Highview Surpasses Half A Billion Pounds Of Funding With Latest £130m Capital Raise For Phase One Of Long Duration Energy Storage Facility At Hunterston, Ayrshire
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news story from Highview Power.
Funding Round Enables Build Of “Stability Island” Which Will Deliver Crucial Grid Stability Services; Represents Phase One Of LDES Facility At Hunterston
These two paragraphs outline the funding raised and where it will initially be used.
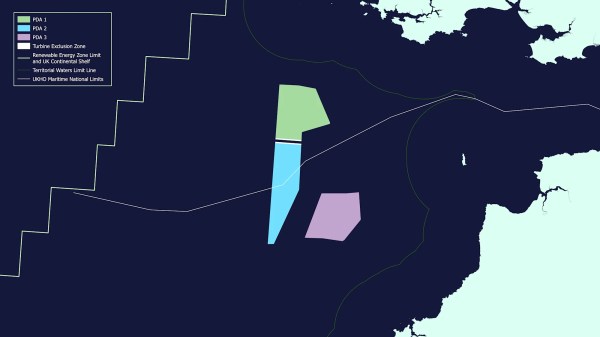
Highview has secured £130 million in funding to commence work on the first stage of its planned 3.2GWh hybrid long-duration energy storage solution in Hunterston, Scotland. This brings the total raised to commercialise and roll out Highview’s long duration storage solutions to over £500 million.
This latest investment round, involving Scottish National Investment Bank (SNIB), the British multinational energy and services company Centrica, and investors including Goldman Sachs, KIRKBI and Mosaic Capital, will fund construction of the first phase of the Hunterston project, a “stability island”, which will provide system support to the electricity grid.
The Concept Of The Stability Island
This paragraph describes the concept of the Stability Island.This stability island is a key component of Highview’s LDES system. It can operate independently of the energy storage elements and will deliver critical inertia, short circuit and voltage support to the UK power grid. The asset will support the grid at a location that faces considerable stability challenges. In turn, this will enable more power to be transmitted from the point of generation in Scotland to areas of high demand, preventing curtailment of wind energy across Scotland
A large amount of energy will be routed through Hunterston from Scotland to England, Wales and the island of Ireland and the stability island will tightly control the flow of energy.
The Facility At Hunterston
These two paragraphs describe the facility at Hunterston.
As well as the stability island, the facility at Hunterston will also eventually incorporate a hybrid long duration energy storage system, combining both liquid air storage and lithium-ion batteries for greater operational performance. This means that the entire facility will be able to send more power to the grid for longer, in a flexible way, maximising the asset for the benefit of the system operator.
The energy storage element of the Hunterston facility received significant validation recently, when it was named as an eligible project for Ofgem’s Cap and Floor support scheme for long duration energy storage, along with a planned facility at Killingholme, Lincolnshire.
I suspect the Stability Island will actually distribute the energy to where it is needed.
Ocean Winds Secures Third Celtic Sea Floating Wind Site
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Ocean Winds has secured the third floating offshore wind site in the Celtic Sea, offered through the Crown Estate’s Round 5 auction earlier this year. The developer is joining Equinor and the Gwynt Glas joint venture, which were awarded rights for two of the three sites offered in Round 5 in June.
This paragraph outlines Ocean Winds’s deal.
On 19 November, the Crown Estate said that Ocean Winds was set to be awarded the rights for a third floating offshore wind site in the Celtic Sea.
There would now appear to be three Celtic Winds deals for wind farms.
- Gwynt Glas – 1.5 GW
- Ocean Winds – 1.5 GW
- Equinor – 1.5 GW
Note.
- 4.5 GW will be able to power a good proportion of South Wales and the South-West peninsular.
- In Gwynt Glas And South Wales Ports Combine Strength In Preparation For Multi-Billion Floating Wind Industry, I talk about partnerships between the wind farms and the ports.
- If you sign up for a large wind farm from the Crown Estate, do you get to have afternoon tea with Charles and Camilla in the garden at Highgrove or even Buckingham Palace?
This map of the wind farms is available from download from this page on the Crown Estate web site.
Note.
- Gwynt Glas is in green.
- Ocean Winds is in blue.
- Equinor is in mauve.
- The white dot to the East of the wind farms is Lundy Island.
This triple wind farm is certainly well-placed to supply power to Cornwall, Devon and South Wales.
Cornwall Insight Forecasts Lower Household Energy Bills In January
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Solar Power Portal.
This is a paragraph from the article.
The Default Tariff Cap is set by the UK’s energy regulator Ofgem as the maximum rate per unit and standing charge that can be billed to customers for their energy use. Cornwall Insight’s latest forecast predicts the cap will fall to £1,733 a year for a typical dual fuel household in the first quarter of 2026.
Consider.
- I am on a dual-fuel tariff for gas and electricity.
- At present, I pay £159 per month or £1,908 per year.
If I was on the new price cap, I’d pay £144.42 per month or about 10 % less.
In Future Will North Africa Be Providing Renewable Energy To Europe?
I believe it is likely that mainland Europe will be getting a considerable amount of renewable energy from Iceland, Ireland, Norway and the UK, and the seas to the North of Europe.
But what about the potential of providing Europe with renewable energy from North Africa?
I asked Google AI, the question in the title of this post and received this answer.
Yes, in the future, North Africa is expected to supply renewable energy to Europe, with potential exports of up to 24 GW through subsea interconnectors. This will be driven by North Africa’s vast solar and wind resources, a strong push for renewable energy in the region, and European demand for clean power. Major projects are planned, but challenges like supply chain constraints and financing hurdles need to be addressed for these projects to be successful.
These are interconnectors I can find.
ELMED
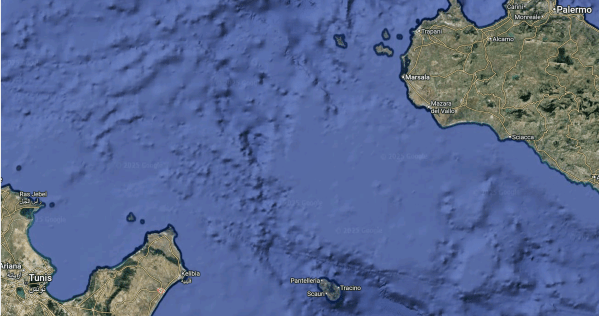
The ELMED interconnector, also known as the Tunisia-Italy interconnector, is a planned 200 km, 600 MW high-voltage direct current submarine power cable between Italy and Tunisia.
This map shows the route of the ELMED interconnector between Tunisia and Italy.
Note.
- Tunis in Tunisia, is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- East of Tunis on the coast is a red blob, which marks the town of Menzel Temime, where the interconnector will connect to a newly-built substation.
- Palermo in Sicily, is in the North-East corner of the map.
- West of Palermo on the North-West coast of Sicily is Trapani, where the interconnector will make landfall in Italy and connect to a substation at .
As with many things engineering designed by Italians, this seems to be an interconnector with a certain simplicity and style.
The Wikipedia entry for the ELMED interconnector gives these further details.
The total cost is budgeted at €850 million.
XLinks
XLinks is a project to build a 3.6 GW interconnector between Morocco and Devon, that appears to have been rejected by the current government.
XLinks shows what engineers think could be possible. More details are given in the Wikipedia entry for the project.
UK Breaks Yearly Record For Rooftop Solar PV Installations
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Solar Power Portal.
This is the sub-heading.
The 2025 rooftop installation figures represent the fifth consecutive year of year-on-year increases in rooftop solar deployments, according to MCS.
A few nuggets from the article.
- The UK has seen rooftop solar installations increase year-on-year since 2021.
- UK rooftop solar PV installations have hit 206,682 so far in 2025, a record for the sector that has pushed the total number of certified small-scale solar installations in the UK to 1.85 million.
- This is according to the latest figures from the Microgeneration Certification Scheme (MCS) Their web site is here.
- Somerset and Cornwall leading the country in installations, with 3,741 and 3,726, respectively. North Yorkshire (2,780), County Durham (2,668) and Wiltshire (2,545) make up the rest of the top five.
Great Britain is described as a very mature market. It certainly seems healthy too!
My Solar Panels
I have solar panels on the flat roof of my house.
In the last twelve months I have been paid.
- 29th November 2024 – £129.66
- 24th February 2025 – £31.58
- 27th May 2025 – £46.27
- 29th August 2025 – £114.63
Note.
- This is a total of £322.16
- There has been no servicing or charges from my energy supplier.
- My solar panels appear to have been installed in April 2016, according to the date on My Solar Panels Are On The Roof.
They’ve certainly been no trouble,
Data Centre In The Shed Reduces Energy Bills To £40
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
An Essex couple have become the first people in the country to trial a scheme that sees them heat their home using a data centre in their garden shed.
These three introductory paragraphs add some detail.
Terrence and Lesley Bridges have seen their energy bills drop dramatically, from £375 a month down to as low as £40, since they swapped their gas boiler for a HeatHub – a small data centre containing more than 500 computers.
Data centres are banks of computers which carry out digital tasks. As the computers process data, they generate lots of heat, which is captured by oil and then transferred into the Bridges’ hot water system.
Mr Bridges, 76, says keeping his two-bed bungalow near Braintree warm was a necessity as his wife has spinal stenosis and is in “a lot of pain” when it gets colder.
I think this simple idea is absolutely brilliant and very technically sound.
Here are some further thoughts.
It Would Be Ideal For A House Like Mine
My house is a modern three-bedroomed house with a garage and when I asked Google AI how many UK houses had garages, I received this answer.
Approximately 38% of dwellings in England have a garage, according to a 2020 report. While a specific UK-wide figure is not available, extrapolating this percentage to the total number of UK dwellings suggests there are over 10 million houses with garages, though the actual figure may vary across different regions.
Looking at the picture in the BBC article, I feel that this HeatHub could fit in my house.
I would expect that any house with a garage, a small garden or a big enough boiler space could accommodate a HeatHub.
Obviously, the house would need.
- A boiler, that provides heating and hot water.
- A good broadband connection.
My house has both.
Would My House’s Heating System Need To Be Modified?
It looks like it’s just a boiler replacement, so I don’t think so, but it may need to be moderbnised with digital controllers to get the best out of the system.
Will There Be Other Systems Like Thermify’s Heat Hub?
Some of our electricity suppliers seem very innovative and the market is very competitive.
Would they just sit back and let coompetitors take their customers? I doubt it!
So I suspect there will be other systems, each with their own features.
I have already, written about heata, which uses similar principles to give affordable hot water in British Gas Partners With heata On Trial To Reuse Waste Heat From Data Processing.
The BBC article gives some examples of data centres used to provide heating, so it is worth reading the full article.
Why The East Of England Can Be An Offshore Hydrogen Leader
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the Eastern Daily Press.
This is the sub-heading.
The East of England’s connected energy system puts it in prime position to be a key player in the offshore hydrogen economy, says Anne Haase, chair of the Hydrogen East Industry Advisory Group.
These two paragraphs add a level of detail.
The East of England’s energy story is increasingly being written onshore. The region is re-writing the playbook for how a sustainable, connected energy system could take shape and deliver. The region isn’t just about tourism – we have a whole industrial ecosystem dwarfing that sector.
We are a net energy exporter to the rest of the UK. We transmit more than 30% of gas, and our infrastructure offers supply security and sustainable energy to not just our region, but to London and the South East.
This is very much a must-read article.
UK, French, And Irish Ports Join Hands In Global Floating Wind Collaboration
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s Associated British Ports (ABP) has teamed up with France’s BrestPort and Ireland’s Shannon Foynes Port to establish the Global Floating Offshore Wind Ports Alliance (FLOW Ports Alliance) to help bring together major floating offshore wind ports across the world and unlock the technology’s full potential.
These first two paragraphs add more detail.
The FLOW Ports Alliance aims to recruit ports in Europe to collaborate on FLOW port design, standardisation, and best operational practices.
It plans to strengthen and accelerate compliant knowledge and experience exchange between ports, share best practices as they emerge through demonstration projects, and share innovations to the benefit of the global FLOW network.
Surely, a global network of ports that can handle construction, operation and maintenance of a range of floating wind platforms, is an excellent idea.
All Recyclable Blades Installed At RWE’s 1.4 GW UK Offshore Wind Farm
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
All 150 recyclable blades have been installed at the 1.4 GW Sofia offshore wind farm, with more than half of the wind turbines now in place at the UK construction site.
These three paragraphs add more details.
All 150 recyclable blades are now installed, with each turbine utilising 50 sets of three blades, marking the UK’s first large-scale use of this technology at an offshore wind farm, RWE, the developer, said.
The recyclable rotor blades used at Sofia are manufactured by Siemens Gamesa at its Hull factory and use a unique resin that enables easy separation of component materials at the end of each blade’s operational life cycle.
In addition, 62 out of 100 Siemens Gamesa 14 MW turbines have now been installed at the site located 195 kilometres off the UK’s east coast. Each turbine features 108-metre blades and a 222-metre rotor diameter. Cadeler is responsible for the installation of the wind turbines.
Note.
- The Sofia wind farm has a hundred turbines, each with the customary three blades.
- Currently the 13 MW Siemens Gamesa turbines in Dogger Bank A and Dogger Bank B are the largest turbines in British waters.
- Sofia’s at 14 MW will be larger.
- But 15 MW monsters are on their way, with RWE’s Norfolk zone appearing to favour 15 MW Vesta turbines.
At the present time, turbine size seems to be creeping up. I would expect this to happen, as turbines become more affordable.
CO2 to SAF: A One-Step Solution
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on the Chemical Engineer.
This is the sub-heading,
Oxford spinout OXCCU has launched a demonstration plant at London Oxford Airport to trial its one-step process of turning CO2 into sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). Aniqah Majid visited the plant to investigate the benefits of its “novel” catalyst
One word in this sub-heading caught my eye.
When I was a young engineer in the Computer Techniques section in the Engineering Department at ICI Plastics Division, I did a small mathematical modelling project for this chemical engineer, using the section’s PACE 231-R analogue computer.

He was impressed and gave the 23-year-old self some advice. “You should apply that beast to catalysts.”
I have never had the chance to do any mathematically modelling of catalysts either at ICI Plastics or since, but I have invested small amounts of my own money in companies working with advanced catalysts.
So when OXCCU was picked up by one of my Google Alerts, I investigated.
I like what I found.
The three raw ingredients are.
- Green Hydrogen
- Carbon dioxide perhaps captured from a large gas-fired powerstation like those in the cluster at Keadby.
- OXCCU’s ‘novel’ catalyst, which appears to be an iron-based catalyst containing manganese, potassium, and organic fuel compounds.
I also suspect, that the process needs a fair bit of energy. These processes always seem to, in my experience.
This paragraph outlines how sustainable aviation fuel or (SAF) is created directly.
This catalyst reduces CO2 and H2 into CO and H2 via a reverse water gas shift (RWGS) process, and then subsequently turns it into jet fuel and water via Fischer-Tropsch (FT).
The Wikipedia entry for Fischer-Tropsch process has this first paragraph.
The Fischer–Tropsch process (FT) is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatures of 150–300 °C (302–572 °F) and pressures of one to several tens of atmospheres. The Fischer–Tropsch process is an important reaction in both coal liquefaction and gas to liquids technology for producing liquid hydrocarbons.
Note.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that to obtain the carbon monoxide and hydrogen or syngas for the Fischer-Tropsch process, excess hydrogen is used, so the OXCCU process may need a lot of affordable hydrogen, some of which will be converted to water in the RWGS process.
- The high temperatures and pressures for the Fischer-Tropsch process will need a lot of energy, as I predicted earlier.
But I don’t see why it won’t work with the right catalyst.
The Wikipedia entry for the Fischer-Tropsch process also says this.
Fischer–Tropsch process is discussed as a step of producing carbon-neutral liquid hydrocarbon fuels from CO2 and hydrogen.
Three references are given, but none seem to relate to OXCCU.
OXCCU have a web site, with this title.
Jet Fuel From Waste Carbon
And this mission statement underneath.
OXCCU’s mission is to develop the world’s lowest cost, lowest emission pathways to make SAF from waste carbon, enabling people to continue to fly and use hydrocarbon products but with a reduced climate impact.
It looks like they intend to boldly go.
Conclusion
My 23-year-old self may have been given some good advice.