Jurgen Maier To Chair Great British Energy
This article in The Times is entitled Pylons Are The Price Of Lower Bills, Keir Starmer Tells Rural Britain.
These are two paragraphs from the article.
Starmer confirmed that Jürgen Maier, the former UK chief executive of the Siemens conglomerate, would chair the energy company.
Maier has advised Labour on rail and transport since December. He was openly critical of the party’s decision to drop a pledge to spend £28 billion a year on green investment, saying the figure was an “absolute minimum” and that scrapping the promise was “not good for climate change or for the growth of our economy”.
Note.
- His Wikipedia entry is impressive.
- He has dual Austrian and British citizenship.
- He went to school in Leeds and is a graduate of Nottingham Trent University.
- He rose to be Chief Executive of Siemens UK and retired in 2019 at 55.
- I have heard him several times on the radio and he seems to talk a lot of sense.
In my view he could be an excellent choice as Chair of Great British Energy.
I also have some further thoughts.
Jürgen Maier And Peter Hendy
Jürgen Maier and Peter Hendy, who is Starmer’s Rail Minister, have remarkably similar backgrounds and I wouldn’t be surprised if they know each other well, through dealings around Siemens’ contract for Transport for London’s new trains for the Piccadilly Line.
When last, were two technological heavyweights, so close to the heart of a UK government?
RWE
German energy company; RWE are the UK’s largest power generator.
- RWE have five gas-fired power stations with a total output of 6.56 GW.
- RWE have two onshore wind farms in operation with a total output of 67 MW.
- RWE have four offshore wind farms in operation with a total output of 1.88 GW.
- RWE have eight offshore wind farms under development with a total output of 9.90 GW.
- RWE also has other electrical gubbins, like an electrolyser in South Wales.
Would Jürgen Maier be an ideal person, to persuade RWE to keep investing in the UK?
When he was with Siemens, he certainly invested heavily in the UK.
The German Problem
Germany’s problem is how they generate electricity.
Sources are as follows for Germany and the UK.
- Coal – 26 % – 1 %
- Natural Gas – 10.5 % – 32 %
- Wind – 32 % – 29.4 %
- Solar 12.2 % – 4.9 %
- Biomass – 9.7 % – 12.3 %
- Nuclear – 1.5 % – 14.2 %
- Hydro – 4.5 % – 1.8 %
- Oil – 0.7 % – 0 %
- Other – 2.9 % – 0 %
- Storage – 0 % – 1 %
- Imports – 0 % – 10.7 %
Note.
- Figures are for 2023.
- Germany is the first percentage.
- UK is the second percentage.
- Germany has pledged to end coal-fired electricity production by 2030.
- Both countries seem to generate similar amounts of electricity from wind, biomass and hydro.
To replace the coal and make up for lack of nuclear, Germany needs to find a new power source.
The German Solution
The Germans are going for hydrogen in a big way.
The title of this page of the RWE web site is Welcome To The Age Of Hydrogen.
The page starts with this paragraph.
RWE is actively involved in the development of innovative hydrogen projects. The H2 molecule is considered to be an important future building block of a successful energy transition. RWE is a partner in over 30 H2 projects and is working on solutions for decarbonising the industry with associations and corporations like Shell, BASF and OGE. Hydrogen projects are comprehensively supported in the separate Hydrogen department of the subsidiary RWE Generation.
I also suggest, that you read this page on the RWE web site called AquaVentus.
The page starts with this RWE graphic.
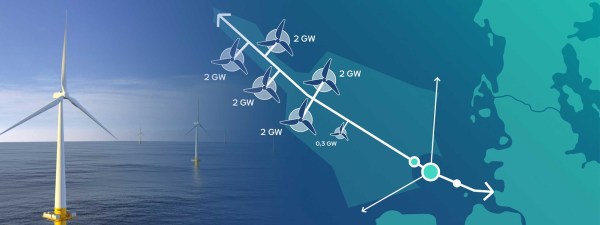
It appears that 10.3 GW of hydrogen will be created by wind farms and piped to North-West Germany.
These two paragraphs outline the AquaVentus initiative .
Hydrogen is considered the great hope of decarbonisation in all sectors that cannot be electrified, e.g. industrial manufacturing, aviation and shipping. Massive investments in the expansion of renewable energy are needed to enable carbon-neutral hydrogen production. After all, wind, solar and hydroelectric power form the basis of climate-friendly hydrogen.
In its quest for climate-friendly hydrogen production, the AquaVentus initiative has set its sights on one renewable energy generation technology: offshore wind. The initiative aims to use electricity from offshore wind farms to operate electrolysers also installed at sea on an industrial scale. Plans envisage setting up electrolysis units in the North Sea with a total capacity of 10 gigawatts, enough to produce 1 million metric tons of green hydrogen.
The page also gives these numbers.
- Total Capacity – 10 GW
- Tonnes Of Green Hydrogen – 1 million
- Members – 100 +
The web site says this about commissioning.
Commissioning is currently scheduled for early/mid 2030s.
The Germans can’t be accused of lacking ambition.
AquaVentus And The UK
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be a undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be a link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea. It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network.
AquaVentus And Aldbrough And Rough Gas Storage
Consider.
- In The Massive Hydrogen Project, That Appears To Be Under The Radar, I describe the Aldbrough Gas Storage.
- In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to turn Rough Gas Storage into the world’s largest hydrogen store.
- There is a small amount of hydrogen storage at Wilhelmshaven.
It looks like the East Riding Hydrogen Bank, will be playing a large part in ensuring the continuity and reliability of AquaVentus.
Dogger Bank South And AquaVentus
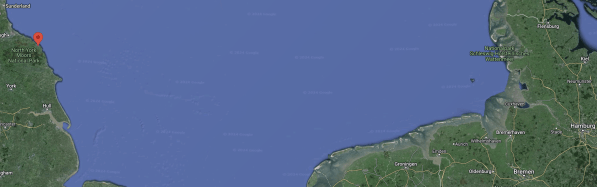
This Google Map shows the North Sea South of Sunderland and the Danish/German border.
Note.
- Sunderland is in the top-left hand corner of the map.
- A white line in the top-right corner of the map is the Danish/German border.
- Hamburg and Bremen are in the bottom-right hand corner of the map.
If you lay the AquaVentus map over this map, I believe that RWE’s Dogger Bank South wind farm could be one of the three 2 GW wind farms on the South-Western side of the AquaVentus main pipeline.
- Two GW would be converted to hydrogen and fed into the AquaVentus main pipeline.
- Two GW of hydrogen will be a nice little earner for UK plc.
- One GW of electricity would be sent to the UK.
But this is only one of many possibilities.
Conclusion
Could Jürgen Maier, be the man to develop British links to AquaVentus for the benefit of both the UK and Germany?
- The UK’s wind farms could provide a lot of hydrogen for AquaVentus.
- Aldbrough And Rough Gas Storage are conveniently places to add the hydrogen storage, that AquaVentus needs.
- AquaVentus can certainly be expanded to Norway, and possibly Orkney and Shetland.
He certainly has a lot of relevant experience.
Smart Train Lease Aims ‘To Make Renting Trains As Easy And Simple As Renting A Car’
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette International.
These four paragraphs outline the scheme.
Siemens Mobility has established a leasing subsidiary that would enable train operators to use its Mireo Smart battery, hydrogen and electric multiple-units without needing to make long-term investment commitments.
Smart Train Lease GmbH would make available at short notice multiple-units already approved for operation. These could be short or medium-term leases, with services such as maintenance available as part of the package. The aim is to provide operators with an economical way to quickly and flexibly expand their fleets and try out more sustainable traction technologies.
‘We want to make renting trains as easy and simple as renting a car, and thus help accelerate the mobility transition’, the leasing company’s CEO Benjamin Dobernecker explained on February 14.
Smart Train Lease will initially operate in Germany, although it plans to expand throughout Europe in the medium term.
I like this idea and I think it will work.
Metier Management Systems And Artemis
When four of us started Metier Management Systems in 1977 to sell our mini-computer-based project management system; Artemis, we generally rented or leased our systems, although we did sell some as the years progressed.
- For a fixed fee per month, a company got a project management computer and all the software.
- The fixed fee included installation, first line support, training and software updates.
- We could also supply extra training and project management consultancy at appropriate rates.
- The only extra costs to the client were the electricity to power the hardware and the paper to put in the printer.
- We also allowed clients to convert leases into outright sales.
This simple sales model appealed to a lot of our clients.
- The cost of the system was easy to budget.
- Many of our clients were happy with leasing or renting computer equipment.
- As the system was desk-sized, it easily fitted the average office.
But the leasing model was very advantageous to us.
- Most of our clients were large high-value quality organisations like big oil companies, nationalised industries and engineering consultancies.
- Our Finance Director and our Bank Manager at Lloyds Bank devised a plan, whereby we bundled a number of high-quality leases together and sold the bundle to Lloyds Bank’s leasing company.
The money we received gave us a healthy cash flow.
- The cash flow was then used to fund Research and Development and to finance more sales.
- If say someone like BP or Shell should phone up or send a fax, wanting a system immediately, we were generally able to fulfil their request.
I am sure that Siemens Mobility will be using a similar model.
They will aim to have trains in stock to fulfil clients needs.
So if Deutsche Bahn phone up saying have you got a three-car battery-electric train that works with 15 KVAC and has a range of 100 kilometres for next Monday, Siemens Mobility can generally say yes.
What helps is that the modular Mireo Smart multiple unit comes in battery, hydrogen and electric versions.
Extras could include full servicing a driver.
So Siemens Mobility will plug the train together and deliver it.
How Would Siemens Use The Leasing Model In Great Britain?
Consider.
- There are a lot of routes that need to be decarbonised in Great Britain.
- Many of these routes have electrification at one or both ends.
- Often these routes terminate in a bay platform.
- On most of these routes a two-, three-, four- or five-car train will be sufficient capacity.
- In the Desiro City, Siemens have a train, that is acceptable to Great Britain.
- If routes in Great Britain are to be electrified, they must be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead wires.
- Trains would be 100 mph, so they wouldn’t be limited as to routes.
- A Mireo-B has a range of between 80-100 kilometres or 49.7-74.6 miles.
I am sure Siemens Desiro City or its European equivalent; Mireo can be developed into a family of trains suitable for GB!
- The basic train would be two driving cars.
- Length would be increased by coupling trailer cars between the two driving cars.
- Hydrogen power would be in one of the trailers.
- Batteries would be under an appropriate number of cars.
Battery trains would be able to use a simple automatic charger, similar to the one, that I described in GWR Trialling Transformative Ultra-Rapid Charging Train Battery.
An Example – Mid-Cornwall Metro
This map shows the Mid-Cornwall Metro.
Consider.
- Newquay and Par is 20.8 miles.
- Falmouth Docks and Par is 30.8 miles.
- Newquay and Falmouth Docks is 51.6 miles.
- The maximum speed between Par and Newquay is around 30 mph
- The maximum speed between Par and Falmouth Docks is around 50-70 mph
- There are twelve intermediate stations.
- There is a reverse at Par station.
- Charging would be easy to install at Falmouth Docks, Newquay and Par.
- In Par Station – 10th February 2024, I suggested that Par station could be fully-electrified, so that expresses could have a Splash-and-Dash on their way to London and Penzance. If all platforms at Par were electrified the Mid-Cornwall Metro trains could charge from the electrification, as they reversed.
There are two main ways that the Mid-Cornwall Metro might operate.
- There would be chargers at Newquay and Falmouth Docks and trains would shuttle the 51.6 miles between the two stations.
- There would only be charging at Par and trains would after charging at Par go alternatively to Newquay and Falmouth Docks.
The first might need smaller batteries and the second would only need one charger.
An Example – Uckfield Branch
The Uckfield branch is in Southern England.
- It is not electrified between Hurst Green Junction and Uckfield, which is 24.7 miles.
- There are eight intermediate stations.
- The line can accommodate ten-car trains.
There is space at Uckfield station for a charger.
Charging would be at Uckfield station and North of Hurst Green Junction, where it will use the existing electrification.
Conclusions
This leasing/rental model will surely encourage train operators to replace diesels with appropriate zero-carbon alternatives on routes that need to be decarbonised.
New Mobile Rail Charging Facility For Long Marston
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article from Rail Technology Magazine.
This is the sub-heading.
Porterbrook has signed a £1.7 million deal with Siemens Mobility to purchase an innovative Rail Charging Converter (RCC) for its Long Marston Rail Innovation Centre. The cutting-edge technology will make battery charging and 25kV power supply possible in areas of the UK railway where overhead line equipment is not currently available.
This first paragraph describes the system.
The RCC is a modular and containerised system that uses power electronics to provide a fully compliant, standard connection between the modern three-wire electricity grid and the single-wire railway. It essentially reduces the electrification infrastructure needed by being able to plug into existing power cables and deliver the ideal power supply for trains.
These two paragraphs describe how the RCC was designed and funded, and how it will be used in the future.
The original development of the RCC was supported by the Department for Transport through Innovate UK’s First of a Kind programme. The team will install the novel charging solution at Long Marston, enabling the charging of trains with batteries, fed from existing standard local power supply cables.
Compatible with all overhead line equipment powered trains, the small, low-cost design of the RCC enables the removal of diesel passenger train operation on routes without continuous electrification.
I suspect we’ll see other manufacturers like Hitachi ABB Power Grids and Furrer+Frey launch similar products.
This page gives full details of the award to Siemens Mobility.
Project Title: 25kV Battery Train Charging Station Demonstration
Lead Organisation: Siemens Mobility Ltd.
Project Grant: £59,910
Public Description:
The UK rail industry is committed to decarbonisation, including the removal of diesel trains by 2040.
Replacing diesel trains with electric, hydrogen or battery bi-mode rolling stock provides faster, smoother and more reliable journeys, as well as eliminating local pollution and greatly reducing carbon dioxide.
To enable clean, green electric bi-mode operation without continuous electrification requires enhancement of the power supply to existing electrification and novel charging facilities to support bi-mode trains.
No small, low-cost solution is currently available for charging facilities that are compatible with standard UK trains and locally available power supplies and space.
Siemens Mobility, working with ROSCO, TOCs and Network Rail, will deliver a novel AC charging solution enabling simple installation of small, low-cost rapid charging facilities fed from existing standard local power supply cables.
Compatible with all OLE-powered trains, the novel design enables the removal of diesel passenger train operation on non-electrified routes across the UK, while minimising land requirements and modifications required to existing station structures.
£59,910 seems to be good value for the helping with the design of a universal charging system for 25 KVAC battery-electric trains in the UK.
I have a few thoughts.
Will The Rail Charging Converter (RCC) Charge Third Rail Trains?
As new third-rail systems are effectively systems non grata, I suspect that third-rail trains will be charged by fitting a pantograph and the appropriate electrical gubbins.
Most modern third-rail electrical multiple units have a roof that is ready for a pantograph and can be converted into dual-voltage trains.
What Trains Will Be Able To Be Charged Using An RCC?
I suspect it will be any train with a battery, a pantograph and the appropriate electrical gubbins.
Battery-electric trains that could have a pantograph include.
- Alstom Electrostar and Aventra
- CAF Civity
- Hitachi Class 385 train
- Hitachi Class 800 train
- Siemens Desiro and Mireo
- Stadler Class 777 train
- Stadler Flirt and Akku
- Vivarail Class 230 train
I suspect it could charge all trains in the UK, where batteries have been proposed to be added.
What Is Meant By Mobile?
I suspect transportable and temporary would be a better description.
This gallery show Felixstowe station and a Class 755 train, which can be fitted with batteries.
Suppose that testing was to be done at Felixstowe of a battery-electric Class 755 train.
- The containerised electrical system would be placed somewhere convenient.
- A short length of overhead wire would be erected in the platform.
- The system would then be connected together and to the electrical supply.
- After testing, it could be used to charge a train.
It would be very convenient for operation of the railway, if it could be installed and taken out overnight.
Conclusion
It looks a well-designed system.
UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
A new partnership between the UK and German governments has been agreed on 3 November to help secure safe, affordable, and clean energy for consumers in both nations for the long-term and bolster energy security. Both countries commit to strengthening cooperation in renewables, notably offshore wind and electricity interconnection.
These two paragraphs introduce the deal.
Under the new partnership signed in London by Energy Security Secretary Claire Coutinho and Germany’s Vice Chancellor, Robert Habeck, the UK and Germany have reaffirmed their shared ambition and commitment to net zero and progressing the energy transition.
Europe’s two largest economies have also doubled down on commitments made under the Paris Agreement to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees.
i think this could be a worthwhile follow-up to the relationship, that Boris Johnson and Olaf Scholz seemed to encourage after their high profile meeting in April 2022.
This press release from Downing Street is entitled PM meeting with German Chancellor Olaf Scholz: 8 April 2022 and this is the first two paragraphs.
The Prime Minister welcomed German Chancellor Olaf Scholz to Downing Street this afternoon to discuss the West’s response to Putin’s barbaric invasion of Ukraine.
The two leaders shared their disgust at the Russian regime’s onslaught and condemned Putin’s recent attacks.
I wrote Armoured Vehicles For Ukraine based on some of the things said in the press conference after what seemed to be a very wide discussion.
But it was these paragraphs in the press release that caught my eye.
They also agreed on the need to maximise the potential of renewable energy in the North Sea and collaborate on climate ambitions and green energy.
The Prime Minister said he wanted to further deepen the UK’s relationship with Germany, and intensify its cooperation across defence and security, innovation and science.
After Boris and Olaf’s meeting at Downing Street, I have been able to write these posts about the Anglo-German energy relationship and also make some other observations.
- Mona, Morgan And Morven
- UK-German Energy Link Reaches Financial Close
- RWE, Siemens and other German companies seem to be building a strong presence in the UK.
- Rolls-Royce are doing the same in Germany.
Claire Coutinho and Robert Habeck seem to be wanting to continue the co-operation, judging by this paragraph from the article on offshoreWIND,biz.
The energy and climate partnership sees both countries commit to enhancing cooperation in renewables, particularly in offshore wind and electricity interconnection, including offshore hybrid interconnection.
The most significant part of this paragraph is the mention of offshore hybrid interconnection.
If you want more details on their meeting, this document is the official UK Government declaration.
I have my thoughts.
What Is Meant By Offshore Hybrid Interconnection?
Type “Offshore Hybrid Interconnection” into Google and the first page is this page from National Grid, that is entitled Offshore Hybrid Assets, that has this sub-heading.
How the North Sea has the potential to become Europe’s green energy ‘powerhouse’
This is the introductory paragraph.
Now more than ever we need more renewable energy to make energy cleaner, more affordable, and more secure. The North Sea offers an incredible opportunity for the UK and our European neighbours to deliver huge increases in offshore wind. But delivering new offshore wind will require more infrastructure, which will have an impact on communities.
Hybrid is all-purpose comfort word like cashmere, platinum or puppies.
The page on the National Grid web site describes The Next Generation Interconnector with these paragraphs.
Interconnectors already provide a way to share electricity between countries safely and reliably. But what if they could do much more than that? What if interconnectors could become an offshore connection hub for green energy?
Instead of individual wind farms connecting one by one to the shore, offshore hybrid assets (OHAs) will allow clusters of offshore wind farms to connect all in one go, plugging into the energy systems of neighbouring countries.
And then there is this section entitled Tomorrow’s Solution: Offshore Wind And Interconnectors In Harmony, where this is said.
Today, offshore wind and interconnectors operate alongside each other, connecting to the shore individually. In the future, offshore hybrid assets could enable offshore wind and interconnection to work together as a combined asset.
We now call this type of infrastructure an offshore hybrid asset (OHA), but we used to refer to it as a multi-purpose interconnector (MPI). We changed it because we work so closely together with Europe, it made sense to use the same terminology.
The page on the National Grid web site also has an interactive graphic, which shows the benefit of the approach.
LionLink
National Grid are already developing LionLink, with Dutch grid operator; TenneT, which will be a multi-purpose interconnector linking the UK and the Netherlands.
LionLink is described on this page from National Grid, where this is the sub-heading.
We’re developing a first-of-its-kind electricity link to connect offshore wind between the UK and the Netherlands.
This is the introductory paragraph.
Designed together with our Dutch partners TenneT, LionLink (formerly known as EuroLink) is an electricity link that can supply around 1.8 gigawatts of clean electricity, enough to power approximately 1.8 million British homes. By connecting Dutch offshore wind to Dutch and British markets via subsea electricity cables called interconnectors, LionLink will strengthen our national energy security and support the UK’s climate and energy goals.
Will we be planning a similar electric handshake with the Germans?
How Much Offshore Wind Power Are We Talking About?
This is answered by the last two paragraphs of the article on offshoreWIND.biz.
Around 75 per cent of installed offshore wind capacity in the North Sea is in German and British waters. This is helping to drive the UK’s ambition for up to 50 GW of offshore wind, including up to 5 GW of floating wind, by 2030, the governments said.
Germany is aiming at installing 30 GW by 2030.
That is an Anglo-German starter for eighty GW.
Electrolysers In The Middle If The North Sea
Why Not?
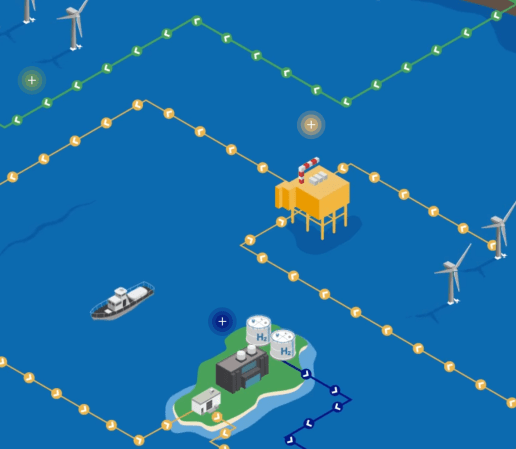
This is a clip from National Grid’s graphic on the page that introduces Offshore Hybrid Assets,
It shows an offshore hydrogen electrolyser.
- You could have an offshore hybrid asset that went between say Bacton in Norfolk and Hamburg via these assets.
- One or more wind farms in UK territorial waters.
- A mammoth offshore electrolyser, with hydrogen storage, possibly in a depleted gas field.
- One or more wind farms in German territorial waters.
Electricity will be able to go three ways; to the UK, to Germany or to the electrolyser.
The Involvement Of German Energy Companies In UK Territorial Waters
Wikipedia lists offshore fifteen wind farms, that have German owners in UK territorial waters, that total 12,960 MW.
This compares with.
- Equinor – 6 wind farms totalling 6466 MW.
- Ørsted – 15 wind farms totalling 9683 MW.
- Scottish Power – 2 wind farms totalling 5,000 MW.
- SSE Renewables – 15 wind farms totalling 15,591 MW.
- Vattenfall – 6 wind farms totalling 4384 MW.
As there is a number of partnerships, these figures only show the relative sizes of the investment by individual companies.
But at nearly 13 GW, the amount of total German investment in UK territorial waters is substantial.
Is This Solely An Anglo-German Club Or Can Others Join?
Consider.
- It seems to me, that because of the LionLink, the Dutch are already involved.
- TenneT is also a large electricity distributor in Germany.
- Countries with substantial shares of the water and winds of the North Sea in addition to Germany, the Netherlands and the UK, include Belgium, Denmark and Norway.
- The UK has interconnectors with Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Norway and the Netherlands.
It appears that the world’s largest multi-national power generator is evolving by stealth.
North Sea Wind Power Hub
This concept seems to have developed around 2017, by Danish, Dutch and German interests.
The Wikipedia entry introduces it like this.
North Sea Wind Power Hub is a proposed energy island complex to be built in the middle of the North Sea as part of a European system for sustainable electricity. One or more “Power Link” artificial islands will be created at the northeast end of the Dogger Bank, a relatively shallow area in the North Sea, just outside the continental shelf of the United Kingdom and near the point where the borders between the territorial waters of Netherlands, Germany, and Denmark come together. Dutch, German, and Danish electrical grid operators are cooperating in this project to help develop a cluster of offshore wind parks with a capacity of several gigawatts, with interconnections to the North Sea countries. Undersea cables will make international trade in electricity possible.
Currently, the UK is developing these wind farms on their portion of the Dogger Bank.
- Doggerbank A – 1235 MW – Started producing electricity in 2023.
- Doggerbank B – 1235 MW – Planned commissioning in 2024.
- Doggerbank C – 1218 MW – Planned commissioning in 2025.
- Doggerbank D – 1320 MW – Being planned.
- Doggerbank South – 3000 MW – Being planned.
Note.
- That’s a total of 8 GW.
- A, B, C and D are being developed by a consortium of SSE Renewables and Equinor.
- South is being developed by RWE.
- This web site is for Dogger Bank D.
- This web site is for Dogger Bank South.
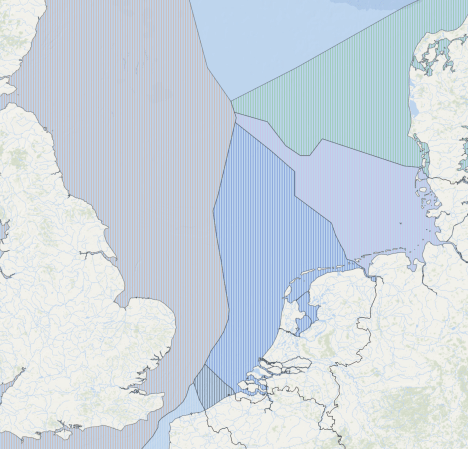
This map from the European Atlas of the Seas, shows the various exclusive economic zones (EEZ) in the North Sea.
Note.
- The pinkish zone to the East of the UK, is the UK’s EEZ.
- The light blue zone at the top is Norway’s EEZ.
- The greenish zone in the North-East corner of the map is Denmark’s EEZ.
- The light blue zone below Denmark’s EEZ is Germany’s EEZ.
- Then we have the EEZs for The Netherlands, Belgium and France.
The Dogger Bank is situated where the British, Dutch, German and Norwegian EEZs meet.
All five Dogger Bank wind farms are in British waters.
The Wikipedia entry for the Dogger Bank says this about its size.
The bank extends over about 17,600 square kilometres (6,800 sq mi), and is about 260 by 100 kilometres (160 by 60 mi) in extent. The water depth ranges from 15 to 36 metres (50 to 120 ft), about 20 metres (65 ft) shallower than the surrounding sea.
This probably makes it easy to accommodate a large fixed-foundation wind farm.
Overlaying the map in the Wikipedia entry, with the EEZ map, I’m fairly sure that the northeast end of the Dogger Bank is close to where the EEZs meet.
Progress On The North Sea Wind Power Hub
The North Sea Wind Power Hub has a web site, but it seems to be more about thinking than doing.
It seems to have been hijacked by that august body; The Institute of Meetings Engineers.
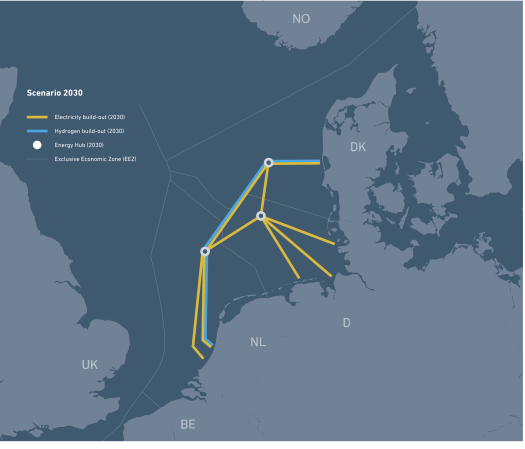
This page on the web site, which is entitled Explore The Future Energy Highways, has a simple interactive map.
This shows its vision for 2030.
Note.
- Yellow is electricity links to be built before 2030.
- Blue is hydrogen links to be built before 2030.
- Feint lines indicate the EEZ boundaries.
There are two problems with this layout.
- It doesn’t connect to the Dogger Bank area, where the original plan as detailed in Wikipedia talked about “Power Link” artificial islands.
- No hydrogen is delivered direct to Germany.
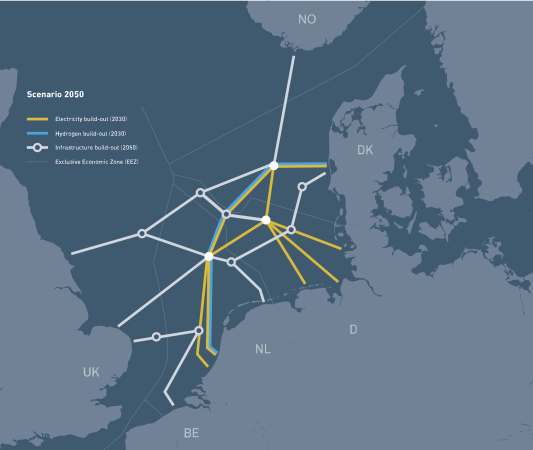
This shows its vision for 2050.
Note.
- Yellow, blue and feint lines are as before.
- White is electricity links to be built before 2050.
- There appears to be a node on the Dogger Bank in the German EEZ. This node could be connected to the “Power Link” artificial islands.
- The Southernmost connection to East Anglia could be Bacton.
- The other Norfolk connection could be where wind farms are already connected.
- The Northern connection could be Teesside, where some of the Dogger Bank wind farms connect.
- If the Northern connection to England is Teesside, then first node, which is in the British EEZ, could be one of the offshore sub-stations in the Dogger Bank wind farm complex.
This all seems a lot more feasible.
A New Offshore Hybrid Asset Between Teesside And Germany
Consider.
- A new offshore sub-station will be needed in the German EEZ to connect the “Power Link” artificial islands to the power network.
- The new offshore sub-station will eventually have three interconnectors to the German coast.
- Only the 1218 MW Dogger Bank C wind farm will be connected to the Teesside onshore substation.
- Germany has a power supply problem, after shutting down nuclear power stations and building more coal-fired power stations.
A new Offshore Hybrid Asset between Teesside and Germany could be created by building the following.
- A the new offshore sub-station in the German EEZ to connect the “Power Link” artificial islands to the power network.
- An interconnector between a sub-station of the Dogger Bank wind farm complex and the new sub-station
- A second interconnector to connect the new sub-station for the “Power Link” artificial islands to the German electricity grid.
All of the work would be done mainly in the German EEZ, with a small amount in the British EEZ.
Where Does Dogger Bank South Fit In?
Consider.
- Dogger Bank South is planned to be a 3 GW wind farm.
- It will need a 3 GW connection to the onshore electricity grid.
- Creyke Beck substation is the proposed location for the onshore connection.
- It is owned by German electricity company; RWE.
Could it be that some of the electricity produced by Dogger Bank South is going to be sent to Germany or to another node to produce hydrogen?
It certainly illustrates the value of an Offshore Hybrid Asset.
Overview – Siemens Energy Electrolyser Deal Dwarfs Rest In Q1 2023
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Renewables Now.
This is the first paragraph.
The global electrolyser market concluded the first quarter of 2023 with a variety of equipment supply deals, partnerships, framework agreements and even some firm contracts. Siemens Energy stood out with the news of its selection to equip a “world-scale” eFuels facility in Texas with a total capacity of 1,800 MW.
The article is a good summary of the electrolyser market.
Siemens Completes Study To Decarbonise Major UK Industrial Estate By 2038
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item on Siemens UK web site.
This is the sub-heading.
Siemens has proposed a road-map for decarbonising Trafford Park, one of Europe’s largest industrial estates, to support Trafford Council’s aims for the Greater Manchester borough to achieve net zero by 2038.
This three paragraphs outline the proposal.
The Low Carbon Trafford Park 2038 study, proposed by Siemens, aims to identify, cost and measure the impacts of low carbon technologies at the industrial estate. It covers a broad range of solutions, from waste to energy and heat recovery from energy intensive industrial players, to the potential for solar photovoltaics across the park to generate 147 GWh of clean energy.
The study acts as a blueprint for the council to consider as it works to eliminate the 714,000 tonnes of carbon emitted from Trafford Park each year. The estate is home to 1,330 businesses employing more than 35,000 people, with a dense population of industrial and commercial occupiers over an area of 4.6 sq miles.
The Council aims to use the roadmap to facilitate stakeholder engagement and collaboration across the industrial park, aligning business and environmental goals to different commercial segments across recommended technological and behavioural measures. It will then consider its broader recommendations as part of a long-term plan in partnership with occupiers.
This is decarbonisation on a grand scale!
- Siemens expects the decarbonisation of Trafford Park to attract new business to the Park and maintain and enhance its standing as a commercial and industrial hub in the region.
- The measures recommended would require £1.2 billion of private and public investment to achieve a 94% reduction in emissions.
- The study provided Trafford Council with modelling of an extensive range of measures for conserving gas and electricity and for generating clean energy on-site.
This page on the Siemens web site is entitled Smart Infrastructure For A Sustainable Future, outlines some of the company’s solutions.
Conclusion
It will be interesting to see how Trafford Park decarbonises.
Battery Train Pilot Project On Challenging’ Westerwald Routes
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
It is only a small order for three Mireo Plus B battery-electric multiple-units from Siemens Mobility, but I feel, it is significant that engineers and managers are confident that a battery-electric multiple unit can handle a challenging route.
GeoPura’s Construction World First
On the GeoPura web site there is a case study, which is entitled Construction World First.
These two paragraphs outline what was done.
Working in partnership with Siemens Energy our hydrogen fuel cell system, has provided off grid power and heat to National Grid’s UK Viking Link construction site.
The fuel cell system removes the need for diesel generators and provides innovative, sustainable, low carbon energy to the Viking Link interconnector project site.
The interesting thing, is that the heat that the hydrogen fuel cell gives out is collected and used to heat the remote site.
This last paragraph, explains the need for off grid power.
Off grid power is needed as this site didn’t have a grid connection for at least six to eight months, and the fuel cell system provided enough heat and power for the construction village during that time, removing the need for diesel generators.
There’s more in this Siemens Energy report.
Offshore Wind Turbines Need To Be Standardised, Energy Transition Industrialised To Reach Targets, Says Siemens Energy VP For Western Europe
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Governments need to move from talking about policies to implementation, the offshore wind industry needs to employ standardisation, and clear rules and regulations need to be set for green hydrogen in order to move faster with large-scale deployment and achieve meaningful progress in limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
The guy has a point, as mass production of anything is generally more efficient and creates more units in a given time.
But can a diverse group of politicians, agree on a standard for turbines, fixed foundations, floaters, cables and sub-stations and then make sure all are identical and clip together like Lego? I doubt it!
And how would you fit innovative designs like TwinHub into a standard.
This image shows one of their TwinHub turbine installations being towed into place.
At least it could be built to hold two standard turbines.
ECML Net Zero Traction Decarbonisation
This project was one of the winners in the First Of A Kind 2022 competition run by Innovate UK.
In this document, this is said about the project.
Project No: 10036245
Project title: ECML Net Zero Traction Decarbonisation
Lead organisation: SIEMENS MOBILITY LIMITED
Project grant: £59,983
Public description: Electrification is the foundation of all modern railways and fundamental to decarbonisation. Through
delivering faster, smoother, quieter and more reliable train services, rail electrification reduces
industry fuel cost by 45%, rolling stock costs by 33%, and track maintenance costs by 10-20%
(compared to diesel operation). Electric railways are the most efficient, lowest carbon form of
transportation in the UK.
Network Rail operates the largest power distribution network in the UK, and is the largest consumer
of electricity in the UK, consuming 4TWh electricity per year. Power is provided from the electricity
supply industry, a mix of gas, nuclear, coal and renewables, emitting approximately 944,000 tonnes
of carbon dioxide annually. Connecting new renewable generation directly to the railway reinforces
the railway power supply, while reducing coal and gas use in the UK and is a longstanding Network
Rail industry challenge statement. To date, engineering incompatibilities between renewable,
electricity supply systems and the railway single-phase electrical and other railway systems have
prevented local renewable connection in rail.
In a world first, Siemens Mobility, working with British Solar Renewables, DB Cargo UK, Network
Rail, ECML operators, and the University of York, will directly connect large-scale renewable
generation to the East Coast Mainline. The demonstrator phase will deliver up to 1GWh green
electricity direct to trains each year, reducing UK gas imports by 151,000 cubic metres and carbon
emissions by 236 tonnes annually. It will gather vital data creating a new green industry, creating a
precedent and setting standards to enable larger scale roll-out across the UK.
My Thoughts And Conclusion
This page on the Network Rail web site is entitled Power Supply Upgrade.
Since 2014, Network Rail and its partners have been upgrading the overhead electrification and the associated substations and electricity supply on the East Coast Main Line (ECML).
- It is not a small project which includes fifty new substations and 1,600 km. of new cabling between London and Edinburgh.
- When complete, fleets of electric trains on the route will be receiving high-quality electric power from the upgraded overhead electrification.
However, the East Coast Main Line is unique among British electrified main lines, in that it runs more or less close to a coast, that is populated by a large number of massive wind farms.
I believe the objective of this project, is to more directly connect the massive wind farms to the East Coast Main Line.
Lessons learned could then be applied to other electrified main lines.
We may even see onshore wind farms or small modular nuclear reactors built to power the railways.