Newport To Swindon Via Gloucester – 14th June 2025
Because of engineering works, we came home from Newport via a diversion through Gloucester.
I took these pictures.
Note.
- I had sat on the right side of the train facing forward.
- We were accompanied my the thud, thud, thud of an underfloor diesel engine, as most of the route is not electrified.
- Newport and Gloucester is 44.8 miles.
- Gloucester and Swindon is 36.7 miles.
- Newport and Swindon is 81.5 miles.
- Newport and Swindon are fully-electrified stations.
- The first four pictures show Trains for Wales Premier Service.
- The Gloucester and Newport Line joins the South Wales Main Line at Severn Tunnel Junction station.
- As you travel towards Gloucester, the bridges over the Severn and the Wye can be clearly seen.
- There are two former nuclear power stations ;Berkeley and Oldbury, on the far bank of the River Severn.
- The large white wind turbine is close to Berkeley.
- Oldbury is further down the river.
As yesterday, the route is commonly used as a diversion route, when engineering works close the electrified main line through the Severn Tunnel.
I have some further thoughts.
Electrification Of Newport And Swindon
The distances involved are as follows.
- Newport and Gloucester is 44.8 miles.
- Gloucester and Swindon is 36.7 miles.
- Newport and Swindon is 81.5 miles.
As Hitachi’s Intercity Battery Trains are likely to have a range of around a hundred miles, they should be able to handle the diversion.
A short length of electrification could be erected in Gloucester station to charge any battery-electric trains, that needed a boost.
I believe full electrification is not needed.
Regulator Approves New Go-op Train Service Between Swindon, Taunton and Weston-super-Mare
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from the Office of Rail and Road.
This is the sub-heading.
The rail regulator has given the go ahead for new train services between Swindon, Taunton and Weston-super-Mare from the end of 2025. The regulator has also set conditions on its approval to ensure the new, co-operatively owned operator has sufficient finance and rolling stock in place in good time.
These paragraphs from the press release give more details.
Go-op plans to operate return weekday and weekend services between Taunton and Weston-super-Mare, Taunton and Westbury, Taunton and Swindon, and Frome and Westbury.
It will compete with Great Western Railway (GWR), a public service operator. Go-op plans to start in December 2025 at the earliest, and must do so no later than December 2026 in order to use the capacity ORR has granted.
As part of ORR’s decision, Go-op must provide evidence to ORR of the necessary finance to start operations, fund level crossing enhancements, and that the necessary rolling stock has been secured. ORR’s decision requires Go-op to do this without delay, and no later than November 2025.
I must admit I’m a little surprised at the Office of Rail and Road giving approval.
There is more on the Go-op web site.
Leisure Market Boom? GWR’s Vision For Direct Bristol-Oxford Services
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Magazine.
This is the first paragraph.
Great Western Railway has hopes on running direct services between Bristol Temple Meads and Oxford from September 14, subject to approval of its new trial proposal by the Department for Transport and Network Rail. The move is a test of growth in demand for leisure travel by train.
It is an interesting idea.
These are some points about the service, given in the article.
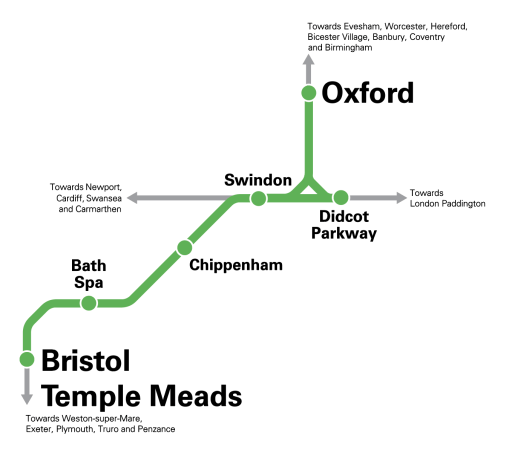
- The route will be via Swindon, Chippenham and Bath Spa.
- Fastest journey time would be 71 minutes.
- The route will be aimed at the leisure market.
- There will be two trains per day (tpd) in each direction on Saturdays.
This is GWR’s handy route map.
These are my thoughts.
Will The Trains Call At Didcot Parkway?
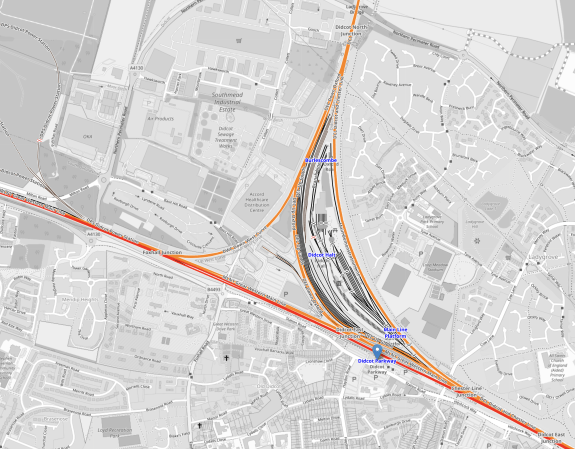
This OpenRailwayMap shows Didcot Parkway station and the large triangular junction, that connects Oxford to the Great Western Main Line.
Note.
- The red tracks are the Great Western Main Line.
- The blue arrow indicates Didcot Parkway station.
- Oxford station is about ten miles to the North.
- Chords in the junction allow trains to go between Oxford and Paddington and Oxford and Swindon, with or without a stop at Didcot Parkway station.
The article says that GWR has asked to run the following services.
- 1018 Bristol Temple Meads-Oxford – Would arrive at Oxford at 1129.
- 1155 Oxford-Bristol Temple Meads (via Didcot) – Would arrive at Bristol Temple Meads at 1306.
- 1518 Bristol Temple Meads-Oxford – Would arrive at Oxford at 1629.
- 1712 Oxford-Bristol Temple Meads – Would arrive at Bristol Temple Meads at 1823.
Note.
- I suspect that the 1155 will reverse at Didcot Parkway station.
- There is a two train per hour (tph) service between Didcot Parkway and London Paddington stations.
- It looks like the four services could be run by a single train shuttling up the Great Western Main Line.
Would it be sensible if all Oxford and Bristol trains called at Didcot Parkway station, so that travellers could use the London service to their advantage?
But, calling at Didcot Parkway station would slow the service as there would need to be a reverse.
What Class Of Train Would Be Used?
Consider.
- A Bristol and Didcot Parkway via Bath Spa service takes 55 minutes.
- This is an average speed of 71.1 mph over a distance of 65.2 miles.
- 24.4 miles at the Bristol end of the route is not electrified.
- 10.3 miles at the Oxford end of the route is not electrified.
- The four services can be run by a single train shuttling up the Great Western Main Line.
It looks to me, that a bi-mode train with good performance is needed.
So I suspect that a five-car Class 800 or Class 802 train will be used.
Will The Train Be Battery-Electric Powered?
This is an interesting possibility.
- An ideal route for a battery electric train, is surely one with a long electrified section in the middle, which can be used to fully charge the train’s batteries.
- The train would have to run for 48.8 miles on its own power at the Bristol end of the route.
- The train would have to run for 20.6 miles on its own power at the Oxford end of the route.
The data sheet for a battery-electric Class 800/802 train can be downloaded from this page on the Hitachi web site.
In a section on the page, which is entitled Intercity Battery Trains, this is said.
A quick and easy application of battery technology is to install it on existing or future Hitachi intercity trains. Adding just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%.
Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance. Hitachi Rail’s modular design means this can be done without the need to re-engineer or rebuild the train and return them to service as quickly as possible for passengers.
The range of 70 km is 43.5 miles, which would appear to be a little bit short to go from the end of the electrification at Chippenham to Bristol Temple Meads and back.
But various measures could be taken to make sure the train can handle the route.
- The regenerative braking strategy could be used to conserve battery power.
- A second battery could be added to the train.
- Methods to charge the train at Bristol Temple Meads could be installed.
As London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads is an important route, I suspect that Hitachi and Great Western Railway have a strategy to handle trains from Chippenham and sending them back.
Could This Route Be A Trial Route For Battery-Electric Trains?
Consider.
- Hitachi and Great Western Railway wouldn’t want to introduce an unreliable train without full full testing.
- Trains can probably limp to either Stoke Gifford or Reading depots, after a battery failure.
- Great Western Railway could test a new route.
- A full test only needs one train.
- Passenger reaction to a battery-electric train can be assessed.
- Staff need to be trained.
- The route can be run by a standard bi-mode if required.
- It could be the world’s first high-speed battery-electric train.
- Enthusiasts would flock to have a ride.
Could this be a trial service to make sure everything goes right?
Extending The Elizabeth Line – Connecting Great Western Main Line Services To The Central Tunnel
If say it was ever needed to run a train between Oxford or Swindon stations and the Central Tunnel of the Elizabeth Line, three things must be possible.
Trains Would Have To Be Compatible With The Central Tunnel Of The Elizabeth Line
As any train would have to be compatible with the platform-edge doors in the central tunnel of the Elizabeth Line, the trains would have to be dimensionally identical to the current Class 345 trains.
- Nine cars
- Possibility of lengthening to ten cars.
- 204.73 metres long.
- 6 sets of doors per carriage
- Ability to run under full digital signalling.
I covered this in detail in Extending The Elizabeth Line – High Speed Trains On The Elizabeth Line.
Trains Would Need A 125 mph Capability To Travel On The Fast Lines Of The Great Western Main Line
They would be designed for a higher speed of at least 110 or 125 mph, to enable running on the fast lines.
The faster running would ease scheduling of the trains.
Effectively, the train would be a Class 345 train with more features and considerably more grunt.
Trains Must Be Able To Connect Between The Fast Lines And The Central Tunnel Of The Elizabeth Line At Royal Oak
This map from cartometro.com shows the track layout at Royal Oak.
Note.
- The Elizabeth Line is shown in purple.
- Great Western Railway (GWR) tracks are shown in black.
- Where the Elizabeth Line shares the tracks with GWR services the tracks are shown in black and purple.
This map shows an enlargement of Kensal Green East Junction in the North-West corner of the previous map.
Note.
- The top pair of lines lead to the Elizabeth Line Depot at Old Oak Common.
- the pair of lines that are shown in black and purple handle Elizabeth Line and GWR local services.
- The pair of black lines are the Great Western Main Line.
- North Pole Depot is used by GWR for their Hitachi trains.
This map shows an enlargement between Ladbroke Grove Junction and Royal Oak.
Note.
- In the South-East corner of the map is Subway junction, which appears to have two crossovers for maximum flexibility.
- To the East of Subway junction the curved line indicates the Royal Oak Portal of the Elizabeth Line Central Tunnel.
- To the West of Subway junction, there is Paddington New Yard, where there is five tracks labelled CRL Eastbound, Turnback C, Turnback B, Turnback A and CRL Westbound from North to South.
- Turnback C, Turnback B and Turnback A are the three turnback sidings, where trains are turned back East through the Elizabeth Line Central Tunnel.
- CRL Eastbound and CRL Westbound can be followed across the map to the black and purple lines of the Elizabeth Line to the West of Ladbroke Grove junction.
- At present the Western section of the Elizabeth Line terminates in Paddington station. Crossovers at Portobello junction appear to connect the Western section of the Elizabeth Line into Paddington station.
- More crossovers also appear to connect the Great Western Main Line to the CRL Eastbound and CRL Westbound through Paddington New Yard.
I am fairly sure that the track layout at Royal Oak allows trains to go both ways between Great Western Main Line and the Elizabeth Line Central Tunnel.