to Windsor line.
- A step-free bridge across the tracks.
- Construction of a single-track railway with 25 KVAC overhead electrification and a passing looop, between the new platform 0 at Staines and Platform 3 at Heathrow Terminal 5 station.
- Run four trains per hour in both directions between Heathrow Terminal 5 and Staines stations.
- This plan would would add two trains per hour through the Central Tunnel.
Various Journeys Would Be As Follows
This OpenRailwayMap shows Staines junction and the positions of the three platforms.
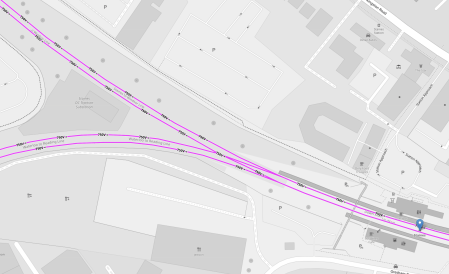
Note.
- The Windsor Line goes North-West.
- The Reading Line goes West.
- The Waterloo Line Goes East.
- Platform 1 is on the North side of the tracks.
- Platform 2 is on the South side of the tracks.
- The bay platform, which I’ve numbered 0, will be on the North side of the tracks towards Windsor.
- I suspect the step-free bridge will be over the tracks and replace the current rickety structure.
- The bridge would be a short walk from all three platforms.
Interchanges would be as follows.
- Windsor to Heathrow – Walk between Platforms 1 and 0.
- Reading to Heathrow – Walk between Platforms 1 and 0.
- Heathrow to Windsor – Cross the bridge between Platforms 0 and 2.
- Heathrow to Reading – Cross the bridge between Platforms 0 and 2.
- Waterloo to Heathrow – Cross the bridge between Platforms 2 and 0.
- Heathrow to Waterloo – Walk between Platforms 0 and 1.
Note.
- All trains to or from Heathrow use Platform 0.
- All trains to Waterloo use Platform 1.
- All trains going away from Waterloo use Platform 2.
- Reading and Heathrow gain a step-free route at 2 tph.
- All interchanges at Staines station would be step-free.
- A train like London Crosslink, which used to go between Feltham and Woking, would use Platform 1 going towards Feltham and Platform 2 going towards Woking.
Staines station would gain step-free access to all Heathrow terminals, all Elizabeth Line and High Speed Two stations.
Could Anglia Railways’ London Crosslink Be Recreated As Part Of The London Overground?
I like the idea of the London Crosslink service, that ran for a few years between East Anglia and Hampshire via the North London Line and Staines.
My arguments for its restoration are described in Could Anglia Railways’ London Crosslink Be Recreated As Part Of The London Overground?
At various times in my life, it would have been very useful.
Today, as I live about fifteen minutes from Highbury and Islington station, I could use London Crosslink for the following reasons.
- Visiting friends and family in Hampshire.
- Going to Heathrow Airport, especially Terminal 5.
- Visiting friends in East Anglia.
- Going to football at Ipswich.
- Exploring new parts of England.
- I would wait at home and time my departure to catch a booked train at a fully step-free station.
Conclusions
Extending the Elizabeth Line to Staines gives these advantages.
- Staff at Heathrow, who live in the Staines area get easy access to the airport.
- Buses and coaches between Heathrow and the local area may be reviewed.
- Less cars will be used to get to and from the airport.
- Reading and Heathrow gain a step-free route at 2 tph.
- A lot of stations would gain a step-free route to all terminals at Heathrow, and all Elizabeth Line and High Speed Two stations.
There may well be other advantages.
Welsh Government Backs Marine Power Systems’ Floating Wind Tech With GBP 8 Million
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The Welsh government has invested GBP 8 million (approximately EUR 9.4 million) in Marine Power Systems (MPS) to support the commercialisation of its floating offshore wind technology.
These three paragraphs add more detail to the story.
According to the company, the funding will accelerate the deployment of its PelaFlex platform, a floating wind solution designed for deep-water sites where conventional fixed-bottom foundations are not viable.
Marine Power Systems said the investment will help move the technology from advanced development towards commercial-scale deployment and manufacturing. The company also plans to expand its industrial and assembly capabilities in the UK.
The PelaFlex platform has been designed to simplify fabrication, installation and long-term operations while enabling wind farms to be located further offshore where wind speeds are typically stronger and more consistent, MPS says.
The offshore wind industry in Wales seems to be gearing up for a big expansion.
Gwynt Glas is the collective name for the three 1.5 GW floating wind farms in the Western Approaches and in Gwynt Glas And South Wales Ports Combine Strength In Preparation For Multi-Billion Floating Wind Industry, I describe the initial agreement that started the Gwynt Glas project.
To my mind, Associated British Ports and the wind farm developers are making sure they can carpet the Western Approaches, with offshore wind farms.
In Ocean Winds Enters Lease Agreement With Crown Estate For 1.5 GW Celtic Sea Floating Wind Project, I talk in general about the progress of the first three 1.5 GW floating wind farms in Gwynt Glas and in particular about leasing of the third wind farm.
These two posts, indicate that the Port of Port Talbot is preparing itself to produce the floaters for floating wind turbines.
- BW Ideol, ABP To Explore Serial Production Of Floating Wind Foundations At Port Talbot
- Two Ports Advance To Next Stage Of UK Gov Funding For Floating Wind
It certainly appears, that South Wales will be able to build the heavyweight gubbins for floating offshore wind.
According to Was South Wales Once The World’s Largest Coal Exporter? it was, and in 1913, the region produced 57 million tons of coal, with more than half exported.
It does look like South Wales is going to repeat the economic success with offshore energy.
I’ve heard tales from elderly Welshmen talking of the coal ships in the docks of South Wales and will we be seeing gas tankers in the docks of South Wales?
Was South Wales Once The World’s Largest Coal Exporter?
I asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this answer.
Yes, South Wales was once the world’s largest coal-exporting region and home to the busiest coal-exporting ports in the world. During its peak in 1913, the South Wales coalfield supplied almost one-third of total global coal exports, with Cardiff and Barry leading the world as the top coal ports.
Key details regarding the coal boom in South Wales:
Peak Production: In 1913, the region produced 57 million tons of coal, with more than half exported.
Top Export Ports: In 1913, Barry was recognized as the world’s largest coal-exporting port, closely followed by Cardiff.
The “Coal Metropolis”: Cardiff became the world’s leading coal and shipping metropolis, with the Cardiff Coal Exchange setting the global price for steam coal.
Economic Impact: The boom drove massive population growth in the South Wales Valleys and created tremendous wealth for cities like Cardiff, Barry, and Newport.
Global Demand: Welsh coal was highly sought after for its high quality, fueling steamships, railways, and industries across the world, from Russia to South America.
By 1920, the industry employed over 270,000 miners, but it saw a steep decline thereafter due to economic depression, international competition, and the exhaustion of accessible reserves.
How Much B12 In An M & S Liver And Bacon For One?
I asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this answer.
An M&S Lamb’s Liver and Bacon meal (typically 450g for one) is an exceptionally high source of Vitamin B12 due to the high concentration in liver, likely providing well over 100 µg (micrograms) of B12 per pack.
Key Facts Regarding B12 in M&S Liver and Bacon:
Liver Density: Lamb’s liver contains roughly 85–90 micrograms of Vitamin B12 per 100g.
Component Breakdown: The 450g meal contains approximately 16% liver (approx. 72g of liver).
Total Content Estimate: Based on the 72g of liver, a single 450g meal likely contains roughly 60–70 µg of Vitamin B12, which is over 2,000% of the daily recommended intake.
Additional Sources: The bacon and gravy also contribute to this total.
The UK Reference Nutrient Intake (RNI) for adults is 1.5 micrograms daily, making this meal a significant source.
As I wuld have expected, this ready meal is a good source of B12.
NextEnergy Solar Fund To Shift To Energy Storage And Divest Solar in Strategic Overhaul
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on the Solar Power Portal.
This is the sub-heading.
As part of the reset, NextEnergy said it will increase its energy storage exposure up to 30% of its gross asset value, a significant increase on its current rate of 10%.
These two paragraphs give more of their reasoning.
NextEnergy Solar Fund has completed a “strategic reset” of its investment strategy which will see it focus on energy storage assets and increase project sales.
As part of the reset, NextEnergy said it will increase its energy storage exposure up to 30% of its gross asset value, a significant increase on its current rate of 10%. The company said the shift would “enhance the Company’s existing stable revenues generated by its operational solar assets and support future revenues”.
In Is Sumitomo Heavy Industries Highview Power Energy Storage System On Line At Hiroshima?, I describe a power supply system developed by Sumitomo Heavy Industries to supply a stable 5 MW to a LNG Terminal, using these components.
- A Cold Source
- Solar Panels
- A 5 MW/20 MWh Highview Power liquid-air CRYObattery.
Do Sumitomo Heavy Industries believe that a combination of energy and/or battery sources working together gives the quality of stable power, that is needed by today’s modern factories, facilities and buildings?
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I very much believe stable power supplies are a good thing and Sumitomo Heavy Industries obviously feel that Highview Power’s liquid air CRYObatteries are a good way to provide them.
The adding of a battery into a solar-powered renewable power supply, would surely, increase the amount of batteries that NextEnergy were financing.
How Much B12 In A M & S Chicken Jalfrezi With Basmati Rice For One?
I asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this answer.
Based on typical nutritional data for similar prepared chicken and rice meals, a 400g serving of M&S Chicken Jalfrezi with Basmati Rice likely contains a significant portion of the recommended daily intake of Vitamin B12, largely derived from the chicken breast.
Protein Content: The 400g meal generally provides approximately 32.8g of protein.
Estimated B12: As a rich source of animal protein, 100g of chicken typically provides a significant portion of daily B12. While specific B12 figures for this exact M&S product are not explicitly listed in the search results, similar chicken curry meals provide roughly 0.5–1.0 µg or more per 100g, suggesting a 400g pack could meet or exceed the typical daily adult requirement (around 1.5–2.4 µg).
Nutritional Summary for M&S Chicken Jalfrezi with Rice (400g):
Protein: ~32.8g
Calories: ~372–544 kcal
Fat: ~6.8g–20g
Carbs: ~45.2g–56.4g
The dish contains marinated chargrilled chicken breast, red peppers, and basmati rice.
Five New Railway Stations To Open Over Next Month
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Opening dates have been announced for five new railway stations in the West Midlands following a £185m project to reinstate links not used in decades.
These two paragraphs add more details.
On the Black Country line, new stations for Willenhall and Darlaston open on 19 March. The sites were last visited by trains in 1965.
On 7 April, Camp Hill Line stations Moseley Village, Kings Heath, and Pineapple Road open, allowing locals access to neighbourhood services for the first time since World War Two.
I shall go up, some time on or after the 7th and see all five stations.
Would Extending The Elizabeth Line To Staines Offer Any Advantages?
I asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this answer.
Extending the Elizabeth line to Staines offers significant advantages, including improved direct access to Heathrow Airport from Surrey/south-west London, reduced road traffic congestion, and enhanced connectivity for commuters. Proposed as part of the Heathrow Southern Railway project, it would provide a “game-changer” link and support economic growth around Heathrow.
Key Advantages of Extending the Elizabeth Line to Staines:
Improved Airport Access: The extension would provide a direct, sustainable, zero-emission rail link to Heathrow for commuters and travelers from Staines, Virginia Water, and surrounding areas.
Reduced Congestion & Environmental Impact: The project is estimated to reduce road traffic by approximately 3 million journeys annually, significantly lowering emissions.
Faster Commutes & Connectivity: It would create a new, faster route from Surrey and Hampshire (via Staines) to key locations like Heathrow, Old Oak Common (for HS2), and central London.
Relieving Existing Lines: The extension would help relieve overcrowding on the South Western Main Line into London Waterloo.
Utilizing Existing Infrastructure: The project would likely use the underground space already created at Terminal 5 to facilitate a southward extension.
Challenges and Considerations:
Funding and Cost: The project requires significant upfront investment, requiring collaboration between private sectors, Transport for London, and the Department for Transport.
Capacity Constraints: The existing Elizabeth line is already high-demand, and integrating a new, long branch would require careful capacity management.
This extension is closely tied to proposals for a Southern Rail Access to Heathrow, intended to support the expansion of the airport and the economic development of the surrounding region.
Is There Enough Staff Car Parking At Heathrow Airport?
I asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this answer.
While Heathrow Airport provides designated staff parking areas—including N1, N2, and N5 near Terminal 5—finding space can be difficult due to high demand, and recent substantial fee increases have caused tension. Dedicated staff, including those for car-sharing, have access to, and must display, valid permits in, secured, monitored areas.
Key Details on Staff Parking:
Locations: Staff parking is generally located on the Northern Perimeter Road, particularly serving Terminal 5.
Costs: MoneySavingExpert Forum indicates that parking costs may be paid for by employers like British Airways, or directly by the employee.
Rising Costs: In 2024, monthly staff parking charges were increased significantly, leading to complaints from unions regarding the cost for workers.
Capacity Issues: With thousands of staff, parking can be limited, though special areas are allocated for car-sharing to encourage efficiency.
For most employees, options include using the designated, secure staff car parks, or utilizing the airport’s Sustainable Travel Guide options, which provide, alternative, more sustainable transport solutions.
Staff parking certainly seem a problem and it can only get worse, as more staff are recruited.
Is More Capacity Between Heathrow Airport And Central London, Needed On The Elizabeth Line?
I asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this answer.
Yes, additional capacity on the Elizabeth line between Heathrow Airport and Central London is needed to manage high demand, despite it being a major upgrade. While the line has greatly improved connectivity, studies suggest that rising passenger demand, particularly from potential airport expansion, may require increasing services from 6 to 8 trains per hour to prevent future overcrowding.
Key Considerations Regarding Capacity:
High Demand: Passenger demand grew by ~40% between June 2022 and October 2023, with further growth expected.
Infrastructure Constraints: Increasing services beyond 6 trains per hour is challenging due to the need for signaling upgrades and potential platform length limitations.
Alternative Solutions: Experts suggest the Western Rail Link to Heathrow could relieve pressure by allowing direct access from the west, rather than requiring travel into central London first.
Future Upgrades: Further improvements, including enhanced signalling on the Piccadilly line and other rail links, are seen as necessary to handle future passenger surges.
Currently, the Elizabeth line provides up to 12 trains per hour (including Elizabeth line and Heathrow Express) on the relief lines, making it nearly at capacity.
Note.
- When I use the Elizabeth Line, I deliberately avoid trains going to and from Heathrow, unless I’m going that way, as they are too crowded with passengers and oversized cases.
- High Speed Two, the West London Orbital Railway and the North London Line will bring passengers for Heathrow Airport to Old Oak Common station.
- Surely, as Heathrow gets bigger and increases its passenger numbers. the Elizabeth Line will need to be increased in capacity.
I believe Elizabeth Line capacity needs to be increased soon.