Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network
On my last stud farm, we had three regular fuel deliveries.
- Propane to heat the house and offices.
- Red diesel to power the tractor and farm machinery.
- Road diesel to power the horse box and a couple of diesel cars, that went on the roads.
Note.
- Like most farms in the UK, we didn’t have mains gas.
- The local low-life of whom you never speak their name, used to regularly steal the diesel.
- Stealing of diesel in rural areas of the UK is a big industry.
- The police did nothing to stop the thefts as the culprits are untouchable.
- We had two boilers, that both ran on the propane.
- Modern boilers can be converted from propane to use hydrogen.
- All cars, trucks, farm vehicles and machinery on the stud farm could in the future use hydrogen.
Propane and diesel would be replaced by clean hydrogen.
Delivering The Fuel
Consider.
- Propane and diesel are currently delivered in rural areas by truck.
- Hydrogen will be delivered the same way and stored in a tank designed for hydrogen, which could be similar in appearance to current propane tanks.
- Boilers would be directly piped to the hydrogen tank.
- The technology exists to fill hydrogen-powered vehicles and equipment from hydrogen tanks.
- I believe that a thief-proof hydrogen tank would be possible.
- The hydrogen will be delivered as needed in a hydrogen-powered truck.
I believe companies like Centrica, will develop the technology so that farms and businesses could have their own hydrogen system.
Supplying The Hydrogen
Electrolysers would be needed around the country.
Some could be based on nuclear sites, where others could be powered by offshore wind.
Hydrogen Safety
Hydrogen safety has its own Wikipedia entry.
The entry starts with a description of the Hindenberg Disaster, which has a detailed Wikipedia entry of its own.
I’ve spoken to someone, who was there; Dory Previn, who later wrote a song about it.
The Hydrogen safety Wikipedia entry has this paragraph.
There are many codes and standards regarding hydrogen safety in storage, transport, and use. These range from federal regulations, ANSI/AIAA, NFPA, and ISO standards. The Canadian Hydrogen Safety Program concluded that hydrogen fueling is as safe as, or safer than, compressed natural gas (CNG) fueling,
I’ve also talked to German schoolchildren about their hydrogen trains and as you are educated about hydrogen, the fear decreases and the safety increases.
Hydrogen-Powered Lawnmowers And Garden Tractors
Everybody likes a lush, green lawn.
Surely, yours is better, if your lawnmower emits no carbon dioxide!
Electric will work, but if you have a hydrogen-powered lawnmower, that can be filled from your central heating tank, that is better.
Collateral Benefits
These would be collateral benefits.
- One set of tankers would be replaced by a single zero-carbon hydrogen tanker, thus reducing road traffic.
- I believe there would be less fuel theft.
- Rural businesses, that needed gas like blacksmiths could be supplied.
- A lot of buildings with a propane-fuelled boiler could be converted to hydrogen.
It would be a path to decarbonisation of the rural economy.
How Big Is The Off-Grid Energy Market?
A document on the House of Commons web site says this.
An estimated 4.4 million households across Great Britain were not connected to the gas grid in 2021. This was 15.1% of domestic properties.
If the average gas bill is £100/month, then that is £1200/year, which works out at £5,280,000,000.
When you add in off-grid businesses, that would need fuel and hydrogen fuel for vehicles and agricultural equipment, the market can’t be much short of £10 billion.
Conclusion
As it is a multi-billion pound marketplace. someone will develop it.
Sizewell C And Hydrogen
The Sizewell C web site has a page with a title of Hydrogen and SZC.
The page asks this question.
Why Does Sizewell C Want To Produce Hydrogen?
It gives this answer.
Nuclear is a great way of producing hydrogen as it generates huge amounts of reliable, low-carbon energy. Nuclear and hydrogen are also two clean technologies that can help us make big reductions in carbon emissions. While both technologies are vital on their own, at Sizewell C we have an exciting vision to bring them together.
The page is worth a read about how they will use the hydrogen, which will include.
- Providing Wrightbus hydrogen-powered buses to link the main construction site with Park-and-Ride sites on the A 12 at Darsham and Wickham Market.
- Powering vehicles and machinery on the main construction site.
- Supplying hydrogen to Freeport East.
- Refuelling hydrogen vehicles.
I have a few thoughts.
Supplying Hydrogen To Users
On my last stud farm, we had three fuel deliveries.
- Propane to heat the house.
- Red diesel to power the farm machinery.
- Road diesel to power the horse box and a couple of diesel cars, that went on the roads.
Note.
- Like most farms in East Anglia, we didn’t have mains gas.
- The local low-life of whom you never speak their name, used to regularly steal the diesel.
- We had two boilers, that ran on the propane.
- All farm vehicles and machinery will in the future use hydrogen.
- Propane and diesel would be replaced by clean hydrogen.
I believe companies like Centrica, will develop the technology so that farms and businesses could have their own hydrogen system, that would be topped-up accordingly, by road tankers, which themselves would be fuelled by hydrogen.
One set of tankers would be replaced by another zero-carbon set.
Sizewell sits on the Suffolk Coast and it appears, there will be a new road link to the A 12, which connects to Suffolk’s main road system.
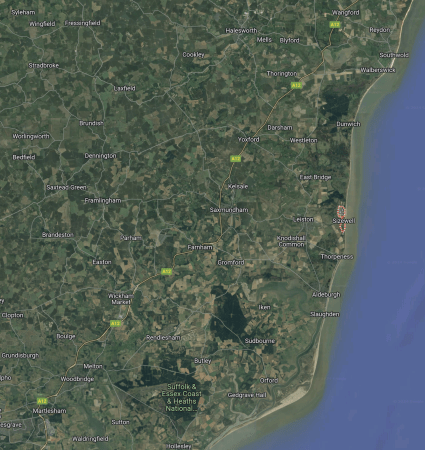
This map shows Sizewell C and East Suffolk.
Note.
- The Sizewell site is outlined in pink on the coast, about halfway up the map.
- The A 12 road and the East Suffolk Line run almost parallel to the coast between Ipswich in the South and Lowestoft and Yarmouth in the North.
Energy use in East Suffolk would be transformed and all because there will be a plentiful supply of zero-carbon hydrogen.
Hydrogen And The Arts
Suffolk has been an artistic county for hundreds of years and some works of art, like casting bronzes, firing pottery or working with glass or wrought iron need a lot of energy. Local hydrogen networks supplied by tanker, as propane is now could help to decarbonise one of the most difficult of professions.
Pink Hydrogen
This page on the National Grid web site explains the various hydrogen colours.
It describes pink hydrogen like this.
Pink hydrogen is generated through electrolysis powered by nuclear energy. Nuclear-produced hydrogen can also be referred to as purple hydrogen or red hydrogen.
In addition, the very high temperatures from nuclear reactors could be used in other hydrogen productions by producing steam for more efficient electrolysis or fossil gas-based steam methane reforming.
I also call it Barbie hydrogen.
Sizewell C would be an ideal place to create pink hydrogen.
Before Sizewell C is up and running, the electrolyser at Sizewell could be powered by Sizewell B or even offshore wind.
Sizewell C – South Park And Ride
This document on the Planning Inspectorate web site, is a description of the Southern Park and Ride for the Sizewell C Project.
This Google Map shows the area of the Park-and-Ride site.
Note.
- Wickham Market is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The dual-carriageway is the Wickham Markey by-pass, which is part of the A12 between Ipswich and Lowestoft.
- Close to Lower Hacheston is the Northern junction of the by-pass which connects the B1116 and B 1078 roads to the A 12.
- If my memory serves me correctly, there is a small roundabout to the North of the A12, where the B 1116 and B 1078 cross, which is referred to as Fiveways Roundabout in some of the documentation.
- Wickham Market station is in the South-East corner of the map.
I know the area well, as I used to live less than ten miles to the West of Fiveways roundabout.
This shows the area to the North of Fiveways roundabout to a large scale.
The document on the Planning Inspectorate says this about the site.
The site comprises approximately 26.4 hectares (ha) of predominantly
agricultural land and highway land located north-east of Wickham Market.
The part of the site which would contain the parking and buildings, postal
consolidation building and Traffic Incident Management Area (TIMA) is
approximately 18ha in size, and located to the east of the B1078/B1116, to
the north of the A12. The remainder of the site encompasses a section of
the A12, and an associated slip road where highway improvements are
proposed to form the site access, and associated signage and road
markings, see Chapter 1, Figure 1.1 of this volume.
These are my thoughts.
There Is No Rail Connection
I wrote about the Northern Park-and-Ride in Sizewell C – North Park And Ride and there is one big difference.
The Northern Park-and-Ride is an easy walk from Darsham station.
- Darsham station has an hourly four-car train to Lowestoft and Ipswich.
- Some or all trains could be doubled in capacity as Greater Anglia has enough stock to do this.
- If required, trains could be run to and from London and intermediate stations.
- In the past, Network Rail have developed plans to extend the service as far as Yarmouth.
I believe that a rail connection at the Southern Park-and-Ride could have added flexibility for workers in Ipswich travelling to the Sizewell site.
Bus Routes
The frequency and timing of park and ride buses would depend on the
working patterns adopted during construction of the Sizewell C main
development site, and the number of workers to be moved during the shift
changeover periods. More frequent services would operate during staff
changeover and shift start/end periods. It is anticipated that there would be
three to nine buses from the proposed development per hour during shift
changeover period, and an hourly service outside shift changeover periods.There would be a maximum of 100 daily bus arrivals and 100 daily bus
departures from the proposed development to the Sizewell C main
development site. These buses would use the A12, two village bypass and
Sizewell link road once operational to travel to and from the Sizewell C main development site.
This Google Map shows the A 12 between the South Park-and-Ride site and Yoxford.
Note.
- Yoxford is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Wickham Market is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The A 12 is the cream road linking the two villages.
- The Southern Park-and-Ride will be to the North-East of Wickham Market.
- The Northern Park-and-Ride is a couple of miles North of Yoxford.
- Yoxford and Wickham Market are 11.8 miles apart.
This third Google Map shows the route between Yoxford and Sizewell.
Note.
- Yoxford is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Sizewell is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Leiston Abbey is indicated by the arrow to the North of Leiston.
The B 1122 can be picked out through Middleton Moor and Theberton and then as it skirts Leiston Abbey.
It appears that both Park-and-Ride sites, use the same connection between the A 12 and Sizewell C.
Objections To The Park-and-Ride
This petition on change.org is entitled Stop Sizewell C Park and Ride at Wickham Market.
The petitioner is objecting on the following grounds.
- The size of the site.
- Spoiling of views.
- Disturbance to walkers and horse riders.
- Terrestrial ecology and ornithology will be affected by the site.
- Increase in traffic.
This was the petitioner’s conclusion.
In conclusion I oppose the Sizewell C southern park and ride site at Wickham Market and believe it should be sited further south on the A12 away from residential areas and near the A14.
The Ipswich Northern By-Pass
There is another large project scheduled for Ipswich in the next few years; the Ipswich Northern By-Pass.
This map clipped from the Ipswich Borough Council web site shows possible routes.
Note.
- Wickham Market is in the North-East corner of the map.
- One of the aims of the Northern by-pass is to open up land for housing.
- The railway between Ipswich and Darsham stations goes via Westerfield, Wiidbridge, Melton andWickham Market.
- Perhaps by phasing the developments, an area could be used for a Park-and-Ride, which has a road connection to the A 12.
- When the need for Park-and-Ride for Sizewell has decreased, the site could be handed over to housing.
It would certainly help, if the route of the Northern by-pass was settled soon.
Sizewell C – Where Will The Workers Live?
I have now written about, where the two Park-and-Ride sites are to be built.
- The Northern Park-and-Ride is proposed for Darsham.
- The Southern Park-and-Ride is proposed for Wickham Market.
I can now write about where the workers could be billeted.
I suspect there could be a Bibby Stockholm solution, where accommodation barges are used.
This Google Map shows the centre of Ipswich.
Note.
- There is a lot of space on the River Orwell.
- Ipswich station is in the North-West corner of the map.
- There could be a shuttle bus between the barge and the station.
- Trains could take workers to Darsham for buses to Sizewell.
There could even be direct buses to Sizewell.
This Google Map shows the centre of Lowestoft.
Note.
- The Bibby Stockholm is 100 metres long with a beam of 30 metres.
- Lowestoft station is close to the port.
Workers could take the train direct to the Northern Park-and-Ride for Sizewell C.
Sizewell C – North Park And Ride
This document on the Planning Inspectorate web site, is a description of the Northern Park-and-Ride for the Sizewell C Project.
This Google Map shows the area of the Park-and-Ride site.
Note.
- The main road running SW-NE is the A 12 between Ipswich, Felixstowe and Woodbridge in the South and Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth in the North.
- The East Suffolk Line runs North-South at the West side of the map.
- Darsham station, which is indicated by the red logo on a white background is situated, where road and railway cross.
- The Fox Inn is in the village of Darsham and indicated by an orange arrow.
- The pink arrow to the North-West of the Fox Inn indicates White House Farm.
- The lane going North-West from the A 12 to the North of the farm is Willow Marsh Lane.
The document on the Planning Inspectorate says this about the site.
The site comprises approximately 27.9 hectares (ha) of predominantly
agricultural land but also includes sections of the A12 and Willow Marsh Lane
towards the north of the site. It is located west of the village of Darsham and
west of the A12, to the east of the East Suffolk line, and to the north of
Darsham railway station (see Chapter 1, Figure 1.1 of this volume). Further
detail on the site and the environmental baseline is provided in Chapters 1
and 4 to 12 of this volume of the Environmental Statement.
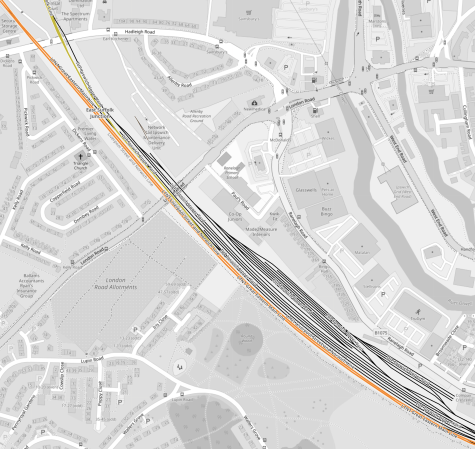
This second Google Map shows Darsham station.
Note.
- Darsham station has long platforms.
- Crossing the line is by means of the level crossing.
- The Budgens store, which is indicated by the blue arrow also sells fuel.
- The station has a bus service.
- The Southern end of the Park-and-Ride site lies between the railway and the road at the North of the map.
The document on the Planning Inspectorate says this about walking between the Park-and-Ride site and the station.
There would be a pedestrian route from Darsham railway station along the
footway on the A12 to the south-east of the site. Pedestrians accessing the
site would leave the A12 and enter through a security gate provided in the
security fencing. Further details of access measures (such as key fobs,
CCTV, intercom system) would be agreed at the detailed design stage.
I could probably manage that at 76.
These are further thoughts.
The Current Rail Service
Currently, the rail service is as follows.
- One train per hour (tph) in both directions.
- |Trains are Class 755 trains, built by Stadler in Switzerland a few years ago.
- Each train can carry up to 229 passengers.
- Up to three trains can run together.
- Trains going to and from Lowestoft in the North call at Oulton Broad South, Beccles, Brampton and Halesworth.
- Trains going to and from Ipswich in the South call at Saxmundham, Wickham Market, Melton and Woodbridge.
- Travellers for London Liverpool Street change at Ipswich.
- The first train from London Liverpool Street would get you to Darsham at 11:00.
- This is not a bad train service but it could be improved.
Direct Trains Between London Liverpool Street And Lowestoft
In 2016, I wrote Making Sense Of The New East Anglia Franchise.
I wrote the following about Greater Anglia’s plans to run four trains per day between London Liverpool Street and Lowestoft.
There are going to be four direct services between London and Lowestoft each day. This probably initially means two trains to London in the morning peak and two trains back in the evening one.
When, I first moved back to Suffolk in the 1970s, I regularly caught a diesel-hauled train from Wickham Market to London for the day.
This is all motherhood and apple pie for those in Lowestoft wanting to go to London, but I suspect it isn’t the easiest service for a train operator to schedule efficiently and make money.
Would a train operator really want to start a full train at Lowestoft at say six in the morning and then have it wait around all day in London before returning in the evening?
The East Suffolk Line from Ipswich to Lowestoft has the following characteristics.
- It is fifty miles long.
- It is not electrified.
- It has a speed limit of 40-55 mph.
- There are nine intermediate stations. Many are just a single platform, and car parking is fairly limited.
- It has enough double-track and a passing loop at Beccles station to run a train in both directions at the same time.
- As it ran long trains in the past, I suspect, that most of the stations have platforms that can handle at least six-carriage trains.
- Trains would appear to take around ninety minutes for the whole journey
But the most important characteristic, is that every time the line is improved, more passengers come rushing out of the woodwork.
There would certainly be no problem with running bi-mode Flirts on this route, as London-Lowestoft is just the type of route for which they are designed.
- They would use their on-board diesel engines on the East Suffolk Line.
- As some would work along the busy lines to London, I suspect their top speed under electric power would be the same as the EMUs.
- Services to and from London, once on the Great Eastern Main Line, would join the high-speed race to and from the capital.
- At the start and finish of the day, the trains could use the electrified main line to position between Ipswich and Crown Point depot at around 100 mph.
- Abellio could use either a single three- or four-car train or perhaps two trains coupled together.
This service would pass through Darsham station, so it could provide a direct link between London and the Park-and-Ride.
It might also stop at stations like Manningtree, Colchester, Chelmsford and Stratford.
I am fairly certain, that a London Liverpool Street and Lowestoft services, that stopped at Darsham station, would improve labour availability and construction efficiency at Sizewell C.
A Connection To Yarmouth
There used to be a direct Yarmouth to Lowestoft Line, but now it is possible to use the Wherry Lines, with a reverse at Reedham station.
So will we be seeing the direct London-Lowestoft trains being extended to Yarmouth?
As Yarmouth hasn’t had a direct connection to London for years and there are lots of fast, capable new trains, I wouldn’t be surprised.
Especially, as Network Rail are talking about reinstating the Reedham Chord to create a more direct route between East Anglia’s largest North-Eastern towns. This is said about the Reedham Chord in Direct Yarmouth Services in the Wikipedia entry for Lowestoft station.
In January 2015, a Network Rail study proposed the reintroduction of direct services between Lowestoft and Yarmouth by reinstating a spur at Reedham. Services could once again travel between two East Coast towns, with an estimated journey time of 33 minutes, via a reconstructed 34-chain (680 m) north-to-south arm of the former triangular junction at Reedham, which had been removed in c. 1880. The plans also involve relocating Reedham station nearer the junction, an idea which attracted criticism.
If we take these current approximate timings.
- Ipswich to Lowestoft takes 90 minutes.
- Lowestoft to Reedham takes 27 minutes.
- Reedham to Yarmouth takes 16 minutes.
That means the service today would take 133 minutes, with a train reverse at Reedham station.
Note.
- Modern three-car bi-mode Flirt trains, with better speed, acceleration and braking than the current Class 170 trains.
- The short-cut along the Reedham Chord, which could save as much as ten minutes.
- A few selective improvements to save a minute here and there.
- Lowestoft station is redeveloped forty metres to the West and eighty metres to the South, as detailed in Wikipedia under Relocation Of The Station.
- I think it would be possible for an Ipswich-Yarmouth service to do the trip in around two hours.
The service would have the following characteristics.
- It would be timetabled for under the all-important two hours.
- Trains would turnround efficiently in a few minutes at either end of the line.
- It could be hourly with four trains or two-hourly with just two, used to run the service.
- All stops would be at the same minutes past each hour at each station.
- Trains would always leave Ipswich and Yarmouth at the same number of minutes past the hour.
- Lowestoft and Yarmouth get a regular hourly direct train service in just thirty-three minutes.
- Intriguingly if the trains left Ipswich and Yarmouth at the same time, they would pass each other at Beccles station, which incorporates a passing loop.
- As Beccles and its passing loop, fits so well into this schedule, I suspect that it was designed with the Reedham Chord and this type of service in mind.
- There would be no prizes for guessing the beer, that should be served on a train on this route.
I don’t think any better than an hourly service, could be run, without some extra passing loops or double-track.
This extension would make commuting between Sizewell and Yarmouth easier.
Bus Route Between Darsham And Sizewell
The document on the Planning Inspectorate says this about the buses and the route.
There would be a maximum of 100 daily bus arrivals and 100 daily bus
departures from the proposed development to the Sizewell C main
development site.Bus services between the proposed development and the Sizewell C main
development site would travel south on the A12 and use the new A12/B1122
roundabout (Yoxford Roundabout – see Volume 7 of the ES) to access the
B1122 and the Sizewell link road (once operational – see Volume 6 of the
ES) towards the Sizewell C main development site.
This Google Map shows Darsham station and the Sizewell site, as it exists today.
Note.
- The Sizewell site is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Darsham station is in the North-West corner of the map.
This second Google Map shows the A 12 between Darsham station and Yoxford.
Note.
- Darsham station is at the top of the map on the A 12.
- The village of Yoxford is on an S-bend of the A 12.
- A B& B is marked by a pink arrow.
The B 1122 connects Yoxford to the South-East corner of the map.
This third Google Map shows the route between Yoxford and Sizewell.
Note.
- Yoxford is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Sizewell is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Leiston Abbey is indicated by the arrow to the North of Leiston.
The B 1122 can be picked out through Middleton Moor and Theberton and then as it skirts Leiston Abbey.
Sizewell C seem to have made a good effort to get the workers to the site.
Why Isn’t A Passenger Train Run Between Ipswich And The Sizewell Site?
In Network Rail Prepares To Send Four Trains A Night Through Suffolk To Sizewell, I came to this conclusion.
I am fairly certain, that it is possible to move four freight trains in and out of the Sizewell site during the night, without doing any major works to the East Suffolk Line between Ipswich and Saxmundham junction.
- Adding extra track at Wickham Market would probably cause major disruption.
- Some level crossings will probably be improved.
But without a full double track between Ipswich and Saxmundham junction, I doubt there could be any increase in passenger services.
But with those track works, it might be possible to run an hourly service between Ipswich and Aldeburgh with calls at Westerfield, Woodbridge, Wickham Market, Saxmundham, Sizewell and Leiston.
This would give a two tph service between Saxmundham and Ipswich.
Objections To The Park-and-Ride
This document from Darsham Parish Council is entitled Consultation Response To Sizewell C.
This is the first paragraph.
Darsham Parish Council (Darsham PC) continues to oppose the proposed location of the Northern Park and Ride (NPR). We believe its location on an already busy single carriageway section of the A12 just north of the level crossing at Darsham Station, coupled with proposed roundabouts at Willow Marsh Lane and the A1120 junction in Yoxford are a recipe for traffic chaos extending northwards up the A12. We have no confidence in the traffic estimates submitted by EDF, which we believe underestimate the amount of local, through, agricultural and tourist traffic. This will be exacerbated by the proposed motel and further proposed development south of the station. We believe that traffic congestion on this main artery into Suffolk will adversely impact tourism throughout the AONB, which generates more than £360 million pa to the local economy (2018 figure). Further, we believe these volumes of traffic will generate excessive noise, vibration and pollution with serious negative impacts on those living alongside or close to the A12. Most significantly, Darsham PC has been advised that location of the NPR on this site could pose a significant flood risk to the railway (see below).
The Parish Council is also worried about flood risk to the railway.
The site of the NPR slopes down from Willow Marsh Lane towards the railway. A consulting engineer has advised us that the heavy clay soil here could pose a drainage and flood risk problem when compacted during the construction period. An appropriate sustainable semi-permeable surface could be utilised for car parking spaces to reduce run-off, with suitable drainage and reservoir capacity at the southern end to protect the railway from flooding. We submitted this evidence to EDF during the consultation period, but it has been ignored.
I suspect as with the opposition to Sizewell B, the opposition is led by second home owners, worried about the value of their investment.
Network Rail Prepares To Send Four Trains A Night Through Suffolk To Sizewell
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the East Anglian Daily Times.
These are the first two paragraphs.
There will be improvements to the East Suffolk Line between Ipswich and Saxmundham and to the little-used Leiston branch line which will become busier with up to four trains a night carrying construction materials to the Sizewell C site.
However there are no plans at present to create a new passing loop at Wickham Market which would be needed to allow construction trains to travel by day so most of these trains will have to use the line at night.
Note.
- Trains access the Sizewell site from Saxmundham junction on the East Suffolk Line.
- Between Saxmundham and Halesworth stations is double track.
- With the exception of a passing loop at Beccles station between Halesworth and Lowestoft stations is single track.
- Saxmundham junction and Lowestoft station is 26.2 miles.
- Between Saxmundham and Woodbridge stations is mainly single track.
- Between Woodbridge and Ipswich stations is double track.
- Saxmundham junction and Ipswich station is 22.8 miles.
It is a classic line, that was partly singled by British Rail to try and cut operating costs.
A passing loop at Wickham Market could make operation of the line easier.
- The last train in the evening leaves Saxmundham station at around 23:00 for Lowestoft.
- The first train in the morning leaves Saxmundham station at around 06:00 for Ipswich and Harwich International.
This would give a seven hour window in which to move four trains out of the Sizewell site and four trains in.
This OpenRailwayMap shows Ipswich Yard which is a set of freight sidings to the North of Ipswich station.
Note.
- The orange tracks are the Great Eastern Main Line.
- Ipswich station is just off the map to the South-East.
- The yellow track in the North-West corner is the East Suffolk Line to Saxmundham and Sizewell.
- The black lines diagonally across the map is Ipswich Yard, where wait if required, when coming out or going into the Port of Felixstowe.
I would expect that trains destined for Sizewell will wait in Ipswich Yard before being moved in at night.
These are my further thoughts.
Moving Trains Into And Out Of The Sizewell C Site
A map of the proposed rail layout in the Sizewell C site was published in the February 2019 Edition of Modern Railways showed at least four sidings in the site.
- We can assume that at the beginning of each night, there are.
- Up to four trains in the Sizewell C site, that need to come out of the site.
- Up to four trains in Ipswich Yard, that need to enter the site.
- As each train leaves the Sizewell C site, it creates a free siding for the next incoming train.
The process could be started by the four trains in the Sizewell C site, leaving nose-to-tail like a herd of elephants, but perhaps five minutes apart.
The outgoing trains would then park-up in Ipswich Yard or position themselves to get ready to bring in the next load.
Once all the outgoing trains, were clear of the Sizewell site, the four incoming trains, could trundle into the site.
Note.
- Effectively, there would be a night-time single-track railway exclusively handling freight trains into and out of the Sizewell C site, between the site and Ipswich Yard.
- With more sidings on the Sizewell C site, the limit could be higher than the currently proposed four trains per night in each direction.
- The number of and length of the trains could be adjusted, so that the deliveries of materials to the site, were in an optimal manner, which hopefully would increase the efficiency of the construction.
- There are twenty level crossings between Ipswich and Saxmundham junction and another five between Saxmundham junction.
Did poor delivery performance contribute to cost and time overruns at the more difficult-to-support, rail-isolated Hinckley Point C power station?
Conclusion
I am fairly certain, that it is possible to move four freight trains in and out of the Sizewell site during the night, without doing any major works to the East Suffolk Line between Ipswich and Saxmundham junction.
- Adding extra track at Wickham Market would probably cause major disruption.
- Some level crossings will probably be improved.
But without a full double track between Ipswich and Saxmundham junction, I doubt there could be any increase in passenger services.
UK ESO Unveils GBP 58 Billion Grid Investment Plan To Reach 86 GW of Offshore Wind By 2035
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Great Britain’s electricity system operator (ESO) has proposed a GBP 58 billion (approximately EUR 68 billion) investment in the electricity grid. The proposal outlines a vision for incorporating an additional 21 GW of offshore wind into the grid by 2035, which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
These three paragraphs add more details to what the investment in the grid means for offshore wind.
The ESO released on 19 March the first Beyond 2030 report. The plan sets up the necessary infrastructure to transfer power to and from future industries, as electricity demand is expected to rise by 64 per cent by 2035, according to the ESO.
The grid operator said that the plan connects a further 21 GW of offshore wind in development off the coast of Scotland to the grid in an efficient and coordinated way which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
The proposals could assist the UK government in meeting the sixth Carbon Budget and allow for the connection of Crown Estate Scotland’s ScotWind leasing round.
These are my thoughts.
How Much Offshore Wind Is In The Pipeline?
This Wikipedia entry is a List Of Offshore Wind Farms In The United Kingdom.
It gives these figures for wind farms in various operational an development states.
- Operational – 14,703 MW
- Under Construction – 5,202 MW
- Pre-Construction – 6,522 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 3 – 12 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 4 – 1,428 MW
- Early Planning – England – 18,423 MW
- Early Planning – Wales – 700 MW
- Early Planning – Scotland – 30,326 MW
Note.
- These add up to a total of 77,316 MW.
- If all the wind farms in the Wikipedia entry are commissioned, the UK will be short of the 86,000 MW total by 8,664 MW.
- Some wind farms like Ossian could be increased in size by a few GW, as I reported in Ossian Floating Wind Farm Could Have Capacity Of 3.6 GW.
It looks like only another 7,164 MW of offshore wind needs to be proposed to meet the required total.
This article on offshoreWIND.biz is entitled The Crown Estate Opens 4.5 GW Celtic Sea Floating Wind Seabed Leasing Round, will add another 4,500 MW to the total, which will raise the total to 81,816 MW.
The article also finishes with this paragraph.
Round 5 is expected to be the first phase of development in the Celtic Sea. In November 2023, the UK Government confirmed its intention to unlock space for up to a further 12 GW of capacity in the Celtic Sea.
A further 12 GW of capacity will take the total to 93,816 MW.
In Three Shetland ScotWind Projects Announced, I talked about three extra Scotwind wind farms, that were to be developed to the East of Shetland.
These will add 2.8 GW, bringing the total to 96,616 MW.
I don’t think the UK has a problem with installing 86 GW of offshore wind by 2035, so we must create the electricity network to support it.
The Electricity Network In 2024
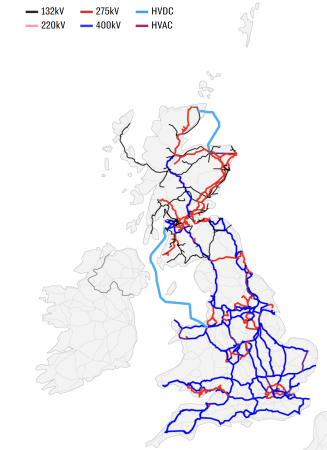
I clipped this map from this article in The Telegraph, which is entitled Britain’s Energy System Will Not Hit Net Zero Until 2035, National Grid Tells Labour.
The dark blue lines are the 400 kV transmission lines.
- The one furthest East in East Anglia serves the Sizewell site, which hosts the Sizewell B nuclear power station and will be the home of Sizewell C nuclear power station, unless the Green or LibDem Parties are a member of a coalition government.
- Kent and Sussex seem to be encircled by 400 kV lines, with small spurs to the interconnectors to Europe.
- Two 400 kV lines appear to serve the South-West peninsular, with one going along the South Coast and the other further North. I suspect these two motorways for electricity explain, why the Morocco-UK Power Project terminates in Devon.
- London seems to have its own M25 for electricity.
- There also appears to be an East-West link to the North of London linking Sizewell in the East and Pembroke in the West. Both ends have large power stations.
- There also appear to be two 400 kV lines from Keadby by the Humber Estuary to North Wales with the pumped storage hydro power station at Dinorwig.
- Two more 400 kV lines link Yorkshire to the South of Scotland.
- A lonely Northern cable connects Edinburgh and the North of Scotland.
The red lines, like the one encircling central London are the 275 kV transmission lines.
- Think of these as the A roads of the electricity network.
- They encircle London often deep underground or under canal towpaths.
- They reinforce the electricity network in South Wales.
- Liverpool appears to have its own local network.
- They also seem to provide most of the capacity North of and between Edinburgh and Glasgow.
Newer cables are starting to appear on this map.
There are two light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- The 1.2 GW Caithness – Moray Link does what it says in the name and it connects the far North of Scotland direct towards Aberdeen.
- The much larger 2.25 GW Western HVDC Link connects Hunterston near Glasgow to Flintshire Bridge near Liverpool. Note how it passes to the West of the Isle of Man.
Not shown on the map are the smaller 500 MW Moyle Interconnector and the recently-opened 600 MW Shetland HVDC Connection.
The Electricity Network In 2050
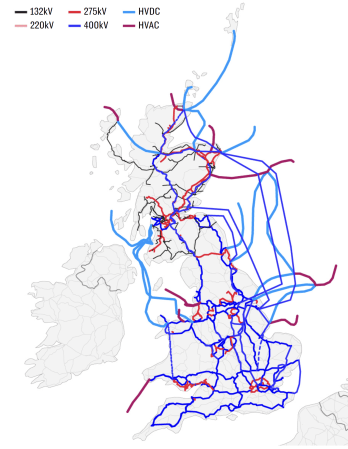
This second map shows how the network will look in 2050.
Note.
- The colours are the same, as the previous map.
- Although, I do think there are some errors in which have been used.
- There are a lot more cables.
There are several more light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- Shetland is now linked to the North of Scotland by the Shetland HVDC Connection.
- There appears to be a cluster of HVDC interconnectors at Caithness HVDC switching station, near Wick, including a new one to Orkney, to go with the others to Moray and Shetland.
- The 2 GW Scotland England Green Link 1 will run from Torness in Southeast Scotland to Hawthorn Pit substation in Northeast England.
- The 2 GW Eastern Green Link 2 will run from Sandford Bay, at Peterhead in Scotland, to the Drax Power Station in Yorkshire, England.
- There also appear to be two or possibly three other offshore cables linking the East Coast of Scotland with the East Coast of England.
- If the Eastern cables are all 2 GW, that means there is a trunk route for at least 8 GW between Scotland’s wind farms in the North-East and Eastern England, which has the high capacity wind farms of Dogger Bank, Hornsea and around the Lincolnshire and East Angliam coasts.
- Turning to the Western side of Scotland, there appears to be a HVDC connection between the Scottish mainland and the Outer Hebrides.
- South-West of Glasgow, the Western HVDC Link appears to have been duplicated, with a second branch connecting Anglesey and North-West Wales to Scotland.
- The Moyle Interconnector must be in there somewhere.
- Finally, in the South a link is shown between Sizewell and Kent. It’s shown as 400 kV link but surely it would be a HVDC underwater cable.
There are also seven stubs reaching out into the sea, which are probably the power cables to the wind farms.
- The red one leading from South Wales could connect the wind farms of the Celtic Sea.
- The blue link North of Northern Ireland could link the MachairWind wind farm to the grid.
- The other two red links on the West Coast of Scotland could link to other ScotWind wind farms.
- The red link to the North of East Anglia could link RWE’s Norfolk wind farms to the grid.
- The other stubs in the East could either connect wind farms to the grid or be multi-purpose interconnectors linking to Germany and the Netherlands.
It looks to me, that National Grid ESO will be taking tight control of the grid and the connected wind farms, as an integrated entity.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I can’t disagree with that philosophy.
Hydrogen Production
In How Germany Is Dominating Hydrogen Market, I talked about how Germany’s plans to use a lot of hydrogen, will create a large world-wide demand, that the UK because of geography and large amounts of renewable energy is in an ideal place to fulfil.
I can see several large electrolysers being built around the UK coastline and I would expect that National Grid ESO have made provision to ensure that the electrolysers have enough electricity.
Would I Do Anything Different?
Consider.
- If it is built the Morocco-UK Power Project will terminates in Devon.
- There could be more wind farms in the Celtic Sea.
- It is likely, that the wind farms in the Celtic Sea will connect to both Pembroke and Devon.
- Kent has interconnectors to the Continent.
Would a Southern HVDC link along the South Coast between Devon and Kent be a good idea?
Conclusion
Looking at the proposed list of wind farms, a total in excess of 96 GW could be possible, which is ten GW more than needed.
The network not only serves the UK in a comprehensive manner, but also tees up electricity for export to Europe.
LionLink: Proposed Windfarm Cabling Sites In Suffolk Are Revealed
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
National Grid has revealed where it wants to build energy infrastructure for cabling between the UK and the Netherlands.
These four paragraphs describe the project.
The power line, called LionLink, would connect offshore wind farms in the North Sea.
The energy company wants the cables to reach land at either Walberswick or Southwold, both in Suffolk.
A converter station would be built on the outskirts of nearby Saxmundham and could cover a six-hectare area.
That would then connect to a substation being built at the village of Friston, also in Suffolk, as part of the offshore wind plans.
But the plans have brought the Nimbies out in force.
This Google Map shows the Suffolk Coast, to the South of Southwold.
Note.
- Southwold and Walberswick in the North-East corner of the map.
- Saxmundham is just up from the South-West corner of the map, with Friston to its East.
- Sizewell with the 1.2 GW Sizewell B nuclear power station is on the coast directly East of Saxmundham.
- Sizewell B is planned to be joined by the 3.2 GW Sizewell C nuclear power station.
- LionLink is likely to have a capacity of 2 GW.
- I also believe that at least another GW of offshore wind power will be squeezed in along this section of coast.
The Sizewell site is connected to the National Grid at Bullen Lane substation to the West of Ipswich.
These pictures show the pylons that were built in the 1960s to connect Sizewell A to the National Grid.
I doubt, they would be allowed to be erected today.
One alternative would be to use T-pylons, like these built to connect Hinckley Point C to the National Grid.
There is more on T-pylons in this press release from National Grid, which is entitled National Grid Energise World’s First T-Pylons.
This Google Map shows the area between Ipswich and the coast.
Note.
- Sizewell is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Felixstowe, Harwich and Freeport East are at the mouth of the rivers Orwell and Stour.
- The Bullen Lane substation is to the West of Ipswich and shown by the red arrow.
Looking at maximum power flows in Suffolk and Somerset, we get.
- North-East Suffolk to the National Grid at Bullen Lane – 7.4 GW.
- Hinckley Point C to the National Grid – 3.26 GW.
I am led to the conclusion, that there need to be a doubling of the pylons between North-East Suffolk and Bullens Lane.
I can understand why the Nimbies have been aroused.
I believe that National Grid will have to take the undersea route along the coast of Essex and Suffolk, to get the electricity to its markets.
RWE Acquires 4.2-Gigawatt UK Offshore Wind Development Portfolio From Vattenfall
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from RWE.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- Highly attractive portfolio of three projects at a late stage of development, with grid connections and permits secured, as well as advanced procurement of key components
- Delivery of the three Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone projects off the UK’s East Anglia coast will be part of RWE’s Growing Green investment and growth plans
- Agreed purchase price corresponds to an enterprise value of £963 million
These two paragraphs outline the deal.
RWE, one of the world’s leading offshore wind companies, will acquire the UK Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone portfolio from Vattenfall. The portfolio comprises three offshore wind development projects off the east coast of England – Norfolk Vanguard West, Norfolk Vanguard East and Norfolk Boreas.
The three projects, each with a planned capacity of 1.4 gigawatts (GW), are located 50 to 80 kilometres off the coast of Norfolk in East Anglia. This area is one of the world’s largest and most attractive areas for offshore wind. After 13 years of development, the three development projects have already secured seabed rights, grid connections, Development Consent Orders and all other key permits. The Norfolk Vanguard West and Norfolk Vanguard East projects are most advanced, having secured the procurement of most key components. The next milestone in the development of these two projects is to secure a Contract for Difference (CfD) in one of the upcoming auction rounds. RWE will resume the development of the Norfolk Boreas project, which was previously halted. All three Norfolk projects are expected to be commissioned in this decade.
There is also this handy map, which shows the location of the wind farms.
Note that there are a series of assets along the East Anglian coast, that will be useful to RWE’s Norfolk Zone development.
- In Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base, I talked about how the Port of Great Yarmouth will be the operational base for the Norfolk Zone wind farms.
- Bacton gas terminal has gas interconnectors to Belgium and the Netherlands lies between Cromer and Great Yarmouth.
- The cable to the Norfolk Zone wind farms is planned to make landfall between Bacton and Great Yarmouth.
- Sizewell is South of Lowestoft and has the 1.25 GW Sizewell B nuclear power station, with the 3.2 GW Sizewell C on its way, for more than adequate backup.
- Dotted around the Norfolk and Suffolk coast are 3.3 GW of earlier generations of wind farms, of which 1.2 GW have connections to RWE.
- The LionLink multipurpose 1.8 GW interconnector will make landfall to the North of Southwold
- There is also the East Anglian Array, which currently looks to be about 3.6 GW, that connects to the shore at Bawdsey to the South of Aldeburgh.
- For recreation, there’s Southwold.
- I can also see more wind farms squeezed in along the coast. For example, according to Wikipedia, the East Anglian Array could be increased in size to 7.2 GW.
It appears that a 15.5 GW hybrid wind/nuclear power station is being created on the North-Eastern coast of East Anglia.
The big problem is that East Anglia doesn’t really have any large use for electricity.
But the other large asset in the area is the sea.
- Undersea interconnectors can be built to other locations, like London or Europe, where there is a much greater need for electricity.
- In addition, the UK Government has backed a consortium, who have the idea of storing energy by using pressurised sea-water in 3D-printed concrete hemispheres under the sea. I wrote about this development in UK Cleantech Consortium Awarded Funding For Energy Storage Technology Integrated With Floating Wind.
A proportion of Russian gas in Europe, will have been replaced by Norfolk wind power and hydrogen, which will be given a high level of reliability from Suffolk nuclear power.
I have some other thoughts.
Would Hydrogen Be Easier To Distribute From Norfolk?
A GW-range electrolyser would be feasible but expensive and it would be a substantial piece of infrastructure.
I also feel, that placed next to Bacton or even offshore, there would not be too many objections from the Norfolk Nimbys.
Hydrogen could be distributed from the site in one of these ways.
- By road transport, as ICI did, when I worked in their hydrogen plant at Runcorn.
- I suspect, a rail link could be arranged, if there was a will.
- By tanker from the Port of Great Yarmouth.
- By existing gas interconnectors to Belgium and the Netherlands.
As a last resort it could be blended into the natural gas pipeline at Bacton.
In Major Boost For Hydrogen As UK Unlocks New Investment And Jobs, I talked about using the gas grid as an offtaker of last resort. Any spare hydrogen would be fed into the gas network, provided safety criteria weren’t breached.
I remember a tale from ICI, who from their refinery got a substantial amount of petrol, which was sold to independent petrol retailers around the North of England.
But sometimes they had a problem, in that the refinery produced a lot more 5-star petrol than 2-star. So sometimes if you bought 2-star, you were getting 5-star.
On occasions, it was rumoured that other legal hydrocarbons were disposed of in the petrol. I was once told that it was discussed that used diluent oil from polypropylene plants could be disposed of in this way. But in the end it wasn’t!
If hydrogen were to be used to distribute all or some of the energy, there would be less need for pylons to march across Norfolk.
Could A Rail Connection Be Built To The Bacton Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows the area between North Walsham and the coast.
Note.
- North Walsham is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- North Walsham station on the Bittern Line is indicated by the red icon.
- The Bacton gas terminal is the trapezoidal-shaped area on the coast, at the top of the map.
ThisOpenRailwayMap shows the current and former rail lines in the same area as the previous Google Map.
Note.
- North Walsham station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The yellow track going through North Walsham station is the Bittern Line to Cromer and Sheringham.
- The Bacton gas terminal is on the coast in the North-East corner of the map.
I believe it would be possible to build a small rail terminal in the area with a short pipeline connection to Bacton, so that hydrogen could be distributed by train.
There used to be a branch line from North Walsham station to Cromer Beach station, that closed in 1953.
Until 1964 it was possible to get trains to Mundesley-on-Sea station.
So would it be possible to build a rail spur to the Bacton gas terminal along the old branch line?
In the Wikipedia entry for the Bittern Line this is said.
The line is also used by freight trains which are operated by GB Railfreight. Some trains carry gas condensate from a terminal at North Walsham to Harwich International Port.
The rail spur could have four main uses.
- Taking passengers to and from Mundesley-on-Sea and Bacton.
- Collecting gas condensate from the Bacton gas terminal.
- Collecting hydrogen from the Bacton gas terminal.
- Bringing in heavy equipment for the Bacton gas terminal.
It looks like another case of one of Dr. Beeching’s closures coming back to take a large chunk out of rail efficiency.
Claire Coutinho And Robert Habeck’s Tete-a-Tete
I wrote about their meeting in Downing Street in UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties.
- Did Habeck run the RWE/Vattenfall deal past Coutinho to see it was acceptable to the UK Government?
- Did Coutinho lobby for SeAH to get the contract for the monopile foundations for the Norfolk Zone wind farms?
- Did Coutinho have a word for other British suppliers like iTMPower.
Note.
- I think we’d have heard and/or the deal wouldn’t have happened, if there had been any objections to it from the UK Government.
- In SeAH To Deliver Monopiles For Vattenfall’s 2.8 GW Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Project, I detailed how SeAH have got the important first contract they needed.
So it appears so far so good.
Rackheath Station And Eco-Town
According to the Wikipedia entry for the Bittern Line, there are also plans for a new station at Rackheath to serve a new eco-town.
This is said.
A new station is proposed as part of the Rackheath eco-town. The building of the town may also mean a short freight spur being built to transport fuel to fire an on-site power station. The plans for the settlement received approval from the government in 2009.
The eco-town has a Wikipedia entry, which has a large map and a lot of useful information.
But the development does seem to have been ensnared in the planning process by the Norfolk Nimbys.
The Wikipedia entry for the Rackheath eco-town says this about the rail arrangements for the new development.
The current rail service does not allow room for an extra station to be added to the line, due to the length of single track along the line and the current signalling network. The current service at Salhouse is only hourly during peak hours and two-hourly during off-peak hours, as not all trains are able to stop due to these problems. Fitting additional trains to this very tight network would not be possible without disrupting the entire network, as the length of the service would increase, missing the connections to the mainline services. This would mean that a new 15-minute shuttle service between Norwich and Rackheath would have to be created; however, this would interrupt the main service and cause additional platforming problems. Finding extra trains to run this service and finding extra space on the platforms at Norwich railway station to house these extra trains poses additional problems, as during peak hours all platforms are currently used.
In addition, the plans to the site show that both the existing and the new rail station, which is being built 300m away from the existing station, will remain open.
. As the trains cannot stop at both stations, changing between the two services would be difficult and confusing, as this would involve changing stations.
I feel that this eco-town is unlikely to go ahead.
Did RWE Buy Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone To Create Green Hydrogen For Europe?
Consider.
- Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone is a 4.2 GW group of wind farms, which have all the requisite permissions and are shovel ready.
- Bacton Gas terminal has gas pipelines to Europe.
- Sizewell’s nuclear power stations will add security of supply.
- Extra wind farms could be added to the Norfolk Zone.
- Europe and especially Germany has a massive need for zero-carbon energy.
The only extra infrastructure needing to be built is the giant electrolyser.
I wouldn’t be surprised if RWE built a large electrolyser to supply Europe with hydrogen.
Wrightbus To Provide Hydrogen Buses For Sizewell C Nuclear Plant
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Ballymena bus manufacturer Wrightbus is providing four hydrogen buses to the Sizewell C nuclear power site as part of a pilot scheme.
These first three paragraphs outline the scheme.
If successful, up to 150 buses could be ordered, making it one of the largest hydrogen bus fleets in the world.
Construction of the plant is to begin next year and multiple vehicles will be needed to move workers to and from the site.
Sizewell C will test the performance of four double-decker buses.
As I used to live in that area, I know the buses are bad and this will surely help.