Very Light Rail Trial For Heathfield Branch?
The title of this post, is the same as that of an article in the May 2024 Edition of Modern Railways.
This is the first four paragraphs.
Investigations are ongoing as to whether the disused Heathfield branch line in Devon could be used as a test route for the Revolution Very Light Rail (RVLR) vehicle.
Heathfield Rail Link Association (HRLA) says a survey has been completed along the four-mile line from Newton Abbot, which was last used by timber trains in 2017 and hasn’t seen a regular passenger service since 1959.
The work, by Lampitt Rail, has been completed for Eversholt Rail, one of the firms behind RVLR, a hybrid vehicle, which aims to help reduce costs on existing branch lines and those earmarked for reopening.
A spokesman for Eversholt said the line is one of more than 200 potential opportunities for RVLR ahead for 2026, when it’s hoped tests will start on branch lines around the country using three new battery prototypes.
These are my thoughts and observations.
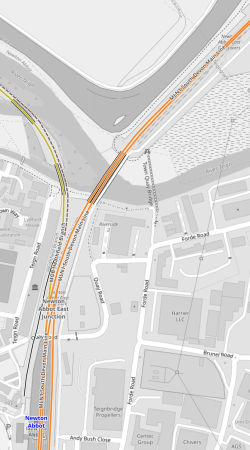
The Heathfield Branch
This OpenRailwayMap shows the Heathfield branch.
Note.
- The former site of Heathfield station is indicated by the blue arrow.
- The yellow track is the Heathfield branch.
- The orange track is the Cornwall Main Line, that goes through Newton Abbot station to Plymouth and Penzance stations.
This second OpenRailwayMap shows the track layout Newton Abbot station.
As there are three platforms, I suspect that matters can be arranged to turn an occasional train from the branch.
How Will The Revolution VLR Be Charged?
The Modern Railways article says this about charging.
Eversholt Rail and partner firm Transport Design International have stated they will build three new battery-powered vehicles for the 2026 tests, which will need rapid charging points, made up of two rails in-between the running lines which would contact a shoe hanging from the train. HRLA is working with UK Power Networks to find locations for these chargers, including at Newton Abbot.
It sounds very much like the Vivarail/GWR Fast Charge equipment.
What Will Be The Range Of The Revolution VLR?
The range of the Revolution VLR has not been stated.
But this is stated in the Modern Railways article.
Heathfield Rail Link Association (HRLA) says a survey has been completed along the four-mile line from Newton Abbot.
So will the train be able to do a round trip on one charge or just a single journey?
Or could this route be a strong possibility, as the Revolution VLR has the range to do a round trip on one charge?
Is Alstom’s Proposal For A Service Between London Euston And Wrexham Part Of A Cunning Plan?
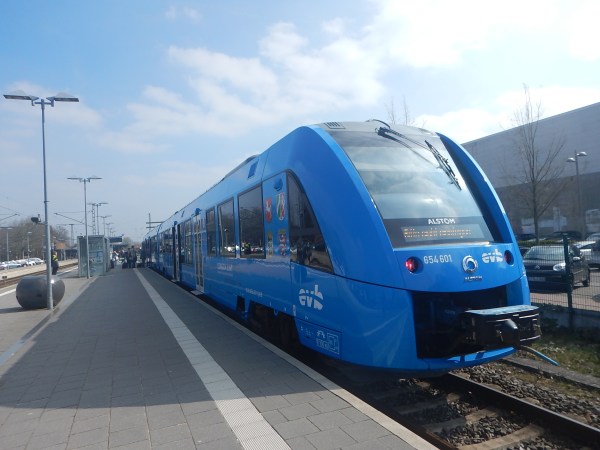
Alstom have built and introduced into service between Buxtehude and Cuxhaven in Germany, the Coradia iLint hydrogen-powered train. The prototype has performed demonstrations in Austria, Canada, The Netherlands and Saudi Arabia.
This picture shows a Coradia iLint in Germany.
In the UK, Alstom had a plan to convert redundant Class 321 trains into a fleet of hydrogen-powered trains called Breeze, which I wrote about in Hydrogen Trains Ready To Steam Ahead, in January 2019.
This visualisation is from Alstom.
I suspect it didn’t appeal to train companies, as no orders appear to have been received.
But you can’t criticise Alstom for not trying, as in November 2021, they signed an agreement with Eversholt Rail Group to develop a hydrogen-powered Aventra, which I wrote about in Alstom And Eversholt Rail Sign An Agreement For The UK’s First Ever Brand-New Hydrogen Train Fleet.
This visualisation is from Alstom.
Visually, it looks just like any other Aventra and much better than the previous Breeze design.
In March 2018, I wrote Bombardier Bi-Mode Aventra To Feature Battery Power, which was based on this article in Rail Magazine.
These are a few points from the article.
- Development has already started.
- Battery power could be used for Last-Mile applications.
- The bi-mode would have a maximum speed of 125 mph under both electric and diesel power.
- The trains will be built at Derby.
- Bombardier’s spokesman said that the ambience will be better, than other bi-modes.
- Export of trains is a possibility.
- Bombardier’s spokesman also said, that they have offered the train to three new franchises. East Midlands, West Coast Partnership and CrossCountry.
Have Alstom looked at what they bought from Bombardier and decided the following train is possible, if they add some of their technology?
- A train the size needed by the customer, up to a length of at least ten cars.
- 125 mph under 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- 100 mph with 750 VDC third rail electrification.
- Running on hydrogen away from electrification.
- 100 mph maximum speed running on hydrogen.
- A range of perhaps 500 miles, if it can emulate the hydrogen-powered Coradia iLint.
A train with this specification would have several applications in the UK.
- Fully-electric routes.
- Electric routes with perhaps a hundred miles of unelectrified track.
- Scenic routes, where the Nimbies wouldn’t like electrification.
These points should also be born in mind.
- There are now 110 mph Aventras in service with West Midland Trains on the West Coast Main Line.
- I recently came back from Cardiff to London in a twelve-car Class 387 train and there wasn’t too many unhappy passengers. It was certainly better than a rail replacement bus. I wrote about the trip in Cardiff To Reading In A Class 387 Train.
- Alstom believe you can certainly fit their hydrogen gubbins in an Aventra.
- The hydrogen gubbins appear to be from Cummins, who have a worldwide support network.
- Cummins can also supply complete hydrogen support systems. A truck can refuel the train, at one end of the route?
- Alstom have been doing the market research with the hydrogen-powered Coradia iLint, so I suppose they know what the market needs.
Could Alstom, with help from Cummins, have a zero-carbon 200 kph train and support systems, which has a hydrogen range of up to a thousand kms for export markets like the United States, Africa, Australia, India and South America?
Two big world-leading companies are surely better than one!
But Alstom has one big problem!
How do you fully test a 125 mph hydrogen-powered train?
- I know with aircraft, if you change the engine type on an existing aircraft, you only have to certify the engine and this is done on a Supplementary Type Certificate.
- Is it the same with trains, so a 110 mph Class 730 train, which is in service with West Midlands Trains, could be the basis of certifying a hydrogen-powered Aventra?
- The Coradia iLint was only a change from diesel to a hybrid hydrogen-electric engine, so was it certified this way?
- With the Coradia iLint, it seemed to go into service quite quickly, so did it do much of the testing in service?
I looks to me, that London Euston and Wrexham is an ideal route for a hydrogen bi-mode 125 mph train.
- The route has electrified sections, some of which have high operating speeds.
- The route has a convenient hydrogen supply from INEOS at Runcorn at the Northern end.
- Change between hydrogen and electric power would always take place in a station.
- A round trip needs less than 200 miles of running on hydrogen.
- South of Nuneaton, no hydrogen is used, so the train will be like a Class 730 train, that already uses the route.
- There are depots that can service Aventras on the route.
It is certainly a possibility, that the London Euston and Wrexham service will be used to test and showcase Alstom’s new Hydrogen Aventra.
Bedford And Bletchley For £1.30 Return
I am not talking, rubbish, but that is the ticket price, I was charged to go between Bedford and Bletchley stations today.
Note.
- I bought the two tickets from the machine at Bedford station.
- I did get £0.70 pence off for my Senior Railcard.
These are some more pictures I took along the route.
Note.
- Platform 1a at Bedford station is electrified.
- The train was a Class 150 train, that had had a quality refurbishment.
- The stations were neat and tidy.
- The flyover and the extra platforms at Bletchley station seemed ready for the East West Railway.
- There were several level crossings.
- Platform 6 at Bletchley station is electrified.
- Trains took over fifteen minutes to turn at both ends of the journey.
- Bedford and Bletchley is 16.2 miles
- The train was moderately full both ways.
This press release from London Northwestern Railway is entitled London Northwestern Railway: Full Timetable To Resume On Marston Vale Line As £1 tickets Launched.
This is an extract.
The full hourly train service will resume on Monday 19 February. To celebrate its return and encourage passengers to return to the route, LNR is also announcing a major ticket offer today. For three months from Monday, a single journey between any two stations on the Marston Vale Line will cost just £1 (50p for children). The promotion represents a discount of up to 90% on the usual fare, depending on the journey.
Jonny Wiseman, LNR customer experience director, said: “The return of the full timetable to the Marston Vale Line is fantastic news and marks the end of a frustrating period for our customers.
“Our focus now is on encouraging passengers to make full use of their local train service, which is why we have reduced the cost of a trip on the line to £1 for the next three months.
When were tickets between Bedford and Bletchley, last this price?
Will Bedford And Bletchley Be Electrified?
It is not a question of will, as the route already is.
- Platform 1a at Bedford is already electrified.
- Platform 6 at Bletchley is already electrified.
- The schedule gives battery-electric trains sufficient time to charge, whilst the driver changes ends at the two terminal stations.
- Bedford and Bletchley is just 16.2 miles.
- There is even electrified track from Platform 6 at Bletchley station to Bletchley depot, which is being extended.
All it needs is a small fleet of battery-electric trains, which have a 25 KVAC overhead capability.
These pictures show a Class 321 Renatus.
Note.
- The trains were recently refurbished by Greater Anglia.
- In Eversholt Rail And Vivarail To Develop Class 321 BEMU, I talked about how Eversholt Rail planned to get Vivarail to convert the Class 321 Renatus trains into battery-electric multiple units.
- The Class 321 train is a 100 mph four-car train.
- Four-car trains would future proof the route for many years.
- Thirty trains were converted to the Renatus specification.
These trains converted to battery-electric multiple units could certainly handle Bletchley and Bedford services.
Could Four-Car Battery Electric Multiple Units Handle The Next Phase Of East West Rail?
It is likely, when the East West Rail opens that this could be the service.
- Oxford and Milton Keynes – 2 tph – Calling at Oxford Parkway, Bicester Village, Winslow and Bletchley
- Oxford and Bedford – 2 tph – Calling at Oxford Parkway, Bicester Village, Winslow, Bletchley, Woburn Sands, Ridgmont and Bedford St Johns
- Bletchley and Bedford – 2 tph – Calling at Fenny Stratford, Bow Brickhill, Woburn Sands, Aspley Guise, Ridgmont, Lidlington, Millbrook, Stewartby, Kempston Hardwick and Bedford St Johns
Note.
- tph is trains per hour.
- I have assumed that the existing Bletchley and Bedford service is doubled in frequency.
- I estimate that Oxford and Milton Keynes Central is 41.6 miles.
- I estimate that Oxford and Bedford is 54.7 miles.
This would mean the following.
- Oxford and Bletchley would have a frequency of 4 tph.
- Bletchley and Bedford would have a frequency of 4 tph.
- Oxford station would have to charge and turn 4 tph.
- Bedford station would have to charge and turn 4 tph.
- Bletchley station would have to charge and turn 2 tph.
- Milton Keynes Central station would have to charge and turn 2 tph.
There would need to be some form of charging at Oxford.
But Oxford station has two North-facing bay platforms.
These platforms could be electrified or fitted with a Vivarail/GWR Fast Charger.
As it takes less than fifteen minutes to fully-charge a train, two platforms could charge eight tph.
Battery Traction Trial Ahead As TransPennine Express Fortunes Improve
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette International.
This is the sub-heading.
Overcrowding and short-notice cancellations at state-owned TransPennine Express have declined since the December timetable change, prompting Managing Director Chris Jackson to suggest the operator is in a ‘better place’.
It is a must-read article and the section called Battery Power Trial, says this.
Meanwhile, the Class 802 trainset which was damaged in a shunting accident in March 2022 remains out of traffic. Although No 802 207 has now been repaired, it will not be returning to service yet, as it is receiving modifications for use as a battery testbed.
This will see a 6 m long, 2·2 m wide battery module installed in place of one of the existing engines, which will improve fuel efficiency by using two diesel powerpacks rather than three.
The battery module will provide top-up power for peak demand and give regenerative braking capability when operating in diesel mode, which the trains currently do not have. Arrival and departure at stations is also to be trialled in battery mode to assess noise and air-quality improvements. The train is planned to re-enter traffic in December.
‘We’re supplying that unit to support what we think is a sensible industry scheme to look at whether we can do something to move from bi-mode to tri-mode, which could be beneficial for the industry from a green perspective’, Jackson confirms.
That looks to be a good plan, but I can’t help feeling that battery power for the Class 802 trains has been a long time coming.
This press release from Hitachi is entitled Hitachi And Eversholt Rail To Develop GWR Intercity Battery Hybrid Train – Offering Fuel Savings Of More Than 20%, which announced the project was published on the 15th December 2020.
It will be four years from when Hitachi and Eversholt Rail said go, before the prototype is running.
Is this why LNER bought their new trains from CAF?
Three New Battery-Only Revolution Very Light Rail Vehicles
This title of this post, is the same as that as this press release from Eversholt Rail Group.
These are the three bullet points.
- Eversholt Rail funding three brand-new Revolution Very Light Rail vehicles for passenger trials and ongoing operation.
- Manufactured in the UK by Transport Design International.
- Battery-only propulsion, providing zero-emissions operation.
These three paragraphs fill out the story.
Innovative new lightweight passenger trains that will help decarbonise Britain’s railways are to be trialled after a new deal was announced this week.
The new Revolution Very Light Rail vehicles will run entirely on battery power and could be carrying passengers within three years. A new system of lineside fast charging will mean the whole operation has zero emissions.
Some of Britain’s major rail operators are already showing interest in the RVLR vehicles as they seek to fulfil promises to make rail ‘cleaner’.
This is also said about looking for routes, to trial the new vehicles.
Eversholt Rail and TDI are working with key stakeholders across the UK rail industry to agree routes and services where operators can run passenger-carrying trials using these new vehicles. These trials will generate actual passenger demand data to support business cases for long-term deployment of RVLR vehicles as well as providing further passenger and operator feedback on their design and capabilities.
I have some thoughts and questions.
What Is The Top Speed?
A lot of questions like this are answered by this article on Rail Engineer, which is entitled Very Light Rail – A Revolution.
These can be ascertained from this comprehensive article.
- Top Speed – 65 mph
- Seats – 56
- Wheelchair space
- PRM TSI accessibility compatible
- Tare Weight – 24.8 tonnes
- USB Charging
For comparison these figures relate to a PRM-compliant Class 153 diesel train.
- Top Speed – 75 mph
- Seats – 59
- Tare Weight – 41.2 tonnes
This picture shows one of the Class 153 trains at Matlock Bath station.
There are still around thirty in service in the UK.
Can Two Revolution VLRs Run As A Two-Car Train?
From the pictures on the web, the trains have buffers and space for a coupler, so until someone says they must always run as single units, I’ll assume they can at least run as a pair.
Can A Revolution VLR Recharge Its Batteries Using Conventional 25 KVAC Overhead Electrification?
One route, that is a possibility for running using Revolution VLR must surely be the Greenford Branch, which connects to the electrified Great Western Main Line at West Ealing station.
In this and at several other places on the network, it could be easier to charge the trains using the existing overhead electrification or an extension of it.
Another possibility; the Marston Vale Line is also electrified at both Bedford and Bletchley.
In New Mobile Rail Charging Facility For Long Marston, I talked about how Siemens are developing a mobile charger, which initially will be deployed at Long Marston.
It could be very useful for efficient operation, if the batteries on a Revolution VLR could be charged in a number of places, which included conventional electrification.
If charging only happened, whilst trains were stationary, a lightweight pantograph and appropriate electrical gubbins might be sufficient.
Can A Revolution VLR Replace A Class 153 Train?
I suspect on some routes this will be possible, but on others, the speed or hill-climbing requirements might be too stiff for the lightweight train.
But, if I was designing a train like the Revolution VLR, I’d make sure it fitted as many markets as possible.
The picture was taken at Matlock Bath station on the Derwent Valley Line, which is a single track with a fifty mph limit and an uphill climb. I suspect that the Revolution VLR would be designed to handle the uphill part of the route, but would the train be able to handle the speed of the Midland Main Line to Derby.
The Revolution VLR would probably attract more passengers, so it might be necessary to double up the service by running a pair.
Can A Pair Of Revolution VLRs Replace A Class 150 Train?
I don’t see why not!
Could The West London Orbital Use Revolution VLRs?
This might be a proposed route that could use Revolution VLRs.
The two routes would be.
- West Hampstead and Hounslow.
- Hendon and Kew Bridge.
Both services would use the Dudding Hill Line and serve Neasden, Harlesden, Old Oak Common and Acton, with a frequency of four trains per hour (tph).
Although this service could be run using conventional multiple units, it might be more affordable to use Revolution VLRs charged on sections of line that are already electrified.
Could the Greenford Branch Use Revolution VLRs?
The Greenford Branch would be a classic application and trains could be charged by fitting a charger in the bay platform at West Ealing station.
In An Automated Shuttle Train On The Greenford Branch Line, I did a rough calculation to see if an automated shuttle could achieve four tph.
Four tph might be too ambitious, but automatic trains shuttling along a branch line might be an affordable way to provide zero-carbon trains with an adequate capacity.
- The driver would drive the train using the sort of remote control used for drones.
- The driver would sit in a convenient place on the train, with CCTV to help them see everything.
- When the train was ready to leave, the driver would push a button to tell the train to move to the next station.
- On arrival at the next station, the doors will open.
- The process would repeat along the line.
If this method of operation sounds vaguely familiar, the Victoria Line has used it since 1067.
Although the Victoria Line drivers always sit in the front.
But on a line with no other trains running at the same time, all they need is a good view of the doors.
Branch lines that could be run in this way could include.
Bodmin Parkway and Bodmin General
Brockenhurst and Lymington Pier
Grove Park and Bromley North
Lancaster and Morecambe
Liskeard and Looe
Lostwithiel and Powey
Maidenhead and Marlow
March and Wisbech
Par and Newquay
Plymouth and Gunnislake
Romford and Upminster
Sittingbourne and Sheerness-on-Sea
Slough and Windsor Central
Southall and Brentford
St. Erth and St. Ives
Truro and Falmouth Docks
Twyford and Henley-on-Thames
Watford Junction and St. Albans Abbey
West Ealing and Greenford
Wickford and Southminster
Wymondham and Dereham
TransPennine Express Releases Blueprint For Improving Service And Fleet Upgrade
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Technology Magazine.
This is the sub-heading.
TransPennine Express (TPE), which transferred to the government’s owning group (DOHL) earlier this year, has set out its plans to address many of the issues which have caused problems and disruption for rail customers.
These three paragraphs summarize their plans.
Making Journeys Better: A Prospectus gives clear detail of the issues TPE has faced during the past two years as well as outlining how TPE, under DOHL, will work to make things better, having completed an in-depth review of the business.
Part of the plans involve the operators plans for its new fleet. Its New Trains Programme outlines its long term view for decarbonisation. The report states that TPE will look towards new technology on its fleet to overcome the lack of clarity on the full electrification of the line.
This, it states will help with the cascading and removal of diesel trains faster across its network.
It always looked to me, that TPE under First Group, brought rather a dog’s breakfast of trains, when a unified fleet of Class 802 trains, as per Hull Trains, might have been easier to operate.
- They are already retiring the Class 68 locomotives and their Mark 5 coaches, so surely to decarbonise their services, a number of battery electric high speed trains would be an idea.
- They are already testing Class 802 battery-electric trains for Hitachi and Eversholt Rail.
- I also feel that CAF could offer a suitable battery-electric train, based on the Class 397 train.
TPE say in the example, that they expect a decision later in the month.
TransPennine Express Services And Battery Electric Trains
These are their services and how they would be effected by battery-electric trains.
- Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.
- Liverpool Lime Street And Hull – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.. – 42 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and Micklefield.
- Manchester Airport and Saltburn – Fully-electrified between Manchester Airport and Northallerton after TransPennine Upgrade. – 33.6 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and Northallerton. Would eliminate overnight noise problems at Redcar.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Newcastle – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Scarborough – Fully-electrified between Manchester Piccadilly and York after TransPennine Upgrade. – 42.1 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and York.
- York and Scarborough – Electrified at York – 42.1 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at York.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Huddersfield – Electrified at Manchester Piccadilly – 25.5 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at Manchester Piccadilly.
- Leeds and Huddersfield – Electrified at Leeds – 17.2 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at Leeds.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes – 125,6 miles unelectrified – In Electrification Of The Hope Valley Line, I show how this route can be run by battery-electric trains that charged on existing electrification a short new section of electrification at Cleethorpes.
Note.
- If Manchester Victoria and Huddersfield, is not electrified, battery-electric trains would be able to cross the 25.8 miles of unelectrified track on battery power.
- If Leeds and Huddersfield, is not electrified, battery-electric trains would be able to cross the 17.2 miles of unelectrified track on battery power.
- I am assuming that the TransPennine Upgrade between Manchester and Leeds will be completed, so that between Liverpool Lime Street and Leeds is fully-electrified.
- The only new infrastructure needed would be electrification at Cleethorpes to charge the trains.
All services except for Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes could be run using battery-electric trains with a range on a full battery of at least 100 miles and with no additional electrification.
Electrifying Cleethorpes Station
This Google Map shows Cleethorpes station.
These pictures show the station in June 2023, when it appears to be going through a platform refurbishment.
I don’t think it would be the most difficult station to electrify.
- There are four platforms.
- As the station is likely to get more battery-electric services, including one from King’s Cross, I would suspect that at least three out of the four platforms would be electrified.
- Although, the station is Grade II Listed, there doesn’t appear to be any canopies or important architectural details, that would get in the way of electrification.
Once Cleethorpes station had been successfully electrified, similar installations could be applied at other stations like Saltburn, Scarborough and Skegness.
Conclusion
If TransPennine Express were to buy the right number of battery-electric trains with a hundred mile range, they can decarbonise all their routes in a train factory.
Chiltern Electrification Alternatives Studied
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Chiltern Railways is working to present the Department for Transport with options for a fleet renewal programme, with London Marylebone being the only non-electrified London terminal and pressure for the withdrawal of diesel trains continuing to mount, particularly from local residents.
Industry insiders report that this could see at least the 39 two and three-car Class 165 diesel multiple-units replaced.
Note.
- The Class 165 trains were built in 1990-1992 and refurbished around the turn of the century.
- Chiltern Railways have 28 two-car and 11 three-car Class 165 trains.
- Chiltern Railways also have ten similar two-car, nine three-car and nine four-car Class 168 trains.
- In addition, Great Western Railway has 20 two-car and 16 three-car Class 165 trains, and 23 Class 166 trains.
- The Class 165 and Class 166 trains are 90 mph units, whereas the Class 168 trains are 100 mph units.
As Chiltern’s study would appear to rule out electrification, could all of these trains be replaced with an appropriate number of a new class of 100 mph zero-carbon independently-powered multiple units?
In Alstom And Eversholt Rail Sign An Agreement For The UK’s First Ever Brand-New Hydrogen Train Fleet, I talked about a proposed hydrogen train fleet.
These trains are described as three-car in Alstom’s press release.
- Most Aventras are 100 mph trains.
- They could easily be lengthened to four cars by the addition of an extra car.
- It may even be possible, that these trains could be fitted with a pantograph for working on electrified lines.
The only problem, I can envisage, is that a two-car version might not have enough space for the hydrogen and electrical gubbins.
Chiltern’s Locomotive-Hauled Mark III Stock
Greater Anglia have replaced locomotive-hauled Mark III stock with multiple units and it appears to have been successful.
Could Chiltern’s locomotive-hauled Mark III stock be replaced by six-car hydrogen-powered Aventras, with a long-distance interior?
Other Routes
Alstom and Eversholt Rail announced their agreement in November 2021.
Since then, I have written these posts, where the proposed Alstom Hydrogen Aventra could have an application.
- Adding Buxton And Manchester Piccadilly To The Bee Network
- ‘Castle’ HSTs To Be Withdrawn By Great Western Railway
- Proposals Submitted To Create Darlington To Dales Rail Link
- Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And Teesside
- Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And The Reopened Northumberland Line
- Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And Extension Of The Birmingham Cross-City Line
- Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And Great Western Branch Lines Between Paddington And Oxford
- Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And The Uckfield Branch
Note.
- A two-car version would surely increase the number of applications.
- A 110 mph capability would allow the trains to mix it with high speed trains on fast lines.
- Bombardier proposed a 125 mph bi-mode Aventra. Could this be achieved with hydrogen power?
I feel the eight applications, I listed, could be the start of something a lot bigger.
Conclusion
Alstom and Eversholt Rail Group appear to have done their research.
GWR And Vivarail
This is an attempt to make some sense about what is happening between GWR and the assets of Vivarail.
These are some random thoughts.
Ongoing Maintenance Of Existing Trains
Currently, there are four operators in the UK, with various types of Vivarail‘s Class 230 trains.
- Great Western Railway – 1 – Infrastructure under construction for trial on the Greenford Branch.
- Island Line – 5 – In operation.
- Transport for Wales – 5 – Undergoing testing prior to entering service.
- West Midlands Trains – 3 – Withdrawn from service indefinitely in December 2022.
Note.
- West Midlands Trains withdrew the trains because of uncertainty about the servicing of the trains.
- West Midlands Trains are getting complaints about the bus replacement service.
- All operators will probably need assistance to service the trains.
- Great Western Railway and Island Line are First Group companies.
Could First Group have got in first, so they can protect their interests with a professional Vivarail train maintenance organisation?
Mark Hopwood
In Special Train Offers A Strong Case For Reopening Fawley Line, I said this.
This is another quote from the Rail Magazine article.
However, SWR’s Mark Hopwood favours a much bolder plan. “We’d have to take a decision, once we knew the line was going ahead. But my personal belief is that we should be looking for a modern environmentally-friendly train that can use third-rail electricity between Southampton and Totton and maybe operate on batteries down the branch line.”
Pressed on whether that would mean Vivarail-converted former-London Underground stock, Hopwood adds. “It could be. Or it could be a conversion of our own Class 456, which will be replaced by new rolling stock very shortly. But I don’t think this is the time to use old diesels.
Mark Hopwood is now the Managing Director of Great Western Railway and he seems to be in favour of battery-electric trains. I agree totally with his statement about old diesels.
Mark Hopwood And The Cholsey And Wallingford Branch
According to LinkedIn, Mark Hopwood is also the President at the Cholsey and Wallingford Railway
- This is a two-and-a-half mile long standard gauge heritage railway.
- It used to be a branch line, that served the town of Wallingford.
- It connects to the Great Western Main Line in a bay platform at Cholsey station.
- Wallingford station has now been demolished.
- The heritage railway uses a new site on the south side of St. Johns Road.
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the branch line.
Note.
- Cholsey station and the Great Western Main Line is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- The current Wallingford station is in the North-Eastern corner.
- The Cholsey and Wallingford Railway is shown in yellow.
This Google Map shows Cholsey station.
Note.
- There are four through platforms for Great Western Railway services.
- Platforms 1 and 2 for the fast services are on the Western side.
- Platforms 3 and 4 for the slow services are on the Eastern side.
- Bay Platform 5 is tucked in the North-East corner of the station and is the terminus for services on the Cholsey and Wallingford Railway.
- There are only 55 parking spaces.
Is the number of parking spaces sufficient for the station, if a lot of passengers drive from Wallingford?
Could a commercial service run between Cholsey and Wallingford?
Consider.
- Wallingford is a town of nearly twelve thousand people.
- Cholsey station has two trains per hour (tph) between Paddington and Didcot Parkway stations, with extra services between Oxford and Reading stations in the Peaks.
- There is only limited parking at Cholsey station.
- Most GWR branch lines are run by an hourly service.
- I feel that two-car battery-electric train could provide one or two tph on the branch.
- Charging would probably be needed at only one end of the branch line.
- As all the through lines at Cholsey station are electrified with 25 KVAC overhead wires, I suspect that charging would be provided at that station.
A two-car battery-electric train could probably provide a commercial service on this branch, if the Cholsey and Wallingford Railway wanted a revenue stream.
First Group Services That Could Be Run By Battery-Electric Trains
These Great Western Railway and South Western Railway services might be suitable for battery-electric services.
- Newbury and Bedwyn – Newbury is electrified.
- West Ealing and Greenford – West Ealing is electrified.
- Slough and Windsor and Eton Central – Slough is electrified.
- Maidenhead and Marlow – Maidenhead is electrified.
- Twyford and Henley-on-Thames – Twyford is electrified.
- Reading and Gatwick Airport – Partially electrified.
- Reading and Redhill – Partially electrified.
- Reading and Basingstoke – Partially electrified.
- Didcot Parkway and Oxford – Didcot Parkway is electrified.
- Weston-super-Mare and Severn Beach – No electrification.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Avonmouth – No electrification.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Filton Abbey Wood – No electrification.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Portishead – Proposed – No electrification.
- Swindon and Westbury – Swindon is electrified.
- Exmouth and Paignton – No electrification.
- Exeter Central and Okehampton – No electrification.
- Exeter Central and Barnstaple – No electrification.
- Plymouth and Gunnislake – No electrification.
- Liskeard and Looe – No electrification.
- Par and Newquay – No electrification.
- Truro and Falmouth Docks – No electrification.
- St. Erth and St. Ives- No electrification.
- Romsey and Salisbury – Partially electrified.
- Southampton Central and Fawley – Proposed – Partially electrified.
Note.
- Most services are one or two tph or less.
- Reading and Basingstoke, Didcot Parkway and Oxford, Exmouth and Paignton, and Romsey and Salisbury are 2 tph.
- I have included the proposed Bristol Temple Meads and Portishead and Southampton Central and Fawley services.
- All electrification is 25 KVAC overhead except for the North Downs Line between Reading and Gatwick Airport via Redhill, and Romsey and Salisbury, which are 750 VDC third rail.
There are a total of 24 services. As each 2 tph service will need two trains and the North Downs services probably six, a rough calculation, indicates there would need to be a minimum of over thirty trains, to convert all these services to battery-electric operation.
This simple analysis makes Mark Hopwood’s enthusiasm, that I quoted earlier understandable.
The Requirement For First Group Battery-Electric Trains
Consider.
- Most of the services can accommodate three or four-car trains.
- A few services can only be run with two-car trains.
- Some services will need running with 25 KVAC overhead electrification for operation or deploying to and from the depot.
- Some services will need running with 750 VDC third-rail electrification for operation or deploying to and from the depot.
- A modern interior with or without a fully-accessible toilet is needed.
- Ability to recharge in a platform fitted with electrification or a charging system in under ten minutes.
- A reasonable cruising speed where electrification is needed for deployment.
This suggests to me, that two train types will be needed.
- A Vivarail-style two-car train for branches like West Ealing and Greenford and Southampton Central and Fawley.
- A three- or four-car dual-voltage electric multiple unit, based on something like an Alstom Aventra, a Bombardier Electrostar or a British Rail-era Class 321 train.
The Class 321 train could be ideal.
- It is a 100 mph train.
- It is a four-car train, that can be shortened to three-cars.
- Versions are available for both 25 KVAC overhead and 750 VDC third-rail electrification.
- Some have been converted to a modern Renatus interior, with a fully-accessible toilet.
- Greater Anglia have run Class 321 Renatus trains between London and Norwich.
- The Class 321 Renatus trains are fitted with a modern AC-based traction system.
- Eversholt Rail and Vivarail were working on a Class 321 BEMU, which I wrote about in Eversholt Rail And Vivarail To Develop Class 321 BEMU.
- Other operators like Northern, Scotrail and Transport for Wales might like a Class 321 BEMU.
Could First Group convert the Class 321 trains?
In What Train Is This?, I talk about a refurbishment of a GWR Class 150 train, that was one of the best I’ve seen.
I suspect that First Group could do the conversion, with a little help from their friends, like Wabtec and the ex-Vivarail employees, that they’ve hired.
Could The Class 387 Trains Be Converted To Battery-Electric Operation?
It was in February 2015, that I wrote Is The Battery Electric Multiple Unit (BEMU) A Big Innovation In Train Design?, after a ride in public service on Bombardier’s test battery-electric train based on a Class 379 train.
The Class 387 and Class 379 trains are very similar and with Vivarail’s battery and charging expertise, I believe that both Class 379 and Class 387 trains could be converted into modern four-car battery-electric trains.
- They would have a 100 mph or possibly a 110 mph operating speed, so could work routes like the Great Western Main Line amongst the thundering herds of Hitachis.
- The interiors would be suitable for longer routes like Cardiff Central and Exeter or Waterloo and Exeter via Salisbury.
- Great Western Railway have 33 Class 387 trains.
- Thirty Class 379 trains are wasting space in sidings.
I believe that with modern battery technology, these trains could have a battery range in excess of ninety miles.
This would enable services like Cardiff Central and Exeter St. Davids and Exeter St. Davids and Salisbury.
With judicious use of charging stations in stations like Bristol Temple Meads, Exeter St. Davids and Salisbury, all First Group main line services, that are not run by the Hitachi trains could be converted to battery-electric operation.
Conclusion
I believe a well-thought out plan is emerging.
Eversholt Rail And Vivarail To Develop Class 321 BEMU
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Eversholt Rail.
These three paragraphs introduce the project.
Eversholt Rail and Vivarail have signed an agreement aimed at developing battery power – and range extension – to the Class 321 ‘Renatus’ fleet.
The 30 unit ‘Renatus’ fleet is a product of £65m investment in AC traction, air conditioning and upgraded interior. Completed in 2019, it provides a high-quality passenger experience, proven reliability in intensive operations and is widely compatible on the UK network. This fleet is currently operating on the Greater Anglia network until the introduction of their new trains is completed.
Eversholt Rail and Vivarail are committed to supporting the UK Government’s ambition to decarbonise its rail sector by 2050, and the Scottish Government’s objective of doing so by 2035. This proven and reliable fleet is an excellent fit in terms of characteristics, fleet size and availability for conversion to a Battery Electric Multiple Unit (BEMU). Vivarail, as the designers and manufacturers of the UK’s only battery and hybrid trains currently in passenger service are well positioned to progress this development.
This paragraph talks about the design objectives.
We will be working together to develop a design to integrate battery technology to provide between 20 to 30 miles of self-propulsion. Enabling the fleet to operate on non-electrified or partly electrified routes would offer the opportunity to increase the range of modern, low-carbon options to accommodate passenger demand; to enable fleet cascades; to improve the passenger experience; and to bring air quality and decarbonisation benefits to local areas.
I have a few thoughts on what I have read so far.
Vivarail’s Technology
In Battery Class 230 Train Demonstration At Bo’ness And Kinneil Railway, I talked about a ride in the battery version of Vivarail’s Class 230 train.
The train impressed me, as it did others that day.
I know that the train is late on being introduced on the Borderlands Line in Wales, but then all bi-mode or tri-mode trains seem to be having software problems.
In D-Train Order For Marston Vale Confirmed, I talked about the technicalities of Vivarail’s battery train.
Battery Prototype
The article also gives more details of the battery prototype.
- The train has four battery rafts, each with a capacity of 106 kWh
- Range is up to fifty miles with a ten minute charge at each end of the journey.
- Range will increase as battery technology improves.
- The train is charged using a patented automatic charging point.
- The batteries will have a seven-year lifespan, backed by a full warranty.
- Battery rafts would appear to be interchangeable with the diesel generators.
- Hydrogen power will be used within the next few years.
The specification seems comprehensive and it would appear there is a high degree of innovative automation and well-thought-out electrical engineering.
Train Energy Consumption
The train has the following characteristics.
- Two cars
- 424 kWh of battery capacity.
- 50 mile range
This gives a consumption 4.24 kWh/per car/per mile.
In an article in the October 2017 Edition of Modern Railways, which is entitled Celling England By The Pound, Ian Walmsley says this in relation to trains running on the Uckfield Branch, which is probably not much more taxing than the Marston Vale Line.
A modern EMU needs between 3 and 5 kWh per vehicle mile for this sort of service.
I am surprised that the Class 230 train lies in the 3-5 kWh range, but then I’m not sure of the weights of the two trains.
I estimate two-car units to weigh as follows.
- Class 230 train plus batteries – Around 50 tonnes.
- Electrostar – Around 90 tonnes
- Aventra – Around 80 tonnes
I shall get some better figures, when I actually see the trains, as the weight is on the side.
Note.
I should say, that I have met some of Vivarail’s designers and I have been impressed.
They were also very complimentary about the D78 Stock, where it appears no expense was spared by Transport for London to keep them up to scratch.
I will apply Ian Walmsley’s rule in the extract to the Class 321 train.
- Four cars
- Thirty miles
- As the Class 321 Renatus has a modern traction system, I’ll assume it is efficient and uses 3 kWh per vehicle mile for a gentle short branch line.
- These figures would need a 360 kWh battery.
If the consumption was 5 kWh per vehicle mile, it would be a 600 kWh battery.
Under Train Space
There is plenty of space under a Class 321 train, as these pictures show.
My design would see a battery under each car, if that were possible to even out the weight.
The Renatus Interior
These pictures show the Renatus train and interior.
Not bad for a train approaching its mid-thirties.
Will The Train Have Third-Rail Shoe Gear?
I have read the technical documents for Porterbrook’s Class 769 train, which this is based on the Class 319 train.
In the Wikipedia entry for the Class 319 train, this is said,
Class 321 passenger units and Class 325 postal units were developed from the Class 319 design, using similar traction equipment and the same steel body design, with revised cab designs. The 325 units used a Networker style cab design.
It looks like except for cosmetic differences in the drivers cab, the Class 319, Class 321 and Class 325 trains are identical under the skin.
Does this mean that like the Class 319 train, Class 321 trains can be fitted with third-rail shoes?
It should be noted, that if the trains can be fitted with third-rail shoes, then Vivarail’s Fast Charge system can be used to charge the train.
Could Other Trains Be Converted?
It certainly looks like in addition to the Class 321 trains, both the Class 319 and Class 325 trains can be converted to battery-electric power.
These three trains are all members of British Rail’s Mark 3 family, which were designed before computers were used in structural design to be able to withstand the force of a twenty-four tonne cement truck falling on them from a bridge. On the 5th of November 2010, this nightmare scenario happened in the Oxshott Rail Accident and no-one was killed.
So to avoid the scrapyard, trains based on the Mark 3 coach, like the Class 320, Class 322, Class 455 and Class 456 trains will be happy to sign up to the Eversholt Rail and Vivarail conversion process.
- The Class 320 trains are three-cars, so would offer another type of train.
- The Class 322 trains are four-cars, were built for the Stanstead Express.
- The Class 455 trains are four-cars with third-rail gear, so would offer another type of train.
- The Class 456 trains are two-cars with third-rail gear, so would offer another type of train.
In SWR Says Farewell To ‘456’s, I talk about converting the two-car Class 456 trains after Mark Hopwood, who is now a big cheese at Great Western Railway, suggested the conversion to create a useful two-car battery-electric train.
If you doubt, the quality of the bodies and interiors of these trains from another era, I suggest you go to Liverpool Street station and take a ride in one of Greater Anglia’s Class 321 Renatus trains.
As there are six classes that could be converted, various different types of train can be converted to suit an operator’s needs.
Main Line Speed
Most of these trains are 100 mph trains, with drivers telling me, that they have superb brakes to handle stopping from that speed.
However, Class 455 and Class 456 trains are only 75 mph trains, with some of the Class 320 trains being only 90 mph trains.
Accidents And Incidents
As far as I can tell, none of these trains has had a serious accident, that has resulted in the death of a passenger.
Even the Oxshott Rail Accident only resulted in two serious and five minor injuries, with one of the serious injuries being the driver of the cement truck.
It is a remarkable safety record.
Possible Routes
I will do these on a company-by-company basis, as all companies needs are different.
c2c
c2c is an all-electric company.
I doubt there is a possibility of the company needing any battery-electric trains.
Chiltern Railways
Chiltern Railways is an all-diesel company.
They effectively have three different types of motive power and the solutions for each will be different.
- Six Class 68 locomotives haul Chiltern’s flagship main line services. As there are thirty-four of these modern locomotives in operation in the UK, I would suspect their manufacturer; Stadler will come up with a zero-carbon solution for application to these locomotives. I suspect they will become hydrogen-powered.
- Workhorses are 28 Class 168 trains totalling eighty-five carriages. One has been converted to hybrid operation by Rolls-Royce mtu and I suspect that Rolls-Royce mtu have a plan to make all these trains zero-carbon by 2030.
- There are also 39 Class 165 trains, which are diesel Networkers, dating from the 1990s.
I suspect that as the Networkers are the oldest in the fleet, these might be replaced with new rolling stock or some cascaded Turbostars.
I also wonder, whether Chiltern’s owner; Deutsche Bahn is watching the development of the Rolls-Royce mtu solution as it could be very applicable in Germany.
Govia Thameslink Railway
Govia Thameslink Railway is an all-electric railway except for two services, where diesel multiple units are used.
- Eastbourne and Ashford International – 25.4 miles one-way – Charge at Eastbourne and Ashford International using existing electrification or a charger.
- London Bridge and Uckfield – 25 miles one way – Charge at Hurst Green and Uckfield using existing electrification or a charger.
Note.
- The trains would need a third-rail capability.
- The company also has a fleet of nineteen forty-year-old Class 313 trains, which are used on Coastway services.
- The Class 321 BEMUs could take over all Coastway services between Ashford International and Portsmouth, which would probably make things easier for the operator, with respect to staff training.
The addition of a fleet of Class 321 BEMUs or similar would surely be a sensible move to improve Govia Thameslink Railway services.
Great Western Railway
This article on Railway Gazette is entitled GWR Seeks Input To Decarbonisation Plan.
This is the first four paragraphs.
Great Western Railway is to undertake a market engagement exercise to support its development of a decarbonisation plan including a move away from diesel traction.
The operator is seeking industry input to inform the creation of a Future Fleet & Depot Proposal, setting out ‘affordable’ options for decarbonisation whilst improving and aligning services to future customer needs.
This could include automated rapid battery charging and innovative approaches to energy supply.
The Future Fleet & Depot Proposal will be submitted to the Department for Transport. If accepted by DfT, GWR would then begin procurement of rolling stock and supporting infrastructure. It envisages that this could get underway in September 2024.
It looks a good plan.
In Converting Class 456 Trains Into Two-Car Battery Electric Trains, I opened the post with this quote from Mark Hopwood who at the time was the interim Managing Director of South Western Railway and in Special Train Offers A Strong Case For Reopening Fawley Line, I quote him as saying the following about the trains for the Fawley Branch Line.
However, SWR’s Mark Hopwood favours a much bolder plan. “We’d have to take a decision, once we knew the line was going ahead. But my personal belief is that we should be looking for a modern environmentally-friendly train that can use third-rail electricity between Southampton and Totton and maybe operate on batteries down the branch line.”
Pressed on whether that would mean Vivarail-converted former-London Underground stock, Hopwood ads. “It could be. Or it could be a conversion of our own Class 456, which will be replaced by new rolling stock very shortly. But I don’t think this is the time to use old diesels.
Mark Hopwood is so right about using old diesels and he has moved on to be Managing Director of Great Western Railway.
Could Mr. Hopwood be a driving force behind the decarbonisation of the Great Western Railway?
These trains will be possibilities for battery-electric trains.
- Newbury and Bedwyn – Four cars – 13.3 miles one way – Charge at Newbury using existing electrification
- West Ealing and Greenford – Two cars – 2.5 miles one-way – Charge at West Ealing
- Slough and Windsor & Eton Central – Four cars – 2.8 miles one-way – Charge at Slough using existing electrification
- Maidenhead and Marlow – Two cars – 7.1 miles one way – Charge at Maidenhead using existing electrification – Four car trains could run between Bourne End and Paddington
- Twyford and Henley-on-Thames – Four cars – 4.6 miles one-way – Charge at Twyford using extended existing electrification – Trains could run to Paddington
- Reading and Gatwick Airport – Four cars – 17.4 and 12.1 mile sections without electrification – Charge on existing third-rail electrification
- Reading and Redhill – Four cars – 17.4 and 12.1 mile sections without electrification – Charge on existing third-rail electrification
- Reading and Basingstoke – Four cars – 13.6 miles one-way – Charge at Reading using existing electrification
- Didcot Parkway and Oxford – Four cars – 10.3 miles one-way – Charge at Didcot Parkway using existing electrification
- Didcot Parkway and Banbury – Four cars – 33 miles one-way – Charge at Didcot Parkway using existing electrification – Charger or electrification needed at Banbury
- Cardiff Central and Portsmouth Harbour – Probably needs electrification in the Bristol area.
- Cardiff Central and Taunton – Probably needs electrification in the Bristol area.
- Weston-super-Mare and Severn Beach – Two/Four cars – 45 miles one-way – Charge at Bristol Temple Meads, Weston-super-Mare and Severn Beach
- Bristol Temple Meads and Avonmouth – Two/Four cars – 16.6 miles one-way – Charge at Bristol Temple Meads and Avonmouth
- Bristol Temple Meads and Filton Abbey Wood – Four cars – 4.4 miles one-way – Charge at Bristol Temple Meads
- Great Malvern and Westbury – Probably needs electrification in the Bristol area.
- Gloucester and Weymouth – Probably needs electrification in the Bristol area.
- Swindon and Westbury – Two/Four cars 32.5 miles one-way – Charge at Swindon and Westbury
- Exmouth and Paignton – Four cars – 39.5 miles one-way – Charge at Exeter St. Davids, Exmouth and Paignton
- Exeter Central and Barnstaple – Two/Four cars – 39.6 miles one-way – Charge at Exeter St. Davids and Barnstaple
- Exeter Central and Okehampton – Two/Four cars – 25.6 miles one-way – Charge at Exeter St. Davids and Okehampton
- Plymouth and Gunnislake – Two cars – 14.6 miles one-way – Charge at Plymouth and Gunnislake
- Liskeard to Looe – Two cars – 8.3 miles one-way – Charge at Liskeard
- Par and Newquay – Two cars – 20.8 miles one-way – Charge at Par and Newquay
- Truro and Falmouth Docks – 11.8 miles one-way – Charge at Truro
- St Erth and St Ives – 4.2 miles one-way – Charge at St. Erth
Note.
- Many of the charging stations could be standard systems that are available from companies like Furrer+Frey and Vivarail.
- Or alternatively, a short length of 25 KVAC overhead electrification could be erected.
- I suspect major stations like Bristol Temple Meads, Exeter St. Davids and Plymouth will be electrified.
- There probably needs to be more electrification in the Bristol area.
- Mark Hopwood’s nose, that said two-car trains will be needed, is probably right.
- Some of the trains would need a third-rail capability.
I suspect that with appropriate charging or electrification nearly all of Great Western Railways services can be run using battery-electric trains.
It does appear that Eversholt Rail Group and Vivarail have got the specification of the trains very close to the ideal, with respect to Great Western Railway’s needs.
Southeastern
Southeastern is a fully-decarbonised train operating company, with respect to passenger services.
But it wants to reopen the Hoo Branch, which will need some self-powered trains. I wrote about this in Effort To Contain Costs For Hoo Reopening.
The Class 321 BEMU would surely be a possibility to extend London and Gravesend services, by a distance of about a dozen miles to a new station at Hoo.
These trains would need a third-rail capability.
Highland Council Forges Green Hydrogen Pact
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on renews.biz.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Getech subsidiary H2 Green has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Highland Council in Scotland aimed at creating a regional network of green hydrogen hubs across the Scottish Highlands.
Under the terms of the MoU, H2 Green and the Highland Council will produce a regional plan to develop a network of green hydrogen hubs at optimal locations across the region.
The first hub appears to be in Inverness, as I wrote in Hydrogen Hub Plan Will Cut Transport Sector Emissions In The Highlands.
But that is only the start.
- Green hydrogen will be used in transport in the Highlands.
- By-products like oxygen and heat will be distributed.
- Delivery of Highland decarbonisation will be planned.
- SGN Commercial Services will service large-volume customers.
- Agreements are in place for Eversholt Rail to deploy their hydrogen-powered trains on the Far North and West Highland Lines of Scotland.
This statement from Jonathan Copus of Getech, sums up the objectives of the hydrogen project.
These activities combined with the Highland Council initiative are set to establish the Highlands as the leading UK-centre for decarbonisation and innovation; they will also support job creation, deliver energy security and provide a sustainable path for the region’s net zero transition.
I believe that a similar approach could be taken in other parts of the UK. Cornwall, East Anglia, Lincolnshire, much of Wales and the Borderlands between England and Scotland come to mind.
Each region will probably, decarbonise slightly differently and each will develop more and more innovative ways to use the hydrogen.
Conclusion
Hydrogen will play a large part in the decarbonisation of the UK.