Do Rolls-Royce mtu Have A Plan To Decarbonise Their Diesel Engines For Rail Applications?
Data Sheets For Rolls-Royce mtu Diesel Engines For Trains
These are data sheets for various Rolls-Royce mtu diesel engines that can be used in rail applications.
Rolls-Royce Releases mtu Rail Engines For Sustainable Fuels
The title of this section, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
These four bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- mtu Series 1300, 1500 and 1800 engines already released; Series 1600 and 4000 to follow shortly
- Up to 90% CO2 savings by operating existing engines with Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO/renewable diesel)
- Locally emission-free operation possible in combination with mtu Hybrid PowerPack
- Field tests with DB Cargo and RDC Autozug Sylt
This is the first paragraph.
Rolls-Royce is taking a significant step towards even more climate-friendly rail transport with the release of mtu rail engines for use with sustainable fuels. With synthetic diesel fuels of the EN15940 standard, CO2 emissions can be reduced by up to 100 percent compared to fossil diesel. Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO or renewable diesel), which is already commercially available today, reduces CO2 emissions by up to 90 percent. If the fuels are produced with the help of renewable energy and green hydrogen – through what is termed a Power-to-X process – existing rail vehicles can be operated in a completely CO2-neutral manner. The mtu Series 1800 engines which are used in mtu PowerPacks, as well as Series 1300 and 1500 for locomotives and multi-purpose vehicles, are already approved for use with synthetic fuels such as HVO. Series 1600 and versions of Series 4000 engines will follow in the near future. The release of engines for climate-friendly fuels requires a series of tests and trials and Rolls-Royce has found strong partners for this activity. DB Cargo and RDC Autozug Sylt have already tested or are currently testing mtu Series 4000 engines with HVO in their locomotives.
How Does That Fit With The UK’s Population Of Rolls-Royce mtu Diesel Engines?
These classes of train have Rolls-Royce mtu engines.
- Class 43 power cars – 6V 4000 R41R
- Class 168 train – 6R 183 TD 13H
- Class 170 train – 6R 183 TD 13H
- Class 172 train – 12V 1800 R83
- Class 195 train – 12V 1800 R85L
- Class 196 train – 12V 1600 R85L
- Class 197 train – 12V 1600 R85L
- Class 800 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 801 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 802 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 805 train – 12V 1600 R80L
- Class 810 train – 12V 1600 R80L
Note.
- Class 168 and 170 trains seem to be powered by older model Rolls Royce mtu engines.
- Class 180, 220,221 and 222 trains are powered by Cummins engines.
- I can’t find what engines power Class 805 and 810 trains, but it is reasonable to assume they have the same engines as the other Hitachi trains.
- As CAF are building LNER’s new tri-mode trains, I suspect these trains will also have Rolls Royce mtu engines.
It would appear that all the Rolls-Royce mtu rolling stock in the UK, with the possible exception of the Class 168 and 170 trains will be able to run on sustainable fuels.
Rolls Royce mtu And Hydrogen
This press release from Rolls-Royce is entitled Rolls-Royce Successfully Tests mtu Engines With Pure Hydrogen.
This is the first paragraph.
Rolls-Royce today announces that it has conducted successful tests of a 12-cylinder gas variant of the mtu Series 4000 L64 engine running on 100% hydrogen fuel. The tests, carried out by the Power Systems business unit, showed very good characteristics in terms of efficiency, performance, emissions and combustion. These tests mark another important step towards the commercial introduction of hydrogen solutions to meet the demand of customers for more sustainable energy.
Engines of mtu’s 4000 family are used in Class 43 power cars, so surely these developments could lead to hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
The picture shows a Class 43 power car at Glasgow Queen Street station.
Could Rolls-Royce mtu hydrogen power keep these iconic trains running for a few more years?
In ‘Spirit of Innovation’ Stakes Claim To Be The World’s Fastest All-Electric Vehicle, I look at Rolls-Royce’s Spirit of Innovation, which set the record for an electric vehicle at 555.9 km/hour.
As the InterCity125 already holds the record for the fastest diesel train, perhaps Rolls-Royce will attempt to set a record for the fastest hydrogen-powered train?
Decarbarbonising The CAF Class 195, 196 And 197 Trains
If Rolls-Royce mtu develop a hydrogen version of the 1800 diesel engine, then this could be used to fully decarbonise the CAF trains.
The operators may consider it’s not worth it and continue with using sustainable fuels.
But the possibility is surely there.
There must also be the possibility of developing a fuel cell replacement for the 1800 diesel, that can be slotted into the train.
Decarbarbonising The Hitachi Class 80x Trains
Hitachi are developing battery packs and the data sheet can be downloaded from this page on the Hitachi web site.
Decarbarbonising The CAF Tri-Mode Trains
I feel that as CAF usually use Rolls-Royce mtu engines, I suspect these trains will be designed, so they can be converted to hydrogen.
Conclusion
Rolls-Royce mtu appear to be on a path to decarbonise all their diesel engines.
Lumo Carbon Data Shows Its Trains Are 22 Times Greener Than Flying
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Advent.
These paragraphs detail how the figures were obtained.
To mark the second anniversary of its branding as ‘Lumo’, the operator commissioned consultancy firm Arup to provide an independent report about all direct emissions from its operations; emissions from the grid-supplied energy it uses; and other emissions in its supply chain.
Scope 1: Direct emissions from operations that are owned and controlled by Lumo;
Scope 2: Emissions from the use of grid-supplied electricity, heat, steam and/or cooling by Lumo;
Scope 3: All other emissions that occur in the value chain of Lumo.In the last two years, Lumo has carried over two million passengers. The figures reveal that, per passenger, emissions from a London-to-Edinburgh journey are twenty-two times the level for flying (149 kgCO2e) than for using Lumo (6.8kgCO2e).
I have a few thoughts.
Carbon Savings With LNER
LNER’s Class 801 trains are similar to Lumo’s Class 803 trains.
The main difference, is that the LNER have emergency diesel engines, whereas Lumo have emergency batteries to run the trains systems, if the catenary goes down.
So LNER on balance will generate a bit more carbon than Lumo.
But the difference will be marginal.
Carbon Savings With Avanti West Coast
Avanti’s Class 390 trains to Scotland, are all-electric, so there will be a carbon-saving.
Probably about the same as with LNER.
Avanti West Coast’s New Class 807 Trains
If the Class 807 trains were cars, they would be Lotuses.
- They are electric only and have no heavy diesel engines or traction batteries.
- They don’t even have emergency batteries for when the catenary fails.
- They have a redesigned nose. Is it more aerodynamic?
- The heavy tilt mechanism is history.
- As with all the other Hitachi high speed trains, they are capable of 125 mph, or 140 mph if the signalling permits.
These trains will undoubtedly have faster acceleration and deceleration and could probably knock minutes off the timings at all the stops.
Tucked away beside the Grand Union Sets Out Stirling Ambitions article in the December 2022 Edition of Modern Railways is a report on Avanti West Coast’s application for a second service between Euston and Liverpool.
This is said.
Avanti West Coast has applied for access rights for its second hourly Euston to Liverpool service, starting from December 2023, although a phased introduction of the new service is likely. This would make use of Avanti’s new fleet of 10×7-car Class 807 Hitachi EMUs, which are expected to enter service from Autumn 2023. The ‘807s’ would be deployed on the current hourly Liverpool service, on which a call at Liverpool South Parkway would be added. (provision is made for this in the December 2022 timetable.).
Pendolinos would then operate the second service each hour, calling at Lichfield Trent Valley and Tamworth.
A linespeed project is in progress to raise the permissible speed for non-tilting trains on the West Coast Main Line, and Avanti’s new Hitachi trains will take advantage of this.
I can’t wait to go to Liverpool in one of these trains.
Their carbon emissions should be in line with Lumo.
Avanti West Coast’s New Class 805 Trains
These are equivalent to the Class 802 trains, but with probably Class 807 train interiors and looks.
I wonder how long these trains will keep their diesel engines before battery power is the most affordable option.
Once they go battery-electric, their carbon emissions should be in line with Lumo.
Conclusion
I can’t see any other mantra than.
Electric good, diesel bad
Especially, if like most computers, it’s just plug and play.
High Speed Two To Crewe
There has been a lot of speculation about the Northern end of High Speed Two, so I might as well add sort out a few facts and add a bit of speculation of my own.
Sample Times Between London And Crewe
These are selected times from the 27th September 2023.
- 07:30 – Glasgow Non-Stop – 1:29
- 07:33 – Manchester Piccadilly – 1:37 – Stops at Stafford
- 07:43 – Liverpool Lime Street – 1:40 – Stop at Milton Keynes
- 08:30 – Glasgow Non-Stop – 1:29
- 08:33 – Manchester Piccadilly – 1:37 – Stop at Stafford
- 08:43 – Liverpool Lime Street – 1:40 – Stop at Milton Keynes
- 09:02 – Holyhead – 1:40 – Stop at Stafford
- 15:02 – Chester – 1:40 – Stops at Tamworth, Liverpool Trent Valley and Stafford
Note.
- The 07:30 and 08:30 Glasgow services appears to be pathed for one of the Pendolino electric trains and were run by Pendolinos.
- The 07:33 and 08:33 Manchester services appears to be pathed for one of the Pendolino electric trains and were run by Pendolinos.
- The 07:43 and 08:43 Liverpool services appears to be pathed for one of the new Class 807 electric trains, but were run by Pendolinos.
- The 15:02 Chester service appears to be pathed for one of the new Class 805 bi-mode trains.
- All services except the Glasgow services stop at Crewe.
- As London Euston and Crewe is 158 miles, the non-stop Glasgow services average 107 mph, the one-stop Manchester service averages 98 mph and the one-stop Liverpool service averages 95 mph.
I have some further thoughts.
How Long Does A Stop Take?
I’ve looked at some stops of Glasgow, Liverpool and Manchester services
Crewe
Looking at timings between Weaver Junction and Norton Bridge, I have found the following times.
- Glasgow-Euston – 23 minutes
- Liverpool-Euston – 28 minutes
Note.
- Manchester services don’t go through Weaver Junction.
- Weaver Junction and Norton Bridge are respectively North and South of Crewe.
- The Liverpool service stops at Crewe, where it has a dwell time of two minutes.
- The Glasgow service goes straight through Crewe.
The Crewe stop takes a total of 5 minutes of which 3 minutes are deceleration and acceleration to and from linespeed.
Stafford
Looking at timings between Norton Bridge and Colwich, I have found the following times.
- Glasgow-Euston – 7½ minutes
- Liverpool-Euston – 7½ minutes
- Manchester -Euston – 14 minutes
Note.
- Norton Bridge and Colwich are respectively North and South of Stafford.
- The Manchester service stops at Stafford, where it has a dwell time of two minutes.
- The Glasgow and Liverpool services go straight through Stafford.
The Stafford stop takes a total of 6½ minutes of which 4½ minutes are deceleration and acceleration to and from linespeed.
Milton Keynes
Looking at timings between Weedon and Bletchley, I have found the following times.
- Glasgow-Euston – 11½ minutes
- Liverpool-Euston – 16 minutes
- Manchester -Euston – 12½ minutes
Note.
- Weedon and Bletchley are respectively North and South of Milton Keynes.
- The Liverpool service stops at Milton Keynes, where it has a dwell time of one minute.
- The Glasgow and Manchester services go straight through Milton Keynes.
The Milton Keynes stop takes a total of 4 minutes of which 3 minutes are deceleration and acceleration to and from linespeed.
Average Speeds Between Crewe And London
London Ruston and Crewe is 158 miles according to Real Time Trains.
So what would times would various average speeds deliver?
- 100 mph – 95 minutes
- 110 mph – 86 minutes
- 120 mph – 79 minutes
- 125 mph – 76 minutes
- 130 mph – 73 minutes
- 140 mph – 68 minutes
Obviously, any average speed with over 125 mph running, will need full digital signalling.
Liverpool And London In Two Hours
Tucked away beside the Grand Union Sets Out Stirling Ambitions article in the December 2022 Edition of Modern Railways is a report on Avanti West Coast’s application for a second service between Euston and Liverpool.
This is said.
Avanti West Coast has applied for access rights for its second hourly Euston to Liverpool service, starting from December 2023, although a phased introduction of the new service is likely. This would make use of Avanti’s new fleet of 10×7-car Class 807 Hitachi EMUs, which are expected to enter service from Autumn 2023. The ‘807s’ would be deployed on the current hourly Liverpool service, on which a call at Liverpool South Parkway would be added. (provision is made for this in the December 2022 timetable.).
Pendolinos would then operate the second service each hour, calling at Lichfield Trent Valley and Tamworth.
A linespeed project is in progress to raise the permissible speed for non-tilting trains on the West Coast Main Line, and Avanti’s new Hitachi trains will take advantage of this.
I’ll take a quick look at the Crewe and Runcorn section.
- It is 22.5 miles.
- It takes 19 minutes.
- That is an average speed of 71 mph.
- Crewe and Weaver Junction has a speed limit of at least 110 mph
- Runcorn and Weaver Junction has a speed limit of at least 90 mph for most of the way.
- If with their superior performance, the new Class 807 trains could average 90 mph between Crewe and Runcorn, they would take 15 minutes.
- Achieving the 90 mph average may need a bit of track realignment and some signaling changes.
The four minutes saved would be enough to handle the extra stop at Liverpool South Parkway.
Consider.
- Currently, Pendolino trains do Liverpool and Crewe in 38 minutes, which includes the stop at Runcorn.
- My calculation with the Class 807 trains, shows that with a bit of extra signalling, the new trains could do Liverpool and Crewe in 38 minutes with the two stops.
- The stop at Crewe will subtract 5 minutes from the base journey time.
- The stop at Milton Keynes will subtract 4 minutes from the base journey time.
This means the base journey time between Crewe and London will be 73 minutes.
This would indicate that the trains would be running at 130 mph to achieve the two hours.
But there are five accelerations and five decelerations on a journey between London and Liverpool and the new Class 807 trains are the Lotuses of Hitachi’s family of AT-300 trains; lightweight and powerful.
Suppose they could save thirty seconds for each acceleration and deceleration.
The base journey time between Crewe and London will be 78 minutes.
This would indicate that the trains would be running at over 120 mph to achieve the two hours.
I certainly feel, that Liverpool and London in two hours is certainly possible using the new Class 807 trains.
London and Crewe with two stops would be times at one hour and twelve minutes.
But what about the Pendolinos?
- My last return trip from Liverpool did a practice call at Liverpool South Parkway and still arrived in London a few minutes early.
- The Pendolinos will still benefit from any improvements, between Crewe and Runcorn, which could reduce the Liverpool and Crewe time from 38 minutes to 34 minutes.
- The stop at Crewe will subtract 5 minutes from the base journey time.
- The stops at Lichfield Trent Valley and Tamworth will both subtract 4 minutes from the base journey time.
This means the base journey time between Crewe and London will be 73 minutes, which is the same as for the Class 807 trains.
This would indicate that the trains would be running at 130 mph to achieve the two hours.
Could this average speed be achieved by the selective application of full digital signalling, perhaps on the Trent Valley Line?
But it does appear to me, that the Pendolinos can get very close to two hours between London and Liverpool.
London and Crewe with three stops would be times at one hour and sixteen minutes.
Crewe And London Non-Stop
Consider.
- Pendolinos between London and Glasgow, go non-stop between London and Crewe.
- I have calculated that Pendolinos between London and Liverpool, will take one hour and sixteen minutes with three stops between London and Crewe.
- The three stops take a total of thirteen minutes.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see London and Glasgow Pendolinos take one hour and three minutes between London and Crewe.
This would knock twenty-six minutes off journey times between London and Glasgow.
Conclusion
I believe that with relatively minor improvements on the West Coast Main Line and the Liverpool branch, the following can be achieved.
- Liverpool and London can be around two hours with new Class 807 trains or Pendolinos.
- Liverpool and London services can increase their calls in the Midlands.
- London and Glasgow services can be nearly half-an-hour faster.
- The fastest London and Crewe services could be just over an hour using Pendolinos.
I also believe that the only serious infrastructure needed is some track realignment and some updated signalling.
See Also
Could High Speed Two Finish At Lichfield?
The Diesel Power Of The Class 805 Trains
Avanti West Coast’s new Class 805 trains, will probably start running between London Euston and Chester, Shrewsbury and North Wales before the end of the year.
But will they have the 560 kW engines of the Class 800 trains or the the 700 kW engines of the Class 802 trains?
On this page of Eversholt Rail’s web site, there is a detailed specification for a Class 802 train.
It says these trains have a top speed of 110 mph on diesel.
But it also says this about the design of the trains.
They have been designed to meet the operational requirements of the West of England route and are used on services out of London Paddington to Plymouth and Penzance.
The class 802 is almost identical to the class 800, the differences are that class 802s have a higher rated engine output to tackle the gradients through Devon and Cornwall, and a superior diesel range to provide the IET experience to the wider Greater Western Network, they also have a larger brake resistor which reduces brake pad usage and requires less maintenance.
Wikipedia also says that these are the diesel engine sizes in the three main classes of these Hitachi AT 300 trains.
- Class 800 train – 560 kW – Three engines for five cars
- Class 801 train – 560 kW – One emergency engine for five cars
- Class 802 train – 700 kW – Three engines for five cars
- Class 810 train – 735 kW – Four engines for five cars
All these four trains have similar bodyshells and running gear, so I suspect that to run at similar cruising speeds, similar amounts of power will be needed.
If the Class 802 train has a speed of 110 mph on diesel, then a rough estimate of the cruising speed of a train with the 560 kW engines can be estimated by doing this simple calculation. Note that air resistance is proportional to the square of the speed.
Square root (110*110 *560/700) = 98.4 mph
I have looked on OpenRailwayMap at all the tracks to the West of Wolverhampton, where these trains will run and the highest maximum operating speed I can find is 90 mph.
As the Class 805 trains have a reprofiled nose, which could be more aerodynamic, they may be able to cruise at 90 mph.
I believe that a train with three 560 kW engines will suit Avanti West Coast purposes well.
What Is The Operating Speed Of The Class 810 trains?
I can use a similar calculation to estimate the maximum operating speed of the Class 810 trains, that will operate on the Midland Main Line.
Consider.
- The Class 802 train has a total power of 2100 kW
- The Class 810 train has a total power of 2940 kW
- The Class 810 train with only three working engines has a total power of 2205 kW
I can estimate the cruising speed by doing this simple calculation, which is similar to the one for the Class 805 train.
Square root (110*110 *2940/2100) = 130 mph
I can also do it for a train running on three engines.
Square root (110*110 *2205/2100) = 113 mph
I looks to me, that the following is possible.
- As Class 810 trains can achieve the maximum speed of 125 mph on both diesel and electric power, the timetable is independent of the progress of the electrification.
- If the 125 mph sections are ignored, the fastest sections of line have a maximum speed of 110 mph, which could be possible on three engines.
- North of the electrification, where the maximum speed is only 110 mph, engines could be selectively rested to avoid overheating.
Four engines give a lot of interesting options.
I can’t wait to take a ride.
Could The Class 810 Trains Be Fitted With Batteries?
When, the electrification reaches Market Harborough station, there will be no 125 mph sections on the Midland Main Line, which are not electrified.
This Hitachi infographic shows the Hitachi Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train.
A Class 810 version of this train would have three diesel engines and one battery pack.
- It would have all the features of the infographic.
- My calculations give it a top speed of 113 mph on a route, where the maximum speed North of the electrification is 110 mph.
- I also suspect, it could bridge any small gaps in the electrification.
It would have the very positive effects of saving fuel and cutting pollution in stations.
Rockton To Buy Up To 40 Heart Aerospace ES-30 Electric Aircraft
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Aviation Source News.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Swedish investment and aircraft leasing company Rockton has confirmed that it will acquire up to 40 of Heart Aerospace’s regional electric aircraft, the ES-30.
The purchase confirmation converts an earlier letter of intent with the Swedish aircraft manufacturer into firm purchase orders for 20 aircraft with purchase rights for 20 more.
It’s good to see a leasing company getting involved, as it probably means that the finances are viable.
The Wikipedia entry for Heart Aerospace, describes the range of the ES-30 like this.
The ES-30 is planned to have a 108 nautical miles (200 kilometres; 124 miles) fully electric range or a 215 nmi (398 km; 247 mi) range when also using generators powered by aviation biofuel. A range of 430 nmi (800 km; 490 mi) could be possible if only 25 passengers are carried.
These are some UK airport to airport distances.
- Aberdeen – Kirkwall – 124 miles
- Aberdeen – Sumburgh – 188 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Cork – 192 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Anglesey – Ronaldsway – 58 miles
- Anglesey – Shannon – 186 miles
- Anglesey – Waterford – 130 miles
- Birmingham – Belfast – 226 miles
- Birmingham – Dublin – 200 miles
- Birmingham – Edinburgh – 250 miles
- Birmingham – Glasgow – 260 miles
- Birmingham – Inverness – 363 miles
- Birmingham – Kirkwall – 451 miles
- Birmingham – Newcastle – 178 miles
- Birmingham – Newquay – 198 miles
- Birmingham – Schipol – 402 miles
- Birmingham – Sumburgh – 513 miles
Birmingham – Wick – 418 miles - Edinburgh – Schipol – 473 miles
- Gatwick – Edinburgh – 356 miles
- Gatwick – Schipol – 374 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast – 106 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast City – 103 miles
- Glasgow – Derry – 121 miles
- Glasgow – Kirkwall – 221 miles
- Glasgow – Sumburgh – 300 miles
- Glasgow – Stornoway – 177 miles
- Haverfordwest – Waterford – 94 miles
- Haverfordwest – Newquay – 94 miles
- Heathrow – Newquay – 212 miles
- Humberside – Schipol – 333 miles
- Inverness – Kirkwall – 106 miles
- Inverness – Sumburgh – 190 miles
- Leeds – Schipol – 386 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast City – 151 miles
- Liverpool – Cardiff – 135 miles
- Liverpool – Dublin – 140 miles
- Liverpool – Haverfordwest – 127 miles
- Liverpool – Norwich – 180 miles
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway – 89 miles
- London City – Haverfordwest – 167 miles
- London City – Humberside – 145 miles
- London City – Manchester – 161 miles
- London City – Norwich – 100 miles
- Manchester – Schipol 413 miles
- Newcastle – Cardiff – 230 miles
- Newcastle – Belfast City – 168 miles
- Newcastle – Newquay – 346 miles
- Newcastle – Schipol – 395 miles
- Newquay – Brest – 140 miles
- Newquay – Cardiff 98 miles
- Newquay – Cork – 180 miles
- Newquay – Deauville – 241 miles
- Newquay – Dinard – 183 miles
- Newquay – Dublin – 212 miles
- Newquay – Guernsey – 128 miles
- Newquay – Jersey – 152 miles
- Newquay – Nantes – 211 miles
- Newquay – Orly – 351 miles
- Newquay – Rouen – 285 miles
- Newquay – Scillies – 68 miles
- Newquay – Waterford – 150 miles
- Norwich – Schipol – 277 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast – 75 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City – 62 miles
- Ronaldsway – Birmingham – 165 miles
- Ronaldsway – Dublin – 80 miles
- Ronaldsway – East Midlands – 161 miles
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow – 123 miles
- Ronaldsway – Leeds – 121 miles
- Ronaldsway – Manchester – 109 miles
- Southend – Schipol – 180 miles
- Stansted – Aberdeen – 379 miles
- Stansted – Edinburgh – 316 miles
- Stansted – Glasgow – 334 miles
- Stansted – Inverness – 426 miles
- Stansted – Schipol – 335 miles
- Stansted – Wick – 472 miles
- Sumburgh – Bergen – 226 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Note.
- I have included Schipol, as in certain areas of the UK, passengers sometimes fly long-haul from Schipol.
- I have included Haverfordwest, as it will be close to all the wind farm activity in the Celtic Sea.
- I have included Anglesey, as I think it has possibilities.
- The distances wee calculated using on of the Free Map Tools.
These are some more specific thoughts.
The Basic ES-30 And The UK
With a range of 124 miles, I don’t believe that the range is long enough for the UK.
But saying that there are some established routes, where it should be able to operate.
- Glasgow – Belfast
- Glasgow – Belfast City
- Glasgow – Derry
- Haverfordwest – Waterford
- Haverfordwest – Newquay
- Inverness – Kirkwall
- Liverpool – Haverfordwest
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway
- London City – Norwich
- Newquay – Cardiff
- Newquay – Scillies
- Ronaldsway – Belfast
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City
- Ronaldsway – Dublin
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow
- Ronaldsway – Leeds
- Ronaldsway – Manchester
These routes have the following in common.
- They are mostly between major airports with advanced facilities.
- Most airports served have access to renewable electricity.
- Some of the routes can support hundred seat airliners.
- Fifty percent go to the Isle of Man.
I can see several routes between the UK and the island of Ireland and to and from the Isle of Man using ES 30 aircraft.
The Extended Range ES-30 And The UK
The 247 mile range of the extended range ES-30, brings lots more routes into play.
Key routes could be the following.
- Aberdeen – Kirkwall
- Aberdeen – Sumburgh
- Anglesey – Cork
- Anglesey – Shannon
- Birmingham – Belfast
- Birmingham – Dublin
- Birmingham – Newcastle
- Birmingham – Newquay
- Glasgow – Kirkwall
- Glasgow – Stornoway
- Heathrow – Newquay
- Inverness – Sumburgh
- Liverpool – Belfast City
- Liverpool – Dublin
- Liverpool – Norwich
- London City – Haverfordwest
- London City – Humberside
- London City – Manchester
- Newcastle – Belfast City
- Newcastle – Cardiff
- Newquay – Brest
- Newquay – Cork
- Newquay – Deauville
- Newquay – Dinard
- Newquay – Dublin
- Newquay – Guernsey
- Newquay – Jersey
- Newquay – Nantes
- Newquay – Waterford
- Ronaldsway – Birmingham
- Ronaldsway – East Midlands
There will also be other routes.
The Extended Range With 25 Passengers ES-30 And The UK
The 490 mile range of the extended range ES-30 with only 25 passengers, brings a few more routes into play.
- Birmingham – Edinburgh
- Birmingham – Glasgow
- Birmingham – Inverness
- Birmingham – Kirkwall
- Birmingham – Schipol
- Birmingham – Wick
- Edinburgh – Schipol
- Gatwick – Edinburgh
- Gatwick – Schipol
- Glasgow – Sumburgh
- Humberside – Schipol
- Leeds – Schipol
- Manchester – Schipol
- Newcastle – Newquay
- Newcastle – Schipol
- Newquay – Orly
- Newquay – Rouen
- Norwich – Schipol
- Southend – Schipol
- Stansted – Aberdeen
- Stansted – Edinburgh
- Stansted – Inverness
- Stansted – Glasgow
- Stansted – Schipol
- Stansted – Wick
Note.
- All airports East of Birmingham and Manchester seem to be close enough to Schipol for an Extended Range ES-30 with 25 passengers to serve the route.
- Most major Scottish Airports can be reached from Stansted.
- Flying from Gatwick to Scottish Airports is around forty miles longer than flying from Stansted.
Liverpool Airport
Liverpool Airport could be a major destination for the ES 30, as it could be a key airport for flying between the UK and the island of Ireland.
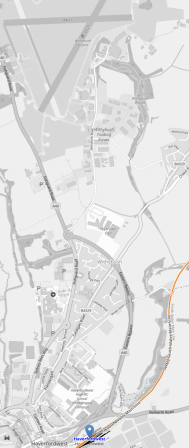
Liverpool would obviously need the electric infrastructure, but I also believe it needs a better connection to the major railway station at Liverpool South Parkway, which has extensive rail connections.
This Google Map shows the area between Liverpool South Parkway station and the airport.
Note.
- Liverpool South Parkway station is marked by the red arrow in the North-West corner of the map.
- The airport is in the opposite corner, with the terminal to the North of the runway.
- The main railway between the South and Liverpool Lime Street passes to the South of the station.
- The A561 passes across to the South of the railway and to the North of the airport.
I suspect some form of people mover like the Luton DART can be built between the station and the airport.
It should be noted that as Hunts Cross has only one platform for Merseyrail Northern Line trains and this could be a factor in limiting the line’s capacity. So could a second platform be installed at the airport to both act as an airport station and to increase the frequency on the Northern Line?
I believe that in a couple of years, journey times between Euston and Liverpool South Parkway will be under two hours and they will only get shorter with High Speed Two. With a fast connection between the airport and the station, there could be a sub-three-hour zero-carbon route between London and the island of Ireland.
- Avanti West Coast Class 805 train to Liverpool South Parkway.
- People mover to the airport.
- Electric aircraft on the 140 miles to Dublin.
Dublin air traffic are usually efficient in getting planes in quickly.
Glasgow Airport
Glasgow Airport could be a major destination for the ES 30, as it could be a key airport for flying between the UK and the island of Ireland.
As with Liverpool Airport it needs a better connection to the rail network.
If Glasgow Airport is successful running zero-carbon aircraft to Ireland, this could change all previous thinking on a Glasgow Airport Rail Link.
Ronaldsway Airport
Geography and electric airliners could be very kind to Ronaldsway Airport and the Isle of Man.
- Electric airliners can easily reach much of the island of Ireland and the UK mainland between Glasgow and Birmingham, from Ronaldsway Airport with ease.
- The Isle of Man will in a couple of years be surrounded by wind farms.
- With other developments on the island, it could sell itself to the UK and Ireland, as a green holiday destination.
But what would the motorcycle enthusiasts say?
Anglesey Airport
I believe that Anglesey Airport could be brought to life in a big way by electric aircraft like the ES-30 or the Eviation Alice.
These are flight distances from Anglesey Airport.
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Cork – 192 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Anglesey – Ronaldsway – 58 miles
- Anglesey – Shannon – 186 miles
- Anglesey – Waterford – 130 miles
All of these except for Cork, Derry, Shannon and Waterford would be possible in the basic ES-30.
This Google Map shows the airport, which is also labelled as RAF Valley.
Note that the North Wales Coast Line passes the site on the North-East side.
At present, Avanti West Coast trains take nearly four hours between London and Holyhead.
But later this year, new bi-mode Class 805 trains will replace, the current diesel only Class 221 trains.
- The current diesel only trains take two hours and five minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- The current diesel only trains take one hour and forty-three minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
- The fastest electric trains take one hour and twenty-nine minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
- High Speed Two trains will take 56 minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
When you consider that a lot of the North Wales Coast Line, is straight and flat, I can see the following times being possible, with some improvement and smart electrification between Crewe and Holyhead and a smaller number of stops.
- Crewe and Anglesey Airport – One hour and twenty minutes
- London Euston and Anglesey Airport – Two hours and fifty minutes
With High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains, the London Euston and Anglesey Airport time could be below two hours and thirty minutes.
I believe that with a well-designed terminal at Anglesey Airport, this could be the fastest zero-carbon way between London and Ireland.
Haverfordwest Airport
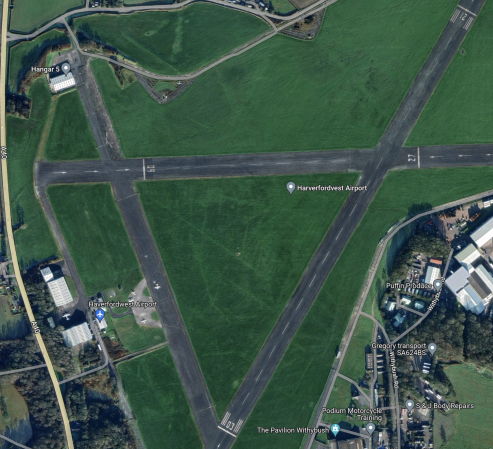
This Google Map shows the location of Haverfordwest Airport in the East of Pembrokeshire.
This second Google Map shows a close-up of the airport.
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the airport and the nearest railway station.
Note.
- Haverfordwest Airport is at the top of the map.
- Haverfordwest station is at the bottom of the map.
- There are rail connections to Cardiff, Fishguard, Milford Haven, Pembroke Dock and Swansea from the the station.
- Rail passengers for London would change at Swansea.
The road looks good between the airport and the station, so would an electric bus to handle transfers be ideal?
Consider.
- I have flown myself into Haverfordwest Airport and there were no navigation or operational problems that I can remember.
- With all the wind farm development planned for the coast of Pembrokeshire and the Celtic Sea, I feel that an airport in the area with regular flights to London and perhaps Waterford in Ireland could be essential.
- London City and Haverfordwest airports are 167 miles apart
- Waterford and Haverfordwest airports are 94 miles apart
- Quiet electric aircraft may ease any planning problems.
- Will a helicopter base be needed for serving wind farms in the Celtic Sea?
I believe, Haverfordwest Airport could be converted into a high-class airport for the Eastern tip of South Wales.
Haverfordwest Airport could also attract other services, given that the Welsh Government have a policy of not building new roads.
I have a feeling that quiet electric airliners will lead to the development of airports like Haverfordwest as feeder airports for the Heathrows and Schipols of this world.
Waterford Airport
Waterford Airport has recently been expanded and it appears from the Wikipedia entry, they are expecting more tourists.
This Google Map shows the position of the airport and the railway station in Waterford.
Note.
- The red arrow at the top of the map indicates Waterford station on the Northern side of the city.
- The airport is indicated by the blue dot in the South-East corner of the map.
- The airport is about ten kilometres from the City Centre.
In the past, Waterford has been quite a busy airport, but Covid-19 seems to have killed most of the traffic.
So could a zero-carbon service between Waterford and Haverfordwest be profitable?
- Those working with the wind energy in the Celtic Sea might find route useful.
- It would give a low-carbon route between Waterford and South Wales, which some might like.
- I also believe that the novelty of flying in an electric plane would attract passengers.
Waterford and Haverfordwest might be one of those routes, where electric planes might be worth trying.
This Google Map shows the Celtic Sea.
Note.
- Waterford Airport is indicated in red on the South-East corner of Ireland.
- Haverfordwest Airport is on the South-Western tip of Wales.
- Newquay Airport is in the South-East corner of the map on the North coast of Cornwall.
There could be as much as 50 GW of floating wind farms installed in this area.
I feel that there could be a case for a triangular Haverfordwest, Newquay and Waterford service.
Newquay Airport
Newquay Airport has been in the news recently because of the antics of Richard Branson and Virgin Orbit.
This Google Map shows the airport in relation to the town.
Note.
- The airport is in the North-East corner and boasts a long runway.
- The airport serves well over a dozen destinations.
- The town of Newquay is in the South-West corner of the map.
- Newquay station is by the sea.
All of these places would be suitable destinations for electric aircraft.
- Birmingham
- Brest
- Cardiff
- Cork
- Deauville
- Dinard
- Dublin
- Guernsey
- Heathrow
- Jersey
- Nantes
- Orly
- Rouen
- Scillies
- Waterford
Newquay Airport could get very busy with electric aircraft supporting tourism and the developing wind power industry.
This second Google Map shows the town centre and station.
Surely, having the station by Great Western Beach is good marketing.
In The Proposed Mid-Cornwall Metro, I talked about a plan to run an hourly Metro service between Newquay and Falmouth.
This article on Rail Technology Magazine is dated January 2023 and entitled Mid Cornwall Metro Secures £50m In Levelling Up Funding, where these are the first two paragraphs.
Following yesterday’s major Levelling Up funding announcement, the government has pledged an almost £50m grant to improve the railways linking Newquay, St Austell, Truro and Falmouth in Cornwall.
This financial aid to improve Cornwall Rail links represents the only successful bid out of four that were submitted to the Levelling up funding. The improvement scheme will be helmed by a partnership with Great Western Railway and Network Rail.
Note.
- I believe this means the Mid-Cornwall Metro will be built.
- Especially as looks like it will cost less than £100 million.
- As this Metro will serve Newquay, it shouldn’t be too difficult to link the plane with the train, with perhaps a zero-carbon bus.
- The Metro would then link Newquay Airport to the main population centres of Newquay, St Austell, Truro and Falmouth.
- If the Metro could be run using zero-carbon trains, that would surely put the icing on the cake!
The map from OpenRailwayMap shows the route.
Note.
- Newquay is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Trains spend around 6-7 minutes waiting at Newquay.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner marks Par station, where a chord will be reinstated to allow trains to go between Newquay and St. Austell.
- Par is the nearest station to the Eden Centre.
- Newquay and Par is 20.6 miles.
- The route, then goes along the Cornish Main Line, through St. Austell and then on to Truro.
- Par and Truro is 18.9 miles.
- At Truro the Metro would take the Falmouth branch.
- Falmouth and Truro is 11.8 miles.
- Trains spend around 7-8 minutes waiting at Falmouth Docks
- The total route is just over fifty miles, which probably means that battery-electric trains could work the route with charging at each end, whilst the train is turned round.
This airport and metro combination could give a big-boost to zero-carbon tourism.
Inverness Airport
Inverness Airport has recently been expanded with a station on the Inverness and Aberdeen Line.
Consider.
- Electric aircraft like the ES-30 will be able to reach both Kirkwall on Orkney and Sumburgh on Shetland from both Inverness and Aberdeen Airports.
- Sumburgh would need an extended range ES-30.
- Flights would be a few miles shorter from Inverness than from Aberdeen.
- Kirkwall and Sumburgh is only 85 miles, so there may be possibilities for serving both Orkney and Shetland with one flight.
- Extended range ES-30s might be able to do return trips to Kirkwall without a major charge at Kirkwall.
- I once flew in my Cessna-340 to Kirkwall to see the original turbine, that was placed on the island. There is a lot of cold forbidding sea in the area. Perhaps the slightly shorter trip from Inverness, might be better for everybody’s nerves?
- Just as the oil and gas industry did in the last century, I can see the offshore wind power industry generating a lot of passenger traffic to the Orkney and Shetland Islands.
Both Inverness and Aberdeen can be reached from Stansted by an ES-30 carrying a reduced passenger load.
Birmingham Airport
Birmingham Airport could become a major base for electric aircraft.
The 247 mile range of the extended range ES-30 would allow it to be able to reach the following places.
- Belfast
- Dublin
- Newcastle
- Newquay
- Ronaldsway
Reduce the passenger load slightly to 25 passengers and the plane would be able to reach.
- Edinburgh
- Glasgow
- Inverness
- Kirkwall
- Wick
But Birmingham Airport is only 65 minutes from Euston and will in the future be served by High Speed Two, in under an hour.
The airport also has a large catchment area of its own, who might be tempted to choose flying zero-carbon.
Spokes From Speke
In the 1980s, I went to a presentation from Royal Mail in Ipswich about guaranteed next day delivery of parcels. It was important to me, as I was writing software that needed to get from Ipswich, where it was created to London, where it would be tested and installed on customers machines. We also needed to get copies to our customers in Edinburgh and Aberdeen.
The Royal Mail’s latest concept of Spokes From Speke was described.
- All urgent parcels and First Class mail would be collected from the local sorting office and taken to the local airport, which in our case would probably have been Stansted.
- These consignments would then be flown to Speke Airport as Liverpool Airport was known in those days at around midnight.
- They would then be sorted and reloaded onto other planes to complete their journey.
- The planes would then return home and the parcels and mail would be delivered by truck to the local sorting office.
Aircraft used included Short Skyvans and piston-engined twins. Some we’re the quietest of aircraft.
I have heard or read somewhere that in some airports, there were complaints about noisy aircraft flying in and out in the middle of the night.
Now fifty years on companies are looking to speed up deliveries.
- In the UK, companies are experimenting with 100 mph overnight parcels trains.
- This article on Railway Gazette is entitled Varamis Rail Launches Regular Express Light Freight Service.
- Eversholt Rail are putting money behind converting redundant electric multiple units into parcel trains.
But DHL in the USA are going another way and have ordered twelve Alice aircraft from Eviation.
It looks like the cargo Alice could have a useful load of just over a tonne and a range of around 290 miles.
I can envisage flights of near-silent silent Alices sneaking into and out of airports in the middle of the night to deliver and collect urgent parcels.
Techniques like Spokes From Speke will come again, but this time with electric aircraft.
How Would The ES-30 Compare With An Eviation Alice?
The Wikipedia entry for the Eviation Alice gives these figures.
- Passengers – 9
- Maximum Speed – 300 mph
- Range – 290 miles
- Take-off distance – 840 metres
- Landing distance – 620 metres
Note.
- These are figures that most pilots would expect from an aircraft of this size.
- My Cessna 340 was about the same and about eight percent slower.
- It also had a much longer range.
If you look at my list of flights, these will not be possible.
- Birmingham – Inverness – 363 miles
- Birmingham – Kirkwall – 451 miles
- Birmingham – Schipol – 402 miles
- Bimingham – Sumburgh – 513 miles
Birmingham – Wick – 418 miles - Edinburgh – Schipol – 473 miles
- Gatwick – Edinburgh – 356 miles
- Gatwick – Schipol – 374 miles
- Glasgow – Sumburgh – 300 miles
- Humberside – Schipol – 333 miles
- Leeds – Schipol – 386 miles
- Manchester – Schipol 413 miles
- Newcastle – Newquay – 346 miles
- Newcastle – Schipol – 395 miles
- Newquay – Orly – 351 miles
- Stansted – Wick – 472 miles
- Sumburgh – Bergen – 226 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Note.
- Most routes that are too long are to Schipol or Scotland.
- Anglesey appears to have Ireland extremely well covered.
- Birmingham, Glasgow and Liverpool keep their Irish routes.
- Newquay is still a hub, that would promote tourism in Cornwall and only loses the Orly connection, although it keeps the flight to Heathrow.
- Ronaldsway still looks to be a possible zero-carbon airport.
I would suggest that a range of 290 miles, is an ideal one for an electric aircraft in the UK, as it can handle a large number of routes.
These are routes that I feel would attract a large number of passengers.
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast – 106 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast City – 103 miles
- Glasgow – Derry – 121 miles
- Heathrow – Newquay – 212 miles
- Inverness – Kirkwall – 106 miles
- Inverness – Sumburgh – 190 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast – 153 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast City – 151 miles
- Liverpool – Dublin – 140 miles
- Liverpool – Norwich – 180 miles
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway – 89 miles
- London City – Humberside – 145 miles
- London City – Manchester – 161 miles
- Newcastle – Cardiff – 230 miles
- Newcastle – Belfast City – 168 miles
- Newquay – Brest – 140 miles
- Newquay – Cardiff 98 miles
- Newquay – Cork – 180 miles
- Newquay – Deauville – 241 miles
- Newquay – Scillies – 68 miles
- Newquay – Waterford – 150 miles
- Norwich – Schipol – 277 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City – 62 miles
- Ronaldsway – Dublin – 80 miles
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow – 123 miles
- Southend – Schipol – 180 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Alice may not be big enough for some routes.
But it will be a wonderful route-proving aircraft for the larger ES-30 and other zero-carbon aircraft.
Conclusion
There will be a lot of uses for battery-electric aircraft in the UK.
Thoughts On High Speed Two
These are a few thoughts about High Speed Two, after the reports of major changes today.
This article on the BBC is entitled HS2 Line Between Birmingham And Crewe Delayed By Two Years.
This is the sub-heading.
The Birmingham to Crewe leg of high speed railway HS2 will be delayed by two years to cut costs.
These are the three opening paragraphs.
Some of the design teams working on the Euston end of the line are also understood to be affected.
Transport secretary Mark Harper blamed soaring prices and said it was “committed” to the line linking London, the Midlands and North of England.
HS2 has been beset by delays and cost rises. In 2010, it was expected to cost £33bn but is now expected to be £71bn.
Delivering The Benefits Of High Speed Two Early
It is my belief that with a large project taking a decade or more , it is not a bad idea to deliver some worthwhile benefits early on.
The Elizabeth Line opened in stages.
- The new Class 345 trains started replacing scrapyard specials in 2017.
- The rebuilt Abbey Wood station opened in 2017.
- Paddington local services were transferred to the Elizabeth Line in 2019.
- Outer stations reopened regularly after refurbishment from 2018.
- The through line opened in May 2022.
There’s still more to come.
Some projects wait until everything is ready and everybody gets fed up and annoyed.
Are there any parts of High Speed Two, that could be completed early, so that existing services will benefit?
In 2020, the refurbishment of Liverpool Lime Street station and the tracks leading to the station was completed and I wrote about the station in It’s A Privilege To Work Here!, where this was my conclusion.
Wikipedia says this about Liverpool Lime Street station.
Opened in August 1836, it is the oldest still-operating grand terminus mainline station in the world.
I’ve used Lime Street station for fifty-five years and finally, it is the station, the city needs and deserves.
I’ve been to grand termini all over the world and Lime Street may be the oldest, but now it is one of the best.
Are there any stations, that will be served by High Speed Two, that should be upgraded as soon as possible to give early benefits to passengers, staff and operators?
Avanti West Cost have solved the problem of the short platforms at Liverpool South Parkway station, by ordering shorter Class 807 trains. Will High Speed Two lengthen the platforms at this station?
A good project manager will need to get all the smaller sub-projects in a row and work out what is the best time to do each.
Digital Signalling
I would assume, as this will be needed for High Speed Two services in the West Coast Main Line to the North of Crewe, this is surely a must for installing as early as possible.
If the existing trains could run for a hundred miles at 140 mph, rather than the current 125 mph, that would save five worthwhile minutes.
Trains could run closer together and there is the possibility of organising services in flights, where a number of trains run together a safe number of minutes apart.
Remove Bottlenecks On Classic Lines, That Could Be Used By High Speed Two
I don’t know the bottlenecks on the West Coast Main Line, but there are two on the East Coast Main Line, that I have talked about in the past.
Could ERTMS And ETCS Solve The Newark Crossing Problem?
Improving The North Throat Of York Station Including Skelton Bridge Junction
Hopefully, the digital signalling will solve them.
Any bottlenecks on lines that will be part of High Speed Two, should be upgraded as soon as possible.
Birmingham And Crewe
I will start by looking at the leg between Birmingham and Crewe.
This section of the HS2 map shows High Speed Two between Birmingham and Lichfield.
Note.
- The blue circle on the left at the bottom of the map is Birmingham Curzon Street station.
- The blue circle on the right at the bottom of the map is Birmingham Interchange station.
- The High Speed Two to and from London passes through Birmingham Interchange station.
- The branch to Birmingham Curzon Street station connects to the main High Speed Two at a triangular junction.
- North of the triangular junction, High Speed Two splits.
- The Eastern branch goes to East Midlands Parkway station.
- The Northern branch goes to Crewe, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Preston and Scotland.
At the top of the map, the Northern branch splits and lines are shown on this map.
Note.
- The junction where the Northern and Eastern branches divide is in the South-East corner of the map.
- To the North of Lichfield, the route divides again.
- The Northern purple line is the direct line to Crewe.
- The shorter Southern branch is a spur that connects High Speed Two to the Trent Valley Line, which is the current route taken by trains between London Euston and Crewe, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Preston and Scotland.
- Crewe station is in the North-West corner of the map.
The route between the junction to the North of Lichfield and Crewe is essentially two double-track railways.
- High Speed Two with a routine operating speed of 205 mph.
- The Trent Valley Line with a routine operating speed of 140 mph.
- High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains can run on all tracks.
- High Speed Two Full-Size trains may be able to run on the Trent Valley Line at reduced speed.
- Eighteen trains per hour (tph) is the maximum frequency of High Speed Two.
I feel in an emergency, trains will be able to use the other route.
Will This Track Layout Allow An Innovative Build?
Suppose the link to the Trent Valley Line was built first, so that High Speed Two trains from London for Crewe, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Preston and Scotland, could transfer to the Trent Valley Line as they do now.
- All lines used by High Speed Two services North of the junction, where High Speed Two joins the Trent Valley Line would be updated with digital signalling and 140 mph running. This will benefit current services on the line. For instance Euston and Liverpool/Manchester services could be under two hours.
- The current services would be replaced by High Speed Two services run by High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains.
- The direct High Speed Two route between Lichfield and Crewe would now be built.
- When this section of High Speed Two is complete, High Speed Two services would use it between Lichfield and Crewe.
- As the direct route would be built later, this would delay the building of the Birmingham and Crewe high-speed route.
Currently, trains run the 41.8 miles between Lichfield and Crewe in 28 minutes, which is an average speed of 89.6 mph.
I can build a table of average speeds and times for Lichfield and Crewe.
- 100 mph – 25.1 minutes – 2.9 minutes saving
- 110 mph – 22.8 minutes – 5.2 minutes saving
- 120 mph – 20.9 minutes – 7.1 minutes saving
- 125 mph – 20.1 minutes – 7.9 minutes saving
- 130 mph – 19.3 minutes – 8.7 minutes saving
- 140 mph – 17.9 minutes – 10.1 minutes saving
- 160 mph – 15.7 minutes – 12.3 minutes saving
- 180 mph – 13.9 minutes – 14.1 minutes saving
- 200 mph – 12.5 minutes – 15.5 minutes saving
Note.
- Even a slight increase in average speed creates several minutes saving.
- Times apply for both routes.
I believe that a 125 mph average should be possible on the Trent Valley route, which may be enough for Euston and Liverpool/Manchester services to be under two hours.
Improving Classic Lines Used By High Speed Two North Of Lichfield
Real Time Trains shows these figures for a Glasgow Central to Euston service.
- Glasgow and Lichfield Trent Valley is 298.2 miles.
- Glasgow and Lichfield Trent Valley takes five hours.
This is an average speed of 59.6 mph.
Note.
- The average speed is low considering the trains are capable of cruising at 125 mph and 140 mph with digital signalling.
- High Speed Two services between Euston and Glasgow will use the classic network, to the North of Lichfield.
I can build a table of average speeds and times for Glasgow and Lichfield.
- 100 mph – 179 minutes – 121 minutes saving
- 110 mph – 163 minutes – 157 minutes saving
- 120 mph – 149 minutes – 151 minutes saving
- 125 mph – 143 minutes – 157 minutes saving
- 130 mph – 138 minutes – 162 minutes saving
- 140 mph – 128 minutes – 172 minutes saving
This table illustrates why it is important to improve all or as many as possible of classic lines used by High Speed Two to enable 140 mph running, with full digital signalling. Obviously, if 140 mph is not feasible, the speed should be increased to the highest possible.
Routes that could be updated include.
- London Euston and Glasgow Central
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street
- London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly (all routes)
- London Euston and Blackpool
- London Euston and Holyhead
- London Euston and Shrewsbury
Not all these routes will be served by High Speed Two, but they could be served by 140 mph trains.
What Times Would Be Possible?
The InterCity 225 was British Rail’s ultimate electric train and these two paragraphs from its Wikipedia entry, describe its performance.
The InterCity 225 was designed to achieve a peak service speed of 140 mph (225 km/h); during a test run in 1989 on Stoke Bank between Peterborough and Grantham, an InterCity 225 was recorded at a speed of 162 mph (260.7 km/h). Its high speed capabilities were again demonstrated via a 3hr 29mins non-stop run between London and Edinburgh on 26 September 1991. British regulations have since required in-cab signalling on any train running at speeds above 125 mph (201 km/h) preventing such speeds from being legally attained in regular service. Thus, except on High Speed 1, which is equipped with cab signalling, British signalling does not allow any train, including the InterCity 225, to exceed 125 mph (201 km/h) in regular service, due to the impracticality of correctly observing lineside signals at high speed.
The InterCity 225 has also operated on the West Coast Main Line (WCML). In April 1992, one trainset achieved a new speed record of two hours, eight minutes between Manchester and London Euston, shaving 11 minutes off the 1966 record. During 1993, trials were operated to Liverpool and Manchester in connection with the InterCity 250 project.
- The fastest London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly services appear to be two hours and six minutes tomorrow, with stops at Nuneaton and Stoke-on-Trent.
- The fastest London King’s Cross and Edinburgh service is four hours seventeen minutes tomorrow.
It does appear that British Rail’s 1980s-vintage InterCity 225 train did very well.
Trains that would be able to run at 140 mph with updated signalling include.
- Alstom Class 390
- Hitachi Class 800, 801, 802, 803, 805, 807 and 810
- British Rail InterCity 225
- High Speed Two Classic-Compatible.
All are electric trains.
Could High Speed Two, West Coast Main Line and East Coast Main Line Services Be Run By High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains?
I don’t see why not!
- They would be able to use short stretches of High Speed Line like Lichfield and Crewe.
- LNER and CrossCountry could also use the trains.
- High Speed Two is providing the framework and it’s there to be used, provided the paths are available.
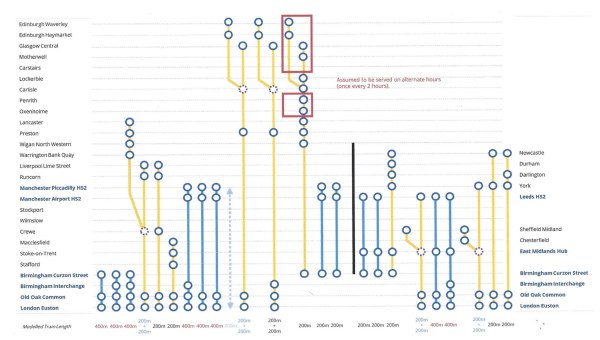
This graphic shows the preliminary schedule.
It only shows ten trains going through Crewe, so there could be up to eight spare high speed paths between Birmingham and Crewe.
Could High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains Be Used To Advantage On The East Coast Main Line?
I published this extract from the Wikipedia entry for the InterCity 225 earlier.
The InterCity 225 was designed to achieve a peak service speed of 140 mph (225 km/h); during a test run in 1989 on Stoke Bank between Peterborough and Grantham, an InterCity 225 was recorded at a speed of 162 mph (260.7 km/h). Its high speed capabilities were again demonstrated via a 3hr 29mins non-stop run between London and Edinburgh on 26 September 1991.
The London and Edinburgh run was at an average speed of around 112 mph.
I wonder what time, one of LNER’s Class 801 trains, that are all-electric could do, once the new digital signalling has been fully installed on the route? I suspect it would be close to three hours, but it would depend on how long the trains could run at 140 mph.
It should be noted that the Selby Diversion was designed for 160 mph, when it was built by British Rail in the 1980s.
In Are Short Lengths Of High Speed Line A Good Idea?, I look at the mathematics of putting in short lengths of new railway, which have higher speeds, where this was part of my conclusion.
I very much feel there is scope to create some new high speed sections on the current UK network, with only building very little outside of the current land used by the network.
I would love to know what some of Network Rail’s track experts feel is the fastest time possible between London and Edinburgh that can be achieved, by selective upgrading of the route.
If some of the trains were High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains, with a top speed of 205 mph, provided the track allowed it, there could be some interesting mathematics balancing the costs of track upgrades, new trains with what passengers and operators need in terms of journey times.
Could High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains Be Used To Advantage On The West Coast Main Line?
Much of what I said about the East Coast Main Line would apply to the West Coast Main Line.
But in addition, the West Coast Main Line will be a superb place to test the new High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains.
I believe, that before High Speed Two opens, we’ll see High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains, carrying passengers between Euston and Avanti West Coast’s destinations.
Could High Speed Two Be Split Into Two?
Consider.
- Under earlier plans, the East Coast Main Line to the North of York, will be used by High Speed Two.
- With digital signalling the East Coast Main Line will support continuous running at 140 mph for long sections of the route.
- The East Coast Main Line has a recently-rebuilt large Southern terminal at King’s Cross with eleven platforms and good suburban services and excellent connections to the London Underground.
- The East Coast Main Line has a very large Northern terminal at Edinburgh Waverley with twenty platforms and good local train connections.
- There are large intermediate stations on the East Coast Main Line at Doncaster, Leeds, Newcastle, Peterborough and York. All these stations have good local train connections.
- The East Coast Main Line has important branches to Cambridge, Harrogate, Huddersfield, Hull King’s Lynn, Lincoln, Middlesbrough, Nottingham, Scarborough, Sheffield, Skegness and Sunderland.
We are talking about an asset, that needs improving rather than sidelining.
Could High Speed Two Be A One-Nation Project?
Over three years ago, I wrote Could High Speed Two Be A One-Nation Project? and tried to answer the question in the title.
But now the core network is better defined, perhaps it is time to look at extending the High Speed network again.
The next few sections look at possible extensions.
Serving Chester And North Wales
I looked at this in Could High Speed Two Trains Serve Chester And North Wales?, which I have updated recently.
This was my conclusion.
It looks to me, that when High Speed Two, think about adding extra destinations, Chester and Holyhead could be on the list.
I also suspect that even without electrification and High Speed Two services, but with the new Class 805 trains, the route could be a valuable one for Avanti West Coast.
These are current and promised times for the two legs to Holyhead.
- Euston and Crewe – 90 minutes – Fastest Class 390 train
- Euston and Crewe – 55 minutes – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train from Wikipedia
- Crewe and Holyhead – 131 minutes – Fastest Class 221 train
- Crewe and Holyhead – 70 minutes – 90 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 63 minutes – 100 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 57 minutes – 110 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 53 minutes – 120 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 45 minutes – 140 mph average speed
Note.
- I have assumed that Crewe and Holyhead is 105.5 miles.
- The operating speed of the North Wales Coast Line is 90 mph.
- In the following estimates, I have assumed a change of train at Crewe, takes 6 minutes.
I think there are several options to run fast services to Chester and North Wales.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- The fastest Class 221 train between Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 3 hours 41 minutes.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way, but with perhaps less stops and some track improvement
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- 110 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 2 hours 27 minutes.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead uprated largely to 125 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- 120 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 2 hours 23 minutes.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead Crewe and Holyhead electrified and uprated to 140 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- 140 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 2 hours 15 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, the Class 805 train to Holyhead
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- The fastest Class 221 train between Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 3 hours 12 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, the Class 805 train to Holyhead, but with perhaps less stops and some track improvement
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 110 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 58 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, the Class 805 train to Holyhead, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead uprated largely to 125 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 120 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 54 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, Class 805 train to Holyhead, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead electrified and uprated to 140 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 140 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 46 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train all the way, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead electrified and uprated to 140 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 140 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 40 minutes.
From these estimates, I have come to these conclusions.
- A sub-two and a half-hour service can be attained with the new Class 805 trains and some improvements to the tracks along the North Wales Coast Line.
- A sub-two hour service can be attained with a High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe and a Class 805 train to Hplyhead along a 140 mph electrified North Wales Coast Line.
- If the North Wales Coast Line is electrified, the journey from London Euston, Birmingham Interchange, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester would be zero-carbon.
We should be looking to building a zero-carbon fast passenger ferry for sailing between Holyhead and Dublin.
- The current fastest ferries appear to take three hours and 15 minutes, which means that a six-hour low-carbon journey between London Euston and Dublin, should be possible with the new Class 805 trains, prior to the opening of High Speed Two.
- A five-hour journey after the opening of High Speed Two to Crewe and electrification of the North Wales Coast Line should be possible.
If the advanced zero-carbon ferry could knock an hour off the journey, four hours between London and Dublin along a spectacular coastal railway with a fast sea voyage, would be a route that would attract passengers.
- High Speed Two would need to be opened to Crewe.
- The North Wales Coast Line would need to be upgraded to a 140 mph digitally-signalled line.
- The North Wales Coast Line would need to be electrified.
- Full electrification may not be needed, as discontinuous electrification will have advanced to provide zero-carbon running, in a more affordable and less disruptive manner.
- Trains could either be High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains all the way from London or there could be a change at Crewe to Class 805 trains.
- The ferry would use the best zero-carbon and operational technology.
The improvement and electrification of the North Wales Coast Line could be planned to take place in a relaxed manner, so that journey times continuously got quicker.
I would start the improvement of the North Wales Coast Line, as soon as possible, as all these improvement will be used to advantage by the new Class 805 trains.
Serving West And South West England And South Wales
Suppose you want to go between Glasgow and Cardiff by train, after High Speed Two has opened.
- You will take one of the half-hourly High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains between Glasgow Central and London.
- Three and a half-hours later, you will get off the train in one of the below ground platforms at Old Oak Common station.
- A short ride in an escalator or lift and you will be in the Great Western Railway station at ground level.
- From here, fifty minutes later, you will be in Cardiff.
The journey will have taken four hours and twenty minutes.
This may seem a long time but currently Glasgow and Cardiff by train takes over seven hours by train.
- Glasgow and Bristol Temple Meads takes eight hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 5 hours.
- Glasgow and Cheltenham Spa takes six hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 5 hours and 30 minutes.
- Glasgow and Penzance takes twelve hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 8 hours and 33 minutes.
- Glasgow and Swansea takes nearly nine hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 6 hours and 9 minutes.
The High Speed Two route only has one simple change, whereas some routes now have up to four changes.
Conclusion
West Coast Main Line Electro-Diesels On Test
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
This is the first paragraph.
The first two of 13 Hitachi Class 805 electro-diesel trainsets ordered for Avanti West Coast services are undergoing testing on the West Coast Main Line ahead of entry into service later this year.
These Class 805 trains will go to places like Chester, Bangor and Holyhead via Crewe.
It is interesting to look at various Crewe to London Euston services this morning.
- 0740 – Class 390 train – From Liverpool – One Stop – 1 hour 40 minutes
- 0755 – Class 221 train – From Holyhead – One Stop – 1 hour 40 minutes
- 0832 – Class 390 train – From Manchester – One Stop – 1 hour 37 minutes
- 0844 – Class 390 train – From Glasgow – 1 hour 28 minutes
Note.
- The first field is the four-figure time that the train left Crewe.
- The last field is the journey time between Crewe to London Euston.
- The Class 390 and 805 trains will use electricity to run between Crewe and London Euston, whereas the Class 221 train will use diesel.
- Crewe and London Euston is 158 miles.
- The Glasgow train covers the 158 miles at an average speed of 107.7 mph.
I have some thoughts.
What Will Be The Time For A Class 805 Train Between Crewe And London Euston?
Consider.
- From Crewe, the Class 805 train will be using the electrification to London Euston.
- The Class 390 train can tilt, whereas the Class 805 train can’t!
- The Class 805 train is at least three tonnes lighter per car, than the Class 390 train.
- The lighter weight and possibly more power of the Class 805 trains, will give better acceleration.
- There is twenty-one years of difference in the build dates of the two trains. In that time, I also suspect that Network Rail have improved the track between Crewe and London Euston.
- Norton Bridge junction has been improved to avoid conflicts.
- It would be very convenient for Avanti West Coast and Network Rail, if the performance under electrification of the two trains were similar.
For these reasons, I believe that the performance of a non-stop Crewe And London Euston service using a Class 805 train will be such that it can match that of a Class 390 train.
I would also expect that with a similar stopping pattern between Crewe And London Euston, there would be little to choose between the two trains.
I can see with its better acceleration and lighter weight that the time between Crewe and London Euston will be perhaps a dozen minutes faster than the current time.
Using the electrification will also save a lot of diesel fuel with all its emissions.
Along The North Wales Coast Line
Consider.
- Crewe and Holyhead is 105.5 miles and takes two hours and two minutes in a typical service.
- These figures give an average speed of 52 mph.
- There are six stops, which are scheduled to take a total of ten minutes.
- About half the North Wales Coast Line has a maximum operating speed of 90 mph, but through Chester, Llandudno Junction and West of Bangor, the operating speed is 75 mph or less.
I am fairly sure, that with both the current Class 221 trains and the new Class 805 trains, it will be the track, rather than the train that determines the average speed.
It would therefore appear that if the average speed can be raised by track improvements these time savings could be achieved.
- 60 mph – 105.5 mins – 16.5 mins
- 70 mph – 90 mins – 32.5 mins
- 80 mph – 79 mins – 43 mins
- 90 mph – 70 mins – 52 mins
- 100 mph – 63 mins – 59 mins
- 110 mph – 58 mins – 64 mins
- 120 mph – 53 mins – 69 mins
- 130 mph – 49 mins – 73 mins
- 140 mph – 45 mins – 77 mins
Note.
- The first column is the average speed.
- The second column is the time between Holyhead and Crewe.
- The third column is the saving.
- I suspect that 90 or 100 mph would be the highest possible practical average speed.
- Trains average 100 mph on several long sections of the Great Eastern Main Line.
- I put in the higher speeds to show what is possible, if the North Wales Coast Line were to be converted into a 140 mph electrified line with digital signalling.
Even at these relatively slow speeds compared to High Speed Two, there are considerable time savings to be made, just by improving the tracks.
Incidentally, High Speed Two is quoted in Wikipedia as aiming for a Crewe and London Euston time of 56 minutes, so by averaging 100 mph between Crewe and Holyhead, London Euston and Holyhead could be under two hours.
Batteries And Class 805 Trains
I wouldn’t be surprised that soon after the Class 805 trains are delivered, they could be converted to a version of Hitachi’s Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train, the specification of which is shown in this Hitachi infographic.
Note.
- I suspect that the batteries will be used to handle regenerative braking on lines without electrification, which will save diesel fuel and carbon emissions.
- The trains accelerate faster, than those they replace.
- The claimed fuel and carbon saving is twenty percent.
- It is intended that these trains will be introduced in 2023.
But Hitachi have not given any predictions of the range of these trains on battery power alone.
However, they do claim a battery range of 56 miles for the Hitachi Regional Battery Train, which is based on similar technology.
These trains could help in speeding the stops between Crewe and Holyhead.
- Batteries would be charged at Holyhead and on the electrification to the South of Crewe.
- At each stop, trains would use a proportion of the power in the battery to accelerate faster and save fuel and cut emissions.
- Battery power would be used in stations for train hotel power.
- Westbound trains would arrive in Holyhead and Southbound trains would arrive in Crewe, with not much power in the battery.
I suspect that, whether diesel or battery power is used, will be controlled by a sophisticated computerised control system.
Electrification Along The North Wales Coast Line
I think this will eventually happen to allow High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains to run to Chester and along the North Wales Coast Line to Llandudno, Bangor and Holyhead.
But there is no benefit to be gained in electrifying until higher speeds are possible, after track improvements.
I believe these times will be possible with track improvements and the opening of High Speed Two.
- Holyhead and Crewe – Class 805 train and 80 mph average – 79 mins
- Holyhead and Crewe – Class 805 train and 90 mph average – 70 mins
- Holyhead and Crewe – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train, electrification and 100 mph average – 63 mins
- Crewe and London Euston – Class 805 train – 80 mins
- Crewe and London Euston – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train – 56 mins
Note, electrification will be needed, to run High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains along the North Wales Coast Line.
I am confident that these times will be possible.
- Holyhead and London Euston – Class 805 train and 90 mph average along the coast – 2 hours 30 mins
- Holyhead and London Euston – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train and 100 mph average along the coast – 2 hours
The current time between Holyhead and London Euston is over three hours 45 minutes.
Conclusion
These trains will certainly speed up trains to North Wales.
Avanti West Coast Looks To Recover
The title of this post is the same as an article in the March 2022 Edition of Modern Railways.
These are some points from the article.
Passengers Numbers Are Recovering
This is a paragraph.
Mr. Wittingham says the recovery has been strongest on the Anglo-Scottish and Liverpool corridors, while Manchester have begun to bounce back. Slowest to recover is the London to West Midlands market; ‘there’s several operators here and we were the main carrier of business passengers, and that sector has been recovering more slowly than leisure’ says Mr. Whittingham.
Phil Whittingham is MD of Avanti West Coast.
Train Numbers Are Recovering
Avanti are building up train numbers from Euston after the pandemic.
Frequencies are as follows in trains per hour (tph)
- Pre-Covid – 9
- During the pandemic – 4
- From December 2021 – 7
- Omicron – 4
- From February 2022 – 6
- From May 2022 – 6+
Avanti have reacted to demand.
Three Classes Of Travel
This is a paragraph.
Avanti’s business has historically been driven by leisure travel – before Covid this accounted for broadly 60 % of passengers, with most of the rest travelling for business plus a smaller number of commuters. ‘The demand is there, and we think by next year we’ll be on the way to full recovery’ says Mr. Whittingham. ‘Leisure has been strong, especially at weekends, but the missing bit is the corporate market.’
Avanti have been running a marketing campaign and it appears to have been successful.
This paragraph describes Avanti’s new Standard Premium class.
Last year, Avanti West Coast launched a new class of travel – Standard Premium. This was first introduced in May on an upgrade-only basis before going fully live in September with the option to book online in advance. The new class sits between Standard and First, giving passengers larger seats and greater space but without some of the extras that come with First Class Travel such as complimentary refreshments and lounge access.
These are Mr. Whittingham’s comments on the three classes.
The current split of passengers is 84% Standard, 12 % First and 4 % Standard Premium, but given the latter has been in place for less than a year there is clearly scope for growth. ‘Our research shows people have been upgrading to Standard Premium rather than downgrading from First’.
I have yet to try Standard Premium, but I will next time I use Avanti.
Refreshments
Avanti have decided to serve different refreshments in Standard Premium and First classes.
- In Standard Premium, they are now offering At Seat Orders.
- In First, they have updated the menu.
Both seem to have been well-received.
I like this statement from Mr. Whittingham.
We’ve tried to make it a more personalised service with a less rigid structure, so we give customers what they want, when they want it, rather than when we want to give it to them.
A Consistent Offer
This is a paragraph.
Mr. Whittingham says Avanti has not yet confirmed whether t will offer three classes of travel on the new Hitachi trains it has ordered, but says the aim is to provide a more consistent offer. Assisting this will be changes in the ongoing Pendolino refurbishment, where 11-car sets are having Coach G converted from First to Standard accommodation, meaning all Pendolinos, whether nine-car or 11-car, will have three coaches for First and Standard Premium passengers.
My instinct says that the four trains will be something like.
- Class 390 train – Pendolino – Nine-car – three First/Standard Premium cars – six Standard cars
- Class 390 train – Pendolino – Eleven-car – three First/Standard Premium cars – eight Standard cars
- Class 805 train – Hitachi – Five-car – one First/Standard Premium car – four Standard cars
- Class 807 train – Hitachi – Seven-car – two First/Standard Premium car – five Standard cars
Note.
- The Class 805 and Class 807 Hitachi trains are very much plug-and-play and can be lengthened or shortened as required.
- A regular passenger between London and Liverpool, who regularly upgrades from Standard to Standard Premium in a Class 390 train could be a bit miffed if he couldn’t, because the service was being run by a Class 807 train.
- Hitachi would probably be very happy to add extra cars to the Class 805 and Class 807 trains.
As the Class 390 Pendolino trains are being refurbished, I do wonder if they will be receiving some fittings from the Hitachi trains to make sure the trains are consistent to both on-board staff and passengers.
Pendolino Investment
The Pendolino refurbishment is comprehensive.
- It is one of the largest such programmes ever undertaken in the UK.
- Leasing company; Angel Trains are funding the work.
- Alstom are doing the work at Widnes.
- There appears to be a smooth plan to refurbish all trains.
- Coach G will be converted from First to Standard accommodation in eleven-car trains.
- Mr. Whittingham says that all trains will come out looking like a new train.
The eleven-car trains are being converted first, as the conversion of Coach G gives a capacity benefit of around thirty seats.
The awful seats in Standard Class will be replaced with Lumo-style seats and laptop-friendly fold-down tables.
These seats will be a big improvement!
New Trains Coming
This paragraph introduces the new trains.
The second major fleet investment from Avanti is the £350 million for new trains from Hitachi, financed by Rock Rail. These comprise 13×5-car Class 805 bi-modes, ordered for destinations off the electrified route including North Wales and Shrewsbury and 10×7-car Class 807 electrics. Deployment plans for the latter are still being worked through but are likely to include services to Birmingham and Liverpool, and potentially to Blackpool.
What is not said in this paragraph, is that all trains have a redesigned front end, which I suspect is more aerodynamic.
The all-electric Class 807 trains have no diesel engines or batteries, so have they been put on a diet, to improve the acceleration?
In Will Avanti West Coast’s New Trains Be Able To Achieve London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street In Two Hours?, I came to these conclusions.
- A two hour service between London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street will be possible with Avanti West Coast’s new Class 807 trains.
- The current Class 390 trains could go a bit faster and if they cut out a couple of stops could probably break two hours.
I also calculated that a two tph service between London and Liverpool in two hours would need nine trains.
Timetable Changes
This paragraph introduces the article’s section on timetable changes.
The project in turn feeds into a major timetable change planned by Avanti and other West Coast main line operators. This will be the first significant change to West Coast main line schedules since 2008; ‘the world has changed, and we need to think about how we best serve our markets’ says Mr Whittingham.
This paragraph sums up the major changes.
Of note are the planned changes to the pattern of London to West Midlands services; the pre-Covid 20-minute interval would be amended to offer faster journey times and greater connectivity. Also featuring in the new timetable aspirations would be additional Trent Valley calls in some Liverpool and Manchester services; Mr Whittingham cites as one benefit of this the potential for improved journey times between the North West and the East Midlands via a change of train at Nuneaton. The Hitachi trains, with their better acceleration, will be particularly useful on services with more frequent stops.
The next three sections will look at some timetable changes in a bit more detail.
London And West Midlands Services
Replacement of twenty diesel Class 221 trains with thirteen bi-mode Class 805 trains will mean a major reorganisation of services to the West Midlands.
- Some current diesel services will now be electric.
- All services between Birmingham New Street and Euston will now be electric.
- No services will run on diesel under live electrification.
- Avanti have promised to serve Walsall.
- There will be extra services to Shrewsbury and other places.
The electric services will also speed up some services to the West Midlands.
North West And East Midlands Services
I will look at train times for services between the North West (Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly) and the East Midlands (Leicester, Nottingham and Lincoln), where passengers change at Nuneaton.
These are the current fastest possible times according to the National Rail journey planner.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Leicester -2:24 with changes at Crewe and Nuneaton,
- Manchester Piccadilly and Leicester – 2:11 with change at Sheffield
- Liverpool Lime Street and Nottingham – 2:42 with no changes
- Manchester Piccadilly and Nottingham – 1:51 with no changes
- Liverpool Lime Street and Lincoln- 3:42 with changes at Sheffield and Doncaster
- Manchester Piccadilly and Lincoln – 2:38 with change at Sheffield
Note that times are in hours:minutes.
These are all current times for the various legs if the route is via Nuneaton.
- Avanti West Coast – Liverpool Lime Street and Nuneaton – 1:18
- Avanti West Coast – Manchester Piccadilly and Nuneaton – 1:13
- CrossCountry – Nuneaton and Leicester – 0:27
- East Midlands Railway – Leicester and Nottingham – 0:48 – Time from Leicester and Lincoln service.
- East Midlands Railway – Leicester and Nottingham – 0:20 – Time from St. Pancras and Nottingham service.
- East Midlands Railway – Leicester and Lincoln -1:42 – Time from Leicester and Lincoln service.
- East Midlands Railway – Nottingham and Lincoln -0:52 – Time from Leicester and Lincoln service.
Note that the two Avanti West Coast times have been estimated by taking the time from Real Time Trains and adding three minutes for the acceleration or deceleration at Nuneaton.
These would be possible times between the North West and the East Midlands via Nuneaton.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Leicester – 1:47
- Manchester Piccadilly and Leicester – 1:42
- Liverpool Lime Street and Nottingham – 2:37
- Manchester Piccadilly and Nottingham – 2:32
- Liverpool Lime Street and Lincoln- 3:31
- Manchester Piccadilly and Lincoln – 3:26
Note that I am assuming changes at Nuneaton and Leicester are cross-platform or same platform changes that take two minutes.
But there is another level of improvement possible.
Suppose that East Midlands Railway’s Lincoln and Leicester service were to be extended to Nuneaton and run by a train with this specification.
- 125 mph operating speed.
- Battery-electric power.
- 100 mph operating speed on battery power.
- Range of 56 miles on battery
- Ability to use the Midland Main Line electrification, when it is erected.
Charging stations would be needed at Nuneaton and Lincoln.
These would be possible times between the North West and the East Midlands via Nuneaton with the one change at Nuneaton.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Leicester – 1:45
- Manchester Piccadilly and Leicester – 1:40
- Liverpool Lime Street and Nottingham – 2:05
- Manchester Piccadilly and Nottingham – 2:00
- Liverpool Lime Street and Lincoln- 2:57
- Manchester Piccadilly and Lincoln – 2:52
Note.
I am assuming that the timings for the Nuneaton and Leicester and the Nottingham and Lincoln legs are as for the current trains.
I am assuming the change at Nuneaton is a cross-platform or same platform change that takes two minutes.
Trains run on battery where tracks are not electrified.
I can build a table of current times, times via Nuneaton and savings.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Leicester -2:24 – 1:45 – 0:39
- Manchester Piccadilly and Leicester – 2:11 – 1:40 – 0.31
- Liverpool Lime Street and Nottingham – 2:42 – 2:05 – 0:37
- Manchester Piccadilly and Nottingham – 1:51 – 2:00 – 0.09 slower
- Liverpool Lime Street and Lincoln- 3:42 – 2:57 – 0.45
- Manchester Piccadilly and Lincoln – 2:38 – 2:52 – 0:14 slower
It does appear that by using the 125 mph speed of the West Coast Main Line has a positive effect on some times from the North West to the East Midlands.
But times could be reduced further.
- Installing full digital signalling, that would enable 140 mph running between Crewe and Nuneaton, could save ten minutes.
- Improving the Nuneaton and Leicester and the Nottingham and Lincoln legs could allow faster running.
The more I look at changing at Nuneaton, I feel it is a good idea.
- It improves the connections between East Midlands Parkway and Loughborough and the North West.
- It improves the connections between Cambridge, Peterborough and Stansted Airport and the North West, if the change at Nuneaton is to CrossCountry’s Stansted Airport and Birmingham New Street service.
- It improves the connections between Coventry and Leamington Spa and the North West.
Avanti have come up with a cunning plan, worthy of Baldrick at his best.
A Second Hourly Service Between London And Liverpool
A paragraph talks about the second hourly service between London and Liverpool.
Avanti still has ambitions to introduce a second hourly service between Euston and Liverpool, but when this will come in will depend on demand recovery.
Consider.
- If would be desirable if some or all trains running on the route could achieve a timing of two hours between London and Liverpool.
- It is felt that the second service should stop at Liverpool South Parkway station, where the platforms are too short for eleven-car Class 390 trains.
- Avanti have stated they would like more stops in the Trent Valley, especially at Nuneaton, where they would connect to services to the East Midlands.
- Nuneaton is almost exactly halfway between London and Liverpool.
- Running two tph with Class 807 trains would need nine trains and Avanti have only ordered ten in total.
I believe that a practical timetable like this could work.
- Class 390 train – one tph – Non-stop or perhaps a single stop in the Midlands – Under two hours
- Class 807 train – one tph – Stopping at Nuneaton, Stafford, Crewe, Runcorn and Liverpool South Parkway – Current time or better
An hourly service between London and Liverpool in under two hours would surely be a passenger magnet.
Reopening The Oswestry – Gobowen Line
On October 27th this Beeching Reversal Project was given £50,000 to build a case for reopening.
These are my thoughts.
Gobowen Station
Gobowen station appears to be a fine station.
- It is Grade II Listed.
- It has two platforms.
- It is on the Shrewsbury-Chester Line.
- Transport for Wales run trains to Birmingham New Street, Cardiff Central, Chester, Holyhead and Shrewsbury.
- Avanti West Coast will start running services to and from London Euston via Wrexham in December 2022.
Wikipedia says this about the future of the station.
Gobowen station may become the northern terminus of the proposed Cambrian Heritage Railways line to Llynclys, Pant and Blodwel via Oswestry. Shropshire Council was to acquire the coal yard at Gobowen for railway-related uses, including car parking for the station. If the plans are fully realised, the station would have three platforms, one of which would be for the Heritage Railway.
It does look as if, Shropshire Council have got the money for a full study.
This Google Map shows Gobowen station.
Note.
- The two tracks of the Chester-Shrewsbury Line each have a platform.
- Step-free access is by the level crossing, which is at the North end of the station.
- It looks like it would be space to convert the Northbound platform into an island platform, where the Western platform face would be for the heritage trains.
This second Google Map shows the tracks at the South end of Gobowen station.
Note.
There is a set of points to allow trains to access a third platform at Gobowen station.
The single-track line to Oswestry branches off to the West at the bottom of the map.
It would appear that a bay platform at Gobowen station can be created to handle trains to Oswestry.
Oswestry Station
Oswestry station appears to be another fine station.
- It is also Grade II Listed.
- It has just a single platform.
- It appears to be owned by the local authority.
This Google Map shows the station.
Note.
- The station is the large building with the chimneys in the South-East corner of the map.
- The single platform is behind it.
- The platform is long enough to take a 1200 metre long train.
This station would make an ideal terminus.
The Track Between Oswestry And Gobowen
The track is single-track with a couple of foot crossings, so I don’t think it will need much to bring it up to a modern standard.
A Shuttle Service Between Oswestry And Gobowen
I suspect a two-car shuttle train between the two stations would suffice for most of the day.
Transport for Wales have some Class 230 trains and these would be ideal. They could even be battery-electric trains if a battery charging system were to be installed at one station.
Could Avanti West Coast Run A Service To London?
It looks like Avanti West Coast’s Class 805 trains could run along the line between Gobowen and Oswestry.
So could Avanti’s planned service to Gobowen terminate at Oswestry instead?
It would all depend on the passenger forecasts and actual numbers
Could Avanti West Coast Run A Battery-Electric Service To London?
Consider.
- Oswestry is a town of 17,500 people, so probably has a reasonable electricity supply, especially if it were to be backed up by a battery.
- The amount of renewable electricity produced over the border in Wales is only going to grow.
- There is plenty of space at Oswestry to put in a charging system to replace the batteries.
Distances are as follows.
- Crewe and Chester – 21.1 miles
- Chester and Gobowen – 24.6 miles
- Gobowen and Oswestry – 3.3 miles
This is a total distance of 49 miles.
Avanti West Coast have ordered thirteen bi-mode Class 805 trains, which will replace the diesel Class 221 trains currently working between London Euston and Chester. Holyhead and Shrewsbury.
- They will run at 125 mph between Euston and Crewe using electric power.
- If full in-cab digital signalling were to be installed on the electrified portion of the route, they may be able to run at 140 mph in places under the wires.
- They will use diesel power on the North Wales Coast Line to reach places like Chester, Holyhead and Wrexham.
- According to an article in Modern Railways, the Class 805 trains could be fitted with batteries.
I wouldn’t be surprised that when they are delivered, they are a version of the Hitachi’s Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train, the specification of which is shown in this Hitachi infographic.
Note.
- I suspect that the batteries will be used to handle regenerative braking on lines without electrification, which will save diesel fuel and carbon emissions.
- The trains accelerate faster, than those they replace.
- The claimed fuel and carbon saving is twenty percent.
- It is intended that these trains will be introduced next year.
But Hitachi have not given any predictions of the range of these trains on battery power alone.
However, they do claim a battery range of 56 miles for the Hitachi Regional Battery Train, which is based on similar technology.
I believe it would be possible to run a zero-carbon London Euston and Oswestry service.
- The trains would be Class 805 trains fitted with batteries.
- Trains could stop at Milton Keynes Central, Lichfield Trent Valley, Stafford, Crewe, Chester, Wrexham General and Gobowen.
- Trains would use electrification between London Euston and Crewe.
- Trains would recharge their batteries South of Crewe and at Oswestry.
I doubt that a battery-electric zero-carbon train serving Cheshire, Shropshire and North-East Wales would have a negative effect on the area.
Just as Hull and Lincoln seem to be moving towards a frequency of one train per two hours from London, I wonder if this service could ever attain the same frequency.
Onward From Oswestry
Cambrian Heritage Railways are planning to run services past Oswestry on their heritage railway.
Will this be a good idea?
Where Now For First Group?
First Group are a shareholder in Avanti West Coast.
They also own Lumo, who last week launched their open-access service between London and Edinburgh. Their marketing is all about being green and sustainable.
I just wonder if a battery-electric service to Gobowen is successful, they will apply this model all over the group.
Hull Trains service between London and Hull is an obvious possibility for a battery-electric zero-carbon service.
Conclusion
It looks to me, that reopening of the Oswestry – Gobowen Line opens up other possibilities.
Through Settle And Carlisle Service Under Consideration
The title of this post, is the same as that of an article in the June 2021 Edition of Modern Railways.
This is the first paragraph.
Plans for a new Leeds to Glasgow through service via the Settle and Carlisle line are being developed, with CrossCountry and the Department for Transport starting to look at the possible scheme.
It sounds like a sensible idea to me.
The article also suggests the following.
- CrossCountry is a possible operator.
- CrossCountry are keen to improve services between Leeds and Glasgow
- The trains could be InterCity 125s, freed up, by a the arrival of Class 221 trains from Avanti West Coast, when they receive their new Class 805 trains.
- Maintenance of the trains wouldn’t be a problem, as this could be done at Neville Hill in Leeds or Craigentinny in Edinburgh.
- Services could start in December 2023.
I have a few thoughts of my own!
The Route
The route between Leeds and Carlisle is obvious, but there are two routes between Carlisle and Glasgow.
Trains would probably choose a route and call at stations to maximise passenger numbers.
These stations are on the various routes.
- Settle and Carlisle – Shipley, Bingley, Keighley, Skipton, Gargrave, Hellifield, Long Preston, Settle, Horton in Ribblesdale, Ribblehead, Dent, Garsdale, Kirkby Stephen, Appleby, Langwathby, Lazonby & Kirkoswald and Armathwaite
- Glasgow South Western – Dunlop, Stewarton, Kilmaurs, Kilmarnock, Auchinleck, New Cumnock, Kirkconnel, Sanquhar, Dumfries, Annan and Gretna Green
- West Coast Main – Motherwell, Carstairs and Lockerbie
There are certainly a lot of possibilities.
Upgrading The InterCity 125 Trains
CrossCountry appear to have enough InterCity 125 trains to muster five in a two Class 43 power car and seven Mark 3 coach formation.
They may not be fully in-line with the latest regulations and there may be a need for a certain degree of refurbishment.
These pictures show some details of a refurbished Great Western Railway Castle, which has been fitted with sliding doors.
Will The InterCity 125 Trains Be Shortened?
Scotrail’s Inter7City trains and Great Western Railway’s Castle trains have all been shortened to four or five coaches.
This picture shows a pair of Castles.
Journey Times, Timetable And Frequency
The current journey time between Leeds and Glasgow Central stations via the East Coast Main Line is four hours and eight minutes with nine stops.
The Modern Railways article says this about the current service.
The new service would be targeted at business and leisure travellers, with through journey times competitive with road and faster than the current direct CrossCountry Leeds to Glasgow services via the East Coast main line.
I would expect that CrossCountry are looking for a time of around four hours including the turn round.
- Stops could be removed to achieve the timing.
- The trains could run at 125 mph on the West Coast Main Line.
This could enable a train to have the following diagram.
- 0800 – Depart Leeds
- 1200 – Depart Glasgow Central
- 1600 – Depart Leeds
- 2000 – Depart Glasgow Central
- Before 2400 – Arrive Leeds
Note.
- A second train could start in Glasgow and perform the mirrored timetable.
- Timings would probably be ideal for train catering.
- Trains would leave both termini at 0800, 1200, 1600 and 2000.
- The timetable would need just two trains.
I also think, if a second pair of trains were to be worked into the timetable, there could be one train every two hours on the route, if the demand was there.
I certainly believe there could be a timetable, that would meet the objectives of attracting business and leisure passengers away from the roads.
Tourism And Leisure Potential
The Settle and Carlisle Line is known as one of the most scenic railway lines in England, if not the whole of the UK.
There are important tourist sites all along the route between Leeds and Glasgow
- Leeds – The station is well-connected in the City Centre.
- Saltaire – For the World Heritage Site and Salt’s Mill
- Keighley – For the Keighley and Worth Heritage Railway
- Settle – The town of Settle is worth a visit.
- Ribblehead – For the famous Ribblehead Viaduct
- Appleby – For the Horse Fair.
- Carlisle – The station is well-connected in the City Centre.
- Glasgow – Glasgow Central station is well-connected in the City Centre.
Many of the stations are used by walkers and others interested in country pursuits.
I believe that it is a route that needs a quality rail service.
Travel Between London and Towns Along The Settle And Carlisle Line
In Thoughts On Digital Signalling On The East Coast Main Line, I said this.
I think it is highly likely that in the future, there will be at least one train per hour (tph) between London Kings Cross and Leeds, that does the trip in two hours.
It may seem fast compared to today, but I do believe it is possible.
With a timely connection at Leeds station, will this encourage passengers to places along the Settle and Carlisle line to use the train?
What About the Carbon Emissions?
The one problem with using InterCity 125 trains on this route, is that they are diesel-powered, using a pair of Class 43 locomotives.
But then there are over a hundred of these diesel-electric locomotives in service, nearly all of which are now powered by modern MTU diesel engines, which were fitted in the first decade of this century.
Consider.
- The locomotives and the coaches they haul have an iconic status.
- Great Western Railway and Scotrail have recently developed shorter versions of the trains for important routes.
- There are over a hundred of the locomotives in service.
- Companies like ULEMCo are developing technology to create diesel-powered vehicles that can run on diesel or hydrogen.
- There is plenty of space in the back of the locomotives for extra equipment.
- MTU have a very large number of diesel engines in service. It must be in the company’s interest to find an easy way to cut carbon emissions.
- I believe that the modern MTU diesel engines could run on biodiesel to reduce their carbon footprint.
And we shouldn’t forget JCB’s technology, which I wrote about in JCB Finds Cheap Way To Run Digger Using Hydrogen.
If they could develop a 2 MW hydrogen engine, it could be a shoe-in.
I believe that for these and other reasons, a solution will be found to reduce the carbon emissions of these locomotives to acceptable levels.
Conclusion
In this quick look, it appears to me that a Glasgow and Leeds service using InterCity 125 trains could be a very good idea.