Rockton To Buy Up To 40 Heart Aerospace ES-30 Electric Aircraft
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Aviation Source News.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Swedish investment and aircraft leasing company Rockton has confirmed that it will acquire up to 40 of Heart Aerospace’s regional electric aircraft, the ES-30.
The purchase confirmation converts an earlier letter of intent with the Swedish aircraft manufacturer into firm purchase orders for 20 aircraft with purchase rights for 20 more.
It’s good to see a leasing company getting involved, as it probably means that the finances are viable.
The Wikipedia entry for Heart Aerospace, describes the range of the ES-30 like this.
The ES-30 is planned to have a 108 nautical miles (200 kilometres; 124 miles) fully electric range or a 215 nmi (398 km; 247 mi) range when also using generators powered by aviation biofuel. A range of 430 nmi (800 km; 490 mi) could be possible if only 25 passengers are carried.
These are some UK airport to airport distances.
- Aberdeen – Kirkwall – 124 miles
- Aberdeen – Sumburgh – 188 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Cork – 192 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Anglesey – Ronaldsway – 58 miles
- Anglesey – Shannon – 186 miles
- Anglesey – Waterford – 130 miles
- Birmingham – Belfast – 226 miles
- Birmingham – Dublin – 200 miles
- Birmingham – Edinburgh – 250 miles
- Birmingham – Glasgow – 260 miles
- Birmingham – Inverness – 363 miles
- Birmingham – Kirkwall – 451 miles
- Birmingham – Newcastle – 178 miles
- Birmingham – Newquay – 198 miles
- Birmingham – Schipol – 402 miles
- Birmingham – Sumburgh – 513 miles
Birmingham – Wick – 418 miles - Edinburgh – Schipol – 473 miles
- Gatwick – Edinburgh – 356 miles
- Gatwick – Schipol – 374 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast – 106 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast City – 103 miles
- Glasgow – Derry – 121 miles
- Glasgow – Kirkwall – 221 miles
- Glasgow – Sumburgh – 300 miles
- Glasgow – Stornoway – 177 miles
- Haverfordwest – Waterford – 94 miles
- Haverfordwest – Newquay – 94 miles
- Heathrow – Newquay – 212 miles
- Humberside – Schipol – 333 miles
- Inverness – Kirkwall – 106 miles
- Inverness – Sumburgh – 190 miles
- Leeds – Schipol – 386 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast City – 151 miles
- Liverpool – Cardiff – 135 miles
- Liverpool – Dublin – 140 miles
- Liverpool – Haverfordwest – 127 miles
- Liverpool – Norwich – 180 miles
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway – 89 miles
- London City – Haverfordwest – 167 miles
- London City – Humberside – 145 miles
- London City – Manchester – 161 miles
- London City – Norwich – 100 miles
- Manchester – Schipol 413 miles
- Newcastle – Cardiff – 230 miles
- Newcastle – Belfast City – 168 miles
- Newcastle – Newquay – 346 miles
- Newcastle – Schipol – 395 miles
- Newquay – Brest – 140 miles
- Newquay – Cardiff 98 miles
- Newquay – Cork – 180 miles
- Newquay – Deauville – 241 miles
- Newquay – Dinard – 183 miles
- Newquay – Dublin – 212 miles
- Newquay – Guernsey – 128 miles
- Newquay – Jersey – 152 miles
- Newquay – Nantes – 211 miles
- Newquay – Orly – 351 miles
- Newquay – Rouen – 285 miles
- Newquay – Scillies – 68 miles
- Newquay – Waterford – 150 miles
- Norwich – Schipol – 277 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast – 75 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City – 62 miles
- Ronaldsway – Birmingham – 165 miles
- Ronaldsway – Dublin – 80 miles
- Ronaldsway – East Midlands – 161 miles
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow – 123 miles
- Ronaldsway – Leeds – 121 miles
- Ronaldsway – Manchester – 109 miles
- Southend – Schipol – 180 miles
- Stansted – Aberdeen – 379 miles
- Stansted – Edinburgh – 316 miles
- Stansted – Glasgow – 334 miles
- Stansted – Inverness – 426 miles
- Stansted – Schipol – 335 miles
- Stansted – Wick – 472 miles
- Sumburgh – Bergen – 226 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Note.
- I have included Schipol, as in certain areas of the UK, passengers sometimes fly long-haul from Schipol.
- I have included Haverfordwest, as it will be close to all the wind farm activity in the Celtic Sea.
- I have included Anglesey, as I think it has possibilities.
- The distances wee calculated using on of the Free Map Tools.
These are some more specific thoughts.
The Basic ES-30 And The UK
With a range of 124 miles, I don’t believe that the range is long enough for the UK.
But saying that there are some established routes, where it should be able to operate.
- Glasgow – Belfast
- Glasgow – Belfast City
- Glasgow – Derry
- Haverfordwest – Waterford
- Haverfordwest – Newquay
- Inverness – Kirkwall
- Liverpool – Haverfordwest
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway
- London City – Norwich
- Newquay – Cardiff
- Newquay – Scillies
- Ronaldsway – Belfast
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City
- Ronaldsway – Dublin
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow
- Ronaldsway – Leeds
- Ronaldsway – Manchester
These routes have the following in common.
- They are mostly between major airports with advanced facilities.
- Most airports served have access to renewable electricity.
- Some of the routes can support hundred seat airliners.
- Fifty percent go to the Isle of Man.
I can see several routes between the UK and the island of Ireland and to and from the Isle of Man using ES 30 aircraft.
The Extended Range ES-30 And The UK
The 247 mile range of the extended range ES-30, brings lots more routes into play.
Key routes could be the following.
- Aberdeen – Kirkwall
- Aberdeen – Sumburgh
- Anglesey – Cork
- Anglesey – Shannon
- Birmingham – Belfast
- Birmingham – Dublin
- Birmingham – Newcastle
- Birmingham – Newquay
- Glasgow – Kirkwall
- Glasgow – Stornoway
- Heathrow – Newquay
- Inverness – Sumburgh
- Liverpool – Belfast City
- Liverpool – Dublin
- Liverpool – Norwich
- London City – Haverfordwest
- London City – Humberside
- London City – Manchester
- Newcastle – Belfast City
- Newcastle – Cardiff
- Newquay – Brest
- Newquay – Cork
- Newquay – Deauville
- Newquay – Dinard
- Newquay – Dublin
- Newquay – Guernsey
- Newquay – Jersey
- Newquay – Nantes
- Newquay – Waterford
- Ronaldsway – Birmingham
- Ronaldsway – East Midlands
There will also be other routes.
The Extended Range With 25 Passengers ES-30 And The UK
The 490 mile range of the extended range ES-30 with only 25 passengers, brings a few more routes into play.
- Birmingham – Edinburgh
- Birmingham – Glasgow
- Birmingham – Inverness
- Birmingham – Kirkwall
- Birmingham – Schipol
- Birmingham – Wick
- Edinburgh – Schipol
- Gatwick – Edinburgh
- Gatwick – Schipol
- Glasgow – Sumburgh
- Humberside – Schipol
- Leeds – Schipol
- Manchester – Schipol
- Newcastle – Newquay
- Newcastle – Schipol
- Newquay – Orly
- Newquay – Rouen
- Norwich – Schipol
- Southend – Schipol
- Stansted – Aberdeen
- Stansted – Edinburgh
- Stansted – Inverness
- Stansted – Glasgow
- Stansted – Schipol
- Stansted – Wick
Note.
- All airports East of Birmingham and Manchester seem to be close enough to Schipol for an Extended Range ES-30 with 25 passengers to serve the route.
- Most major Scottish Airports can be reached from Stansted.
- Flying from Gatwick to Scottish Airports is around forty miles longer than flying from Stansted.
Liverpool Airport
Liverpool Airport could be a major destination for the ES 30, as it could be a key airport for flying between the UK and the island of Ireland.
Liverpool would obviously need the electric infrastructure, but I also believe it needs a better connection to the major railway station at Liverpool South Parkway, which has extensive rail connections.
This Google Map shows the area between Liverpool South Parkway station and the airport.
Note.
- Liverpool South Parkway station is marked by the red arrow in the North-West corner of the map.
- The airport is in the opposite corner, with the terminal to the North of the runway.
- The main railway between the South and Liverpool Lime Street passes to the South of the station.
- The A561 passes across to the South of the railway and to the North of the airport.
I suspect some form of people mover like the Luton DART can be built between the station and the airport.
It should be noted that as Hunts Cross has only one platform for Merseyrail Northern Line trains and this could be a factor in limiting the line’s capacity. So could a second platform be installed at the airport to both act as an airport station and to increase the frequency on the Northern Line?
I believe that in a couple of years, journey times between Euston and Liverpool South Parkway will be under two hours and they will only get shorter with High Speed Two. With a fast connection between the airport and the station, there could be a sub-three-hour zero-carbon route between London and the island of Ireland.
- Avanti West Coast Class 805 train to Liverpool South Parkway.
- People mover to the airport.
- Electric aircraft on the 140 miles to Dublin.
Dublin air traffic are usually efficient in getting planes in quickly.
Glasgow Airport
Glasgow Airport could be a major destination for the ES 30, as it could be a key airport for flying between the UK and the island of Ireland.
As with Liverpool Airport it needs a better connection to the rail network.
If Glasgow Airport is successful running zero-carbon aircraft to Ireland, this could change all previous thinking on a Glasgow Airport Rail Link.
Ronaldsway Airport
Geography and electric airliners could be very kind to Ronaldsway Airport and the Isle of Man.
- Electric airliners can easily reach much of the island of Ireland and the UK mainland between Glasgow and Birmingham, from Ronaldsway Airport with ease.
- The Isle of Man will in a couple of years be surrounded by wind farms.
- With other developments on the island, it could sell itself to the UK and Ireland, as a green holiday destination.
But what would the motorcycle enthusiasts say?
Anglesey Airport
I believe that Anglesey Airport could be brought to life in a big way by electric aircraft like the ES-30 or the Eviation Alice.
These are flight distances from Anglesey Airport.
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Cork – 192 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Anglesey – Ronaldsway – 58 miles
- Anglesey – Shannon – 186 miles
- Anglesey – Waterford – 130 miles
All of these except for Cork, Derry, Shannon and Waterford would be possible in the basic ES-30.
This Google Map shows the airport, which is also labelled as RAF Valley.
Note that the North Wales Coast Line passes the site on the North-East side.
At present, Avanti West Coast trains take nearly four hours between London and Holyhead.
But later this year, new bi-mode Class 805 trains will replace, the current diesel only Class 221 trains.
- The current diesel only trains take two hours and five minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- The current diesel only trains take one hour and forty-three minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
- The fastest electric trains take one hour and twenty-nine minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
- High Speed Two trains will take 56 minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
When you consider that a lot of the North Wales Coast Line, is straight and flat, I can see the following times being possible, with some improvement and smart electrification between Crewe and Holyhead and a smaller number of stops.
- Crewe and Anglesey Airport – One hour and twenty minutes
- London Euston and Anglesey Airport – Two hours and fifty minutes
With High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains, the London Euston and Anglesey Airport time could be below two hours and thirty minutes.
I believe that with a well-designed terminal at Anglesey Airport, this could be the fastest zero-carbon way between London and Ireland.
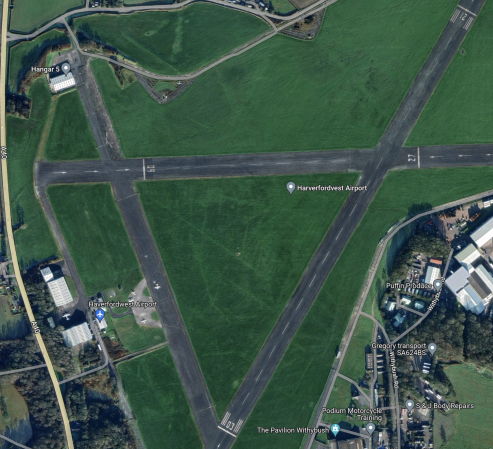
Haverfordwest Airport
This Google Map shows the location of Haverfordwest Airport in the East of Pembrokeshire.
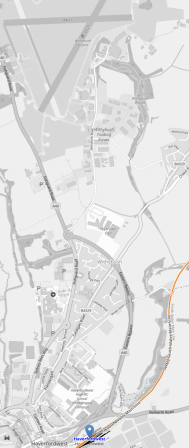
This second Google Map shows a close-up of the airport.
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the airport and the nearest railway station.
Note.
- Haverfordwest Airport is at the top of the map.
- Haverfordwest station is at the bottom of the map.
- There are rail connections to Cardiff, Fishguard, Milford Haven, Pembroke Dock and Swansea from the the station.
- Rail passengers for London would change at Swansea.
The road looks good between the airport and the station, so would an electric bus to handle transfers be ideal?
Consider.
- I have flown myself into Haverfordwest Airport and there were no navigation or operational problems that I can remember.
- With all the wind farm development planned for the coast of Pembrokeshire and the Celtic Sea, I feel that an airport in the area with regular flights to London and perhaps Waterford in Ireland could be essential.
- London City and Haverfordwest airports are 167 miles apart
- Waterford and Haverfordwest airports are 94 miles apart
- Quiet electric aircraft may ease any planning problems.
- Will a helicopter base be needed for serving wind farms in the Celtic Sea?
I believe, Haverfordwest Airport could be converted into a high-class airport for the Eastern tip of South Wales.
Haverfordwest Airport could also attract other services, given that the Welsh Government have a policy of not building new roads.
I have a feeling that quiet electric airliners will lead to the development of airports like Haverfordwest as feeder airports for the Heathrows and Schipols of this world.
Waterford Airport
Waterford Airport has recently been expanded and it appears from the Wikipedia entry, they are expecting more tourists.
This Google Map shows the position of the airport and the railway station in Waterford.
Note.
- The red arrow at the top of the map indicates Waterford station on the Northern side of the city.
- The airport is indicated by the blue dot in the South-East corner of the map.
- The airport is about ten kilometres from the City Centre.
In the past, Waterford has been quite a busy airport, but Covid-19 seems to have killed most of the traffic.
So could a zero-carbon service between Waterford and Haverfordwest be profitable?
- Those working with the wind energy in the Celtic Sea might find route useful.
- It would give a low-carbon route between Waterford and South Wales, which some might like.
- I also believe that the novelty of flying in an electric plane would attract passengers.
Waterford and Haverfordwest might be one of those routes, where electric planes might be worth trying.
This Google Map shows the Celtic Sea.
Note.
- Waterford Airport is indicated in red on the South-East corner of Ireland.
- Haverfordwest Airport is on the South-Western tip of Wales.
- Newquay Airport is in the South-East corner of the map on the North coast of Cornwall.
There could be as much as 50 GW of floating wind farms installed in this area.
I feel that there could be a case for a triangular Haverfordwest, Newquay and Waterford service.
Newquay Airport
Newquay Airport has been in the news recently because of the antics of Richard Branson and Virgin Orbit.
This Google Map shows the airport in relation to the town.
Note.
- The airport is in the North-East corner and boasts a long runway.
- The airport serves well over a dozen destinations.
- The town of Newquay is in the South-West corner of the map.
- Newquay station is by the sea.
All of these places would be suitable destinations for electric aircraft.
- Birmingham
- Brest
- Cardiff
- Cork
- Deauville
- Dinard
- Dublin
- Guernsey
- Heathrow
- Jersey
- Nantes
- Orly
- Rouen
- Scillies
- Waterford
Newquay Airport could get very busy with electric aircraft supporting tourism and the developing wind power industry.
This second Google Map shows the town centre and station.
Surely, having the station by Great Western Beach is good marketing.
In The Proposed Mid-Cornwall Metro, I talked about a plan to run an hourly Metro service between Newquay and Falmouth.
This article on Rail Technology Magazine is dated January 2023 and entitled Mid Cornwall Metro Secures £50m In Levelling Up Funding, where these are the first two paragraphs.
Following yesterday’s major Levelling Up funding announcement, the government has pledged an almost £50m grant to improve the railways linking Newquay, St Austell, Truro and Falmouth in Cornwall.
This financial aid to improve Cornwall Rail links represents the only successful bid out of four that were submitted to the Levelling up funding. The improvement scheme will be helmed by a partnership with Great Western Railway and Network Rail.
Note.
- I believe this means the Mid-Cornwall Metro will be built.
- Especially as looks like it will cost less than £100 million.
- As this Metro will serve Newquay, it shouldn’t be too difficult to link the plane with the train, with perhaps a zero-carbon bus.
- The Metro would then link Newquay Airport to the main population centres of Newquay, St Austell, Truro and Falmouth.
- If the Metro could be run using zero-carbon trains, that would surely put the icing on the cake!
The map from OpenRailwayMap shows the route.
Note.
- Newquay is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Trains spend around 6-7 minutes waiting at Newquay.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner marks Par station, where a chord will be reinstated to allow trains to go between Newquay and St. Austell.
- Par is the nearest station to the Eden Centre.
- Newquay and Par is 20.6 miles.
- The route, then goes along the Cornish Main Line, through St. Austell and then on to Truro.
- Par and Truro is 18.9 miles.
- At Truro the Metro would take the Falmouth branch.
- Falmouth and Truro is 11.8 miles.
- Trains spend around 7-8 minutes waiting at Falmouth Docks
- The total route is just over fifty miles, which probably means that battery-electric trains could work the route with charging at each end, whilst the train is turned round.
This airport and metro combination could give a big-boost to zero-carbon tourism.
Inverness Airport
Inverness Airport has recently been expanded with a station on the Inverness and Aberdeen Line.
Consider.
- Electric aircraft like the ES-30 will be able to reach both Kirkwall on Orkney and Sumburgh on Shetland from both Inverness and Aberdeen Airports.
- Sumburgh would need an extended range ES-30.
- Flights would be a few miles shorter from Inverness than from Aberdeen.
- Kirkwall and Sumburgh is only 85 miles, so there may be possibilities for serving both Orkney and Shetland with one flight.
- Extended range ES-30s might be able to do return trips to Kirkwall without a major charge at Kirkwall.
- I once flew in my Cessna-340 to Kirkwall to see the original turbine, that was placed on the island. There is a lot of cold forbidding sea in the area. Perhaps the slightly shorter trip from Inverness, might be better for everybody’s nerves?
- Just as the oil and gas industry did in the last century, I can see the offshore wind power industry generating a lot of passenger traffic to the Orkney and Shetland Islands.
Both Inverness and Aberdeen can be reached from Stansted by an ES-30 carrying a reduced passenger load.
Birmingham Airport
Birmingham Airport could become a major base for electric aircraft.
The 247 mile range of the extended range ES-30 would allow it to be able to reach the following places.
- Belfast
- Dublin
- Newcastle
- Newquay
- Ronaldsway
Reduce the passenger load slightly to 25 passengers and the plane would be able to reach.
- Edinburgh
- Glasgow
- Inverness
- Kirkwall
- Wick
But Birmingham Airport is only 65 minutes from Euston and will in the future be served by High Speed Two, in under an hour.
The airport also has a large catchment area of its own, who might be tempted to choose flying zero-carbon.
Spokes From Speke
In the 1980s, I went to a presentation from Royal Mail in Ipswich about guaranteed next day delivery of parcels. It was important to me, as I was writing software that needed to get from Ipswich, where it was created to London, where it would be tested and installed on customers machines. We also needed to get copies to our customers in Edinburgh and Aberdeen.
The Royal Mail’s latest concept of Spokes From Speke was described.
- All urgent parcels and First Class mail would be collected from the local sorting office and taken to the local airport, which in our case would probably have been Stansted.
- These consignments would then be flown to Speke Airport as Liverpool Airport was known in those days at around midnight.
- They would then be sorted and reloaded onto other planes to complete their journey.
- The planes would then return home and the parcels and mail would be delivered by truck to the local sorting office.
Aircraft used included Short Skyvans and piston-engined twins. Some we’re the quietest of aircraft.
I have heard or read somewhere that in some airports, there were complaints about noisy aircraft flying in and out in the middle of the night.
Now fifty years on companies are looking to speed up deliveries.
- In the UK, companies are experimenting with 100 mph overnight parcels trains.
- This article on Railway Gazette is entitled Varamis Rail Launches Regular Express Light Freight Service.
- Eversholt Rail are putting money behind converting redundant electric multiple units into parcel trains.
But DHL in the USA are going another way and have ordered twelve Alice aircraft from Eviation.
It looks like the cargo Alice could have a useful load of just over a tonne and a range of around 290 miles.
I can envisage flights of near-silent silent Alices sneaking into and out of airports in the middle of the night to deliver and collect urgent parcels.
Techniques like Spokes From Speke will come again, but this time with electric aircraft.
How Would The ES-30 Compare With An Eviation Alice?
The Wikipedia entry for the Eviation Alice gives these figures.
- Passengers – 9
- Maximum Speed – 300 mph
- Range – 290 miles
- Take-off distance – 840 metres
- Landing distance – 620 metres
Note.
- These are figures that most pilots would expect from an aircraft of this size.
- My Cessna 340 was about the same and about eight percent slower.
- It also had a much longer range.
If you look at my list of flights, these will not be possible.
- Birmingham – Inverness – 363 miles
- Birmingham – Kirkwall – 451 miles
- Birmingham – Schipol – 402 miles
- Bimingham – Sumburgh – 513 miles
Birmingham – Wick – 418 miles - Edinburgh – Schipol – 473 miles
- Gatwick – Edinburgh – 356 miles
- Gatwick – Schipol – 374 miles
- Glasgow – Sumburgh – 300 miles
- Humberside – Schipol – 333 miles
- Leeds – Schipol – 386 miles
- Manchester – Schipol 413 miles
- Newcastle – Newquay – 346 miles
- Newcastle – Schipol – 395 miles
- Newquay – Orly – 351 miles
- Stansted – Wick – 472 miles
- Sumburgh – Bergen – 226 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Note.
- Most routes that are too long are to Schipol or Scotland.
- Anglesey appears to have Ireland extremely well covered.
- Birmingham, Glasgow and Liverpool keep their Irish routes.
- Newquay is still a hub, that would promote tourism in Cornwall and only loses the Orly connection, although it keeps the flight to Heathrow.
- Ronaldsway still looks to be a possible zero-carbon airport.
I would suggest that a range of 290 miles, is an ideal one for an electric aircraft in the UK, as it can handle a large number of routes.
These are routes that I feel would attract a large number of passengers.
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast – 106 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast City – 103 miles
- Glasgow – Derry – 121 miles
- Heathrow – Newquay – 212 miles
- Inverness – Kirkwall – 106 miles
- Inverness – Sumburgh – 190 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast – 153 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast City – 151 miles
- Liverpool – Dublin – 140 miles
- Liverpool – Norwich – 180 miles
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway – 89 miles
- London City – Humberside – 145 miles
- London City – Manchester – 161 miles
- Newcastle – Cardiff – 230 miles
- Newcastle – Belfast City – 168 miles
- Newquay – Brest – 140 miles
- Newquay – Cardiff 98 miles
- Newquay – Cork – 180 miles
- Newquay – Deauville – 241 miles
- Newquay – Scillies – 68 miles
- Newquay – Waterford – 150 miles
- Norwich – Schipol – 277 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City – 62 miles
- Ronaldsway – Dublin – 80 miles
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow – 123 miles
- Southend – Schipol – 180 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Alice may not be big enough for some routes.
But it will be a wonderful route-proving aircraft for the larger ES-30 and other zero-carbon aircraft.
Conclusion
There will be a lot of uses for battery-electric aircraft in the UK.
Birmingham Plays The Green Card
This article in The Times today is entitled Birmingham Airport Set For Hydrogen Take-Off.
These two paragraphs introduce the article.
Birmingham Airport aims to become the first in Britain to operate commercial zero-emission hydrogen-fuelled flights — and by as early as 2025.
The ambitious goal follows the signing of a partnership with the British start-up ZeroAvia whose first trial flight of a 19-seater passenger aircraft powered by hydrogen fuel cells took place last month.
Other points from the article include.
- ZeroAvia is also working with Rotterdam Airport.
- Initially, it is likely that the hydrogen-powered aircraft will be used for cargo.
- The government wants all UK domestic flights to be zero-carbon by 2040.
- Birmingham wants to be zero-carbon by 2033.
- ZeroAvia has received upwards of £20 million of matched-taxpayer funding.
- It has some big backers and well-known airlines, who have placed orders.
These are my thoughts.
ZeroAvia’s Airliners
This paragraph from The Times article describes their first two aircraft.
ZeroAvia is retrofitting turboprops, 19-seater Dornier and in future 80-seater De Havilland Canada Dash 8-400s, with tanks of hydrogen which is converted by fuel cell stacks to energy taken to electric motors that power the propellers. The only emission is water. It is talking to potential new-entrant airframe makers to build all-new hydrogen aircraft of the future.
Note.
- The Dornier 228 is a 19-seater airliner of which over three hundred have been built.
- The de Havilland Canada Dash 8-400 is an 80-seater airliner of which over six hundred have been ordered and over 1200 of all marques of Dash 8s have been built.
Both are workhorses of the smaller airlines all over the world.
As the paragraph from The Times indicates the power system is not conventional, but then most of this new breed of small electric/hydrogen/hybrid airliners have electric propulsion. I suspect that there’s been a marked improvement in the design and efficiency of electric motors.
Electric propulsion should have a substantial noise advantage over turboprops.
ZeroAvia are also retrofitting their two chosen airliners.
This offers advantages in the certifying of the airliners. Providing the changes made to the airframe are not significant, the various certifying authorities in the UK, US and EU will allow previous certification to be carried over.
This means that ZeroAvia only have to thoroughly test and certify the powerplant and its integration into the aircraft.
One of their competitors, the Eviation Alice is a completely new airframe with battery-electric power, so I suspect this aircraft will take longer to certify.
I think ZeroAvia have used this shorter certification time to aim to get their airliners in service first.
Those that don’t win, don’t get the same fame.
Hydrogen At Birmingham Airport
Hydrogen will be needed at Birmingham Airport to refuel ZeroAvia’s airliners.
But will hydrogen also be used on the airside to power some of the heavy vehicles you see on airports.
Look at this page on the Hawaii Technology Development Corporation, which shows a Hydrogen Fuel Cell U-30 Aircraft Tow Tractor. The specification indicates, that it can tow a C-17 or a Boeing 747.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see Birmingham Airport build their own electrolyser nearby both to supply hydrogen-powered aircraft and decarbonise the airside.
To And From Birmingham Airport
Consider.
- Birmingham Airport is connected to Birmingham International station by a free AirRail Link.
- Birmingham International station has an impressive number of services, many of which are electric.
- There will be a people mover to connect to Birmingham Interchange for High Speed Two.
- Birmingham Interchange will have five trains per hour (tph) to and from London, taking under forty minutes.
- There are plans to extend the West Midlands Metro to the airport, with journeys taking thirty minutes from the City Centre.
- Birmingham Airport is at the centre of the UK’s motorway network.
Most public transport to Birmingham Airport will be zero-carbon and the percentage that is will increase.
A Green Air Bridge To Ireland
Currently the fastest services between London and Birmingham International station take a few minutes over the hour.
But after High Speed Two opens, the service will improve.
- High Speed Two will take under forty minutes.
- There will be five tph.
- High Speed Two will connect to the Elizabeth Line and the London Overground at Old Oak Common station.
- Euston station will have better connectivity to the Underground.
This diagram shows High Speed Two services.
Consider.
- Birmingham Interchange has good connections in the North.
- I can see that Birmingham Airport could start to attract lots of passengers going between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland.
- And don’t forget Cardiff, Swansea, Exeter, Isle of Man and New Quay.
- Could Birmingham-Dublin and Birmingham-Belfast be run as frequent shuttles?
- Will there be AirRail tickets between Euston and Belfast and Dublin?
I also wonder if zero-carbon travel will attract passengers?
Zero-Carbon Air Cargo At Birmingham Airport
This article on Railway Gazette is entitled Varamis Rail Launches Regular Express Light Freight Service.
These three paragraphs outline the service from Varamis Rail.
Varamis Rail has launched a 160 km/h express freight service between Glasgow and Birmingham International using a converted electric multiple-unit.
The service is targeted at express parcels and third-party delivery companies seeking next day delivery of consumer goods.
Consignments arriving at the Glasgow hub by 17.30 from Monday to Friday can reach Birmingham at 23.00, with northbound freight arriving at the Birmingham site by 23.00 reaching Glasgow at 05.30 the next morning.
I think this service would interface well with cargo planes operating overnight from Birmingham Airport.
It seems to me, that Spokes at Speke could be reborn at Birmingham.
Conclusion
Birmingham Airport seems to be positioning itself to take advantage of aviation’s new breed of planes.
Transforming High-Speed Rail Logistics
This project was one of the winners in the First Of A Kind 2022 competition run by Innovate UK.
In this document, this is said about the project.
Project No: 10038447
Project title: Transforming High-Speed Rail Logistics
Lead organisation: VARAMIS LTD
Project grant: £396,467
Public description:
Our project is to transform high-speed rail logistics combining a repurposed all electric passenger unit and bespoke consignment device technology to support the conveyance of parcels. This technology, offered alongside a new approach to using space at stations to create easily accessible city-centre distribution hubs, will enable the operation of a new high-speed non-letters parcels service.
The project meets the competitions challenge and scope through: Development and application of new technologies and approaches to rail, innovative reuse of existing rail assets (such as passenger rolling stock converted for light freight), repurposing of space at station hubs (which has been released due to changing passenger demand) and engagement with new to rail logistics operators to develop and grow new high-speed rail freight services.
Furthermore, the project is in support of permanent modal shift from road to rail, delivering rail freight growth, meeting future customer needs, and realising significant emissions reductions which supports the UK’s low emissions target of a 68% reduction by 2030, compared to 1990 levels through modal diversion from road.
My Thoughts And Conclusions
Shuffling The Class 165 Trains
The May 2020 Edition of Modern Railways has an article, which is entitled West Of England Improvements In GWR Deal.
The sub-title is the following.
EMU Trailers Could Be Inserted Into Turbo DMUs
GWR‘s Turbo DMUs are.
- Class 165 trains of which there are fifteen three-car trains and twenty two-car trains.
- Class 166 trains of which there are twenty-one three-car trains.
The article says, they will be internally-refreshed with interiors better suited for long-distance services.
It also looks that they might get hybrid transmissions, if a trial with a Chiltern Class 165 train is successful. In Class 165 Trains To Go Hybrid, I wrote about this trial.
The article says this about the retractioned units.
The additional power available from the new hybrid units would allow the sets to be lengthened with trailers released from withdrawn Class 365 or 465 EMUs, lengtheing two-car Turbos by one vehicle and the three-car sets to five carriages. The EMU vehicles are 20 metres long, rather than the 23 metres of the DMU design, but it is thought integration into the diesel sets would be relatively simple.
This sounds like a cunning plan, from BREL’s book of Cut-And-Paste With Trains.
At the time of writing there are nineteen Class 365 trains in storage, which could release 38 trailer cars. However, Varamis Rail may need some of these trains for their proposed parcel business, that I wrote about in Varamis Plans Electric Freight To Carry Light Goods.
If all the fifty-six trains were to be lengthened, this would need ninety-two trailer cars. So I suspect, that GWR will be awaiting the retirement of some of the 147 Class 465 trains, which are currently in service with Southeastern.
A sister company to GWR, South Western Railway is transferring thirty Class 707 trains to Southeastern. I wrote about the transfer in Southeastern Signs Deal To Lease Unwanted Class 707s. As each pair of Class 707 trains, could release two Class 465 trains containing four trailer cars, this could be the source of sufficient trailer cars to lengthen the Turbos.
This would mean that the following suitable trailer cars would be available.
- Thirty-eight from stored Class 365 trains.
- Sixty from Class 465 trains displaced by Class 707 trains at Southeastern.
It’s a close-run thing.
But there may be trouble ahead, as Chiltern have twenty-eight two-car and eleven three-car Class 165 trains, which would need another fifty trailer cars, if Chiltern decided to lengthen their trains in the same way as GWR.
- There appear to be twenty-one trains or forty-two trailer cars in service with Great Northern.
- Six trailer cars should be available from the previous swaps.
So it looks like they are one train or two trailer cars short, if they want to do a full conversion.
Unless the thirty Class 707 trains going to Southeastern, with their faster operating speed can scoot route the network faster and do the work of more than thirty Class 465 trains.
Varamis Plans Electric Freight To Carry Light Goods
The title of this post, is the same as that of an article in Issue 902 of Rail Magazine.
This is the introductory paragraph.
Freight trains using electric multiple units could be operating on the East Coast Main Line by the end of the year, in plans unveiled by Varamis Rail.
This is their promotional video.
From the video and the Rail Magazine article, the following can be ascertained.
The Route
From the video, the basic route is circular and the concept is explained in the article, by Phil Read; the Managing Director of Varamis Rail.
Our vision is to create a circular network around the UK via both the East Coast Main Line and West Coast Main Line, with a stop/go method of service delivery serving major towns and cities en route.
And we could move goods in both directions.
Longer term, there could be extensions to Bristol and South Wales and into East Anglia.
Note.
- From the video is looks like the main loop will start and finish in London.
- Trains on the main loop will call at Doncaster, Newcastle, Edinburgh, Glasgow, Carlisle, Manchester and Birmingham.
- Varamis have said they will stick to electrified lines.
I like the concept of the route.
- It covers a lot of the country.
- It can be easily extended.
- Extra stops could be easily added. Darlington, Leeds, Peterborough, Preston and Reading come to mind.
With dual-voltage trains, it could even be extended South of London.
The Trains And The Organisation
Varamis are certainly looking to keep the operation efficient and low-cost. This is said about the trains.
The plan is to remove all the internal furnishings in the umits we lease utilise them without altering any of the loading or dynamic characteristics that the trains had when formerly used as passenger trains. I’m in discussions with rolling stock leasing companies and the DfT at present to lease the trains.
The DfT owns all 40 Class 365 trains.
In addition, the following is said.
- Maintenance would be outsourced, with one of two likely companies.
- Operations Director will be appointed soon.
- Company headquarters would be in Doncaster.
- Varamis will employ all their own staff, including drivers, fitters and logistics operators.
A small point is that Phil Read has worked for the Rail Operations Group.
Class 365 Trains
Class 365 trains have the following characteristics.
- Four cars
- Up to three trains can be coupled together.
- 100 mph operating speed.
- Two pairs of wide double doors on the side of each car.
- They are not a train with a reputation for unreliability.
This is a picture of a Class 365 train.
Note.
- They could probably be converted to dual-voltage, by adding third-rail gear.
- The trains could probably be made available at short-notice.
The company talks about an end-on cross-transfer system at their hubs, where goods can be moved through the train.
I will be interested to see what this means, but I suspect it will give a quick and easy transfer of pallets of goods between trains and the trucks doing the local delivery.
Green Logistics
Varamis are marketing their services as Green Logistics.
Conclusion
As someone, who needed this sort of system in the early days of Metier to distribute new copies of the Artemis software, I think the service will fulfil a large need.
I said earlier that I like the concept of the route.
But thinking about it more, I suspect it can be very easily extended.
- Brighton, Portsmouth and Southampton could be served by dual-voltage trains.
- Could for instance a hub in Edinburgh, distribute pallets and parcels to and from the North of Scotland?
- Could bi-mode trains serve the towns and cities on the Midland Main Line?
- A connection to Heathrow would be very valuable.
A large proportion of the country could be connected.
If it existed now, would it help in the fight against COVID-19?