Huddersfield Station – 30th September 2025
This press release on the Network Rail Media Centre is entitled Huddersfield Station Set To Reopen Next Week With New Temporary Layout.
As it is now next week, I went to have a look at the progress today.
I made a mistake and got on a Grand Central Train, which meant, I had to change at York.
Speeding past Drax power station on the Selby Diversion, I took these pictures.
We were only in a 125 mph diesel, so we couldn’t take advantage of the 160 mph running, that the East Coast Main Line’s new signalling might allow on this section. The Wikipedia entry for the Selby Diversion, says this about the possible speeds.
The line was the first purpose-built section of high-speed railway in the UK having a design speed of 125 mph; however, research by British Rail in the 1990s indicated that the route geometry would permit up to 160 mph operation, subject to the necessary overhead line equipment and signalling upgrades. The new line also avoided the speed restriction over the swing bridge at Selby. The former ECML route, the NER’s 1871 York and Doncaster branch line, was closed from Selby northwards.
As the Selby Diversion opened in 1983, I wouldn’t be surprised that the calculations were performed on British Rail Research’s Pace 231-R, which was similar to the one I used at ICI and the pair, that NASA used calculate how to land Apollo on the moon.
When I eventually got to Huddersfield, I took these pictures.
Note.
- In I’ve Just Glimpsed The Future Of Train Travel Across The North Of England And I Like It, there are pictures of Huddersfield station, that were taken on the 21st August, soon after the work started.
- In Huddersfield Station – 15th December 2023, there are pictures of Huddersfield before the work started.
- Much of the work seems to have been done at the Western end of the station to lengthen the platform on the Penistone Line to Sheffield.
- Platform 2 for the Penistone Line has also been renumbered Platform 1.
Work still to be carried out at Huddersfield station, includes refurbishing the roof, installing the electrification and adding a couple of new platforms.
These are my thoughts.
Which Platforms Will Be Electrified?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the proposed electrification in Huddersfield station.
Note.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map indicates Huddersfield atation.
- The two red-and-black tracks going diagonally across the map are the Hudderfield Line.
- The red-and-black colour, indicates that the two tracks will be electrified.
- South of these two tracks, the Penistone Line sneaks into Platform 1 at Huddersfield station.
- The Penistone Line goes to Sheffield in a South-Westerly direction.
- There appears to be a crossover, so that trains from the Penistone Line can use both Platforms 1 and 2 in Huddersfield station.
- The OpenRailwayMap appears to show planned electrification between Stalybridge and Leeds stations.
- To the East of Leeds planned electrification is shown as far as Micklefield and Church Fenton stations.
Once installed, this electrification will create a complete electrified route across the Pennines from Liverpool Lime Street in the West to the East Coast Main Line in the East.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the planned electrification between Micklefield and Hull stations.
Note.
- Red tracks are electrified.
- Black tracks are not electrified.
- York is in the North-West corner of the map, with the electrified East Coast Main Line going through the station North-South.
- South of York, the East Coast Main Line now splits.
- The Western branch includes an electrified line to Micklefield station, Neville Hill depot and Leeds station.
- The Eastern Branch is the Selby Diversion, which is an electrified 160 mph line, that avoids the Selby coalfield.
- Running West-East across the map is the unlectrified Micklefield and Hull Line, which goes via Selby.
- Hull is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Hull is 42 miles from Micklefield and 36.1 miles from the Temple Hirst junction on the Selby Diversion, so it is within range of battery-electric trains, with charging at Hull station.
- Hitachi’s battery-electric Class 802 trains, used by Hull Trains and TransPennine Express, which are currently on test, should certainly be able to serve Hull.
Hull can become an electrified station, without the expense and disruption of full electrification.
How Long Is Platform 1 At Huddersfield Station?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the new Platform 1 at Huddersfield station.
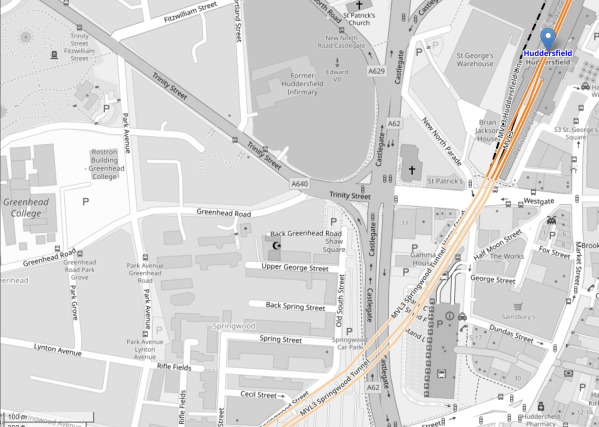
Note.
The blue arrow indicates Huddersfield station.
- The three darker orange lines indicate the two through platforms 2 and 3, and the reconfigured bay platform 1.
- There is a cross-over between platforms 1 and 2, which connects Platform 2 to the Penistone Line.
- In the South-West corner of the map is a hundred metre scale.
- Using the scale, I estimate that the length of the bay platform 1 is around 120 metres.
- In the last two rows of pictures in the gallery of this post, a three car Class 150 train is shown in Platform 1.
- A three car Class 150 train is approximately sixty metres long.
Looking at the pictures, I wouldn’t be surprised if the new platform has been designed to take two three-car Class 150 trains. It would certainly take a pair of two-car Class 150 trains.
Other trains and their lengths that might use the platform include.
- Class 170 – three-car – 70.85 metres
- Class 195 – two-car – 48.05 metres
- Class 195 – three-car – 71.40 metres
- Class 195 – 2 x two-car – 96.10 metres
- Class 810 – five-car – 120 metres
The Class 810 uses 24 metre cars, so that a pair of trains, will fit in St. Pancras. But with perhaps selective door opening could a single Class 810 train run a St. Pancras and Huddersfield service, perhaps with a split and join at Sheffield.
Electrification Across The Pennines
The TransPennine Route will be electrified between Liverpool Lime Street and Micklefield stations, once the current works between Huddersfield and Leeds are complete.
Sections without electrification include.
- Bradford Interchange and Doncaster – 52.1 miles
- Cleethorpes and Doncaster – 52.1 miles
- Harrogate and Leeds – 18.3 miles
- Hazel Grove and Doncaster – 52.6 miles
- Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- Hull and Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- Saltburn and Northallerton – 28.1 miles
- Sunderland and Northallerton – 46.8 miles
- Scarborough and York – 42.1 miles
I expect that Hitachi trains with batteries or CAF’s tri-mode trains will be able to handle these routes in a low-carbon manner.
Electrification Between Stalybridge And Huddersfield
This section is shown as being electrified on OpenRailwayMap.
But as it is only 18 miles and includes the Standedge Tunnels will the route use battery-electric trains?
Thoughts On High Speed Two
These are a few thoughts about High Speed Two, after the reports of major changes today.
This article on the BBC is entitled HS2 Line Between Birmingham And Crewe Delayed By Two Years.
This is the sub-heading.
The Birmingham to Crewe leg of high speed railway HS2 will be delayed by two years to cut costs.
These are the three opening paragraphs.
Some of the design teams working on the Euston end of the line are also understood to be affected.
Transport secretary Mark Harper blamed soaring prices and said it was “committed” to the line linking London, the Midlands and North of England.
HS2 has been beset by delays and cost rises. In 2010, it was expected to cost £33bn but is now expected to be £71bn.
Delivering The Benefits Of High Speed Two Early
It is my belief that with a large project taking a decade or more , it is not a bad idea to deliver some worthwhile benefits early on.
The Elizabeth Line opened in stages.
- The new Class 345 trains started replacing scrapyard specials in 2017.
- The rebuilt Abbey Wood station opened in 2017.
- Paddington local services were transferred to the Elizabeth Line in 2019.
- Outer stations reopened regularly after refurbishment from 2018.
- The through line opened in May 2022.
There’s still more to come.
Some projects wait until everything is ready and everybody gets fed up and annoyed.
Are there any parts of High Speed Two, that could be completed early, so that existing services will benefit?
In 2020, the refurbishment of Liverpool Lime Street station and the tracks leading to the station was completed and I wrote about the station in It’s A Privilege To Work Here!, where this was my conclusion.
Wikipedia says this about Liverpool Lime Street station.
Opened in August 1836, it is the oldest still-operating grand terminus mainline station in the world.
I’ve used Lime Street station for fifty-five years and finally, it is the station, the city needs and deserves.
I’ve been to grand termini all over the world and Lime Street may be the oldest, but now it is one of the best.
Are there any stations, that will be served by High Speed Two, that should be upgraded as soon as possible to give early benefits to passengers, staff and operators?
Avanti West Cost have solved the problem of the short platforms at Liverpool South Parkway station, by ordering shorter Class 807 trains. Will High Speed Two lengthen the platforms at this station?
A good project manager will need to get all the smaller sub-projects in a row and work out what is the best time to do each.
Digital Signalling
I would assume, as this will be needed for High Speed Two services in the West Coast Main Line to the North of Crewe, this is surely a must for installing as early as possible.
If the existing trains could run for a hundred miles at 140 mph, rather than the current 125 mph, that would save five worthwhile minutes.
Trains could run closer together and there is the possibility of organising services in flights, where a number of trains run together a safe number of minutes apart.
Remove Bottlenecks On Classic Lines, That Could Be Used By High Speed Two
I don’t know the bottlenecks on the West Coast Main Line, but there are two on the East Coast Main Line, that I have talked about in the past.
Could ERTMS And ETCS Solve The Newark Crossing Problem?
Improving The North Throat Of York Station Including Skelton Bridge Junction
Hopefully, the digital signalling will solve them.
Any bottlenecks on lines that will be part of High Speed Two, should be upgraded as soon as possible.
Birmingham And Crewe
I will start by looking at the leg between Birmingham and Crewe.
This section of the HS2 map shows High Speed Two between Birmingham and Lichfield.
Note.
- The blue circle on the left at the bottom of the map is Birmingham Curzon Street station.
- The blue circle on the right at the bottom of the map is Birmingham Interchange station.
- The High Speed Two to and from London passes through Birmingham Interchange station.
- The branch to Birmingham Curzon Street station connects to the main High Speed Two at a triangular junction.
- North of the triangular junction, High Speed Two splits.
- The Eastern branch goes to East Midlands Parkway station.
- The Northern branch goes to Crewe, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Preston and Scotland.
At the top of the map, the Northern branch splits and lines are shown on this map.
Note.
- The junction where the Northern and Eastern branches divide is in the South-East corner of the map.
- To the North of Lichfield, the route divides again.
- The Northern purple line is the direct line to Crewe.
- The shorter Southern branch is a spur that connects High Speed Two to the Trent Valley Line, which is the current route taken by trains between London Euston and Crewe, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Preston and Scotland.
- Crewe station is in the North-West corner of the map.
The route between the junction to the North of Lichfield and Crewe is essentially two double-track railways.
- High Speed Two with a routine operating speed of 205 mph.
- The Trent Valley Line with a routine operating speed of 140 mph.
- High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains can run on all tracks.
- High Speed Two Full-Size trains may be able to run on the Trent Valley Line at reduced speed.
- Eighteen trains per hour (tph) is the maximum frequency of High Speed Two.
I feel in an emergency, trains will be able to use the other route.
Will This Track Layout Allow An Innovative Build?
Suppose the link to the Trent Valley Line was built first, so that High Speed Two trains from London for Crewe, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Preston and Scotland, could transfer to the Trent Valley Line as they do now.
- All lines used by High Speed Two services North of the junction, where High Speed Two joins the Trent Valley Line would be updated with digital signalling and 140 mph running. This will benefit current services on the line. For instance Euston and Liverpool/Manchester services could be under two hours.
- The current services would be replaced by High Speed Two services run by High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains.
- The direct High Speed Two route between Lichfield and Crewe would now be built.
- When this section of High Speed Two is complete, High Speed Two services would use it between Lichfield and Crewe.
- As the direct route would be built later, this would delay the building of the Birmingham and Crewe high-speed route.
Currently, trains run the 41.8 miles between Lichfield and Crewe in 28 minutes, which is an average speed of 89.6 mph.
I can build a table of average speeds and times for Lichfield and Crewe.
- 100 mph – 25.1 minutes – 2.9 minutes saving
- 110 mph – 22.8 minutes – 5.2 minutes saving
- 120 mph – 20.9 minutes – 7.1 minutes saving
- 125 mph – 20.1 minutes – 7.9 minutes saving
- 130 mph – 19.3 minutes – 8.7 minutes saving
- 140 mph – 17.9 minutes – 10.1 minutes saving
- 160 mph – 15.7 minutes – 12.3 minutes saving
- 180 mph – 13.9 minutes – 14.1 minutes saving
- 200 mph – 12.5 minutes – 15.5 minutes saving
Note.
- Even a slight increase in average speed creates several minutes saving.
- Times apply for both routes.
I believe that a 125 mph average should be possible on the Trent Valley route, which may be enough for Euston and Liverpool/Manchester services to be under two hours.
Improving Classic Lines Used By High Speed Two North Of Lichfield
Real Time Trains shows these figures for a Glasgow Central to Euston service.
- Glasgow and Lichfield Trent Valley is 298.2 miles.
- Glasgow and Lichfield Trent Valley takes five hours.
This is an average speed of 59.6 mph.
Note.
- The average speed is low considering the trains are capable of cruising at 125 mph and 140 mph with digital signalling.
- High Speed Two services between Euston and Glasgow will use the classic network, to the North of Lichfield.
I can build a table of average speeds and times for Glasgow and Lichfield.
- 100 mph – 179 minutes – 121 minutes saving
- 110 mph – 163 minutes – 157 minutes saving
- 120 mph – 149 minutes – 151 minutes saving
- 125 mph – 143 minutes – 157 minutes saving
- 130 mph – 138 minutes – 162 minutes saving
- 140 mph – 128 minutes – 172 minutes saving
This table illustrates why it is important to improve all or as many as possible of classic lines used by High Speed Two to enable 140 mph running, with full digital signalling. Obviously, if 140 mph is not feasible, the speed should be increased to the highest possible.
Routes that could be updated include.
- London Euston and Glasgow Central
- London Euston and Liverpool Lime Street
- London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly (all routes)
- London Euston and Blackpool
- London Euston and Holyhead
- London Euston and Shrewsbury
Not all these routes will be served by High Speed Two, but they could be served by 140 mph trains.
What Times Would Be Possible?
The InterCity 225 was British Rail’s ultimate electric train and these two paragraphs from its Wikipedia entry, describe its performance.
The InterCity 225 was designed to achieve a peak service speed of 140 mph (225 km/h); during a test run in 1989 on Stoke Bank between Peterborough and Grantham, an InterCity 225 was recorded at a speed of 162 mph (260.7 km/h). Its high speed capabilities were again demonstrated via a 3hr 29mins non-stop run between London and Edinburgh on 26 September 1991. British regulations have since required in-cab signalling on any train running at speeds above 125 mph (201 km/h) preventing such speeds from being legally attained in regular service. Thus, except on High Speed 1, which is equipped with cab signalling, British signalling does not allow any train, including the InterCity 225, to exceed 125 mph (201 km/h) in regular service, due to the impracticality of correctly observing lineside signals at high speed.
The InterCity 225 has also operated on the West Coast Main Line (WCML). In April 1992, one trainset achieved a new speed record of two hours, eight minutes between Manchester and London Euston, shaving 11 minutes off the 1966 record. During 1993, trials were operated to Liverpool and Manchester in connection with the InterCity 250 project.
- The fastest London Euston and Manchester Piccadilly services appear to be two hours and six minutes tomorrow, with stops at Nuneaton and Stoke-on-Trent.
- The fastest London King’s Cross and Edinburgh service is four hours seventeen minutes tomorrow.
It does appear that British Rail’s 1980s-vintage InterCity 225 train did very well.
Trains that would be able to run at 140 mph with updated signalling include.
- Alstom Class 390
- Hitachi Class 800, 801, 802, 803, 805, 807 and 810
- British Rail InterCity 225
- High Speed Two Classic-Compatible.
All are electric trains.
Could High Speed Two, West Coast Main Line and East Coast Main Line Services Be Run By High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains?
I don’t see why not!
- They would be able to use short stretches of High Speed Line like Lichfield and Crewe.
- LNER and CrossCountry could also use the trains.
- High Speed Two is providing the framework and it’s there to be used, provided the paths are available.
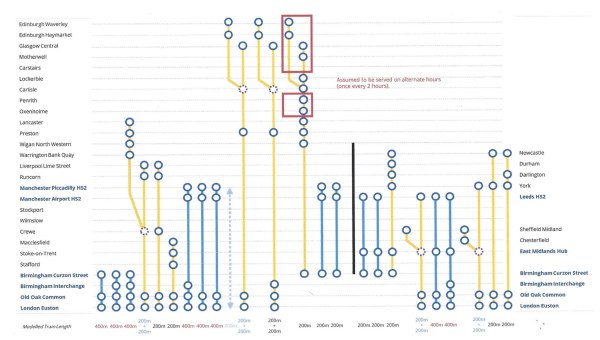
This graphic shows the preliminary schedule.
It only shows ten trains going through Crewe, so there could be up to eight spare high speed paths between Birmingham and Crewe.
Could High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains Be Used To Advantage On The East Coast Main Line?
I published this extract from the Wikipedia entry for the InterCity 225 earlier.
The InterCity 225 was designed to achieve a peak service speed of 140 mph (225 km/h); during a test run in 1989 on Stoke Bank between Peterborough and Grantham, an InterCity 225 was recorded at a speed of 162 mph (260.7 km/h). Its high speed capabilities were again demonstrated via a 3hr 29mins non-stop run between London and Edinburgh on 26 September 1991.
The London and Edinburgh run was at an average speed of around 112 mph.
I wonder what time, one of LNER’s Class 801 trains, that are all-electric could do, once the new digital signalling has been fully installed on the route? I suspect it would be close to three hours, but it would depend on how long the trains could run at 140 mph.
It should be noted that the Selby Diversion was designed for 160 mph, when it was built by British Rail in the 1980s.
In Are Short Lengths Of High Speed Line A Good Idea?, I look at the mathematics of putting in short lengths of new railway, which have higher speeds, where this was part of my conclusion.
I very much feel there is scope to create some new high speed sections on the current UK network, with only building very little outside of the current land used by the network.
I would love to know what some of Network Rail’s track experts feel is the fastest time possible between London and Edinburgh that can be achieved, by selective upgrading of the route.
If some of the trains were High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains, with a top speed of 205 mph, provided the track allowed it, there could be some interesting mathematics balancing the costs of track upgrades, new trains with what passengers and operators need in terms of journey times.
Could High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains Be Used To Advantage On The West Coast Main Line?
Much of what I said about the East Coast Main Line would apply to the West Coast Main Line.
But in addition, the West Coast Main Line will be a superb place to test the new High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains.
I believe, that before High Speed Two opens, we’ll see High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains, carrying passengers between Euston and Avanti West Coast’s destinations.
Could High Speed Two Be Split Into Two?
Consider.
- Under earlier plans, the East Coast Main Line to the North of York, will be used by High Speed Two.
- With digital signalling the East Coast Main Line will support continuous running at 140 mph for long sections of the route.
- The East Coast Main Line has a recently-rebuilt large Southern terminal at King’s Cross with eleven platforms and good suburban services and excellent connections to the London Underground.
- The East Coast Main Line has a very large Northern terminal at Edinburgh Waverley with twenty platforms and good local train connections.
- There are large intermediate stations on the East Coast Main Line at Doncaster, Leeds, Newcastle, Peterborough and York. All these stations have good local train connections.
- The East Coast Main Line has important branches to Cambridge, Harrogate, Huddersfield, Hull King’s Lynn, Lincoln, Middlesbrough, Nottingham, Scarborough, Sheffield, Skegness and Sunderland.
We are talking about an asset, that needs improving rather than sidelining.
Could High Speed Two Be A One-Nation Project?
Over three years ago, I wrote Could High Speed Two Be A One-Nation Project? and tried to answer the question in the title.
But now the core network is better defined, perhaps it is time to look at extending the High Speed network again.
The next few sections look at possible extensions.
Serving Chester And North Wales
I looked at this in Could High Speed Two Trains Serve Chester And North Wales?, which I have updated recently.
This was my conclusion.
It looks to me, that when High Speed Two, think about adding extra destinations, Chester and Holyhead could be on the list.
I also suspect that even without electrification and High Speed Two services, but with the new Class 805 trains, the route could be a valuable one for Avanti West Coast.
These are current and promised times for the two legs to Holyhead.
- Euston and Crewe – 90 minutes – Fastest Class 390 train
- Euston and Crewe – 55 minutes – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train from Wikipedia
- Crewe and Holyhead – 131 minutes – Fastest Class 221 train
- Crewe and Holyhead – 70 minutes – 90 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 63 minutes – 100 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 57 minutes – 110 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 53 minutes – 120 mph average speed
- Crewe and Holyhead – 45 minutes – 140 mph average speed
Note.
- I have assumed that Crewe and Holyhead is 105.5 miles.
- The operating speed of the North Wales Coast Line is 90 mph.
- In the following estimates, I have assumed a change of train at Crewe, takes 6 minutes.
I think there are several options to run fast services to Chester and North Wales.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- The fastest Class 221 train between Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 3 hours 41 minutes.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way, but with perhaps less stops and some track improvement
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- 110 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 2 hours 27 minutes.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead uprated largely to 125 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- 120 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 2 hours 23 minutes.
Pre-HS2 – Class 805 all the way, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead Crewe and Holyhead electrified and uprated to 140 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest Class 390 train between Euston and Crewe.
- 140 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 2 hours 15 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, the Class 805 train to Holyhead
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- The fastest Class 221 train between Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 3 hours 12 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, the Class 805 train to Holyhead, but with perhaps less stops and some track improvement
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 110 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 58 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, the Class 805 train to Holyhead, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead uprated largely to 125 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 120 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 54 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe, Class 805 train to Holyhead, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead electrified and uprated to 140 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 140 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 46 minutes.
After-HS2 – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train all the way, but with perhaps less stops and Crewe and Holyhead electrified and uprated to 140 mph
I believe this train will match the following.
- The fastest High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train between Euston and Crewe.
- 140 mph train Crewe and Holyhead.
This would give a time of 1 hours 40 minutes.
From these estimates, I have come to these conclusions.
- A sub-two and a half-hour service can be attained with the new Class 805 trains and some improvements to the tracks along the North Wales Coast Line.
- A sub-two hour service can be attained with a High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train to Crewe and a Class 805 train to Hplyhead along a 140 mph electrified North Wales Coast Line.
- If the North Wales Coast Line is electrified, the journey from London Euston, Birmingham Interchange, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester would be zero-carbon.
We should be looking to building a zero-carbon fast passenger ferry for sailing between Holyhead and Dublin.
- The current fastest ferries appear to take three hours and 15 minutes, which means that a six-hour low-carbon journey between London Euston and Dublin, should be possible with the new Class 805 trains, prior to the opening of High Speed Two.
- A five-hour journey after the opening of High Speed Two to Crewe and electrification of the North Wales Coast Line should be possible.
If the advanced zero-carbon ferry could knock an hour off the journey, four hours between London and Dublin along a spectacular coastal railway with a fast sea voyage, would be a route that would attract passengers.
- High Speed Two would need to be opened to Crewe.
- The North Wales Coast Line would need to be upgraded to a 140 mph digitally-signalled line.
- The North Wales Coast Line would need to be electrified.
- Full electrification may not be needed, as discontinuous electrification will have advanced to provide zero-carbon running, in a more affordable and less disruptive manner.
- Trains could either be High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains all the way from London or there could be a change at Crewe to Class 805 trains.
- The ferry would use the best zero-carbon and operational technology.
The improvement and electrification of the North Wales Coast Line could be planned to take place in a relaxed manner, so that journey times continuously got quicker.
I would start the improvement of the North Wales Coast Line, as soon as possible, as all these improvement will be used to advantage by the new Class 805 trains.
Serving West And South West England And South Wales
Suppose you want to go between Glasgow and Cardiff by train, after High Speed Two has opened.
- You will take one of the half-hourly High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains between Glasgow Central and London.
- Three and a half-hours later, you will get off the train in one of the below ground platforms at Old Oak Common station.
- A short ride in an escalator or lift and you will be in the Great Western Railway station at ground level.
- From here, fifty minutes later, you will be in Cardiff.
The journey will have taken four hours and twenty minutes.
This may seem a long time but currently Glasgow and Cardiff by train takes over seven hours by train.
- Glasgow and Bristol Temple Meads takes eight hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 5 hours.
- Glasgow and Cheltenham Spa takes six hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 5 hours and 30 minutes.
- Glasgow and Penzance takes twelve hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 8 hours and 33 minutes.
- Glasgow and Swansea takes nearly nine hours, but using High Speed Two and GWR will take 6 hours and 9 minutes.
The High Speed Two route only has one simple change, whereas some routes now have up to four changes.
Conclusion
Are Short Lengths Of High Speed Line A Good Idea?
In New ‘HS3’ Link To Yorkshire Proposed By Thinktank After Region’s HS2 Axe, I showed that a short length of faster by-pass line could give decent ties savings.
So in this post, I will look at home much time, diversions or by-passes like the Selby Diversion could save.
The diversion runs between Temple Hirst Junction and Colton Junction.
- It is 13.8 miles long.
- A typical train takes 7.5 minutes, which is an average speed of 115 mph.
- But Wikipedia claim that the route was well-designed and British Rail felt it was good for 160 mph.
So what times are possible at various speeds?
- 115 mph – 7.5 minutes
- 120 mph – 6.9 minutes
- 130 mph – 6.4 minutes
- 140 mph – 5.9 minutes
- 150 mph – 5.5 minutes
- 160 mph – 5.2 minutes
- 180 mph – 4.6 minutes
They are not great savings, but if you could increase operating speed on straight sections of thirty miles and raise the average speed from 120 to 180 mph, that would save five minutes. It would all mount up.
If you look at the railway maps of the UK, there are sections of the East Coast Main Line, Great Western Main Line, Midland Main Line and West Coast Main Line, where the track is straight and sometimes as many as four-tracks.
Stevenage Station And Stoke Junction
A simple example in a few years could be between just North of Stevenage station and Stoke junction, which after current works and some others could be four tracks all the way.
- It is 72.2 miles.
- Trains take 39 minutes.
- My timings give an average speed of 111 mph.
- There are a number of level crossings.
- Flat junctions at Hitchin and Werrington have been replaced with grade separated junctions.
Note that it is longer than the Cologne-Aachen high speed railway in Germany, which is only 43 miles long and has an operating speed of 250 kph or 155.3 mph.
Savings on the Stevenage and Stoke stretch could be as follows.
- 140 mph – eight minutes
- 155.3 mph – eleven minutes
- 160 mph – twelve minutes
- 180 mph – fifteen minutes.
- 200 mph – seventeen minutes.
This alone could mean that London Kings Cross and Leeds could be around two hours with trains such as the proposed High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains.
It couldn’t be extended to the North very easily as Stoke Tunnel is between Stoke junction and Grantham.
This Google Map shows the tunnel.
If it could easily be converted into a four-track cutting, this would add nearly six miles to the four-track section with high speed lines in the middle and slow lines on the outside.
A Diversion At York
When improving speeds and times on the East Coast Main Line, a diversion at York is sometimes mentioned.
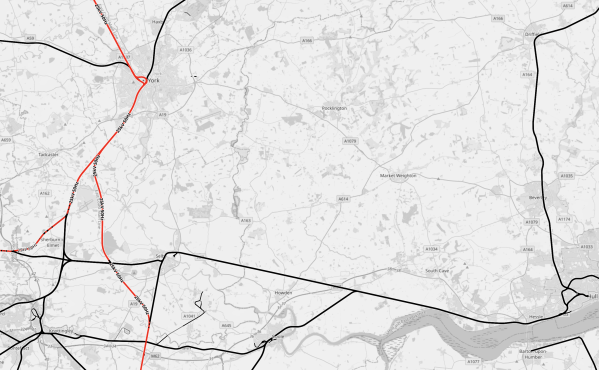
The Google Map shows the East Coast Main Line, as it goes through York station.
Note.
- York station is in the South East corner of the map.
- The River Ouse meandering North from near the station, before turning West at the top of the map.
- The East Coast Main Line running North from the station to the West of the river.
The railway crosses the river just to the North of Skelton junction.
This Google Map shows the tracks at York in more detail.
Note.
- The River Ouse in the North-East corner of the map.
- The East Coast Main Line through York station curving round the Railway Museum, before going North.
- A second rail route and sidings to the West of the East Coast Main Line can be seen.
Could a diversion route be created between Holgate and Skelton junctions on railway land?
- It would be about two miles long.
- It could be built to also sort out the bottleneck at Skelton junction.
- It might be possible to extend the fast line to Northallerton station.
This could create up to thirty miles of fast lines between Holgate junction and Northallerton.
A Diversion At Durham
When improving speeds and times on the East Coast Main Line, a diversion at Durham is sometimes mentioned.
The Google Map shows the East Coast Main Line, as it goes through Durham station.
Note.
- I have arranged the map so that the East Coast Main Line goes between the South-West and North-East corners of the map.
- Durham station is clearly visible.
- The railway line curves East towards the station around Nevilles Cross after running North from the South.
This Google Map shows the East Coast Main Line, as it goes through Chester-le-Street station.
Note.
- Chester-le-Street station is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The East Coast Main Line runs North-South down the middle of the map.
- About halfway down the map, the East Coast Main Line starts to veer to the East.
If you look at the bigger picture of these maps, it appears that to serve Durham, the line took a loop to the East, so would a diversion cut off the corner between Chester-le-Street and Nevilles Cross and put Durham on a loop?
It would be a bit shorter, but it could be built to enable running at a higher speed.
Short German High Speed Lines
I have travelled a lot on German trains and they have some of our problems.
- Infrastructure dating back to the times of Kaiser Bill.
- A high mileage of track without electrification.
- Less high speed railways than France or Spain.
They are creating several high speed railways.
Earlier, I indicated that the Cologne-Aachen high speed railway, which is only 43 miles long, has an operating speed of 250 kph.
Other short high speed railways include.
- Lübeck–Hamburg railway – 39 miles – 200 kph.
- Lübeck–Puttgarden railway – 55.1 miles – 200 kph.
- Mannheim–Stuttgart high-speed railway – 62 miles – 280 kph
- Nuremberg–Erfurt high-speed railway – 66 miles – 300 kph
- Stuttgart–Wendlingen high-speed railway – 9.5 miles – 250 kph
- Wendlingen–Ulm high-speed railway – 37 miles – 250 kph
Note, that the Germans are still upgrading lines to 200 kph or 125 mph.
The Germans would appear to favour some shorter high speed lines, so it must be a worthwhile philosophy.
Conclusion
I very much feel there is scope to create some new high speed sections on the current UK network, with only building very little outside of the current land used by the network.
As with Germany would it be worthwhile to upgrade some lines to 125 mph running?
These could be possibilities.
- Basingstoke and Exeter – Currently 121 miles at 90 mph – Not electrified
- London Liverpool Street and Norwich – Currently 114.5 miles at 100 mph – Electrified
- North Wales Main Line – Currently 84.4 miles at 90 mph – Not electrified
- Reading and Taunton – Currently 107 miles at 110 mph – Not electrified
There are probably others.