Technology Behind Siemens Mobility’s British Battery Trains Hits The Tracks
This title of this post is the same as that of this news item from Siemens, which was published in December 2024.
These three bullet points introduce the news item.
- The Mireo Plus B battery train is rolled out in the East Brandenburg network, Germany, using the same technology as the British Desiro Verve project.
- The Desiro Verve would save £3.5 billion and 12 million tonnes in CO2 emissions for Britain’s railways over 35 years.
- The development marks the latest step of this technology’s journey to Britain’s railways.
No-one, including me, seemed to have spotted this news item, especially, since it is significant to both the UK and Germany.
But then parts of Siemens’s home country; Germany and Yorkshire, where they are building, a train factory to build London’s new Piccadilly Line trains have something big in common – There is a distinct shortage of electric trains and the overhead wires to power them.
So did German engineers, egged on by pints of British real ale, realise that their battery-electric technology for the Mireo Plus B battery-electric train, would turn a Desiro City multiple unit, like the Class 700, 707 or 717 into battery-electric trains.
These are three paragraphs from the Siemens news item.
The innovative technology behind Siemens Mobility’s British battery trains has been rolled out in the East Brandenburg network in Germany.
31 of the company’s Mireo Plus B trains are being phased in to the Berlin Brandenburg metropolitan region, beginning on Sunday (15 December) and is the latest proof point of the technology that underpins the Desiro Verve project in Britain. This follows the debut of this technology on 27 new trains in the Ortenau region of Germany in April, with more set to arrive in Denmark in 2025.
The British Desiro Verve trains would be assembled at Siemens Mobility’s new Train Manufacturing Facility in Goole, East Riding of Yorkshire, formally opened by the Transport Secretary and Mayor of London in October.
I’d always wondered, what Siemens would do with this factory, when it had finished making the Piccadilly Line trains.
It also should be noted, that the boss of Siemens UK, when the Goole factory was planned was Jürgen Maier, who according to his Wikipedia entry has Austrian, British and German citizenship and is now the boss of Great British Energy.
I believe that Siemens have big plans for the Goole factory.
One thing it has, that at the present time could be a problem in Germany, is large amounts of renewable electricity and hydrogen, so will energy-intensive components for trains be made at Goole?
It will be interesting to see how the Goole factory develops.
The Desiro Verve Train For The UK and Ireland
In the Siemens news item, their Joint CEO for the UK and Ireland; Sambit Banerjee, says this.
The Desiro Verve would be assembled at our state-of-the-art Goole Rail Village in Yorkshire and offers an integrated solution to replace Britain’s aging diesel trains without having to electrify hundreds of miles of track, saving the country £3.5 billion over 35 years and providing a practical path to decarbonising British railways.”
In June, Siemens Mobility identified how the Desiro Verve could save Britain’s railways £3.5 billion over 35 years compared with using diesel-battery-electric ‘tri-mode’ trains. This would support the Government’s aim of removing diesel-only trains from Britain’s railways by 2040.
The British trains would be powered by overhead wires on already electrified routes, then switch to battery power where there are no wires. That means only small sections of the routes and/or particular stations have to be electrified with overhead line equipment (OLE), making it much quicker and less disruptive to replace diesel trains compared to full electrification.
I agree with his philosophy.
The Rail Charging Converter
When I wrote Cameron Bridge Station – 15th May 2025, I described how a short length of overhead electrification could be erected at the station to charge passing trains, using their pantographs.
Cameron Bridge station is lucky in that there is already a 132,000 KVAC electricity connection to the distillery next door.
But at other places, where there is no connection, you could wait as long as seven years to be connected to the grid.
So Siemens have come up with the Rail Charging Converter, that provides a local electricity supply to support the charger.
It is described in this paragraph from the news item.
This OLE can also be installed much more quickly using Siemens Mobility’s innovative Rail Charging Converter (RCC), which makes it possible to plug directly into the domestic grid – potentially cutting delivery times for OLE from seven years to as little as 18 months.
This Siemens visualisation shows a Verve train and an RCC.
This arrangement could be used in sensitive countryside or close to historic buildings.
Modern Railways – June 2025
There is an article about the Siemens technology in the June 2025 Edition of Modern Railways.
It is called The Battery Revolution Starts In Long Marston for which this is part of the sub-heading.
New technology being installed by Siemens Mobility at Porterbrook’s test facility paves the way for widespread use of battery trains in the UK.
The article is a must-read.
Conclusion
Siemens appear to have the technology with their Rail Charging Converter and battery-electric trains like the Verve and the Mireo Plus B, to be able to decarbonise lines without electrification all over the world.
Would larger gauge trains be delivered from Germany and smaller gauge ones from Goole?
I wouldn’t be surprised that a version for a German S-Bahn could share more characteristics, with a small British train, than a large German one.
I can also see an underground railway, that was built without power in the tunnels. So if you were building the Waterloo and City Line today, would it be battery-electric and charged at each end of the line using a pantograph?
Grand Central To Submit Application For Direct Services Between Lincolnshire And London
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from Grand Central.
These three bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Grand Central has today launched an application process for direct services between Cleethorpes, Grimsby, Habrough, Scunthorpe and London – plans to bring significant benefits to underserved areas.
- The application will be welcomed by communities, businesses, and organisations, who have been actively campaigning for the introduction of direct rail links to London.
- If approved, the new services could unlock £30.1 million annually for the region.
These three paragraphs add more details.
Grand Central has today notified Network Rail of its plans to operate new direct services between Lincolnshire and London that, if approved by the rail regulator (the ORR), will bring significant benefits to underserved areas across Lincolnshire and the wider region.
Under the proposals, direct services to London will be provided from Cleethorpes, Grimsby, Habrough, and Scunthorpe, with Grand Central planning to operate the services from as early as December 2026.
The plan makes best use of capacity on the rail network by running trains from the proposed new stops before connecting into existing Grand Central services at Doncaster.
The service seems very similar to the proposed King’s Cross and Cleethorpes service described in the this section of the Grand Central Wikipedia entry, where this is said.
In December 2017, Grand Central announced plans to bid for a service from London King’s Cross to Cleethorpes in early 2018 for a date in 2020. It would involve the existing Bradford Interchange service extended to ten coaches from London to Doncaster then dividing with five coaches going to Cleethorpes via Scunthorpe, Barnetby, Habrough and Grimsby. The other five coaches would be the existing service to Bradford Interchange. This proposal would require permission for a split of trains as it has not been used on the East Coast Main Line before. In February 2018, Grand Central announced plans for an additional call at Crow The company planned to operate four trains per day from 2020. However, in July 2018, the Office of Rail and Road announced new access charges which would affect the business case for the new service, leading to Grand Central announcing that it would delay bidding until 2019.
Note.
- It appears that the service is not calling at Crow.
- By splitting and joining at Doncaster, Grand Central will be getting more coaches and passengers, up and down a single path between King’s Cross and Doncaster stations.
- Grand Central run four trains per day (tpd) between King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange, so as four tpd will be running between King’s Cross and Doncaster stations, it appears Grand Central will be running a full service.
It appears that open access applications come to those who wait eight years.
I have some further thoughts.
What Class Of Trains Do Grand Central Currently Use?
According to Real Time Trains on Friday the 21st of March 2025, two Class 180 trains and two Class 221 trains each ran a service between King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange stations.
Both type of train appear to be able to run as a pair of trains.
As Bradford is the UK City of Culture in 2025, that could prove useful.
What Trains Will Grand Central Use For The New Service?
It would appear that either type of train type could run the service,
So it would probably come down to factors like reliability, comfort and what is available.
I Was Mildly Surprised When I Saw This Application Had Gone In
But, circumstances change.
- Grand Central now run two Class 221 trains, in addition to the Class 180 trains.
- There are more Class 221 trains in store, if needed.
- The UK has had several changes of government since the original application in 2017 and track-access charges may have been reduced.
- Cleethorpes station has been refurbished.
Cleethorpes Station – 28th June 2023 shows the station in 2023.
But a new problem has arisen. The new Transport Secretary doesn’t seem keen on open access services, from some of the things she’s said.
Perhaps, she has had a change of heart or as she looks to be a good doer, someone has bought her a decent meal of fish and chips in Cleethorpes? My meal in the town is described in Lunch On The Pier In Cleethorpes.
But would Grand Central put in an application, if they knew they were wasting their money?
Or could this be an application funded by all the open access operators to get a definitive view on the government’s policy?
Could The Cleethorpes Service Be Run By Battery-Electric Trains?
Consider.
- Doncaster and Cleethorpes are 52.1 miles apart.
- Surprisingly Doncaster and Bradford Interchange are 52.1 miles apart.
- King’s Cross and Doncaster are 155.9 miles apart and fully-electrified.
- A battery that had enough capacity to do the return trips from Doncaster to either Cleethorpes or Bradford Interchange, would be easily recharged on the way to and from London.
With careful calculation of the battery size and good capacity management, I also suspect a battery-electric train could be able to take the GNGE Diversion via Lincoln.
Could The Cleethorpes Service Be Run By Hydrogen-Electric Trains?
Consider the daily services will be made up of these runs.
- Eight runs between London and Bradford Interchange each consisting of 155.9 miles on wires and 52.1 miles on hydrogen.
- Eight runs between London and Cleethorpes each consisting of 155.9 miles on wires and 52.1 miles on hydrogen.
Which means there are 833.6 miles per day run on hydrogen.
If there are four trains running the service as now, that is 208.4 miles per train per day on hydrogen.
A hydrogen-powered train with this daily range is very much a possibility.
The German Dimension To Grand Central Trains
Consider.
- Grand Central are owned by Arriva.
- Arriva are owned by Deutche Bahn.
- Siemens have a train factory at Goole close to Doncaster.
- Siemens have built quite a few electric multiple units for various UK railways.
- Siemens have designs for battery-electric and hydrogen-electric multiple units, that would be suitable for Grand Central Trains.
- Jürgen Maier was senior in Siemens UK, when the train factory at Goole was built and is now chair of Great British Energy.
I believe that Siemens at Goole could build trains, that would do nicely for Grand Central Trains.
- It would surely be handy for Grand Central Trains to have their fleet stabled in easy reach of the factory.
- In addition, hydrogen will soon be readily-available in the Doncaster area.
Grand Central trains could do a lot worse than buy trains built or assembled at Siemen’s factory at Goole.
Energy In – Hydrogen And Carbon Dioxide Out
This article was inspired by this article in the Sunday Times, which is entitled ‘It’s A Slog’: Life Inside Britain’s Last Coal Power Station.
The article is about Ratcliffe-on-Soar power station, which is next to East Midlands Parkway station.
This is the first paragraph of the station’s Wikipedia entry.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar Power Station is a coal-fired power station owned and operated by Uniper at Ratcliffe-on-Soar in Nottinghamshire, England. Commissioned in 1968 by the Central Electricity Generating Board, the station has a capacity of 2,000 MW. It is the last remaining operational coal-fired power station in the UK, and is scheduled to close in September 2024.
I took these pictures of the power station in 2019.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar is the last of a number of large coal-fired power stations, that were built in the area, mainly along the River Trent.
- Rugeley – 600 MW – 1961
- Drakelow – 1630 MW – 1964
- Willington – 800 MW – 1962
- Castle Donington – 600 MW – 1958
- Ratcliffe-on-Soar – 2000 MW – 1968
- High Marnham – 1000 MW – 1959
- Cottam – 2000 MW – 1968
- West Burton – 2000 MW – 1968
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 10,630 MW of electricity.
- There are also a few large gas-fired power stations along the river, that are still operating.
- Both coal and gas-fired stations use the water from the River Trent for cooling.
At the mouth of the river, there is the Keadby cluster of gas-fired power stations.
- Keadby 1 – 734 MW – 1996
- Keadby 2 – 849 MW – 2023
- Keadby 3 – 910 MW – 2027
- Keadby Hydrogen – 900 MW – 2030
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 3,393 MW of electricity.
- Keadby 2 is the most efficient CCGT in the world.
- Keadby 3 will be fitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby 2 has been designed to be retrofitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby Hydrogen will be fuelled by zero-carbon hydrogen.
As the years progress, I can see the Keadby cluster of power stations becoming a large zero-carbon power station to back-up wind farms in the North Sea.
- Hydrogen power stations will emit no carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide from all gas-fired stations will be captured.
- Some carbon dioxide will be sold on, to companies who can use it, in industries like construction, agriculture and chemical manufacture.
- The remaining carbon dioxide will be stored in depleted gas fields.
As technology improves, more carbon dioxide will be used rather than stored.
Other Power Sources In The Humberside Area
In the next few sub-sections, I will list the other major power sources in the Humberside area.
Drax Power Station
Drax power station is a shadow of its former self, when it was one of the power stations fed by the newly discovered Selby coalfield.
These days it is a 2,595 MW biomass-fired power station.
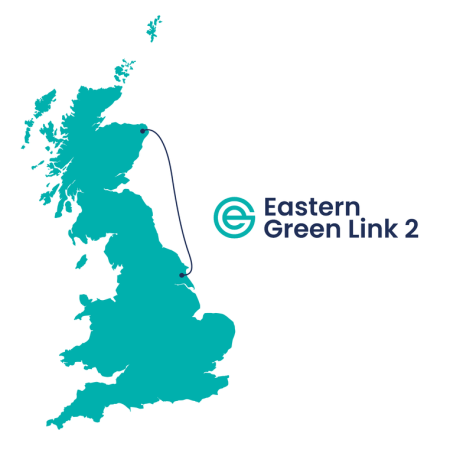
Eastern Green Link 2
Eastern Green Link 2 will be a 2 GW interconnector between Peterhead in Scotland and Drax.
It is shown in this map.
Note.
- Most of the route is underwater.
- It is funded by National Grid.
- Contracts have been signed, as I talk about in Contracts Signed For Eastern Green Link 2 Cable And Converter Stations.
- It is scheduled to be completed by 2029.
This interconnector will bring up to 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity to Drax and Humberside.
Drax has the substations and other electrical gubbins to distribute the electricity efficiently to where it is needed.
2 GW could also reduce the amount of biomass used at Drax.
In the long term, if the concept of the four Eastern Green Links is successful, I could see another Eastern Green Link to Drax to replace imported biomass at Drax.
I also, don’t see why a smaller Drax can’t be run on locally-sourced biomass.
Solar Farms And Batteries Along The River Trent
As the coal-fired power stations along the River Trent are demolished, solar farm developers have moved in to develop large solar farms.
Salt End Power Station And Chemical Works
These two paragraphs from the Wikipedia entry for Salt End describes the hamlet and its power station and chemical works.
Salt End or Saltend is a hamlet in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, in an area known as Holderness. It is situated on the north bank of the Humber Estuary just outside the Hull eastern boundary on the A1033 road. It forms part of the civil parish of Preston.
Salt End is dominated by a chemical park owned by PX group, and a gas-fired power station owned by Triton Power. Chemicals produced at Salt End include acetic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonia, bio-butanol, bio-ethanol, ethyl acetate (ETAC) and ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) with animal feed also being produced on site.
I wonder, if running the complex on hydrogen would give cost and marketing advantages.
Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage Facility
This page on the SSE Thermal web site is entitled Plans For World-Leading Hydrogen Storage Facility At Aldbrough.
This is the most significant paragraph of the page, that is definitely a must-read.
With an initial expected capacity of at least 320GWh, Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage would be significantly larger than any hydrogen storage facility in operation in the world today. The Aldbrough site is ideally located to store the low-carbon hydrogen set to be produced and used in the Humber region.
This is a hydrogen storage facility for a much wider area than Humberside.
Rough Gas Storage Facility
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Rough Gas Storage Facility.
Rough is a natural gas storage facility under the North Sea off the east coast of England. It is capable of storing 100 billion cubic feet of gas, nearly double the storage capacities in operation in Great Britain in 2021.
In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to convert the Rough gas storage into a massive hydrogen storage.
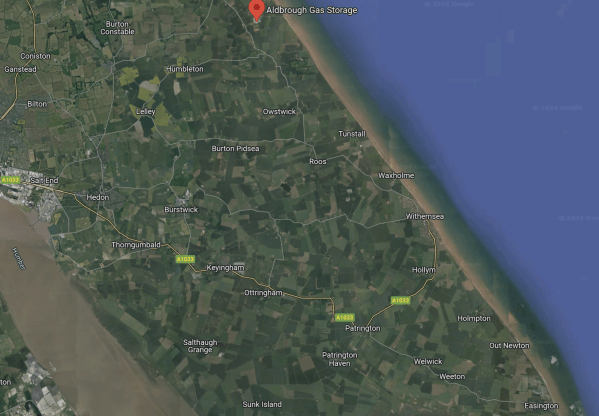
The Location Of Aldbrough Gas Storage, Rough Gas Storage, Salt End And Easington Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows between Salt End and the coast.
Note.
- The river crossing the South-West corner of the map is the Humber.
- Salt End with its power station and chemical works is on the North Bank of the Humber, where the river leaves the map.
- Aldbrough Gas Storage is marked by the red arrow at the top of the map.
- Easington Gas Terminal is in the South-East corner of the map.
- According to Wikipedia, gas flows into and out of the Rough Gas Storage are managed from Easington.
Looking at the map, I feel that the following should be possible.
- The two gas storage sites could be run together.
- Salt End power station and the related chemical works could run on hydrogen.
- Salt End will always have a reliable source of hydrogen.
- This hydrogen could be green if required.
All the chemical works at Salt End, could be run on a zero-carbon basis. Would this mean premium product prices? Just like organic does?
Enter The Germans
The Germans have a huge decarbonisation problem, with all their coal-fired power stations and other industry.
Three massive projects will convert much of the country and industry to hydrogen.
- H2ercules, which is a project of OGE and RWE, will create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen, to where it is needed.
- In Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal, I describe how Uniper are going to build a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhelmshaven.
- AquaVentus is an RWE project that will use 10.3 GW of offshore wind power in German territorial waters to create a million tonnes per year of green hydrogen.
These would appear to be three of Europe’s largest hydrogen projects, that few have ever heard of.
AquaVentus And The UK
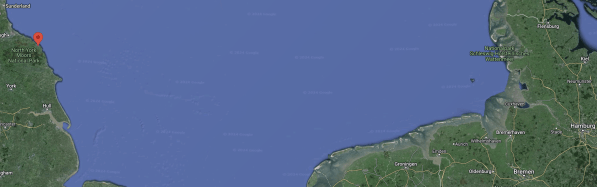
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that delivers hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea.
It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network in the North Sea.
These are my thoughts about development of the AquaVentus network.
Hydrogen Production And AquaVentus
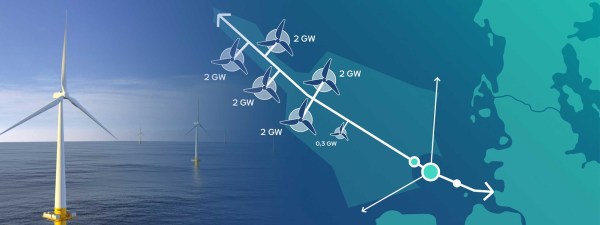
This RWE graphic shows the layout of the wind farms feeding AquaVentus.
Note.
- There is a total of 10.3 GW.
- Is one of the 2 GW web sites on the UK-side of AquaVentus, the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm, which is being developed by RWE?
- Is the 0.3 GW wind farm, RWE’s Norfolk wind farm cluster, which is also being developed by RWE?
Connecting wind farms using hydrogen pipelines to Europe, must surely mitigate the pylon opposition problem from Nimbys in the East of England.
As the AquaVentus spine pipeline could eventually connect to Peterhead, there will be other opportunities to add more hydrogen to AquaVentus.
Hydrogen Storage And AquaVentus
For AquaVentus to work efficiently and supply a large continuous flow of hydrogen to all users, there would need to be storage built into the system.
As AquaVentus is around 200 kilometres in length and natural gas pipelines can be up to 150 centimetres in diameter, don’t underestimate how much hydrogen can be stored in the pipeline system itself.
This page on the Uniper web site is entitled Green Wilhelmshaven: To New Horizons.
This is a sentence on the page.
Access to local hydrogen underground storage at the Etzel salt cavern site.
An Internet search gives the information, that Etzel gas storage could be developed to hold 1 TWh of hydrogen.
That would be enough hydrogen to supply 10 GW for a hundred hours.
Note that the UK branch of AquaVentus reaches the UK, just to the South of the massive hydrogen storage facilities at Aldbrough and Rough.
It would appear that both Germany and the UK are connected to AquaVentus through substantial storage.
I am certain, that all country connections to AquaVentus will have substantial storage at the country’s hydrogen terminal.
AquaDuctus
This would appear to be the first part of the AquaVentus network and has its own web site.
The web site is entitled Nucleus Of A Offshore Hydrogen Backbone.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The project partners are focusing on a scalable, demand-driven infrastructure: By 2030, AquaDuctus will connect the first large hydrogen wind farm site, SEN-1, with a generation capacity of approximately one gigawatt. SEN-1 is located in the German EEZ in the northwest of Helgoland. The pipeline will transport at a length of approx. 200 km green hydrogen produced from offshore wind to the German mainland and from there to European consumers via the onshore hydrogen infrastructure.
In the next project stage, AquaDuctus will be extended to the remote areas of the German exclusive economic zone towards the tip of the so-called duck’s bill. By that, additional future hydrogen wind farm sites will be connected. Along its way AquaDuctus will provide interconnection points with the opportunity for linking of adjacent national offshore hydrogen infrastructures originating from Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium and United Kingdom which opens the door for Europe-wide offshore hydrogen transport by pipeline.
There is also an interactive map, that gives more details.
This paragraph explains, why the Germans have chosen to bring the energy ashore using hydrogen, rather than traditional cables.
Recent studies show that offshore hydrogen production and transport via pipelines is faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly than onshore electrolysis with a corresponding connection of offshore wind turbines via power cables. The German federal government has also recognized this advantage and has clearly expressed its intention to promote offshore hydrogen production in the North Sea.
I suspect, that some UK offshore wind farms will use the same techniques.
Hydrogen Production For The UK
Electrolysers will probably be built along the East Coast between Peterhead and Humberside and these will feed hydrogen into the network.
- Some electrolysers will be offshore and others onshore.
- Turning off windfarms will become a thing of the past, as all surplus electricity will be used to make hydrogen for the UK or export to Europe.
- Until needed the hydrogen will be stored in Albrough and Rough.
Backup for wind farms, will be provided using hydrogen-fired power stations like Keadby Hydrogen power station.
Financial Implications
I reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there would be winners all round.
Rishi Sunak had the cards and he played them very badly.
It is now up to Keir Starmer, Great British Energy and Jürgen Maier to play those cards to link the energy systems of the UK and Germany to ensure security and prosperity for Europe.
Jurgen Maier To Chair Great British Energy
This article in The Times is entitled Pylons Are The Price Of Lower Bills, Keir Starmer Tells Rural Britain.
These are two paragraphs from the article.
Starmer confirmed that Jürgen Maier, the former UK chief executive of the Siemens conglomerate, would chair the energy company.
Maier has advised Labour on rail and transport since December. He was openly critical of the party’s decision to drop a pledge to spend £28 billion a year on green investment, saying the figure was an “absolute minimum” and that scrapping the promise was “not good for climate change or for the growth of our economy”.
Note.
- His Wikipedia entry is impressive.
- He has dual Austrian and British citizenship.
- He went to school in Leeds and is a graduate of Nottingham Trent University.
- He rose to be Chief Executive of Siemens UK and retired in 2019 at 55.
- I have heard him several times on the radio and he seems to talk a lot of sense.
In my view he could be an excellent choice as Chair of Great British Energy.
I also have some further thoughts.
Jürgen Maier And Peter Hendy
Jürgen Maier and Peter Hendy, who is Starmer’s Rail Minister, have remarkably similar backgrounds and I wouldn’t be surprised if they know each other well, through dealings around Siemens’ contract for Transport for London’s new trains for the Piccadilly Line.
When last, were two technological heavyweights, so close to the heart of a UK government?
RWE
German energy company; RWE are the UK’s largest power generator.
- RWE have five gas-fired power stations with a total output of 6.56 GW.
- RWE have two onshore wind farms in operation with a total output of 67 MW.
- RWE have four offshore wind farms in operation with a total output of 1.88 GW.
- RWE have eight offshore wind farms under development with a total output of 9.90 GW.
- RWE also has other electrical gubbins, like an electrolyser in South Wales.
Would Jürgen Maier be an ideal person, to persuade RWE to keep investing in the UK?
When he was with Siemens, he certainly invested heavily in the UK.
The German Problem
Germany’s problem is how they generate electricity.
Sources are as follows for Germany and the UK.
- Coal – 26 % – 1 %
- Natural Gas – 10.5 % – 32 %
- Wind – 32 % – 29.4 %
- Solar 12.2 % – 4.9 %
- Biomass – 9.7 % – 12.3 %
- Nuclear – 1.5 % – 14.2 %
- Hydro – 4.5 % – 1.8 %
- Oil – 0.7 % – 0 %
- Other – 2.9 % – 0 %
- Storage – 0 % – 1 %
- Imports – 0 % – 10.7 %
Note.
- Figures are for 2023.
- Germany is the first percentage.
- UK is the second percentage.
- Germany has pledged to end coal-fired electricity production by 2030.
- Both countries seem to generate similar amounts of electricity from wind, biomass and hydro.
To replace the coal and make up for lack of nuclear, Germany needs to find a new power source.
The German Solution
The Germans are going for hydrogen in a big way.
The title of this page of the RWE web site is Welcome To The Age Of Hydrogen.
The page starts with this paragraph.
RWE is actively involved in the development of innovative hydrogen projects. The H2 molecule is considered to be an important future building block of a successful energy transition. RWE is a partner in over 30 H2 projects and is working on solutions for decarbonising the industry with associations and corporations like Shell, BASF and OGE. Hydrogen projects are comprehensively supported in the separate Hydrogen department of the subsidiary RWE Generation.
I also suggest, that you read this page on the RWE web site called AquaVentus.
The page starts with this RWE graphic.
It appears that 10.3 GW of hydrogen will be created by wind farms and piped to North-West Germany.
These two paragraphs outline the AquaVentus initiative .
Hydrogen is considered the great hope of decarbonisation in all sectors that cannot be electrified, e.g. industrial manufacturing, aviation and shipping. Massive investments in the expansion of renewable energy are needed to enable carbon-neutral hydrogen production. After all, wind, solar and hydroelectric power form the basis of climate-friendly hydrogen.
In its quest for climate-friendly hydrogen production, the AquaVentus initiative has set its sights on one renewable energy generation technology: offshore wind. The initiative aims to use electricity from offshore wind farms to operate electrolysers also installed at sea on an industrial scale. Plans envisage setting up electrolysis units in the North Sea with a total capacity of 10 gigawatts, enough to produce 1 million metric tons of green hydrogen.
The page also gives these numbers.
- Total Capacity – 10 GW
- Tonnes Of Green Hydrogen – 1 million
- Members – 100 +
The web site says this about commissioning.
Commissioning is currently scheduled for early/mid 2030s.
The Germans can’t be accused of lacking ambition.
AquaVentus And The UK
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be a undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be a link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea. It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network.
AquaVentus And Aldbrough And Rough Gas Storage
Consider.
- In The Massive Hydrogen Project, That Appears To Be Under The Radar, I describe the Aldbrough Gas Storage.
- In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to turn Rough Gas Storage into the world’s largest hydrogen store.
- There is a small amount of hydrogen storage at Wilhelmshaven.
It looks like the East Riding Hydrogen Bank, will be playing a large part in ensuring the continuity and reliability of AquaVentus.
Dogger Bank South And AquaVentus
This Google Map shows the North Sea South of Sunderland and the Danish/German border.
Note.
- Sunderland is in the top-left hand corner of the map.
- A white line in the top-right corner of the map is the Danish/German border.
- Hamburg and Bremen are in the bottom-right hand corner of the map.
If you lay the AquaVentus map over this map, I believe that RWE’s Dogger Bank South wind farm could be one of the three 2 GW wind farms on the South-Western side of the AquaVentus main pipeline.
- Two GW would be converted to hydrogen and fed into the AquaVentus main pipeline.
- Two GW of hydrogen will be a nice little earner for UK plc.
- One GW of electricity would be sent to the UK.
But this is only one of many possibilities.
Conclusion
Could Jürgen Maier, be the man to develop British links to AquaVentus for the benefit of both the UK and Germany?
- The UK’s wind farms could provide a lot of hydrogen for AquaVentus.
- Aldbrough And Rough Gas Storage are conveniently places to add the hydrogen storage, that AquaVentus needs.
- AquaVentus can certainly be expanded to Norway, and possibly Orkney and Shetland.
He certainly has a lot of relevant experience.