Could Doncaster Sheffield Airport Become A Hydrogen Airport?
I asked Google AI, what is the current status of Doncaster Sheffield Airport and received this reply.
Doncaster Sheffield Airport (DSA) is currently in a state of active, public-funded redevelopment after closing in late 2022 due to financial issues, with plans to reopen for passenger flights by late 2027 or 2028, following significant funding (around £160m) secured by the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority (SYMCA) for the City of Doncaster Council to take over operations and rebuild commercial viability, with freight and general aviation potentially returning sooner.
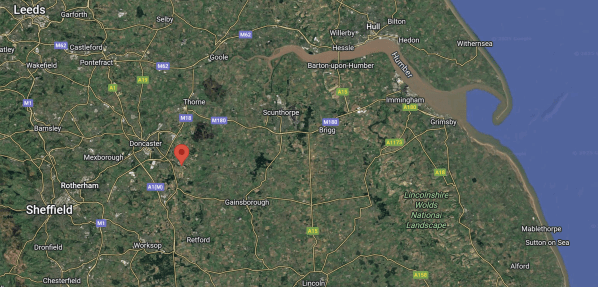
This Google Map shows the location of the airport.
Note.
- The distinctive mouth of the River Humber can be picked out towards the North-East corner of the map.
- Hull and Grimsby sit in the mouth of the Humber.
- The red arrow indicates Doncaster Sheffield Airport.
- Leeds is in the North-West corner of the map.
- The towns and city of Doncaster, Rotherham and Sheffield can be picked out to the West of the airport.
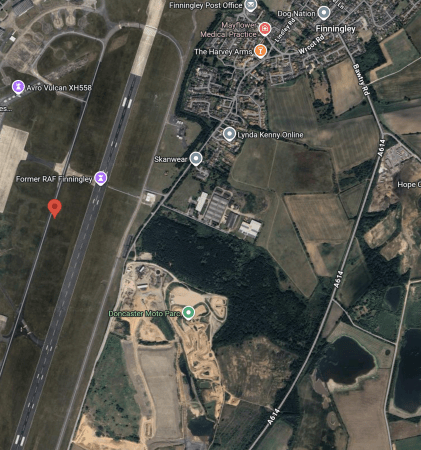
This second Google Map shows a close-up of the airport.
On my visit to NASA in the 1980s, where an Artemis system was used to project manage the turnround of the Space Shuttle, I was asked questions by one of NASA’s support people about RAF Finningley. Nothing too technical, but things like what is Doncaster like.
When I asked why, they said there’s a high chance that a Space Shuttle could land at RAF Finningley, as it has one of the best runways for a very heavy aircraft in Europe.
Looking at the runway, it is a long and wide runway that was built for heavy RAF nuclear bombers like Valiants, Victors and Vulcans.
I believe that we will eventually see hydrogen- and/or nuclear-powered airliners flying very long routes across the globe, just as a nuclear-powered example, attempted to do in the first episode of the TV series Thunderbirds, which was called Trapped in the Sky and has this Wikipedia entry.
Just as the Space Shuttle did, these airliners and their air-cargo siblings will need a large runway.
Doncaster Sheffield Airport already has such a runway.
These hydrogen- and nuclear-powered aircraft will make Airbus A 380s look small and will need runways like the one at Finningley.
But I don’t think we’ll ever see nuclear-powered aircraft in the near future, so the aircraft will likely be hydrogen.
Other things in favour of making Doncaster Sheffield Airport, an airport for long range hydrogen aircraft include.
- The airport is close to the massive hydrogen production and storage facilities being developed on Humberside at Aldbrough and Rough.
- The airport could be connected to the Sheffield Supertram.
- The airport could be connected to the trains at Doncaster station, which has 173 express trains per day to all over the country.
- The airport would fit well with my thoughts on hydrogen-powered coaches, that I wrote about inFirstGroup Adds Leeds-based J&B Travel To Growing Coach Portfolio
- The airport might even be able to accept the next generation of supersonic aircraft.
- The airport could certainly accept the largest hydrogen-powered cargo aircraft.
- The Airport isn’t far from Doncaster iPort railfreight terminal.
Did I read too much science fiction?
I have some further thoughts.
Do Electric Aircraft Have A Future?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
Yes, electric aircraft absolutely have a future, especially for short-haul, regional, and urban air mobility (UAM), promising quieter, zero-emission flights, but battery limitations mean long-haul flights will rely more on hydrogen-electric or Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) for the foreseeable future. Expect to see battery-electric planes for shorter trips by the late 2020s, while hybrid or hydrogen solutions tackle longer distances, with a significant shift towards alternative propulsion by 2050.
That doesn’t seem very promising, so I asked Google AI what range can be elected from electric aircraft by 2035 and received this answer.
By 2035, fully electric aircraft ranges are expected to be around 200-400 km (125-250 miles) for small commuter planes, while hybrid-electric models could reach 800-1,000 km (500-620 miles), focusing on short-haul routes due to battery limitations; larger, long-range electric flight remains decades away, with hydrogen propulsion targeting 1,000-2,000 km ranges for that timeframe.
Note.
- I doubt that many prospective passengers would want to use small commuter planes for up to 250 miles from Doncaster Sheffield airport with hundreds of express trains per day going all over the UK mainland from Doncaster station.
- But Belfast City (212 miles), Dublin (215 miles) and Ostend (227 miles), Ronaldsway on the Isle of Man (154 miles) and Rotterdam(251 miles) and Schipol 340 miles) may be another matter, as there is water to cross.
It looks like it will be after 2035 before zero-carbon aircraft will be travelling further than 620 miles.
My bets would be on these aircraft being hydrogen hybrid aircraft.
What Will The Range Of Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft In 2040?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
By 2040, hydrogen-powered commercial aircraft are projected to have a range that covers short- to medium-haul flights, likely up to 7,000 kilometers (approximately 3,780 nautical miles), with some models potentially achieving longer ranges as technology and infrastructure mature.
The range of these aircraft will vary depending on the specific technology used (hydrogen fuel cells versus hydrogen combustion in modified gas turbines) and aircraft size.
It looks like we’ll be getting there.
This Wikipedia entry is a list of large aircraft and there are some very large aircraft, like the Antonov An-225, which was destroyed in the Ukraine War.
A future long-range hydrogen-powered airline must be able to match the range of current aircraft that will need to be replaced.
I asked Google AI what airliner has the longest range and received this reply.
The longest-range airliner in service is the Airbus A350-900ULR (Ultra Long Range), specifically configured for airlines like Singapore Airlines to fly extremely long distances, reaching around 9,700 nautical miles (18,000 km) for routes like Singapore to New York. While the A350-900ULR holds records for current operations, the upcoming Boeing 777-8X aims to compete, and the Boeing 777-200LR was previously known for its exceptional range.
I believe that based on the technology of current successful aircraft, that an aircraft could be built, that would be able to have the required range and payload to be economic, with the first version probably being a high-capacity cargo version.
What Would An Ultra Long Range Hydrogen-Powered Airliner Look Like?
Whatever the aircraft looks like it will need to be powered. Rolls-Royce, appear to be destining a future turbofan for aircraft called the Ultrafan, which has this Wikipedia entry.
I asked Google AI, if Rolls-Royce will produce an Ultrafan for hydrogen and received this answer.
Rolls-Royce is actively developing the UltraFan architecture to be compatible with hydrogen fuel in the future, but the current UltraFan demonstrator runs on Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). The company has a research program dedicated to developing hydrogen-powered engines for future aircraft, aiming for entry into service in the mid-2030s.
I asked Google AI, if Rolls-Royce have had major difficulties converting engines to hydrogen and received this answer.
Rolls-Royce has not encountered insurmountable difficulties but faces significant engineering and logistical challenges in converting engines to run on hydrogen. The company has made substantial progress in testing both stationary and aero engines using pure hydrogen, confirming its technical feasibility.
Given the company’s success in developing engines in the past, like the R Type, Merlin, RB 211, Pegasus, Trent, mtu 4000 and others, I suspect there’s a high chance of a successful hydrogen-powered Ultrafan.
If you look at a history of large passenger and cargo aircraft over the last sixty years, there has been a lot of the following.
- Conversion of one type of aircraft to a totally different type.
- Fitting new engines to a particular type.
- Fitting new avionics to a particular type.
Examples include.
- Fitting new CFM-56 engines to DC-8s.
- The first two Nimrods were converted from unsold Comet 4Cs.
- Converting Victor bombers to RAF tanker aircraft.
- Converting BA Tristars to RAF tanker aircraft.
- Converting DC-8s to cargo aircraft.
- Airbus converted five Airbus A 300-600 into Belugas, which have this Wikipedia entry.
- Airbus converted six Airbus A 330-200F into BelugaXLs, which have this Wikipedia entry.
- Converting two Boeing-747s to carry Space Shuttles ; one from American Airlines and one from Japan Airlines, which have this Wikipedia entry.
Note.
- Most of these examples have been successful.
- The last three examples have been very successful.
- Most of these applications do not have a human cargo.
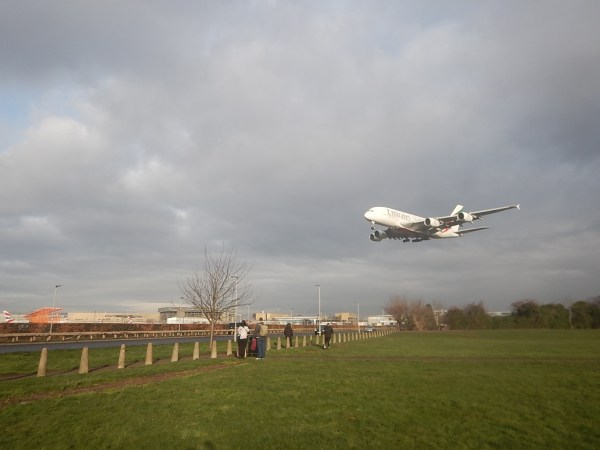
This picture shows an Emirates Air Lines’s Airbus A 380 on finals at Heathrow.
Note.
- The aircraft was landing on Runway 27 L.
- The four engines and the vertical oval cross-section of the fuselage are clearly visible.
- The Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 380 shows two floors across the fuselage; the upper floor with eight seats in 2-4-2 and the lower floor with ten seats in 3-4-3, and a pair of LD3 cargo containers in the basement.
I’d be interested to know, how much hydrogen could be put in the basement and how far it could take the plane with a full load of passengers!
This link to the Wikipedia entry, shows the cross section in detail.
Note
I wouldn’t be surprised that the first application of large hydrogen aircraft will be for cargo and it could be an Airbus Beluga or perhaps an Airbus A 380 freighter?
Thoughts On The Airbus A 390
Ask Google what she knows about the Airbus A 390 and you get this AI Summary.
The Airbus A390 is a three-deck, six-engine aircraft that can carry around 1,000 passengers. It’s based on the A380, but with a third deck and extra engines. The A390 was custom-built for Qantas to fly between Melbourne and New York.
Google got their summary from this page on steemit.
Search for images of the Airbus A 390 and you get several images of this unusual three-deck aircraft, that looks like a widened Airbus A 380 with six engines.
These are some of my thoughts.
Wikipedia Entries
There is no Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 390.
But.
- There is a Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 380.
- There is also a Wikipedia entry for the six unusual Airbus Beluga XLs, which are used to transport two pairs of Airbus A 350 wings between factories.
The A 390 is supposedly based on the A 380 and the Beluga XL appears to have a fuselage that is a bit like the Airbus A 390.
Will The Airbus A 390 Fly?
After reading the two Wikipedia entries, I am fairly sure that an Airbus A 390 airliner, as shown in the pictures would be able to fly.
Although, I must say, that I was surprised, at seeing an Airbus Beluga XL on video. This is a Beluga XL landing at Heathrow.
So I think we can say, that Airbus know more than a bit about the aerodynamics of three-deck fuselages.
The Antonov An-225 Mriya
This aircraft designed and built in the Soviet Union , does have a Wikipedia entry.
These three paragraphs from the start of the entry, give some details of this unusual and very large aircraft.
The Antonov An-225 Mriya (Ukrainian: Антонов Ан-225 Мрія, lit. ’dream’ or ‘inspiration’) was a strategic airlift cargo aircraft designed and produced by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union.
It was originally developed during the 1980s as an enlarged derivative of the Antonov An-124 airlifter for transporting Buran spacecraft. On 21 December 1988, the An-225 performed its maiden flight; only one aircraft was ever completed, although a second airframe with a slightly different configuration was partially built. After a brief period of use in the Soviet space programme, the aircraft was mothballed during the early 1990s. Towards the turn of the century, it was decided to refurbish the An-225 and reintroduce it for commercial operations, carrying oversized payloads for the operator Antonov Airlines. Multiple announcements were made regarding the potential completion of the second airframe, though its construction largely remained on hold due to a lack of funding. By 2009, it had reportedly been brought up to 60–70% completion.
With a maximum takeoff weight of 640 tonnes (705 short tons), the An-225 held several records, including heaviest aircraft ever built and largest wingspan of any operational aircraft. It was commonly used to transport objects once thought impossible to move by air, such as 130-ton generators, wind turbine blades, and diesel locomotives.
This further paragraph described the destruction of the aircraft.
The only completed An-225 was destroyed in the Battle of Antonov Airport in 2022 during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy announced plans to complete the second An-225 to replace the destroyed aircraft.
I feel that the Mriya is significant for the Airbus A 390 for three reasons.
- Mriya was a six-engine heavy-lift cargo aircraft developed from a certified four-engine transport.
- Mriya was starting to make a name for being able to move over-sized cargo around the world.
- Given the parlous state of parts of the world and the ambitions of some of its so-called leaders, I believe, as I suspect others do, that a heavy-lift cargo aircraft is needed for disaster relief.
So are Airbus looking at the possibilities of converting some unwanted A 380 airliners into the heavy-lift aircraft, that they believe the world needs?
- They may even want some for their own purposes.
- Jeff Bezos or Elon Musk may need a heavy-lift aircraft for their space programs.
Converting some unwanted Airbus A 380s into heavy-lift cargo aircraft could be a more affordable route, than designing and building new aircraft from scratch.