Offshore Construction Work Resumes On Revolution Wind After US Judge’s Ruling
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
A US judge in Washington has cleared the way for work to resume on the 704 MW Revolution Wind offshore wind farm after granting a temporary injunction that lifted the federal stop-work order imposed in August.
These two paragraphs add details to the post.
On 22 August, the US Department of the Interior’s (DOI) Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) issued a stop-work order halting all offshore construction activities on the 704 MW project, which is already 80 per cent completed, according to its developers, Ørsted and Skyborn Renewables.
A few days later, the joint venture challenged the stop-work order in the US District Court for the District of Columbia, while Connecticut and Rhode Island filed their own lawsuits against the decision on the same day.
I’ve written about this project before in ‘This Has Nothing To Do With National Security’ | Revolution Wind Halt Leaves Connecticut Leaders Demanding Answers
How Will The UK Power All These Proposed Data Centres?
On Wednesday, a cardiologist friend asked me if we have enough power to do Trump’s UK AI, so I felt this post might be a good idea.
Artificial Intelligence Gave This Answer
I first asked Google AI, the title of this post and received this reply.
The UK will power proposed data centres using a mix of grid-supplied low-carbon electricity from sources like offshore wind and through on-site renewable generation, such as rooftop solar panels. Data centre operators are also exploring behind-the-meter options, including battery storage and potential future nuclear power, to meet their significant and growing energy demands. However, the UK’s grid infrastructure and high energy prices present challenges, with industry calls for grid reform and inclusion in energy-intensive industry support schemes to facilitate sustainable growth.
Google also pointed me at the article on the BBC, which is entitled Data Centres To Be Expanded Across UK As Concerns Mount.
This is the sub-heading.
The number of data centres in the UK is set to increase by almost a fifth, according to figures shared with BBC News.
These are the first three paragraphs.
Data centres are giant warehouses full of powerful computers used to run digital services from movie streaming to online banking – there are currently an estimated 477 of them in the UK.
Construction researchers Barbour ABI have analysed planning documents and say that number is set to jump by almost 100, as the growth in artificial intelligence (AI) increases the need for processing power.
The majority are due to be built in the next five years. However, there are concerns about the huge amount of energy and water the new data centres will consume.
Where Are The Data Centres To Be Built?
The BBC article gives this summary of the locations.
More than half of the new data centres would be in London and neighbouring counties.
Many are privately funded by US tech giants such as Google and Microsoft and major investment firms.
A further nine are planned in Wales, one in Scotland, five in Greater Manchester and a handful in other parts of the UK, the data shows.
While the new data centres are mostly due for completion by 2030, the biggest single one planned would come later – a £10bn AI data centre in Blyth, near Newcastle, for the American private investment and wealth management company Blackstone Group.
It would involve building 10 giant buildings covering 540,000 square metres – the size of several large shopping centres – on the site of the former Blyth Power Station.
Work is set to begin in 2031 and last for more than three years.
Microsoft is planning four new data centres in the UK at a total cost of £330m, with an estimated completion between 2027 and 2029 – two in the Leeds area, one near Newport in Wales, and a five-storey site in Acton, north-west London.
And Google is building a data centre in Hertfordshire, an investment worth £740m, which it says will use air to cool its servers rather than water.
There is a map of the UK, with dots showing data centres everywhere.
One will certainly be coming to a suitable space near you.
Concerns Over Energy Needs
These three paragraphs from the BBC article, talk about the concerns about energy needs.
According to the National Energy System Operator, NESO, the projected growth of data centres in Great Britain could “add up to 71 TWh of electricity demand” in the next 25 years, which it says redoubles the need for clean power – such as offshore wind.
Bruce Owen, regional president of data centre operator Equinix, said the UK’s high energy costs, as well as concerns around lengthy planning processes, were prompting some operators to consider building elsewhere.
“If I want to build a new data centre here within the UK, we’re talking five to seven years before I even have planning permission or access to power in order to do that,” he told BBC Radio 4’s Today programme.
But in Renewable Power By 2030 In The UK, I calculated that by 2030 we will add these yearly additions of offshore wind power.
- 2025 – 1,235 MW
- 2026 – 4,807 MW
- 2027 – 5,350 MW
- 2028 – 4,998 MW
- 2029 – 9,631 MW
- 2030 – 15,263 MW
Note.
- I have used pessimistic dates.
- There are likely to be more announcements of offshore wind power in the sea around the UK, in the coming months.
- As an example in Cerulean Winds Submits 1 GW Aspen Offshore Wind Project In Scotland (UK), I talk about 3 GW of offshore wind, that is not included in my yearly totals.
- The yearly totals add up to a total of 58,897 MW.
For solar power, I just asked Google AI and received this answer.
The UK government aims to have between 45 and 47 gigawatts (GW) of solar power capacity by 2030. This goal is set out in the Solar Roadmap and aims to reduce energy bills and support the UK’s clean power objectives. The roadmap includes measures like installing solar on new homes and buildings, exploring solar carports, and improving access to rooftop solar for renters.
Let’s assume that we only achieve the lowest value of 45 GW.
But that will still give us at least 100 GW of renewable zero-carbon power.
What will happen if the wind doesn’t blow and the sun doesn’t shine?
I have also written about nuclear developments, that were announced during Trump’s visit.
- Centrica And X-energy Agree To Deploy UK’s First Advanced Modular Reactors
- Is Last Energy The Artemis Of Energy?
- National Grid And Emerald AI Announce Strategic Partnership To Demonstrate AI Power Flexibility In The UK
- Nuclear Plan For Decommissioned Coal Power Station
- Raft Of US-UK Nuclear Deals Ahead Of Trump Visit
- Rolls-Royce Welcomes Action From UK And US Governments To Usher In New ‘Golden Age’ Of Nuclear Energy
This is an impressive array of nuclear power, that should be able to fill in most of the weather-induced gaps.
In Renewable Power By 2030 In The UK, I also summarise energy storage.
For pumped storage hydro, I asked Google AI and received this answer.
The UK’s pumped storage hydro (PSH) capacity is projected to more than double by 2030, with six projects in Scotland, including Coire Glas and Cruachan 2, potentially increasing capacity to around 7.7 GW from the current approximately 3 GW. This would be a significant step towards meeting the National Grid’s required 13 GW of new energy storage by 2030, though achieving this depends on policy support and investment.
There will also be smaller lithium-ion batteries and long duration energy storage from companies like Highview Power.
But I believe there will be another source of energy that will ensure that the UK achieves energy security.
SSE’s Next Generation Power Stations
So far two of these power stations have been proposed.
Note.
- Both power stations are being designed so they can run on natural gas, 100 % hydrogen or a blend of natural gas and hydrogen.
- Keadby will share a site with three natural gas-powered power stations and be connected to the hydrogen storage at Aldbrough, so both fuels will be available.
- Ferrybridge will be the first gas/hydrogen power station on the Ferrybridge site and will have its own natural gas connection.
- How Ferrybridge will receive hydrogen has still to be decided.
- In Hydrogen Milestone: UK’s First Hydrogen-to-Power Trial At Brigg Energy Park, I describe how Centrica tested Brigg gas-fired power station on a hydrogen blend.
- The power stations will initially run on natural gas and then gradually switch over to lower carbon fuels, once delivery of the hydrogen has been solved for each site.
On Thursday, I went to see SSE’s consultation at Knottingley for the Ferrybridge power station, which I wrote about in Visiting The Consultation For Ferrybridge Next Generation Power Station At Knottingley.
In the related post, I proposed using special trains to deliver the hydrogen from where it is produced to where it is needed.
Could HiiROC Be Used At Ferrybridge?
Consider.
- HiiROC use a process called thermal plasma electrolysis to split any hydrocarbon gas into hydrogen and carbon black.
- Typical input gases are chemical plant off gas, biomethane and natural gas.
- Carbon black has uses in manufacturing and agriculture.
- HiiROC uses less energy than traditional electrolysis.
- There is an independent power source at Ferrybridge from burning waste, which could be used to ower a HiiROC system to generate the hydrogen.
It might be possible to not have a separate hydrogen feed and still get worthwhile carbon emission savings.
Conclusion
I believe we will have enough electricity to power all the data centres, that will be built in the next few years in the UK.
Some of the new power stations, that are proposed to be built, like some of the SMRs and SSE’s Next Generation power stations could even be co-located with data centres or other high energy users.
In Nuclear Plan For Decommissioned Coal Power Station, I describe how at the former site of Cottam coal-fired power station, it is proposed that two Holtec SMR-300 SMRs will be installed to power advanced data centres. If the locals are objecting to nuclear stations, I’m sure that an SSE Next Generation power station, that was burning clean hydrogen, would be more acceptable.
Visiting The Consultation For Ferrybridge Next Generation Power Station At Knottingley
Yesterday, I visited the first meeting for the consultation on Ferrybridge Next Generation Power Station, which was held in the old town hall at Knottingley.
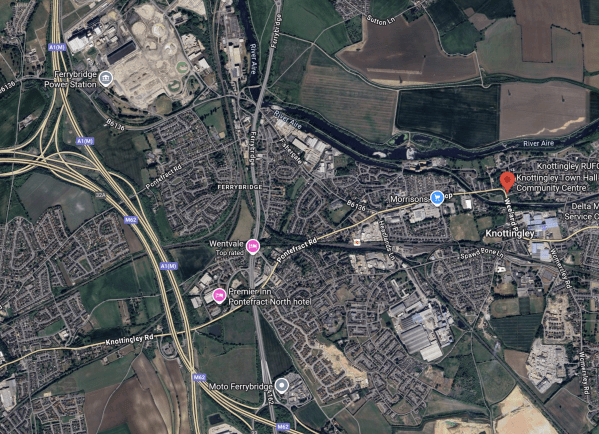
This Google Map shows the power station in relation to Knottingley.
Note.
- The meeting was held in the Knottingley Town Tall Community Centre, which is marked by the red arrow.
- I had arrived by train from Wakefield at Knottingley station and I was lucky enough to be able to get a taxi to the Town Hall.
- Knottingley station is marked on the map about a twenty-minute walk to the West of the Town Hall.
- The Ferrybridge power station site is in the North-West corner of the map and appears to be bordered by the B6136 road.
- The A1 (M) and the M 62 motorways run North-South past the power station site.
- The A (M) motorway continues North-South to Newcastle and Scotland, and London respectively.
- The M62 motorway continues West-East to Liverpool and Manchester, and Hull respectively.
- The well-appointed Moto Ferrybridge services is accessible from both motorways.
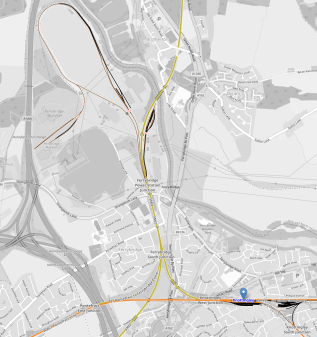
This OpenRailwayMap shows the rail lines in the area.
Note.
- The A 62 and A 1(M) motorways running down the West side of the map.
- Knottingley station is on the Pontefract Line, and is marked by a blue arrow.
- The Pontefract Line could have connections from both East and West to the Ferrybridge power station site via Ferrybridge Power Station junction.
- The loop, where the merry-go-round coal trains turned, appears to be still intact at the North of the power station site.
Will these rail lines be any use in the building and operation of the new power station?
These are my thoughts.
Fuel For The Power Station
The brochure for the consultation says this about the fuel for the Ferrybridge Next Generation Power Station.
Ferrybridge Next Generation Power Station will be designed to run on 100% hydrogen, natural gas or a
blend of natural gas and hydrogen.
The brochure has an informative section, which is entitled Natural Gas Pipeline Corridors.
Additionally, I should say, that I lived within a couple of hundred metres of a major gas pipeline in Suffolk, for over twenty years and it was the most unobtrusive of neighbours.
The brochure also says this about hydrogen safety.
As with all of our sites, appropriate measures will be
in place to ensure safe operation. Hydrogen is not
inherently more dangerous than other fuel sources.Hydrogen is flammable and must be handled with care,
just like other flammable fuels. To ignite, hydrogen
must be combined with an additional oxidising agent,
such as air or pure oxygen, in a specific concentration
and with an ignition source (a spark).
It is nearly sixty years ago now, since I worked as an Instrument Engineer, in ICI’s Castner-Kellner works at Runcorn, where hydrogen, chlorine and caustic soda were produced by the electrolysis of brine.
The plant was an unhealthy one, as it used a lot of mercury and my main task, was to design instruments to detect mercury in air and operators’ urine.
The Wikipedia entry for the Castner-Kellner process is a fascinating read and explains why it is being replaced by much better modern mercury-free processes.
I asked Google AI, if the Castner-Kellner process is still used and received this reply.
No, the Castner-Kellner process, a type of mercury cell for producing chlorine and caustic soda, is now largely obsolete due to occupational health and mercury pollution concerns, though a few plants may still operate globally. Modern chlor-alkali processes primarily use safer diaphragm cell and membrane cell technologies to produce chlorine and other chemicals from brine electrolysis.
I suspect that countries, where life is cheap, still use this process, which is very dangerous to those that work on the plant.
INEOS now own ICI in Cheshire and they still produce a large proportion of the hydrogen, chlorine and caustic soda, that the UK needs, but in a much safer way.
The question has to be asked about how hydrogen will be delivered to the Ferrybridge site.
Consider.
- SSE are developing a large hydrogen store at Aldbrough.
- Centrica are developing a large hydrogen store at Brough.
- Both of these stores could be connected to the German AquaVentus system, as the Germans are short of hydrogen storage.
- There is an East Coast Hydrogen Delivery Plan, which could probably have an extension pipeline to the Ferrybridge site.
- The East Coast Hydrogen Delivery Plan, talks of a hydrogen capacity of 4.4 GW.
I don’t feel, that this is the sort of project, that will be delivered until the mid-2030s, at the earliest.
There is also one other important development, that will require hydrogen at Ferrybridge.
I asked Google AI, if there will be hydrogen-powered coaches by 2030 and received this reply.
Yes, there will be hydrogen-powered coaches and buses by 2030, particularly in the UK and EU, with government strategies and funding promoting their deployment, especially for routes requiring high range and quick refueling where battery-electric models may be less suitable. For example, the EU’s CoacHyfied project is developing fuel cell coaches, and the UK government envisions hydrogen playing a role in its transport decarbonization by 2030, with potential to accelerate its zero-emission bus goals.
The nearest you can get to a hydrogen-powered coach in England, is to take an upmarket Wrightbus upmarket hydrogen-powered bus between Sutton station and Gatwick Airport.
- It is mouse quiet and vibration-free.
- It handles the hills with alacrity.
- I wrote about my journey in Sutton Station To Gatwick Airport By Hydrogen-Powered Bus.
That journey convinced me of the superiority in many ways of a hydrogen bus or coach over its diesel cousins.
I believe that this superiority will see large growth in hydrogen-powered long-distance coaches in the next few years.
But I also feel that some specialist transport, like horse transport, will go the hydrogen route.
As there are services at Ferrybridge, where two important motorways cross, I can envisage that the services will need to be able to refuel passing hydrogen buses, coaches trucks and other heavy vehicles, as well as the occasional car.
So would it be possible to supply hydrogen for the motorway services, by the same route as the power station?
I believe that the hydrogen could come from Saltend to the East of Hull, so I gave Google AI the phrase “Saltend zero-carbon hydrogen” and received this reply.
Saltend is home to several initiatives for producing and utilizing zero-carbon hydrogen, most notably the H2H Saltend project by Equinor, which aims to build the world’s largest hydrogen production plant with carbon capture capabilities by 2026 to supply industrial users at the Saltend Chemicals Park. Additionally, a new green hydrogen facility is planned for the park by Meld Energy with a target operation in early 2027, and a separate low-carbon hydrogen plant by ABP, HiiROC, and px Group is also being developed to meet local industrial demand. These projects collectively contribute to the broader Zero Carbon Humber initiative, which seeks to significantly reduce industrial emissions in the region.
Note.
- Saltend will certainly have enough zero-carbon hydrogen for everybody who wants it.
- Delivery dates in a couple of years are being talked about.
- Local industrial demand could be satisfield using specialised trucks, just as ICI used in the 1960s.
- As the Germans want to connect their AquaVentus system to Humberside, any excess hydrogen, could always be sold across the North Sea.
- OpenRailwayMap shows that Saltend is rail-connected.
But how do you get hydrogen between Saltend and Ferrybridge?
I am sure, that hydrogen could be delivered by truck from Saltend to Ferrybridge, but would the locals allow a stream of hydrogen trucks on the roads.
On the other hand, both Saltend and Ferrybridge are both rail-connected, so would it be possible to deliver the hydrogen by rail?
Google AI says this about railway wagons for hydrogen.
Railway wagons for hydrogen transport include liquid hydrogen tank cars (tankers) for transporting cryogenic liquid hydrogen and compressed gas tank cars for carrying hydrogen in its gaseous state or bound within carrier mediums like ammonia or methanol. Hydrogen fuel cell technology is also being developed for use on trains themselves, with a hydrogen fuel cell generator wagon providing power for main-line, non-electrified freight routes.
I believe that it will be possible to develop trains of an appropriate length to shuttle hydrogen between where it is produced and where it is used.
Such a specially-designed shuttle train would be ideal for moving hydrogen between Saltend and Ferrybridge.
- Once at Ferrybridge, the train would be connected to the local hydrogen system feeding the power station, the motorway services and any local businesses that needed hydrogen.
- The trains could be hydrogen fuel cell powered, so they could use any convenient route.
- Like hydrogen powered buses, I suspect they could be mouse quiet.
- The trains would be sized to perhaps deliver a day’s hydrogen at a time.
- There could only be minor changes needed to the rail system.
- If required, the trains could could deliver their cargo in the dead of night.
It could even be based on the contept of the TruckTrain, which I wrote about in The TruckTrain.
There Are Lies, Damned Lies And Trumpkopf’s Medical Statistics
With apologies to Benjamin Disraeli and/or Mark Twain