Wylfa: UK Government In Talks To Buy Nuclear Site – Report
The title of this post, is the same as that as this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK government is reportedly in talks to take control of a site in north Wales where a planned nuclear project was scrapped in 2019.
These paragraphs outline the story.
State-owned Great British Nuclear is “in early discussions” with Hitachi, which owns the land at Wylfa, on Anglesey, the Financial Times reported.
A government spokesman said Wylfa was one of many “potential sites” that could host nuclear projects.
Hitachi abandoned its plans there in January 2019.
An unnamed minister told the FT that “tentative negotiations” with Hitachi had already begun, but said a deal might not be reached until after a general election expected later this year.
Tom Greatrex, chief executive of the Nuclear Industry Association and Virginia Crosbie, MP for Ynys Môn both welcomed the talks.
These are my thoughts.
Where Is Wylfa?
This Google Map shows Anglesey.
Wylfa power station is near Wylfa Head at the top of the map, where they are indicated by the cluster of red arrows.
This Google Map shows the power station to a larger scale.
Note.
- The red arrow named Magnox marks the decommissioned Magnox power station.
- The topmost red arrow marks Wylfa Head.
- The rightmost red arrow marks Porth y Wylfa, which looks like a small harbour.
- On some maps the square building to the East of the power station is marked as Wylfa sub-station.
- There certainly appears to be an overhead transmission line leading South from the power station complex.
Virginia Crosbie, MP for Ynys Môn, also said this according to the BBC article.
The nuclear industry is unanimous that Wylfa is the best site in Europe for large-scale nuclear,” she said, adding that it would be “the largest inward investment” in Welsh history and “transformational” for the people of north-west Wales.
But I do wonder, if when you have cleared the Wylfa site leaving the sub-station, that it could be a site where renewables could come ashore and be fed into the grid.
Why Is Wylfa The Best Site In Europe For Large-Scale Nuclear?
Given the protests about putting new power transmission lines across Norfolk and Suffolk, I feel that Wylfa’s largest asset could be its high capacity connection to the UK’s grid.
According to the Wikipedia entry for Wylfa power station, this is said about Wylfa B.
Horizon Nuclear Power, originally an E.ON and RWE joint venture, bought by Hitachi in 2012, announced in 2009 intentions to install about 3,000 MWe of new nuclear plant at Wylfa. Horizon planned to build two advanced boiling water reactors (ABWRs) at a site to the south of the existing Wylfa station.
It would seem that the high capacity connection to the UK’s grid, is capable of handling a 3 GW power station at Wylfa, which could be very useful in the grand scheme of things.
This is also said in the Wikipedia entry for Wylfa power station.
On 4 April 2017, Horizon submitted a Site Licence Application to the Office for Nuclear Regulation. The scheme was extended to include a tunnel under the Menai Strait to carry the power cables to protect the conservation worth of the Strait and the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
Horizon certainly seemed to try hard to get Wylfa B under construction.
As I said earlier, the Wylfa site could be an ideal site to connect offshore renewables to the grid.
Train Frequency Focus In North Wales Transport Commission’s Interim Recommendations
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette International.
This is the first paragraph.
The North Wales Transport Commission chaired by Lord Burns has published its interim recommendations for the development and delivery of an integrated multi-modal transport system in the region.
The following sections, outline the recommendations for rail services.
Chester Station Improvements
The North Wales Transport Commission (NWTC) supports proposed improvements at Chester station to enable additional services to operate.
This page on Transport for Wales detailed the improvements at Chester station, where this is said.
Transport for Wales is delivering significant improvements to Chester Station. The project primarily focuses on customer improvements within the station, with work to include new branding and signage, a new passenger assist point, cycle stands, roaming mics and hearing loop systems, a new full station CCTV system, toilet refurbishments on the concourse and platforms 4 and 7, a new changing place toilet, customer waiting room upgrade, water refill unit, platform and concourse seating and waste facilities.
New Customer Information Screens will be installed throughout Chester station increasing the train service information available on the platforms and within the station waiting rooms. We’ll also be installing new screens for onward journeys, including bus, and an interactive screen which will be installed on the concourse.
Improvement works in the concourse also include, repurposing of the ticket office to create a new retail unit for the future, a new rental unit, a new customer service desk with ticket selling facilities, additional ticket vending machines, a repositioned gate line with additional standard and wide aisle gates. A new quiet room will also be introduced as a place for customers who require a safe, isolated space whilst waiting for their train.
TfW is working closely with industry partners to minimise disruption during these works for both customers and the local community. Customers are encouraged to plan in extra time to allow for potential disruption during this work. Signage and hoardings will be erected at the station in advance of and throughout, these significant improvement works, and communications will be provided at the station, onboard services and online, to advise of any temporary changes to accommodate the work on site at the station.
Note.
- It looks a serious level of improvement for customers.
- The Chester and Wrexham Line was improved in 2017, with full double-tracking and higher maximum speeds.
- It looks like completion is some time in 2024.
Nothing is said about extra train services.
North Wales Main Line
The NWTC says this about the North Wales Main Line.
On the North Wales Main Line, it says the priority should be service frequency improvements and supporting infrastructure works between Crewe and Llandudno. Improvements to signalling and line capacity from Llandudno to Bangor and Holyhead would require larger scale works, which should be planned so that they are ready to progress as and when funding is available.
I went to Holyhead earlier in the year and more trains would be welcome.
Borderlands Line
The NWTC says this about the Borderlands Line.
Signalling and line capacity improvements are required along the Borderlands Line, the commission believes. A key constraint is the sidings for the Hanson site at Padeswood, where freight trains block the line for up to an hour, and the commission says this needs to be resolved before other work to improve the line can proceed.
There should be investment to reduce journey times and increase service frequencies between Wrexham and Liverpool to significantly increase the attractiveness of the route.
I talked about the freight problem in New Trains Could Be Operating Through Flintshire From May But No Green Light For Two An Hour Service.
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the track layout at Padeswood site.
I was able to follow a train on Real Time Trains, as it left Padeswood Cement Works.
- It moved to the sidings alongside the Borderlands Line.
- It then joined the Borderlands Line and went Northwards through Buckley, Hawarden, Shotton and Hawarden Bridge stations before stopping in Dee Marsh Sidings.
- The engine then changed ends and brought the train back down the Borderlands Line to Wrexham.
- The train then continued to its destination via Ruabon, Gobowen and Shrewsbury.
This movement doesn’t seem too bad, so has there been some signalling and track improvements?
Shrewsbury And Chester Line
The NWTC says this about the Shrewsbury and Chester Line.
The commission says it has not seen a pressing case for full electrification of the Shrewsbury to Chester line, and the priority should be signalling improvements at Gobowen.
I thought that Shrewsbury and Chester might have been electrified, as it could be used to charge battery-electric going between England and Wales. But it will be some years before Transport for Wales get a battery-electric train strategy together.
On the other hand the two cities are only 42 miles apart, which is in range of battery-electric trains.
Conwy Valley And Cambrian Coast Lines
The NWTC says this about the Conwy Valley Line and the Cambrian Coast Line.
There could be merit in introducing increased frequencies on the Conwy Valley and Cambrian Coast lines during the peak season. Service enhancements and infrastructure improvements such as passing loops may be beneficial, ‘as has happened to similar lines in Devon and Cornwall’, but ’in the immediate future, those communities served by stations along the route should have access to enhanced bus services to reduce dependence on car use’.
This seems like a sensible and non-disruptive plan.
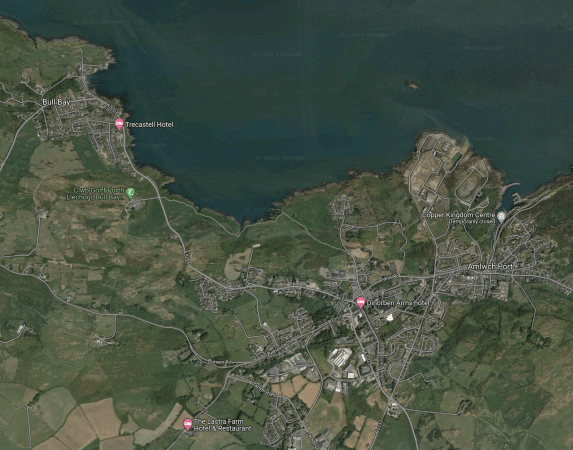
Anglesey Central Railway
The NWTC says this about the Anglesey Central Railway to Amlwch.
NWTC ‘is not persuaded’ that there is a case for opening the line to Amlwch, and says ’more urgent improvements to existing lines and services should take a higher priority’.
The Anglesey Central Railway reopening would appear to be a fairly simple project as the track is mostly already there, so this might be the sort of project, that finds itself moving up the list, if related housing or commercial developments are proposed.
This Google Map shows Amlwch and the surrounding area.
With all the tidal, nuclear and wind energy possibilities in the area, I would never rule out the rail link to Amlwch being restored.
Associated Octel used to have bromine works in Amlwch and more details can be found in this web site.
I’ve worked in chemical works with chlorine, fluorine and bromine and my advice is be very careful with them.
Criccieth And Bangor
NWTC says this about reopening the route between Criccieth and Bangor.
NWTC ‘is not persuaded’ that there is a case for opening the line between Criccieth and Bangor, and says ’more urgent improvements to existing lines and services should take a higher priority’.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the area of the reopening.
Note.
- The orange line going across the top of the map is North Wales Coast Line between Chester in the East and the Port of Holyhead on Anglesey.
- Towards the North-East corner of the map, Bangor station is indicated by the blue lettering.
- The Menai Strait runs between the Welsh mainland and the Island of Anglesey.
- The important town of Caernarfon can be picked out.
- The orange line at the bottom of the map is the Cambrian Line, which connects to Shrewsbury and Aberystwyth.
- This line terminates at Pwllheli on the Lleyn Peninsular in the South-West corner of the map.
A dotted line indicates a disused railway between the Southern coast of the peninsular and Bangor via Caernarfon, which I assume is the railway that has been proposed for reinstatement.
It could be a valuable addition to the railways of North Wales and could help to promote tourism.
Station And Other Improvements On The Borderlands Line
This is said about station and other improvements on the Borderlands Line.
The commission supports a new station at Deeside Industrial Park, and enhancements at Shotton to improve connectivity between the high and low-level platforms.
It says frequency enhancements should be prioritised over new stations, and fleet improvements should facilitate the frequency enhancements. It endorses the proposed use of Merseyrail’s Class 777 battery-electric trainsets on the Borderlands Line.
I feel that the Class 777 trains, which could travel under Liverpool are a shoe-in.
Conclusion
North Wales will be getting the railway it need to promote education, employment, leisure and tourism.
West Coast Main Line Electro-Diesels On Test
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
This is the first paragraph.
The first two of 13 Hitachi Class 805 electro-diesel trainsets ordered for Avanti West Coast services are undergoing testing on the West Coast Main Line ahead of entry into service later this year.
These Class 805 trains will go to places like Chester, Bangor and Holyhead via Crewe.
It is interesting to look at various Crewe to London Euston services this morning.
- 0740 – Class 390 train – From Liverpool – One Stop – 1 hour 40 minutes
- 0755 – Class 221 train – From Holyhead – One Stop – 1 hour 40 minutes
- 0832 – Class 390 train – From Manchester – One Stop – 1 hour 37 minutes
- 0844 – Class 390 train – From Glasgow – 1 hour 28 minutes
Note.
- The first field is the four-figure time that the train left Crewe.
- The last field is the journey time between Crewe to London Euston.
- The Class 390 and 805 trains will use electricity to run between Crewe and London Euston, whereas the Class 221 train will use diesel.
- Crewe and London Euston is 158 miles.
- The Glasgow train covers the 158 miles at an average speed of 107.7 mph.
I have some thoughts.
What Will Be The Time For A Class 805 Train Between Crewe And London Euston?
Consider.
- From Crewe, the Class 805 train will be using the electrification to London Euston.
- The Class 390 train can tilt, whereas the Class 805 train can’t!
- The Class 805 train is at least three tonnes lighter per car, than the Class 390 train.
- The lighter weight and possibly more power of the Class 805 trains, will give better acceleration.
- There is twenty-one years of difference in the build dates of the two trains. In that time, I also suspect that Network Rail have improved the track between Crewe and London Euston.
- Norton Bridge junction has been improved to avoid conflicts.
- It would be very convenient for Avanti West Coast and Network Rail, if the performance under electrification of the two trains were similar.
For these reasons, I believe that the performance of a non-stop Crewe And London Euston service using a Class 805 train will be such that it can match that of a Class 390 train.
I would also expect that with a similar stopping pattern between Crewe And London Euston, there would be little to choose between the two trains.
I can see with its better acceleration and lighter weight that the time between Crewe and London Euston will be perhaps a dozen minutes faster than the current time.
Using the electrification will also save a lot of diesel fuel with all its emissions.
Along The North Wales Coast Line
Consider.
- Crewe and Holyhead is 105.5 miles and takes two hours and two minutes in a typical service.
- These figures give an average speed of 52 mph.
- There are six stops, which are scheduled to take a total of ten minutes.
- About half the North Wales Coast Line has a maximum operating speed of 90 mph, but through Chester, Llandudno Junction and West of Bangor, the operating speed is 75 mph or less.
I am fairly sure, that with both the current Class 221 trains and the new Class 805 trains, it will be the track, rather than the train that determines the average speed.
It would therefore appear that if the average speed can be raised by track improvements these time savings could be achieved.
- 60 mph – 105.5 mins – 16.5 mins
- 70 mph – 90 mins – 32.5 mins
- 80 mph – 79 mins – 43 mins
- 90 mph – 70 mins – 52 mins
- 100 mph – 63 mins – 59 mins
- 110 mph – 58 mins – 64 mins
- 120 mph – 53 mins – 69 mins
- 130 mph – 49 mins – 73 mins
- 140 mph – 45 mins – 77 mins
Note.
- The first column is the average speed.
- The second column is the time between Holyhead and Crewe.
- The third column is the saving.
- I suspect that 90 or 100 mph would be the highest possible practical average speed.
- Trains average 100 mph on several long sections of the Great Eastern Main Line.
- I put in the higher speeds to show what is possible, if the North Wales Coast Line were to be converted into a 140 mph electrified line with digital signalling.
Even at these relatively slow speeds compared to High Speed Two, there are considerable time savings to be made, just by improving the tracks.
Incidentally, High Speed Two is quoted in Wikipedia as aiming for a Crewe and London Euston time of 56 minutes, so by averaging 100 mph between Crewe and Holyhead, London Euston and Holyhead could be under two hours.
Batteries And Class 805 Trains
I wouldn’t be surprised that soon after the Class 805 trains are delivered, they could be converted to a version of Hitachi’s Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train, the specification of which is shown in this Hitachi infographic.
Note.
- I suspect that the batteries will be used to handle regenerative braking on lines without electrification, which will save diesel fuel and carbon emissions.
- The trains accelerate faster, than those they replace.
- The claimed fuel and carbon saving is twenty percent.
- It is intended that these trains will be introduced in 2023.
But Hitachi have not given any predictions of the range of these trains on battery power alone.
However, they do claim a battery range of 56 miles for the Hitachi Regional Battery Train, which is based on similar technology.
These trains could help in speeding the stops between Crewe and Holyhead.
- Batteries would be charged at Holyhead and on the electrification to the South of Crewe.
- At each stop, trains would use a proportion of the power in the battery to accelerate faster and save fuel and cut emissions.
- Battery power would be used in stations for train hotel power.
- Westbound trains would arrive in Holyhead and Southbound trains would arrive in Crewe, with not much power in the battery.
I suspect that, whether diesel or battery power is used, will be controlled by a sophisticated computerised control system.
Electrification Along The North Wales Coast Line
I think this will eventually happen to allow High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains to run to Chester and along the North Wales Coast Line to Llandudno, Bangor and Holyhead.
But there is no benefit to be gained in electrifying until higher speeds are possible, after track improvements.
I believe these times will be possible with track improvements and the opening of High Speed Two.
- Holyhead and Crewe – Class 805 train and 80 mph average – 79 mins
- Holyhead and Crewe – Class 805 train and 90 mph average – 70 mins
- Holyhead and Crewe – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train, electrification and 100 mph average – 63 mins
- Crewe and London Euston – Class 805 train – 80 mins
- Crewe and London Euston – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train – 56 mins
Note, electrification will be needed, to run High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains along the North Wales Coast Line.
I am confident that these times will be possible.
- Holyhead and London Euston – Class 805 train and 90 mph average along the coast – 2 hours 30 mins
- Holyhead and London Euston – High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train and 100 mph average along the coast – 2 hours
The current time between Holyhead and London Euston is over three hours 45 minutes.
Conclusion
These trains will certainly speed up trains to North Wales.
Scotland’s Renewable Energy Jackpot: Hydrogen Exports Alone Could Be worth £25 Billion A Year By 2045
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the Edinburgh News.
This is the sub-heading.
Scotland is a phenomenally energy rich country. For decades the largest oil-producing nation in the European Union, it is now set to trail-blaze as a leader in renewable energy.
The title and sub-heading say it all for Scotland.
But these words could equally well apply to Anglesey, Cornwall, Devon, East Anglia, Humberside, Liverpool and Morecambe Bays, the Severn Estuary and Pembrokeshire.
We also mustn’t forget the Dogger Bank!
Anglesey Hydrogen Can Bridge UK’s Energy Gap Says Economics Expert
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the University of Bangor web site.
This is the sub title.
Anglesey can become a UK leader in hydrogen energy technology, cleaning up the transport sector and creating high quality jobs across North Wales, according to a leading Welsh economic expert.
The University of Bangor is a respected university, that goes back to the nineteenth century.
But for Liverpool giving me an unconditional offer, as Bangor was one of the universities on my UCCA form, I could have studied in the North-West corner of Wales.
After a resume of where we are with hydrogen in the world, Dr. Edward Jones of Bangor University outlines how North West Wales can be turned into a hydrogen hub, to join similar hubs at Deeside in Flintshire and at Milford Haven in Pembrokeshire.
This is a paragraph of the article.
Dr Jones believes hydrogen could also hold the key to powering transport in future through a Welsh invention from the 19th century (the hydrogen fuel cell was developed in Swansea by William Grove in 1842).
William Grove was an interesting lawyer and scientist.
Dr. Jones would appear to be very much in favour of using hydrogen to take Wales forward to being zero-carbon in 2050.
I have written a few posts about the transformation of Anglesey and North West Wales, as Wales moves towards this goal. I also have some other thoughts of my own.
Holyhead Hydrogen Hub
This is happening and I wrote about it in Holyhead Hydrogen Hub Planned For Wales.
High Speed Two To Holyhead
I believe this could be a way to create a zero-carbon route between London and Dublin in under five hours and I wrote about it in Could High Speed Two Serve Holyhead?.
- London and Holyhead in a battery-equipped High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train should be under three hours.
- A single High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train would run between London and Holyhead, with a passenger capacity of around five hundred. It would probably split and join with another service at Crewe.
- Discontinuous electrification would be provided along the North Wales Coast Line.
- The trains could call at Old Oak Common, Birmingham Interchange, Chester, Crewe, Llandudno Junction and Bangor.
A High Speed catamaran would speed passengers between Holyhead and Dublin in under two hours.
Hydrogen-Powered Catamarans From Holyhead
The dynamics of a diesel-powered high speed catamaran are well-proven, with some large craft transporting passengers and vehicles on sea crossings all over the world.
Type “hydrogen-powered high speed catamaran” into Google and you get several hits to research and development projects, but no-one appears to have taken a large high speed craft and converted it to hydrogen.
But I do believe that someone somewhere is developing a hydrogen-powered catamaran with something like the following specification.
- 200 passengers
- 100-mile range
- 60 knot operating speed.
The HSC Francisco is a high speed craft that plies between Buenos Aires and Montevideo carrying over a thousand passengers and a hundred cars at 58 knots. It is powered by gas-turbine engines running on liquified natural gas.
I believe I’m not asking for the impossible.
Anglesey Airport As A Zero-Carbon Airport
Anglesey Airport uses part of RAF Valley and has hosted services to Cardiff.
This Google Map shows the runways of RAF Valley.
Note.
- The longest runway 14/32 is over two thousand metres long.
- Rhosneigr station in the South East corner of the map.
- The facilities of Anglesey Airport to the North-East of the runways.
The railway forms the border of the airport, as this second Google map shows.
The railway is straight as it passes the Airport and there would be space for a two-hundred metre bi-directional step-free platform for passengers for the Airport.
Airbus are proposing a hydrogen-powered ZEROe Turbofan.
If you think it looks familiar, I believe that Airbus are proposing to develop the aircraft out of the current Airbus A320neo.
- The capacity will be up to 200 passengers.
- The range will be up to 2000 miles.
- Dublin and Anglesey Airports are just 71.5 miles apart.
- The cruising speed of Mach 0.78 would be irrelevant on this route, as it would probably fly a route to minimise noise.
The plane would probably be able to do several trips between Anglesey and Dublin without refuelling.
As the Port of Holyhead is developing a hydrogen infrastructure, I suspect that to provide hydrogen refuelling at Anglesey Airport would be possible.
I believe that by combining hydrogen-powered aircraft with battery-electric trains, some difficult sea crossings can be made carbon-free.
I believe that Anglesey Airport could be key to a zero-carbon London and Ireland service.
- Airbus are also proposing a 100-seat ZEROe Turboprop.
- Belfast, Cork, Derry and Shannon would also be in range.
Flights could also continue to and from Cardiff.
Reopening The Anglesey Central Railway
This has been proposed as a Beeching Reversal project.
I wrote about it in Reopening The Anglesey Central Railway.
It could be reopened as a zero-carbon railway.
Conclusion
There is a lot of scope to use hydrogen in North West Wales and Anglesey.
Reopening The Anglesey Central Railway
Note that this post was updated in October 2021.
The Anglesey Central Railway is a disused branch railway, where the track-bed is intact although overgrown, that runs across the Island of Anglesey from the North Wales Coast Line to the port town of Amlwch.
It carried freight until 1993 and is one of those remote lines, where a case can be made for reopening., using simple station designs and affordable trains.
On its route it serves the County Town of Llangefni and these stations are proposed, either on the branch or the island
With the existing stations on the North Wales Coast Line, a useful local railway could be created.
But would it be value for money?
These are a few of my thoughts.
Bangor Station
Bangor station looks like the ideal place to terminate the service from the Anglesey Central Railway.
This Google Map shows Bangor station.
Note.
- Anglesey is to the West.
- There are four tracks through the station. This will allow trains to overtake.
- Only the outside two tracks have platforms.
- The platforms are long enough to handle at least a two-hundred metre long train. They could even be long enough to handle a pair of Aventi West Coast’s new Class 805 trains, which would be 260 metres long.
- There are a couple of Anglesey-facing sidings, which probably could be converted into at least one bay platform.
- I suspect in a city like Bangor, there is probably enough electric power to provide charging facilities in an Anglesey-facing bay platform.
I can’t see any problems with terminating Anglesey Central Railway services at Bangor.
Battery-Electric Trains Between Bangor And Amlwch
Consider.
- Bangor and Amlwch would be around 25 miles.
- Modern battery-electric trains have a range of up to 80 miles.
- Battery-electric trains can fully recharge in 15 minutes.
This means that with charging facilities at Bangor, modern battery-electric trains could handle a return journey between Bangor and Amlwch.
I suspect that a very acceptable two trains per hour (tph) should be possible.
Hydrogen Trains Between Bangor And Amlwch
These would also be possible, once a refuelling strategy has been decided.