Three New Battery-Only Revolution Very Light Rail Vehicles
This title of this post, is the same as that as this press release from Eversholt Rail Group.
These are the three bullet points.
- Eversholt Rail funding three brand-new Revolution Very Light Rail vehicles for passenger trials and ongoing operation.
- Manufactured in the UK by Transport Design International.
- Battery-only propulsion, providing zero-emissions operation.
These three paragraphs fill out the story.
Innovative new lightweight passenger trains that will help decarbonise Britain’s railways are to be trialled after a new deal was announced this week.
The new Revolution Very Light Rail vehicles will run entirely on battery power and could be carrying passengers within three years. A new system of lineside fast charging will mean the whole operation has zero emissions.
Some of Britain’s major rail operators are already showing interest in the RVLR vehicles as they seek to fulfil promises to make rail ‘cleaner’.
This is also said about looking for routes, to trial the new vehicles.
Eversholt Rail and TDI are working with key stakeholders across the UK rail industry to agree routes and services where operators can run passenger-carrying trials using these new vehicles. These trials will generate actual passenger demand data to support business cases for long-term deployment of RVLR vehicles as well as providing further passenger and operator feedback on their design and capabilities.
I have some thoughts and questions.
What Is The Top Speed?
A lot of questions like this are answered by this article on Rail Engineer, which is entitled Very Light Rail – A Revolution.
These can be ascertained from this comprehensive article.
- Top Speed – 65 mph
- Seats – 56
- Wheelchair space
- PRM TSI accessibility compatible
- Tare Weight – 24.8 tonnes
- USB Charging
For comparison these figures relate to a PRM-compliant Class 153 diesel train.
- Top Speed – 75 mph
- Seats – 59
- Tare Weight – 41.2 tonnes
This picture shows one of the Class 153 trains at Matlock Bath station.
There are still around thirty in service in the UK.
Can Two Revolution VLRs Run As A Two-Car Train?
From the pictures on the web, the trains have buffers and space for a coupler, so until someone says they must always run as single units, I’ll assume they can at least run as a pair.
Can A Revolution VLR Recharge Its Batteries Using Conventional 25 KVAC Overhead Electrification?
One route, that is a possibility for running using Revolution VLR must surely be the Greenford Branch, which connects to the electrified Great Western Main Line at West Ealing station.
In this and at several other places on the network, it could be easier to charge the trains using the existing overhead electrification or an extension of it.
Another possibility; the Marston Vale Line is also electrified at both Bedford and Bletchley.
In New Mobile Rail Charging Facility For Long Marston, I talked about how Siemens are developing a mobile charger, which initially will be deployed at Long Marston.
It could be very useful for efficient operation, if the batteries on a Revolution VLR could be charged in a number of places, which included conventional electrification.
If charging only happened, whilst trains were stationary, a lightweight pantograph and appropriate electrical gubbins might be sufficient.
Can A Revolution VLR Replace A Class 153 Train?
I suspect on some routes this will be possible, but on others, the speed or hill-climbing requirements might be too stiff for the lightweight train.
But, if I was designing a train like the Revolution VLR, I’d make sure it fitted as many markets as possible.
The picture was taken at Matlock Bath station on the Derwent Valley Line, which is a single track with a fifty mph limit and an uphill climb. I suspect that the Revolution VLR would be designed to handle the uphill part of the route, but would the train be able to handle the speed of the Midland Main Line to Derby.
The Revolution VLR would probably attract more passengers, so it might be necessary to double up the service by running a pair.
Can A Pair Of Revolution VLRs Replace A Class 150 Train?
I don’t see why not!
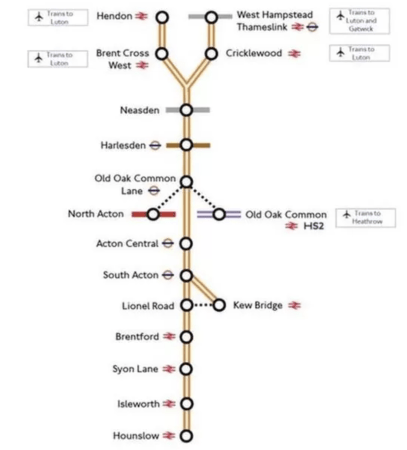
Could The West London Orbital Use Revolution VLRs?
This might be a proposed route that could use Revolution VLRs.
The two routes would be.
- West Hampstead and Hounslow.
- Hendon and Kew Bridge.
Both services would use the Dudding Hill Line and serve Neasden, Harlesden, Old Oak Common and Acton, with a frequency of four trains per hour (tph).
Although this service could be run using conventional multiple units, it might be more affordable to use Revolution VLRs charged on sections of line that are already electrified.
Could the Greenford Branch Use Revolution VLRs?
The Greenford Branch would be a classic application and trains could be charged by fitting a charger in the bay platform at West Ealing station.
In An Automated Shuttle Train On The Greenford Branch Line, I did a rough calculation to see if an automated shuttle could achieve four tph.
Four tph might be too ambitious, but automatic trains shuttling along a branch line might be an affordable way to provide zero-carbon trains with an adequate capacity.
- The driver would drive the train using the sort of remote control used for drones.
- The driver would sit in a convenient place on the train, with CCTV to help them see everything.
- When the train was ready to leave, the driver would push a button to tell the train to move to the next station.
- On arrival at the next station, the doors will open.
- The process would repeat along the line.
If this method of operation sounds vaguely familiar, the Victoria Line has used it since 1067.
Although the Victoria Line drivers always sit in the front.
But on a line with no other trains running at the same time, all they need is a good view of the doors.
Branch lines that could be run in this way could include.
Bodmin Parkway and Bodmin General
Brockenhurst and Lymington Pier
Grove Park and Bromley North
Lancaster and Morecambe
Liskeard and Looe
Lostwithiel and Powey
Maidenhead and Marlow
March and Wisbech
Par and Newquay
Plymouth and Gunnislake
Romford and Upminster
Sittingbourne and Sheerness-on-Sea
Slough and Windsor Central
Southall and Brentford
St. Erth and St. Ives
Truro and Falmouth Docks
Twyford and Henley-on-Thames
Watford Junction and St. Albans Abbey
West Ealing and Greenford
Wickford and Southminster
Wymondham and Dereham
TfL Considers Replacing Over Half Of London Overground Trains Within The Next 4 Years
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on MyLondon.
This is the sub-heading.
The trains were specially built for the dimensions of the Overground network
This paragraph outlines, why the trains may be replaced.
The 57 Class 378 ‘Capitalstar’ trains which provide the majority of services on London Overground could disappear as soon as June 2027, as Transport for London (TfL) officials decide what to do with them as their leases expire. The five carriage walkthrough trains have helped revolutionise the Overground network, being built to special dimensions to fit the unique profile of the suburban routes they run on – notably the East London line, where trains use the narrow single-bore Thames Tunnels.
Note.
- The Class 378 trains, which I use regularly, still seem to be performing well!
- They could do with a lick of paint and a tidying up in places.
- Would it be too much to ask for power sockets and wi-fi?
- The other London Overground trains, the Class 710 trains can’t run through the Thames Tunnel on the East London Line, as they have no means to evacuate passengers in the tunnel in an emergency.
- More Class 378 trains are needed for the East London Line to increase services, but these can be obtained by transferring trains from the North London Line and replacing those with new Class 710 trains.
I live near the two Dalston stations on the London Overground and the thing we need most is more capacity.
I have some thoughts on London Overground’s future trains.
Increased Services On The Current Network
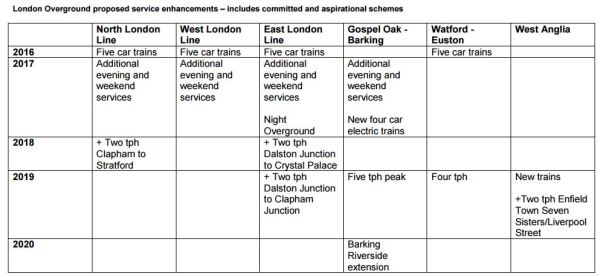
Plans exist to increase the frequency on various London Overground services and this graphic sums up what was planned a few years ago.
Note the extra two trains per hour (tph) between the following stations.
- Clapham Junction and Stratford
- Dalston Junction and Crystal Palace
- Dalston Junction and Clapham Junction
- Enfield Town and Liverpool St. via Seven Sisters
I think only Route 1 services have been increased.
I know signalling updates are holding up the extra trains on the East London Line, but are more trains needed to fully implement the extra services?
- Routes 2 and 3 services will need Class 378 trains because of the tunnel and these would be transferred from the North London Line.
- Route 4 would need Class 710 trains, as the service already uses them.
So there may be a need for more Class 710 trains.
West London Orbital Railway
The graphic doesn’t mention the West London Orbital Railway.
- There would be two routes between West Hampstead and Hounslow and Hendon and Kew Bridge using the Dudding Hill Line.
- The tracks already exist.
- Some new platforms and stations would be needed.
- The route would probably need improved signalling.
- Four tph on both routes would probably be possible.
- The West London Orbital Railway would connect to the Great Western Railway, the North London and Elizabeth Lines and High Speed Two at Old Oak Common station.
I believe it could be run by battery-electric versions of either the Class 378 or Class 710 trains. This would avoid electrification.
As some commentators have suggested that the West London Orbital Railway and the Gospel Oak and Barking Line would be connected, I would expect that new battery-electric Class 710 trains would be used.
Adding On-board Energy Storage To The Class 378 Trains
In Will London Overground Fit On-board Energy Storage To Class 378 Trains?, I asked whether it would be worthwhile.
I finished with these two sentences.
I have no idea how much electricity would be saved by regenerative braking on the London Overground, but various applications of regenerative braking technology talk of electricity savings of between ten and twenty percent.
I think it is only a matter of time before the technology is proven to be sufficiently reliable and the numbers add up correctly for the Class 378 trains to be fitted with on-board energy storage.
What would be the advantages from fitting on-board energy storage?
- There would be the savings of electricity by the use of regenerative braking to the batteries.
- Trains could be rescued from the Thames Tunnel, if there was a power failure.
- Hotel power would be maintained, if there was a power failure.
- Trains can be moved in depots and sidings without power.
- Trains would be able to move in the event of cable theft.
- Short route extensions might be possible.
- Could battery power be used to serve Euston during the rebuilding process for High Speed Two?
- Do Network Rail want to remove third-rail electrification from Euston station for safety or cost reasons?
There could be a saving in train operating costs.
We know the trains are coming up for a new lease.
Suppose the leasing company fitted them with new batteries and some other customer-friendly improvements like new seat covers, better displays, litter bins, power sockets and wi-fi.
- The leasing company would be able to charge more, as they have added value to the trains.
- TfL would be saving money due to less of an electricity bill.
- The passenger numbers might increase due to the extra customer-friendly features.
- Electrification might be removed from places where theft is a problem.
- Third-rail electrification could be removed from Euston station. It’s only 2.8 miles to South Hampstead station, where third-rail electrification already exists.
Get it right and passengers, TfL, Network Rail and the leasing company would all be winners.
Development North Of Kew Bridge Station
This Google Map shows the large site to the North of Kew Bridge station.
Note.
- Kew Bridge station in the South-East corner of the map.
- The M4 passing around the North of the site.
- The triangle of railway lines going to Hounslow in the West, South Acton in the North and Barnes and Waterloo in the East.
Some of the plans for the site have been disclosed.
Brentford’s New Stadium
I took these pictures from a train, as I passed through yesterday.
Brentford Community Stadium is planned to open in Summer 2020.
Step-Free Access At Kew Bridge Station
Currently, Kew Bridge station is not step-free.
Searching the Internet, I found this document on the Hounslow Borough Council web site, which is dated April the 15th 2019 and entitled Step-Free Access To Many Of Hounslow’s Stations Proceeding At Pace!
This is an extract.
Kew Bridge is also set to benefit from accessibility improvements when the new Brentford stadium opens. The London-bound platform is to be made step free and the council is working with SWR and NR to explore how step-free access from the country-bound platform to the street can also be delivered. A feasibility study is due to progress later this year.
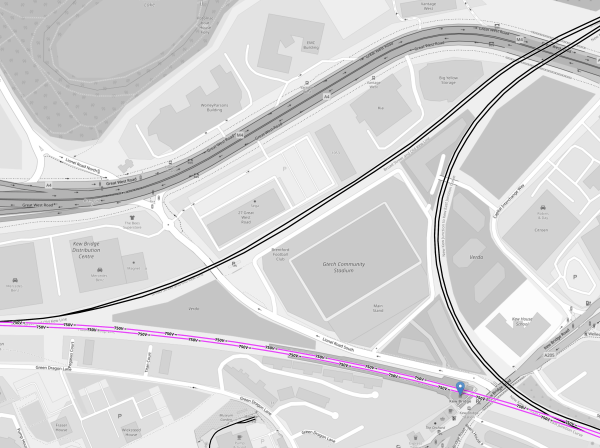
This map from carto.metro.free.fr shows the lines at Kew Bridge station.
The two lines, through the disused platforms at Kew Bridge station could be used as a terminus, by the proposed West London Orbital Railway.
I’m sure Brentford FC wouldn’t object to more trains serving their new ground.
Preparations For The West London Orbital
This picture was taken as I looked through the short tunnel, that connects the current Platform 1 to the disused platform shown on the map of the lines.
It appears that the rubbish and shrubbery of many decades is being cleared.
Could it be in connection with making the London-bound platform step-free?
It would also allow surveyors to assess how much work is needed to get the platform back into use for the West London Orbital Railway.
Development To The South Of The Station
This picture shows a large site behind the station building and the country-bound platform
The location of the site can be seen behind the Express Tavern on this Google Map.
The map also shows how the flats developed on the South side of the tracks have limited the ability to put a second footbridge over the tracks to whisk passengers from London to the stadium.
I wonder, if a route could be built, through the developments, to deliver step-free access to the country-bound platform.
But it would be the wrong side for the stadium!
A step-free bridge is needed at Kew Bridge station.
The Cafe At Kew Bridge Station
Whilst at the station, I had a welcoming coffee.
It’s certainly better than your average chain coffee shop.
I could also wait watching a Departures display.
Kew Bridge Station And The New Brentford Stadium Site
I went to Kew Bridge station to see if anything could be seen of the new Brentford Community Stadium site.
You can’t see much of the stadium, but to my mind you could make the station a lot more attractive.
Look at this Google Map of the station and the Southern part of the stadium site.
Note.
- The stadium is proposed to be on the northern part of the cleared site backing on to the northern side of the triangular junction, of which two of the lines meet at the station.
- The South-Eastern part of the site will be mainly residential.
- The closeness of the London Museum of Water and Steam and the River Thames to the station.
- In Transport for London’s plans for the Gospel Oak to Barking Line, extension to Houslow via the Dudding Hill Line and this junction is a distinct possibility.
- The platforms at Kew Bridge station are very long.
- If trains were ever to be restored to the northern side of the junction, a station begind the stadium could be connected to Kew Bridge station by lineside walkways.
- If trains were ever to be restored to the eastern side of the junction, they could serve Kew Bridge station.
- The Kew Bridge station building is Grade 2 Listed.
I think that even an average architect could make Kew Bridge station, a superb gateway to the stadium and the other developments.