Haventus Chosen To Accelerate Opportunities For Floating Offshore Wind In Scotland
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Cerulean Winds.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- The under-construction Ardersier Energy Transition Facility owned by Haventus, is selected by Cerulean, the floating wind company with 3GW under development in the Central North Sea
- Announcement marks major boost to future of offshore floating wind in Scotland, as UK floating offshore wind supply chain takes shape
- Cerulean Winds to leverage its unique experience in floating infrastructure from oil and gas sector, in particular, Alliance Contracting
These four paragraphs add detail to the post.
Haventus, owner of the under-construction Ardersier Energy Transition Facility, located near Inverness, Scotland, has been selected by Cerulean Winds, the lead developer of 3GW+ UK floating offshore wind, as its chosen deployment port.
Ardersier Energy Transition Facility, which has secured £400 million of funding, including a £100 million credit facility from the UK National Wealth Fund & Scottish National Investment Bank, will be Scotland’s largest offshore wind facility on the North Sea coast. Cerulean’s commitment to using the facility marks a major step toward realising the UK and Scottish governments’ vision of creating a world-leading floating offshore wind (FLOW) industrial base.
By 2050, FLOW could contribute more than £47 billion to the UK economy and employ 100,000 people. Ardersier will support achieving these targets by deploying and servicing offshore wind installations, providing green jobs and establishing a UK supply chain to rival international competitors.
The Cerulean alliance’s first project will be the Aspen development, a 1 GW wind farm in the Central North Sea approximately 100km from shore, that is targeting first power between 2028-29. The project is designed to enable Scotland’s supply chain and direct more than £1 billion of investment in FLOW manufacturing and service support in the country, with the Ardersier Energy Transition Facility acting as a strategic hub. This early investment will help establish the industrial foundation needed to maximise domestic economic benefits from ScotWind’s planned buildout from 2030.
The numbers are huge and hopefully the initial returns will provide the capital to develop the later wind farms.
In some ways, I’m disappointed, as this is the sort of project, I’d love to be writing the software for.
I also these days have no family responsibilities and only need to look after myself.
Highland Council Greenlights West Of Orkney Windfarm Onshore Plans
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The Highland Council has approved the onshore plans of the 2 GW West of Orkney Windfarm project, being developed by TotalEnergies, Corio Generation, and Renewable Infrastructure Development Group (RIDG) in Scotland.
These are the first three paragraphs.
The onshore application for planning permission in principle was approved on 4 June and outlines the underground cables and electrical infrastructure required to connect the offshore wind farm to the national transmission network.
Last year, the project became the first ScotWind proposal to submit both its offshore consent application to Scottish Ministers and its onshore planning application to The Highland Council.
The onshore application provides information on proposed cable landfalls on the north Caithness coast, the project’s substation at Spittal in Caithness, and the underground cables which will extend around 25 kilometres and connect to the substation.
According to the project page of the West of Orkney wind farm web site, the target for commissioning of the wind farm is 2029.
This wind farm appears to be making a play to be the first of the ScotWind Leasing developments to be commissioned.
I have some thoughts.
Converting The Flotta Oil Terminal To The Flotta Hydrogen Hub
This first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Flotta Oil Terminal, describes it like this.
The Flotta oil terminal is a major crude oil reception, processing, storage and export facility on the island of Flotta, in the south of Scapa Flow in the Orkney Islands. It receives and processes crude oil delivered by a subsea pipeline from the Piper, Claymore, Tartan and Golden Eagle platforms and associated fields. The terminal includes facilities for exporting stabilised crude oil (and formerly liquefied petroleum gases) by tanker.
It is now proposed to add the Flotta Hydrogen Hub to the Flotta Oil Terminal.
This document on the Repsol web site, describes the Flotta Oil Terminal.
- This page is the Flotta Hydrogen Hub web site.
- This page discusses, what will be done with the green hydrogen produced by electrolysis.
- The green hydrogen page, has an excellent map of the hydrogen and electricity flows to and from the Flotta Hydrogen Hub.
The Flotta Oil Terminal will be developed into a major hydrogen production and distribution facility.
Ørsted, Simply Blue, Subsea7 Submit Application For 100 MW Scottish Floating Wind Farm
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Ørsted, Simply Blue Group and Subsea7, through their joint venture partnership in Scotland, have submitted an offshore consent application for the proposed 100 MW Salamander floating offshore wind farm, one of the 13 projects selected in Scotland’s Innovation and Targeted Oil and Gas (INTOG) leasing round.
The article starts with a map that shows the location of the Salamander floating offshore wind farm and it shows how the sea is getting very crowded 35 kilometres off Peterhead.
This map shows the various ScotWind leases, around the North of Scotland.
The numbers are Scotwind’s lease number in their documents.
These are the Scotwind wind farms to the North-East of Scotland.
- 1 – BP Alternative Energy Investments – 859 km² – 2.9 GW – Fixed
- 2 – SSE Renewables – 859 km² – 2.6 GW – Floating
- 3 – Falck Renewables Wind – 280 km² – 1.2 GW – Floating
- 4 – Shell – 860 km² – 2.0 GW – Floating
- 5 – Vattenfall – 200 km² – 0.8 GW – Floating
- 6 – DEME – 187 km² – 1.0 GW – Fixed
- 9 – Ocean Winds – 429 km² – 1.0 GW – Fixed
- 10 – Falck Renewables Wind – 134 km² – 0.5 GW – Floating
- 11 – Scottish Power Renewables – 684 km² – 3.0 GW – Floating
- 12 – BayWa r.e. UK – 330 km² – 1.0 GW – Floating
Note.
- Salamander is located to the South of wind farms 10, 11 and 12 and to the North-West of wind farm 5.
- These windfarms total up to 16 GW.
- 4.9 GW are fixed foundation wind farms.
- 11.1 GW are floating wind farms.
These are my thoughts.
The Salamander Project
In the big scheme of things, the 100 MW Salamander wind farm, is rather a tiddler of a wind farm.
On the Salamander wind farm web site, a section gives the Project Goals.
- Our innovative pre-commercial stepping-stone concept will use novel floating foundations to (i) maximise Scottish content, (ii) enable the Scottish supply chain to gear up for the future floating offshore wind commercial opportunities in ScotWind and (iii) reduce the financial, environmental and technology risks of floating offshore wind.
- The Salamander project will contribute to the Scottish Government and UK Government net-zero targets. The project can contribute to the Scottish government’s target of 11 GW of installed offshore wind by 2030, as well as the UK government’s target of 5 GW of operational floating offshore wind by the same date.
- We are dedicated to developing a sustainable and transformative project, working with the oceans, and enabling communities to benefit from Project Salamander. Therefore, we commit to having a continuous and strong stakeholder and community engagement.
It appears to me, that the Salamander project will be a pathfinder for the 11.1 GW of floating wind farms to be built off Peterhead.
Bringing The Electricity South
National Grid are building four interconnectors between Eastern Scotland and Eastern England.
- Eastern Green Link 1 – Torness and Hawthorn Pit
- Eastern Green Link 2 – Peterhead and Drax
- Eastern Green Link 3 – Westfield and Lincolnshire
- Eastern Green Link 4 – Peterhead and Lincolnshire
Note.
- All interconnectors are 2 GW.
- All interconnectors are offshore for a long part of their route.
- It also appears that National Grid are burying much of the onshore sections.
But the 4 GW of interconnectors will only be able to bring a quarter of the offshore electricity generated in the Peterhead area to the South.
What Will Happen To The Excess Electricity?
Consider.
- There could be 16 GW of planned offshore wind power around Peterhead and North-East Scotland.
- There is only 4 GW of interconnector capacity between Peterhead and Eastern England.
- There is another 6.8 GW of electricity around North-West Scotland.
- There is 2.8 GW of electricity being developed to the East of Shetland.
- The Crown Estate is thinking of increasing the size of some offshore wind farms.
It is likely, that other wind farms will be built in the seas around the North of Scotland.
It appears that the North of Scotland could have at least 20 GW of excess electricity.
Possible solutions would include.
- Developing energy intensive industries like metal refining.
- More interconnectors to Denmark, England, Ireland and Norway.
- Storage of the electricity in giant pumped storage hydroelectric power stations.
- Creation of green hydrogen for export.
Note.
- Aluminium refining has been developed in the North of Scotland before.
- More interconnectors are a possibility, especially as Scotland is developing cable manufacturing capacity.
- Some maps show extra interconnectors between West Scotland and Merseyside.
- At least 70 GWh of pumped storage hydroelectric power stations are being developed along the Great Glen.
- I suspect that the pumped storage hydroelectric power stations could be connected to the wind farms, by cables under the waters of Loch Ness.
But surely, production of green hydrogen for export would be a very good way to go.
- Extra electrolysers could be added as required.
- Because of the interconnectors down both East and West Coasts, electrolysers could be built in England, where there is a large need for hydrogen.
- Hydrogen would be exported initially by tanker ships.
- At some point in the future, it might be viable to build a hydrogen pipeline to connect to the growing European hydrogen network.
The giant pumped storage hydroelectric power stations and the hydrogen electrolysers would be sized to make sure, that no wind power is never wasted.
Conclusion
The 100 MW Salamander floating wind farm may only be small, but it will prove the technology, the manufacturing and the supply chains, so that Scotland can have a second energy boom from the North Sea.
But this boom will certainly last longer than a hundred years.
UK ESO Unveils GBP 58 Billion Grid Investment Plan To Reach 86 GW of Offshore Wind By 2035
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Great Britain’s electricity system operator (ESO) has proposed a GBP 58 billion (approximately EUR 68 billion) investment in the electricity grid. The proposal outlines a vision for incorporating an additional 21 GW of offshore wind into the grid by 2035, which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
These three paragraphs add more details to what the investment in the grid means for offshore wind.
The ESO released on 19 March the first Beyond 2030 report. The plan sets up the necessary infrastructure to transfer power to and from future industries, as electricity demand is expected to rise by 64 per cent by 2035, according to the ESO.
The grid operator said that the plan connects a further 21 GW of offshore wind in development off the coast of Scotland to the grid in an efficient and coordinated way which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
The proposals could assist the UK government in meeting the sixth Carbon Budget and allow for the connection of Crown Estate Scotland’s ScotWind leasing round.
These are my thoughts.
How Much Offshore Wind Is In The Pipeline?
This Wikipedia entry is a List Of Offshore Wind Farms In The United Kingdom.
It gives these figures for wind farms in various operational an development states.
- Operational – 14,703 MW
- Under Construction – 5,202 MW
- Pre-Construction – 6,522 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 3 – 12 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 4 – 1,428 MW
- Early Planning – England – 18,423 MW
- Early Planning – Wales – 700 MW
- Early Planning – Scotland – 30,326 MW
Note.
- These add up to a total of 77,316 MW.
- If all the wind farms in the Wikipedia entry are commissioned, the UK will be short of the 86,000 MW total by 8,664 MW.
- Some wind farms like Ossian could be increased in size by a few GW, as I reported in Ossian Floating Wind Farm Could Have Capacity Of 3.6 GW.
It looks like only another 7,164 MW of offshore wind needs to be proposed to meet the required total.
This article on offshoreWIND.biz is entitled The Crown Estate Opens 4.5 GW Celtic Sea Floating Wind Seabed Leasing Round, will add another 4,500 MW to the total, which will raise the total to 81,816 MW.
The article also finishes with this paragraph.
Round 5 is expected to be the first phase of development in the Celtic Sea. In November 2023, the UK Government confirmed its intention to unlock space for up to a further 12 GW of capacity in the Celtic Sea.
A further 12 GW of capacity will take the total to 93,816 MW.
In Three Shetland ScotWind Projects Announced, I talked about three extra Scotwind wind farms, that were to be developed to the East of Shetland.
These will add 2.8 GW, bringing the total to 96,616 MW.
I don’t think the UK has a problem with installing 86 GW of offshore wind by 2035, so we must create the electricity network to support it.
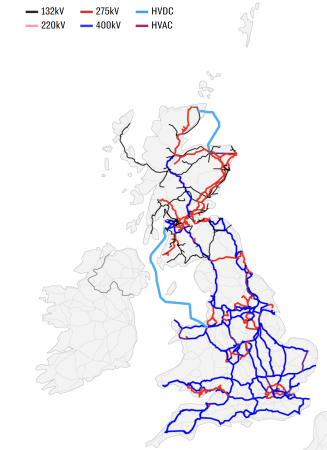
The Electricity Network In 2024
I clipped this map from this article in The Telegraph, which is entitled Britain’s Energy System Will Not Hit Net Zero Until 2035, National Grid Tells Labour.
The dark blue lines are the 400 kV transmission lines.
- The one furthest East in East Anglia serves the Sizewell site, which hosts the Sizewell B nuclear power station and will be the home of Sizewell C nuclear power station, unless the Green or LibDem Parties are a member of a coalition government.
- Kent and Sussex seem to be encircled by 400 kV lines, with small spurs to the interconnectors to Europe.
- Two 400 kV lines appear to serve the South-West peninsular, with one going along the South Coast and the other further North. I suspect these two motorways for electricity explain, why the Morocco-UK Power Project terminates in Devon.
- London seems to have its own M25 for electricity.
- There also appears to be an East-West link to the North of London linking Sizewell in the East and Pembroke in the West. Both ends have large power stations.
- There also appear to be two 400 kV lines from Keadby by the Humber Estuary to North Wales with the pumped storage hydro power station at Dinorwig.
- Two more 400 kV lines link Yorkshire to the South of Scotland.
- A lonely Northern cable connects Edinburgh and the North of Scotland.
The red lines, like the one encircling central London are the 275 kV transmission lines.
- Think of these as the A roads of the electricity network.
- They encircle London often deep underground or under canal towpaths.
- They reinforce the electricity network in South Wales.
- Liverpool appears to have its own local network.
- They also seem to provide most of the capacity North of and between Edinburgh and Glasgow.
Newer cables are starting to appear on this map.
There are two light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- The 1.2 GW Caithness – Moray Link does what it says in the name and it connects the far North of Scotland direct towards Aberdeen.
- The much larger 2.25 GW Western HVDC Link connects Hunterston near Glasgow to Flintshire Bridge near Liverpool. Note how it passes to the West of the Isle of Man.
Not shown on the map are the smaller 500 MW Moyle Interconnector and the recently-opened 600 MW Shetland HVDC Connection.
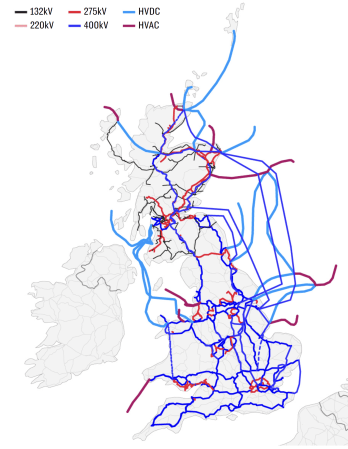
The Electricity Network In 2050
This second map shows how the network will look in 2050.
Note.
- The colours are the same, as the previous map.
- Although, I do think there are some errors in which have been used.
- There are a lot more cables.
There are several more light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- Shetland is now linked to the North of Scotland by the Shetland HVDC Connection.
- There appears to be a cluster of HVDC interconnectors at Caithness HVDC switching station, near Wick, including a new one to Orkney, to go with the others to Moray and Shetland.
- The 2 GW Scotland England Green Link 1 will run from Torness in Southeast Scotland to Hawthorn Pit substation in Northeast England.
- The 2 GW Eastern Green Link 2 will run from Sandford Bay, at Peterhead in Scotland, to the Drax Power Station in Yorkshire, England.
- There also appear to be two or possibly three other offshore cables linking the East Coast of Scotland with the East Coast of England.
- If the Eastern cables are all 2 GW, that means there is a trunk route for at least 8 GW between Scotland’s wind farms in the North-East and Eastern England, which has the high capacity wind farms of Dogger Bank, Hornsea and around the Lincolnshire and East Angliam coasts.
- Turning to the Western side of Scotland, there appears to be a HVDC connection between the Scottish mainland and the Outer Hebrides.
- South-West of Glasgow, the Western HVDC Link appears to have been duplicated, with a second branch connecting Anglesey and North-West Wales to Scotland.
- The Moyle Interconnector must be in there somewhere.
- Finally, in the South a link is shown between Sizewell and Kent. It’s shown as 400 kV link but surely it would be a HVDC underwater cable.
There are also seven stubs reaching out into the sea, which are probably the power cables to the wind farms.
- The red one leading from South Wales could connect the wind farms of the Celtic Sea.
- The blue link North of Northern Ireland could link the MachairWind wind farm to the grid.
- The other two red links on the West Coast of Scotland could link to other ScotWind wind farms.
- The red link to the North of East Anglia could link RWE’s Norfolk wind farms to the grid.
- The other stubs in the East could either connect wind farms to the grid or be multi-purpose interconnectors linking to Germany and the Netherlands.
It looks to me, that National Grid ESO will be taking tight control of the grid and the connected wind farms, as an integrated entity.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I can’t disagree with that philosophy.
Hydrogen Production
In How Germany Is Dominating Hydrogen Market, I talked about how Germany’s plans to use a lot of hydrogen, will create a large world-wide demand, that the UK because of geography and large amounts of renewable energy is in an ideal place to fulfil.
I can see several large electrolysers being built around the UK coastline and I would expect that National Grid ESO have made provision to ensure that the electrolysers have enough electricity.
Would I Do Anything Different?
Consider.
- If it is built the Morocco-UK Power Project will terminates in Devon.
- There could be more wind farms in the Celtic Sea.
- It is likely, that the wind farms in the Celtic Sea will connect to both Pembroke and Devon.
- Kent has interconnectors to the Continent.
Would a Southern HVDC link along the South Coast between Devon and Kent be a good idea?
Conclusion
Looking at the proposed list of wind farms, a total in excess of 96 GW could be possible, which is ten GW more than needed.
The network not only serves the UK in a comprehensive manner, but also tees up electricity for export to Europe.
BlueFloat, Renantis And Ørsted Move Forward With 1 GW Scottish Floater
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Stromar Offshore Wind Farm Limited, a joint venture between Ørsted, BlueFloat Energy, and Renantis, has submitted the environmental impact assessment (EIA) scoping and habitats regulations appraisal (HRA) screening reports for the 1 GW floating offshore wind farm in Scotland.
These are the first three paragraphs, which outline the progress that has been made so far.
The reports for the project, which is located approximately 50 kilometres from the Port of Wick, were delivered to the Marine Directorate and Aberdeenshire Council.
The EIA scoping reports outline the plans for the development, addressing both onshore and offshore considerations while the HRA screening reports outline the key protected sites and species of relevance to the Stromar development area. The HRA screening reports also present how impacts will be assessed in more detail at the next stage, the developer said.
The project team will now schedule several community consultation events in Spring 2024 to ensure stakeholders are fully informed and that their views are considered in the site selection, design, and development of the project, according to the developer.
This map shows the various ScotWind leases.
Note.
- The numbers are Scotwind’s lease number in their documents.
- 10 is now Stromar
- This is the Stromar web site.
- One of the partners; Falck Renewables changed its name to Renantis in 2022.
- The next stage is to be awarded a Contract for Difference.
The Internet is suggesting a completion date of 2028.
ABP To Explore Opportunities For Offshore Wind Port In Scotland
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Associated British Ports (ABP) has signed an agreement to investigate an area for the development of infrastructure to support offshore wind manufacturing, assembly, and marshalling and green energy on the Cromarty Firth in Scotland, within the Inverness Cromarty Firth Green Freeport.
This first paragraph gives a bit more information including the possible location.
The area, located within the proposed Nigg and Pitcalzean area of the Green Freeport, could support both fixed-bottom and floating offshore wind projects and play a major role in the development of current and future ScotWind leasing rounds, said ABP.
This Google Map shows the location of the Port of Nigg.
Note.
- The Moray Firth with Inverness at its Southern end is the large body of water in the centre of the Southern half of the map.
- The Port of Nigg is on Cromarty Firth and marked by a red arrow.
- Nigg and Pitcalzean are to the North of the port.
This second Google Map shows an enlarged view of the port.
Note.
- Pitcalzean House is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The Port of Nigg is in the centre of the map.
- The water to the West and South of the port is Cromarty Firth.
- The yellow structures in the port are fixed-bottom foundations for wind farms.
Inverness & Cromarty Firth Green Freeport has a web site.
A Quote From Henrik Pedersen
Henrik Pedersen is CEO of ABP and the article quotes him as saying this.
We’re excited to explore the potential of Nigg, applying our experience across the UK, including at our Ports of Grimsby, Hull, Lowestoft and Barrow which already host significant offshore wind activity and at Port Talbot, where we are developing a Floating Offshore Wind port project. We look forward to working with key local partners, the community, and public sector stakeholders.
The article also has this final paragraph.
The Floating Offshore Wind Taskforce’s recently published “Industry Roadmap 2040”, estimated that planed floating offshore wind projects in Scottish waters alone will require three to five integration ports.
There is certainly going to be a significant number of ports, that will be supporting offshore wind activity.
WES Starts Testing Combined Floating Wind And Wave Energy Models
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Wave Energy Scotland (WES) has started a series of tank tests of floating wind and wave energy structures at the University of Edinburgh’s FloWave facility to explore the potential benefits the synergy between the two technologies could bring.
These two paragraphs introduce the technology.
The tank tests currently being completed by WES use sea states which are representative of one of the future floating wind lease sites on the west coast of Scotland, leased through the ScotWind program and which has an appropriate water depth and wave resource for large-scale wave energy exploitation.
The physical model used for the testing incorporates multiple identical wave energy absorbers mounted onto a semi-submerged, triangular floating platform.
Have we got enough research facilities to test devices like these?
I can find these.
With Edinburgh, that makes five.
Thoughts On The Future Of Orkney
This article on the BBC is entitled Orkney Votes To Explore ‘Alternative Governance‘
This is the sub-heading.
Orkney councillors have voted to investigate alternative methods of governance amid deep frustrations over funding and opportunities.
These paragraphs outline the story.
Council leader James Stockan said the islands had been “held down” and accused the Scottish and UK governments of discrimination.
His motion led to media speculation that Orkney could leave the UK or become a self-governing territory of Norway.
It was supported by 15 votes to six.
It means council officers have been asked to publish a report to Orkney’s chief executive on options of governance.
This includes looking at the “Nordic connections” of the archipelago and crown dependencies such as Jersey and Guernsey.
A further change which would see the revival of a consultative group on constitutional reform for the islands was accepted without the need for a vote.
My Thoughts On The Economic Future Of The Islands
The economic future of Orkney looks good.
Tourism and the traditional industries are on the up, but the islands could play a large part in renewable energy.
The West of Orkney offshore wind farm, which will be a 2 GW wind farm with fixed foundations, is being developed and a large hydrogen production hub at Flotta is being proposed, along with the development of a large quay in Scapa Flow for the assembly of floating wind farms.
The West of Orkney wind farm could be the first of several.
If the future wind farms are further from shore, they will most likely be based on floating technology, with the turbines and their floats assembled in Scapa Flow, from components shipped in from mainland UK and Europe.
Political Future
With a good financial future assured, I believe that Orkney will be able to choose where its political future lies. It could be a Crown Dependency or join Norway.
Whichever way it goes, it could be an island that effectively prints money, by turning electricity into hydrogen and shipping it to countries like Germany, The Netherlands, Poland and Sweden!
From a UK point of view, a Crown Dependency could be a favourable move.
Would Shetland follow the same route?
Offshore Hydrogen Production And Storage
Orkney is not a large archipelago and is just under a thousand square kilometres in area.
It strikes me, that rather than using up scarce land to host the large electrolysers and hydrogen storage, perhaps it would be better, if hydrogen production and storage was performed offshore.
Aker Northern Horizons
In Is This The World’s Most Ambitious Green Energy Solution?, I talk about Northern Horizons, which is an ambitious project for a 10 GW floating wind farm, which would be built a hundred kilometres to the North-East of Shetland, that would be used to produce hydrogen on Shetland.
Other companies will propose similar projects to the West and East of the Northern islands.
This map shows the sea, that could be carpeted with armadas of floating wind farms.
Consider.
- There are thousands of square miles of sea available.
- As the crow flies, the distance between Bergen Airport and Sumburgh Airport in Shetland is 226 miles.
- A hundred mile square is 10,000 square miles or 2590 square kilometres.
- In ScotWind Offshore Wind Leasing Delivers Major Boost To Scotland’s Net Zero Aspirations, I calculated that the floating wind farms of the Scotwind leasing round had an energy density of 3.5 MW per km².
- It would appear that a hundred mile square could generate, as much as nine GW of green electricity.
How many hundred mile squares can be fitted in around the UK’s Northern islands?
Irish ESB Joins Northland Power On Two Scottish Offshore Wind Projects
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
ESB will acquire a 24.5 per cent interest in Northland Power’s ScotWind projects, the fixed-bottom offshore wind farm Spiorad na Mara and the floating wind project Havbredey. Northland will retain 75.5 per cent in each project and continue to lead their development, construction, and operation
This is the first paragraph.
The companies have signed definitive agreements on ESB’s purchase of project stakes, with all commitments made prior to the agreements to remain in place.
Last month, I wrote ESB Invests In Floating Offshore Wind Mooring Tech. so are they in acquisitive mode?
This map from Cross Estate Scotland shows all the ScotWind contracts.
ESB now lrasr the following stakes in ScotWind.
Their details are as follows.
- 14 – Havbredey – Floating – 1500 MW – 25 %
- 16 – Spiorad na Mara – Fixed – 840 MW – 25 %
- 20 – Unnamed – Floating – 500 MW – 100 %
These figures mean they lease about a GW.
I have my thoughts.
Will There Be A Multi-Purpose Interconnector between Ireland And Scotland?
Nothing has been mentioned yet, but could new wind farms om the future to the West of the Hebrides be connected to both the North of Scotland and the North of Ireland by a multi-purpose interconnector?
BP And EnBW Hire Kent For 2.9 GW Scottish Offshore Wind Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Engineering and design service provider Kent has been awarded a contract by EnBW and BP to carry out pre-Front End Engineering Design (FEED) studies for the 2.9 GW Morven offshore wind project in Scotland.
Morven offshore wind farm would appear to be on its way.
According to Wikipedia’s list of UK offshore wind farms, the water depth in the Morven wind farm is between 65-75 metres.
- Total power is given as 2907 MW, which indicates that 14 MW turbines could be used.
- Siemens Gamesa 14 MW turbines have a blade length of 108 metres and their 10 MW have a blade length of 94 metres.
- This would seem to indicate that the wind turbine will be as much as 160 to 185 metres above the sea-bed.
A radical design of fixed foundation will be needed.
In Entrion Wind Wins ScotWind Feasibility Deal For Its 100-Metre Depth Foundation Tech, I look at technology that might work.
I also say this about work I did in Cambridge in the early 1970s.
The structures, I mathematically-modelled were for a company called Balaena Structures, that had been started by two Cambridge University engineering professors. The structures were about a hundred metres high and perhaps thirty metres in diameter.
They would have been built horizontally in the sort of dock, where you would build a supertanker and would have been floated into position horizontally. Water would then be let in to the cylinder and they would turn to the vertical. From that position, they would be lowered to the sea-bed by adjusting the water in the cylinder. They had a method of holding the Balaena to the seabed, which relied mainly on the weight of the structure and what they called the gum-boot principle.
Sadly, they never sold any platforms and the company folded.
Until recently, you could find the expired patents on the Internet.
I believe that a development of the Balaena design could be the solution to deep water fixed foundations.