National Grid Pioneers UK-First Trial Of 3D Printed Technology For Low-Carbon Substations
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These three bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Collaboration with Hyperion Robotics and the University of Sheffield will trial low-carbon 3D-printed concrete foundations including at National Grid’s Deeside Centre for Innovation in North Wales
- Innovation could reduce waste, carbon emissions and costs to consumers of network construction
- If rolled out across National Grid substations the technology could save up to 705 tons of concrete and 323 tons of CO2 and deliver £1.7 million in consumer savings versus traditional methods over a 10-year period
These two paragraphs give more details.
National Grid is working with Hyperion Robotics and the University of Sheffield on a UK-first trial to manufacture, install and test 3D-printed substation foundations, which have the potential to reduce construction-driven carbon emissions and reduce costs to consumers of network construction. This is part of National Grid’s commitment to leverage innovation to future-proof the network.
If the project is successful and the technology is rolled out across all National Grid substations, it is estimated it could save up to 705 tons of concrete and 323 tons of CO2 over a 10-year period, and deliver £1.7 million in consumer savings versus traditional methods.
The foundation design will deliver significant savings across the entire value chain.
- 70% reduction in concrete usage
- 80% less soil displacement
- 65% decrease in embodied carbon emissions
- 70% weight reduction compared to typical foundations
- 50% reduction in site operative hours, streamlining production
The foundations will be designed and produced in Finland by Hyperion Robotics, and tested at full-scale by the University of Sheffield. Further field testing will then be carried out at National Grid’s state-of-the-art testing facility, the Deeside Centre for Innovation in North Wales, later in 2025.
Conclusion
I like this technology and I suspect there are many other applications of 3D Concrete Printing.
National Grid Starts Work On New Substation In Buckinghamshire To Power Data Centres
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These three bullet points act as sub-headings.
-
New substation site at Uxbridge Moor in Buckinghamshire will power new data centres –delivering economic growth and enabling UK digitalization
-
Site to feature two SF6-free gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) substations to minimise environmental footprint
-
Work comes as National Grid is planning £35 billion investment in its transmission network between 2026 to 2031
This is the first paragraph.
National Grid is starting work on its new Uxbridge Moor substation in Buckinghamshire which will connect over a dozen new data centres to its network.
This Google Map shows the current Iver substation.
The road on the left is Western section of the M25, which gives an idea of the size of the substation.
These two paragraphs give more details of the new Uxbridge Moor substation.
The requests from data centres to connect at Uxbridge Moor will require around 1.8GW of new capacity, equivalent to adding a mid-sized city to the grid on the outskirts of London. When built, it will be the largest new substation on National Grid’s network by gigawatt capacity.
The new substation site borders National Grid’s existing Iver 400kV substation in Buckinghamshire, which has reached capacity and cannot be expanded to meet the demand from data centres and other customers for connections in the area.
Nothing about the new substation appears small!
The cost of the Uxbridge Moor substation does not appear to have been disclosed by National Grid, but they do say this about their projected total spend in the next few years.
National Grid is planning £35 billion of investment between 2026 to 2031 to connect both large sources of demand such as data centres and gigafactories, and new sources of electricity generation such as wind and solar.
But then it’s not their fault, that the UK is a superb place for renewable energy and we generally speak English.
Eastern Green Link 2 Moves Up A Gear Using Low Carbon Fuel For Material Handling Trucks
The title of this post is the same, as that of this press release from National Grid.
These three bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Eastern Green Link 2 (EGL2), a high voltage direct current (HVDC) 436km subsea transmission cable connecting Scotland and England, is being delivered as a joint venture by National Grid Electricity Transmission and SSEN Transmission.
- Project sustainability efforts are accelerating by adopting Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil (HVO) fuelled trucks to move materials in Yorkshire.
- The introduction of HVO fuel will deliver up to 90% reduction in direct CO2 emissions.
The use of HVO fuel is good and the carbon dioxide emission savings are to be welcomed, but there is only so much of this HVO fuel available.
If hydrogen-fueled trucks were available, then this would deliver up to 100% reduction in direct CO2 emissions.
This paragraph from the press release talks about where the HVO fuel will be used.
HVO, a low-carbon biofuel made from waste vegetable oils, will be used at the Wren Hall converter station site in North Yorkshire, where 20-tonne construction trucks will transport approximately 370,000 tonnes of quarry stone from a quarry 27 miles away. This switch from conventional diesel to HVO is expected to deliver up to a 90% reduction in direct CO2 emissions and an 80% reduction in other harmful emissions such as particulate matter.
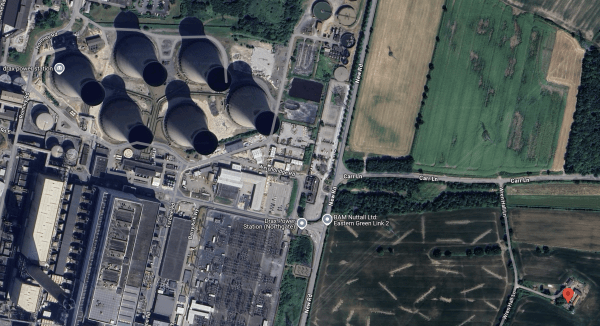
This Google Map shows the location of Wren Hall with respect to Drax power station.
Note.
- The six large cooling towers of the Drax power station are in the North-West corner of the map.
- Google Maps indicate, where they think Wren Hall is, with a red arrow.The lane running North-South to the West of the red arrow is called Wren Hall Lane.
- There is a legend saying BAM Nuttall Ltd Eastern Green Link 2 on the opposite side of the square of lanes to the red arrow.
Click the map to show it to a larger scale.
It looks to me, that if hydrogen could be provided on the Drax site, then the 370,000 tonnes of quarry stone from a quarry 27 miles away could be brought to the site by hydrogen-powered 20-tonne construction trucks.
So how could hydrogen be provided on the Drax site?
- Drax is a 2.6 GW biomass power station, so I’m sure that some electricity could be used to generate hydrogen.
- Drax is a rail-connected site, so hydrogen could be brought in by rail.
- Depending on the amount of hydrogen needed, hydrogen could surely be brought in by road.
I feel that if hydrogen-powered 20-tonne construction trucks were available, this transfer of quarry stone could be performed carbon-free.
Conclusion
This project illustrates a problem with large infrastructure projects all over the UK.
Moving the large amounts of stone, concrete, sand and rubble into and out of construction sites generates a lot of carbon dioxide and pollution from the 20-tonne trucks employed.
If I were to be given Ed Miliband’s job of Secretary of State for Energy Security and Net Zero, one of my first actions, would be to say that all new 20 tonne construction and cement trucks would have to be zero carbon.
I suspect, that zero-carbon with trucks this size, will mean hydrogen, as the weight of the battery would destroy the mathematics of the truck.
This would obviously reduce carbon emissions, but more importantly, what would it do for the health of those working on large construction sites?
In MAN Expands Its Zero-Emission Portfolio, I show MAN’s heavy hydrogen trucks.
This is an articulated heavy hydrogen truck.
I’m sure that MAN could build a hydrogen-powered 20-tonne construction truck.
In Cummins Agrees To Integrate Its Hydrogen ICE Technology Into Terex® Advance Trucks, I talk about the solution to the cement truck problem.
This is a side view of the top-of-the-range monster.
Note.
- Front is to the right.
- I suspect the driver doesn’t have to get out of the cab to discharge the concrete.
- The engine is at the rear with vertical exhausts.
- All axles are driven.
You’d certainly notice one of these if they were to be used in the City of London.
And this is the baby of the range.
Three axles is normal for the UK. so I wonder if this machine will ever make it across the pond.
This last paragraph in the original article describes the X15H hydrogen internal combustion engine.
The X15H was showcased at the Advanced Clean Transportation (ACT) Expo in May (2023), along with its hydrogen ICE-powered concept truck. The X15H features a 700-bar pressure 80kg capacity hydrogen storage system and a range of more than 500 miles, with up to 500 horsepower.
Could one of these trucks really deliver ready-mix concrete from London to Manchester and return?
The trucks would appear to be available, so let’s get a few over and try them out.
Incidentally, if someone had told me ten years ago, there would be rear-wheel drive trucks like Volkswagen Beetles, I’d have said they were wrong in no uncertain terms.
The Wren Hall substation would appear to be an ideal trial project for hydrogen-powered construction trucks and cement trucks.
UK, Netherlands To Connect Grids via Nederwiek 3 Offshore Wind Farm
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Dutch Climate and Green Growth Minister Sophie Hermans has included LionLink, said to be the first direct-current hybrid interconnector, in the country’s latest Offshore Wind Energy Development Framework. LionLink will use the offshore grid connection of Nederwiek 3 offshore wind farm in the Netherlands to connect to both the Dutch and the UK onshore high-voltage grids.
These are points from the article.
- The interconnector can also be used as an additional high-voltage link to exchange electricity between the countries.
- With LionLink now added to the offshore wind development framework, TenneT may now make investments in the project, which the Dutch transmission system operator (TSO) is realising in close cooperation with UK partner National Grid Ventures (NGV).
- Nederwiek 3 is planned to be launched in 2026.
The offshore grid between the UK and Europe is on its way.
Lakeside Facility Connects To Grid And Becomes UK’s Largest Transmission Connected Battery
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- National Grid plugs TagEnergy’s 100MW battery project in at its Drax substation.
- Following energisation, the facility in North Yorkshire is the UK’s largest transmission connected battery energy storage system (BESS).
- The facility is supporting Britain’s clean energy transition, and helping to ensure secure operation of the electricity system.
This paragraph introduces the project.
A battery storage project developed by TagEnergy is now connected and energised on the electricity transmission network, following work by National Grid to plug the facility into its 132kV Drax substation in North Yorkshire.
- Lakeside Energy Park’s 100MW/200MWh facility is now the largest transmission connected BESS project in the UK following energisation.
- The new facility will boost the capacity and flexibility of the network, helping to balance the system by soaking up surplus clean electricity and discharging it back when the grid needs it.
- To ensure a safe connection, National Grid, working with its contractor Omexom, upgraded its Drax 132kV substation to accommodate the additional clean power.
- Works included extending the busbars – which enable power flows from generation source on to power lines – upgrading busbar protection and substation control systems, and installing an operational tripping scheme, all of which helps keep the network stable and operating securely.
Owned and operated by TagEnergy – with Tesla, Habitat Energy and RES as project partners – the newly-connected battery will help exploit the clean electricity potential of renewable projects in the region, storing and releasing green energy to power homes and businesses and also helping to relieve any system constraints.
National Grid’s adjacent Drax 400kV substation already hosts the connection for Drax power station – the UK’s largest biomass facility – and will also connect the Eastern Green Link 2 electrical superhighway when it starts importing clean energy from Scotland in 2029.
Drax power station seems to be growing into a large node with several gigawatts of electricity, the UK’s largest BESS, a large biomass power station and the Eastern Green Link 2 electrical superhighway which will import clean energy from Scotland from 2029.
Drax appears to be transforming from the dirty man of the UK into a Jolly Green Giant.
I can see further power stations and sources, storage devices and technology joining the party at Drax.
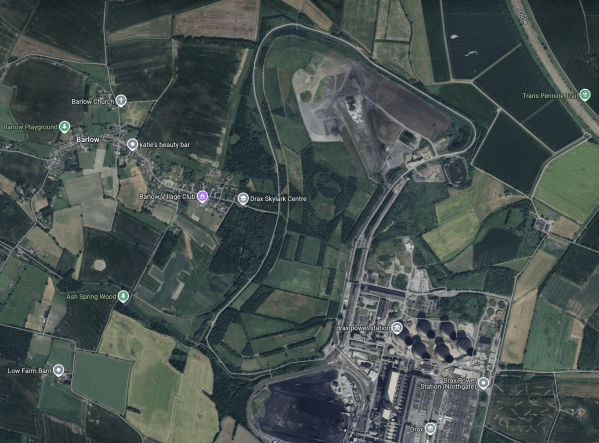
This Google Map shows the Drax site.
Note.
- The cooling towers can be picked out in the South-East quarter of the map.
- The site is rail and road connected, with the River Ouse nearby.
- There is a lot of space.
Surely, Drax would have a big enough space, with a high quality and high capacity electrical connection for Ørsted and Highview Power to put one of their three 200 MW/2.5 GWh batteries, that I talked about in Centrica Business Solutions And Highview Power.
What Are Offshore Hybrid Assets?
The title of this post is the same as that of a story explaining energy from National Grid.
This is the sub-heading.
Offshore Hybrid Assets or OHAs (formerly known as multi-purpose interconnectors) are a new generation of subsea technology that will connect clusters of offshore wind farms to multiple countries.
This is the first paragraph.
OHAs will help to speed up the connection of offshore wind and maximise the use of wind generation. They will also reduce the impact on local communities by reducing the amount of connection points and onshore infrastructure required to connect this clean energy to the shore.
The story goes on to discuss OHAs and how they are being developed.
It is very much a must read.
Energy In – Hydrogen And Carbon Dioxide Out
This article was inspired by this article in the Sunday Times, which is entitled ‘It’s A Slog’: Life Inside Britain’s Last Coal Power Station.
The article is about Ratcliffe-on-Soar power station, which is next to East Midlands Parkway station.
This is the first paragraph of the station’s Wikipedia entry.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar Power Station is a coal-fired power station owned and operated by Uniper at Ratcliffe-on-Soar in Nottinghamshire, England. Commissioned in 1968 by the Central Electricity Generating Board, the station has a capacity of 2,000 MW. It is the last remaining operational coal-fired power station in the UK, and is scheduled to close in September 2024.
I took these pictures of the power station in 2019.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar is the last of a number of large coal-fired power stations, that were built in the area, mainly along the River Trent.
- Rugeley – 600 MW – 1961
- Drakelow – 1630 MW – 1964
- Willington – 800 MW – 1962
- Castle Donington – 600 MW – 1958
- Ratcliffe-on-Soar – 2000 MW – 1968
- High Marnham – 1000 MW – 1959
- Cottam – 2000 MW – 1968
- West Burton – 2000 MW – 1968
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 10,630 MW of electricity.
- There are also a few large gas-fired power stations along the river, that are still operating.
- Both coal and gas-fired stations use the water from the River Trent for cooling.
At the mouth of the river, there is the Keadby cluster of gas-fired power stations.
- Keadby 1 – 734 MW – 1996
- Keadby 2 – 849 MW – 2023
- Keadby 3 – 910 MW – 2027
- Keadby Hydrogen – 900 MW – 2030
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 3,393 MW of electricity.
- Keadby 2 is the most efficient CCGT in the world.
- Keadby 3 will be fitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby 2 has been designed to be retrofitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby Hydrogen will be fuelled by zero-carbon hydrogen.
As the years progress, I can see the Keadby cluster of power stations becoming a large zero-carbon power station to back-up wind farms in the North Sea.
- Hydrogen power stations will emit no carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide from all gas-fired stations will be captured.
- Some carbon dioxide will be sold on, to companies who can use it, in industries like construction, agriculture and chemical manufacture.
- The remaining carbon dioxide will be stored in depleted gas fields.
As technology improves, more carbon dioxide will be used rather than stored.
Other Power Sources In The Humberside Area
In the next few sub-sections, I will list the other major power sources in the Humberside area.
Drax Power Station
Drax power station is a shadow of its former self, when it was one of the power stations fed by the newly discovered Selby coalfield.
These days it is a 2,595 MW biomass-fired power station.
Eastern Green Link 2
Eastern Green Link 2 will be a 2 GW interconnector between Peterhead in Scotland and Drax.
It is shown in this map.
Note.
- Most of the route is underwater.
- It is funded by National Grid.
- Contracts have been signed, as I talk about in Contracts Signed For Eastern Green Link 2 Cable And Converter Stations.
- It is scheduled to be completed by 2029.
This interconnector will bring up to 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity to Drax and Humberside.
Drax has the substations and other electrical gubbins to distribute the electricity efficiently to where it is needed.
2 GW could also reduce the amount of biomass used at Drax.
In the long term, if the concept of the four Eastern Green Links is successful, I could see another Eastern Green Link to Drax to replace imported biomass at Drax.
I also, don’t see why a smaller Drax can’t be run on locally-sourced biomass.
Solar Farms And Batteries Along The River Trent
As the coal-fired power stations along the River Trent are demolished, solar farm developers have moved in to develop large solar farms.
Salt End Power Station And Chemical Works
These two paragraphs from the Wikipedia entry for Salt End describes the hamlet and its power station and chemical works.
Salt End or Saltend is a hamlet in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, in an area known as Holderness. It is situated on the north bank of the Humber Estuary just outside the Hull eastern boundary on the A1033 road. It forms part of the civil parish of Preston.
Salt End is dominated by a chemical park owned by PX group, and a gas-fired power station owned by Triton Power. Chemicals produced at Salt End include acetic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonia, bio-butanol, bio-ethanol, ethyl acetate (ETAC) and ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) with animal feed also being produced on site.
I wonder, if running the complex on hydrogen would give cost and marketing advantages.
Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage Facility
This page on the SSE Thermal web site is entitled Plans For World-Leading Hydrogen Storage Facility At Aldbrough.
This is the most significant paragraph of the page, that is definitely a must-read.
With an initial expected capacity of at least 320GWh, Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage would be significantly larger than any hydrogen storage facility in operation in the world today. The Aldbrough site is ideally located to store the low-carbon hydrogen set to be produced and used in the Humber region.
This is a hydrogen storage facility for a much wider area than Humberside.
Rough Gas Storage Facility
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Rough Gas Storage Facility.
Rough is a natural gas storage facility under the North Sea off the east coast of England. It is capable of storing 100 billion cubic feet of gas, nearly double the storage capacities in operation in Great Britain in 2021.
In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to convert the Rough gas storage into a massive hydrogen storage.
The Location Of Aldbrough Gas Storage, Rough Gas Storage, Salt End And Easington Gas Terminal
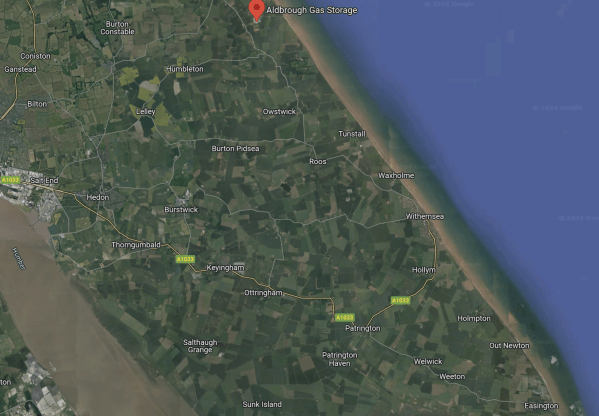
This Google Map shows between Salt End and the coast.
Note.
- The river crossing the South-West corner of the map is the Humber.
- Salt End with its power station and chemical works is on the North Bank of the Humber, where the river leaves the map.
- Aldbrough Gas Storage is marked by the red arrow at the top of the map.
- Easington Gas Terminal is in the South-East corner of the map.
- According to Wikipedia, gas flows into and out of the Rough Gas Storage are managed from Easington.
Looking at the map, I feel that the following should be possible.
- The two gas storage sites could be run together.
- Salt End power station and the related chemical works could run on hydrogen.
- Salt End will always have a reliable source of hydrogen.
- This hydrogen could be green if required.
All the chemical works at Salt End, could be run on a zero-carbon basis. Would this mean premium product prices? Just like organic does?
Enter The Germans
The Germans have a huge decarbonisation problem, with all their coal-fired power stations and other industry.
Three massive projects will convert much of the country and industry to hydrogen.
- H2ercules, which is a project of OGE and RWE, will create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen, to where it is needed.
- In Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal, I describe how Uniper are going to build a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhelmshaven.
- AquaVentus is an RWE project that will use 10.3 GW of offshore wind power in German territorial waters to create a million tonnes per year of green hydrogen.
These would appear to be three of Europe’s largest hydrogen projects, that few have ever heard of.
AquaVentus And The UK
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that delivers hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea.
It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network in the North Sea.
These are my thoughts about development of the AquaVentus network.
Hydrogen Production And AquaVentus
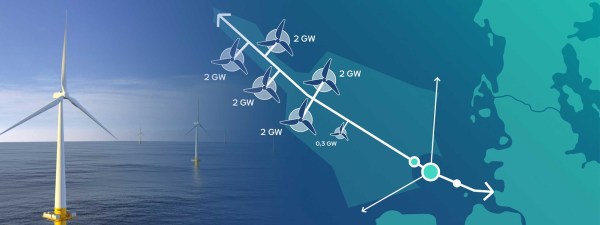
This RWE graphic shows the layout of the wind farms feeding AquaVentus.
Note.
- There is a total of 10.3 GW.
- Is one of the 2 GW web sites on the UK-side of AquaVentus, the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm, which is being developed by RWE?
- Is the 0.3 GW wind farm, RWE’s Norfolk wind farm cluster, which is also being developed by RWE?
Connecting wind farms using hydrogen pipelines to Europe, must surely mitigate the pylon opposition problem from Nimbys in the East of England.
As the AquaVentus spine pipeline could eventually connect to Peterhead, there will be other opportunities to add more hydrogen to AquaVentus.
Hydrogen Storage And AquaVentus
For AquaVentus to work efficiently and supply a large continuous flow of hydrogen to all users, there would need to be storage built into the system.
As AquaVentus is around 200 kilometres in length and natural gas pipelines can be up to 150 centimetres in diameter, don’t underestimate how much hydrogen can be stored in the pipeline system itself.
This page on the Uniper web site is entitled Green Wilhelmshaven: To New Horizons.
This is a sentence on the page.
Access to local hydrogen underground storage at the Etzel salt cavern site.
An Internet search gives the information, that Etzel gas storage could be developed to hold 1 TWh of hydrogen.
That would be enough hydrogen to supply 10 GW for a hundred hours.
Note that the UK branch of AquaVentus reaches the UK, just to the South of the massive hydrogen storage facilities at Aldbrough and Rough.
It would appear that both Germany and the UK are connected to AquaVentus through substantial storage.
I am certain, that all country connections to AquaVentus will have substantial storage at the country’s hydrogen terminal.
AquaDuctus
This would appear to be the first part of the AquaVentus network and has its own web site.
The web site is entitled Nucleus Of A Offshore Hydrogen Backbone.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The project partners are focusing on a scalable, demand-driven infrastructure: By 2030, AquaDuctus will connect the first large hydrogen wind farm site, SEN-1, with a generation capacity of approximately one gigawatt. SEN-1 is located in the German EEZ in the northwest of Helgoland. The pipeline will transport at a length of approx. 200 km green hydrogen produced from offshore wind to the German mainland and from there to European consumers via the onshore hydrogen infrastructure.
In the next project stage, AquaDuctus will be extended to the remote areas of the German exclusive economic zone towards the tip of the so-called duck’s bill. By that, additional future hydrogen wind farm sites will be connected. Along its way AquaDuctus will provide interconnection points with the opportunity for linking of adjacent national offshore hydrogen infrastructures originating from Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium and United Kingdom which opens the door for Europe-wide offshore hydrogen transport by pipeline.
There is also an interactive map, that gives more details.
This paragraph explains, why the Germans have chosen to bring the energy ashore using hydrogen, rather than traditional cables.
Recent studies show that offshore hydrogen production and transport via pipelines is faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly than onshore electrolysis with a corresponding connection of offshore wind turbines via power cables. The German federal government has also recognized this advantage and has clearly expressed its intention to promote offshore hydrogen production in the North Sea.
I suspect, that some UK offshore wind farms will use the same techniques.
Hydrogen Production For The UK
Electrolysers will probably be built along the East Coast between Peterhead and Humberside and these will feed hydrogen into the network.
- Some electrolysers will be offshore and others onshore.
- Turning off windfarms will become a thing of the past, as all surplus electricity will be used to make hydrogen for the UK or export to Europe.
- Until needed the hydrogen will be stored in Albrough and Rough.
Backup for wind farms, will be provided using hydrogen-fired power stations like Keadby Hydrogen power station.
Financial Implications
I reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there would be winners all round.
Rishi Sunak had the cards and he played them very badly.
It is now up to Keir Starmer, Great British Energy and Jürgen Maier to play those cards to link the energy systems of the UK and Germany to ensure security and prosperity for Europe.
Where’s The Plan, Rishi?
In RWE Goes For An Additional 10 GW Of Offshore Wind In UK Waters In 2030, I detailed how RWE intended to add an extra 10 GW of offshore wind to the seas around the UK.
As our current offshore wind capacity is around 15 GW, another 10 GW would surely be very welcome.
My post also outlined H2ercules, which is Germany’s massive project to create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen to Southern Germany.
I also gave details of the hydrogen hub at Wilhelmshaven, which is being built by Uniper to feed H2ercules with green hydrogen from around the world.
I believe that some of this hydrogen for H2ercules will take a short trip across the North Sea from UK waters, after being created by offshore electrolysers.
Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech – June 11
I also reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
It is now nine days since Rishi made that speech and I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He particularly mentioned.
- New gas-powered stations
- Trebling our offshore wind capacity
- Having new fleets of small modular reactors.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there will be winners all round.
Rishi also said this, in his speech.
As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too.
The gas-powered stations, offshore wind farms and the fleets of small modular reactors, will be part of the equation.
But I believe, we need three other components to complete our energy security.
- The upgrading of the National Grid.
- The building of four x 2 GW interconnectors between Scotland and Eastern England.
- Large amounts of energy storage.
Note.
- The Great Grid Upgrade and the four x 2 GW interconnectors are being planned.
- In Huge Boost To UK Supply Chain As National Grid Launches The Great Grid Partnership With Seven New Industry Partners, All United In The Drive To Deliver The Great Grid Upgrade, I describe how National Grid has setup the Great Grid Partnership to deliver the Great Grid Upgrade.
- In UK Infrastructure Bank, Centrica & Partners Invest £300M in Highview Power Clean Energy Storage Programme To Boost UK’s Energy Security, I describe how the big boys do a deal with Highview Power to create affordable batteries for the UK and the world.
- In Grid Powers Up With One Of Europe’s Biggest Battery Storage Sites, I describe how the very large Swardeston BESS is to be built near Norwich.
- In Mercia Power Response & RheEnergise Working Together To Build Long Duration Energy Storage Projects In The UK, I describe another UK-developed long duration energy storage system, which is now being planned.
- In National Grid Shares Proposals For Green Electricity Projects In Lincolnshire And West Norfolk, Needed To Boost Home-Grown Energy Supplies And Progress Towards Net Zero, I describe National Grid’s projects in the East of England.
- In UK ESO Unveils GBP 58 Billion Grid Investment Plan To Reach 86 GW of Offshore Wind By 2035, I show how we’re not that far away from 86 GW by 2035.
- In 400k For National Grid Innovation Projects As Part Of Ofgem Fund To Help Shape Britain’s Net Zero Transition, I describe how National Grid is using innovation to help target net-zero by 2035.
- In Iberdrola Preparing Two East Anglia Offshore Wind Projects For UK’s Sixth CfD Round, I describe how Iberdrola is getting 1.7 GW ready for commissioning in 2026.
- In National Grid To Accelerate Up To 20GW Of Grid Connections Across Its Transmission And Distribution Networks, I describe how National Grid are accelerating the development of the electricity networks. 10 GW of battery storage is a collateral benefit.
These ten projects, most of which are financed and/or underway, would appear to be good foundations, on which to build the Great Grid Upgrade.
It looks to me, that National Grid, RWE, Centrica, Iberdrola and others, by just doing what comes naturally have offered the next government a road to a future.
It will be interesting, what gets said before the election.
UK Infrastructure Bank, Centrica & Partners Invest £300M in Highview Power Clean Energy Storage Programme To Boost UK’s Energy Security
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from Highview Power.
This is the sub-heading.
Highview Power kickstarts its multi-billion pound renewable energy programme to accelerate the UK’s transition to net zero in Carrington, Manchester.
These three paragraphs outline the investment.
Highview Power has secured the backing of the UK Infrastructure Bank and the energy industry leader Centrica with a £300 million investment for the first commercial-scale liquid air energy storage (LAES) plant in the UK.
The £300 million funding round was led by the UK Infrastructure Bank (UKIB) and the British multinational energy and services company Centrica, alongside a syndicate of investors including Rio Tinto, Goldman Sachs, KIRKBI and Mosaic Capital.
The investment will enable the construction of one of the world’s largest long duration energy storage (LDES) facilities in Carrington, Manchester, using Highview Power’s proprietary LAES technology. Once complete, it will have a storage capacity of 300 MWh and an output power of 50 MWs per hour for six hours. Construction will begin on the site immediately, with the facility operational in early 2026, supporting over 700 jobs in construction and the supply chain.
Note.
- The backers are of a high quality.
- The Carrington LDES appears to be a 50 MW/300 MWh battery.
It finally looks like Highview Power is on its way.
These are my thoughts on the rest of news item.
Centrica’s Involvement
This paragraph talks about Centrica’s involvement.
Energy leader Centrica comes on board as Highview Power’s strategic partner and a key player in the UK’s energy transition, supporting Carrington and the accelerated roll-out of the technology in the UK through a £70 million investment. The programme will set the bar for storage energy systems around the world, positioning the UK as the global leader in energy storage and flexibility.
I suspect that Centrica have an application in mind.
In Centrica Business Solutions Begins Work On 20MW Hydrogen-Ready Peaker In Redditch, I talk about how Centrica is updating an old peaker plant.
In the related post I refer to this news item from Centrica Business Systems.
This paragraph in the Centrica Business Systems news item, outlines Centrica’s plans.
The Redditch peaking plant is part of Centrica’s plans to deliver around 1GW of flexible energy assets, that includes the redevelopment of several legacy-owned power stations, including the transformation of the former Brigg Power Station in Lincolnshire into a battery storage asset and the first plant in the UK to be part fuelled by hydrogen.
As Redditch power station is only 20 MW, Centrica could be thinking of around fifty assets of a similar size.
It seems to me, that some of these assets could be Highview Power’s LDES batteries of an appropriate size. They may even be paired with a wind or solar farm.
Larger Systems
Highview Power’s news item, also has this paragraph.
Highview Power will now also commence planning on the next four larger scale 2.5 GWh facilities (with a total anticipated investment of £3 billion). Located at strategic sites across the UK, these will ensure a fast roll-out of the technology to align with UK LDES support mechanisms and enable the ESO’s Future Energy Scenario Plans.
Elsewhere on their web site, Highview Power say this about their 2.5 GWh facilities.
Highview Power’s next projects will be located in Scotland and the North East and each will be 200MW/2.5GWh capacity. These will be located on the national transmission network where the wind is being generated and therefore will enable these regions to unleash their untapped renewable energy potential and store excess wind power at scale.
So will the four larger systems have a 200MW/2.5GWh capacity?
They could, but 200 MW may not be an appropriate output for the location. Or a longer duration may be needed.
Highview Power’s design gives the flexibility to design a system, that meets each application.
Working With National Grid
Highview Power’s news item, also has this sentence.
Highview Power’s technology will also provide stability services to the National Grid, which will allow for the long-term replacement of fossil fuel-based power plants for system support.
Highview Power’s technology is also an alternative to Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) of a similar capacity.
How does Highview Power’s technology compare with the best lithium-ion systems on price, performance and reliability?
Curtailment Of Wind Farms
Highview Power’s news item, also has these two paragraphs.
This storage will help reduce curtailment costs – which is significant as Britain spent £800m in 2023 to turn off wind farms.
Highview Power aims to accelerate the roll-out of its larger facilities across the UK by 2035 in line with one of National Grid’s target scenario forecasts of a 2 GW requirement from LAES, which would represent nearly 20% of the UK’s long duration energy storage needs. By capturing and storing excess renewable energy, which is now the cheapest form of electricity, storage can help keep energy costs from spiralling, and power Britain’s homes with 24/7 renewable clean energy.
I can see several wind farms, that are regularly curtailed would have a Highview Power battery installed at their onshore substation.
Receently, I wrote Grid Powers Up With One Of Europe’s Biggest Battery Storage Sites, which described how Ørsted are installing a 300 MW/600 MWh Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) at Swardeston substation, where Hornsea Three connects to the grid.
I would suspect that the purpose of the battery is to avoid turning off the wind farm.
Would a Highview Power battery be better value?
What’s In It For Rio Tinto?
I can understand, why most companies are investing, but Rio Tinto are a mining company. My only thought is that they have a lot of redundant holes in the ground, that cost them a lot of money and by the use of Highview Power’s technology, they can be turned into productive assets.
Collateral Benefits
Highview Power’s news item, also has this paragraph.
Beyond contributing to the UK’s energy security by reducing the intermittency of renewables, Highview Power’s infrastructure programme will make a major contribution to the UK economy, requiring in excess of £9 billion investment in energy storage infrastructure over the next 10 years – with the potential to support over 6,000 jobs and generate billions of pounds in value add to the economy. It will also contribute materially to increasing utilisation of green energy generation, reducing energy bills for consumers and providing significantly improved energy stability and security.
If Highview Power can do that for the UK, what can it do for other countries?
No wonder companies of the quality of Centrica, Rio Tinto and Goldman Sachs are investing.
Grid Powers Up With One Of Europe’s Biggest Battery Storage Sites
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Orsted’s huge facility in Norfolk will store energy generated by its offshore wind farm
These three paragraphs give more details of the project.
The world’s largest developer of offshore wind farms is planning to build a vast battery storage facility near Norwich.
Orsted will install the energy storage system, which will be one of the largest in Europe, on the same site as the onshore converter station for its Hornsea 3 wind farm in Swardeston, Norfolk.
The project will store energy generated by Hornsea 3 when weather conditions are windy and when electricity supply exceeds demand so that it can be discharged later to help to balance the nation’s electricity grid.
Note.
- There is also a visualisation and a map.
- Tesla batteries will be used.
- The The battery will have an output of 300 MW, with a capacity of 600 MWh. So it is another two-hour BESS.
- It should be operational in 2026.
- The battery is on a 35-acre site.
- Cost is given as £8.5 billion, but that would appear to include the 2852 MW Hornsea 3 wind farm.
The BBC is reporting that local residents are worried about fire safety.
I have some thoughts of my own.
The Location Of The Swardeston Substation
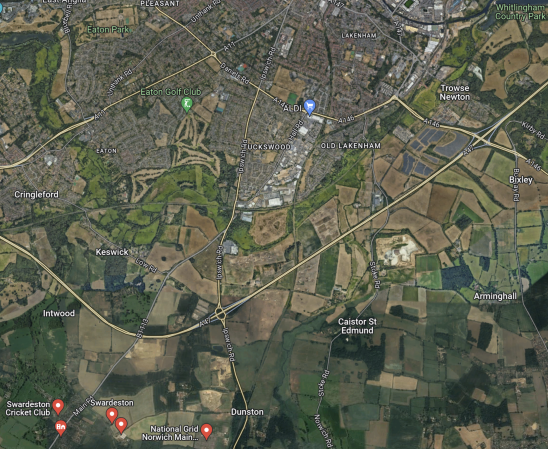
This Google Map shows the location of the Swardeston substation, which will also host the Swardeston BESS.
Note.
- The East-West road is the A 47 Norwich by-pass.
- Norwich is to the North of the by-pass.
- Just to the left-centre of the map, the main A 140 road runs between Norwich and Ipswich, which has a junction with the A 47.
- The A 140 passes through the village of Dunston, which is to the East of the National Grid sibstation, which will host the connection to the Hornsea Three wind farm.
This second Google Map shows the A 140 in detail from the junction to the A 47 to the Swardeston substation.
Note.
- The Swardeston substation is on a substantial site.
- The Norwich to Tilbury transmission line will have its Northern end at Swardeston substation.
- Once the infrastructure is complete at Swardeston substation, Hornsea Three wind farm will be connected to the electricity infrastructure around London.
There would appear to be plenty of space at the site for all National Grid’s plans.
Capital Cost Compared To Big Nuclear
Hornsea Three is a 2852 MW wind farm, that will cost with the battery and a few extras £8.5 billion or around around £ 3 billion per gigawatt.
Hinckley Point C on the other hand will cost between £ 31-35 billion or £ 9.5-10.7 billion per gigawatt.
Conclusion
National Grid would appear to be using a BESS at Swardeston substation to improve the reliability and integrity of the Hornsea Three wind farm.
How many other big batteries will be placed, where large wind farms connect to the National Grid?
As an Electrical and Control Engineer, I certainly, believe that energy storage at major substations, is a proven way to improve the grid.