SeaTwirl AB Signs Agreement To Explore Ehe Feasibility Of Electrification Of Aquaculture In Chile
The title of this post, is the same, as that of this press release from SeaTwirl.
This is the sub-heading.
SeaTwirl AB has entered into an agreement to carry out a feasibility study for electrification of fish farms together with a global industrial supplier. The intention of the collaboration is to assess the use of SeaTwirl’s floating vertical-axis wind turbines to provide renewable electricity to offshore-based equipment at aquaculture assets in Chile.
These three paragraphs add more details.
The feasibility study will cover a comprehensive scope, including energy demand and power system requirements, environmental site conditions, cost assessments, supply chain opportunities, and logistics in Chilean waters with the intention to reduce dependence on diesel. The study is expected to be completed during 2026, and the results will help determine next steps.
Chile is home to one of the largest aquaculture industries in the world, and the sector is pursuing ambitious sustainability goals including lower emissions, increased use of renewable power and reduced risk of spills. While the contractual value of the agreement is limited, at approximately SEK 0,8 million, the engagement will generate revenue and represent an important step in SeaTwirl’s commercialization effort.
“This collaboration marks an exciting step towards our purpose to enable floating wind power wherever it is needed, and to expand the use of floating wind technology beyond traditional grid-connected applications. The aquaculture industry has a clear need for offshore renewable energy, and we believe our technology can deliver a robust and cost-effective solution. It is also a major milestone to become involved in the southern hemisphere where many of the challenges we try to address, such as limited availability of cranes, vessels, and yard infrastructure, may be more challenging than in the north. We see significant potential in the aquaculture segment and look forward to beginning this journey in South America”, says Johan Sandberg, CEO of SeaTwirl.
I do find it strange, that the two vertical wind turbines, that both seem to be more than prototypes are both Scandinavian.
The Ventum Dynamics turbine, that I talked about in Are These Turbines An Alternative To Solar Panels? is Norwegian and this one is installed on Skegness Pier.
IKEA could sell these for DIY-enthusiasts to assemble and erect. On my stud, I used to have a barn, that could certainly have taken two of these 1.5 KW VX175 turbines.
This link is video of a dancing and swimming SeaTwirl.
If you follow, the SeaTwirl video to its conclusion, you’ll see one being erected in the sea. I can assure you that in the 1970s, my 25-year-old self, did the calculations for a reusable oil production platform called a Balaena, which erected on the same principle. So, I’m fairly certain, that SeaTwirls can be an alternative to traditional wind turbines.
First Monopile In At ‘Most Ecological Offshore Wind Farm Yet’
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Van Oord, using its installation vessel Boreas, installed the first monopile at the Ecowende offshore wind farm on 3 December. The project, a joint venture between Shell, Eneco and Chubu Electric Power, is being built off the coast of the Netherlands and is said to become the most ecological offshore wind farm to date.
These four paragraphs add more details.
The offshore wind farm, located approximately 53 kilometres off the Dutch coast near IJmuiden, will have 52 monopile foundations produced by Sif and Smulders supporting 52 Vestas V236-15.0 MW wind turbines.
The offshore wind farm is dubbed “the most ecological to date” since it incorporates several technologies and methodologies that are nature-inclusive, including monopiles coming in two diameters, 8.8 metres and 9.3 metres, to support varying turbine tower heights, as research indicates that higher turbine tip heights may allow birds to fly more safely between the structures, reducing collision risks.
Some of the wind turbines will feature red blades as part of a trial to assess whether increased visibility reduces bird collisions.
Offshore construction on Ecowende (Hollandse Kust West Site VI) offshore wind farm started in September with the installation of eco-friendly scour protection.
Note.
- It looks like its a 780 MW wind farm.
- They’re certainly looking after the birds.
- Scour protection is mainly to protect the wind farm, but at least it’s eco-friendly.
But then the Dutch must know a bit about building windmills, that last a long time.
US Installs 11.7 GW Of Clean Power In Record Q3
The title of this post, is the same as an article on Renewables Now.
Searching for the title of this post on Google AI gives this informative answer.
The United States installed a record 11.7 gigawatts (GW) of new utility-scale clean power capacity in the third quarter of 2025, marking a 14% increase over the same period in 2024. The data comes from the American Clean Power Association’s (ACP) latest “Clean Power Quarterly Market Report”.Key highlights from the report:
- Total Capacity: The 11.7 GW of new capacity includes utility-scale solar, energy storage, and onshore wind projects.
- Storage Surge: Battery storage set a new Q3 record with 4.7 GW installed, ensuring 2025 is on pace to be the biggest year for clean power deployment yet.
- Solar & Wind: Solar accounted for a large portion of new installations, and land-based wind increased 131% over Q3 2024.
- Strong Year Overall: Year-to-date installations reached 30.9 GW, already surpassing the pace of the previous record-setting year of 2024.
Despite the strong performance, the report also warns of future risks due to policy and regulatory uncertainty. Leading indicators, such as power purchase agreements (PPAs), fell significantly year-over-year, which points to potential slowdowns ahead. The full report with underlying datasets is available to ACP members, while a public version can be accessed via the press release on their website.
£100m ‘Global Players’ Wind Farm Deal To Create 300 Jobs
The title of this post, is the same as this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
A £100m deal which will create about 300 jobs has been agreed between the developers of two Irish Sea offshore wind farms and Belfast Harbour.
These three paragraphs add more detail.
The joint developers of the Mona and Morgan offshore wind farms will lease Belfast Harbour’s D1 terminal for the assembly and preparation of wind turbine components.
Work is being carried out to get the site ready for use from 2028.
Joe O’Neill, chief executive of Belfast Harbour, described it as a “huge deal”, not just for the harbour but for Belfast and the wider region.
Joe O’Neill seems happy with the deal, if you read the full BBC article.
This Google Map shows Belfast Harbour with the D1 Terminal in the centre.
Note.
- The red arrow indicates the D1 Terminal.
- It appears to be within walking distance of Belfast City Airport.
- The harbour is not that far from the city centre.
I would expect, this could be an ideal harbour to prepare wind turbines for erection.
But Where Will The Cruise Ships Dock In Belfast, If The D1 Terminal Is Being Used To Prepare And Assemble Wind Turbines?
Google AI gave this answer to my question!
Cruise ships will dock at a new deepwater berth at Belfast Harbour’s D3 terminal starting with the 2028 cruise season. This new facility is a dual-purpose terminal being built to accommodate both the largest cruise vessels and the assembly and installation of offshore wind turbines.
Note.
- The date fits with the new site for turbine work being ready by 2028.
- The new D3 Terminal will take some of the largest cruise vessels.
- I suspect, it will be able to supply ships with suitable low-carbon fuel, as required.
- Could it also take the very large ships used to install turbines?
- It’s almost as if Belfast Harbour are making an attraction of the turbines.
Google AI gives this overview of the D3 Terminal.
The Belfast Harbour D3 cruise terminal is a new £90 million dual-purpose deepwater quay under construction, designed to accommodate the world’s largest cruise ships and support the offshore wind energy industry. Construction on the project, which is Belfast Harbour’s largest-ever investment, began in April 2025 and is expected to be operational for the 2028 cruise season. The facility will include a 340m quay and new terminal building for passengers, and will be converted for cargo handling during the cruise season.
It certainly looks like Belfast is designing a dual-purpose terminal, that will bring the maximum benefit to the city and its people.
Which Offshore Wind Projects Will Use Belfast Harbour?
Google AI gave this answer to my question!
The Mona and Morgan offshore wind farms, being developed by EnBW and JERA Nex bp, will use Belfast Harbour. The port’s D1 terminal will serve as the hub for the assembly and marshalling of wind turbine components for these projects, which are planned for the Irish Sea and are expected to be operational by 2028.
I suspect there will be others.
EDF Developing Offshore Wind-Powered Hydrogen Production Project In French EEZ
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
EDF Power Solutions has invited applications for a tender for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) services and hazard studies as part of a project to develop an offshore hydrogen production station in France’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
This is the first paragraph.
The project, dubbed HYODE (HYdrogen Offshore DunkerquE), will produce green hydrogen by coupling offshore wind farms with an offshore electrolyser near Dunkirk, France, and is planned to also include storage and transport by ship to port, forming what EDF describes as an “innovative solution” to help scale green hydrogen production.
I asked Google AI, if there are any operational offshore hydrogen electrolysers and received this answer.
Yes, there are operational offshore electrolyser projects, though large-scale, dedicated offshore hydrogen platforms are still in development. The first operational offshore production on an existing gas platform is planned for late 2024 with the PosHYdon project. Additionally, a pilot project in the UK is testing the full integration of a hydrogen electrolyser onto an existing offshore wind turbine, with another project in the Netherlands installing an offshore hydrogen production and storage platform.
But, I did get this page on page on the Ramboll web site, which is entitled The Rise Of Offshore Hydrogen Production At Scale, which has this introductory paragraph.
The stage is set for producing green hydrogen from offshore wind and desalinated seawater. Building on existing and proven technology, offshore wind farms have the potential to become future production hubs for green hydrogen production at scale to meet increasing demand.
That sounds very promising, especially, if proven technology is borrowed from the offshore oil and gas industry.
It’s
Offshore Wind Developer Gets DNV Concept Certification for Floating Foundation Design
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
BayWa r.e. has received concept certification from DNV for its BayFloat floating wind semi-submersible concrete substructure and mooring system design. The design was validated using the 22 MW generic reference turbine “IEA-22-280-RWT”
These three introductory paragraphs give a few more details.
The certification process was conducted in accordance with DNV-SE-0422:2021-09 “Certification of floating wind turbines” scheme, including DNV-ST-0119:2021-06 “Floating wind turbine structures” as the governing standard, BayWa r.e. says.
The assessment concluded that the BayFloat concrete floating substructure, including the mooring system design, is feasible for further development and qualifies for DNV concept-level certification.
BayWa r.e. collaborated with the engineering company Ramboll on the design and certification process, with Ramboll providing design services, expert insights and engineering advice.
Note.
- Certification must be a good thing.
- If you are unfamiliar with DNV, then their Wikipedia entry, is a good place to start.
- As I was doing the calculations for a floating oil platform in the 1970s, I don’t see why floating wind turbines won’t work!
- Especially, as floating wind turbines, seem to have a higher capacity factor than fixed.
- Concrete also worked for oil and gas platforms, so why won’t it work for wind?
In fact I quite like this design.
These are some other thoughts and information.
The Buchan Wind Farm
Baywa r.e. are also developing the 960MW Buchan floating wind farm about 75 km North-East of Fraserburgh.
The Buchan Wind Farm web site says this about the technology to be used.
The project has identified BW Ideol’s patented Damping Pool® floating substructure as its preferred foundation option, with BW Ideol working actively to establish a manufacturing centre at the Ardersier Energy Transition Facility being developed at the former oil and gas fabrication yard on the Moray Firth.
Perhaps, Baywa r.e. are seeing if they can do better.
The Original Article
The original article also links to several designs of floating wind float design, so it is well worth a full read.
But then, each have their advantages in materials used, ease of construction, methods of assembly, ease of tow-out and erection and most importantly; cost!
Wind Farms Generate Record Power On Cold November Evening
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Turbines produced record high of 22.7 gigawatts of electricity at 7.30pm on Tuesday last week, accounting for 55 per cent of Britain’s electricity mix.
These two introductory paragraphs add more detail.
Britain’s wind farms generated a record 22.7 gigawatts of electricity on Tuesday evening last week, enough to power more than 22 million homes.
The National Energy System Operator (Neso) said the new high was set at 7.30pm on November 11, beating a previous record of 22.5 gigawatts on December 18, 2024.
In addition.
Yesterday, I wrote Ocean Winds Secures Third Celtic Sea Floating Wind Site, which will add 4.5 GW by 2035.
In Renewable Power By 2030 In The UK, I calculated these pessimistic offshore wind power totals for 206-2030.
- 2025 – 1,235 MW
- 2026 – 4,807 MW
- 2027 – 5,350 MW
- 2028 – 4,998 MW
- 2029 – 9,631 MW
- 2030 – 15,263 MW
This adds up to a total of 58,897 MW.
Conclusion
We shall be needing some new ways to export electricity to Europe.
Ocean Winds Secures Third Celtic Sea Floating Wind Site
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Ocean Winds has secured the third floating offshore wind site in the Celtic Sea, offered through the Crown Estate’s Round 5 auction earlier this year. The developer is joining Equinor and the Gwynt Glas joint venture, which were awarded rights for two of the three sites offered in Round 5 in June.
This paragraph outlines Ocean Winds’s deal.
On 19 November, the Crown Estate said that Ocean Winds was set to be awarded the rights for a third floating offshore wind site in the Celtic Sea.
There would now appear to be three Celtic Winds deals for wind farms.
- Gwynt Glas – 1.5 GW
- Ocean Winds – 1.5 GW
- Equinor – 1.5 GW
Note.
- 4.5 GW will be able to power a good proportion of South Wales and the South-West peninsular.
- In Gwynt Glas And South Wales Ports Combine Strength In Preparation For Multi-Billion Floating Wind Industry, I talk about partnerships between the wind farms and the ports.
- If you sign up for a large wind farm from the Crown Estate, do you get to have afternoon tea with Charles and Camilla in the garden at Highgrove or even Buckingham Palace?
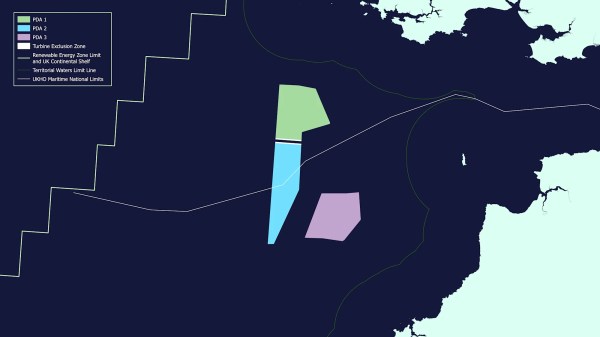
This map of the wind farms is available from download from this page on the Crown Estate web site.
Note.
- Gwynt Glas is in green.
- Ocean Winds is in blue.
- Equinor is in mauve.
- The white dot to the East of the wind farms is Lundy Island.
This triple wind farm is certainly well-placed to supply power to Cornwall, Devon and South Wales.
UK, French, And Irish Ports Join Hands In Global Floating Wind Collaboration
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s Associated British Ports (ABP) has teamed up with France’s BrestPort and Ireland’s Shannon Foynes Port to establish the Global Floating Offshore Wind Ports Alliance (FLOW Ports Alliance) to help bring together major floating offshore wind ports across the world and unlock the technology’s full potential.
These first two paragraphs add more detail.
The FLOW Ports Alliance aims to recruit ports in Europe to collaborate on FLOW port design, standardisation, and best operational practices.
It plans to strengthen and accelerate compliant knowledge and experience exchange between ports, share best practices as they emerge through demonstration projects, and share innovations to the benefit of the global FLOW network.
Surely, a global network of ports that can handle construction, operation and maintenance of a range of floating wind platforms, is an excellent idea.
All Recyclable Blades Installed At RWE’s 1.4 GW UK Offshore Wind Farm
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
All 150 recyclable blades have been installed at the 1.4 GW Sofia offshore wind farm, with more than half of the wind turbines now in place at the UK construction site.
These three paragraphs add more details.
All 150 recyclable blades are now installed, with each turbine utilising 50 sets of three blades, marking the UK’s first large-scale use of this technology at an offshore wind farm, RWE, the developer, said.
The recyclable rotor blades used at Sofia are manufactured by Siemens Gamesa at its Hull factory and use a unique resin that enables easy separation of component materials at the end of each blade’s operational life cycle.
In addition, 62 out of 100 Siemens Gamesa 14 MW turbines have now been installed at the site located 195 kilometres off the UK’s east coast. Each turbine features 108-metre blades and a 222-metre rotor diameter. Cadeler is responsible for the installation of the wind turbines.
Note.
- The Sofia wind farm has a hundred turbines, each with the customary three blades.
- Currently the 13 MW Siemens Gamesa turbines in Dogger Bank A and Dogger Bank B are the largest turbines in British waters.
- Sofia’s at 14 MW will be larger.
- But 15 MW monsters are on their way, with RWE’s Norfolk zone appearing to favour 15 MW Vesta turbines.
At the present time, turbine size seems to be creeping up. I would expect this to happen, as turbines become more affordable.