Green Hydrogen – Meranti Green Steel Launches Green Iron Project In Oman
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Hydrogen Central.
The title shows how if you have plenty of energy, you can produce green steel.
Surely, if the Omanis can do it, we can attract a company to make green steel in the UK, as we have lots of renewable energy around our shores.
All the current steelmakers do is blackmail the UK Government into paying them subsidies.
Siemens Mobility Looks To Build Battery Trains In Goole
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway News.
These first three paragraphs add more details.
Siemens Mobility has announced plans to build battery-powered trains in Goole, Yorkshire, to replace ageing fleets on Britain’s railway.
The manufacturer envisions that battery trains could replace rolling stock for operators such as Chiltern, Great Western Railway (GWR), Northern, ScotRail, TransPennine Express (TPE) and Transport for Wales (TfW) within the next decade.
This would mitigate the need to electrify all sections of the track to deliver zero-emission solutions. In doing so, 3.5 billion GBP could be saved and 12 million tonnes of CO2 emissions could be avoided over 35 years.
Note.
- The post is dated in June 2024, so I am sorry I didn’t spot it earlier.
- It talks in detail about Siemens’ plans for battery-electric trains.
- It also talks about the Siemens’ Rail Charging Converter, which can power short lengths of overhead wires for charging trains from the domestic grid.
- I also talked about Siemens’ technology in Technology Behind Siemens Mobility’s British Battery Trains Hits The Tracks.
It is certainly a must-read article.
South Eastern Railway Deploys IsoMat Thermal Technology To Keep Trains On The Tonbridge To Hastings Line Running In Hot Weather
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item on the Network Rail web site.
This is the sub-heading.
A new type of technology is being trialled on the Tonbridge to Hastings railway line to help keep trains running in hotter weather, and more reliable journeys for passengers and freight customers.
These two paragraphs add more details.
The South Eastern Railway has partnered with UK green tech start-up Flint Engineering to combat excessive heat in railway signalling cabinets that can exceed 70°C, with a new patented system that requires no power, maintenance, or internal cabinet modifications, and can be installed in under an hour.
Flint’s innovative IsoMat technology delivers peak temperature reductions of over 21%, on the hottest days, transferring thermal energy thousands of times more efficiently than copper or aluminium alone.
This is one of those ideas, that could be filed under Too Good To Be True.
This picture shows the device in operation.
I can see this device having many uses, in the most surprising places.
National Grid Has Awarded £12bn In HVDC Supply Chain Agreements
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These are the first three paragraphs.
National Grid has completed the award of its High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) civil works supply chain framework, with £12bn worth of agreements confirmed. This announcement marks the third and final stage of our £59bn supply chain framework awards and underlines the commitment to delivering the energy infrastructure needed to support the Great Grid Upgrade and the UK’s energy transition.
A total of six HVDC converter civil works suppliers have been awarded positions on Lot 1 of the Framework Agreement totalling approximately £9.07bn. In addition, three HVDC onshore cable civil works suppliers being awarded places on Lot 2 of the Framework, worth an estimated £3.7bn. The successful HVDC converter civils suppliers are Balfour Beatty, BAM Nuttall, Galliford Try, Laing O’Rourke, Skanska and Taylor Woodrow. The HVDC onshore cable civils Framework has been awarded to Balfour Beatty, Murphy, and VolkerFitzpatrick.
Contracts have been secured for a five-year period, with the potential to extend for a further three years. Both Frameworks cover confirmed and anticipated projects, including Eastern Green Link 4, in partnership with SP Energy Networks and LionLink in partnership with TenneT .
These are a lot of money allocated to projects, that will be delivered in the next few years.
Where’s the consolidated plan for capital expenditure from the Water Industry?
Water is also simpler, than electricity, as you are only dealing with one country. If you go through the paragraphs above, you’ll find TenneT, who do a similar job to National Grid in the Netherlands and parts of Germany.
I also found this advert from Thames Water, in a Southeastern train last week.
Does this indicate that Thames Water has project management problems?
Iceland Is Calling
This was an advert in Bank station, yesterday.

I’ve been to Iceland and it made a good break from hot weather.
There is now a Geothermal Exhibition In Iceland.
I asked Google AI, if you can have a tour of one of the geothermal projects in Cornwall and received this answer.
There are two main deep geothermal projects in Cornwall with public-facing aspects: the United Downs Deep Geothermal Project and the Eden Geothermal Project. While both are operational or nearing completion, direct public tours of the operating power plants themselves aren’t yet a standard offering. Instead, you can visit the Eden Project, which is heated by its geothermal system, and learn about the technology there, or potentially visit the United Downs project site to see the developments.
Hopefully, I’ll be able to see more in a couple of years.
Centrica Enters Into Long Term Natural Gas Sale & Purchase Agreement
The title of this post, is the same as this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading,
Centrica plc today confirmed that its trading arm, Centrica Energy, has entered into a natural gas sale and purchase agreement with US-based Devon Energy Corporation.
This first paragraph adds a few more details.
Under the agreement, Devon Energy will supply 50,000 (MMBtu) per day of natural gas over a 10‑year term starting in 2028. This is equivalent to five LNG cargoes per year. The volumes will be indexed to European gas hub price (TTF). This sale and purchase agreement supports Centrica’s objective of managing market price risk in its LNG portfolio by aligning feed gas pricing with European gas prices whilst providing Devon Energy with international price exposure.
At a first look, it looks a lot of gas.
In Investment In Grain LNG, I talk about Centrica’s purchase of the Grain LNG Terminal from National Grid. But the Grain LNG Terminal comes with several things that Centrica might need for gas from Devon.
- A large amount of gas storage.
- The ability to convert liquid natural gas (LNG) into gas suitable for consumers.
- Space to build more storage if required.
- The ability to store LNG for other companies.
- Two jetties for delivering the LNG to the Grain LNG Terminal.
- The ability to load tankers with LNG, so that it can be sold on to third parties like say the Germans or the Poles.
Centrica also say this about their use of the Grain LNG Terminal in this press release, that describes the purchase of the terminal.
Aligned with Centrica’s strategy of investing in regulated and contracted assets supporting the energy transition, delivering predictable long-term, inflation-linked cash flows, with 100% of capacity contracted until 2029, >70% until 2038 and >50% until 2045.
Centrica have obviously modelled their gas supply and delivery and I believe they have come up with a simple strategy, that will work.
How Will Centrica Use The Gas From The Grain LNG Terminal?
The Wikipedia entry for the Grain LNG Terminal says this about the terminal delivering gas into the gas grid.
The terminal can handle up to 15 million tonnes per annum of LNG, has a storage capacity for one million cubic metres of LNG, and is able to regasify up to 645 GWh per day (58 million cubic metres per day) for delivery into the high pressure gas National Transmission System (NTS).
Note.
- This will be one of the major uses of the gas.
- I wouldn’t be surprised if these capacities will be increased significantly, so that more gas can be stored and processed.
In Investment in Grain LNG, I outlined how I believe that hydrogen and ammonia will be produced for the bunkering of ships on one of busiest sea lanes in Europe, if not the world.
Some LNG will be used to create these zero-carbon fuels.
Some modern ships, also run on natural gas, so I asked Google AI about their operation and received this answer.
Ships can run on natural gas, specifically liquefied natural gas (LNG), by using it as a fuel source in specially designed engines. LNG is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state at -162°C, making it easier to store and transport. This liquid form is then used to power the ship’s engines, either directly or by burning the boil-off gas (BOG) that naturally occurs when LNG warms up.
This means that some LNG could be used to directly fuel these ships.
What Is The Gas Capacity Of The Grain LNG Terminal?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The Grain LNG Terminal, the largest LNG import terminal in Europe, has a storage capacity of 1,000,000 cubic meters (m³) and an annual throughput capacity of 15 million tonnes of LNG. This is equivalent to about 20% of the UK’s total gas demand. The terminal also has the capacity to deliver 25% of the UK’s daily gas demand.
As the space is there, I wouldn’t be surprised to see Centrica increase the capacity of the terminal, as in cold weather, emergency gas for Germany can be delivered quicker from Kent than the United States.
Could The Grain LNG Terminal Accept Gas Deliveries From The United States?
I’m certain that it already does.
Could The Grain LNG Terminal Accept Gas Deliveries From The UK?
If we start extracting gas again from under the seas around the UK, could the Grain LNG Terminal be used to store it?
Yes, but it would have to be liquified first.
It would be more energy efficient to process the extracted gas, so it could be used directly and gasify enough gas at Grain LNG Terminal from storage to make up any shortfall.
Conclusion
Centrica have done some very deep joined up thinking, by doing a long term gas deal and the Grain LNG Terminal purchase so that they have the gas to supply and somewhere to keep it, until it is needed.
Investment in Grain LNG
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This sub-heading outlines the deal.
Centrica plc (the “Company”, “Centrica”) is pleased to announce the acquisition of the Isle of Grain liquified natural gas terminal (“Grain LNG”) in partnership1 with Energy Capital Partners LLP (“ECP”) from National Grid group (“National Grid”) for an enterprise value of £1.5 billion. After taking into account approximately £1.1 billion of new non-recourse project finance debt, Centrica’s 50% share of the equity investment is approximately £200 million.
The press release lists these key points.
- Grain LNG delivers vital energy security for the UK, providing critical LNG import/export, regasification and rapid response gas storage capacity to balance the energy system.
- Aligned with Centrica’s strategy of investing in regulated and contracted assets supporting the energy transition, delivering predictable long-term, inflation-linked cash flows, with 100% of capacity contracted until 2029, >70% until 2038 and >50% until 2045.
- Opportunities for efficiencies to create additional near-term value, and future development options including a combined heat and power plant, bunkering, hydrogen and ammonia.
- Highly efficient funding structure, with Centrica’s equity investment of approximately £200 million alongside non-recourse project financing.
- Strong life of asset returns aligned with Centrica’s financial framework, with an expected unlevered IRR2 of around 9% and an equity IRR2 of around 14%+
Underpins delivery of £1.6 billion end-2028 EBITDA target3 – Centrica’s share of EBITDA expected to be approximately £100 million per annum and cash distributions expected to be around £20 million on average per annum for 2026-2028, representing an attractive yield on Centrica’s equity investment - Partnership with ECP (part of Bridgepoint Group plc), one of the largest private owners of natural gas generation and infrastructure assets in the U.S. with direct experience in supporting grid reliability.
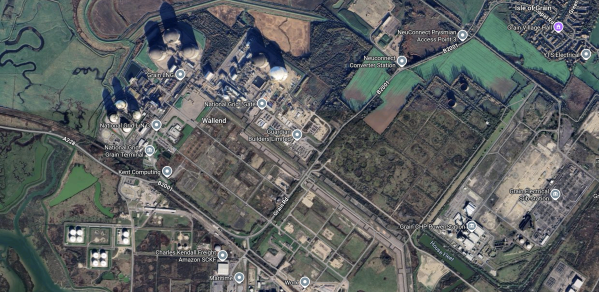
This Google Map shows the various energy assets on the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- It appears that works for the 1, 400 MW NeuConnect interconnector to Wilhelmshaven in Germany, are taking place in the North-East corner of the map.
- Grain CHP powerstation is a 1,275MW CCGT power station, which is owned by German company; Uniper, that is in the South-East corner of the map, which can also supply up to 340MW of heat energy recovered from the steam condensation to run the vapourisers in the nearby liquefied natural gas terminal.
- The Grain LNG terminal is at the Western side of the map.
- In the Thames Estuary to the East of the Isle of Grain, I estimate that there are about 1,500 MW of wind turbines.
I find it interesting that two of the assets are German owned.
I have some thoughts.
It Is A Large Site With Space For Expansion
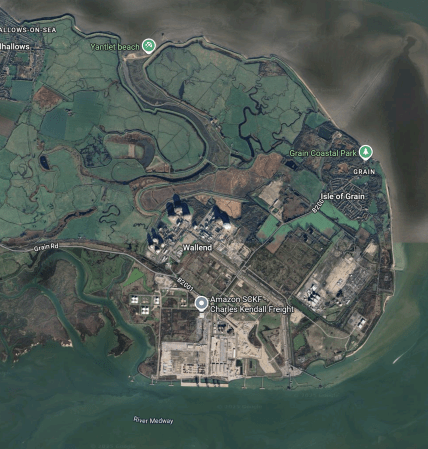
This Google Map shows the whole of the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- The Grain LNG terminal is around the label Wallend.
- The River Medway runs East-West at the bottom of the map.
- Gas tankers deliver and take on gas at jetties on the North Bank of the Medway.
There could be space to expand the terminal, if the RSPB would allow it.
As an example, I asked Google AI, if peregrine falcons nest on chemical plants and got this reply.
Yes, peregrine falcons do nest on chemical plants. They have adapted to using various urban and industrial structures, including chemical plants, for nesting. This is particularly true in areas where natural cliff habitats are scarce.
Peregrine falcons are known for their adaptability, and their population has seen a resurgence in recent decades, partly due to their ability to utilize man-made structures. These structures often mimic their natural cliffside nesting
Cliffs do seem scarce on the Isle of Grain. I also asked Google AI, if peregrine falcons ate small rodents, as several chemical and other plants, where I’ve worked, had a rodent problem. One plant had a cat problem, as there had been so many rats. This was the reply.
Yes, peregrine falcons do eat small rodents, though they primarily consume birds. While their diet mainly consists of other birds like pigeons, doves, and waterfowl, they will also hunt and eat small mammals, including rodents such as mice, rats, and voles. They are opportunistic hunters and will take advantage of readily available prey, including insects, amphibians, and even fish.
I’m sure if Centrica wanted to expand, they’d employ the best experts.
Who Are ECP?
One of the key points of the press release is that this deal is a partnership with ECP (part of Bridgepoint Group plc), one of the largest private owners of natural gas generation and infrastructure assets in the U.S. with direct experience in supporting grid reliability.
The Wikipedia entry for ECP or Energy Capital Partners has this first section.
Energy Capital Partners Management, LP (ECP) is an American investment firm headquartered in Summit, New Jersey. It focuses on investments in the energy sector. The firm has additional offices in New York City, Houston, San Diego, Fort Lauderdale and Seoul.
In August 2024, ECP merged with Bridgepoint Group to form a private assets investment platform.
The Wikipedia entry for the Bridgepoint Group has this first paragraph.
Bridgepoint Group plc is a British private investment company listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
The company had started as part of NatWest.
Are The Germans Going To Take Away Some Of Our Electricity?
Consider.
- Germany has a big need to replace Russian gas and indigenous coal, and to decarbonise.
- Neuconnect is a 1.4 GW interconnector between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven in Germany. It is scheduled to be completed in 2028.
- The Grain CHP powerstation is a 1,275MW CCGT power station, which is owned by German company; Uniper, could almost keep NeuConnect working at full power on its own.
- I said earlier, in the Thames Estuary to the East of the Isle of Grain, I estimate that there are about 1,500 MW of wind turbines. One of which is part German-owned.
The Germans are also building a large electrolyser at Wilhelshaven, which is described by Google AI like this.
The Wilhelmshaven Green Energy Hub will initially feature a 500MW electrolyzer, with plans to potentially expand to 1GW, according to Energy Monitor. The hub, a joint project between Tree Energy Solutions (TES) and EWE, aims to produce green hydrogen using renewable energy sources like offshore wind. The 500MW electrolyzer is scheduled to be operational by 2028.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see that the Wilhelmshaven electrolyser were to be powered by British-generated electricity flowing down NeuConnect.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include A Combined Heat And Power Plant
This objective was set in one of the key points.
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Grain LNG Terminal.
Grain LNG Terminal is a Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) terminal on the Isle of Grain, 37 miles (60 km) east of London. It has facilities for the offloading and reloading of LNG from ships at two jetties on the River Medway; for storing and blending LNG; for truck loading; and regasifying and blending natural gas to meet UK specifications. The terminal can handle up to 15 million tonnes per annum of LNG, has a storage capacity for one million cubic metres of LNG, and is able to regasify up to 645 GWh per day (58 million cubic metres per day) for delivery into the high pressure gas National Transmission System (NTS). The facility is owned and operated by National Grid Grain LNG Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of National Grid.
Note.
- This paragraph was written before the Centrica takeover.
- The terminal also converts liquid natural gas into gas to be distributed around the UK.
The heat needed to convert the liquid natural gas to gas is provided by the Grain CHP power station.
- Currently 340 MW of heat is provided.
- If the Grain LNG terminal is expanded, it will probably need more heat.
I can see Centrica building a combined heat and power (CHP) power station, that can be expanded to meet the current and future needs of gasification at the Grain LNG terminal.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see the CHP power station fitted with carbon capture, as Kent is surely one county, where carbon dioxide can be used in food production, so we can generate our carbon dioxide and eat it.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Hydrogen
This objective was set in one of the key points.
Consider.
- Centrica are an investor in HiiROC, who have a unique method of generating affordable zero-carbon hydrogen called thermal plasma electrolysis, which uses a fifth of the electricity, that traditional electrolysis does.
- HiiROC can use natural gas as a feedstock. Centrica won’t be short of that at Grain.
- There is space to build a large HiiROC system at the Isle of Grain site.
- The hydrogen could be taken away by tanker ships.
Like the electricity , which will use the 450 mile NeuConnect interconnector, the hydrogen could even be exported to Wilhelmshaven in Germany by pipeline.
Wilhelmshaven is being setup to be a major German hub to both generate, import and distribute hydrogen.
I asked Google AI, how much hydrogen a GWh would produce and received this answer.
A GWh of electricity can produce approximately 20-22 tonnes of hydrogen through electrolysis, depending on the efficiency of the electrolyzer. Modern commercial electrolyzers operate at an efficiency of roughly 70-80%, meaning they require about 50-55 kWh of electricity to produce 1 kg of hydrogen. A GWh (1 gigawatt-hour) is equal to 1,000,000 kWh, and 1 tonne of hydrogen contains roughly 33.33 MWh of energy.
As it is claimed on the web that HiiROC is five times more efficient than traditional electrolysis, it could need around 10-11 kWh to produce one kg. of hydrogen.
1 GWh would produce between 90-100 tonnes of hydrogen.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Ammonia
This objective was set in one of the key points.
I asked Google AI if ammonia can be produced from hydrogen and received this answer.
Yes, ammonia (NH3) can be produced from hydrogen (H2) through a process called the Haber-Bosch process. This process involves combining hydrogen with nitrogen (N2) from the air, under high temperature and pressure, in the presence of a catalyst.
Ammonia has a large number of uses, including making fertiliser and the powering of large ships.
I asked Google AI, if there are small Haber-Bosch processes to make ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen and received this answer.
Yes, there are efforts to develop smaller-scale Haber-Bosch processes for ammonia production. While the traditional Haber-Bosch process is typically associated with large industrial plants, research and development are exploring ways to adapt it for smaller, distributed production, particularly for localized fertilizer or fuel applications.
I wondered if Centrica are involved in the efforts to develop smaller-scale Haber-Bosch processes for ammonia production.
Google AI gave me this quick answer.
Centrica is involved in research related to the Haber-Bosch process, particularly in the context of transitioning to a low-carbon energy future. They are exploring how to adapt the Haber-Bosch process, which is crucial for fertilizer production but also a significant source of CO2 emissions, to utilize renewable energy sources. This includes investigating the use of green hydrogen produced from water electrolysis and renewable electricity. Centrica is also involved in research related to using ammonia as a fuel, including potentially for power generation
That looks to be a very positive answer. Especially, as local low-carbon fertiliser production could be a very powerful concept.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Bunkering
This objective was set in one of the key points.
Bunkering is the process of refuelling ships.
I didn’t know much about bunkering, when I started to read Centrica’s press release, but the Wikipedia entry, was a good way to get some information.
This section in the Wikipedia entry is entitled Two Types Of Bunkering, where this is said.
The two most common types of bunkering procedure at sea are “ship to ship bunkering” (STSB), in which one ship acts as a terminal, while the other moors. The second type is “stern line bunkering” (SLB), which is the easiest method of transferring oil but can be risky during bad weather.
Over the years, I have found, that two zero-carbon fuels are under development, for powering ships; hydrogen and ammonia. Others are developing ships powered by naturalo gas.
I asked Google AI if hydrogen can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, hydrogen can power ships. It can be used as a fuel for fuel cells, which generate electricity to power the ship’s propulsion and other systems, or it can be burned in modified combustion engines. Hydrogen offers a zero-emission solution for shipping, with water vapor being the only byproduct when used in fuel cells.
Google AI also told me this.
The world’s first hydrogen-powered cruise ship, the “Viking Libra”, is currently under construction and is scheduled for delivery in late 2026. This innovative vessel, a collaboration between Viking Cruises and Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri, will utilize hydrogen for both propulsion and electricity generation, aiming for zero-emission operation.
I also asked Google AI if ammonia can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, ammonia can be used to power ships and is considered a promising alternative fuel for the maritime industry. Several companies and organizations are actively developing ammonia-powered ship designs and technologies. While challenges remain, particularly around safety and infrastructure, ammonia is seen as a key potential fuel for decarbonizing shipping.
Finally, I asked I asked Google AI if natural gas can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, ships can be powered by natural gas, specifically in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG). LNG is increasingly used as a marine fuel, offering environmental benefits over traditional fuels like diesel.
It would seem to be a case of you pays your money and makes a choice between one of four technologies; ammonia, hydrogen fuel-cell, hydrogen-ICE and LNG.
I looks to me, that if Centrica provide bunkering services for ships, they have the means to cover most of the market by providing hydrogen and ammonia, in addition to natural gas.
Although, I don’t know much about bunkering, I do feel that the two current methods, that work for oil, could be made to work for these fuels.
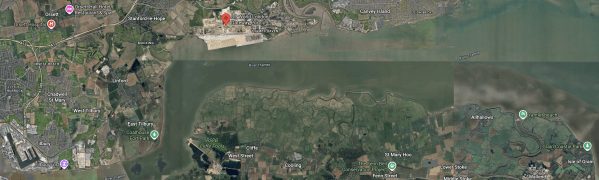
This Google Map shows the Thames Estuary.
Note.
- The Port of Tilbury is in the South-West corner of the map.
- London Gateway is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Isle of Grain is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Other ports between Tilbury and the Isle of Grain include Barking, Dagenham, Dartford, Erith, Greenwich, Northfleet, Purfleet, Silvertown and Thurrock.
There was never a more true phrase than – “Location, Location and Location”. And the Isle of Grain would appear to be in the right place to send out a bunkering tanker to a passing ship, that was calling at a port in London or just passing through the Strait of Dover.
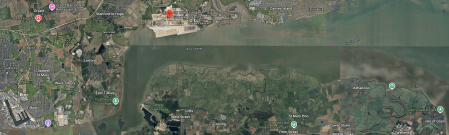
This Google Map shows the Thames between London Gateway and the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- London Gateway is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Isle of Grain is in the South-East corner of the map.
It seems to me, that a refuelling philosophy could easily be worked out.
How Large is The Bunkering Market?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The world bunker fuel market is a multi-billion dollar industry, with the market size valued at USD 150.93 billion in 2023. It is projected to reach USD 242.29 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% according to SkyQuest Technology. In terms of volume, the global bunker demand was estimated at 233.1 million metric tons in 2023 according to the IMO.
The market is not small!
Demonstration Of Commercial-Size Hydrogen Module
The title of this post, is the same as that of news item on the SunHydrogen web site.
This is the sub-heading.
SunHydrogen has successfully demonstrated live operation of its commercial-size 1.92m² hydrogen module, producing renewable hydrogen using only sunlight and water. This major milestone showcases the scalability and off-grid potential of the company’s renewable hydrogen production technology.
These first three paragraphs add more details.
SunHydrogen, developer of a breakthrough technology to produce renewable hydrogen using sunlight and water, today announced the successful live operation of its 1.92 m² (20.7 sq. ft.) hydrogen module. Conducted in an open prototype housing, the demonstration marks a pivotal milestone in the company’s path toward commercial-scale, renewable hydrogen production.
The 1.92m² hydrogen module, which uses only sunlight and water to produce hydrogen, represents the most advanced version of SunHydrogen’s proprietary hydrogen production technology. Engineered to operate independent of the electrical grid, the system integrates solar collection and hydrogen production into a single unit, offering a modular and scalable solution for distributed renewable hydrogen.
“This successful demonstration of the commercial-size reactor underscores the progress we’ve made in bringing our technology out of the lab and into the real world,” said Tim Young, CEO of SunHydrogen.
There is a video of this demonstration.
On their home page, there is a section called A Breakthrough In Clean Energy, where this is said.
SunHydrogen has developed a breakthrough technology to produce renewable hydrogen using sunlight and any source of water.
By optimizing the science of water electrolysis at the nano-level, our low-cost photoelectrochemical technology uses sunlight to separate hydrogen from water, making the process truly green from start to finish.
I will accept their word that it is truly green, but it is truly unique in that it doesn’t appear to use only sunlight to generate hydrogen.
US Floating Wind Platform Developer Issues RFI To Fabricators Worldwide
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Aikido Technologies, which recently secured a spot at a Norwegian offshore demo site, has released an RFI for its 15 MW ‘AO60’ floating wind platform to offshore wind fabricators.
These are the first four paragraphs which add more details.
The California-based floating wind foundation developer said on social media that it had issued the RFI to more than ten “top-tier offshore wind fabricators from around the world”.
The RFI has been released in three separate packages, each tailored to a specific type of facility: one for standard offshore steel shops, one for tubular/jacket yards, and one for monopile/tower facilities.
“This is how we can build 1, 50 or 100 of these units with existing fabrication capabilities, with components that can be easily transported around the world for final assembly at a local port. No need for custom yards, custom vessels or custom ports”, Aikido Technologies said.
In May 2025, the company was allocated a slot for its AO60 platform at the Marine Energy Test Centre (METCentre) in Norway, where Aikido will deploy what it says is a first-of-its-kind 15 MW demonstration project.
As someone, who wrote project management computer systems for thirty years, I like Aikido’s plans and feel they would be well suited to the UK, where we have quite a few local ports, that would appear suitable for final assembly of the A060 platforms.
In Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project, I describe the expansion of the Port of Great Yarmouth.
These two paragraphs describe the work to be done.
Peel Ports said it would invest between £50m and £60m in Great Yarmouth’s Outer Harbour by developing the southern terminal, creating a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
Port director Richard Goffin said the construction work, which is set to begin in 2026, would “complete” the port as laid out in a business case in the early 2000s.
This image from Peel Ports Group shows how the Port of Great Yarmouth will look after the the proposed development.
As the Port of Great Yarmouth has a depth of ten metres it could be an ideal base for the assembly and maintenance of floating wind turbines.