Crown Estate Mulls Adding 4 GW Of Capacity From Existing Offshore Wind Projects
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The Crown Estate has revealed that it is taking steps to enable the generation of up to an additional 4 GW of electricity from several offshore wind projects in development, within the timeframe of the 50 GW 2030 target.
These are the first two paragraphs.
This follows requests from the developers of seven offshore wind farm projects who believe additional capacity can be generated from the areas of the seabed they hold existing rights for.
According to the Crown Estate, the technology has advanced and more capacity could be developed at projects that are already underway.
The seven wind farms are.
- Awel y Môr – Estimates 500 MW – Fixed – RWE
- Dogger Bank D – 1320 MW – Fixed – SSE Renewables, Equinor
- Dudgeon and Sheringham Shoal Extension – 719 MW – Fixed – Equinor
- Five Estuaries – TBD – Fixed – RWE
- North Falls – 504 MW – Fixed – SSE Renewables, RWE
- Rampion 2 – 1200 MW – Fixed – E-ON
Note.
- The Dudgeon and Sheringham Shoal Extensions seem to have been combined.
- One website connected to the wind farm, gives Five Estuaries as 353 MW.
- All are fixed wind farms.
- All are by large, established developers.
The total size is 4596 MW, using 500 MW for Awel y Môr and 353 MW for Five Estuaries.
Uprating by 8596/4596 could give these capacities.
- Awel y Môr – 935 MW
- Dogger Bank D – 2469 MW
- Dudgeon and Sheringham Shoal Extension – 1345 MW
- Five Estuaries – 660 MW
- North Falls – 943 MW
- Rampion 2 – 2244 MW
The total size is 8596 MW
Conclusion
This seems to be a sensible way to increase offshore wind capacity.
National Grid To Accelerate Up To 20GW Of Grid Connections Across Its Transmission And Distribution Networks
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These four bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- Connection dates of 10GW of battery projects accelerated at transmission level, and 10GW of capacity unlocked at distribution level, both part of the Electricity System Operator (ESO)’s connections five-point plan.
- Battery energy storage projects connecting to the transmission network to be offered new connection dates averaging four years earlier than their current agreement.
- The accelerated 20GW equates to the capacity of six Hinkley Point C nuclear power stations.
- Work is part of ongoing collaborative industry efforts, together with Ofgem and government, to speed up and reform connections.
This is the opening paragraph.
National Grid is accelerating the connection of up to 20GW of clean energy projects to its electricity transmission and distribution networks in England and Wales as part of ongoing collaborative work across industry.
As I write this, the UK is generating 38.5 GW of electricity, so another 20 GW will be a large increase in capacity.
I shall look at what National Grid are proposing in sections.
10 GW Of Battery Power
These two paragraphs, outline the plan for 10 GW of battery power.
On its transmission network, 19 battery energy storage projects worth around 10GW will be offered dates to plug in averaging four years earlier than their current agreement, based on a new approach which removes the need for non-essential engineering works prior to connecting storage.
The new policy is part of National Grid’s connections reform initiative targeting transmission capacity, spearheaded by the ESO – which owns the contractual relationship with connecting projects – and actioned jointly with National Grid Electricity Transmission (ET), the part of the business which designs and builds the transmission infrastructure needed in England and Wales to plug projects in.
It looks to me that someone has been doing some serious mathematical modelling of the UK’s electricity network.
Fifty years ago, I provided the differential equation solving software, that enabled the Water Resources Board to plan, where reservoirs and pipelines were to be built. I have no idea how successful it was, but we don’t seem to have any serious water supply problems, except when there is equipment failures or serious drought.
But modelling water and electrical networks is mathematically similar, with rainfall, pipelines and reservoirs in the water network and power generation, transmission lines and batteries and pumped storage hydroelectricity in the electricity network.
I’d be interesting to know what software was used to solve the mathematical model.
I certainly agree with the solution.
Two of our modern sources of renewable energy; solar and wind are not very predictable, but cost a lot of capital investment to build.
So it is very wrong not to do something positive with any excess electricity generated. And what better place to put it than in a battery, so it can be retrieved later.
The earlier, the batteries come on stream, the earlier, the batteries can save all the excess electricity.
So moving the plug in dates for battery storage four years earlier is a very positive thing to do.
A simple calculation shows that for 10 GW, we would need nineteen batteries of about 526 MW.
Ideally, like power stations, they would be spread around the country.
Could Pumped-Storage Hydroelectricity Be Used?
The largest battery in the UK is the Dinorwig pumped-storage hydroelectric power station, which is commonly known as Electric Mountain or Mynydd Gwefru if you’re Welsh.
- It opened in 1984, after a ten years of construction.
- It has a power output of 1.8 GW.
- The energy storage capacity of the station is around 9.1 GWh.
Roughly, every gigawatt of output is backed up by 5 GWh of storage.
If the proposed nineteen new batteries have the same power to storage ratio as Electric Mountain, then each battery will have a storage capacity of 2.63 GWh
SSE Renewables are planning two large pumped-storage hydroelectric power stations in Scotland.
- Coire Glas – 1.5 GW/30 GWh – Possible completion in 2031.
- Loch Sloy – 152.5 MW/25 GWh – See SSE Unveils Redevelopment Plans For Sloy Hydro-Electric Power Station.
A quick calculation, says we’d need seven pumped-storage hydroelectric power stations, which need a lot of space and a handy mountain.
I don’t think pumped-storage hydroelectric would be feasible.
Could Lithium-Ion Batteries Be Used?
My mathematical jottings have shown we need nineteen batteries with this specification.
- An output of about 526 MW.
- A storage capacity of around 2.63 GWh
This Wikipedia entry gives a list of the world’s largest battery power stations.
The current largest is Vistra Moss Landing battery in California, which has this specification.
- An output of 750 MW.
- A storage capacity of 3 GWh
Reading the Wikipedia entry for Vistra Moss Landing, it appears to have taken five years to construct.
I believe that nineteen lithium-ion batteries could handle National Grid’s need and they could be built in a reasonable time.
Could Any Other Batteries Be Used?
Rounding the battery size, I feel it would be better have twenty batteries with this specification.
- An output of 500 MW.
- A storage capacity of 2.5 GWh
Are there any companies that could produce a battery of that size?
Form Energy
Form Energy are well-backed with an MIT heritage, but their largest proposed battery is only 10 MW/1 GWh.
They could be a possibility, but I feel it’s only a small chance.
Highview Power
Highview Power say this about their next projects on this page of their web site.
Highview Power’s next projects will be located in Scotland and the North East and each will be 200MW/2.5GWh capacity. These will be located on the national transmission network where the wind is being generated and therefore will enable these regions to unleash their untapped renewable energy potential and store excess wind power at scale.
Note.
- This is more like the size.
- Work is now underway at Carrington – a 50MW / 300MWh plant at Trafford Energy Park near Manchester.
- Highview’s technology uses liquid air to store energy and well-proven turbo-machinery.
- Highview have a co-operation agreement with Ørsted
They are a definite possibility.
10 GW Of Extra Unlocked Capacity
These two paragraphs, outline the plan for 10 GW of extra unlocked capacity.
On its distribution network in the Midlands, South West of England and South Wales, the additional 10GW of unlocked capacity announced recently is set to accelerate the connection of scores of low carbon technology projects, bringing forward some ‘shovel ready’ schemes by up to five years.
National Grid has already been in contact with more than 200 projects interested in fast tracking their distribution connection dates in the first wave of the capacity release, with 16 expressing an interest in connecting in the next 12 months and another 180 looking to connect within two to five years.
This page from National Grid ESO, lists the actions that were taken to release the extra grid capacity.
Conclusion
This looks to be a very good plan from National Grid.
UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
A new partnership between the UK and German governments has been agreed on 3 November to help secure safe, affordable, and clean energy for consumers in both nations for the long-term and bolster energy security. Both countries commit to strengthening cooperation in renewables, notably offshore wind and electricity interconnection.
These two paragraphs introduce the deal.
Under the new partnership signed in London by Energy Security Secretary Claire Coutinho and Germany’s Vice Chancellor, Robert Habeck, the UK and Germany have reaffirmed their shared ambition and commitment to net zero and progressing the energy transition.
Europe’s two largest economies have also doubled down on commitments made under the Paris Agreement to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees.
i think this could be a worthwhile follow-up to the relationship, that Boris Johnson and Olaf Scholz seemed to encourage after their high profile meeting in April 2022.
This press release from Downing Street is entitled PM meeting with German Chancellor Olaf Scholz: 8 April 2022 and this is the first two paragraphs.
The Prime Minister welcomed German Chancellor Olaf Scholz to Downing Street this afternoon to discuss the West’s response to Putin’s barbaric invasion of Ukraine.
The two leaders shared their disgust at the Russian regime’s onslaught and condemned Putin’s recent attacks.
I wrote Armoured Vehicles For Ukraine based on some of the things said in the press conference after what seemed to be a very wide discussion.
But it was these paragraphs in the press release that caught my eye.
They also agreed on the need to maximise the potential of renewable energy in the North Sea and collaborate on climate ambitions and green energy.
The Prime Minister said he wanted to further deepen the UK’s relationship with Germany, and intensify its cooperation across defence and security, innovation and science.
After Boris and Olaf’s meeting at Downing Street, I have been able to write these posts about the Anglo-German energy relationship and also make some other observations.
- Mona, Morgan And Morven
- UK-German Energy Link Reaches Financial Close
- RWE, Siemens and other German companies seem to be building a strong presence in the UK.
- Rolls-Royce are doing the same in Germany.
Claire Coutinho and Robert Habeck seem to be wanting to continue the co-operation, judging by this paragraph from the article on offshoreWIND,biz.
The energy and climate partnership sees both countries commit to enhancing cooperation in renewables, particularly in offshore wind and electricity interconnection, including offshore hybrid interconnection.
The most significant part of this paragraph is the mention of offshore hybrid interconnection.
If you want more details on their meeting, this document is the official UK Government declaration.
I have my thoughts.
What Is Meant By Offshore Hybrid Interconnection?
Type “Offshore Hybrid Interconnection” into Google and the first page is this page from National Grid, that is entitled Offshore Hybrid Assets, that has this sub-heading.
How the North Sea has the potential to become Europe’s green energy ‘powerhouse’
This is the introductory paragraph.
Now more than ever we need more renewable energy to make energy cleaner, more affordable, and more secure. The North Sea offers an incredible opportunity for the UK and our European neighbours to deliver huge increases in offshore wind. But delivering new offshore wind will require more infrastructure, which will have an impact on communities.
Hybrid is all-purpose comfort word like cashmere, platinum or puppies.
The page on the National Grid web site describes The Next Generation Interconnector with these paragraphs.
Interconnectors already provide a way to share electricity between countries safely and reliably. But what if they could do much more than that? What if interconnectors could become an offshore connection hub for green energy?
Instead of individual wind farms connecting one by one to the shore, offshore hybrid assets (OHAs) will allow clusters of offshore wind farms to connect all in one go, plugging into the energy systems of neighbouring countries.
And then there is this section entitled Tomorrow’s Solution: Offshore Wind And Interconnectors In Harmony, where this is said.
Today, offshore wind and interconnectors operate alongside each other, connecting to the shore individually. In the future, offshore hybrid assets could enable offshore wind and interconnection to work together as a combined asset.
We now call this type of infrastructure an offshore hybrid asset (OHA), but we used to refer to it as a multi-purpose interconnector (MPI). We changed it because we work so closely together with Europe, it made sense to use the same terminology.
The page on the National Grid web site also has an interactive graphic, which shows the benefit of the approach.
LionLink
National Grid are already developing LionLink, with Dutch grid operator; TenneT, which will be a multi-purpose interconnector linking the UK and the Netherlands.
LionLink is described on this page from National Grid, where this is the sub-heading.
We’re developing a first-of-its-kind electricity link to connect offshore wind between the UK and the Netherlands.
This is the introductory paragraph.
Designed together with our Dutch partners TenneT, LionLink (formerly known as EuroLink) is an electricity link that can supply around 1.8 gigawatts of clean electricity, enough to power approximately 1.8 million British homes. By connecting Dutch offshore wind to Dutch and British markets via subsea electricity cables called interconnectors, LionLink will strengthen our national energy security and support the UK’s climate and energy goals.
Will we be planning a similar electric handshake with the Germans?
How Much Offshore Wind Power Are We Talking About?
This is answered by the last two paragraphs of the article on offshoreWIND.biz.
Around 75 per cent of installed offshore wind capacity in the North Sea is in German and British waters. This is helping to drive the UK’s ambition for up to 50 GW of offshore wind, including up to 5 GW of floating wind, by 2030, the governments said.
Germany is aiming at installing 30 GW by 2030.
That is an Anglo-German starter for eighty GW.
Electrolysers In The Middle If The North Sea
Why Not?
This is a clip from National Grid’s graphic on the page that introduces Offshore Hybrid Assets,
It shows an offshore hydrogen electrolyser.
- You could have an offshore hybrid asset that went between say Bacton in Norfolk and Hamburg via these assets.
- One or more wind farms in UK territorial waters.
- A mammoth offshore electrolyser, with hydrogen storage, possibly in a depleted gas field.
- One or more wind farms in German territorial waters.
Electricity will be able to go three ways; to the UK, to Germany or to the electrolyser.
The Involvement Of German Energy Companies In UK Territorial Waters
Wikipedia lists offshore fifteen wind farms, that have German owners in UK territorial waters, that total 12,960 MW.
This compares with.
- Equinor – 6 wind farms totalling 6466 MW.
- Ørsted – 15 wind farms totalling 9683 MW.
- Scottish Power – 2 wind farms totalling 5,000 MW.
- SSE Renewables – 15 wind farms totalling 15,591 MW.
- Vattenfall – 6 wind farms totalling 4384 MW.
As there is a number of partnerships, these figures only show the relative sizes of the investment by individual companies.
But at nearly 13 GW, the amount of total German investment in UK territorial waters is substantial.
Is This Solely An Anglo-German Club Or Can Others Join?
Consider.
- It seems to me, that because of the LionLink, the Dutch are already involved.
- TenneT is also a large electricity distributor in Germany.
- Countries with substantial shares of the water and winds of the North Sea in addition to Germany, the Netherlands and the UK, include Belgium, Denmark and Norway.
- The UK has interconnectors with Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Norway and the Netherlands.
It appears that the world’s largest multi-national power generator is evolving by stealth.
North Sea Wind Power Hub
This concept seems to have developed around 2017, by Danish, Dutch and German interests.
The Wikipedia entry introduces it like this.
North Sea Wind Power Hub is a proposed energy island complex to be built in the middle of the North Sea as part of a European system for sustainable electricity. One or more “Power Link” artificial islands will be created at the northeast end of the Dogger Bank, a relatively shallow area in the North Sea, just outside the continental shelf of the United Kingdom and near the point where the borders between the territorial waters of Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark come together. Dutch, German, and Danish electrical grid operators are cooperating in this project to help develop a cluster of offshore wind parks with a capacity of several gigawatts, with interconnections to the North Sea countries. Undersea cables will make international trade in electricity possible.
Currently, the UK is developing these wind farms on their portion of the Dogger Bank.
- Doggerbank A – 1235 MW – Started producing electricity in 2023.
- Doggerbank B – 1235 MW – Planned commissioning in 2024.
- Doggerbank C – 1218 MW – Planned commissioning in 2025.
- Doggerbank D – 1320 MW – Being planned.
- Doggerbank South – 3000 MW – Being planned.
Note.
- That’s a total of 8 GW.
- A, B, C and D are being developed by a consortium of SSE Renewables and Equinor.
- South is being developed by RWE.
- This web site is for Dogger Bank D.
- This web site is for Dogger Bank South.
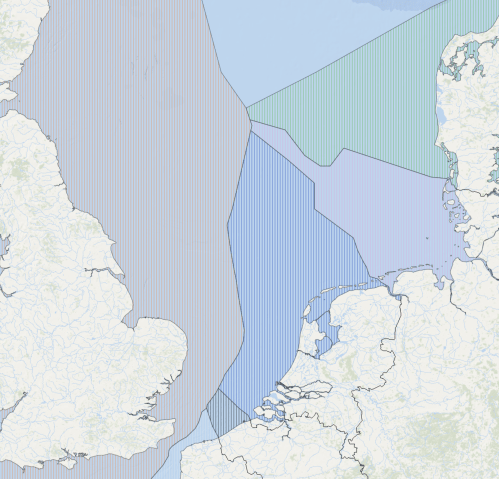
This map from the European Atlas of the Seas, shows the various exclusive economic zones (EEZ) in the North Sea.
Note.
- The pinkish zone to the East of the UK, is the UK’s EEZ.
- The light blue zone at the top is Norway’s EEZ.
- The greenish zone in the North-East corner of the map is Denmark’s EEZ.
- The light blue zone below Denmark’s EEZ is Germany’s EEZ.
- Then we have the EEZs for The Netherlands, Belgium and France.
The Dogger Bank is situated where the British, Dutch, German and Norwegian EEZs meet.
All five Dogger Bank wind farms are in British waters.
The Wikipedia entry for the Dogger Bank says this about its size.
The bank extends over about 17,600 square kilometres (6,800 sq mi), and is about 260 by 100 kilometres (160 by 60 mi) in extent. The water depth ranges from 15 to 36 metres (50 to 120 ft), about 20 metres (65 ft) shallower than the surrounding sea.
This probably makes it easy to accommodate a large fixed-foundation wind farm.
Overlaying the map in the Wikipedia entry, with the EEZ map, I’m fairly sure that the northeast end of the Dogger Bank is close to where the EEZs meet.
Progress On The North Sea Wind Power Hub
The North Sea Wind Power Hub has a web site, but it seems to be more about thinking than doing.
It seems to have been hijacked by that august body; The Institute of Meetings Engineers.
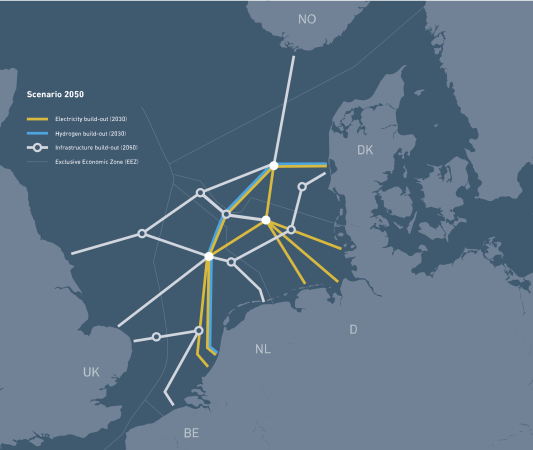
This page on the web site, which is entitled Explore The Future Energy Highways, has a simple interactive map.
This shows its vision for 2030.
Note.
- Yellow is electricity links to be built before 2030.
- Blue is hydrogen links to be built before 2030.
- Feint lines indicate the EEZ boundaries.
There are two problems with this layout.
- It doesn’t connect to the Dogger Bank area, where the original plan as detailed in Wikipedia talked about “Power Link” artificial islands.
- No hydrogen is delivered direct to Germany.
This shows its vision for 2050.
Note.
- Yellow, blue and feint lines are as before.
- White is electricity links to be built before 2050.
- There appears to be a node on the Dogger Bank in the German EEZ. This node could be connected to the “Power Link” artificial islands.
- The Southernmost connection to East Anglia could be Bacton.
- The other Norfolk connection could be where wind farms are already connected.
- The Northern connection could be Teesside, where some of the Dogger Bank wind farms connect.
- If the Northern connection to England is Teesside, then first node, which is in the British EEZ, could be one of the offshore sub-stations in the Dogger Bank wind farm complex.
This all seems a lot more feasible.
A New Offshore Hybrid Asset Between Teesside And Germany
Consider.
- A new offshore sub-station will be needed in the German EEZ to connect the “Power Link” artificial islands to the power network.
- The new offshore sub-station will eventually have three interconnectors to the German coast.
- Only the 1218 MW Dogger Bank C wind farm will be connected to the Teesside onshore substation.
- Germany has a power supply problem, after shutting down nuclear power stations and building more coal-fired power stations.
A new Offshore Hybrid Asset between Teesside and Germany could be created by building the following.
- A the new offshore sub-station in the German EEZ to connect the “Power Link” artificial islands to the power network.
- An interconnector between a sub-station of the Dogger Bank wind farm complex and the new sub-station
- A second interconnector to connect the new sub-station for the “Power Link” artificial islands to the German electricity grid.
All of the work would be done mainly in the German EEZ, with a small amount in the British EEZ.
Where Does Dogger Bank South Fit In?
Consider.
- Dogger Bank South is planned to be a 3 GW wind farm.
- It will need a 3 GW connection to the onshore electricity grid.
- Creyke Beck substation is the proposed location for the onshore connection.
- It is owned by German electricity company; RWE.
Could it be that some of the electricity produced by Dogger Bank South is going to be sent to Germany or to another node to produce hydrogen?
It certainly illustrates the value of an Offshore Hybrid Asset.
Scotland’s Largest Offshore Wind Farm Is Now Operational
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Seagreen Wind Energy.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
-
First Minister Humza Yousaf says Seagreen milestone takes Scotland a step closer to net zero
-
UK’s newest offshore wind farm is generating enough renewable energy to power almost 1.6m homes annually
-
Seagreen is now Scotland’s largest and the world’s deepest fixed-bottom offshore wind farm
These two paragraphs outline the current state of the project.
SSE Renewables, part of SSE plc, and its partner TotalEnergies have announced all 114 Vestas V164-10.0 MW turbines at the 1.1GW Seagreen Offshore Wind Farm off the coast of Scotland are now fully operational and are generating clean, renewable energy to Britain’s power grid.
Situated 27km off the Angus coast in the North Sea’s Firth of Forth, Seagreen is now Scotland’s largest wind farm as well as the world’s deepest fixed-bottom offshore wind farm, with its deepest foundation installed at a record 58.7 metres below sea level^. Seagreen is operated from a dedicated onshore Operations and Maintenance Base at Montrose Port.
Note.
- The capacity of the wind farm is 1,075MW.
- First power was in August 2022.
- It looks like that the original completion date was in 2024, but it was moved forward to October 2023, which has been met.
It seems that the project management was planned well.
World’s Largest Offshore Wind Farm Produces Power For The First Time
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from SSE.
These bullet points sum up the press release.
- UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak hails Dogger Bank’s role in bolstering energy security, creating jobs, lowering costs, and achieving Net Zero
- First power achieved at UK’s Dogger Bank as the first of 277 turbines installed 130km from UK coast
- Dogger Bank is now connected via HVDC technology to Britain’s national grid and providing renewable power to homes and businesses
- Each rotation of the first turbine’s 107m long Haliade-X blades can produce enough clean energy to power an average home for two days
- When complete Dogger Bank will deliver clean energy to six million homes annually
I will repeat a highlight of important paragraphs from the press release.
The Size Of The Dogger Bank Wind Farms
When fully complete, Dogger Bank’s world-record-beating 3.6GW capacity will comprise 277 giant offshore turbines capable of producing enough clean energy to power the equivalent of six million homes annually and deliver yearly CO2 savings equivalent to removing 1.5 million cars from the road.
Note.
- The first 1.2 GW section is scheduled for completion in the next few months.
- Two more sections of the Dogger Bank wind farm will eventually raise the capacity to 6 GW.
This cluster of wind farms certainly shows what can be achieved with British offshore wind power.
Innovative HVDC Technology
Dogger Bank also marks the first use of HVDC transmission technology to connect a British wind farm to National Grid’s UK energy network. This includes the installation of the world’s first unmanned offshore HVDC substation platform at the site, as well as first use of Hitachi Energy’s HVDC Light® transmission system which was successfully executed in record time of 38 months with the highest safety and quality standards.
Note.
- HVDC technology appears to be a more efficient way of transmitting energy under the sea and is now generally used for interconnectors.
- This page on the Hitachi Energy web site is entitled Dogger Bank HVDC Connection and gives a good description of the connection and its advantages.
The HVDC Technology and its installation looks like a real achievement, that can be applied to lots of other offshore wind farms.
XLCC seem to be doing the right thing in building an HVDC cable factory in Scotland. Check out their web site.
Scotland’s 25 GWh Energy Storage Arriving By Stealth
In SSE Unveils Redevelopment Plans For Sloy Hydro-Electric Power Station, I introduced SSE Renewable’s plan to convert the UK’s largest hydro-electric power station into a pumped storage hydroelectric station, that can store 25 GWh of electricity and generate 152.5 MW of electricity.
After a public consultation in July, which unfortunately, I was unable to get to, SSE have now published a comprehensive document, which details their plans.
These are some points from the document.
- There will be no increase in the generating capacity of 152.5 MW, which is about half the size of a gas-fired power station.
- SSE designed a similar scheme for Sloy in 2009.
- Pumped storage systems need a lot of water. The Loch Sloy scheme has Loch Lomond.
- The development of pumped storage at Sloy would only require construction work to be carried out in the grounds of the existing power station.
- No permanent new works would be required at Sloy Dam or outside of the existing station boundary.
- A new above ground structure would be required which would contain a main hall with vehicular access, laydown areas, an overhead travelling crane, electrical switchgear and control systems.
- A new underground pump hall would be required to house two pumps. This would link to the intake structure and would be approximately 20m below the existing ground level.
- The existing tailrace to Loch Lomond, will be used to bring water to the pumps.
- Construction could start in 2025, with completion in 2027.
This redevelopment is a much less complex construction project, than building the original power station in the 1950s.
It also looks like the construction will not cause much disruption in the local area.
Hence my view, that this storage is arriving by stealth and won’t be noticed by those passing the power station.
After reading this SSE document, I wonder how many similar 1950s hydroelectric power stations have been upgraded to pumped storage stations in the last few years.
Also, if their Sloy scheme is successful, will SSE be looking for other hydroelectric power stations to convert to pumped storage?
This article on renews.biz is entitled Vattenfall Plans To Build 730MW Of Swedish Hydro Power, where this is a paragraph.
Vattenfall is also conducting a pilot study to investigate reinstating the Juktan power station on the Storjuktan lake adjacent to the Umeälven river in Västerbotten, to a pumped storage plant with a capacity of up to 380MW.
Note.
- Juktan power station was built as a pumped storage station and converted to a standard one.
- It has a web page.
- As the paragraph says it could be converted back!
So other companies and countries are thinking the same way!
Strathclyde University’s Prediction
This page on the Strathclyde University web site, gives these figures in GWh for the possible amounts of pumped storage that can be added to existing schemes.
- Errochty – 16
- Glasgarnock – 23
- Luichart – 38
- Clunie – 40
- Fannich – 70
- Rannoch – 41
- Fasnakyle – 78
- Tummel – 38
- Ben Lawers – 12
- Nant – 48
- Invermoriston – 22
- Invergarry – 41
- Quoich – 27
- Sloy – 20
That is a total of 514 GWh.
These figures must give SSE food for thought.
These new schemes are also being planned.
- Balliemeanoch – 1.5GW/45 GWh
- Coire Glas – 1.5 GW/30 GWh
- Corrievarkie – 600 MW/14.5 GWh
- Fearna – 1.8 GW/37 GWh
- Loch Earba – 900 MW/33 GWh
- Loch Kemp – 300 MW/9 GWh
- Loch Na Cathrach/Red John – 450 MW/2.8 GWh
These could bring the potential pumped storage in Scotland to 685.3 GWh.
Fourth Phase Could Bring 2 GW More To World’s Already Largest Offshore Wind Farm Under Construction
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Dogger Bank D, the potential fourth phase of the Dogger Bank Wind Farm, whose first three phases totalling 3.6 GW are currently being built, is planned to have a generation capacity of around 2 GW. If built, the fourth phase would bring the total installed capacity of the UK project – already the world’s largest offshore wind farm under construction – to over 5.5 GW.
This is the introductory paragraph.
SSE Renewables and Equinor, which own the Dogger Bank A, B and C offshore wind farms through a consortium that also comprises Vårgrønn, have now launched a public consultation period on the Dogger Bank D proposals that runs until 7 November.
As RWE are developing the 3 GW Dogger Bank South, the Dogger Bank wind farm will be up to 8.5 GW in a few years.
SSE And RWE Tweak North Falls Project Following Public Input, DCO Application Now Expected In 2024
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
RWE and SSE Renewables have made a number of changes to the North Falls offshore wind project in the UK, a proposed extension to the existing 504 MW Greater Gabbard, whose implementation will likely move the planned date for filing a development consent order (DCO) application into 2024. The most significant changes to the project plans include removing the northern array area and reducing the number and height of wind turbines.
These two paragraphs introduce the article.
The developers are tweaking the project following a review of the feedback received from the North Falls statutory consultation held during the summer.
Initially, North Falls comprised two offshore array areas totalling 150 square kilometres and will now have a single array occupying 95 square kilometres. This also moves the wind farm farther offshore, with its closest point to shore now being 42 kilometres, 20 kilometres farther out at sea than proposed originally.
It looks like RWE and SSE Renewables have listened to the public and acted.
But then the developers are two of the most experienced in the UK.
How Britain’s Biggest Natural Battery Can Help Deliver Net Zero
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in the New Statesman.
This is the sub-heading.
SSE wants to double the nation’s flexible electricity storage capacity.
These two paragraphs introduce the article.
After previous delays and false starts, governments and businesses across the world are pushing towards the common goal of net zero. The energy sector is arguably the area with the biggest responsibility to work towards this target, and there is no time for complacency.
Ensuring clean, renewable energy sources such as hydrogen, wind and solar power become a larger part of the grid will be critical for the sector in its push towards net zero. A key facet of the clean energy drive will be having sufficient storage for each renewable power source kept in reserve, to be used as and when required as a crucial back-up mechanism. In last spring’s energy security review the government outlined its commitment to support long duration storage projects.
It is certainly very comprehensive and a must read.
This sentence illustrates the financial problem with pumped storage.
SSE is calling on the UK government to help it commit to building the Coire Glas storage facility by providing one simple policy decision that will send a clear signal as to how government intends to support the deployment of long duration electricity storage. The project doesn’t need subsidising, SSE states, but it would benefit from revenue stabilisation, and clarity on such support sooner rather than later.
Hopefully, this article will help get the required support.
Coire Glas
Coire Glas will have an output of 1500 MW and a storage capability of 30 GWh.
There is more information at the Coire Glas web site.
The project could be up and running by the early 2030s.
Loch Sloy Pumped Storage
The article also mentions the Loch Sloy Pumped Storage scheme, that has been recently announced by SSE.
I wrote about this 25 GWh scheme in SSE Unveils Redevelopment Plans For Sloy Hydro-Electric Power Station.
SSE haven’t announced much more about this scheme and it is not mentioned on the Sloy/Awe web site.