Paddington And Minehead By Train
Two projects announced in the last six months may make this a possibility.
- FirstGroup’s Paddington and Paignton Service
- The West Somerset Tidal Lagoon
Neither project has the full permissions it needs, but if Lumo do stop at Taunnton and the West Somerset Tidal Lagoon is built, if could open up an interesting possibility.
In Thoughts On Lumo’s Proposed Paddington And Paignton Service, I stated that a train could take two hours between Paddington and Taunton, if it went for a fast non-stop run to Bath Spar station.
In MP Pushes For Tidal Lagoon In Bristol Channel, I said this.
I believe that for the lagoon project to be complete, the West Somerset Railway needs to be turned into a fully-operational branch line between Minehead and Taunton to improve access for residents, visitors and workers to Minehead and other places in West Somerset.
Surely, with a quick change of train, passengers could be in Minehead thirty minutes after arriving at Taunton.
In recent years several new branch lines have open in the UK and been given time to attract new passengers.
- The Borders Railway to Tweedbank
- Merseyrail to Headbolt Lane
- The Northumberland Line to Ashington
- ScotRail to Leven.
- The Dartmouth Line to Okehampton
None appear to be in any danger of being closed.
I very much feel, that if the West Somerset Railway, ran a full service between Minehead and Taunton, it would follow the same pattern.
New Bid To Connect Heritage Railway To Mainline
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
The is the sub-heading.
A bid to connect one of the longest heritage railways in Britain with mainline services has taken a step forward.
These are the first two paragraphs.
West Somerset Railway (WSR) and Somerset Council have now submitted a business plan to the government to restore the mainline from Taunton to the final WSR stop at Bishop’s Lydeard.
The proposal suggests Bishop’s Lydeard could become a commuter and tourist hub.
There has been several attempts to connect the branch to Taunton station.
These are my thoughts.
Minehead, Bishop’s Lydeard And Hinckley Point C
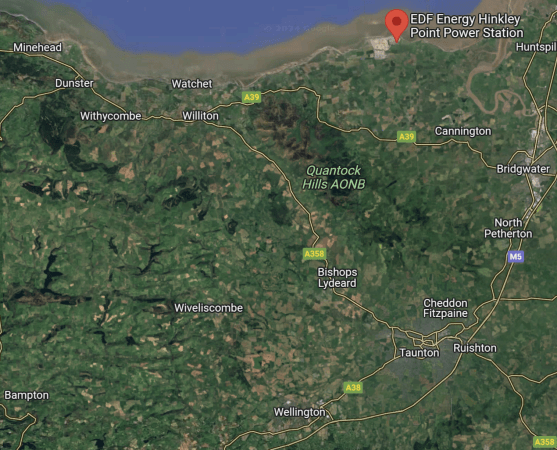
This Google Map shows the area.
Note.
- Minehead is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Hinckley Point power station is indicated by the red arrow.
- Bishop’s Lydeard is in the middle of the map.
- The M5 motorway curves diagonally between the North-East and South-West corners of the map.
- There are motorway services at Taunton Deane, which is to the South of Taunton and Cullompton, which is a few miles South-West of Wellington.
- The large town of Taunton is the junction of the London and Exeter and the Bristol and Exeter railway lines.
- The town of Wellington will be getting a new railway station.
It is a very busy area and it will only get busier, as the availability of power will only attract industry, like the battery factory pencilled in for Bridgewater.
The Major Effect Of Hinckley Point C
Hinckley Point C will generate 3.26 GW of electricity and to operate the power station will need around nine hundred workers.
I can also expect that the Hinckley Point site will get involved in other energy handling and use.
- The site would be an ideal place for a large electrolyser to produce hydrogen.
- Wind turbines in the Bristol Channel could use Hinckley’s grid connection.
- Energy could be stored on the site. It could be an ideal location for one of Highview Power’s 200 MW/3.25 GWh liquid air batteries.
- Hydrogen could be exported using coastal tankers.
- Interconnectors could take electricity to Cornwall, Devon, Wales and Ireland.
All of these activities would create needs for workers at all levels.
- A rail connection to Taunton and Bristol, will probably be needed to bring workers into Hinckley Point.
- A rail connection would be ideal for bringing construction materials, steel and other heavy goods into and out of the Hinckley Point site.
- Hydrogen could also be taken out in rail tankers.
- Nuclear waste could be taken out by train.
I think it is highly likely, that Hinckley Point will need a rail connection for efficient operation.
Sizewell C And Hydrogen
Hydrogen is so important to the philosophy of the design and construction of Sizewell C, that hydrogen has its own section on the Sizewell C web site.
Hydrogen produced by nuclear power stations like Hinckley Point C, is called pink hydrogen, but like green hydrogen it is zero-carbon and pollution-free.
Hinckley Point C And Hydrogen
I can envisage Hinckley Point C will create a lot of hydrogen both for use locally and distribution to remote users.
- Hydrogen could be delivered locally by truck, just as propane is today around the world.
- Coastal tankers could distribute the hydrogen from a jetty.
- Pipelines could connect the two nearby motorway service stations to the power station site.
Just as is happening at Sizewell, a local hydrogen network could be built.
Hydrogen Refuelling On The M5
Consider.
- In MAN Expands Its Zero-Emission Portfolio, I talked about MAN’s new hydrogen-powered hTGX truck, which has been designed with a 600 km. or 373 mile range.
- As Cullompton, which is the Southernmost of the two services on the M5 that are close to Hinckley Point C, is only 124.9 miles from Penzance, it should be possible for a truck, with a range similar to that of the MAN hTGX to do a round trip from the Southern end of the M5 to Penzance, without refuelling.
- As the total length of the M5 is only 163 miles, a hydrogen-powered truck with the range of the MAN hTGX would be able to do a delivery anywhere along the motorway and return to the hydrogen from Hinckley Point C, without refuelling.
- MAN are saying that the hTGX truck can be refuelled in less than fifteen minutes.
It looks to me, that a hydrogen electrolyser at Hinckley Point C would be ideally located to provide pink hydrogen for a zero-carbon hydrogen-powered route to and from the far South-West.
I believe that if there were a best-in-class hydrogen-refuelling facility close to Hinckley Point C, it would encourage those who regularly drove to Devon and Cornwall to look seriously at hydrogen-powered vehicles.
The Nature Of The Hinckley Point C Rail Link
Sizewell C are using a simple practical approach to connect the Sizewell C site to the nearby East Suffolk Line.
- The existing freight sidings are being expanded.
- Two Park-and-Ride sites are being created at stations in the East Suffolk Line.
- A link road will be built between the railway and the Sizewell C site.
- A fleet of hydrogen-powered double-deck buses has been ordered to take workers between the railway and the power station.
- The signalling on the East Suffolk Line is being improved.
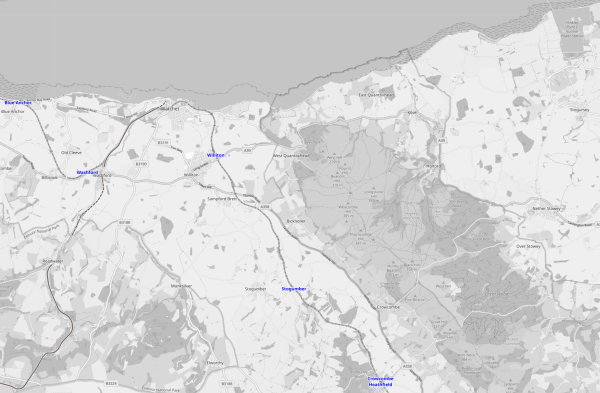
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the Northern end of the West Somerset Railway and its relationship to Hinckley Point C power station.
Note.
- Hinckley Point C power station is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Crowcombe & Heathfield, Stogumber, Sampford Brett, Doniford Halt, Williton, Watchet, Washford and Blue Anchor are existing or former stations on the West Somerset Railway.
- Existing stations are shown in blue.
- West of Blue Anchor are the two existing stations of Dunster and Minehead.
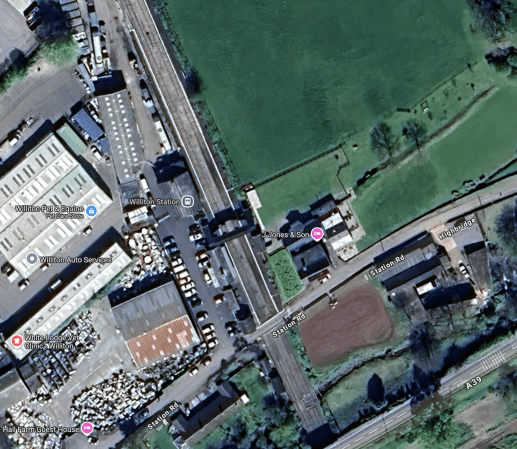
This Google Map shows Williton station, which is the nearest station to Hinckley Point C.
Note.
- The station has a footbridge, which was erected in 2011, so is probably in good condition.
- There are several Listed buildings on the site.
- Going East on the A39 should lead to Hinckley Point C.
I suspect a quality bus company could build a small fleet of buses to shuttle workers, visitors and others to Hinckley Point C.
As I’m sure, hydrogen will be in plentiful supply, I’m certain hydrogen-powered buses could be used.
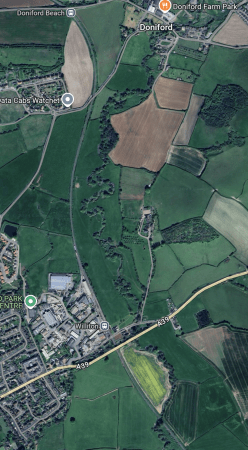
This Google Map shows a longer section of the West Somerset Line through Williton station.
Note.
- The West Somerset Line runs North-South down the map.
- Doniford Halt station is at the top of the map, where the coast road crosses the railway on a bridge.
- Williton station is in the middle of the map, where the A39 crosses the railway.
Looking at the railway, which runs mainly between fields, I wouldn’t be surprised that if Hinckley Point wanted a freight siding, they could fit one in.
Go-op
Go-op are an open access railway company, that wants to run services in Somerset.
I wrote about their successful application in Regulator Approves New Go-op Train Service Between Swindon, Taunton and Weston-super-Mare.
This is the first paragraph of their Wikipedia entry.
Go-op Cooperative Ltd.,[ branded as Go-op, is an open access train operating company, proposing to operate a service in south-west England between Taunton and Swindon, via Westbury. It aims to become the first cooperatively owned train operating company in the United Kingdom, to improve access to the public transport infrastructure through open access rail services linking main lines to smaller market towns, and by co-ordinating services with light rail, bus links and car pools.
If you read their Wikipedia entry and their web site, they seem to have ambition and be different.
According to Wikipedia, they have made no less than five different proposals, but it is the fourth that I find interesting.
In 2021, Go-op began discussions with Network Rail for services between Swindon and Bishops Lydeard (just beyond Taunton), which it hoped to begin in mid-2022. At first there could only be three services per day, due to congestion between Swindon and Westbury; a further three could be provided to Frome or Westbury, connecting with existing services to Swindon. These plans would also improve local services on the TransWilts Line, calling at Trowbridge and Melksham.
The plans for Bishops Lydeard would restore the link broken in 1971 between the national network and the preserved West Somerset Railway, which runs leisure services to Minehead.
This sounds very much like an extended and simplified version of the West Somerset Line proposal.
But it does look like two groups have looked at the infrastructure and what is needed and come to similar conclusions.
Perhaps, they have other things in common like train procurement and servicing.
Stadler Presents A World First In Berlin
The title of this section, is the same as that of this press release from Stadler.
These are the first two paragraphs.
With the RS ZERO, the rail vehicle manufacturer is presenting the successor to the successful Regio-Shuttle RS1 model. There is a choice of two modern and environmentally friendly drive technologies: Hydrogen and battery. Both will enable CO2 emission-free operation of secondary lines in the future.
Stadler today unveiled the prototype of the new RS ZERO, the innovative successor to the successful RS1 Regio-Shuttle. The Regio-Shuttle has been one of the most popular vehicles in German regional rail transport for 28 years, with around 500 RS1 vehicles currently in operation in Germany and the Czech Republic. Stadler is building on this proven technology and integrating state-of-the-art, environmentally friendly drive systems. The RS ZERO is optionally available with a hydrogen and/or battery drive and thus not only sets new standards for environmentally friendly rail transport, but also presents a world first.
These pictures from Chemnitz Trams And The Chemnitz Model, show the Regio-Shuttle RS1.
Note.
- The Regio-Shuttles can run as up to seven car trains.
- These Regio-Shuttles are electro-diesel.
- The distinctive diagonal windows.
- They can carry 170 passengers at 75 mph.
- They can run as train-trams using the Chemnitz model on compatible tram networks.
The Regio-Shuttle Wikipedia entry gives more details.
This image from the press release shows the prototype RS ZERO.
It looks very similar to my pictures from Chemnitz.
I have a few thoughts.
Comparison To A Class 150 Train
A Class 150 train can carry up to 149 seated passengers at 75 mph, which is similar to the RS ZERO.
As Stadler have built trains for Greater Anglia, Merseyrail and the Glasgow Subway, I believe that Stadler could build an RS ZERO, that would fit the UK loading gauge.
In What Train Is This?, I show the standard of interior, that can be achieved by refurbishing a Class 150 train, but unlike the RS ZERO, the train won’t be zero-carbon.
Does The RS ZERO Have A Toilet?
This is a paragraph from the press release.
The prototype of the RS ZERO presented today in Berlin is a one-car vehicle with hydrogen drive. Stadler is demonstrating the numerous design options with a multi-purpose area equipped for carrying bicycles, pushchairs and bulky luggage, lounge and comfort zones, standard and privacy seats, a wheelchair space, WC and a train office.
The train appears to be able to have what an operator might need.
What Will Be The Range Of An RS ZERO On Hydrogen?
I suspect, Stadler will provide a train, that will handle the route.
Would Stadler Be Able To Produce An RS ZERO That Could Satisfy The West Somerset/Go-op Requirement?
I obviously, can’t answer that.
But.
- The train is zero-carbon.
- It’s the right size.
- I suspect that the hydrogen fuel will be available from Hinckley Point C.
- The design has a proven track record.
- The train is not by any means vapourware!
- Stadler need a launch order.
- An experienced ROSCO would probably finance the trains.
One perk is that those involved in buying the train, could probably wangle a trip to Chemnitz to see several Regio-Shuttle RS1 trains at work.
Note that Chemnitz used to be Karl-Marx Stadt, so some of our Government will feel nostalgic.
But I do believe, this could be a very handy train to decarbonise branch and secondary lines in the UK.
Regulator Approves New Go-op Train Service Between Swindon, Taunton and Weston-super-Mare
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from the Office of Rail and Road.
This is the sub-heading.
The rail regulator has given the go ahead for new train services between Swindon, Taunton and Weston-super-Mare from the end of 2025. The regulator has also set conditions on its approval to ensure the new, co-operatively owned operator has sufficient finance and rolling stock in place in good time.
These paragraphs from the press release give more details.
Go-op plans to operate return weekday and weekend services between Taunton and Weston-super-Mare, Taunton and Westbury, Taunton and Swindon, and Frome and Westbury.
It will compete with Great Western Railway (GWR), a public service operator. Go-op plans to start in December 2025 at the earliest, and must do so no later than December 2026 in order to use the capacity ORR has granted.
As part of ORR’s decision, Go-op must provide evidence to ORR of the necessary finance to start operations, fund level crossing enhancements, and that the necessary rolling stock has been secured. ORR’s decision requires Go-op to do this without delay, and no later than November 2025.
I must admit I’m a little surprised at the Office of Rail and Road giving approval.
There is more on the Go-op web site.
Taunton To Exeter St. Davids – 4th July 2023
I took these pictures as I travelled from Taunton station to Exeter St.Davids station.
This Google Map shows a section of the M5 North of Collumpton.
Note.
- The proximity of the M5 motorway to the railway, in some pictures and the map.
- There is space to plant large numbers of trees between the motorway and the railway.
- There are high voltage overhead electrical cables running along the same corridor.
- Collumpton services are also placed between the motorway and the railway.
I believe that with good landscaping, it would be possible to improve the motorway and railway corridor, between Taunton and South of Collumpton.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the track between Wellington and Collumpton, between Taunton and Exeter.
Note.
- The black line is the railway between Taunton and Exeter.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map indicates the position of the proposed Wellington station.
- Collumpton is in the South-West corner of the map and has also been put forward for a new Collumpton station.
- I talked about the reopening of these two stations in Reopening Of Wellington and Cullompton Stations.
- The M5 to the North of Collumpton runs closely alongside the railway.
- According to Real Time Trains, it takes just under ten minutes to go the thirteen miles between Wellington and Cullompton.
I believe that by using partial electrification, good engineering and innovative landscaping, that sufficient electrification can be erected between Taunton and South of Collumpton, that would ensure the following.
- Trains would leave Taunton going East with enough charge to travel the 89.6 miles to Newbury.
- Trains would leave Taunton going North with enough charge to travel the 51.7 miles to Patchway via Western-super-Mare and Bristol Temple Meads.
- Trains would leave Cullompton going South with enough charge to travel the 32.9 miles to Okehampton.
- Trains would leave Cullompton going South with enough charge to travel the 36.6 miles to Paignton.
- Trains would leave Cullompton going South with enough charge to travel the 60.4 miles to Plymouth.
Note.
- I’ve added Okehampton, as I feel that if Dawlish had another encounter with Poseidon, Okehampton with its proposed Parkway station on the A30 could be the terminus for coaches to and from Cornwall.
- Charging could be needed at Okehampton and Paignton.
- Charging at Okehampton and Paignton, wouldn’t be needed, if the battery-electric trains had enough range to do the return trip.
Electrification of Plymouth and Penzance stations, as I outlined in Thoughts About Electrification Through Devon And Cornwall, would enable battery-electric trains to bridge the gap of 79.5 miles, between these two stations.
Conclusion
It looks like some miles of sympathetic electrification and landscaping between Taunton and South of Cullompton, is the key to running battery-electric train to Devon and Cornwall.
Thoughts About Electrification Through Devon And Cornwall
Distances
I’ll start by looking at a few distances.
- Penzance and Taunton – 162.3 miles
- Penzance and Exeter St. David’s – 131.5 miles
- Penzance and Plymouth – 79.5 miles
- Taunton and Exeter St. David’s – 30.7 miles
- Plymouth and Exeter St. David’s – 52 miles
- Taunton and Newbury – 89.6 miles
- Plymouth and Taunton – 82.8 miles
- Taunton and Paignton – 59 miles
- Taunton and Patchway – 51.7 miles
Note.
- Patchway and Newbury are already electrified to Cardiff Central and London Paddington respectively.
- Bombardier’s engineer told me eight years ago, that the battery-electric Class 379 had a range of sixty miles.
- Stadler’s FLIRT Akku has a Guinness world record of 139 miles on one battery charge. See this page on the Stadler web site.
- Even Stadler’s Class 777 trains for Merseyrail have a range of 84 miles on battery power. See New Merseyrail Train Runs 135km On Battery.
The rail distances in Devon and Cornwall are getting closer to being within the capability of trains fitted with batteries.
Station Stop Times
These are typical times that trains stop in the more important stations between Taunton and Penzance.
- Taunton – < 2 mins
- Tiverton Parkway – < 2 mins
- Exeter St. Davids – 2 mins
- Newton Abbot – < 2 mins
- Totnes – < 2 mins
- Plymouth – 11 minutes
- Devonport – < 2 mins
- Saltash – < 2 mins
- Menheniot – < 2 mins
- Liskeard – < 3 mins
- Bodmin Parkway – 2 mins
- Lostwithiel – 2 mins
- Par – 2 mins
- St. Austell – 2 mins.
- Truro – 2 mins
- Redruth – 2 mins
- Camborne – 2 mins
Note.
- The timings were for today.
- The Cardiff and Penzance services were being run by five-car Class 802 trains.
- Most station stops are around two minutes or less, but Plymouth on this train was eleven minutes.
I find it interesting that the Plymouth stop takes so much longer.
Train Stops At Plymouth
I looked at about twenty trains stopping at Plymouth, that included these services.
- London Paddington and Penzance
- Penzance and London Paddington
- Cardiff Central and Penzance
- Penzance and Cardiff Central
Note.
- I found an average time of eight minutes.
- Eleven minutes was a common stop.
- Eight minutes could be enough time for the rail equivalent of a Formula One splash and dash.
- CrossCountry services were going through the station in three minutes.
I am led to believe that the timetable used by the GWR trains would allow a quick battery charge at Plymouth station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms at Plymouth station.
Note.
- London is to the East and Penzance is to the West.
- Platform numbers increase from South to North.
- The two East-facing bay platforms are Platforms 1 and 2.
- The West-facing bay platform in the South-West corner is Platform 3.
- Platform 4 shares the island with the bay platforms 1, 2 and 3.
- Most trains going to Penzance use Platform 4.
- Platforms 5 and 6 share the centre island platform.
- Platforms 7 and 8 share the Northernmost island platform.
- Most trains going towards London use Platform 7.
- Wikipedia indicates that the track layout is comprehensive and allows a lot of operational flexibility.
Although the station was completed around forty years ago, it could have been designed for handling modern battery-electric trains.
- There are three bay platforms numbered 1 to 3, to charge local services and send them on their way.
- Trains can arrive and depart in the five through platforms, numbered 4 to 8, from either direction.
- Two days ago, a nine-car London Paddington to Plymouth train terminated in Platform 7. After waiting an hour it returned to London. An hour would be enough time to fully-charge a train.
- As many platforms as needed could be electrified.
I am fairly sure, that most battery-electric trains could be timetabled to leave Plymouth station with full batteries.
Turnround At Penzance
I have found these turnrounds.
- 802113 arrived from Paddington at 1142 and left for London at 1215
- 802022 arrived from Paddington at 1307 and left for London at 1415
- 802103 arrived from Paddington at 1500 and left for London at 1615
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms at Penzance station.
Note.
- The three example trains used Platform 1.
- Platform 1 is the long platform on the landward side of the station.
- Platforms are numbered 1 to 4 from left to right.
- An appropriate number of platforms would be electrified to charge trains terminating at Penzance.
Trains would appear to have plenty enough time to recharge, so they would start their return journey with full batteries.
Engineering Ambition
Several times in my life, I’ve got fired up about engineering or software projects and I like to think, I’ve produced the best and fastest solution.
For this reason, I believe that Hyperdrive Innovation, who are now part of Turntide Technologies, and Hitachi will set themselves three objectives with the design of the the battery packs for the Class 802 train.
- The battery-electric Class 802 will outperform the Stadler FLIRT Akku in terms of speed and distance.
- The battery packs will be plug-compatible with the diesel engines, so there will only be minor software modification to the trains.
- The train will be able to be handle all Great Western Railway’s routes without using diesel.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that on many routes the train will cruise at over 110 mph on batteries.
I also suspect they want the Akku’s Guinness world record, which will mean the range will be in excess of 139 miles.
Battery Range Needed For Routes
These are routes that need to be covered by battery-electric Class 802 trains or similar.
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Chester – 22.2 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Holyhead – 105.5 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Llandudno Junction – 65.5 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Wrexham – 34.4 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Shrewsbury and Wolverhampton – 29.7 miles
- Great Western Railway – Penzance and Plymouth – 79.5 miles
- Great Western Railway – Plymouth and Taunton – 82.8 miles
- Great Western Railway – Taunton and Patchway – 51.7 miles
- Great Western Railway – Newbury and Taunton – 89.6 miles
- Great Western Railway – Taunton and Paignton – 59.0 miles
- Great Western Railway – Weston-super-Mare and Chippenham – 43.5 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Great Malvern – 65.6 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Hereford – 86.3 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Worcester Foregate Street – 57.6 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Worcester Shrub Hill – 57.2 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cheltenham Spa and Swindon – 43.2 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cardiff Central and Carmarthen – 77.4 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cardiff Central and Pembroke Dock – 118.9 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cardiff Central and Swansea – 45.7 miles
- Hull Trains – Beverley and Temple Hirst Junction – 44.3 miles
- Hull Trains – Hull and Temple Hirst Junction – 36.1 miles
- LNER – Hull and Temple Hirst Junction – 36.1 miles
- LNER – Middlesbrough and Longlands Junction – 22.2 miles
- LNER – Sunderland and Longlands Junction – 48.5 miles
- LNER – Lincoln Central and Newark Northgate – 16.6 miles
- LNER – Leeds and Bradford – 13 miles
- LNER – Leeds and Harrogate – 18 miles
- LNER – Leeds and Huddersfield – 17 miles
- LNER – Stirling and Inverness – 146 miles
- LNER – Edinburgh Haymarket and Aberdeen – 130 miles
- LNER – Peterborough and Doncaster via Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line – 93.7 miles
- South Western Railway – Basingstoke and Exeter St. David’s – 124.5 miles
- TransPennine – Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- TransPennine – Longlands Junction and Saltburn – 34.7 miles
- TransPennine – York and Scarborough – 42 miles
- TransPennine – Doncaster and Cleethorpes – 52.1 miles
- TransPennine – Stockport and Doncaster – 55.4 miles
- TransPennine – Stockport and Cleethorpes – 107.5 miles
Note.
- Stirling and Inverness and Edinburgh Haymarket and Aberdeen could be shortened by up to thirty miles, by planned electrification in Scotland.
- I have assumed that the TransPennine Upgrade has been completed.
- It looks like a battery-electric Class 802 train could use the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line diversion via Lincoln.
- I am slightly surprised, that the longest stretch of line without electrification and with a passenger service is Basingstoke and Exeter St. David’s.
Charging will be needed at some places to charge the battery-electric trains. Stations fitted with chargers could include Aberdeen, Carmarthen, Cleethorpes, Exeter St. David’s, Hereford, Holyhead, Hull, Inverness, Paignton, Penzance, Pembroke Dock, Plymouth, Swansea, Taunton, Weston-super-Mare, Worcester.
Most chargers would be a length of electrification in the platform, where the battery-electric trains terminated or passed through.
More On LNER’s Ten New Bi-Modes
I wrote about these trains in LNER Seeks 10 More Bi-Modes.
This was my conclusion.
There is a lot of scope to develop LNER’s services.
I think it is likely that the order will go to Hitachi.
But as I indicated, I do believe that there is scope for a manufacturer to design a zero-carbon train, that was able to serve Aberdeen and Inverness.
-
- I suspect a fleet of ten trains would be sufficient.
- Trains would use the 25 KVAC overhead electrification, where it exists and hydrogen or battery power North of the wires.
The trains would also be capable of being upgraded to higher speeds, should the East Coast Main Line be turned into a High Speed Line.
I also think, that whatever trains are bought, there will be a large upgrading of the existing Hitachi fleet, which will add batteries to a lot of trains.
In the July 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled LNER Embraces Pioneering Spirit, which takes the form of an interview with LNER’s Managing Director; David Horne.
In a section, which is entitled ‘225’ Replacement, this is said.
Meanwhile, Mr Horne is looking to what might replace the InterCity 225 fleet, now smartly repainted in a scheme which pays homage to the original ‘Swallow’ livery. While there were fears this fleet may be withdrawn as an economy measure, the ‘225s’ are now on lease until at least next summer.
But Mr Horne says obsolescence issues are a real challenge and LNER will struggle to maintain the fleet beyond 2025, and from the May 2023 timetable change the number of daily diagrams was reduced from five to four to conserve the fleet’s mileage. Much of the heavy maintenance work had previously been carried out at Wabtec’s Doncaster site, but this facility is no longer available, and while a recent reliability improvement programme is bearing fruit, the challenges remain. The crunch point comes with the transition to ETCS at the southern end of the ECML as part of the East Coast Digital Programme – Mr Horne says LNER does not want to fit cab signalling on the ‘225s’.
The solution to this issue is to procure additional trains to run alongside the 65 Azumas, and LNER went out to tender in October 2020 for a fleet of 10 trains with self-power capability.
While a preferred bidder has been identified, the business case to proceed with the procurement is awaiting approval, but Mr Horne is still hopeful this project can be progressed.
The current plan envisages the new trains broadly replacing the ‘225s’ on Leeds and York diagrams, but a major benefit with the new fleet would be during engineering work – at present LNER has to withdraw services to places such as Harrogate and Hull to concentrate its bi-mode Azumas on services using non-electrified diversionary routes, and having more stock with self-power capability would ease the issue.
Currently, LNER has these Azumas and InterCity 225s in its fleet.
- Five-car bi-mode Class 800 trains – 10
- Nine-car bi-mode Class 800 trains – 13
- Five-car electric Class 801 trains – 12
- Nine-car electric Class 801 trains – 30
- Nine-car electric ImterCity 225 trains – 8
Note.
- There are 23 bi-mode trains and 50 electric trains.
- There are 167 bi-mode carriages and 302 electric carriages.
- Currently 31.5 % of the trains are bi-mode.
- With ten new bi-mode trains and no InterCity 225 trains, 44 % of the fleet will be bi-mode.
Is this increase in the percentage of the fleet, that are bi-mode acceptable?
I wonder, if there is a more affordable and flexible way to increase the fleet size.
In the Wikipedia entry for the Class 800 train, there is a section, which is entitled Traction And Generator Units, where this is said.
The Class 800 and Class 802 bi-mode are equipped with three GU per five-car set and five GU per nine-car set; a five-car set has a GU situated under vehicles 2/3/4 and a nine-car set has a GU situated under vehicles 2/3/5/7/8. In comparison, the electric-orientated Class 801 features a single GU for a five to nine-car set, which provides emergency power for limited traction and auxiliaries if the power supply from the overhead line fails. By adding or removing GUs, a Class 800 can be converted into a Class 801 and vice versa.
Let’s look at LNER’s needs, which are actually two separate sub-needs.
- There is a need for ten new trains to replace the InterCity 225 trains.
- There is a need to increase the size of the bi-mode fleet to be able to use the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line and other non-electrified routes to by-pass engineering works.
Note.
- I suspect that as Mr Horne explained, there are only five or possibly four InterCity 225s diagrammed on a particular day, then perhaps ten five-car bi-mode Class 800 trains, might be able to cover for the retirement of the InterCity 225s.
- These trains would work as pairs to Leeds and York to replace the InterCity 225 capacity.
- If required they could split and join at Leeds and York to serve other destinations.
- The diversion route of the Great Eastern Joint Line has an unelectrified distance of 93.7 miles and the route is electrified at both ends.
- Would a battery-electric Class 800 train handle this distance? I suspect if Stadler can do it, then Hitachi and Turntide Technology will be able to do it too!
LNER will have replaced the InterCity 225s and acquired ten new five-car blockade runners.
As an order for ten new five-car battery-electric trains, is not to be sneezed at, I suspect Hitachi will make sure that their new battery-electric variants have enough range.
So this would mean that the range of a five cat battery-electric Class 800 train, should be in excess of 93.7 miles.
It should be noted that the five-car Class 800 and Class 802 trains have specific advantages when it comes to converting them to battery-electric trains.
- They are modern trains, that are still in production, every bit of information about the train is known down to the last nut, bolt and plastic clip.
- Like most modern trains, hey have a sophisticated computer system controlling the train.
- They have spaces for three, four or maybe even five diesel engines under the floor, which could be used for a battery-pack in every car designed to hold a diesel engine.
- The train has an electric bus between nose and tail.
- As is shown, when the trains change between diesel and electric, the pantograph can go up and down with all the alacrity of a whore’s drawers.
- The trains can be converted between bi-mode and electric, by adding or removing diesel packs. I doubt this feature will be removed, as batteries replace diesels.
With my Electrical and Control Engineer’s hard hat on, I doubt there is anything to stop a Class 800 or Class 802 train being fitted with three or more batteries to create a 125 mph train, with a range approaching two hundred miles on battery power.
The initial name of these Hitachi trains was the Hitachi Super Express. Is this train the Hitachi Super Battery Express?
But it would appear, that for their initial needs, LNER, just need a range to handle the near hundred miles of the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line.
Inverness and Aberdeen will come later.
Hull Trains
This page on the Lumo web site is entitled Greener Travel Between Edinburgh And London.
These are the first three paragraphs.
A new, 100% electric rail service is to start running between London and Edinburgh with fares for as little as £14.90 in a bid to encourage greener and more affordable travel between the capitals.
Called Lumo, it will provide low-carbon, affordable long-distance travel for over 1 million passengers per year. Over 74,500 passengers currently fly between Edinburgh and London each month3.
And with single tickets between the capitals starting from just £14.90, Lumo will be a comfortable, convenient alternative to flying that is affordable for all. Some 60% of all single fares will be available at a cost of £30 or less.
I’m sure Hull Trains, who are owned by First Group like Lumo would like to position themselves in the 100 % electric low-carbon box too!
Currently, Hull Trains’s five-car Class 802 trains, run 88.6 and 72.2 miles using diesel on round-trips to Beverley and Hull respectively from London.
If batteries were fitted to their trains to give a battery range of around a hundred miles, Hull Trains could call themselves 100 % electric.
No new infrastructure would be required, but a short length of overhead electrification in a convenient platform at Hull station would ensure the train left for London and Beverley with a full battery.
The pictures show Hull Trains’s Class 802 train in Platform 7 at Hull station.
Penzance And Taunton
This to me is the key section as if you can run a battery-electric train between these two stations it allows so many of the services to be run using zero-carbon traction.
These are distances from Taunton.
- Exeter St. David’s – 30.7 miles
- Newbury – 89.6 miles
- Okehampton – 55.3 miles
- Paignton – 59.0 miles
- Patchway – 51.7 miles
- Plymouth – 82.8 miles
Note.
- I’ve added Okehampton, as I feel that if Dawlish had another encounter with Poseidon, Okehampton with its proposed Parkway station on the A30 could be the terminus for coaches to and from Cornwall.
- All would be possible with a battery-electric train, with a hundred-mile range, leaving Taunton with a full battery.
- Charging could be needed at Okehampton and Paignton.
What is needed is some form of charging in the Taunton area.
This OpenRailwayMap shows Taunton station.
Note.
- The station has four through platforms.
- All Great Western Railway services to and from Devon and Cornwall stop in the station.
- I feel it would be possible to electrify the station, so that all stopping trains could charge the batteries.
But the problem would be, that as typically trains only stop for a couple of minutes at Taunton, there may not be enough time to take enough charge on board.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the track between Wellington and Collumpton, between Taunton and Exeter.
Note.
- The black line is the railway between Taunton and Exeter.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map indicates the position of the proposed Wellington station.
- Collumpton is in the South-West corner of the map and has also been put forward for a new Collumpton station.
- I talked about the reopening of these two stations in Reopening Of Wellington and Cullompton Stations.
- The M5 to the North of Collumpton runs closely alongside the railway.
- According to Real Time Trains, it takes just under ten minutes to go the thirteen miles between Wellington and Collumpton.
This Google Map shows a section of the M5 North of Collumpton.
And this Google Map shows Tiverton Parkway station.
Note how the railway runs alongside the M5 to the West.
I feel that if the two new stations of Wellington and Collumpton are built between Taunton and Exeter St. David’s, then why not partially electrify the route, so that all trains would leave or pass through Taunton and Collumpton stations with full batteries.
- Going West the trains would reach Exeter St. David’s, Okehampton or Plymouth.
- Going East trains would reach Newbury for Reading and Paddington, and Patchway for Cardiff.
I believe that a battery-electric solution is possible, that would enable the decarbonisation of the Great Western Main Line all the way to Penzance.
Possible Regular Services Between West Somerset Railway And Taunton
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Advent.
These are the introductory paragraphs.
Hopes are growing that regular scheduled train services will once more operate between the West Somerset Railway (WSR) and the national rail network.
There is an increasing interest in re-opening long-closed stations and lines on the network. To this end, a partnership working group has been set up to look at the prospects of running scheduled trains between WSR’s Bishops Lydeard station and Taunton, which would safeguard the WSR’s long-term future.
The working group comprises representatives of the Heart of South West Local Enterprise Partnership, Great Western Railway, Network Rail, Somerset County Council, and WSR Plc.
Given the success of the reopened Okehampton station, that I wrote about in Success For The Dartmoor Line, where 2,500 passengers a week have used the trains since last November, I wonder if Somerset is aiming to emulate Devon’s success, with the West Somerset Railway.
There are certainly similarities between the two routes.
Connection To The County Town
Both routes connect to the county town.
- The Dartmoor Line connects to Exeter, which is the county town of Devon.
- The West Somerset Railway connects to Taunton, which is the county town of Somerset.
As the county town usually contains important local services like the council offices and the Courts, this is often convenient.
Connection To The Great Western Railway
Both routes could have excellent connections to the Great Western Railway.
- Exeter St. David’s station is a major interchange.
- Taunton station could be a more important interchange.
Note.
- Both stations have connections to Bristol, London and Cornwall.
- The two stations are well-connected to each other.
- Both stations have six platforms, which include some bay platforms for branch line services.
This Google Map shows the less developed Taunton station.
Note that there appears to be lots of space for development of rail and related development.
Both Branches Were/Are In Use Before Development
Before the Dartmoor Line was reopened, the route was in occasional use for both freight and passenger trains. Great Western Railway have in recent years run InterCity125 trains to Okehampton station.
With reopening the line to Okehampton, there was no major viaduct or bridges to rebuild, although Network Rail took the prudent decision to relay the track.
It would appear that the West Somerset Railway has similar use for both freight and passenger trains. How much work will be needed to bring it up to an acceptable standard.
Great Western Railway Are Providing Initial Weekend Services
On the Dartmoor Line services started between Exeter and Okehampton in 2019 and Wikipedia says this about initial services between Taunton and Bishops Lydeard station.
In 2019, the WSR entered into a partnership with the modern Great Western Railway (GWR) to operate Summer Saturday services to Bishops Lydeard from Taunton beginning on 27 July 2019. The introduction of these GWR services will mark the first time the station has been connected to the rest of the national rail network since its initial closure in 1971.
Is history going to repeat itself?
The First Step
This paragraph from the Rail Advent article, indicates the first step to reopening a service between Taunton and Minehead.
The first task will be to look at the simplest and most effective way in which the link between the WSR and the mainline can be improved, signalled, and operated. An outline business plan will then be developed to estimate how much it would cost.
This Google Map shows the link between the West Somerset Railway and the mainline.
Note.
- The large triangular junction.
- The Bristol-Exeter railway runs East-West across the bottom of the map.
- Minehead is to the North.
- Taunton is to the East.
- A disused line to Barnstaple is to the West.
- The site to the West of the top of the triangular junction is a ballast cleaning site.
It does appear that there could be the space to create an efficient junction linking the two railways.
Initial Regular Services
This was one of the introductory paragraphs.
There is an increasing interest in re-opening long-closed stations and lines on the network. To this end, a partnership working group has been set up to look at the prospects of running scheduled trains between WSR’s Bishops Lydeard station and Taunton, which would safeguard the WSR’s long-term future.
This page on the Railway Touring Company web site is entitled The West Somerset Steam Express.
This paragraph describes the trip.
This series of trains from London Paddington to Minehead features haulage by two steam locomotives in one day.
One steam locomotive will haul our train from London Paddington to the West Somerset Railway at Bishops Lydeard.
The Heritage Railway will then provide a steam locomotive to haul our train to Minehead and back. This provides a truly fascinating day out travelling through beautiful scenery to the Bristol Channel coast.
So it looks like, the initial services on the between Taunton and Bishops Lydeard stations, will duplicate services that are already planned on a very much less frequent basis.
Bishops Lydeard Station
Bishops Lydeard station is the station, where mainline and West Somerset services meet.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the track layout at the station.
Note.
- The station is the Southern terminus of the West Somerset Railway.
- Track is single to the North and South of the station.
- Bishops Lydeard station has two platforms.
- There is a passing loop.
If the terminal station has a serious problem, it doesn’t appear to have much parking.
So it would appear, that a link to Taunton might improve the finances of the West Somerset Railway, by attracting more visitors.
Onward To Minehead
This OpenRailwayMap shows the last section of the West Somerset Railway to Minehead.
Note.
- Minehead station is in the North West corner of the map.
- Minehead station appears to be a well-equipped station, with two platforms.
- Minehead station even has a turntable for turning locomotives.
- There are four or five stations close to the coast.
The Wikipedia entry for Minehead, says this about the town.
The parish of Minehead has a population of approximately 11,981, making it the most populous town in the western part of the Somerset West and Taunton local government district, which in turn, is the worst area in the country for social mobility.
The West Somerset Railway could become both a useful and a real bucket-and-spade railway. Surely, that could generate revenue and level-up the area.
Financing
If you want something to work well, you must get the finances right.
I have lived in Dalston in London for twelve years now. When I moved here after my wife died and I had had a serious stroke, which left me unable to drive, I relied on an antiquated mainly bendy-bus-based public transport system.
Then along came the Overground and fleets of shiny new buses and Hackney and Dalston in particular was more than levelled up with London’s more salubrious boroughs.
Shopping improved with M & S returning after at least seventy years. There’s even a Pret, which boomed during the pandemic.
Transport for London got the financing for the Overground right and they created a success.
Conclusion
Can the initial working group find a financial model so that the West Somerset Railway can do for West Somerset, what the Overground has done for Dalston and the Dartmoor Line appears to be doing for Devon?
I thoroughly hope so!
Bath Spa Station – 28th July 2020
I took these pictures as I twice passed through Bath Spa station.
These are my thoughts.
Electrification Gantries On The Platforms
As somebody, whose eyesight is on the wane, I am not a lover of electrification, where the gantries are bolted to the platforms. These pictures show some installations of this type at Crouch Hill station.
Would electrification gantries like these, be appropriate in Bath Spa station?
Could Lightweight Electrification Gantries Be Placed Between The Tracks?
These pictures show the wide gap between the two tracks in Bath Spa station.
Could double-track lightweight structures, based on a design like this be placed between the tracks?
These structures are made out of laminated wood and are surely a possibility.
A Makeover For Bath Spa Station
If you look at much of the woodwork and paint in the fabric of the station, it appears tired and in need of refurbishment.
Whether the station is electrified or not, the station will need a high-class makeover.
Services Through Bath Spa Station
Three train companies run services through Bath Spa station.
- CrossCountry which only operates diesel trains.
- Great Western Railway operates Class 800 electro-diesel trains and some assorted diesel trains.
- South Western Railway only operates Class 159 diesel trains.
There are also some freight services hauled by diesel locomotives.
Trains leave Bath Spa station using one of three routes via either.
- Bristol Temple Meads station, which is 11.5 miles away without electrification.
- Chippenham station, which is where the electrification to London starts and is 13 miles away.
- Westbury station, which is on the Reading and Taunton Line and 17 miles away without electrification.
Most trains seem to go via Bristol Temple Meads station.
- The distance between Bristol Temple Meads and Chippenham stations are 24.5 miles.
- The distance between Bristol Temple Meads and Westbury stations are 28.5 miles.
Neither distance is that long.
An Alternative To Full Electrification
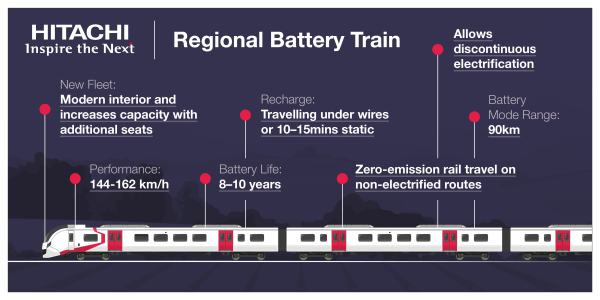
When I look at the distances between Bristol Temple Meads, Chippenham and Westbury stations, they tell me that they are within the range of Hitachi’s Class 800 train with a battery electric capability or Regional Battery Train, which is described in this infographic from the company.
The proposed 90 km or 56 mile range would even be sufficient take a train between Chippenham and Bristol Temple Meads stations on a return trip.
Notes for each station follow.
Bristol Temple Meads
Charging facilities would be needed.
Destinations in battery range would include.
- Bristol Parkway – 6 miles
- Cardiff Central – 5 miles to the electrified Great Western Main Line.
- Cheltenham Spa – 41 miles
- Gloucester – 39 miles
- Taunton – 45 miles
- Weston-super-Mare – 19 miles
Note.
- Return trips to Bristol Parkway and Western-super-Mare would be possible.
- The other destinations will need charging facilities.
Bristol Temple Meads station could become a major hub for battery trains.
All local services and all passing longer distance services could be trains with a battery capability.
I write more about Britol Temnple Meads station as a battery train hub in Bristol Temple Meads Station – 28th July 2020.
Chippenham
A train would leave Chippenham station with a full battery after charging on the fully-electrified route from London.
Chippenham and Weston-super-Mare would be in battery range with a charging facility at Weston-super-Mare station.
It should be noted that every extra mile of electrification past Chippenham, can be added to the distance electric trains with a battery capability can reach.
Westbury
Charging facilities would be needed.
Destinations in battery range would include.
- Salisbury – 24 miles.
- Southampton – 49 miles to the electrified South Western Main Line, at Southampton Central station.
- Weymouth – 53 miles to the electrified South Western Main Line at Dorchester Junction.
Note.
- A return trip to Salisbury would be possible.
- Trains would need to have the capability to access 750 VDC third-rail electrification.
- A few extra miles of electrification may make operation South from Westbury station easier, more reliable and allow more destinations to be included.
Westbury station could be a major hub for battery trains.
This Google Map shows Westbury station and the lines around it.
I would probably electrify a few miles either side of Westbury, so that passing trains could be in contact with the overhead wires for perhaps five to ten minutes and take a good long drink.
- Electrification could be either 25 KVAC overhead or 750 VDC overhead.
- Newbury, where the electrification to London starts is 42 miles away and trains can pick it up at speed.
- Taunton is 47 miles away and could be electrified to Exeter St. Davids.
Great Western Railway could run all their services between London Paddington and the South-West using Class 800 trains with a battery capability.
Conclusion
The prolitical, heritage and engineering problems of electrifying through Bath Spa station can be voided, by electrification and charging facilities at stations like Bristol Temple Meads, Taunton, Westbury and Weston-super-Mare.