New Baltic Sea Interconnector On Horizon As Lithuania, Latvia, and Germany Plan Cross-Border Link
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Lithuania, Latvia, and Germany are planning a joint offshore interconnector that would enable electricity trading between the Baltic countries and Germany and allow for the integration of up to 2 GW of offshore wind capacity in Lithuania and Latvia
These first two paragraphs add more detail to the article.
The energy ministers of the three countries signed a joint declaration of intent on 18 February, paving the way for the development of the Baltic-German PowerLink interconnector, which would, in addition to electricity trading and offshore wind capacity integration, also enable the expansion of onshore renewable energy capacity.
The Lithuanian, Latvian, and German transmission system operators (TSOs) – Litgrid, Augstsprieguma tīkls and 50Hertz – agreed to assess the feasibility of the hybrid electricity interconnection.
As Germany, has the following connections under development in the West.
- AquaVentus to Aberdeen, Humberside, Denmark, Norway and The Netherlands.
- NeuConnect to the Isle of Grain In England.
- GriffinLink, which is an offshore link to England.
The Germans seem to be putting themselves at the centre of an energy distribution system, that has the capability to stabilise European and UK electricity for thousands of years. Especially, if the network grows to include more countries.
This paragraph says this about the Baltic-German PowerLink project.
The Baltic-German PowerLink project concept developed by Litgrid, Augstsprieguma tīkls, and 50Hertz includes a 2 GW, approximately 600 kilometres long hybrid offshore connection, with the connection point in the Baltic States planned to be on the border between Lithuania and Latvia. The exact location is to be determined after technical studies.
Note.
- The interconnectors may be long, but they are not longer than anything built successfully before in European waters.
- The UK and the Island of Ireland are well-linked.
- There would appear to be no need for challenging projects like the Morocco-UK Power Project
I suspect that Germany will get the energy it needs and the British Isles will get a nice little earner.
If Europe is generating large amounts of wind and solar energy with its variable output it will need lots of energy storage.
What Countries Have The Terrain For Pumped Storage Hydro In Europe?
I asked Google AI and received this answer.
Key countries with ideal, high-elevation terrain and significant existing or planned capacity include:
Alpine Region (The Heart of European Pumped Storage):
Switzerland: Extremely high capacity due to steep, mountainous landscapes and significant water sources, hosting the world’s oldest working pumped storage plant.
Austria: Heavily mountainous, it is a major player in PSH expansion and modernization.
France: Home to one of Europe’s largest, the Grand Maison hydroelectric power station.
Italy: Holds high capacity with numerous planned projects.
Germany: Strong existing infrastructure.
Southern Europe:
Spain: Features some of Europe’s largest plants (e.g., La Muela/Cortes-La Muela).
Portugal: Significant recent investment in large-scale projects like the Tâmega complex.
Other Potential Areas:
Norway: High potential due to its mountainous, water-rich terrain.
United Kingdom: High project volume currently under construction.
Balkans & Central Europe:
Countries like Bulgaria, Romania, and the Czech Republic have suitable terrain for further development.
These countries benefit from significant hydraulic head (steep drop) and natural or artificial reservoir potential, making them ideal for storing energy for peak consumption hours.
Note.
- As expected, the Alpine region is Top of the League.
- The UK is holding its own despite its small mountains.
- There is a lot of potential to be developed.
But then Electric Mountain in Snowdonia is certainly at the top table of pumped storage systems despite being built in the 1980s.
What Countries Have The Terrain For Hydrogen Storage In Europe?
I asked Google AI and received this answer.
Key European countries with suitable geological terrain—specifically salt caverns and depleted gas fields—for large-scale, underground hydrogen storage include Germany, the Netherlands, Denmark, the United Kingdom, and France. Other significant regions for storage potential include Spain, Hungary, and Austria, which are developing porous storage facilities.
Key Regions & Terrain Types:
Salt Caverns (North-Western Europe): Germany, the Netherlands, Denmark, France, and the UK have substantial salt deposits suitable for creating caverns, identified as cost-efficient for large-scale storage.
Depleted Gas Fields (Porous Rock): The Netherlands, Germany, and parts of Central/Southern Europe (Spain, Hungary) have significant capacity in existing porous storage, particularly in the North Sea region.
Specific Projects: Germany (Uniper’s Krummhörn project), Netherlands (HyStock), and France (HYPSTER at Etrez) are active, with Spain and Denmark emerging as major hydrogen hubs.
Capacity Potential: The Netherlands, for instance, holds massive potential (35-60 TWh) due to its offshore and onshore depleted fields.
Salt cavern projects, which offer high-deliverability storage, are heavily concentrated in the North-Western European industrial corridor.
I was lucky enough have a tour of ICI’s salt mine in Cheshire, when I worked there in the 1960s and I remember these facts from those days.
- There was enough salt in the ground under Cheshire to last several thousand years.
- Most salt was extracted from boreholes, for making chlorine using electrolysis and the Castner-Kellner process.
- Hydrogen was a by-product and much of it was mixed with coal gas to raise steam for the works.
The same technique used to make boreholes to extract the salt, is used to hollow caverns in the salt to store gases like hydrogen.
Once, when they were digging salt out of the salt mine at Winsford, a worker broke into an unmarked borehole and ICI nearly lost the mine because of the water rushing in.
Two stories stand out from the rescue of the mine.
- There was a need for dry clothes for all the workers, so ICI took a truck to Marks & Spencer in Northwich and emptied it of anything they might need. I was told the story enriched with plagues of locusts.
- A Ford Transit was found to have travelled a few thousand miles underground in axle deep salt slurry. Rather, than scrap it and buy another, it was offered back to Ford, who were delighted to swap it for a new one. I heard that Ford said, that the accelerated corrosion research would have taken many years, if done on the roads.
Always think out of the box.
£1.5 billion Enables UK-US Pair To Get Their Hands On Europe’s Giant LNG Terminal
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Offshore Energy.
This is the sub-heading.
UK-based energy player Centrica and U.S. investment firm Energy Capital Partners (ECP), part of Bridgeport Group, have brought into their fold a liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminal in Kent County, United Kingdom.
This paragraph gives Centrica’s view of the Grain LNG Terminal.
The UK firm portrays the terminal as Europe’s largest LNG regasification facility, with a capacity of 15 million tonnes of LNG a year. Located on the UK’s Isle of Grain, the terminal features unloading infrastructure, regasification equipment, and truck-loading facilities.
In a press release, which is entitled Investment in Grain LNG, that was published in August 2025, Centrica said this.
Opportunities for efficiencies to create additional near-term value, and future development options including a combined heat and power plant, bunkering, hydrogen and ammonia.
The tone of the article in Offshore Energy and the press release is unmistakable. – Centrica intend to make good use of their investment.
I suggest you read both documents fully.
- Europe’s largest LNG regasification facility, with a capacity of 15 million tonnes of LNG a year, will certainly need a large combined heat and power plant.
- Will any spare power from the CHP plant, be sent to Germany, through the 1.4 GW NeuConnect interconnector, which should be commissioned by 2028?
- Hydrogen, ammonia and LNG are the three low-carbon fuels used by modern ships, so I suspect hydrogen and ammonia will be produced on the island.
- Centrica are investors in the efficient hydrogen-generation process ; HiiROC.
- Hydrogen and nitrogen are the two feedstocks for ammonia.
Centrica certainly have big plans for the Grain LNG Terminal.
I shall be following Centrica closely.
Investment in Grain LNG
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This sub-heading outlines the deal.
Centrica plc (the “Company”, “Centrica”) is pleased to announce the acquisition of the Isle of Grain liquified natural gas terminal (“Grain LNG”) in partnership1 with Energy Capital Partners LLP (“ECP”) from National Grid group (“National Grid”) for an enterprise value of £1.5 billion. After taking into account approximately £1.1 billion of new non-recourse project finance debt, Centrica’s 50% share of the equity investment is approximately £200 million.
The press release lists these key points.
- Grain LNG delivers vital energy security for the UK, providing critical LNG import/export, regasification and rapid response gas storage capacity to balance the energy system.
- Aligned with Centrica’s strategy of investing in regulated and contracted assets supporting the energy transition, delivering predictable long-term, inflation-linked cash flows, with 100% of capacity contracted until 2029, >70% until 2038 and >50% until 2045.
- Opportunities for efficiencies to create additional near-term value, and future development options including a combined heat and power plant, bunkering, hydrogen and ammonia.
- Highly efficient funding structure, with Centrica’s equity investment of approximately £200 million alongside non-recourse project financing.
- Strong life of asset returns aligned with Centrica’s financial framework, with an expected unlevered IRR2 of around 9% and an equity IRR2 of around 14%+
Underpins delivery of £1.6 billion end-2028 EBITDA target3 – Centrica’s share of EBITDA expected to be approximately £100 million per annum and cash distributions expected to be around £20 million on average per annum for 2026-2028, representing an attractive yield on Centrica’s equity investment - Partnership with ECP (part of Bridgepoint Group plc), one of the largest private owners of natural gas generation and infrastructure assets in the U.S. with direct experience in supporting grid reliability.
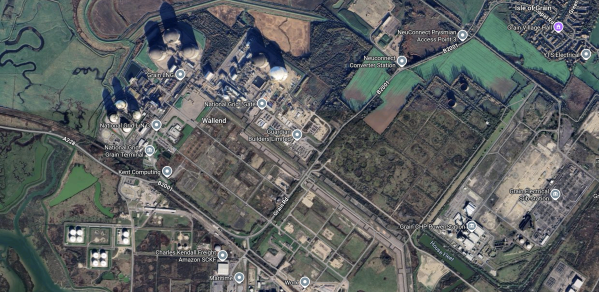
This Google Map shows the various energy assets on the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- It appears that works for the 1, 400 MW NeuConnect interconnector to Wilhelmshaven in Germany, are taking place in the North-East corner of the map.
- Grain CHP powerstation is a 1,275MW CCGT power station, which is owned by German company; Uniper, that is in the South-East corner of the map, which can also supply up to 340MW of heat energy recovered from the steam condensation to run the vapourisers in the nearby liquefied natural gas terminal.
- The Grain LNG terminal is at the Western side of the map.
- In the Thames Estuary to the East of the Isle of Grain, I estimate that there are about 1,500 MW of wind turbines.
I find it interesting that two of the assets are German owned.
I have some thoughts.
It Is A Large Site With Space For Expansion
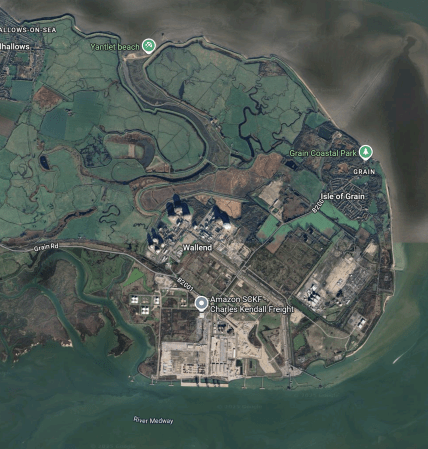
This Google Map shows the whole of the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- The Grain LNG terminal is around the label Wallend.
- The River Medway runs East-West at the bottom of the map.
- Gas tankers deliver and take on gas at jetties on the North Bank of the Medway.
There could be space to expand the terminal, if the RSPB would allow it.
As an example, I asked Google AI, if peregrine falcons nest on chemical plants and got this reply.
Yes, peregrine falcons do nest on chemical plants. They have adapted to using various urban and industrial structures, including chemical plants, for nesting. This is particularly true in areas where natural cliff habitats are scarce.
Peregrine falcons are known for their adaptability, and their population has seen a resurgence in recent decades, partly due to their ability to utilize man-made structures. These structures often mimic their natural cliffside nesting
Cliffs do seem scarce on the Isle of Grain. I also asked Google AI, if peregrine falcons ate small rodents, as several chemical and other plants, where I’ve worked, had a rodent problem. One plant had a cat problem, as there had been so many rats. This was the reply.
Yes, peregrine falcons do eat small rodents, though they primarily consume birds. While their diet mainly consists of other birds like pigeons, doves, and waterfowl, they will also hunt and eat small mammals, including rodents such as mice, rats, and voles. They are opportunistic hunters and will take advantage of readily available prey, including insects, amphibians, and even fish.
I’m sure if Centrica wanted to expand, they’d employ the best experts.
Who Are ECP?
One of the key points of the press release is that this deal is a partnership with ECP (part of Bridgepoint Group plc), one of the largest private owners of natural gas generation and infrastructure assets in the U.S. with direct experience in supporting grid reliability.
The Wikipedia entry for ECP or Energy Capital Partners has this first section.
Energy Capital Partners Management, LP (ECP) is an American investment firm headquartered in Summit, New Jersey. It focuses on investments in the energy sector. The firm has additional offices in New York City, Houston, San Diego, Fort Lauderdale and Seoul.
In August 2024, ECP merged with Bridgepoint Group to form a private assets investment platform.
The Wikipedia entry for the Bridgepoint Group has this first paragraph.
Bridgepoint Group plc is a British private investment company listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
The company had started as part of NatWest.
Are The Germans Going To Take Away Some Of Our Electricity?
Consider.
- Germany has a big need to replace Russian gas and indigenous coal, and to decarbonise.
- Neuconnect is a 1.4 GW interconnector between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven in Germany. It is scheduled to be completed in 2028.
- The Grain CHP powerstation is a 1,275MW CCGT power station, which is owned by German company; Uniper, could almost keep NeuConnect working at full power on its own.
- I said earlier, in the Thames Estuary to the East of the Isle of Grain, I estimate that there are about 1,500 MW of wind turbines. One of which is part German-owned.
The Germans are also building a large electrolyser at Wilhelshaven, which is described by Google AI like this.
The Wilhelmshaven Green Energy Hub will initially feature a 500MW electrolyzer, with plans to potentially expand to 1GW, according to Energy Monitor. The hub, a joint project between Tree Energy Solutions (TES) and EWE, aims to produce green hydrogen using renewable energy sources like offshore wind. The 500MW electrolyzer is scheduled to be operational by 2028.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see that the Wilhelmshaven electrolyser were to be powered by British-generated electricity flowing down NeuConnect.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include A Combined Heat And Power Plant
This objective was set in one of the key points.
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Grain LNG Terminal.
Grain LNG Terminal is a Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) terminal on the Isle of Grain, 37 miles (60 km) east of London. It has facilities for the offloading and reloading of LNG from ships at two jetties on the River Medway; for storing and blending LNG; for truck loading; and regasifying and blending natural gas to meet UK specifications. The terminal can handle up to 15 million tonnes per annum of LNG, has a storage capacity for one million cubic metres of LNG, and is able to regasify up to 645 GWh per day (58 million cubic metres per day) for delivery into the high pressure gas National Transmission System (NTS). The facility is owned and operated by National Grid Grain LNG Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of National Grid.
Note.
- This paragraph was written before the Centrica takeover.
- The terminal also converts liquid natural gas into gas to be distributed around the UK.
The heat needed to convert the liquid natural gas to gas is provided by the Grain CHP power station.
- Currently 340 MW of heat is provided.
- If the Grain LNG terminal is expanded, it will probably need more heat.
I can see Centrica building a combined heat and power (CHP) power station, that can be expanded to meet the current and future needs of gasification at the Grain LNG terminal.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see the CHP power station fitted with carbon capture, as Kent is surely one county, where carbon dioxide can be used in food production, so we can generate our carbon dioxide and eat it.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Hydrogen
This objective was set in one of the key points.
Consider.
- Centrica are an investor in HiiROC, who have a unique method of generating affordable zero-carbon hydrogen called thermal plasma electrolysis, which uses a fifth of the electricity, that traditional electrolysis does.
- HiiROC can use natural gas as a feedstock. Centrica won’t be short of that at Grain.
- There is space to build a large HiiROC system at the Isle of Grain site.
- The hydrogen could be taken away by tanker ships.
Like the electricity , which will use the 450 mile NeuConnect interconnector, the hydrogen could even be exported to Wilhelmshaven in Germany by pipeline.
Wilhelmshaven is being setup to be a major German hub to both generate, import and distribute hydrogen.
I asked Google AI, how much hydrogen a GWh would produce and received this answer.
A GWh of electricity can produce approximately 20-22 tonnes of hydrogen through electrolysis, depending on the efficiency of the electrolyzer. Modern commercial electrolyzers operate at an efficiency of roughly 70-80%, meaning they require about 50-55 kWh of electricity to produce 1 kg of hydrogen. A GWh (1 gigawatt-hour) is equal to 1,000,000 kWh, and 1 tonne of hydrogen contains roughly 33.33 MWh of energy.
As it is claimed on the web that HiiROC is five times more efficient than traditional electrolysis, it could need around 10-11 kWh to produce one kg. of hydrogen.
1 GWh would produce between 90-100 tonnes of hydrogen.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Ammonia
This objective was set in one of the key points.
I asked Google AI if ammonia can be produced from hydrogen and received this answer.
Yes, ammonia (NH3) can be produced from hydrogen (H2) through a process called the Haber-Bosch process. This process involves combining hydrogen with nitrogen (N2) from the air, under high temperature and pressure, in the presence of a catalyst.
Ammonia has a large number of uses, including making fertiliser and the powering of large ships.
I asked Google AI, if there are small Haber-Bosch processes to make ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen and received this answer.
Yes, there are efforts to develop smaller-scale Haber-Bosch processes for ammonia production. While the traditional Haber-Bosch process is typically associated with large industrial plants, research and development are exploring ways to adapt it for smaller, distributed production, particularly for localized fertilizer or fuel applications.
I wondered if Centrica are involved in the efforts to develop smaller-scale Haber-Bosch processes for ammonia production.
Google AI gave me this quick answer.
Centrica is involved in research related to the Haber-Bosch process, particularly in the context of transitioning to a low-carbon energy future. They are exploring how to adapt the Haber-Bosch process, which is crucial for fertilizer production but also a significant source of CO2 emissions, to utilize renewable energy sources. This includes investigating the use of green hydrogen produced from water electrolysis and renewable electricity. Centrica is also involved in research related to using ammonia as a fuel, including potentially for power generation
That looks to be a very positive answer. Especially, as local low-carbon fertiliser production could be a very powerful concept.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Bunkering
This objective was set in one of the key points.
Bunkering is the process of refuelling ships.
I didn’t know much about bunkering, when I started to read Centrica’s press release, but the Wikipedia entry, was a good way to get some information.
This section in the Wikipedia entry is entitled Two Types Of Bunkering, where this is said.
The two most common types of bunkering procedure at sea are “ship to ship bunkering” (STSB), in which one ship acts as a terminal, while the other moors. The second type is “stern line bunkering” (SLB), which is the easiest method of transferring oil but can be risky during bad weather.
Over the years, I have found, that two zero-carbon fuels are under development, for powering ships; hydrogen and ammonia. Others are developing ships powered by naturalo gas.
I asked Google AI if hydrogen can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, hydrogen can power ships. It can be used as a fuel for fuel cells, which generate electricity to power the ship’s propulsion and other systems, or it can be burned in modified combustion engines. Hydrogen offers a zero-emission solution for shipping, with water vapor being the only byproduct when used in fuel cells.
Google AI also told me this.
The world’s first hydrogen-powered cruise ship, the “Viking Libra”, is currently under construction and is scheduled for delivery in late 2026. This innovative vessel, a collaboration between Viking Cruises and Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri, will utilize hydrogen for both propulsion and electricity generation, aiming for zero-emission operation.
I also asked Google AI if ammonia can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, ammonia can be used to power ships and is considered a promising alternative fuel for the maritime industry. Several companies and organizations are actively developing ammonia-powered ship designs and technologies. While challenges remain, particularly around safety and infrastructure, ammonia is seen as a key potential fuel for decarbonizing shipping.
Finally, I asked I asked Google AI if natural gas can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, ships can be powered by natural gas, specifically in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG). LNG is increasingly used as a marine fuel, offering environmental benefits over traditional fuels like diesel.
It would seem to be a case of you pays your money and makes a choice between one of four technologies; ammonia, hydrogen fuel-cell, hydrogen-ICE and LNG.
I looks to me, that if Centrica provide bunkering services for ships, they have the means to cover most of the market by providing hydrogen and ammonia, in addition to natural gas.
Although, I don’t know much about bunkering, I do feel that the two current methods, that work for oil, could be made to work for these fuels.
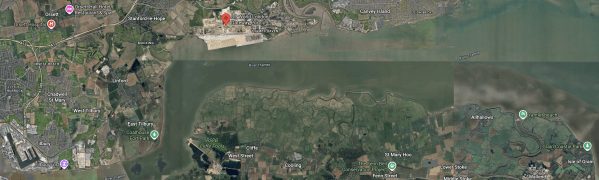
This Google Map shows the Thames Estuary.
Note.
- The Port of Tilbury is in the South-West corner of the map.
- London Gateway is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Isle of Grain is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Other ports between Tilbury and the Isle of Grain include Barking, Dagenham, Dartford, Erith, Greenwich, Northfleet, Purfleet, Silvertown and Thurrock.
There was never a more true phrase than – “Location, Location and Location”. And the Isle of Grain would appear to be in the right place to send out a bunkering tanker to a passing ship, that was calling at a port in London or just passing through the Strait of Dover.
This Google Map shows the Thames between London Gateway and the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- London Gateway is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Isle of Grain is in the South-East corner of the map.
It seems to me, that a refuelling philosophy could easily be worked out.
How Large is The Bunkering Market?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The world bunker fuel market is a multi-billion dollar industry, with the market size valued at USD 150.93 billion in 2023. It is projected to reach USD 242.29 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% according to SkyQuest Technology. In terms of volume, the global bunker demand was estimated at 233.1 million metric tons in 2023 according to the IMO.
The market is not small!
Ministers Will Relax Rules To Build Small Nuclear Reactors
The title of this post is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Britain’s five nuclear power stations, which generate about 6GW in total, powering 13 million homes, are all nearing the end of their lives
These first three paragraphs indicate the reasons why, the government wants to relax the rules.
Ministers are preparing to relax planning rules to make it easier to build mini nuclear power plants in more parts of the country in order to hit green energy targets and boost the industry.
They are also examining whether it is possible to streamline the process for approving the safety of new nuclear power plants as a way to reduce construction delays.
At present rules state that only the government may designate sites for potential nuclear power stations, of which there are eight, severely limiting where they can be built.
The article includes a vote and surprisingly to me, the vote embedded in the article, shows 92 % in favour of relaxing the rules and only 8 % against.
I must admit these figures surprise me, as I’d have thought more would have been against.
Certain Words Frighten The Public
It is because nuclear is one of those words, that I felt that the vote in favour would have been much lower.
Regular readers of this blog will know, that in the 1960s,, I worked for ICI doing itinerant computing and instrumentation tasks, in my first job after leaving Liverpool University with a degree in Control Engineering.
I can now classify the experience as a superb apprenticeship, where I learned a lot that has been useful to me in later life.
For a time, I was working on nuclear magnefic resonance or NMR scans. ICI Mond Division in Runcorn had one of the best installations for analysing chemicals using this technique, which is described in this Wikipedia entry, which starts with these sentences.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz).
One day, the Senior Scientist, who ran the machine came in to work and announced that the property of nuclear magnetic resonance would be replacing X-rays, as the technology had just been used to give a three-dimensional image of something like the tail of a mouse.
Now fifty-five years later, many if not most of us have had MRi scans.
The Wikipedia entry for Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRi, explains, what happened to the dreaded N-word.
MRI was originally called NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging), but “nuclear” was dropped to avoid negative associations.
Perhaps, it would be easier to build nuclear power stations, if the level of science teaching in the UK was better.
The Three Paragraphs In Detail
Earlier, I copied three paragraphs from The Times, into this post.
I shall now look at each in detail.
Paragraph 1
Ministers are preparing to relax planning rules to make it easier to build mini nuclear power plants in more parts of the country in order to hit green energy targets and boost the industry.
I was in Suffolk, when the planning of Sizewell B was undertaken.
There appeared to be little strong opposition, but the general feeling was what there was from second home owners, who were worried that the value of their holiday home would decline.
Employment and commerce created by Sizewell B was certainly good for the area in lots of ways.
At the time, my late wife; C was practicing as a family barrister in chambers in Ipswich. She believed that the building of Sizewell B had had a good effect on the area, as it had injected work and money, which had created the finance to allow a couple to end a marriage, that had long since died. She stated a couple of times, that Sizewell B was good for her practice.
Paragraph 2
They are also examining whether it is possible to streamline the process for approving the safety of new nuclear power plants as a way to reduce construction delays.
My worry about streamlining the process for approving safety, is that we approve nuclear power stations so rarely, do we have the qualified personnel to replace elapsed time with people. I would suggest that we don’t.
But we could have.
- We have some excellent universities, where Nuclear Engineering can be studied.
- How many personnel leave the Royal Navy each year, who could be trained as nuclear safety inspectors?
- If say Rolls-Royce and/or Hitachi are building several small modular nuclear reactors a year in the UK, then nuclear engineering will become fashionable, as electronics was for my generation of engineers and it will attract the brightest students.
Perhaps an established university, with access to the needed skills should be funded to set up a Nuclear Safety Institute
Paragraph 3
At present rules state that only the government may designate sites for potential nuclear power stations, of which there are eight, severely limiting where they can be built.
I can envisage new small modular nuclear reactors being built in the UK, where there is a need for lots of electricity to support developments like.
- Offshore wind farms
- Data centres
- Green steelmaking
- Metal refining
- Hydrogen production.
Rolls-Royce have said that their small reactors will be around 470 MW, so I could imagine power stations of this size being placed on disused coal-fired power station sites to boost power in an area. I have already suggested building some on Drax in The Future Of Drax Power Station.
In some locations, the choice could be between a small modular nuclear reactor and some form of energy storage.
Powering Germany
But there is one controversial area, where we can take advantage.
- The Germans are very short of electricity because of their reliance on coal and Russian gas that needs to be replaced.
- The 1.4 GW NeuConnect interconnector is being built by European and Japanese money between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven.
- The AquaVentus hydrogen system could be extended to Humberside to link with UK hydrogen production and storage.
- A couple of small modular nuclear reactors could be built on Humberside to back up hydrogen production, when the wind isn’t blowing.
But Rolls-Royce and other companies have been putting small nuclear reactors close to the sea bed safely for decades, so why no design an offshore reactor that can be placed at a safe distance offshore?
We would need to solve the Putin and friends problem first, but I can see the UK exporting a lot of electricity and hydrogen produced by nuclear energy.
Iberdrola Preparing Two East Anglia Offshore Wind Projects For UK’s Sixth CfD Round
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
ScottishPower Renewables, Iberdrola’s company in the UK, is getting the East Anglia One North and East Anglia Two offshore wind projects ready for the upcoming auction round for Contracts for Difference (CfD).
These three paragraphs give more details.
This is according to project updates Iberdrola published as part of its financial results for 2023.
Iberdrola says “good progress is being made in the key engineering and design work” for the two projects and, while they were not presented in the UK’s fifth CfD Allocation Round (AR5), preparations are being made to take part in Allocation Round 6 (AR6).
The two offshore wind farms are part of the GBP 6.5 billion (around EUR 7.6 billion) East Anglia Hub project, which also includes East Anglia Three, currently in construction and expected to start delivering electricity in 2026. The 1.4 GW East Anglia Three was awarded Contract for Difference in July 2022.
It is now possible to build a table of Iberdrola’s East Anglian Hub.
- East Anglia One – 714 MW – Commissioned in 2020.
- East Anglia One North – 800 MW – To be commissioned in 2026.
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW – To be commissioned in 2026.
- East Anglia Three – 1372 MW – To be commissioned in 2026.
Note.
- East Anglia One is the largest windfarm in Iberdrola’s history
- These four wind farms are connected to the shore at Bawdsey on the River Deben.
These wind farms are a total of 3786 MW.
In addition there are RWE’s three Norfolk wind farms.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1386 MW – To be commissioned in 2027.
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW – To be commissioned before 2030.
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW – To be commissioned before 2030.
These wind farms are a total of 4146 MW, with a grand total of 7932 MW.
What Will Happen To The Electricity?
Consider.
- It is a lot of electricity.
- The good people of Norfolk are already protesting about the cables and pylons, that will connect the electricity to the National Grid.
- The good people of Suffolk will probably follow, their Northern neighbours.
- The wind farms are owned by Spanish company; Iberdrola and German company; RWE.
I wonder, if someone will build a giant electrolyser at a convenient place on the coast and export the hydrogen to Europe by pipeline or tanker.
- The ports of Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft could probably handle a gas tanker.
- The Bacton gas terminal has gas pipelines to Belgium and The Netherlands.
In addition, there are various electricity interconnectors in use or under construction, that could send electricity to Europe.
- National Grid’s Lion Link to the Netherlands.
- NeuConnect to Germany from the Isle of Grain.
Whoever is the UK’s Prime Minister in 2030 will reap the benefits of these East Anglian and Norfolk wind farms.
In addition.
- The Hornsea wind farm will have tripled in size from 2604 MW to 8000 MW.
- The Dogger Bank wind farm will have grown from 1235 MW to 8000 MW.
- There is 4200 MW of wind farms in Morecambe Bay and around England.
They would be so lucky.
Grain LNG Launches Market Consultation For Existing Capacity
The title of this post is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
This is the sub-heading.
Grain LNG, the largest liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminal in Europe, is pleased to announce the launch of a market consultation for the auction of 375 Gwh/d (approx. 9 mtpa) of existing capacity. The initial consultation phase for the Auction of Existing Capacity will commence on 14 June and run until 26 July.
These paragraphs detail what Grain LNG, which is a subsidiary of National Grid are offering.
GLNG has used the positive feedback received from the recent ‘Expression of Interest’ exercise and subsequent market engagement to offer three lots of capacity:
- Each lot will be entitled to 42 berthing slots, 200,000 m3 of storage and 125GWh/d (approx. 3 mtpa) of regasification capacity from as early as January 2029.
- This product is specifically designed for parties who wish to acquire a substantial stake in a major terminal in Northwest Europe, at a reduced cost and with shorter contract lengths when compared to new-build projects.
- As the terminal’s capacity already exists, parties involved will not be subjected to the FID approvals or potential delays that can arise from construction issues commonly associated with new build terminals.
Simon Culkin, Importation Terminal Manager at Grain LNG, said: “We are really pleased with the high level of interest shown by the market at a time of significant geo-political influence on our energy markets. It has allowed us to engage with potential customers and shape our offering to best meet their needs, whilst optimising access to this strategic asset. “
Reading the Wikipedia entry for the Grain LNG Terminal, it looks like it gets used as a handy store for natural gas.
About Phase 1 (2002–05), Wikipedia says this.
The new facilities enabled the Grain terminal to become a base supply to the NTS, with the ability to deliver gas continuously when required. The cost of the Phase 1 project was £130m. A 20-year contract with BP / Sonatrach enabled Grain LNG to import LNG on a long-term basis from July 2005.
About Phase 2 (2005–08), Wikipedia says this.
The development provided an additional five million tonnes of capacity per annum. All this capacity was contracted out from December 2010. Customers included BP, Iberdrola, Sonatrach, Centrica, E.ON and GDF Suez.
Under Current Facilities, Wikipedia says this.
Grain LNG Ltd does not own the LNG or the gas that it handles but charges for gasifying it. Current (2016) users include BP, Centrica (British Gas Trading), Iberdrola (Spain), Sonatrach (Algeria), Engie (France), and Uniper (Germany).
National Grid must be pleased that some customers seem loyal.
I feel that National Grid’s basic plan is to carry on with more of the same.
But will they develop more storage and other facilities on the site.
There are certainly other projects and interconnectors, that make the Isle of Grain and energy hub connecting the UK, Netherlands and Germany.
- In Did I See The UK’s Hydrogen-Powered Future In Hull Today?, I mentioned, that I thought that the Isle of Grain could be a location for an electrolyser and a hydrogen store.
- In EuroLink, Nautilus And Sea Link, I talk about new interconnectors, if which Nautilus might come to the Isle of Grain.
- In UK-German Energy Link Reaches Financial Close, I talk about NeuConnect, which will be an interconnector between the Isle of Grain ans Wilhelmshaven in Germany.
- The Isle of Grain is the landing point for the BritNed undersea power cable between The Netherlands and the UK.
I could also see National Grid building an East Coast interconnector to bring power from the wind farms off the East Coast of England to the Isle of Grain for distribution.
These are major wind farms South of the Humber.
- Dudgeon – 402 MW
- East Anglia 1 – 714 MW
- East Anglia 1 North – 800 MW
- East Anglia 2 – 900 MW
- Galloper – 504 MW – RWE
- Greater Gabbard – 504 MW
- Gunfleet Sands – 174 MW
- Hornsea 1 – 1218 MW
- Hornsea 2 – 1386 MW
- Hornsea 3 – 2852 MW
- Humber Gateway – 219 MW
- Lincs – 270 MW
- London Array – 630 MW
- Lynn and Inner Dowsing – 194 MW
- Race Bank – 580 MW
- Scroby Sands – 60 MW
- Sheringham Shoal – 317 MW
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW – RWE
- Dogger Bank A – 1235 MW
- Dogger Bank B – 1235 MW
- Dogger Bank C – 1218 MW
- Dogger Bank D – 1320 MW
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW RWE
- East Anglia 3 – 1372 MW
- Norfolk Boreas – 1396 MW
- Norfolk Vanguard – 1800 MW
- Outer Dowsing – 1500 MW
- North Falls – 504 MW – RWE
- Sheringham Shoal and Dudgeon Extensions – 719 MW
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW – RWE
Note.
- These figures give a total capacity of 28,333 MW.
- Five wind farms marked RWE are owned by that company.
- These five wind farms have a total capacity of 5618 MW.
- Will RWE export, their electricity to Germany through NeuConnect?
I can certainly see National Grid building one of the world’s largest electrolysers and some energy storage on the Isle of Grain, if an East Coast Interconnector is built.
Small Nuclear Power Plants To Replace Gas In Quest For Net Zero
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on The Times.
I was very much involved in the writing of project management software in the last three decades of the last century and if there’s one thing we’re generally good at in the UK, it’s complex project management.
Usually problems arise because of political or ignorant senior management meddling.
Our Energy Saviours
I believe our two energy saviours will be floating offshore wind and small nuclear reactors (SMRs) and both need good project management to be built successfully on production lines.
So I don’t see any reason, why we can’t build large numbers of floating offshore wind farms to supply our electricity.
They are also complimentary, in that the fleet of SMRs back up the wind.
Floating Wind First
Floating wind is likely to be developed at scale first, as certifying anything involving nuclear will take an inordinate time.
The electricity from floating wind farms will keep us going, but it is also starting to develop a nice line in exports.
This press release from Drax is entitled Britain Sending Europe Power Lifeline – Report, where this is the sub-title.
For the first time in over a decade, Britain became a net exporter of electricity to its European neighbours, making around £1.5bn for the economy in three months.
Note.
- The report was written by Imperial College.
- Two new interconnectors; Viking Link and NeuConnect between the UK and Europe are under construction.
- Several large wind farms are under construction and will be commissioned in 2023/24 and could add over 4 GW to UK electricity production.
Exports will only get better.
A Sprint For Wind
So we must have a sprint for wind, which will then provide the cash flow to allow the SMRs to roll in.
Or will that be too much for the ultra-greens, who would object to cash-flow from GWs of wind being used to fund SMRs?
National Grid’s North Sea Link Strengthens Electricity Supply And Repays Its Carbon Cost In Just Six Months
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These are three bullet points from the press release.
- World’s longest subsea electricity cable has been in operation since Oct 2021.
- 5.7 terawatt (TWh) hours of clean power have been shared between GB and Norway, strengthening security of supply for consumers in both countries.
- It has saved 800,000 tonnes of carbon in the first year, paying off its carbon cost after only six months of operation.
This must surely be considered a good start.
These two paragraphs describe the operation in the first year.
During its first year of operation, the link has imported 4.6 TWh of clean electricity – enough to power 1.5 million British homes for a year.
North Sea Link has also exported 1.1 TWh to Norway, demonstrating the vital role that interconnectors play in strengthening energy security and maximising the benefits of clean energy sources for consumers across the UK and Europe.
In The Monster In The Mountains That Could Save Europe’s Winter, I describe what makes the North Sea Link so important.
It gives the UK access to the Norwegian Bank Of Electricity or Ulla-Førre, which is a complex of five hydroelectric power stations and a massive lake in the Norwegian mountains to the East of Stavanger.
- The power stations have a total generating capacity of 2.1 GW.
- Lake Blåsjø is able to hold enough water to generate 7800 GWh of electricity.
- Ulla-Førre can also supply electricity to Germany, through the 1.4 GW NordLink.
If Ulla-Førre has a problem, it is that if Norwegian weather is dry, the filling of Lake Blåsjø could be difficult, which is where the interconnector comes into its own, as excess UK wind power or the 1,185 MW Hartlepool nuclear power station, can be used to send electricity to Norway for storage.
In An Update To Will We Run Out Of Power This Winter?, I predicted we will add the following capacity to our renewable generation in the next three years.
- 2023 – 2925 MW
- 3024 – 3726 MW
- 2025 – 6476 MW
This is a total of 13,127 MW.
As a Control Engineer, I can see the following happening.
- Several of the UK’s gas-fired power stations will be mothballed.
- Some of the UK’s gas-fired power stations will be fitted with advanced control systems so they can supply more precise amounts of electricity.
- Some UK electricity is stored in Ulla-Førre for onward sale to Germany.
- Some UK electricity is stored in Ulla-Førre for withdrawal back to the UK, when needed.
One of Ulla-Førre’s main tasks could be to ensure that no UK electricity is wasted.
Conclusion
With all these wind generated electricity and electricity transfers, the Crown Estate, National Grid and the Treasury should be coining it.
The Germans are already building the 1.4 GW NeuConnect between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven to import more electricity.
But I do believe that another interconnector will be needed.
Can We Move The Equilibrium Point Of The Energy Market?
Equilibrium In Systems
As a Control Engineer, I believe that most systems eventually end up in a state of equilibrium.
How many football batches have you watched between two evenly-matched teams that have ended, where the statistics are even and the match has ended in a nil-nil draw or a win by one goal.
Now suppose one manager makes an inspired substitution, one important player gets injured or one player gets sent off.
One team will have an advantage, the statistics will no longer be even and one team will probably win.
The equilibrium point will have been shifted.
Zopa’s Stable Peer-to-Peer Lending System
I used Zopa’s peer-to-peer lending system for several years and found it a very stable system, that over the years paid a steady return of between four and five percent before tax.
I even developed a method to maximise my savings income, which I wrote about in The Concept Of Hybrid Banking.
It was a sad day for me, when Zopa closed its ground-breaking peer-to-peer lending system.
As a Control Engineer, I believe that Zopa’s strength was a well-written computerised algorithm, that matched lenders and borrowers and spread the risk.
- There was no bias in the system, introduced by personal prejudices.
- The algorithm was agnostic and judged all borrowers on their profiles and credit ratings alone.
- Money was allocated under fair rules for borrowers.
- I never borrowed from Zopa, but from my experience of owning half of a finance company, their terms were the most customer-friendly I’ve ever seen.
Someone will go back to the basics of peer-to-peer lending and it can’t be soon enough for both savers and borrowers.
Zopa In Troubled Times
Over the years that I invested in Zopa, my returns stayed very much the same, as the algorithm seemed to be able to maintain sufficient difference between lenders’ returns and borrowers’ rates. I also suspect the dynamics of savvy lenders and borrowers helped to stabilise both the system and the difference between rates.
It even worked through the Banking Crisis of 2008 and other mini-hiccups along the way.
My Conclusion About Zopa
As someone, who knows computing well, I would rate Zopa, one of the best computer systems, I’ve ever seen.
But it showed how a large transactional system can work well.
One of the keys to its success and smooth operation was that the computer was totally in control and it took all transaction decisions without direct human intervention.
The Energy Market
The energy market is a network of energy providers and users.
It is controlled by complicated rules and it has settled into an equilibrium, which involves.
- Importation of energy, which I suspect is not at a low price
- Some high priced energy generators, based on gas, which has a high-price, due to Putin’s war.
- Waste of wind energy due to lack of energy storage.
- The intermittency of renewable sources.
- A lack of gas storage, means that we probably get the wrong end of fluctuations in the gas price.
This results in a high price to consumers.
Can We Move The Equilibrium Point Of The Energy Market?
And we also need to move it quickly to a more favourable place, which benefits everybody!
As a Control Engineer, I believe that there are five ways to move the equilibrium point.
- Stop Putin’s war.
- Increase gas storage.
- Generate more low-cost electricity.
- Increase electricity storage.
- Improve the control algorithm.
I will now look at each in more detail.
Stopping Putin’s War
Giving in to Putin’s ambitions, would be an easy way to solve our energy crisis. But at what cost?
My parents generation, watched as Nazi Germany took over Austria and Czechoslovakia, whilst the world did nothing.
- We mustn’t repeat that mistake.
- We must not flinch in our support of the Ukraine.
- We must be ready to support Moldova, Finland and the Baltic States if Putin expands his ambitions.
I do wonder, if Boris will turn up with Churchillian-style anti-Putin rhetoric all over Eastern Europe.
Increasing Gas Storage
The major gas storage facility is Rough, which is handily close to the Easington gas terminal.
The facility needs maintenance and this paragraph from the Wikipedia entry gives the current status.
In May 2022, the Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, Kwasi Kwarteng, began talks with the site’s owners with a view to reopening the site to help ease the ongoing cost-of-living crisis in the United Kingdom. In June 2022, owners Centrica submitted an application to the North Sea Transition Authority (NSTA), the licencing authority for the UK Government, to reopen the facility. Approval was granted in July. Subsequently, Centrica indicated that they are working hard to restore storage operations at Rough which would depend on securing subsidies from the British government. Centrica was aiming to have some capacity available for the winter of 2022/23 against an overall plan to increase storage capacity gradually over time.
Note.
- Rough can store around 2832 million cubic metres of gas.
- This article on Energy Live News is entitled Reopening Of Rough Storage Gets The All-Clear.
Less well-known is SSE and Equinor’s Aldborough Gas Storage.
These three paragraphs from SSE web site, describe the gas storage.
The Aldbrough Gas Storage facility, in East Yorkshire, officially opened in June 2011. The last of the nine caverns entered commercial operation in November 2012.
The facility, which is a joint venture between SSE Thermal (66%) and Equinor, has the capacity to store around 330 million cubic metres (mcm) of gas.
SSE Thermal and Equinor have consent to increase the storage capacity at the Aldbrough site (Aldbrough Phase 2) and during the last couple of years have been working to involve the local community where appropriate to refine aspects of this project, which has not been progressed to date due to market conditions.
Future plans for the facility, may include converting it to one of the world’s largest hydrogen stores.
In the grand scheme of things, Rough and Aldborough, when you consider that the UK uses 211 million cubic metres of gas every day, will only keep us going for a few days.
But it should be noted, that the Easington gas terminal is connected to the Norwegian gas fields, by the Langeled pipeline.
So Yorkshire and Humberside will be alright.
Generating More Low-Cost Electricity
The only low-cost electricity of any size to come on stream will be wind-power.
This article on Renewables Now is entitled UK Hits 25.5 GW Of Wind Power Capacity.
These wind farms seem to be coming on stream soon or have been commissioned recently.
- Dogger Bank A – 1200 MW – Commissioning 2023 expected
- Dogger Bank B – 1200 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
- Dogger Bank C – 1200 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
- Hornsea Two – 1386 MW – Commissioned 2022
- Moray East – 950 MW – Commissioning 2022 expected
- Neart Na Gaoithe – 450 MW – Commissioning 2024 expected
- Seagreen – 1075 MW – Commissioning 2023 expected
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW – Commissioning 2022 expected
That is expected to be over 5 GW of offshore wind by the end of 2023.
In case there is some double counting, I’ll only say that wind power capacity could be near to 30 GW by December 2023, with perhaps another 3 GW by December 2024.
Other large wind farms in the future include.
- Berwick Bank – 4100 MW – Commissioning 2028 expected
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW – Commissioning 2026 expected
- East Anglia Three – 1400 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Inch Cape Phase 1 – 1080 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Hornsea Three – 2800 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Moray West – 294 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Morgan and Mona – 3000 MW – Commissioning for 2028 expected
- Morven – 2900 MW – Commissioning for 2028 expected
- Norfolk Boreas – 1400 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Norfolk Vanguard – 1400 MW – Construction start planned for 2023
- Sofia – 1400 MW – Commissioning 2026 expected
That is over 14 GW of wind power.
I should also take note of solar and onshore wind power detailed in this document from the Department of Business, Industry and Industrial Strategy that lists all the Contracts for Difference Allocation Round 4 results for the supply of zero-carbon electricity.
It gives these figures and dates.
- Solar – 251 MW – Commissioning 2023/24 expected
- Solar – 1958 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
- Onshore Wind – 888 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
I can now build a yearly table of renewables likely to be commissioned in each year.
- 2022 – 3193 MW
- 2023 – 2275 MW
- 2024 – 701 MW
- 2025 – 5246 MW
- 2026 – 2300 MW
- 2027 – 6974 MW
- 2028 – 11400 MW
Note.
- Where a double date has been given, I’m taking the latter date.
- I have assumed that Norfolk Vanguard will be commissioned in 2028.
- I have ignored Hinckley Point C, which should add 3.26 GW in mid-2027.
- I have only taken into account one of the Scotwind wind farms in Scotland, some of which could be commissioned by 2028.
- I have assumed that BP’s Mona, Morgan and Morven will all be commissioned by 2028.
This is a total of 32 GW or an average of nearly 5 GW per year.
Increasing Electricity Storage
Big schemes like the 1.5 GW/ 30 GWh Coire Glas and 600 MW Cruachan 2 will help, but with 32 GW of renewable energy to be installed before 2028 and energy prices rocketing, we need substantial energy storage in the next couple of years.
One feasible plan that has been put forward is that of Highview Power’s CEO; Rupert Pearce,, that I wrote about in Highview Power’s Plan To Add Energy Storage To The UK Power Network.
The plan is to build twenty of Highview Power’s CRYOBatteries around the country.
- Each CRYOBattery will be able to store 30 GWh.
- Each CRYOBattery will be one of the largest batteries in the world.
- They will have three times the storage of the pumped storage hydroelectric power station at Dinorwig.
- They will be able to supply 2.5 GW for twelve hours, which is more output than Sizewell B nuclear power station.
Note.
- The first 30 GWh CRYOBattery is planned to be operational by late 2024.
- 600 GWh distributed around the country would probably be sufficient.
I believe that as these batteries are made from standard proven components, they could be built fairly quickly.
Paying For The Energy Storage
This press release from Highview Power is entitled New Analysis Reveals Extent Of UK Renewable Energy Waste, which makes these three bullet points.
- Enough renewable energy to power 500,000 homes a day wasted since the energy crisis began.
- 8 out of 10 Britons want more investment in boosting Britain’s energy resilience.
- UK spent £390 million turning off wind farms and using gas since September 2021.
Note.
- As the press release was published in July 2022, was the £390 million for ten months.
- Will this level of spend continue, as we’re not creating any electricity storage or building any factories that will start in a year or so, that will need large amounts of electricity?
- The Germans are at least building the NeuConnect interconnector between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven.
- As we’re adding up to 5 GW per year to our renewable energy systems, this problem will surely get worse and we’ll spend more money switching off wind turbines.
We have the money to build a very large amount of energy storage.
Improving The Control Algorithm
A better control algorithm would always help and politicians should only be allowed to set objectives.
Conclusion
There is a chance we’ll have an oversupply of electricity, but this will have effects in the UK.
- Gas-fired power-stations will be retired from front-line service to produce electricity.
- Some will question the need for nuclear power.
- Gas may even be used selectively to provide carbon dioxide for agricultural, scientific and industrial processes.
- Industries that need a lot of electricity may build factories in the UK.
- We will have a large supply of green hydrogen.
But it should bring the price of electricity down.
Renewable Power’s Effect On The Tory Leadership Election
I wouldn’t normally comment on the Tory Leadership Election, as I don’t have a vote and my preference has already been eliminated.
But after reading this article on the Telegraph, which is entitled Britain Will Soon Have A Glut Of Cheap Power, And World-Leading Batteries To Store It, I feel I have to comment both about this election and the General Election, that will follow in a few years.
These two paragraphs from the article illustrate the future growth of offshore wind power.
It is a point about the mathematical implications of the UK’s gargantuan push for renewables. Offshore wind capacity is going to increase from 11 to 50 gigawatts (GW) by 2030 under the Government’s latest fast-track plans.
RenewableUK says this country currently has a total of 86GW in the project pipeline. This the most ambitious rollout of offshore wind in the world, ahead of China at 78GW, and the US at 48GW.
If we assume that there is eight years left of this decade, that means that we should install about 4.9 GW of offshore wind every year until 2030. If we add in planned solar and onshore wind developments, we must be looking at at least 5 GW of renewable energy being added every year.
We have also got the 3.26 GW Hinckley Point C coming on stream.
I think we can say, that when it comes to electricity generation, we will not be worried, so Liz and Rishi can leave that one to the engineers.
If we have an electricity problem, it is about distribution and storage.
- We need more interconnectors between where the wind farms are being built and where the electricity will be used.
- National Grid and the Government have published plans for two interconnectors between Scotland and England, which I wrote about in New Electricity ‘Superhighways’ Needed To Cope With Surge In Wind Power.
- We need energy storage to back up the wind and solar power, when the wind isn’t blowing and the sun isn’t shining.
I think it is reasonable to assume, that we will get the interconnectors we need and the Telegraph article puts forward a very feasible and affordable solution to the energy storage problem, which is described in these two paragraphs from the article.
That is now in sight, and one of the world leaders is a British start-up. Highview Power has refined a beautifully simple technology using liquid air stored in insulated steel towers at low pressure.
This cryogenic process cools air to minus 196 degrees using the standard kit for LNG. It compresses the volume 700-fold. The liquid re-expands with a blast of force when heated and drives a turbine, providing dispatchable power with the help of a flywheel.
The article also talks of twenty energy storage systems, spread around the UK.
- They will have a total output of 6 GW.
- In total they will be able to store 600 GWh of electricity.
The first one for Humberside is currently being planned.
Surely, building these wind and solar farms, interconnectors and energy storage systems will cost billions of pounds.
Consider.
- Wind and solar farms get paid for the electricity they generate.
- , Interconnectors get paid for the electricity they transfer.
- Energy storage systems make a profit by buying energy when it’s cheap and selling it, when the price is better.
- In World’s Largest Wind Farm Attracts Huge Backing From Insurance Giant, I talked about how Aviva were funding the world’s largest wind farm at Hornsea.
- National Grid has a history of funding interconnectors like the North Sea Link from large financial institutions.
I believe that the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and the waters around our combined shores will become the largest zero-carbon power station in the world.
This will attract engineering companies and financial institutions from all over the world and we will see a repeat of the rush for energy that we saw for oil and gas in the last century.
If we get the financial regime right, I can see a lot of tax money flowing towards the Exchequer.
The big question will be what do we do with all this energy.
- Some will be converted into hydrogen for transport, the making of zero-carbon steel and cement and for use as a chemical feedstock.
- Industries that use a lot of electricity may move to the UK.
- A large supply of electricity and hydrogen will make it easy to decarbonise housing, offices and factories.
The Telegraph article also says this.
Much can be exported to the Continent through interconnectors for a fat revenue stream, helping to plug the UK’s trade deficit, and helping to rescue Germany from the double folly of nuclear closures and the Putin pact. But there are limits since weather patterns in Britain and Northwest Europe overlap – partially.
I suspect that more energy will be exported to Germany than most economists think, as it will be needed and it will be a nice little earner for the UK.
Given the substantial amount of German investment in our wind industry, I do wonder, if Boris and Olaf did a deal to encourage more German investment, when they met in April this year.
- BP have been backed with their wind farms by a German utility company.
- RWE are developing the Sofia wind farm.
- Only last week, the deal for the NeuConnect interconnector between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven was signed.
- Siemens have a lot of investments in the UK.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see more German investments in the next few months.
The Golden Hello
Has there ever been a Prime Minister, who will receive such a golden hello, as the one Liz or Rishi will receive in September?
The Tory Leadership Election
Some of the candidates said they would reduce taxes , if they won and Liz Truss is still saying that.
I wonder why Rishi isn’t saying that he would reduce taxes, as he must know the cash flow that is coming. It may be he’s just a more cautious soul.