UK ESO Unveils GBP 58 Billion Grid Investment Plan To Reach 86 GW of Offshore Wind By 2035
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Great Britain’s electricity system operator (ESO) has proposed a GBP 58 billion (approximately EUR 68 billion) investment in the electricity grid. The proposal outlines a vision for incorporating an additional 21 GW of offshore wind into the grid by 2035, which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
These three paragraphs add more details to what the investment in the grid means for offshore wind.
The ESO released on 19 March the first Beyond 2030 report. The plan sets up the necessary infrastructure to transfer power to and from future industries, as electricity demand is expected to rise by 64 per cent by 2035, according to the ESO.
The grid operator said that the plan connects a further 21 GW of offshore wind in development off the coast of Scotland to the grid in an efficient and coordinated way which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
The proposals could assist the UK government in meeting the sixth Carbon Budget and allow for the connection of Crown Estate Scotland’s ScotWind leasing round.
These are my thoughts.
How Much Offshore Wind Is In The Pipeline?
This Wikipedia entry is a List Of Offshore Wind Farms In The United Kingdom.
It gives these figures for wind farms in various operational an development states.
- Operational – 14,703 MW
- Under Construction – 5,202 MW
- Pre-Construction – 6,522 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 3 – 12 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 4 – 1,428 MW
- Early Planning – England – 18,423 MW
- Early Planning – Wales – 700 MW
- Early Planning – Scotland – 30,326 MW
Note.
- These add up to a total of 77,316 MW.
- If all the wind farms in the Wikipedia entry are commissioned, the UK will be short of the 86,000 MW total by 8,664 MW.
- Some wind farms like Ossian could be increased in size by a few GW, as I reported in Ossian Floating Wind Farm Could Have Capacity Of 3.6 GW.
It looks like only another 7,164 MW of offshore wind needs to be proposed to meet the required total.
This article on offshoreWIND.biz is entitled The Crown Estate Opens 4.5 GW Celtic Sea Floating Wind Seabed Leasing Round, will add another 4,500 MW to the total, which will raise the total to 81,816 MW.
The article also finishes with this paragraph.
Round 5 is expected to be the first phase of development in the Celtic Sea. In November 2023, the UK Government confirmed its intention to unlock space for up to a further 12 GW of capacity in the Celtic Sea.
A further 12 GW of capacity will take the total to 93,816 MW.
In Three Shetland ScotWind Projects Announced, I talked about three extra Scotwind wind farms, that were to be developed to the East of Shetland.
These will add 2.8 GW, bringing the total to 96,616 MW.
I don’t think the UK has a problem with installing 86 GW of offshore wind by 2035, so we must create the electricity network to support it.
The Electricity Network In 2024
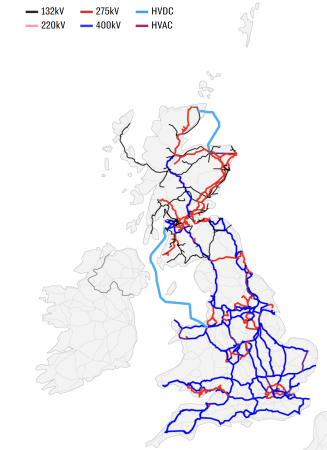
I clipped this map from this article in The Telegraph, which is entitled Britain’s Energy System Will Not Hit Net Zero Until 2035, National Grid Tells Labour.
The dark blue lines are the 400 kV transmission lines.
- The one furthest East in East Anglia serves the Sizewell site, which hosts the Sizewell B nuclear power station and will be the home of Sizewell C nuclear power station, unless the Green or LibDem Parties are a member of a coalition government.
- Kent and Sussex seem to be encircled by 400 kV lines, with small spurs to the interconnectors to Europe.
- Two 400 kV lines appear to serve the South-West peninsular, with one going along the South Coast and the other further North. I suspect these two motorways for electricity explain, why the Morocco-UK Power Project terminates in Devon.
- London seems to have its own M25 for electricity.
- There also appears to be an East-West link to the North of London linking Sizewell in the East and Pembroke in the West. Both ends have large power stations.
- There also appear to be two 400 kV lines from Keadby by the Humber Estuary to North Wales with the pumped storage hydro power station at Dinorwig.
- Two more 400 kV lines link Yorkshire to the South of Scotland.
- A lonely Northern cable connects Edinburgh and the North of Scotland.
The red lines, like the one encircling central London are the 275 kV transmission lines.
- Think of these as the A roads of the electricity network.
- They encircle London often deep underground or under canal towpaths.
- They reinforce the electricity network in South Wales.
- Liverpool appears to have its own local network.
- They also seem to provide most of the capacity North of and between Edinburgh and Glasgow.
Newer cables are starting to appear on this map.
There are two light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- The 1.2 GW Caithness – Moray Link does what it says in the name and it connects the far North of Scotland direct towards Aberdeen.
- The much larger 2.25 GW Western HVDC Link connects Hunterston near Glasgow to Flintshire Bridge near Liverpool. Note how it passes to the West of the Isle of Man.
Not shown on the map are the smaller 500 MW Moyle Interconnector and the recently-opened 600 MW Shetland HVDC Connection.
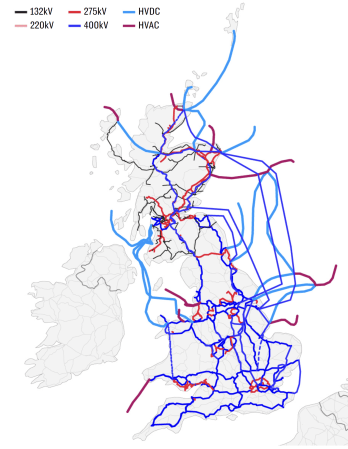
The Electricity Network In 2050
This second map shows how the network will look in 2050.
Note.
- The colours are the same, as the previous map.
- Although, I do think there are some errors in which have been used.
- There are a lot more cables.
There are several more light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- Shetland is now linked to the North of Scotland by the Shetland HVDC Connection.
- There appears to be a cluster of HVDC interconnectors at Caithness HVDC switching station, near Wick, including a new one to Orkney, to go with the others to Moray and Shetland.
- The 2 GW Scotland England Green Link 1 will run from Torness in Southeast Scotland to Hawthorn Pit substation in Northeast England.
- The 2 GW Eastern Green Link 2 will run from Sandford Bay, at Peterhead in Scotland, to the Drax Power Station in Yorkshire, England.
- There also appear to be two or possibly three other offshore cables linking the East Coast of Scotland with the East Coast of England.
- If the Eastern cables are all 2 GW, that means there is a trunk route for at least 8 GW between Scotland’s wind farms in the North-East and Eastern England, which has the high capacity wind farms of Dogger Bank, Hornsea and around the Lincolnshire and East Angliam coasts.
- Turning to the Western side of Scotland, there appears to be a HVDC connection between the Scottish mainland and the Outer Hebrides.
- South-West of Glasgow, the Western HVDC Link appears to have been duplicated, with a second branch connecting Anglesey and North-West Wales to Scotland.
- The Moyle Interconnector must be in there somewhere.
- Finally, in the South a link is shown between Sizewell and Kent. It’s shown as 400 kV link but surely it would be a HVDC underwater cable.
There are also seven stubs reaching out into the sea, which are probably the power cables to the wind farms.
- The red one leading from South Wales could connect the wind farms of the Celtic Sea.
- The blue link North of Northern Ireland could link the MachairWind wind farm to the grid.
- The other two red links on the West Coast of Scotland could link to other ScotWind wind farms.
- The red link to the North of East Anglia could link RWE’s Norfolk wind farms to the grid.
- The other stubs in the East could either connect wind farms to the grid or be multi-purpose interconnectors linking to Germany and the Netherlands.
It looks to me, that National Grid ESO will be taking tight control of the grid and the connected wind farms, as an integrated entity.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I can’t disagree with that philosophy.
Hydrogen Production
In How Germany Is Dominating Hydrogen Market, I talked about how Germany’s plans to use a lot of hydrogen, will create a large world-wide demand, that the UK because of geography and large amounts of renewable energy is in an ideal place to fulfil.
I can see several large electrolysers being built around the UK coastline and I would expect that National Grid ESO have made provision to ensure that the electrolysers have enough electricity.
Would I Do Anything Different?
Consider.
- If it is built the Morocco-UK Power Project will terminates in Devon.
- There could be more wind farms in the Celtic Sea.
- It is likely, that the wind farms in the Celtic Sea will connect to both Pembroke and Devon.
- Kent has interconnectors to the Continent.
Would a Southern HVDC link along the South Coast between Devon and Kent be a good idea?
Conclusion
Looking at the proposed list of wind farms, a total in excess of 96 GW could be possible, which is ten GW more than needed.
The network not only serves the UK in a comprehensive manner, but also tees up electricity for export to Europe.
Ørsted Secures Exclusive Access To Lower-Emission Steel From Dillinger
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Ørsted will be offered the first production of lower-emission steel from German-based Dillinger, subject to availability and commercial terms and conditions. The steel plates are intended to be used for offshore wind monopile foundations in future projects.
These three paragraphs outline the deal.
Under a large-scale supply agreement entered into in 2022, Ørsted will procure significant volumes of regular heavy plate steel from 2024, giving the company access at scale to and visibility of the most crucial raw material in offshore wind while supporting Dillinger to accelerate investments in new lower-emission steel production, according to Ørsted.
The Danish renewable energy giant expects to be able to procure lower-emission steel produced at Dillinger’s facility in Dillingen, Germany, from 2027-2028.
Taking the current technology outlook into account, the reduction of the process-related carbon emissions from production is expected to be around 55-60 per cent compared to conventional heavy plate steel production, Ørsted said.
Increasingly, we’ll see lower emission steel and concrete used for wind turbine foundations.
This press release on the Dillinger web site is entitled Historic Investment For Greater Climate Protection: Supervisory Boards Approve Investment Of EUR 3.5 billion For Green Steel From Saarland.
These are two paragraphs from the press release.
Over the next few years leading up to 2027, in addition to the established blast furnace route, the new production line with an electric arc furnace (EAF) will be built at the Völklingen site and an EAF and direct reduced iron (DRI) plant for the production of sponge iron will be built at the Dillinger plant site. Transformation branding has also been developed to visually represent the transformation: “Pure Steel+”. The message of “Pure Steel+” is that Saarland’s steel industry will retain its long-established global product quality, ability to innovate, and culture, even in the transformation. The “+” refers to the carbon-neutrality of the products.
The availability of green hydrogen at competitive prices is a basic precondition for this ambitious project to succeed, along with prompt funding commitments from Berlin and Brussels. Local production of hydrogen will therefore be established as a first step together with the local energy suppliers, before connecting to the European hydrogen network to enable use of hydrogen to be increased to approx. 80 percent. The Saarland steel industry is thus laying the foundation for a new hydrogen-based value chain in the Saarland, in addition to decarbonizing its own production. In this way, SHS – Stahl-Holding-Saar is supporting Saarland on its path to becoming a model region for transformation.
It sounds to me, that Tata Steel could be doing something similar at Port Talbot.
- Tata want to build an electric arc furnace to replace the blast furnaces.
- There will be plenty of green electricity from the Celtic Sea.
- RWE are planning a very large hydrogen electrolyser in Pembroke.
- Celtic Sea offshore wind developments would probably like a supply of lower emission steel on their door-step.
I would suspect, that Welsh steel produced by an electric arc furnace will match the quality of the German steel, that is made the same way.
Pension Power Backing For New Battery Energy Storage Plant
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Nation.Cymru.
These paragraphs outline the project,
A new battery energy storage plant at the site of a decommissioned power station will be funded by Welsh pensioners.
The plan for the facility at the former Uskmouth B Power Station at the Gwent Wetlands on the edge of Newport, was approved by the city council’s planning committee this January.
The batteries will store excess power during times of “excess supply” and then put that electricity back into the grid when demand is higher.
The Greater Gwent Pension Fund, which manages the retirement savings of more than 65,000 members from Blaenau Gwent, Caerphilly, Monmouthshire Newport and Torfaen councils as well as 52 other active employers in the Gwent region, has revealed it is investing in the project.
According to their Wikipedia entry, the Uskmouth power stations have had rather a chequered history and both appear to be currently non-productive.
- The original coal-fired Uskmouth A has been demolished and the site is now occupied by an 832 MW gas-fired CCGT power station. Currently, it is in a ‘dormant’ state, after its owner entered administration.
- The original coal-fired Uskmouth B has been converted and now can generate 363 MW on a mixture of biomass and waste plastic. Uskmouth B is currently being demolished.
This press release from Quinbrook Infrastructure Partners is entitled Quinbrook To Build Large-Scale Battery Storage Project At Uskmouth, South Wales.
This is the sub-heading.
Uskmouth will be one of the largest storage projects in the UK and will directly support the UK’s energy transition.
These first two paragraphs outline the project.
Quinbrook Infrastructure Partners (“Quinbrook”), a specialist investment manager focused on renewables, storage and grid support infrastructure has acquired the exclusive development rights for one of the UK’s largest battery storage projects to date.
The planned 230MW / 460MWh Battery Energy Storage System (“BESS”), will be located at the site of the former Uskmouth coal fired power station in south Wales (“Project Uskmouth”) and will seek to utilise existing power transmission infrastructure and provide a new lease of life to the area. Uskmouth was acquired from Simec Atlantis Energy Limited (“SAE”). Quinbrook has partnered with Energy Optimisation Solutions Limited (“EOS”) in the origination and development of Project Uskmouth, which represents a major anchoring project in the planned re-development and regeneration of the Uskmouth site into a Sustainable Energy Park that will support innovative future industry. Quinbrook considers these types of regeneration projects as key to making meaningful contributions to delivery of the Government’s Levelling Up ambitions.
Note.
- The battery can supply 230 MW for two hours.
- It looks like the battery will replace the older of the two power stations and work with the relatively-modern 832 MW gas-fired CCGT power station.
- Will they act as backup to renewables?
As there are very few renewables in the area, will this work with the wind farms being developed in the Celtic Sea or are Quinbrook anticipating wind farms South of Newport in the Bristol Channel?
I have a few thoughts.
Will Uskmouth Work With Hinckley Point C?
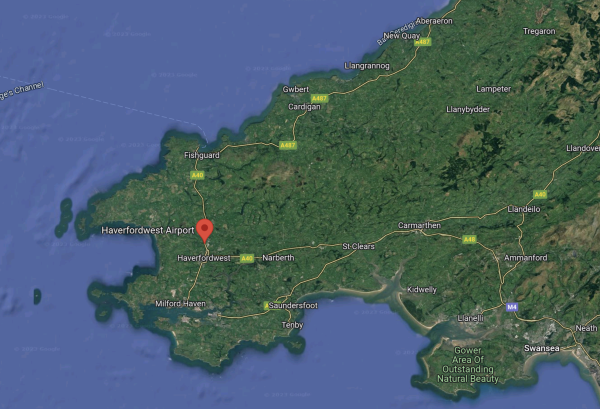
This Google Map shows the relative locations of Uskmouth and Hinckley Point C.
Note.
- Uskmouth is just South of Newport, in the North-East corner of the map.
- I estimate that Uskmouth and Hinckley Point C are 24.7 miles apart.
A cable across the Bristol Channel would surely increase the energy security of South Wales.
Will There Be Wind Farms In The Bristol Channel?
I feel that this is inevitable.
This document on the Welsh Government web site is entitled Future Potential For Offshore Wind In Wales, was written by The Carbon Trust.
This paragraph is the document’s assessment of wind farms in the Bristol Channel.
Despite high energy demand and good infrastructure, environmental conditions in the Bristol Channel
makes this area challenging for offshore wind development. In addition to lower average wind speeds,
the Bristol Channel has complex seabed, including areas of hard rock, and is exposed to strong tidal
currents from the Severn Estuary. Seabed conditions and tidal currents were the main drivers behind
cancellation of the Atlantic Array project and it is considered unlikely that a developer would look to
revive this site in the near-term, particularly given competition with other more favourable UK sites.
That doesn’t seem very promising.
But this is the document’s assessment of wind farms in the Pembrokeshire Atlantic area.
Exposure to the prevailing south-westerly Atlantic wind and swells means that the waters off
Pembrokeshire have excellent wind speeds, often exceeding 10 m/s, but also a harsher wave
environment than elsewhere in Wales. Significantly, water depths quickly increase to over 50m,
suggesting that floating foundations are likely to be required, particularly if projects are located
further from shore, which is likely given constraints from environmental impact and seascape near to
the Pembrokeshire Coast National Park.Grid infrastructure is constrained for thermal generation but should not be a barrier to new
renewables. The Greenlink interconnector could also support the addition of new capacity. The region
has good port infrastructure at Milford Haven and Pembroke Dock, which is already actively pursuing
upgrades to future proof the port for potential offshore wind deployment.
That is a lot more promising.
- Some demonstration wind farms are under development.
- Hopefully, the steel would be available at Port Talbot.
- I can see this area, having almost 50 GW of floating wind.
I do feel though, that once the sea off Pembrokeshire is full of wind farms, that developers will turn their attention to the more difficult waters of the Bristol Channel.
Is The Uskmouth BESS A Good Investment?
The Nation.Cymru article discusses this and what they say is well worth reading.
My feelings are that the BESS will be very busy balancing electricity on the South Wales Coast and to and from Ireland using the 500 MW Greenlink Interconnector, which opens this year.
These electrical systems are relatively easy to model and I suspect Quinbrook wouldn’t be investing, if the BESS was not going to generate a substantial income.
BW Ideol, ABP To Explore Serial Production Of Floating Wind Foundations At Port Talbot
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
BW Ideol and Associated British Ports (ABP) have signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) that will see the manufacturer of concrete floating wind foundations and ABP investigating the feasibility of serial production at Port Talbot. The MOU has been signed in preparation for the Celtic Sea leasing round, BW Ideol said on Monday (11 December).
These two paragraphs outline the plans of BW Ideol and ABP have for Port Talbot.
According to the company, Port Talbot is the only Celtic Sea port with the scale and technical capabilities to fully maximise the Celtic Sea supply chain opportunity and is ideally located as a manufacturing base since it lies 120-140 kilometres from the floating offshore wind areas outlined by The Crown Estate for the upcoming leasing round.
The news on the MOU between ABP and BW Ideol comes shortly after ABP announced plans to invest around GBP 500 million (approximately EUR 573 million) to upgrade a site in Port Talbot and turn it into a major floating offshore wind hub.
This Google Map shows Port Talbot Port.
Note.
- It also looks like there is a Heidelberg Cement facility at the South side of the port.
- Port Talbot also has a Tata steelworks.
- The railway and the M4 Motorway are nearby.
- There’s certainly a lot of water.
The port appears well-placed for raw materials and there is quite a bit of free space to build and launch the concrete floaters.
This page on the BW Ideol web site describes their Floatgen demonstrator.
The first section is headed by BW Ideol’s First Floater In Operation, where this is said.
Built around a European consortium of 7 partners, Floatgen is a 2MW floating wind turbine demonstrator installed off the coast of Le Croisic on the offshore experimentation site of the Ecole Centrale de Nantes (SEM-REV). This project is being supported by the European Union as part of the FP7 programme. Floatgen is France’s first offshore wind turbine. 5 000 inhabitants are supplied with its electricity.
It looks like it is or almost is a proven system.
The page talks of two large benefits.
- Innovation at all levels.
- The highest local content of any floating wind turbine.
For the second, the following is said
In comparison to other steel floating foundations, which are imported from abroad, the use of concrete for BW Ideol’s floating foundation allows the construction to be located as close as possible to the deployment site. Construction at the Saint-Nazaire port was therefore a natural and optimal solution and has created a lot of local content. Additionally, the mooring system was manufactured by LeBéon Manufacturing in Brittany. For the majority of all other components or logistical activities, the Floatgen partners have also opted for suppliers within the Saint-Nazaire region.
Note.
- Will ABP and BW Ideol use a similar philosophy at Port Talbot?
- Will low-carbon concrete be used to construct the floaters?
I can certainly see the logic of BW Ideol and ABP getting together at Port Talbot.
Crown Estate Details Round 5 Plans
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The Crown Estate has revealed details of a new leasing round, known as Round 5, for three commercial-scale floating wind projects in the Celtic Sea.
These are the first two paragraphs, which outline the three initial projects.
Located off the coast of South Wales and South West England, the sites will have a combined capacity of up to 4.5 GW, enough to supply four million homes with renewable energy.
The new wind farms are expected to be the first phase of commercial development in the region, with the UK Government confirming as part of its Autumn Statement in November its intention to unlock space for up to a further 12 GW of capacity in the Celtic Sea.
It looks like there could be another 7.5 GW available.
These four paragraphs indicate that the Crown Estate. expect the developers to to develop the local infratructure.
New details about the Round 5 auction include upfront investment in important workstreams to de-risk the process for developers and accelerate the deployment of projects.
This includes a multi-million-pound programme of marine surveys to better understand the physical and environmental properties around the locations of the new wind farms, as well as carrying out a Plan-Level Habitats Regulations Assessment early on in the process.
An Information Memorandum published today, on 7th December, also includes details of a series of contractual commitments for developers to create positive social and environmental impacts, focused on skills and training, tackling inequalities in employment, environmental benefits, and working with local communities.
In addition, bidders will be required to demonstrate commitments for the timely access to the port infrastructure needed to develop their projects, the Crown Estate said.
But it also appears that the Crown Estate are doing their bit by carrying out marine surveys.
Conclusion
It looks like the Crown Estate are making thing easier for developers, so that they increase the interest in Celtic Sea wind farms.
We’ll see if the strategy is successful, when contracts are awarded.
The Crown Estate Refines Plans For Celtic Sea Floating Wind
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Crown Estate.
This is the first part of the press release.
The Crown Estate has set out further details on its plans for Offshore Wind Leasing Round 5, which aims to establish new floating offshore wind technology off the coast of Wales and South West England. The update includes details on the final planned locations for the new windfarms, as well as further information on a multi-million-pound programme of marine surveys.
Round 5 is expected to be the first phase of development in the Celtic Sea, with The Crown Estate working to catalyse and accelerate the UK’s energy transition, and to de-risk developments to speed up their deployment. This includes investing in an upfront Habitats Regulation Assessment, an extensive programme of marine surveys and working with the Electricity System Operator on a coordinated approach to grid design.
This latest update follows a period of engagement with developers and wider stakeholders on proposals set out in July over how to make best use of available space in the Celtic Sea. As a result of the feedback received, The Crown Estate has confirmed that:
- Three Project Development Areas (PDAs) of roughly equal size are expected to be made available to bidders, as opposed to the previously proposed four PDAs of varying sizes
- No bidder will be able to secure an Agreement for Lease for more than one PDA
- As a result of bringing forward three equal-sized PDAs – each with a potential capacity of up to 1.5GW – the overall capacity available through Round 5 has increased from a possible 4GW to up to 4.5GW, enough to power more than 4 million homes
Note.
- Another 4.5 GW of offshore wind should hit the queue.
- It sounds like they have been listening to developers.
To find out more of the potential of the Celtic Sea, I recommend this article on the Engineer, which is entitled Unlocking The Renewables Potential Of The Celtic Sea.
I’ll go along with what this article says and accept that 50 GW of wind capacity could be installed in the Celtic Sea.
Is Sizewell C Needed?
I am generally pro-nuclear, but I am not sure if building a large nuke at Sizewell is the right action.
Consider.
- East Anglia has 3114 MW of offshore wind in operation.
- East Anglia has 6772 MW of offshore wind under construction, with Contracts for Difference or proposed.
- Vattenfall are considering abandoning development of their large wind farms off the Norfolk coast, which are proposed to have a capacity of 3196 MW.
- If the two Vattenfall wind farms don’t get built, it is likely that East Anglia will have around 6700 MW of offshore wind capacity.
- Sizewell C has a proposed nameplate capacity of 3260 MW. Some might argue, that to back up East Anglia’s offshore wind power, it needs to be larger!
- Norfolk and Suffolk no large electricity users, so are Vattenfall finding they have a product no one wants to buy.
- National Grid is developing four interconnectors to bring power from Scotland to the Eastern side of England, which will back up wind power in the East with the massive Scottish pumped storage, that is being developed.
- National Grid and their Dutch equivalent; TenneT are developing LionLink to connect the UK and the Netherlands to clusters of wind farms between our countries in the North Sea.
- Kent and East Anglia have several gas and electric interconnectors to Europe.
- Sizewell is well-connected to England’s grid.
These are my thoughts.
Energy Storage At Sizewell
Consider.
- Sizewell is well connected to the grid.
- It has the sea on one side.
- It could easily be connected to the large offshore wind farms, thirty miles out to sea.
If large energy storage could be built on the Sizewell site or perhaps under the sea, then this energy could be recovered and used in times of low wind.
Perhaps the technology of the STORE Consortium, which I discussed in UK Cleantech Consortium Awarded Funding For Energy Storage Technology Integrated With Floating Wind, could be used.
In this system, energy is stored in 3D-printed concrete hemispheres under the sea.
A Small Nuclear Reactor Cluster At Sizewell
Rolls-Royce are proposing that their small modular reactors will have a capacity of 470 MW.
Perhaps a cluster of seven small modular reactors at Sizewell, with a building schedule matched to the need to back up wind farms would be better and easier to finance.
I also feel a cluster of SMRs would have less risk and would be less likely to be delayed.
Where Is Generating Capacity Needed In The UK?
These areas already have large amounts of offshore wind in operation or proposed to be built before 2030.
- Celtic Sea
- North Wales
- Liverpool Bay
- Cumbria
- Scotland
- Scotland’s Offshore Islands
- North East England
- Humberside
- Lincolnshire
- East Anglia
- Thames Estuary
- Kent
- Sussex
Amongst the back up for these wind farms, there are only two modern nuclear stations; Sizewell B and the still-to-open Hinckley Point C.
If you look at a map of England and its power generation, there is a tremendous gap of capacity South of a line between Hinckley Point and Brighton, with little or no offshore wind and no nuclear.
There is probably a need for a large nuke near Weymouth.
Alternatively, perhaps several SMRs could be built underneath places like Salisbury Plain, Dartmoor and Exmoor!
Conclusion
We probably need the nuclear electricity from another Hinckley Point C-sized nuclear power station, so that we have adequate back-up for offshore wind.
But I am not sure that Sizewell is the right place to build it.
UK Offshore Wind Pipeline Now At 98 GW, Second Only To China – Report
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s pipeline of offshore wind projects has reached 97,944 MW, up from 91,287 MW a year ago, while the global pipeline topped 1.23 TWh, an increase of nearly 400 GW in the last year, according to RenewableUK’s latest EnergyPulse market intelligence data report.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The pipeline includes projects at every stage of development, including operational, under construction, consented, or planned.
The UK total pipeline was second globally at 98 GW, second only to China with 157 GW, followed by the USA in third place with 82 GW, Sweden is fourth with 75 MW, and Brazil fifth with 63 GW.
These is also a pie-chart saying in which part of the UK, wind energy is being developed.
- North Sea (Scotland) – 41,977 MW
- North Sea (England) – 33,845 MW
- Irish Sea – 8,659 MW
- North Atlantic Ocean – 7,435 MW
- Celtic Sea – 4,428 MW
- English Channel – 1,600 MW
As Cilla would say. “What a lorra, lorra lot of wind!”
More Trains To Carmarthen
The last time, I looked at the number of GWR trains to Carmarthen its Wikipedia entry, it was just a couple.
Today, one train per hour (tph) is shown between London Paddington and Swansea, with this supplementary information.
- 7 trains per day continue to Carmarthen, calling at Gowerton (limited), Llanelli, Pembrey & Burry Port, Kidwelly (limited) and Ferryside (limited)
- On Summer Saturdays, 2 trains per day run to Pembroke Dock, calling at all stations between Carmarthen and Pembroke Dock
In Regulator Approves New Grand Union Train Service From Carmarthen To London Paddington, I talked about the plans of Grand Union Trains to run five trains per day (tpd) between London Paddington and Carmarthen.
This would appear to give a total of twelve tpd between London Paddington and Carmarthen.
This page on the Crown Estate web site is entitled Celtic Sea Floating Offshore Wind, where this is said.
The Government has set an ambition to deliver up to 5GW of floating wind by 2030, with rapid expansion anticipated thereafter.
At The Crown Estate, we are committed to helping the UK achieve its net zero ambitions. To support this, we are excited to deliver a new leasing opportunity in the Celtic Sea for the first generation of commercial-scale floating offshore windfarms – unlocking up to 4GW of new clean energy capacity by 2035, kick-starting industry in the region, and providing power to almost four million homes.
We will be inviting full commercial scale projects up to 1GW, which may be developed in a phased or ‘stepping stone’ approach. Recognising the need to develop the UK supply chain and supporting infrastructure for this nascent technology, this approach is deliberately intended to provide opportunities for growth and investment. This will also facilitate the co-ordination of the necessary infrastructure, such as ports and grid connections, all of which are key to the sustainable development of the UK floating wind sector over the long term.
This leasing opportunity will provide the foundation for greater capacity in the future and help establish an exciting new industrial sector for the UK, creating opportunities for significant new investment in jobs, skills and infrastructure for the communities onshore.
It appears to me, that Great Western Railway and Grand Union Trains both believe that there will be large increase in demand for rail travel between London Paddington and Carmarthen and also along the South Wales Coast.
Grand Union Trains are also proposing the building of a new parkway station at Parc Felindre North of Swansea.
But then this area of South Wales and the Celtic Sea, has the four things needed for the development of up to 5 GW of offshore wind; a lot of wind, a large area of empty sea, steel and deep water ports to assemble all the floating wind turbines.
A Zero-Carbon High Speed Railway Between London Paddington And Carmarthen
Consider.
- The Great Western Railway between London Paddington and Carmarthen is 222.5 miles and trains take around three hours and fifty minutes, which is an average speed of 58 mph.
- Between Bristol Parkway and Reading stations, the operating speed is 125 mph.
- In South Wales, the operating speed is generally between 70 and 100 mph.
- Only the 77.4 miles between Cardiff Central and Carmarthen via Swansea is not electrified.
There is probably scope to increase the operating speed using digital signalling and by improving the track.
I would suspect that a time between London Paddington and Carmarthen of under three-and-a-half hours is possible.
The Range Of Battery-Electric Trains
Hitachi have not been specific about the zero-carbon range of their Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train, which is described in this Hitachi infographic.
In Stadler FLIRT Akku Battery Train Demonstrates 185km Range, I talk about Stadler’s record-braking Battery-electric; Akku, which covered 185 km or 115 miles.
I suspect that Hitachi’s engineers and those at their battery suppliers; Turntide Technology will be ultra-competitive, so I wouldn’t be surprised that the zero-carbon range of the Hitachi train is very competitive to the Stadler FLIRT Akku.
A hundred mile range would allow electric services to be run on these routes.
- Cardiff and Carmarthen – 77.4 miles
- Chippenham and Bristol Temple Meads and return – 48.8 miles
- Chippenham and Bristol Western-super-Mare and return – 86.9 miles
- Swindon and Cheltenham Spa and return – 86.5 miles
- East Coast Main Line and Hull and return – 72.2 miles
- Plymouth and Penzance – 79.5 miles
- Taunton and Newbury – 89.6 miles
- York and Scarborough and return – 84.1 miles
I am fairly sure that Hitachi will aim for at least a hundred mile battery range for their Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train.
- This would be competitive with other train manufacturers like Stadler and Siemens.
- They would handle a lot of important routes.
- With development they could probably handle Edinburgh and Inverness.
I can’t wait to have a ride.
Rockton To Buy Up To 40 Heart Aerospace ES-30 Electric Aircraft
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Aviation Source News.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Swedish investment and aircraft leasing company Rockton has confirmed that it will acquire up to 40 of Heart Aerospace’s regional electric aircraft, the ES-30.
The purchase confirmation converts an earlier letter of intent with the Swedish aircraft manufacturer into firm purchase orders for 20 aircraft with purchase rights for 20 more.
It’s good to see a leasing company getting involved, as it probably means that the finances are viable.
The Wikipedia entry for Heart Aerospace, describes the range of the ES-30 like this.
The ES-30 is planned to have a 108 nautical miles (200 kilometres; 124 miles) fully electric range or a 215 nmi (398 km; 247 mi) range when also using generators powered by aviation biofuel. A range of 430 nmi (800 km; 490 mi) could be possible if only 25 passengers are carried.
These are some UK airport to airport distances.
- Aberdeen – Kirkwall – 124 miles
- Aberdeen – Sumburgh – 188 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Cork – 192 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Anglesey – Ronaldsway – 58 miles
- Anglesey – Shannon – 186 miles
- Anglesey – Waterford – 130 miles
- Birmingham – Belfast – 226 miles
- Birmingham – Dublin – 200 miles
- Birmingham – Edinburgh – 250 miles
- Birmingham – Glasgow – 260 miles
- Birmingham – Inverness – 363 miles
- Birmingham – Kirkwall – 451 miles
- Birmingham – Newcastle – 178 miles
- Birmingham – Newquay – 198 miles
- Birmingham – Schipol – 402 miles
- Birmingham – Sumburgh – 513 miles
Birmingham – Wick – 418 miles - Edinburgh – Schipol – 473 miles
- Gatwick – Edinburgh – 356 miles
- Gatwick – Schipol – 374 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast – 106 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast City – 103 miles
- Glasgow – Derry – 121 miles
- Glasgow – Kirkwall – 221 miles
- Glasgow – Sumburgh – 300 miles
- Glasgow – Stornoway – 177 miles
- Haverfordwest – Waterford – 94 miles
- Haverfordwest – Newquay – 94 miles
- Heathrow – Newquay – 212 miles
- Humberside – Schipol – 333 miles
- Inverness – Kirkwall – 106 miles
- Inverness – Sumburgh – 190 miles
- Leeds – Schipol – 386 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast City – 151 miles
- Liverpool – Cardiff – 135 miles
- Liverpool – Dublin – 140 miles
- Liverpool – Haverfordwest – 127 miles
- Liverpool – Norwich – 180 miles
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway – 89 miles
- London City – Haverfordwest – 167 miles
- London City – Humberside – 145 miles
- London City – Manchester – 161 miles
- London City – Norwich – 100 miles
- Manchester – Schipol 413 miles
- Newcastle – Cardiff – 230 miles
- Newcastle – Belfast City – 168 miles
- Newcastle – Newquay – 346 miles
- Newcastle – Schipol – 395 miles
- Newquay – Brest – 140 miles
- Newquay – Cardiff 98 miles
- Newquay – Cork – 180 miles
- Newquay – Deauville – 241 miles
- Newquay – Dinard – 183 miles
- Newquay – Dublin – 212 miles
- Newquay – Guernsey – 128 miles
- Newquay – Jersey – 152 miles
- Newquay – Nantes – 211 miles
- Newquay – Orly – 351 miles
- Newquay – Rouen – 285 miles
- Newquay – Scillies – 68 miles
- Newquay – Waterford – 150 miles
- Norwich – Schipol – 277 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast – 75 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City – 62 miles
- Ronaldsway – Birmingham – 165 miles
- Ronaldsway – Dublin – 80 miles
- Ronaldsway – East Midlands – 161 miles
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow – 123 miles
- Ronaldsway – Leeds – 121 miles
- Ronaldsway – Manchester – 109 miles
- Southend – Schipol – 180 miles
- Stansted – Aberdeen – 379 miles
- Stansted – Edinburgh – 316 miles
- Stansted – Glasgow – 334 miles
- Stansted – Inverness – 426 miles
- Stansted – Schipol – 335 miles
- Stansted – Wick – 472 miles
- Sumburgh – Bergen – 226 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Note.
- I have included Schipol, as in certain areas of the UK, passengers sometimes fly long-haul from Schipol.
- I have included Haverfordwest, as it will be close to all the wind farm activity in the Celtic Sea.
- I have included Anglesey, as I think it has possibilities.
- The distances wee calculated using on of the Free Map Tools.
These are some more specific thoughts.
The Basic ES-30 And The UK
With a range of 124 miles, I don’t believe that the range is long enough for the UK.
But saying that there are some established routes, where it should be able to operate.
- Glasgow – Belfast
- Glasgow – Belfast City
- Glasgow – Derry
- Haverfordwest – Waterford
- Haverfordwest – Newquay
- Inverness – Kirkwall
- Liverpool – Haverfordwest
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway
- London City – Norwich
- Newquay – Cardiff
- Newquay – Scillies
- Ronaldsway – Belfast
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City
- Ronaldsway – Dublin
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow
- Ronaldsway – Leeds
- Ronaldsway – Manchester
These routes have the following in common.
- They are mostly between major airports with advanced facilities.
- Most airports served have access to renewable electricity.
- Some of the routes can support hundred seat airliners.
- Fifty percent go to the Isle of Man.
I can see several routes between the UK and the island of Ireland and to and from the Isle of Man using ES 30 aircraft.
The Extended Range ES-30 And The UK
The 247 mile range of the extended range ES-30, brings lots more routes into play.
Key routes could be the following.
- Aberdeen – Kirkwall
- Aberdeen – Sumburgh
- Anglesey – Cork
- Anglesey – Shannon
- Birmingham – Belfast
- Birmingham – Dublin
- Birmingham – Newcastle
- Birmingham – Newquay
- Glasgow – Kirkwall
- Glasgow – Stornoway
- Heathrow – Newquay
- Inverness – Sumburgh
- Liverpool – Belfast City
- Liverpool – Dublin
- Liverpool – Norwich
- London City – Haverfordwest
- London City – Humberside
- London City – Manchester
- Newcastle – Belfast City
- Newcastle – Cardiff
- Newquay – Brest
- Newquay – Cork
- Newquay – Deauville
- Newquay – Dinard
- Newquay – Dublin
- Newquay – Guernsey
- Newquay – Jersey
- Newquay – Nantes
- Newquay – Waterford
- Ronaldsway – Birmingham
- Ronaldsway – East Midlands
There will also be other routes.
The Extended Range With 25 Passengers ES-30 And The UK
The 490 mile range of the extended range ES-30 with only 25 passengers, brings a few more routes into play.
- Birmingham – Edinburgh
- Birmingham – Glasgow
- Birmingham – Inverness
- Birmingham – Kirkwall
- Birmingham – Schipol
- Birmingham – Wick
- Edinburgh – Schipol
- Gatwick – Edinburgh
- Gatwick – Schipol
- Glasgow – Sumburgh
- Humberside – Schipol
- Leeds – Schipol
- Manchester – Schipol
- Newcastle – Newquay
- Newcastle – Schipol
- Newquay – Orly
- Newquay – Rouen
- Norwich – Schipol
- Southend – Schipol
- Stansted – Aberdeen
- Stansted – Edinburgh
- Stansted – Inverness
- Stansted – Glasgow
- Stansted – Schipol
- Stansted – Wick
Note.
- All airports East of Birmingham and Manchester seem to be close enough to Schipol for an Extended Range ES-30 with 25 passengers to serve the route.
- Most major Scottish Airports can be reached from Stansted.
- Flying from Gatwick to Scottish Airports is around forty miles longer than flying from Stansted.
Liverpool Airport
Liverpool Airport could be a major destination for the ES 30, as it could be a key airport for flying between the UK and the island of Ireland.
Liverpool would obviously need the electric infrastructure, but I also believe it needs a better connection to the major railway station at Liverpool South Parkway, which has extensive rail connections.
This Google Map shows the area between Liverpool South Parkway station and the airport.
Note.
- Liverpool South Parkway station is marked by the red arrow in the North-West corner of the map.
- The airport is in the opposite corner, with the terminal to the North of the runway.
- The main railway between the South and Liverpool Lime Street passes to the South of the station.
- The A561 passes across to the South of the railway and to the North of the airport.
I suspect some form of people mover like the Luton DART can be built between the station and the airport.
It should be noted that as Hunts Cross has only one platform for Merseyrail Northern Line trains and this could be a factor in limiting the line’s capacity. So could a second platform be installed at the airport to both act as an airport station and to increase the frequency on the Northern Line?
I believe that in a couple of years, journey times between Euston and Liverpool South Parkway will be under two hours and they will only get shorter with High Speed Two. With a fast connection between the airport and the station, there could be a sub-three-hour zero-carbon route between London and the island of Ireland.
- Avanti West Coast Class 805 train to Liverpool South Parkway.
- People mover to the airport.
- Electric aircraft on the 140 miles to Dublin.
Dublin air traffic are usually efficient in getting planes in quickly.
Glasgow Airport
Glasgow Airport could be a major destination for the ES 30, as it could be a key airport for flying between the UK and the island of Ireland.
As with Liverpool Airport it needs a better connection to the rail network.
If Glasgow Airport is successful running zero-carbon aircraft to Ireland, this could change all previous thinking on a Glasgow Airport Rail Link.
Ronaldsway Airport
Geography and electric airliners could be very kind to Ronaldsway Airport and the Isle of Man.
- Electric airliners can easily reach much of the island of Ireland and the UK mainland between Glasgow and Birmingham, from Ronaldsway Airport with ease.
- The Isle of Man will in a couple of years be surrounded by wind farms.
- With other developments on the island, it could sell itself to the UK and Ireland, as a green holiday destination.
But what would the motorcycle enthusiasts say?
Anglesey Airport
I believe that Anglesey Airport could be brought to life in a big way by electric aircraft like the ES-30 or the Eviation Alice.
These are flight distances from Anglesey Airport.
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Cork – 192 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Anglesey – Ronaldsway – 58 miles
- Anglesey – Shannon – 186 miles
- Anglesey – Waterford – 130 miles
All of these except for Cork, Derry, Shannon and Waterford would be possible in the basic ES-30.
This Google Map shows the airport, which is also labelled as RAF Valley.
Note that the North Wales Coast Line passes the site on the North-East side.
At present, Avanti West Coast trains take nearly four hours between London and Holyhead.
But later this year, new bi-mode Class 805 trains will replace, the current diesel only Class 221 trains.
- The current diesel only trains take two hours and five minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- The current diesel only trains take one hour and forty-three minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
- The fastest electric trains take one hour and twenty-nine minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
- High Speed Two trains will take 56 minutes between Crewe and London Euston.
When you consider that a lot of the North Wales Coast Line, is straight and flat, I can see the following times being possible, with some improvement and smart electrification between Crewe and Holyhead and a smaller number of stops.
- Crewe and Anglesey Airport – One hour and twenty minutes
- London Euston and Anglesey Airport – Two hours and fifty minutes
With High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains, the London Euston and Anglesey Airport time could be below two hours and thirty minutes.
I believe that with a well-designed terminal at Anglesey Airport, this could be the fastest zero-carbon way between London and Ireland.
Haverfordwest Airport
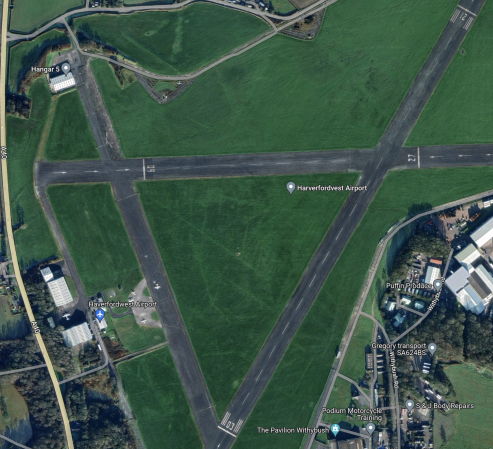
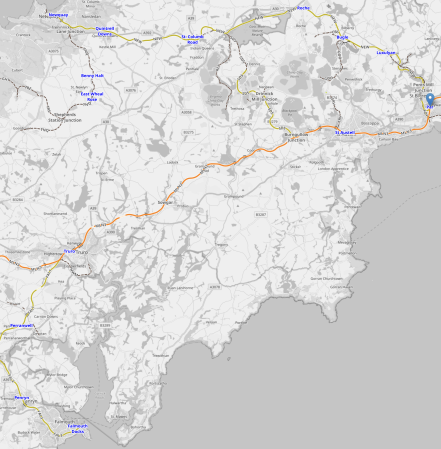
This Google Map shows the location of Haverfordwest Airport in the East of Pembrokeshire.
This second Google Map shows a close-up of the airport.
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the airport and the nearest railway station.
Note.
- Haverfordwest Airport is at the top of the map.
- Haverfordwest station is at the bottom of the map.
- There are rail connections to Cardiff, Fishguard, Milford Haven, Pembroke Dock and Swansea from the the station.
- Rail passengers for London would change at Swansea.
The road looks good between the airport and the station, so would an electric bus to handle transfers be ideal?
Consider.
- I have flown myself into Haverfordwest Airport and there were no navigation or operational problems that I can remember.
- With all the wind farm development planned for the coast of Pembrokeshire and the Celtic Sea, I feel that an airport in the area with regular flights to London and perhaps Waterford in Ireland could be essential.
- London City and Haverfordwest airports are 167 miles apart
- Waterford and Haverfordwest airports are 94 miles apart
- Quiet electric aircraft may ease any planning problems.
- Will a helicopter base be needed for serving wind farms in the Celtic Sea?
I believe, Haverfordwest Airport could be converted into a high-class airport for the Eastern tip of South Wales.
Haverfordwest Airport could also attract other services, given that the Welsh Government have a policy of not building new roads.
I have a feeling that quiet electric airliners will lead to the development of airports like Haverfordwest as feeder airports for the Heathrows and Schipols of this world.
Waterford Airport
Waterford Airport has recently been expanded and it appears from the Wikipedia entry, they are expecting more tourists.
This Google Map shows the position of the airport and the railway station in Waterford.
Note.
- The red arrow at the top of the map indicates Waterford station on the Northern side of the city.
- The airport is indicated by the blue dot in the South-East corner of the map.
- The airport is about ten kilometres from the City Centre.
In the past, Waterford has been quite a busy airport, but Covid-19 seems to have killed most of the traffic.
So could a zero-carbon service between Waterford and Haverfordwest be profitable?
- Those working with the wind energy in the Celtic Sea might find route useful.
- It would give a low-carbon route between Waterford and South Wales, which some might like.
- I also believe that the novelty of flying in an electric plane would attract passengers.
Waterford and Haverfordwest might be one of those routes, where electric planes might be worth trying.
This Google Map shows the Celtic Sea.
Note.
- Waterford Airport is indicated in red on the South-East corner of Ireland.
- Haverfordwest Airport is on the South-Western tip of Wales.
- Newquay Airport is in the South-East corner of the map on the North coast of Cornwall.
There could be as much as 50 GW of floating wind farms installed in this area.
I feel that there could be a case for a triangular Haverfordwest, Newquay and Waterford service.
Newquay Airport
Newquay Airport has been in the news recently because of the antics of Richard Branson and Virgin Orbit.
This Google Map shows the airport in relation to the town.
Note.
- The airport is in the North-East corner and boasts a long runway.
- The airport serves well over a dozen destinations.
- The town of Newquay is in the South-West corner of the map.
- Newquay station is by the sea.
All of these places would be suitable destinations for electric aircraft.
- Birmingham
- Brest
- Cardiff
- Cork
- Deauville
- Dinard
- Dublin
- Guernsey
- Heathrow
- Jersey
- Nantes
- Orly
- Rouen
- Scillies
- Waterford
Newquay Airport could get very busy with electric aircraft supporting tourism and the developing wind power industry.
This second Google Map shows the town centre and station.
Surely, having the station by Great Western Beach is good marketing.
In The Proposed Mid-Cornwall Metro, I talked about a plan to run an hourly Metro service between Newquay and Falmouth.
This article on Rail Technology Magazine is dated January 2023 and entitled Mid Cornwall Metro Secures £50m In Levelling Up Funding, where these are the first two paragraphs.
Following yesterday’s major Levelling Up funding announcement, the government has pledged an almost £50m grant to improve the railways linking Newquay, St Austell, Truro and Falmouth in Cornwall.
This financial aid to improve Cornwall Rail links represents the only successful bid out of four that were submitted to the Levelling up funding. The improvement scheme will be helmed by a partnership with Great Western Railway and Network Rail.
Note.
- I believe this means the Mid-Cornwall Metro will be built.
- Especially as looks like it will cost less than £100 million.
- As this Metro will serve Newquay, it shouldn’t be too difficult to link the plane with the train, with perhaps a zero-carbon bus.
- The Metro would then link Newquay Airport to the main population centres of Newquay, St Austell, Truro and Falmouth.
- If the Metro could be run using zero-carbon trains, that would surely put the icing on the cake!
The map from OpenRailwayMap shows the route.
Note.
- Newquay is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Trains spend around 6-7 minutes waiting at Newquay.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner marks Par station, where a chord will be reinstated to allow trains to go between Newquay and St. Austell.
- Par is the nearest station to the Eden Centre.
- Newquay and Par is 20.6 miles.
- The route, then goes along the Cornish Main Line, through St. Austell and then on to Truro.
- Par and Truro is 18.9 miles.
- At Truro the Metro would take the Falmouth branch.
- Falmouth and Truro is 11.8 miles.
- Trains spend around 7-8 minutes waiting at Falmouth Docks
- The total route is just over fifty miles, which probably means that battery-electric trains could work the route with charging at each end, whilst the train is turned round.
This airport and metro combination could give a big-boost to zero-carbon tourism.
Inverness Airport
Inverness Airport has recently been expanded with a station on the Inverness and Aberdeen Line.
Consider.
- Electric aircraft like the ES-30 will be able to reach both Kirkwall on Orkney and Sumburgh on Shetland from both Inverness and Aberdeen Airports.
- Sumburgh would need an extended range ES-30.
- Flights would be a few miles shorter from Inverness than from Aberdeen.
- Kirkwall and Sumburgh is only 85 miles, so there may be possibilities for serving both Orkney and Shetland with one flight.
- Extended range ES-30s might be able to do return trips to Kirkwall without a major charge at Kirkwall.
- I once flew in my Cessna-340 to Kirkwall to see the original turbine, that was placed on the island. There is a lot of cold forbidding sea in the area. Perhaps the slightly shorter trip from Inverness, might be better for everybody’s nerves?
- Just as the oil and gas industry did in the last century, I can see the offshore wind power industry generating a lot of passenger traffic to the Orkney and Shetland Islands.
Both Inverness and Aberdeen can be reached from Stansted by an ES-30 carrying a reduced passenger load.
Birmingham Airport
Birmingham Airport could become a major base for electric aircraft.
The 247 mile range of the extended range ES-30 would allow it to be able to reach the following places.
- Belfast
- Dublin
- Newcastle
- Newquay
- Ronaldsway
Reduce the passenger load slightly to 25 passengers and the plane would be able to reach.
- Edinburgh
- Glasgow
- Inverness
- Kirkwall
- Wick
But Birmingham Airport is only 65 minutes from Euston and will in the future be served by High Speed Two, in under an hour.
The airport also has a large catchment area of its own, who might be tempted to choose flying zero-carbon.
Spokes From Speke
In the 1980s, I went to a presentation from Royal Mail in Ipswich about guaranteed next day delivery of parcels. It was important to me, as I was writing software that needed to get from Ipswich, where it was created to London, where it would be tested and installed on customers machines. We also needed to get copies to our customers in Edinburgh and Aberdeen.
The Royal Mail’s latest concept of Spokes From Speke was described.
- All urgent parcels and First Class mail would be collected from the local sorting office and taken to the local airport, which in our case would probably have been Stansted.
- These consignments would then be flown to Speke Airport as Liverpool Airport was known in those days at around midnight.
- They would then be sorted and reloaded onto other planes to complete their journey.
- The planes would then return home and the parcels and mail would be delivered by truck to the local sorting office.
Aircraft used included Short Skyvans and piston-engined twins. Some we’re the quietest of aircraft.
I have heard or read somewhere that in some airports, there were complaints about noisy aircraft flying in and out in the middle of the night.
Now fifty years on companies are looking to speed up deliveries.
- In the UK, companies are experimenting with 100 mph overnight parcels trains.
- This article on Railway Gazette is entitled Varamis Rail Launches Regular Express Light Freight Service.
- Eversholt Rail are putting money behind converting redundant electric multiple units into parcel trains.
But DHL in the USA are going another way and have ordered twelve Alice aircraft from Eviation.
It looks like the cargo Alice could have a useful load of just over a tonne and a range of around 290 miles.
I can envisage flights of near-silent silent Alices sneaking into and out of airports in the middle of the night to deliver and collect urgent parcels.
Techniques like Spokes From Speke will come again, but this time with electric aircraft.
How Would The ES-30 Compare With An Eviation Alice?
The Wikipedia entry for the Eviation Alice gives these figures.
- Passengers – 9
- Maximum Speed – 300 mph
- Range – 290 miles
- Take-off distance – 840 metres
- Landing distance – 620 metres
Note.
- These are figures that most pilots would expect from an aircraft of this size.
- My Cessna 340 was about the same and about eight percent slower.
- It also had a much longer range.
If you look at my list of flights, these will not be possible.
- Birmingham – Inverness – 363 miles
- Birmingham – Kirkwall – 451 miles
- Birmingham – Schipol – 402 miles
- Bimingham – Sumburgh – 513 miles
Birmingham – Wick – 418 miles - Edinburgh – Schipol – 473 miles
- Gatwick – Edinburgh – 356 miles
- Gatwick – Schipol – 374 miles
- Glasgow – Sumburgh – 300 miles
- Humberside – Schipol – 333 miles
- Leeds – Schipol – 386 miles
- Manchester – Schipol 413 miles
- Newcastle – Newquay – 346 miles
- Newcastle – Schipol – 395 miles
- Newquay – Orly – 351 miles
- Stansted – Wick – 472 miles
- Sumburgh – Bergen – 226 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Note.
- Most routes that are too long are to Schipol or Scotland.
- Anglesey appears to have Ireland extremely well covered.
- Birmingham, Glasgow and Liverpool keep their Irish routes.
- Newquay is still a hub, that would promote tourism in Cornwall and only loses the Orly connection, although it keeps the flight to Heathrow.
- Ronaldsway still looks to be a possible zero-carbon airport.
I would suggest that a range of 290 miles, is an ideal one for an electric aircraft in the UK, as it can handle a large number of routes.
These are routes that I feel would attract a large number of passengers.
- Anglesey – Belfast – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Belfast City – 109 miles
- Anglesey – Derry – 163 miles
- Anglesey – Dublin – 71 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast – 106 miles
- Glasgow – Belfast City – 103 miles
- Glasgow – Derry – 121 miles
- Heathrow – Newquay – 212 miles
- Inverness – Kirkwall – 106 miles
- Inverness – Sumburgh – 190 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast – 153 miles
- Liverpool – Belfast City – 151 miles
- Liverpool – Dublin – 140 miles
- Liverpool – Norwich – 180 miles
- Liverpool – Ronaldsway – 89 miles
- London City – Humberside – 145 miles
- London City – Manchester – 161 miles
- Newcastle – Cardiff – 230 miles
- Newcastle – Belfast City – 168 miles
- Newquay – Brest – 140 miles
- Newquay – Cardiff 98 miles
- Newquay – Cork – 180 miles
- Newquay – Deauville – 241 miles
- Newquay – Scillies – 68 miles
- Newquay – Waterford – 150 miles
- Norwich – Schipol – 277 miles
- Ronaldsway – Belfast City – 62 miles
- Ronaldsway – Dublin – 80 miles
- Ronaldsway – Glasgow – 123 miles
- Southend – Schipol – 180 miles
- Sumburgh – Kirkwall – 85 miles
Alice may not be big enough for some routes.
But it will be a wonderful route-proving aircraft for the larger ES-30 and other zero-carbon aircraft.
Conclusion
There will be a lot of uses for battery-electric aircraft in the UK.