Where’s The Plan, Rishi?
In RWE Goes For An Additional 10 GW Of Offshore Wind In UK Waters In 2030, I detailed how RWE intended to add an extra 10 GW of offshore wind to the seas around the UK.
As our current offshore wind capacity is around 15 GW, another 10 GW would surely be very welcome.
My post also outlined H2ercules, which is Germany’s massive project to create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen to Southern Germany.
I also gave details of the hydrogen hub at Wilhelmshaven, which is being built by Uniper to feed H2ercules with green hydrogen from around the world.
I believe that some of this hydrogen for H2ercules will take a short trip across the North Sea from UK waters, after being created by offshore electrolysers.
Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech – June 11
I also reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
It is now nine days since Rishi made that speech and I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He particularly mentioned.
- New gas-powered stations
- Trebling our offshore wind capacity
- Having new fleets of small modular reactors.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there will be winners all round.
Rishi also said this, in his speech.
As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too.
The gas-powered stations, offshore wind farms and the fleets of small modular reactors, will be part of the equation.
But I believe, we need three other components to complete our energy security.
- The upgrading of the National Grid.
- The building of four x 2 GW interconnectors between Scotland and Eastern England.
- Large amounts of energy storage.
Note.
- The Great Grid Upgrade and the four x 2 GW interconnectors are being planned.
- In Huge Boost To UK Supply Chain As National Grid Launches The Great Grid Partnership With Seven New Industry Partners, All United In The Drive To Deliver The Great Grid Upgrade, I describe how National Grid has setup the Great Grid Partnership to deliver the Great Grid Upgrade.
- In UK Infrastructure Bank, Centrica & Partners Invest £300M in Highview Power Clean Energy Storage Programme To Boost UK’s Energy Security, I describe how the big boys do a deal with Highview Power to create affordable batteries for the UK and the world.
- In Grid Powers Up With One Of Europe’s Biggest Battery Storage Sites, I describe how the very large Swardeston BESS is to be built near Norwich.
- In Mercia Power Response & RheEnergise Working Together To Build Long Duration Energy Storage Projects In The UK, I describe another UK-developed long duration energy storage system, which is now being planned.
- In National Grid Shares Proposals For Green Electricity Projects In Lincolnshire And West Norfolk, Needed To Boost Home-Grown Energy Supplies And Progress Towards Net Zero, I describe National Grid’s projects in the East of England.
- In UK ESO Unveils GBP 58 Billion Grid Investment Plan To Reach 86 GW of Offshore Wind By 2035, I show how we’re not that far away from 86 GW by 2035.
- In 400k For National Grid Innovation Projects As Part Of Ofgem Fund To Help Shape Britain’s Net Zero Transition, I describe how National Grid is using innovation to help target net-zero by 2035.
- In Iberdrola Preparing Two East Anglia Offshore Wind Projects For UK’s Sixth CfD Round, I describe how Iberdrola is getting 1.7 GW ready for commissioning in 2026.
- In National Grid To Accelerate Up To 20GW Of Grid Connections Across Its Transmission And Distribution Networks, I describe how National Grid are accelerating the development of the electricity networks. 10 GW of battery storage is a collateral benefit.
These ten projects, most of which are financed and/or underway, would appear to be good foundations, on which to build the Great Grid Upgrade.
It looks to me, that National Grid, RWE, Centrica, Iberdrola and others, by just doing what comes naturally have offered the next government a road to a future.
It will be interesting, what gets said before the election.
RWE Orders 15 MW Nordseecluster Offshore Wind Turbines At Vestas
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Vestas has now revealed the name of the project and the client for a conditional contract the company signed in May as an unconditional order came in from RWE for the first phase of its 1.6 GW Nordseecluster offshore wind development in Germany.
This is the first paragraph.
The Denmark-based wind turbine OEM has received a firm order for 44 of its V236-15.0 MW offshore wind turbines for the 660 MW Nordseecluster A, the first phase of RWE’s two-phased Nordseecluster project in Germany.
Note.
- The V236-15.0 MW offshore wind turbine would appear to be Vesta’s largest turbine.
- On the Internet RWE’s Norfolk Vanguard West wind farm is shown as using the same turbine.
Does this mean that the Vestas V236-15.0 MW offshore wind turbine, is now RWE’s standard offshore turbine? This would surely have manufacturing, installation, operation and maintenance advantages.
These wind farms in the UK could use the V236-15.0 MW offshore wind turbines.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1380 MW – 92 turbines
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW – 92 turbines
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW – 92 turbines
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW – 200 turbines
- Awel y Môr – Up to 1100 MW – 73 turbines
- Five Estuaries – up to 1185 MW – 79 turbines
- North Falls – up to 504 MW – 34 turbines
Notes.
- The capacity us as sown on the RWE web site for each wind farm.
- The turbine numbers assume 15 MW turbines.
- The total capacity is 9929 MW.
- The number of turbines is 662.
The Nordseecluster will generate 1600 MW from 107 turbines.
Conclusion
I don’t see any reason, why all these wind farms couldn’t use the V236-15.0 MW offshore wind turbines.
The Core Of Sunak’s Manifesto
I have a feeling, that the core of Sunak’s manifesto is a massive German project called H2ercules, which is intended to bring low-carbon hydrogen to industry in South Germany.
There will be a massive hydrogen hub at Wilhelmshaven on the North-Western coast, which is being built by Uniper, from which hydrogen will be imported and distributed.
I suspect that the Germans aim to source the hydrogen worldwide from places like Australia, the Middle East and Namibia. It would be brought from and round the Cape by tanker. The Suez route would be too risky.
But RWE, who are one of the UK’s largest electricity suppliers, are planning to deliver 7.2 GW of electricity in British waters on the Dogger Bank and North-East of Great Yarmouth.
Both wind farms would be difficult to deliver profitably to the UK, because Eastern England already has enough electricity and the Nimbies are objecting to more pylons.
I believe that RWE will build offshore electrolysers and coastal hydrogen tankers will take the hydrogen to Wilhelmshaven.
H2ercules will be fed with the hydrogen needed.
By the end of the next parliament, the Germans could be paying us substantial sums for green hydrogen, to decarbonise their industry.
Rishi Sunak hinted in his speech, that we will be exporting large amounts of energy.
Much of it will be in the form of green hydrogen to Germany.
If we need hydrogen for our industry, we would create it from some of our own wind farms.
RWE Goes For An Additional 10 GW Of Offshore Wind In UK Waters In 2030
This press release from RWE is entitled RWE And Masdar Join Forces To Develop 3 Gigawatts Of Offshore Wind Projects Off The UK Coast.
This is the last paragraph.
The UK plays a key role in RWE’s strategy to grow its offshore wind portfolio RWE is a leading partner in the delivery of the UK’s Net Zero ambitions and energy security, as well as in contributing to the UK build-out target for offshore wind of 50 GW by 2030. RWE already operates 10 offshore wind farms across the UK. Following completion of the acquisition of the three Norfolk offshore wind projects from Vattenfall announced at the end of 2023, RWE is developing nine offshore wind projects in the UK, representing a combined potential installed capacity of around 9.8 GW, with RWE’s pro rata share amounting to 7 GW. Furthermore, RWE is constructing the 1.4 GW Sofia offshore wind project in the North Sea off the UK’s east coast. RWE’s unparalleled track record of more than 20 years in offshore wind has resulted in 19 offshore wind farms in operation, with a goal to triple its global offshore wind capacity from 3.3 GW today to 10 GW in 2030.
Note.
- Nine offshore wind projects in the UK, representing a combined potential installed capacity of around 9.8 GW
- RWE are saying they intend to add 6.7 GW in 2030.
The eight offshore wind farms, that RWE are developing in UK waters would appear to be.
- Sofia – 1,400 MW
- Norfolk Boreas – 1380 MW
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW
- Awel y Môr – 500 MW
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW
- North Falls – 504 MW
This is a total of 9897 MW, which ties in well with RWE’s new capacity figure of 9.8 GW.
The Location Of RWE’s Offshore Wind Farms
RWE’s wind farms seem to fit in groups around the UK.
Dogger Bank
This wind farm is on the Dogger Bank.
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW – Planned
This wind farm would appear to be rather isolated in the middle of the North Sea.
RWE could have plans to extend it or even link it to other wind farms in the German area of the Dogger Bank.
Lincolnshire Coast
This wind farm is along the Lincolnshire Coast.
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW – 2022
As there probably isn’t much heavy industry, where Triton Knoll’s power comes ashore, this wind farm can provide the power needed in the area.
But any excess power in the area can be exported to Denmark through the Viking Link.
Norfolk Coast
These wind farms are along the Norfolk Coast.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1380 MW – Planned
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW – Planned
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW – Planned
These three wind farms will provide enough energy to provide the power for North-East Norfolk.
North Wales Coast
These wind farms are along the North Wales Coast.
- Awel y Môr – 500 MW – Planned
- Gwynt y Môr – 576 MW – 2015
- Rhyl Flats – 90 MW – 2009
- North Hoyle – 60 MW – 2003
These wind farms will provide enough energy for the North Wales Coast.
Any spare electricity can be stored in the 1.8 GW/9.1 GWh Dinorwig pumped storage hydroelectric power station.
Electric Mountain may have opened in 1984, but it is surely a Welsh giant decades ahead of its time.
Suffolk Coast
These wind farms are along the Suffolk Coast.
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW – Planned
- Galloper – 353 MW – 2018
- North Falls – 504 MW – Planned
These wind farms will provide enough energy for the Suffolk Coast, which except for the Haven Ports, probably doesn’t have many large electricity users.
But if the area is short of electricity, there will be Sizewell B nuclear power station to provide it.
Teesside
This wind farm is along the Teesside Coast
- Sofia – 1,400 MW – Planned
Teesside is a heavy user of electricity.
These six areas total as follows.
- Dogger Bank – 3,000 MW
- Lincolnshire Coast – 857 MW
- Norfolk Coast – 4140 MW
- North Wales Coast – 1226 MW
- Suffolk Coast – 1210 MW
- Teesside – 1,400 MW
Backup for these large clusters of wind farms for when the wind doesn’t blow will be provided as follows.
- Dogger Bank – Not provided
- Lincolnshire Coast- Interconnectors to Denmark and Scotland
- Norfolk Coast – Not provided
- North Wales Coast – Stored in Dinorwig pumped storage hydroelectric power station
- Suffolk Coast – Sizewell B and Sizewell C
- Teesside – Interconnectors to Norway and Scotland and Hartlepool nuclear power stations
Note.
- The interconnectors will typically have a 2 GW capacity.
- The 1.9 GW/9.1 GWh Dinorwig pumped storage hydroelectric power station must be one of the best wind farm backups in Europe.
There is a very solid level of integrated and connected assets that should provide a reliable power supply for millions of electricity users.
How Will Dogger Bank And The Norfolk Coast Wind Clusters Work Efficiently?
The Dogger Bank and the Norfolk Coast clusters will generate up to 3 and 4.14 GW respectively.
So what purpose is large amounts of electricity in the middle of the North Sea?
The only possible purpose will be to use giant offshore electrolysers to create hydrogen.
The hydrogen will then be transported to point of use by pipeline or tanker.
Feeding H2ercules
I described H2ercules in H2ercules.
H2ercules is an enormous project that will create the German hydrogen network.
The H2ercules web site, shows a very extensive project, as is shown by this map.
Note.
- Hydrogen appears to be sourced from Belgium, the Czech Republic, The Netherlands and Norway.
- RWE’s Dogger Bank South wind farm will be conveniently by the N of Norway.
- RWE’s Norfolk cluster of wind farms will be conveniently by the N of Netherlands.
- The Netherlands arrow points to the red circles of two hydrogen import terminals.
For Germany to regain its former industrial success, H2ercules will be needed to be fed with vast amounts of hydrogen.
And that hydrogen could be in large amounts from the UK sector of the North Sea.
Uniper’s Wilhelmshaven Hydrogen Hub
This page on the Uniper web site is entitled Green Wilhelmshaven: To New Horizons
This Uniper graphic shows a summary of gas and electricity flows in the Wilhelmshaven Hydrogen Hub.
Note.
- Ammonia can be imported, distributed by rail or ships, stored or cracked to provide hydrogen.
- Wilhelmshaven can handle the largest ships.
- Offshore wind energy can generate hydrogen by electrolysis.
- Hydrogen can be stored in underground salt caverns.
I suspect hydrogen could also be piped in from an electrolyser in the East of England or shipped in by a hydrogen tanker.
All of this is well-understood technology.
Sunak’s Magic Money Tree
Rishi Sunak promised a large giveaway of tax in his manifesto for the 2024 General Election.
As we are the only nation, who can provide the colossal amounts of hydrogen the Germans will need for H2ercules, I am sure we will be well paid for it.
A few days ago we celebrated D-Day, where along with the Americans and the Canadians, we invaded Europe.
Now eighty years later, our hydrogen is poised to invade Europe again, but this time for everybody’s benefit.
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
I believe that could be Rishi’s Magic Money Tree.
Especially, if the energy is exported through electricity interconnectors or hydrogen or ammonia pipelines and tankers.
Will This Be A Party Anyone Can Join?
Other wind farm clusters convenient for the H2ercules hydrogen import terminals on the North-West German coast include.
- Dogger Bank – SSE, Equinor – 5008 MW
- East Anglian – Iberdrola – 3786 MW
- Hornsea – Ørsted – 8056 MW
That totals to around 16.5 GW of wind power.
I can see offshore electrolysers producing hydrogen all around the coasts of the British Isles.
What Happens If Sunak Doesn’t Win The Election?
RWE and others have signed contracts to develop large wind farms around our shores.
They didn’t do that out of the goodness of their hearts, but to make money for themselves and their backers and shareholders.
Conclusion
I believe a virtuous circle will develop.
- Electricity will be generated in the UK.
- Some will be converted to hydrogen.
- Hydrogen and electricity will be exported to the highest bidders.
- European industry will, be powered by British electricity and hydrogen.
- Money will be paid to the UK and the energy suppliers for the energy.
The more energy we produce, the more we can export.
In the future more interconnectors, wind farms and electrolysers will be developed.
Everybody will benefit.
As the flows grow, this will certainly become a Magic Money Tree, for whoever wins the election.
H2ercules
H2ercules is a project that will create the German hydrogen network.
The H2ercules web site, introduces the project with these two paragraphs.
A faster ramp-up of the hydrogen economy in Germany is more important than ever in order to drive forward the decarbonisation programme, put the German energy system on a more robust footing, and thus contribute towards a green security of supply. What this needs is a geographical realignment of the infrastructure for energy in gas form: Instead of flowing from the east of Germany to the west and south of the country, the gas – natural gas now, hydrogen in the future – will have to make its way in future from generation locations in the north-west to centres of consumption located mainly in the west and south. That also means that new sources will have to be connected, and gaps in existing pipeline networks will have to be closed. To speed up this vital process, OGE and RWE have developed the national infrastructure project “H2ercules”, which is intended to supply consumers in Germany’s south and west with domestically produced green hydrogen from the north of the country, in addition to imported sources. This will involve connecting up the electrolyser capacities that are currently being planned and developing more besides. RWE wants to create up to 1 GW of additional electrolyser capacity as part of the H2ercules project. For the connection component, OGE is planning to put 1,500 km of pipelines in place. For the most part, this will mean converting pipelines from the existing natural gas network to hydrogen, supplemented by newly constructed facilities. Converting natural gas pipelines is not only the more cost-efficient solution, but it also allows for a faster schedule. The system is expected to be supplemented by the planned hydrogen storages of RWE.
The current plan is to complete the project in three stages between 2026 and 2030, in order to connect industries to the hydrogen supply as soon as possible. The aim of this collaboration across multiple value levels is to resolve the chicken-and-egg problem on a super-sized scale and also smooth the way forward for other projects.
Note.
There will be a lot of conversion of the existing natural gas network to hydrogen.
RWE wants to create up to 1 GW of additional electrolyser capacity as part of the H2ercules project.
The second paragraph indicates to me, that they want to move fast.
This map from the H2ercules web site, indicate the proposed size of the network in 2030.
These three paragraphs describe how H2ercules will be developed.
OGE and RWE are both strong companies that aim to combine forces as part of the H2ercules project in order to overcome this Herculean task. While the task for OGE will be to convert the required gas pipelines to hydrogen and construct new pipelines, RWE will expand its electrolyser capacity and import green hydrogen in addition. Gas-fired power stations with a capacity of at least 2 GW will be converted to hydrogen, and new H2 -storages as well as H2-storages repurposed from gas storages on the Dutch border will be connected to the hydrogen supply system.
H2ercules also opens up new opportunities to connect Germany’s future centres of hydrogen consumption to key import routes, first via pipelines from Belgium and the Netherlands, and later via Norway and also from southern and eastern Europe, with the added prospects of import terminals for green molecules in Germany’s north. The project is thus contributing significantly to the creation of a European hydrogen market.
The first additional companies and organisations have already indicated their interest in this project, and it is expected that in the future smaller businesses will benefit in addition to large-scale customers, as the entire industry is guided towards a decarbonised future.
These are my thoughts.
Why Is It Called H2ercules?
I suspect, it’s nothing more, than the Germans wanted a recognisable and catchy name.
- Name selection is not helped by the German for hydrogen, which is wasserstoff.
- Hercules is Herkules in German, which doesn’t really help.
- Projekt Wasserstoff isn’t as memorable as H2ercules, which at least isn’t English.
It looks to me, that the Germans have come up with a good acceptable compromise.
The Wilhemshaven Hydrogen Import Terminal
German energy company; Uniper is building a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhemshaven to feed H2ercules and German industry with hydrogen from places like Australia, Namibia and the Middle East. I wrote about this hydrogen import terminal in Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal.
Wilhelmshaven and Great Yarmouth are 272 miles or 438 kilometres apart, so a pipeline or a tanker link would be feasible to export hydrogen from Notfolk to Germany.
I suspect RWE will build a giant offshore electrolyser close to the Norfolk wind farms and the hydrogen will be exported by tanker or pipeline to Germany or to anybody else who pays the right price.
RWE’s Norfolk Wind Farms
What is interesting me, is what Germany company; RWE is up to. Note they are one of the largest UK electricity producers.
In December 2023, they probably paid a low price, for the rights for 3 x 1.4 GW wind farms about 50 km off North-East Norfolk from in-trouble Swedish company; Vattenfall and have signed contracts to build them fairly fast.
In March 2024, I wrote about the purchase in RWE And Vattenfall Complete Multi-Gigawatt Offshore Wind Transaction In UK.
This map from RWE shows the three wind farms, with respect to the Norfolk coast.
Could it be, that RWE intend to build a giant offshore electrolyser to the East of Great Yarmouth?
- The planning permission for an electrolyser, which is eighty kilometres offshore, would be far easier, than for one onshore.
- The hydrogen pipeline between Norfolk and Germany would be less than 400 kilometres.
- Hydrogen could also be brought ashore in Norfolk, if the price was right.
- The Bacton gas terminal is only a few miles North of Great Yarmouth.
But the big advantage, is that the only onshore construction could be restricted to the Bacton gas terminal.
Adding More Wind Farms To The Electrolyser
Looking at the RWE map, the following should be noted.
South of Norfolk Vanguard East, there is the East Anglian Array wind farm, which by the end of 2026, will consist of these wind farms.
- East Anglia One – 714 MW – 2020
- East Anglia One North – 800 MW – 2026
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW – 2026
- East Anglia Three – 1372 MW – 2026
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- There is a total capacity of 3786 MW
- All wind farms are owned by Iberdrola.
- There may be space to add other sections to the East Anglian Array.
I doubt, it would be difficult for some of Iberdrola’s megawatts to be used to generate hydrogen for Germany.
To the East of Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard East, it’s Dutch waters, so I doubt the Norfolk cluster can expand to the East.
But looking at this map of wind farms, I suspect that around 4-5 GW of new wind farms could be squeezed in to the North-West of the the Norfolk Cluster and South of the Hornsea wind farms.
The 1.5 GW Outer Dowsing wind farm, which is being planned, will be in this area.
I can certainly see 8-10 GW of green electricity capacity being available to electrolysers to the North-East of Great Yarmouth.
Conclusion
UK offshore electricity could be the power behind H2ercules.
- The hydrogen could be sent to Germany by pipeline or tanker ship, as the distance is under 400 kilometers to the Wilhelmshaven hydrogen hub.
- Extra electrolysers and wind farms could be added as needed.
- The hydrogen won’t need to be shipped halfway round the world.
The cash flow won’t hurt the UK.
.
Do RWE Have A Comprehensive Hydrogen Plan For Germany?
What is interesting me, is what Germany company; RWE is up to. They are one of the largest UK electricity producers.
In December 2023, they probably paid a low price, for the rights for 3 x 1.4 GW wind farms about 50 km off North-East Norfolk from in-trouble Swedish company; Vattenfall and have signed contracts to build them fairly fast.
In March 2024, wrote about the purchase in RWE And Vattenfall Complete Multi-Gigawatt Offshore Wind Transaction In UK.
Over the last couple of years, I have written several posts about these three wind farms.
March 2023 – Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base
November 2023 – Aker Solutions Gets Vattenfall Nod To Start Norfolk Vanguard West Offshore Platform
December 2023 – SeAH To Deliver Monopiles For Vattenfall’s 2.8 GW Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Project
Then in July 2023, I wrote Vattenfall Stops Developing Major Wind Farm Offshore UK, Will Review Entire 4.2 GW Zone
Note.
- There does appear to be a bit of a mix-up at Vattenfall, judging by the dates of the reports.Only, one wind farm has a Contract for Difference.
- It is expected that the other two will be awarded contracts in Round 6, which should be by Summer 2024.
In December 2023, I then wrote RWE Acquires 4.2-Gigawatt UK Offshore Wind Development Portfolio From Vattenfall.
It appears that RWE paid £963 million for the three wind farms.
I suspect too, they paid for all the work Vattenfall had done.
This transaction will give RWE 4.2 GW of electricity in an area with very bad connections to the National Grid and the Norfolk Nimbies will fight the building of more pylons.
So have the Germans bought a pup?
I don’t think so!
Where Is Wilhemshaven?
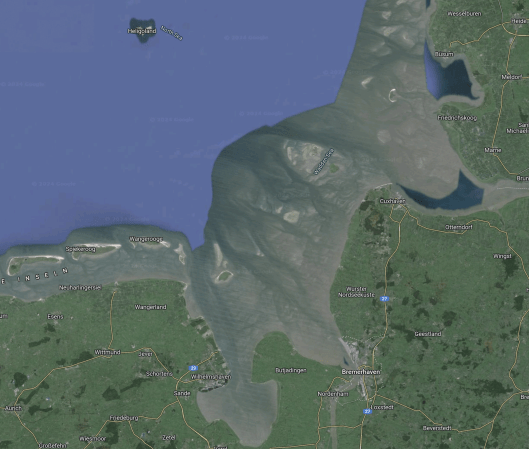
This Google Map shows the location of Wilhemshaven.
Note.
- Heligoland is the island at the top of the map.
- The Germans call this area the Wdden Sea.
- The estuaries lead to Wilhelmshaven and Bremerhaven.
- Cuxhaven is the port for Heligoland, which is connected to Hamburg by hydrogen trains.
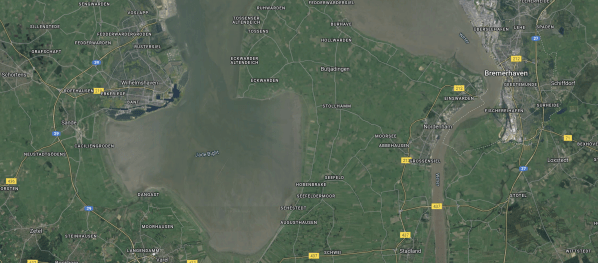
This second map shows between Bremerhaven and Wilhelmshaven.
Note.
- Wilhelmshaven is to the West.
- Bremerhaven is in the East.
- The River Weser runs North-South past Bremerhaven.
I’ve explored the area by both car and train and it is certainly worth a visit.
The Wilhemshaven Hydrogen Import Terminal
German energy company; Uniper is building a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhemshaven to feed German industry with hydrogen from places like Australia, Namibia and the Middle East. I wrote about this hydrogen import terminal in Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal.
I suspect RWE could build a giant offshore electrolyser close to the Norfolk wind farms and the hydrogen will be exported by tanker or pipeline to Germany or to anybody else who pays the right price.
All this infrastructure will be installed and serviced from Great Yarmouth, so we’re not out of the deal.
Dogger Bank South Wind Farm
To make matters better, RWE have also signed to develop the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm.
This could have another giant electrolyser to feed German companies. The wind farm will not need an electricity connection to the shore.
The Germans appear to be taking the hydrogen route to bringing electricity ashore.
Energy Security
Surely, a short trip across the North Sea, rather than a long trip from Australia will be much more secure and on my many trips between the Haven Ports and The Netherlands, I haven’t yet seen any armed Houthi pirates.
RWE And Hydrogen
On this page on their web site, RWE has a lot on hydrogen.
Very Interesting!
H2ercules
This web site describes H2ercules.
The goal of the H2ercules initiative is to create the heart of a super-sized hydrogen infrastructure for Germany by 2030. To make this happen, RWE, OGE and, prospectively, other partners are working across various steps of the value chain to enable a swift supply of hydrogen from the north of Germany to consumers in the southern and western areas of the country. In addition to producing hydrogen at a gigawatt scale, the plan is also to open up import routes for green hydrogen. The transport process will involve a pipeline network of about 1,500 km, most of which will consist of converted gas pipelines.
Where’s the UK’s H2ercules?
Conclusion
The Germans have got there first and will be buying up all of our hydrogen to feed H2ercules.
TetraSpar Demonstrator Floating Wind Turbine Hits 63 Pct Capacity Factor In Norway
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Stiesdal has revealed that its TetraSpar Demonstrator, located in Norway, has reached a capacity factor of 63 per cent.
These three paragraphs give a few more details.
Since its commissioning in late 2021, the TetraSpar Demonstrator has been operational at METCentre in Norway, delivering green energy, gathering data, validating numerical models, supporting research and development projects, and serving as a living laboratory for the development of floating wind technology, said Stiesdal in a recent social media post.
To date, the demonstrator has generated more than 37 GWh of renewable energy, according to the company. The 3.6 MW Siemens Gamesa direct-drive wind turbine and very high wind speeds at the METCentre site combined to yield a capacity factor of 54 per cent, said Stiesdal.
In the first two years of operation, the availability was recorded at 97 per cent and 98.3 per cent, respectively. For 2024, the availability has increased to 99.5 per cent with a capacity factor of almost 63 per cent, according to the company.
I have some further thoughts.
Tetra Offshore Foundations For Any Water Depth
The title of this section, is the same as that of this page on the Siesdal web site.
The page gives a lot of information and says that the TetraSpar can handle water depth of over a thousand metres.
Wind Farm Capacity Factor
The Wikipedia entry for capacity factor says this about the range of wind farm capacity factors.
Wind farms are variable, due to the natural variability of the wind. For a wind farm, the capacity factor is determined by the availability of wind, the swept area of the turbine and the size of the generator. Transmission line capacity and electricity demand also affect the capacity factor. Typical capacity factors of current wind farms are between 25 and 45%. In the United Kingdom during the five year period from 2011 to 2019 the annual capacity factor for wind was over 30%.
From that paragraph, 63 % seems to be extraordinarily good.
Conclusion
The TetraSpar appears to be a powerful concept.
RWE And the Norfolk Wind Farms
In March 2024, I wrote RWE And Vattenfall Complete Multi-Gigawatt Offshore Wind Transaction In UK, which described how Vattenfall had sold 4.2 GW of offshore wind farms, situated off North-East Norfolk to RWE.
This map from RWE shows the wind farms.
Note.
- The Norfolk Zone consists of three wind farms; Norfolk Vanguard West, Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard East.
- The three wind farms are 1.4 GW fixed-foundation wind farms.
- In Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base, I describe how the Port of Great Yarmouth had been selected as the O & M base.
- Great Yarmouth and nearby Lowestoft are both ports, with a long history of supporting shipbuilding and offshore engineering.
The wind farms and the operational port are all close together, which probably makes things convenient.
So why did Vattenfall sell the development rights of the three wind farms to RWE?
Too Much Wind?
East Anglia is fringed with wind farms all the way between the Wash and the Thames Estuary.
- Lincs – 270 MW
- Lynn and Inner Dowsing – 194 MW
- Race Bank – 580 MW
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW
- Sheringham Shoal – 317 MW
- Dudgeon – 402 MW
- Hornsea 3 – 2852 MW *
- Scroby Sands – 60 MW
- East Anglia One North – 800 MW *
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW *
- East Anglia Three – 1372 MW *
- Greater Gabbard – 504 MW
- Galloper – 353 MW
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW *
- North Falls – 504 MW *
- Gunfleet Sands – 172 MW
- London Array – 630 MW
Note.
- Wind farms marked with an * are under development or under construction.
- There is 4339 MW of operational wind farms between the Wash and the Thames Estuary.
- An extra 6781 MW is also under development.
If all goes well, East Anglia will have over 11 GW of operational wind farms or over 15 GW, if the three Norfolk wind farms are built.
East Anglia is noted more for its agriculture and not for its heavy industries consuming large amounts of electricity, so did Vattenfall decide, that there would be difficulties selling the electricity?
East Anglia’s Nimbies
East Anglia’s Nimbies seem to have started a campaign against new overground cables and all these new wind farms will need a large capacity increase between the main substations of the National Grid and the coast.
So did the extra costs of burying the cable make Vattenfall think twice about developing these wind farms?
East Anglia and Kent’s Interconnectors
East Anglia and Kent already has several interconnectors to Europe
- Viking Link – Bicker Fen and Jutland – 1.4 GW
- LionLink – Suffolk and the Netherlands – 1.8 GW – In Planning
- Nautilus – Suffolk or Isle of Grain and Belgium – 1.4 GW – In Planning
- BritNed – Isle of Grain and Maasvlakte – 1.0 GW
- NeuConnect – Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven – 1.4 GW – Under Construction
- GridLink Interconnector – Kingsnorth and Warande – 1.4 GW – Proposed
- HVDC Cross-Channel – Sellinge and Bonningues-lès-Calais – 2.0 GW
- ElecLink – Folkestone and Peuplingues – 1.0 GW
- Nemo Link – Richborough and Zeebrugge – 1.0 GW
Note.
- Five interconnectors with a capacity of 6.4 GW.
- A further four interconnectors with a capacity of 6 GW are on their way.
At 12.4 GW, the future capacity of the interconnectors between South-East England and Europe, is nor far short of South-East English wind power.
There are also two gas pipelines from the Bacton gas terminal between Cromer and Great Yarmouth to Europe.
The Wikipedia entry for the Bacton gas terminal gives these descriptions of the two gas pipelines.
Interconnector UK – This can import gas from, or export gas to, Zeebrugge, Belgium via a 235 km pipeline operating at up to 147 bar. There is a 30-inch direct access line from the SEAL pipeline. The Interconnector was commissioned in 1998.
BBL (Bacton–Balgzand line) – This receives gas from the compressor station in Anna Paulowna in the Netherlands. The BBL Pipeline is 235 km long and was commissioned in December 2006.
It would appear that East Anglia and Kent are well connected to the Benelux countries, with both electricity and gas links, but with the exception of the Viking Link, there is no connection to the Scandinavian countries.
Did this lack of connection to Sweden make convincing the Swedish government, reluctant to support Vattenfall in their plans?
Bringing The Energy From The Norfolk Wind Farms To Market
It looks to me, that distributing up to 4.2 GW from the Norfolk wind farms will not be a simple exercise.
- Other wind farms like the 2852 MW Hornsea 3 wind farm, may need a grid connection on the North Norfolk coast.
- The Nimbies will not like a South-Western route to the National Grid at the West of Norwich.
- An interconnector to Denmark or Germany from North Norfolk would probably help.
But at least there are two gas pipelines to Belgium and the Netherlands.
RWE, who now own the rights to the Norfolk wind farms, have a large amount of interests in the UK.
- RWE are the largest power producer in the UK.
- They supply 15 % of UK electricity.
- They have interest in twelve offshore wind farms in the UK. When fully-developed, they will have a capacity of almost 12 GW.
- RWE are developing the Pembroke Net Zero Centre, which includes a hydrogen electrolyser.
RWE expects to invest up to £15 billion in the UK by 2030 in new and existing green technologies and infrastructure as part of this.
Could this be RWE’s plan?
As the Norfolk wind farms are badly placed to provide electricity to the UK grid could RWE have decided to use the three Norfolk wind farms to produce hydrogen instead.
- The electrolyser could be placed onshore or offshore.
- If placed onshore, it could be placed near to the Bacton gas terminal.
- There are even depleted gas fields, where hydrogen could be stored.
How will the hydrogen be distributed and/or used?
It could be delivered by tanker ship or tanker truck to anyone who needs it.
In Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network, I describe how a rural hydrogen network could be developed, that decarbonises the countryside.
There are three major gas pipelines leading away from the Bacton gas terminal.
- The connection to the UK gas network.
- Interconnector UK to Belgium.
- BBL to The Netherlands.
These pipelines could be used to distribute hydrogen as a hydrogen blend with natural gas.
In UK – Hydrogen To Be Added To Britain’s Gas Supply By 2025, I describe the effects of adding hydrogen to the UK’s natural gas network.
RWE And Vattenfall Complete Multi-Gigawatt Offshore Wind Transaction In UK
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
RWE and Vattenfall have completed the sale of three offshore wind projects in the UK. With the transaction completed, RWE has expanded its offshore wind portfolio in the UK by 4.2 GW.
There is also this RWE infographic, which shows the three wind farms in relation to the East Anglian coast.
RWE are getting to be a big player in UK offshore wind, with these wind farm in operation or planned.
- Galloper – 353 MW – Operation
- Gwynt y Môr – 576 MW – Operation
- Rhyll Flats – 90 MW – Operation
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW – Operation
- Sofia – 1400 MW – Under Construction – Completion in 2026
- Norfolk Boreas – 1380 MW – Planned – Completion in 2027
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW – Planned – Completion before 2030
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW – Planned – Completion before 2030
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW – Planned
- Awel y Môr – 500 MW – Planned
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW – Planned
- North Falls – 504 MW – Planned
That is a total of 11,773 MW, of which 10,607 MW is on the German side of the UK.
With RWE likely to have some success in auctions this year, these figures, are likely to increase and some wind farms will start construction.
How Germany Is Dominating Hydrogen Market
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Hydrogen Fuel News.
This is the sub heading.
With 3827 kilometers of pipeline across the country, Germany is blazing a trail through the continent in terms of hydrogen infrastructure growth.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Indeed, plans within the country are so far advanced that Germany is set to become the biggest importer of hydrogen in Europe and the third biggest in the world, behind global leaders China and Japan.
All this leaves the German transport sector in good stead, with a strong infrastructure supporting clean fuel adoption, while the country transitions towards net zero.
So where are the Germans going to get their hydrogen from?
One possibility is the UK.
- The UK has vast amounts of renewable energy.
- We’re only hundreds of kilometres, instead of thousands of kilometres away.
- RWE; the German energy giant has full or partial interests in about 12,3 GW of UK wind farms.
- RWE is building the Pembroke Net Zero Centre which will generate green and blue hydrogen.
Hydrogen could be exported from the UK to Germany by tanker.
Conclusion
Production and exporting of green hydrogen will become significant industry in the UK.