Rail Minister Marks Completion Of £150m Hope Valley Railway Upgrade
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Rail Magazine.
These first two paragraphs summarise the work.
More reliable journeys are promised on the Hope Valley line between Manchester and Sheffield after a £150 million upgrade was completed in early April.
Over the last three years, the existing platform at Dore & Totley station on the south side of Sheffield has been extended to cope with six-coach trains. Meanwhile the second platform has been rebuilt and commissioned (after it was removed in the 1980s), two mechanical signal boxes have been abolished and a new one-kilometre freight loop laid in the Peak District. At Hathersage, a pedestrian crossing has also been removed and replaced with a footbridge.
These are my thoughts.
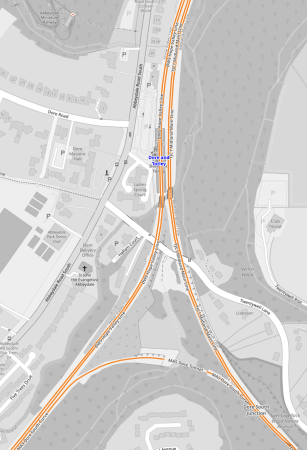
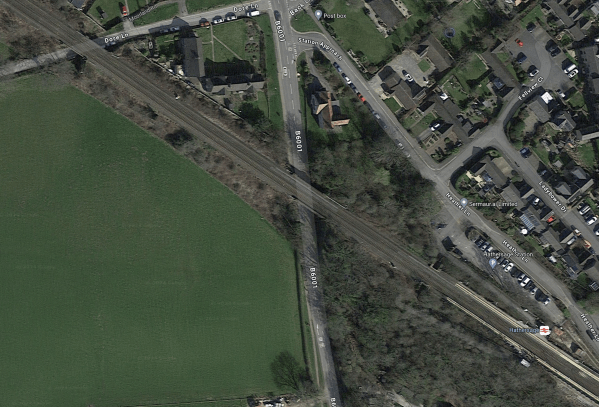
Dore And Totley Station
The Rail Magazine article says this about the improvements at Dore and Totley station.
Replacing two tracks through Dore & Totley removes a single-track bottleneck that often saw Sheffield to Manchester express services held up by slower stopping services and cement trains destined for Earles Sidings. A nine-day shutdown of the route in March was needed to finish the work.
The new platform sits between the Midland Main Line and the Hope Valley line, so can only be reached via the new footbridge or lifts. As well as the usual ‘blister paving’ slabs marking the edge of the platform, other tactile paving has been laid to help people with visual impairments find their way around the station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the new layout of tracks at Dore and Totley station.
Note.
- The four tracks at the North of the map go to Sheffield station.
- The Eastern pair of tracks are the Midland Main Line and they go to the South-East corner of the map for Chesterfield and the South.
- The Western pair of tracks are the Hope Valley Line and they go to the South-West corner of the map for Manchester.
- The blue lettering in the middle of the map indicates Dore and Totley station.
- There is a single track curve between the Midland Main Line and the Hope Valley Line, which is mainly used by freight trains.
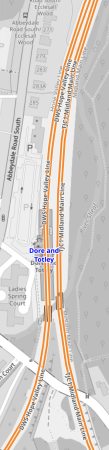
This secondOpenRailwayMap shows Dore and Totley station in greater detail.
The big improvement is that the Hope Valley Line is now double instead of single track, which must eliminate a lot of delays.
These pictures show the station in July 2020.
The pictures clearly show the single track and platform at Dore and Totley station.
Dore South Curve
Dore South Curve links the Southbound Midland Main Line with the Westbound Hope Valley Line.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the curve.
There is a crossover in the South-West corner of the map, so with careful signalling, trains can use the Dore South Curve in both directions.
Bamford Loop
This is a freight loop between Bamford and Hathersage stations.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the loop.
Note.
- The Hope Valley Line goes diagonally across the map.
- Manchester is to the North-West.
- Sheffield is to the South-East.
- Bamford station is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Hathersage station is just off the South-East corner of the map.
- The loop is on the Northern side of the Hope Valley Line.
The loop will most likely be used by trains going to Sheffield or Chesterfield.
Hathersage Footbridge
This Google Map shows Hathersage station.
Note.
- Dore Lane and the B 6001 appear to pass under the railway.
- There appears to be what could be foundations just to the West of the platforms at Hathersage station.
- From pictures found by Google the bridge appears to be a simple steel structure.
I shall have to go and take pictures.
Fast Trains Between Manchester And Nottingham
In the Wikipedia entry for the Hope Valley Line, this is said.
Nottinghamshire County Council and the Department for Transport have investigated the possibility of adding another service that does not call at Sheffield in order to improve the journey time between Nottingham and Manchester. Stopping (and changing direction) in Sheffield, the fastest journey is 110 minutes (in 2019), but the council has estimated bypassing Sheffield would cut the time to 85 minutes. Suggested improvements on a 2+1⁄2-mile (4 km) stretch near Stockport may reduce journey times by 2–3 minutes.
Consider.
- According to Google, the driving time between the two cities is 128 minutes and the motorway route is via the M1 and M62.
- If nearly half-an-hour could be saved between Manchester and Nottingham could be a big saving in journey time.
- Manchester Piccadilly is likely to be rebuilt for High Speed Two and a fast route via Nottingham could be a viable alternative.
- Both Manchester and Nottingham have good local tram and train networks.
- As the electrification of the Midland Main Line progresses, the route will be increasingly suitable for 100 mph battery-electric trains.
A Manchester and Nottingham express service looks to be an easy service to implement after the Hope Valley Line has been improved.
Hourly Stopping Trains Between Manchester And Sheffield
The Wikipedia entry for the Hope Valley Line gives these details for the stopping service between Manchester Piccadilly and Sheffield.
- Trains are hourly.
- Trains call at Reddish North, Brinnington, Bredbury, Romiley, Marple, New Mills Central, Chinley, Edale, Hope, Bamford, Hathersage, Grindleford and Dore & Totley.
- But some services do not call at some or all of Edale, Bamford, Hathersage, Grindleford and Dore & Totley giving some 2-hour gaps between services at these stations.
Let’s hope that some of the extra capacity is used to provide a regular service at all stations on the Hope Valley Line.
As in a few years, it will have electrification at both ends, this route could be very suitable for battery-electric trains.
Completion Date
It appears that the first day, when passengers will be able to use the new upgraded tracks and stations will be Thursday, the 2nd of May.
Conclusion
The improvements, certainly seem to allow extra and improved services through on the Hope Valley Line.
I also feel that in a few years, services will be run by battery-electric trains.
Enterprise: Belfast-Dublin Rail To Receive Multi-Million Investment
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Cross-border rail services between Belfast and Dublin are set to benefit from a £141.9m investment.
These are points from the rest of the article.
- The investment is part of the Peace Plus initiative which funds projects in Northern Ireland and border counties.
- The funding will support a major programme aimed at providing an hourly service between Belfast and Dublin.
- All existing Enterprise trains are to be replaced with brand new trains by the end of this decade leading to faster journey times.
- Ian Campbell from transport company Translink said that the announcement was “good news” and “very much needed”.
- Mr Campbell said the funding would allow the current fleet of four enterprise trains to be replaced by eight new trains.
- He said that these trains would allow a “step up in accessibility and passenger experience”, as well as reducing the journey times by “about 15 minutes”.
- He added that the trains would be “designed ultimately to operate as a net zero service using sustainable technology”.
- Mr Campbell said that the hourly service was “very much needed” as Translink expected there to be demand for two million passenger journeys on the service by 2030.
- Funding is also being provided by the Department for Infrastructure (DfI) in Northern Ireland and the Department of Transport in the Republic of Ireland.
These are my thoughts.
The Enterprise Service
The BBC article describes the service like this.
Jointly operated by Northern Ireland Railways and Iarnród Éireann, the Enterprise train service has provided a transport link between Belfast and Dublin for over 75 years.
These are some points about the tracks and the trains.
- The Northern terminal is Belfast Lanyon Place station.
- The Southern terminal is Dublin Connolly station.
- The Wikipedia entry for the Belfast and Dublin line says the distance is 112 miles, with an operating speed of 90 mph.
The fastest services take two hours and five minutes, which is an average speed of 54 mph.
Electrification Between Dublin And Belfast
Currently, only the nine miles at the Southern end between Dublin Connolly and Malahide stations is electrified using 1,500 V DC overhead.
But there is a program being planned called Dart+, which could see electrification extended by 23 miles to Drogheda station.
New Trains For The Enterprise Service
The BBC article made these points about the new trains.
- Ian Campbell from transport company Translink said that the announcement was “good news” and “very much needed”.
- Mr Campbell said the funding would allow the current fleet of four enterprise trains to be replaced by eight new trains.
- He said that these trains would allow a “step up in accessibility and passenger experience”, as well as reducing the journey times by “about 15 minutes”.
- He added that the trains would be “designed ultimately to operate as a net zero service using sustainable technology”.
This article on Rail Technology Magazine is entitled Multi-Million Pound Transformation For Belfast-Dublin Rail Services.
The last two paragraphs of the article give more details of the trains.
This funding will finance the replacement of the current Enterprise fleet of four train-sets with eight new, modern and sustainable train-sets. Enterprise is jointly operated by Northern Ireland Railways and Iarnród Éireann, and the new trains are designed to evolve as both jurisdictions work towards a fully electrified cross-border rail corridor over the coming decades.
The procurement process for the new train-sets is set to be completed in the coming year, with the fleet expected to be in operation by 2029. The trains will be designed initially to run on electric and battery power, with the possibility to be converted into fully electric operation in the future.
After the DART reaches Drogheda, 32 miles of the Enterprise route will be electrified, with 80 miles unelectrified.
If it is assumed that the Dublin Connolly and Drogheda electrification, means that all trains leave Drogheda for Belfast with a full battery, then it looks to me, that there are three ways, this route could be operated.
- Trains would have a range on excess of 80 miles and would be charged by a short length of overhead wire in or near Belfast Lanyon Place station.
- Trains would have a range on excess of 160 miles and would be charged, whilst running South of Drogheda.
- Trains would be tri-mode trains, with diesel power.
Note.
- Battery-electric multiple units have already been ordered for the Dublin DART from Alstom.
- There are several charging systems available from companies like Furrer+Frey, Hitachi and others.
- The Guinness World Record for a battery-electric train is around 140 miles, but battery technology is improving.
- I suspect range will rule out the second option.
- The first option would be zero-carbon from day one.
Choosing the first option would seem to be the most likely option.
When electrification between Belfast Lanyon Place and Dublin Connolly is completed, all trains could be converted to either all-electric or battery-electric trains.
Could Similar Techniques Be Used To Decarbonise Other Irish Routes?
Just as the Belfast service uses a branch of the electrified DART, as a route out of Dublin, it appears that other Irish routes share tracks with the DART to access stations in the centre of Dublin.
- Cork services share the DART branch to Hazelhatch and Celbridge station.
- Sligo services share the DART branch to Maynooth station.
- Rosslare services share the DART branch to Greystones station.
- Waterford services share the DART branch to Hazelhatch and Celbridge station.
I can see similar trains, that will be used between Dublin and Belfast, being used on other routes to and from Dublin.
Conclusion
Decarbonisation of Dublin and Belfast could be the start of something big and green in the island of Ireland.
I suspect train manufacturers, like Alstom, CAF and Stadler will use all their skills to secure the contract to build the trains for the Enterprise service.
Hydrogen And Electric Propulsion Compared
Stadler have given us an interesting way of comparing the range and other properties of hydrogen-powered and battery-electric trains, as their Flirt H2 and Akku trains have both set Guinness World Records for distance travelled.
The Hydrogen-Powered Flirt-H2
In Stadler’s FLIRT H2 Sets World Record For Hydrogen Powered Train, I write about how a Stadler Flirt-H2 had set a record of 2803 kilometres, without refilling.
This page on the Stadler web site gives details of the Flirt-H2.
- Hydrogen Range – 460 km.
- Operating Speed – 127 kph
- Refuelling Time – < 30 minutes
- Seats – 116
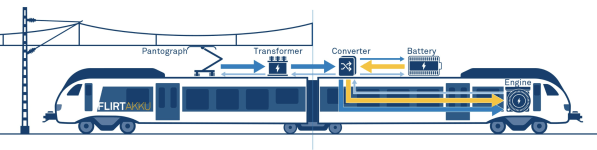
This graphic clipped from the Stadler web site shows the Flirt-H2.
Like Greater Anglia’s Class 755 train, it has a PowerPack in the middle, which contains a fuel cell and the hydrogen tank, instead of the Class 755 train’s diesel engines.
The Battery-Electric Akku
In Flirt Akku And Class 755 Train Compared, I compare a Flirt Akku and Greater Anglia’s Class 755 train, after the battery-electric Akku had set a record of 224 kilometres, with recharging.
This page on the Stadler web site gives details of the Flirt Akku.
- Battery Range – 150 km
- Operating Speed – 160 kph
- Chrging Time – 15 minutes
- Seats – 120-180
This graphic clipped from the Stadler web site shows the Flirt Akku.
At a quick glance, the trains seem to be fairly similar, with the exception of the PowerPack.
- Both have regenerative braking.
- Both have the battery and the power converter on the roof.
- I would expect that the Flirt-H2 could be fitted with a pantograph and a transformer.
- Both trains have two passenger carriages.
I also suspect, both trains can be lengthened by adding extra coaches.
These are my thoughts.
Thoughts On The PowerPack In A Flirt-H2
This picture shows the PowerPark car of a Class 755 train.
Note.
- These PowerPacks have slots for up to four 480 Kw diesel engines.
- PowerPacks on a Class 788/4 train with four diesel engines weighs 27.9 tonnes.
- PowerPacks on a Class 788/3 train has two diesel engines.
- In the UK, trains with PowerPacks have up to four passenger cars.
- The PowerPack has a walkway from one end of the car to the other.
As customers, might like to replace their diesel PowerPacks, with something that was zero-carbon, I would expect, that the hydrogen PowerPack would have the following properties.
- Hydrogen and diesel PowerPacks would be interchangeable.
- The hydrogen PowerPack would come in two handy sizes of hydrogen fuel cell; 0ne and two MW.
- The weight of both hydrogen and diesel PowerPacks would be similar, as if power and weight were similar, then this could help certification.
- The Flirt-H2 for California, which would only have two passenger cars, would have the smaller hydrogen fuel cell.
I would expect that a conservative designer would use any spare space for hydrogen storage.
- Perhaps, there would be one tank either side of the walkway.
- The quoted range of 450 kilometres for the Flirt-H2 is just under 300 miles, so it would probably cover most regional round trips in Europe without refuelling.
- On many routes refuelling would only need to be done once-per-day.
- Refuelling can be some distance from operation.
- Large tanks would explain the thirty minutes refuelling time.
Obviously, large tanks have the collateral benefit of setting distance records.
The Kinetic Energy Of A Flirt-H2 Train
In My First Rides In A Class 755 Train, I calculated the kinetic energy of a Class 755/4 train.
I said this.
I will use my standard calculation.
The basic train weight is 114.3 tonnes.
If each of the 229 passengers weighs 90 kg with Baggage, bikes and buggies, this gives a passenger weight of 20.34 tonnes.
This gives a total weight of 134.64 tonnes.
Using Omni’s Kinetic Energy Calculator gives these figures for the Kinetic energy.
- 60 mph – 13.5 kWh
- 100 mph – 37.4 kWh
- 125 mph – 58.4 kWh
If we are talking about the Greater Anglia Class 755 train, which will be limited to 100 mph, this leads me to believe, that by replacing one diesel engine with a plug compatible battery of sufficient size, the following is possible.
- On all routes, regenerative braking will be available under both diesel and electric power.
- Some shorter routes could be run on battery power, with charging using existing electrification.
- Depot and other short movements could be performed under battery power.
The South Wales Metro has already ordered tri-mode Flirts, that look like Class 755 trains.
The calculation for a Flirt-H2 train is as follows.
Train Weight – 82.3 tonnes
Passenger Weight – 10.4 tonnes
Total Weight – 92.7 tonnes
This gives these kinetic energies
- 60 mph – 9.3 kWh
- 79 mph – 16.0 kWh
- 100 mph – 25.7 kWh
It looks like the 79 mph; Flirt-H2 would only need a 16 KWh battery.
It seems when a battery is not for traction and only handles the regenerative braking, it can be surprisingly small.
Mathematical Advantages Of Hydrogen
I do wonder that on balance, there may be mathematical advantages to hydrogen; long range, less frequent refuelling and small batteries.
But as I indicated in Zillertalbahn Hydrogen Plan Dropped In Favour Of Battery Traction, the decision doesn’t always go hydrogen’s way!
Conclusion
I feel Stadler have the right approach of a modular concept that incorporates both hydrogen-powered and battery-electric trains.
I also think, if you have a route, you want to decarbonise, Stadler have the train for you.
Zillertalbahn Hydrogen Plan Dropped In Favour Of Battery Traction
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
I wrote about this order in Zillertalbahn Orders Stadler Hydrogen-Powered Trains.
I didn’t blog about it but I remembered an article a few years ago about Stadler getting an order from the Zillertalbahn.
It appears the change is down to improvements in battery technology.
Narrow-gauge battery-electric multiple units must be right up Stadler’s street, as they built the new trains for the narrow gauge Glasgow Subway.
Third Rail Or Batteries Could Replace Southern Diesel Trains
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette International.
I first wrote about the Uckfield Branch eight years ago, in Future-Proofing The Uckfield Branch.
Since then I have written about this branch several times and I have also read several articles in the railway press.
These are some of my posts.
- Discontinuous Electrification Using IPEMUs – April 30th, 2016
- Will Innovative Electrification Be Used On The Uckfield Line? – August 24th, 1917
- Battery Trains On The Uckfield Branch – August 26th, 2018
- Battery Electrostars And The Uckfield Branch – September 30th, 2019
- Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And The Uckfield Branch – November 12th, 2021
- Electroflex Battery EMU Plan To End Southern Diesel Operation – January 22nd, 2020
- Uckfield Third Rail Is NR Priority – May 2nd, 2022
- Southeastern Keen On Battery EMUs – August 12th. 2023
It is an utter disgrace that no decision has been made in eight years about how to decarbonise to Uckfield.
The Railway Gazette article says this about third-rail electrification.
GTR is one of two operators participating in a Rail Safety & Standards Board project reviewing the safety, legal and regulatory issues around third rail electrification infill projects. This is looking at whole transport system safety, project and economic risks.
Bi-monthly South of England Diesel Replacement Programme meetings are held by DfT, Network Rail and GTR to review progress and options for third rail electrification of the Uckfield line or battery train trials. This includes reviewing the lessons learned from the use of bi-mode trains by GWR and LNER, and the failed attempt to deploy tri-mode Class 769 units on GWR’s North Downs services.
Could it just be that there is such fear that there will be a major incident, where several people are killed, that third-rail electrification is always turned down, by the Office of Road and Rail?
The Railway Gazette article also says this about battery trains, under a heading of Batteries Viable.
In the absence of electrification, GTR says battery powered trains are also a viable option for its diesel routes. Batteries can be charged while trains are running on electrified lines or through a rapid recharging facility at a terminus, although additional infrastructure and electrical upgrades may be needed.
I suspect that after a few teething troubles, Merseyrail would agree.
Hydrogen is also dismissed with this paragraph.
GTR has considered hydrogen but says it can only be considered a net zero-compliant fuel if it is produced from low or zero-carbon energy sources. It is also relatively inefficient with studies indicating an efficiency rate of around 35% to 40%.
It looks to me, that battery-electric trains are a viable solution.
So would it not be a good idea to take the decision to create a battery-electric prototype from a four-car Electrostar or a Class 350 train, so that the final decision can be taken after everybody on the committee has have a ride first?
Better still, why not stage a competition, where manufacturers, leasing companies or remanufacturers can build a four-car train and enter.
Allow the public to ride in them and then see what is best against a range of criteria.
The King could even get involved, as he’s probably one of the few people left, who rode the original British Rail BEMU between Aberdeen and Ballater, to get to Balmoral.
Fire Safety Of Battery-Electric Vehicles
I notice that there has been talk of fires in battery-electric vehicles on this blog.
So I thought I’d put up a post with an appropriate topic.
There are some things that already could worry me.
- Vivarail had a fire early on.
- The Merseyrail Class 777 trains go in the tunnels under Liverpool.
- The new Piccadilly Line trains will have batteries.
- Did electric vehicle batteries contribute to the ferocity of the fire in the Luton Airport car park?
- Fire brigades are getting very worried about e-scooter and e-bike fires.
- This page on the Internet gives details of recent BESS fires.
- Do we investigate fires and publish the results properly?
I have some questions.
- Would it be sensible to have nationwide database of all batteries?
- Should we use more non-lithium methods in large stationary batteries?
- Should we use more capacitors?
- Should we make it a criminal offence to build or use a non-compliant e-bike or e-scooter?
- Should installing a battery in your house, need a safety certificate?
One half of me says yes and the other says no, to some of these questions.
Great Western Railway’s Battery Train Sets New Distance Record
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Great Western Railway.
This is the sub-heading.
Great Western Railway’s innovative FastCharge battery trial has achieved another significant step – just days after laying claim to a battery train UK distance record without recharging.
These two paragraphs add more detail.
The train demonstrated its capability on Wednesday by travelling a UK record of 86 miles (138km) on battery power alone and without recharging.
Today the Class 230 battery train completed a 70-mile move from Long Marston to Reading Train Care Depot – using just 45 per cent of its battery capacity. GWR’s team of specialist engineers on board the train claim it could have travelled more than 120 miles on a single charge.
There is also this impressive video.
Note.
- In the video, the train is cruising at 36 mph.
- The top speed of the D78 Stock was 45 mph.
- The train looks in excellent condition.
This is a total game-changer for battery-electric trains in the UK.
The train makers, who have demonstrated battery-electric trains; Alstom/Bombardier, CAF, Hitachi, Siemens and Stadler will have to up their distances on battery power to at least 86 miles and possibly 120 miles, as who would want their new product to be outdistanced by second-hand forty-year-old upcycled London Underground trains?
I have some further thoughts.
The Trains Performance In The Real World
Dr. Simon Green, who is GWR’s Engineering Director, said this.
It’s also worth noting that in reaching the 86 miles on Wednesday, the train was operating in a real-world environment, at speeds of up to 60mph, stopping and starting over a hilly route, with elevation changes of up to 200m.
The train exceeded the 84 miles (135km) recorded by a Stadler Class 777 under test conditions in 2022 – believed to have been the greatest distance travelled by a battery train designed for the UK.
Note that the train was running at up to 60 mph.
Timings For The Mid-Cornwall Metro
This map shows the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
I have been looking at the Mid-Cornwall Metro and this service will share the Cornish Main Line with faster services between Par and Truro.
- Expresses and the Mid-Cornwall Metro will both stop at Par, St. Austell and Truro.
- Par and Truro is a distance of 19 miles.
- Expresses between Penzance and Plymouth take around 22-23 minutes to go between Par and Truro.
- This is an average speed of around 50-52 mph.
It looks to me, that there is scope for the Mid-Cornwall Metro and the express trains to run at similar speeds between Par and Truro.
- If the Mid-Cornwall Metro used Class 230 trains running on batteries, these trains should be fast enough to keep out of the way of the expresses.
- Par station has an island platform, where the Mid-Cornwall Metro uses one side (Platform 3) and expresses use the other (Platform 2).
Perhaps, if the timetable was something like this, it would give the best services to passengers.
- All expresses would use Platform 2, if they were stopping at Par station. The current track layout allows this.
- For Westbound passengers the Mid-Cornwall Metro would stop in Platform 3 and the express would stop in Platform 2, so that passengers going to beyond Truro on the Cornish Main Line could to the express on the other platform.
- Between Par and Truro, the Mid-Cornwall Metro would run a couple of minutes behind the express.
- Passengers for the Falmouth Branch could swap trains at Par on wait for the Metro at St. Austell or Truro.
- For Eastbound passengers, between Par and Truro, the Mid-Cornwall Metro would run a couple of minutes behind the express.
- At Par, the Mid-Cornwall Metro would stop in Platform 3 and the express would stop in Platform 2.
- The express would wait at Par for the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
- Passengers for Plymouth and London Paddington would change trains at Par for the express on the other platform.
- Passengers for the Newquay Branch on the express would swap trains at Par or wait for the Metro at St. Austell or Truro.
I suspect there are other patterns, but something like this will combine express services with the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
Simon’s Vision
Simon Green also says this about his vision of how the trains and the related FastCharge technology could be used.
GWR’s FastCharge technology has been designed to solve the problem of delivering reliable, battery-only trains capable of fulfilling timetable services on branch lines, eliminating the use of diesel traction and helping to meet the Government and wider rail industry’s target to reach net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
The use of batteries for extended operation has typically been constrained by their range and meant widespread implementation has, until now, not been possible. It also negates the need for overhead electric lines which are expensive, time consuming to install and impact the landscape.
He’s judging the system as a whole, which is the only way to do it.
Where Could Class 230 Trains Be Used On The Great Western Railway?
These are a few ideas.
- Slough and Windsor & Eton Central – 2.8 miles – 3 cars – FastCharge at Slough
- Maidenhead and Marlow – 7.1 miles – 2 or possibly 3 cars – FastCharge at Maidenhead
- Twyford and Henley-on-Thames – 4.6 miles – 3 cars – FastCharge at Twyford
- Reading and Basingstoke – 15.4 miles – 3 cars – FastCharge at Basingstoke
- Weston-super-Mare and Severn Beach – 32.5 miles – 3 cars – FastCharge at Severn Beach
- Bristol Temple Meads to Avonmouth 8.9 miles – 2 cars – FastCharge at Avonmouth
Bourne End station, where there is a reverse may restrict the length of the service to Marlow.
Newquay Station – 9/10th February 2024
These pictures show Newquay station.
Note.
- It is a small one-platform station.
- It has a few facilities.
- It is located on the main street in the centre of the town.
This Google Map shows Newquay station.
Newquay station appears to have a very long platform.
- This page on Railway Data gives a length of 242 metres.
- It should accommodate a nine-car Class 802 train.
- The station is also close to the beach.
It looks to me that Newquay station is ready for a big surfing festival.
I have a few thoughts.
Adding A Second Platform
These pictures show the space alongside the current single track. At least for a five-car train.
Note.
- I would expect that adding a second platform could be easily done by a competent and experienced construction company.
- There would need to be new track and a set of points, so that a train could use either platform.
- Signalling would be added, so both platforms could be used, either separately or at the same time.
I also expect that the Tregoss Loop would need to be commissioned before the second platform.
Adding Charging For Battery-Electric Trains
Consider.
In GWR Trialling Transformative Ultra-Rapid Charging Train Battery, I talked about the installation of the Vivarail/GWR Fast Charge system at West Ealing station.
In Decarbonising The Mid-Cornwall Metro, I talked about using the Vivarail/GWR Fast Charge system or hydrogen to decarbonise the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
This picture shows the Vivarail/GWR Fast Charge system at West Ealing station.
I feel there would be no problem fitting one of these in one or both of the platforms at Newquay.
But I do feel that the best way to decarbonise services to Newquay, would be to fully-electrify Par station with 25 KVAC overhead wires.
- Mid-Cornwall Metro services would charge their batteries using a pantograph, every time that they reversed in the station.
- Long distance battery-electric services through the station would top up their batteries during a stop at the station.
- Locomotives with batteries will be increasingly used on freight services and charging may be needed for the locomotives used from china clay trains.
Note.
- Par and Falmouth Docks is 30.8 miles.
- Par and Newquay is 20.8 miles.
- Par and Penzance is 44.8 miles
- Par and Plymouth is 34.7 miles.
- Par and Truro is 19 miles.
Par would appear to be a station, that could be easy to electrify and is conveniently placed in the heart of services through Cornwall.
Decarbonising The Mid-Cornwall Metro
Although the Mid-Cornwall Metro will probably run initially using what diesel multiple units, after a year or so, the route will be converted to zero-carbon operation.
Newquay To Falmouth Docks
This map shows the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
These are current timings.
- By train can take almost three hours with changes at Par and Truro.
- By car should take 45 minutes to drive the 24.4 miles according to Google.
Note.
- The train timings are for a typical British Rail-era Diesel Multiple Unit on the branches and something smarter between Truro and Par.
- A Day Return ticket would cost £8.90 without a Railcard.
- If there was a through train, that meant you didn’t have to change trains, I estimate that the time could be as low as one hour and 35 minutes.
I feel that most travellers, who had access to a car, would use that to travel between Newquay and Truro.
Newquay To Falmouth Docks By Electric Train
I have ridden in three battery-electric trains.
- Class 379 train – Manningtree and Harwich in passenger service.
- Class 230 train – Vivarail demonstration
- Class 777 train- Liverpool Central and Headbolt Lane in passenger service.
Note.
- All were mouse-quiet.
- There was no detectable difference, when running on battery power in the trains.
It is my view that battery-electric trains are no second-class solution.
Consider.
- Newquay and Par is 20.8 miles.
- Falmouth Docks and Par is 30.8 miles.
- Newquay and Falmouth Docks is 51.6 miles.
- The maximum speed between Par and Newquay is around 30 mph
- The maximum speed between Par and Falmouth Docks is around 50-70 mph
- There are twelve intermediate stations.
- There is a reverse at Par station.
- Charging would be easy to install at Falmouth Docks, Newquay and Par.
- In Par Station – 10th February 2024, I suggested that Par station could be fully-electrified, so that expresses could have a Splash-and-Dash on their way to London and Penzance. If all platforms at Par were electrified the Mid-Cornwall Metro trains could charge from the electrification, as they reversed.
There are two main ways that the Mid-Cornwall Metro might operate.
- There would be chargers at Newquay and Falmouth Docks and trains would shuttle the 51.6 miles between the two stations.
- There would only be charging at Par and trains would after charging at Par go alternatively to Newquay and Falmouth Docks.
The first might need smaller batteries and the second would only need one charger.
Newquay To Falmouth Docks By Hydrogen-Powered Train
There is only one hydrogen-powered train in service and that is the Alstom Coradia iLint, which is running in Germany.
I feel it is very much an interim design, as Alstom has taken a diesel-mechanical Lint train and swapped the diesel for a hydrogen-powered electricity generator and an electric motor.
But Alstom are putting together a hydrogen-powered train based on an Aventra.
Note.
- The train is three cars.
- I would envisage performance of the hydrogen train would be very similar to that of a similar battery-electric train.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that refuelling of the train would not be a problem, as with all the china clay working nearby, there may well be developments to use hydrogen in the industry to decarbonise the mining.
The Mid-Cornwall Metro and Alstom’s Hydrogen Aventra could be ideal for each other.
Conclusion
I believe, that although the Mid-Cornwall Metro will start operation with diesel multiple units, it will be running in a zero-carbon mode within a few years.
Smart Train Lease Aims ‘To Make Renting Trains As Easy And Simple As Renting A Car’
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette International.
These four paragraphs outline the scheme.
Siemens Mobility has established a leasing subsidiary that would enable train operators to use its Mireo Smart battery, hydrogen and electric multiple-units without needing to make long-term investment commitments.
Smart Train Lease GmbH would make available at short notice multiple-units already approved for operation. These could be short or medium-term leases, with services such as maintenance available as part of the package. The aim is to provide operators with an economical way to quickly and flexibly expand their fleets and try out more sustainable traction technologies.
‘We want to make renting trains as easy and simple as renting a car, and thus help accelerate the mobility transition’, the leasing company’s CEO Benjamin Dobernecker explained on February 14.
Smart Train Lease will initially operate in Germany, although it plans to expand throughout Europe in the medium term.
I like this idea and I think it will work.
Metier Management Systems And Artemis
When four of us started Metier Management Systems in 1977 to sell our mini-computer-based project management system; Artemis, we generally rented or leased our systems, although we did sell some as the years progressed.
- For a fixed fee per month, a company got a project management computer and all the software.
- The fixed fee included installation, first line support, training and software updates.
- We could also supply extra training and project management consultancy at appropriate rates.
- The only extra costs to the client were the electricity to power the hardware and the paper to put in the printer.
- We also allowed clients to convert leases into outright sales.
This simple sales model appealed to a lot of our clients.
- The cost of the system was easy to budget.
- Many of our clients were happy with leasing or renting computer equipment.
- As the system was desk-sized, it easily fitted the average office.
But the leasing model was very advantageous to us.
- Most of our clients were large high-value quality organisations like big oil companies, nationalised industries and engineering consultancies.
- Our Finance Director and our Bank Manager at Lloyds Bank devised a plan, whereby we bundled a number of high-quality leases together and sold the bundle to Lloyds Bank’s leasing company.
The money we received gave us a healthy cash flow.
- The cash flow was then used to fund Research and Development and to finance more sales.
- If say someone like BP or Shell should phone up or send a fax, wanting a system immediately, we were generally able to fulfil their request.
I am sure that Siemens Mobility will be using a similar model.
They will aim to have trains in stock to fulfil clients needs.
So if Deutsche Bahn phone up saying have you got a three-car battery-electric train that works with 15 KVAC and has a range of 100 kilometres for next Monday, Siemens Mobility can generally say yes.
What helps is that the modular Mireo Smart multiple unit comes in battery, hydrogen and electric versions.
Extras could include full servicing a driver.
So Siemens Mobility will plug the train together and deliver it.
How Would Siemens Use The Leasing Model In Great Britain?
Consider.
- There are a lot of routes that need to be decarbonised in Great Britain.
- Many of these routes have electrification at one or both ends.
- Often these routes terminate in a bay platform.
- On most of these routes a two-, three-, four- or five-car train will be sufficient capacity.
- In the Desiro City, Siemens have a train, that is acceptable to Great Britain.
- If routes in Great Britain are to be electrified, they must be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead wires.
- Trains would be 100 mph, so they wouldn’t be limited as to routes.
- A Mireo-B has a range of between 80-100 kilometres or 49.7-74.6 miles.
I am sure Siemens Desiro City or its European equivalent; Mireo can be developed into a family of trains suitable for GB!
- The basic train would be two driving cars.
- Length would be increased by coupling trailer cars between the two driving cars.
- Hydrogen power would be in one of the trailers.
- Batteries would be under an appropriate number of cars.
Battery trains would be able to use a simple automatic charger, similar to the one, that I described in GWR Trialling Transformative Ultra-Rapid Charging Train Battery.
An Example – Mid-Cornwall Metro
This map shows the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
Consider.
- Newquay and Par is 20.8 miles.
- Falmouth Docks and Par is 30.8 miles.
- Newquay and Falmouth Docks is 51.6 miles.
- The maximum speed between Par and Newquay is around 30 mph
- The maximum speed between Par and Falmouth Docks is around 50-70 mph
- There are twelve intermediate stations.
- There is a reverse at Par station.
- Charging would be easy to install at Falmouth Docks, Newquay and Par.
- In Par Station – 10th February 2024, I suggested that Par station could be fully-electrified, so that expresses could have a Splash-and-Dash on their way to London and Penzance. If all platforms at Par were electrified the Mid-Cornwall Metro trains could charge from the electrification, as they reversed.
There are two main ways that the Mid-Cornwall Metro might operate.
- There would be chargers at Newquay and Falmouth Docks and trains would shuttle the 51.6 miles between the two stations.
- There would only be charging at Par and trains would after charging at Par go alternatively to Newquay and Falmouth Docks.
The first might need smaller batteries and the second would only need one charger.
An Example – Uckfield Branch
The Uckfield branch is in Southern England.
- It is not electrified between Hurst Green Junction and Uckfield, which is 24.7 miles.
- There are eight intermediate stations.
- The line can accommodate ten-car trains.
There is space at Uckfield station for a charger.
Charging would be at Uckfield station and North of Hurst Green Junction, where it will use the existing electrification.
Conclusions
This leasing/rental model will surely encourage train operators to replace diesels with appropriate zero-carbon alternatives on routes that need to be decarbonised.