FirstGroup Applies To Run New London To Sheffield Rail Service
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from First Group.
These four paragraphs outline FirstGroup’s initial plans.
FirstGroup plc, the leading private sector transport operator, has today submitted the first phase of an application for a new open access rail service between London and Sheffield to the Office of Rail and Road (ORR).
FirstGroup plans to expand its open access rail operations as part of its award-winning Hull Trains business, building on their successful existing service which has transformed long-distance connectivity between Hull and London.
FirstGroup’s new proposals comprise two return journeys a day from London King’s Cross, calling at Retford, Worksop, Woodhouse and Sheffield, and the company aims to provide a faster link between London and Sheffield than alternative services. Almost three quarters of trips between London and Sheffield are currently made by car, with a further 9% of trips made by coach, and a competitively priced new rail offering will help stimulate a shift in transport mode of choice from road to rail.
The new proposed route will give Sheffield the first regular service from London King’s Cross since 1968 and will also give Worksop in Nottinghamshire the first regular direct London trains in decades. FirstGroup estimates there are 350,000 people in the Worksop and Woodhouse catchment areas who will have direct rail access to London because of these proposals. A sizeable number of rail users in these areas currently drive to Doncaster station to pick up faster services to London rather than travelling via Sheffield, and a convenient rail offering from local stations will also help to reduce the number of these car journeys.
Note.
- The press release says this is only the first phase.
- It appears to be an extension of Hull Trains.
- Comments on a news story based on the press release in The Times, have been generally positive.
These are my thoughts.
The Two Routes Are Similar
Consider.
- Beverley is 44.3 miles from the electrified East Coast Main Line at Temple Hirst Junction.
- Hull is 36.1 miles from the electrified East Coast Main Line at Temple Hirst Junction.
- Sheffield is 23.5 miles from the electrified East Coast Main Line at Retford station.
- There is no electrification at Beverley, Hull or Sheffield.
Note.
- Trains must be capable of having a range sufficient to go from the East Coast Main Line to the destination and back again.
- It is slightly surprising that Sheffield station is closest to the electrification of the East Coast Main Line.
- Hull Train’s electro-diesel Class 802 trains regularly handle the 88.6 miles to Beverley and back.
It does look like an appropriate number of Class 802 trains could handle Hull Trains current and future services to Beverley, Hull and Sheffield.
Hull Trains Need Ten-Car Trains
Consider.
- In Ten-Car Hull Trains, I show some details of Hull Trains using a pair of five-car trains.
- I’ve since seen ten-car Hull Trains regularly.
- There were two ten-car services on the 29th December 2023 between London King’s Cross and Hull.
Hull Trains must procure enough trains for all possible scenarios.
Intermediate Stations Of The Two Routes
Intermediate stations are.
- Going North from London King’s Cross to Hull, trains call at Stevenage (limited), Grantham, Retford, Doncaster, Selby, Howden and Brough.
- Going North from London King’s Cross to Sheffield, trains call at Retford, Worksop and Woodhouse.
There are only a small number of stops on the Sheffield service. Is this to reduce the journey time as much as possible?
What Will Be The Time Of The London King’s Cross And Sheffield Service?
Consider.
- Non-stop trains take 82 minutes between London King’s Cross and Retford, which is 138.6 miles, so it’s an average speed of 101.4 mph.
- Woolmer Green and Retford are 111.7 miles and will in a couple of years, be digitally signalled.
- Non-stop trains take 66 minutes between Woolmer Green and Retford, which is an average speed of 112 mph.
- I have found a direct Retford and Sheffield train, that takes 31 minutes for the 23.5 miles with six stops, which is an average speed of 45 mph.
- The Retford and Sheffield section has a mostly 60 mph maximum speed.
I can now build a table of times between King’s Cross and Retford based on the average speed North of Woolmer Green.
- 125 mph – 72 minutes
- 130 mph – 70 minutes
- 135 mph – 68 minutes
- 140 mph – 66 minutes
Note.
- Getting a high average speed using the power of digital signalling can save several minutes.
- I have measured an InterCity 125 averaging 125 mph on that section.
I can now build a table of times between Retford and Sheffield based on the average speed.
- 45 mph – 31 minutes
- 50 mph – 28 minutes
- 60 mph – 24 minutes
- 70 mph – 20 minutes
- 80 mph – 18 minutes
Note.
- The planned service is expected to stop only twice after Retford, so if we take off two minutes for each of the four stops not taken, this could reduce the time between Retford and Sheffield by 8 minutes.
- There will be a couple of minutes to add for the stop at Retford.
- I feel a typical journey with 125 mph to Retford, 50 mph to Sheffield, could take 94 minutes
- Currently, the fastest London St. Pancras to Sheffield take around 116-118 minutes.
Hull Trains new service could save 22-24 minutes on the current service.
I also feel a fast journey could involve 130 mph to Retford, 60 mph to Sheffield, could take 88 minutes.
Hull Trains new service could save a few minutes over half-an-hour.
Could The Time Of The London King’s Cross And Sheffield Service Be Under 90 Minutes?
I reckon the following is possible.
- After the digital signalling is completed between King’s Cross and Retford, I suspect that a 135 mph average speed can be maintained between Woolmer Green and Retford. This would mean that a King’s Cross and Retford time of 68 minutes would be possible.
- If Network Rail improve the track between Retford and Sheffield, I believe that a 70 mph average could be achieved on the Retford and Sheffield section. This would mean that a Retford and Sheffield time of 20 minutes would be possible.
- I would expect at least six minutes would be saved by missing stops.
This gives a time of 82 minutes between London King’s Cross and Sheffield.
In Anxiety Over HS2 Eastern Leg Future, I said that High Speed Two’s promised London and Sheffield time via a dedicated track would be 87 minutes.
It looks to me that running under full digital signalling on the East Coast Main Line, Hull Trains can beat the HS2 time.
Could Hitachi’s Battery-Electric Trains Handle The Routes?
This page on the Hitachi web site is entitled Intercity Battery Trains.
This is the sub-heading
Accelerate the decarbonisation of intercity rail with batteries.
These paragraphs outline the philosophy of the design of the trains.
A quick and easy application of battery technology is to install it on existing or future Hitachi intercity trains. Hitachi Rail’s modular design means this can be done without the need to re-engineer or rebuild the train and return them to service as quickly as possible for passengers.
Replacing one diesel engine with just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%. Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance.
Wouldn’t it be great, if we could take the diesel engine out of our cars and replace it with an electric power pack?
Paul Daniels would’ve classed it as engineering magic.
But it’s an old engineer’s trick.
As a fifteen year old, I spent time in a rolling mill, building and fitting replacement control systems on large machines. Transistors were used to replace electronic valves and relays.
It’s certainly possible to create a battery pack, that is plug-compatible with an existing diesel generator, that responds to the same control inputs and gives the same outputs.
At the extreme end of this technology, there would be no need to change any of the train’s software.
In The Data Sheet For Hitachi Battery Electric Trains, these were my conclusions for the performance.
- The battery pack has a capacity of 750 kWh.
- A five-car train needs three battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- A nine-car train needs five battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- The maximum range of a five-car train with three batteries is 117 miles.
- The maximum range of a nine-car train with five batteries is 121 miles.
As the East Coast Main Line to Beverley is a round trip is 88.6 miles, I suspect that Hull Trains’s five-car Class 802 trains will need to be fitted with a full-complement of three batteries.
Will Hull Trains Have An Identical Fleet Of Trains?
An identical fleet must have advantages for train staff, maintenance staff and above all passengers.
I believe FirstGroup have two choices.
- They buy an appropriately-sized batch of identical Class 802 trains.
- They convert their current fleet to battery-electric operation and buy an appropriately-sized batch of identical new trains.
Note.
- The second option means that they fully-decarbonise Hull Trains.
- Neither option would need any new infrastructure.
- I feel this means that this order is more likely to go to Hitachi.
It’ll probably all come down to the accountants.
Retford Station
This OpenRailwayMap shows the tracks around Retford station.
Note.
- The red tracks are electrified and are the East Coast Main Line.
- The black ones aren’t electrified.
- Doncaster is to the North.
- The black line to the East goes to Lincoln
- The black line to the West goes to Sheffield
- The red line going South-East goes to Peterborough and London.
The unusual loop allows trains to connect from one direction to another.
This second OpenRailwayMap shows the tracks in more detail.
Note.
- As before red lines are electrified and black ones aren’t
- Platforms 1 and 2 are on the East Coast Main Line.
- Platforms 3 and 4 are on the Sheffield and Lincoln Line.
This third OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms in more detail.
Note.
- The yellow tracks are the 125 mph fast lines of the East Coast Main Line.
- The light blue tracks are the 40 mph relief lines of the East Coast Main Line.
- Northbound tracks are to the left of each pair of lines.
- The dark blue track is the 10 mph chord that connects the Northbound relief line of the East Coast Main Line to the Sheffield and Lincoln Line.
- Platform 1 is on the Southbound relief line.
- Platform 2 is on the Northbound relief line.
- Unusually, both platforms are on the same side of the line.
- In The Lengths Of Hitachi Class 800/801/802 Trains, I state that the full length of an InterCity 225 train is 245.2 metres.
- I suspect that both platforms can accommodate a full length InterCity 225, as the trains have been calling at Retford since the 1980s.
I doubt Retford station has any problem accommodating a pair of Class 802 trains, which it does regularly.
How Do Northbound Trains Go To Sheffield From Retford Station?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the tracks to the South of Retford station in detail.
Note.
- The yellow tracks are the 125 mph fast lines of the East Coast Main Line.
- The light blue tracks are the 40 mph relief lines of the East Coast Main Line.
- Northbound tracks are to the left of each pair of lines.
Trains needing to stop in Retford station will need to cross to the Northbound relief line to enter Platform 2 at Retford station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the curve that connects Platform 2 at Retford station to the Sheffield and Lincoln Line to Sheffield.
Note.
- The green tracks are the 60 mph Sheffield and Lincoln Line.
- Sheffield is to the West.
- The blue tracks are the curve that connects Platform 2 in Retford station to the Sheffield and Lincoln Line.
- There appears to be a grade-separated junction, where the two lines join to the West of Retford station.
A Northbound train to Sheffield will take curve and then join the line to Sheffield.
How Do Southbound Trains Go From Sheffield Through Retford Station?
I suspect trains do the opposite from a train going to Sheffield.
The train takes the curve and then stops in Platform 2 facing South.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the tracks to the South of Retford station in detail.
When the train is cleared by the signals to go South, it will leave Retford station going South on the Northbound relief line.
Note that on the map there are two crossovers, which the train will take to get on the Southbound fast line for Newark and London.
As a Control Engineer, I suspect this is the sort of manoeuvre, that modern digital signalling will make slicker and safer.
How Do Northbound Trains Go To Hull From Retford Station?
On leaving the station, the train will continue along the relief line until it merges with the Northbound fast line for Doncaster.
This is exactly as any Northbound train stopping at Retford does now.
How Do Southbound Trains Go From Hull Through Retford Station?
Currently, trains from Hull stop in Platform 1 on their way to London.
- Trains needing to stop in Retford station will need to cross to the Southbound relief line to enter Platform 1 at Retford station.
- When the train is cleared by the signals to go South, it will leave Retford station going South on the Southbound relief line.
- The Southbound relief line joins the Southbound fast line to the South of the station.
This is exactly as any Southbound train stopping at Retford does now.
Could A Hull And A Sheffield Service Run As A Pair And Split And Join At Retford Station?
Consider.
- Class 802 trains, as used by Hull Trains are designed to be run as a pair of trains, with easy coupling and uncoupling between the two trains.
- Hull Trains regularly run services as a pair of Class 802 trains.
- A pair of trains could leave King’s Cross. They would then split at a convenient station, after which the two trains go to different destinations.
- There are advantages with respect to infrastructure charges.
I feel that Hull Trains two services to Sheffield and Hull/Beverley could work as a pair.
- A pair of trains could leave King’s Cross.
- At Retford station they would split, with one train going to Hull and the other to Sheffield.
Coming South they would join at Retford.
How Would Splitting Of A Hull And Sheffield Service Be Performed At Retford Station?
The procedure would be something like this.
- As the pair of train is stopping in Retford station, it would use the relief line to enter Platform 2.
- It would stop in Platform 2.
- The trains would be uncoupled.
- The front train would go to its destination.
- The rear train would go to its destination.
Note.
- As the track to Doncaster and Hull is faster, the front train should probably be for Hull.
- Platform 2 is electrified, so the Sheffield train could top up its batteries .
- The Sheffield train could lower its pantograph.
Uncoupling takes about two minutes.
How Would Joining Of A Hull And Sheffield Service Be Performed At Retford Station?
Consider.
- Joining would have to be performed in Platform 2, as there is no route for a train from Sheffield to access Platform 1.
- North of Retford station there are two convenient crossovers, to allow a train to cross to the Northbound relief line. There are also a couple of loops, where trains could wait.
- As this is coal-mining country, perhaps, they were part of a freight route between Sheffield and Doncaster?
But this infrastructure would allow, a train from Hull to access Platform 2 at Retford station.
As the Sheffield train can easily access Platform 2, the two trains could meet in Platform 2 and then be joined together for a run to London.
Is There A Problem With Splitting And Joining Of the Hull And Sheffield Services?
Earlier, I said these were the stops of the two services.
- Going North from London King’s Cross to Hull, trains call at Stevenage (limited), Grantham, Retford, Doncaster, Selby, Howden and Brough.
- Going North from London King’s Cross to Sheffield, trains call at Retford, Worksop and Woodhouse.
Surely, if the trains were travelling as a pair, they would need to stop at the same stations to the South of Retford.
But modern digital signalling will allow trains to run closer together, so perhaps this would be the procedure going North.
- The two trains start in the same platform at King’s Cross, with the Sheffield train in front of the Hull train.
- The two trains leave King’s Cross a safe number of minutes apart.
- At its Stevenage and Grantham stops, the Hull train will tend to increase the distance between the two trains.
- The Sheffield train would stop in Platform 2 at Retford station, so that space is left for the Hull train.
- The Hull train will stop behind the Sheffield train in Platform 2 at Retford station.
- The Sheffield train will leave when ready.
- The Hull train will leave when ready.
And this would be the procedure going South.
- The train from Sheffield would line up in Platform 2 at Retford station.
- The train from Hull would line up in Platform 1 at Retford station.
- The train from Sheffield would leave when everything is ready and the train is cleared by the signalling system.
- The train from Hull would leave a safe number of minutes behind the train from Sheffield.
- At its Grantham and Stevenage stops, the Hull train will tend to increase the distance between the two trains.
- The trains could share a platform at King’s Cross.
The digital signalling and the driver’s Mark 1 eyeballs will keep the Hull train, a safe distance behind the faster Sheffield train.
The Capacity Of The Lincoln And Sheffield Line
Looking at the Sheffield and Lincoln Line, it has only an hourly train, that calls at Darnall, Woodhouse, Kiverton Park, Kiverton Bridge, Shireoaks and Worksop between Retford and Sheffield.
- I would suspect that there is enough spare capacity for Hull Trains to run a one train per two hours (tp2h) service between London King’s Cross and Sheffield.
- If LNER feel that a 1 tp2h frequency is viable for Harrogate, Lincoln and other places, surely Hull and East Sheffield could support a similar service from King’s Cross.
If the services could be run by battery-electric trains, capable of running at 140 mph on the East Coast Main Line and giving times of ninety minutes to Sheffield, this could be a success.
Could Woodhouse Station Become A Transport Hub?
This Google Map shows Woodhouse station.
Note.
- It is certainly surrounded by a lot of houses.
- Could it be provided with car-parking?
Although, as this picture shows it is not blessed with lots of facilities.
But.
- The station is in an area, which Sheffield want to develop.
- The Advanced Manufacturing Centre is nearby.
- There are aspirations to run a tram-train between Sheffield and Chesterfield via Darnall, Woodhouse and Barrow Hill stations.
- The station could be on the tram-train route to Stocksbridge, that I wrote about in Reopening The Don Valley Section Of The Former Woodhead Line Between Stocksbridge and Sheffield Victoria To Passenger Services.
Woodhouse station could be an interchange or it could become something bigger like a hub station.
How Many Sheffield Services Per Day Could Be Run?
If the Hull and Sheffield trains run as a flight under control of the digital signalling, this will mean that every Hull train can be paired with a Sheffield train.
- There are five trains per day (tpd) to and from Hull and two to and from Beverley.
- It seems a maximum of one tpd in both directions can be a ten-car train.
- Two five-car trains could fit in a platform at King’s Cross.
I suspect that the maximum number of trains per day to and from Sheffield is the same as for Hull. i.e. seven tpd.
But there is no reason, if they have enough trains and paths are available, that Hull Trains couldn’t add extra services to both destinations.
Onward From Sheffield
Several of those, who have commented on the new service have suggested that the service could go further than Sheffield, with Manchester and Leeds being given specific mentions.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms at the Northern end of Sheffield station.
Note.
- The pink tracks at the East are the Sheffield Supertram.
- Trains to and from Barnsley, Huddersfield, Hull, Leeds, Lincoln and Retford access the station from the Northern end.
- Trains to and from Chesterfield, Derby, London, Manchester and Stockport access the station from the Southern end.
- The tracks in Sheffield station are numbered 1 to 8 from the West.
- There are five through platforms. 1, 2, 5, 6 and 8 and two bay platforms at either end.
- An extension of the service to Manchester via the Hope Valley Line, could go straight through the station.
- An extension of the service to Barnsley, Huddersfield or Leeds, would mean the train reversing at Sheffield.
It looks like an extension to Manchester Piccadilly over the recently upgraded Hope Valley Line would be the easiest extension. But would Avanti West Coast, who have FirstGroup as a shareholder want the competition?
Recently, it has been announced that the Penistone Line to Barnsley and Huddersfield will be upgraded to accept two trains per hour (tph) and allow faster running.
Because Sheffield could be around eighty minutes from London, there could be some smart times to and from the capital.
- Meadowhall in 90 minutes
- Barnsley in 112 minutes.
- Huddersfield in 140 minutes.
Huddersfield could be almost twenty minutes faster than the route via Leeds.
Comments From The Times
These are some readers comments from The Times.
- Hope the prices are competitive with LNER. I rarely go to London from Chesterfield with EMR as they’re so expensive. LNER from Newark is much cheaper but a service from Worksop for me would be perfect.
- Excellent News in so many ways. I hope it really takes off which could help ease the congestion on the M1 and also thin out overcrowding on busy LNER services. It really does deserve to succeed.
- This is excellent news. The Lumo service has been a game changer for me and those living in the north east.
The public seem in favour.
Conclusion
I really like this proposal from FirstGroup.
- It has the possibility to provide Sheffield with a fast train link to London.
- It could run about six trains per day.
- It will be faster than High Speed Two was proposed.
It could be the first service of High Speed Yorkshire.
New LNER Fleet To Have Joint Line Capability
The title of this post, is the same as that of an article in the January 2024 edition of Modern Railways.
This is the text of the article.
LNER’s new fleet of CAF tri-mode trains, for which an order was confirmed in November, has been specified with the capability to operate via the Joint Line via Spalding and Lincoln in case of closures on the East Coast Main Line between Peterborough and Doncaster.
CAF will supply 10×10-car trains with overhead electric, battery and diesel capability, financed by Porterbrook. The inclusion of diesel engines as part of the winning bid, rather than a straightforward battery-electric unit, has surprised some observers, but LNER’s specification was that the fleet should have sufficient self-powered capability to cover the length of the joint line, which is approximately 90 miles. This is currently to be considered to be beyond the scope of battery-power alone, although as the technology evolves diesel engines could be replaced by batteries. The configuration of diesel engines and batteries within the sets has yet to be decided.
LNER frequently uses the Joint Line as a diversionary route, both during planned engineering work and at times of disruption, but only its bi-mode Azumas are currently able to traverse it under their own power (electric sets have been hauled by a diesel locomotive, but this is now a very rare occurrence). The new CAF fleet will replace the InterCity 225 electric fleet, and the self-power capability will provide valuable resilience to LNER to divert via non-electrified routes.
While the ‘225s’ are currently confined to services between King’s Cross and Leeds/York, if the enhanced December 2024 timetable goes ahead as currently planned (see story above) they will operate north of York once again on some of the hourly services which will terminate at Newcastle. However, LNER is having to limit the use of the sets before the Class 91 locomotives and Mk 4 coaches come due for major overhauls: the decision to retain 12 locos and eight rakes of coaches was based on the intended timescale for replacing the fleet at the time, but confirming the order for the new CAF tri-modes has taken longer than anticipated, largely due to delays in receiving Government approval to place the order.
This article has got me thinking.
The InterCity225 Trains Need Replacing Urgently
The Modern Railways article states that the need to replace the InterCity 225s is getting urgent, as more than the Azumas will be needed for the December 2024 timetable and the InterCity 225s are getting to the end of their economic life.
As LNER have been doing reasonably well lately, a cock-up caused by lack of trains at Christmas 2024 would be the last thing they need.
Currently, LNER have enough Mark 4 coaches for eight trains, so ordering ten new CAF tri-mode trains will allow for a small amount of extra services.
The CAF tri-mode trains were only ordered in November 2023, so getting them delivered for December 2024 would be tight.
As I write this on the 31st December 2023, trains from King’s Cross to Leeds included.
- 5 x InterCity225
- 5 x 10-car Azuma
- 7 x 9-car Azuma
- 2 x 5-car Azuma
So there were InterCity 225s running on that day.
A Few Distances Around Lincolnshire
I believe that because of offshore wind, interconnectors and other renewable energy developments, that Lincolnshire will become an energy powerhouse, supporting the East Midlands and also exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe through pipelines and interconnectors.
Because of this and other developments, I believe that rail passenger traffic to and around the county will increase significantly.
These are a few selected distances.
- Doncaster and Cleethorpes – 52.1 miles
- Grantham and Skegness – 58.2 miles
- Lincoln and Doncaster – 36.8 miles
- Lincoln and Newark – 16.8 miles
- Lincoln and Peterborough – 54.8 miles
- Lincoln and Cleethorpes – 47.2 miles
Note.
- This means that the length of the Joint Line, which between Werrington Junction and where it rejoins the East Coast Main Line to the South of Doncaster is no more than ninety miles. This ninety mile distance was assumed in the Modern Railways article.
- Peterborough and Cleethorpes via Lincoln is ninety-two miles.
- I estimate that around four miles could be easily electrified at Werrington, which would reduce these two distances by four miles.
- Newark and Cleethorpes via Lincoln is sixty-four miles.
It looks like if a battery-electric train had a range of 92 miles and there was charging at Cleethorpes and Skegness, Lincolnshire could have a first class zero-carbon rail service.
CAF Tri-Mode Trains And The Joint Line
This is the first sentence in the Modern Railways article.
LNER’s new fleet of CAF tri-mode trains, for which an order was confirmed in November, has been specified with the capability to operate via the Joint Line via Spalding and Lincoln in case of closures on the East Coast Main Line between Peterborough and Doncaster.
Note.
- The Modern Railways article states the Joint Line is approximately 90 miles.
- As I stated earlier with some strategically placed electrification at Werrington and South of Doncaster, this distance without electrification can probably be shortened by a few miles.
It looks like any service run by a CAF tri-mode train will be able to use the Joint Line.
Hitachi Class 801 Trains And The Joint Line
Unless the Joint Line is electrified or the all-electric Class 801 trains are fitted with batteries of a sufficient size the Class 801 trains will not be able to use the Joint Line.
Hitachi Class 800/802 Trains And The Joint Line
If currently, the Class 800/802 trains can handle the Joint Line on their diesel engines, they can continue to do this.
Hitachi Class 803 Trains And The Joint Line
Unless the Joint Line is electrified or Class 803 trains are fitted with batteries of a sufficient size the Class 803 trains will not be able to use the Joint Line.
Hitachi Class 80x Trains With Batteries And The Joint Line
Note that Lumo’s Class 803 trains are already fitted with an emergency battery for hotel power. So Hitachi must have information on how their batteries perform in service.
This press release from Hitachi, which is entitled Hitachi And Eversholt Rail To Develop GWR Intercity Battery Hybrid Train – Offering Fuel Savings Of More Than 20% announced the start of Hitachi’s battery-electric program in December 2020.
This is a paragraph.
The projected improvements in battery technology – particularly in power output and charge – create opportunities to replace incrementally more diesel engines on long distance trains. With the ambition to create a fully electric-battery intercity train – that can travel the full journey between London and Penzance – by the late 2040s, in line with the UK’s 2050 net zero emissions target.
Hitachi have now published this page on their web site, which is entitled Intercity Battery Trains.
The page has this sub-heading.
Accelerate the decarbonisation of intercity rail with batteries
These are the first two paragraphs.
A quick and easy application of battery technology is to install it on existing or future Hitachi intercity trains. Hitachi Rail’s modular design means this can be done without the need to re-engineer or rebuild the train and return them to service as quickly as possible for passengers.
Replacing one diesel engine with just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%. Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance.
It appears to be a masterful application of an old electrical or software engineer’s trick.
In the 1960s, I spent time in two summer holidays building transistorised control systems in a rolling mills to replace obsolete control systems that used thermionic valves and relays.
Are Hitachi just replacing a diesel power pack with a battery pack, that has the same power and control functionality?
In The Data Sheet For Hitachi Battery Electric Trains, I looked at Hitachi’s published data sheet, which has these bullet points.
- 750kW peak power
- Weight neutral
- At least 20% lower CO2 emissions
- 70km on non-electrified routes
- 20% reduction in whole life maintenance costs
- Up to 30% fuel cost savings
- Zero emissions in and out of stations
- Charge on the move
- 10 year life span
Note.
- 750 kW peak power, is around the power of the diesel-engine, that will be replaced.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that powerwise, the battery pack looks like a diesel engine.
- Weight neutral means that acceleration and performance will be unchanged. I suspect this means that current timetables can be achieved.
- Batteries are easier to maintain than diesels.
- It is stated that a train can be fully-decarbonised.
I have a feeling these trains are no ordinary battery-electric trains.
This paragraph, that I quoted earlier gives details on battery range.
Replacing one diesel engine with just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%. Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance.
If one battery can give seventy kilometres or 43.5 miles, what distances would be possible in the various Hitachi Class 80x trains on the UK rail network?
- Five-car Class 800 – Three diesel engines
- Nine-car Class 800 – Five diesel engines
- Five-car Class 801 – One diesel engine
- Nine-car Class 801 – One diesel engine
- Five-car Class 802 – Three diesel engines
- Nine-car Class 802 – Five diesel engines
- Five-car Class 803 – One battery
- Five-car Class 805 – Three diesel engines
- Seven-car Class 807 – No diesel engine or battery
- Five-car Class 810 – Four diesel engines
Note.
- The Class 801 trains have one diesel engine for emergency use.
- The Class 803 trains have one battery for emergency use.
- The Class 807 trains appear to be built for top speed and acceleration and have no unnecessary weight.
In The Data Sheet For Hitachi Battery Electric Trains, I came to the conclusion, that if all diesel engine packs are be replaced by batteries, the train has a range of around 117-121 miles.
If my calculation is correct, I believe that Hitachi battery-electric trains will be capable of using the Joint Line, if all diesel engines are replaced by battery packs.
Surely, if a number of Hitachi trains could use the Joint Line in addition to the ten CAF tri-mode trains, this would minimise disruption to passengers and increase revenue on days, when the East Coast Main Line was closed for engineering works or an incident.
Will The Hitachi Class 80x Trains With Batteries Or The CAF Tri-Mode Trains Have The Longer Range Without Electrification?
Consider.
- Cleethorpes could be the problem, as it is 64 miles from Newark and 92 miles from Peterborough and a round trip without charging at Cleethorpes for a battery-electric might be a trip to far.
- But a tri-mode train like that from CAF with an on-board diesel, should have the range.
- More range for a tri-mode train, just needs bigger fuel tanks.
- I also suspect Cleethorpes has the equipment to refuel a diesel train, as all services to the station are diesel powered.
The article also says this.
The inclusion of diesel engines as part of the winning bid, rather than a straightforward battery-electric unit, has surprised some observers, but LNER’s specification was that the fleet should have sufficient self-powered capability to cover the length of the joint line, which is approximately 90 miles. This is currently to be considered to be beyond the scope of battery-power alone, although as the technology evolves diesel engines could be replaced by batteries.
Could it be that some of LNER’s routes like Aberdeen, Cleethorpes and Inverness have longer running without electrification, than Hitachi’s trains with batteries can achieve. Perhaps, this is why they lost the order?
Pairs Of Hitachi Class 80x Trains With Batteries And The Joint Line
I suspect if one five-car train with batteries can handle the Joint Line, then a pair could also handle it, if the train’s control system allowed it.
Will The Joint Line Be Slower Than The East Coast Main Line?
Consider.
- The Joint Line is not the slowest line in the country and large sections of the route, have a top speed of 60 mph or higher.
- It is surprisingly straight.
- There are some slower sections, through Lincoln and Sleaford.
- The average speed between Peterborough and Lincoln of local trains is about 50 mph.
- The average speed between Doncaster and Lincoln of local trains is about 48 mph.
I suspect that the expresses, should be able to achieve 60 mph between Peterborough and Doncaster, with a small amount of track improvement.
This would mean the following times between Doncaster and Peterborough.
- Via the Joint Line – 90 minutes
- Via East Coast Main Line – 50 minutes
It looks like forty minutes will be added to journey times.
Would There Be Any Point In Running Some Services Via The Joint Line?
Consider.
- Lincoln has one train per two hours (tp2h) to and from King’s Cross.
- A King’s Cross and Doncaster service could use the Joint Line and call at Peterborough, Spalding, Sleaford, Lincoln Central, Gainsborough Lea Road and Doncaster.
- If it terminated at Harrogate, Leeds or York, it could ease congestion on the East Coast Main Line between Peterborough and Doncaster.
- Lincoln is making a name for itself as a University town.
- Lincolnshire is getting more important with respect to renewable energy and innovative food production.
- The frequency would be at least one tp2h.
- If needed, Lincoln Central could be electrified to charge passing trains.
- The service could also go via Cambridge to provide East Anglia and its technological powerhouse with better connections to and from the North.
It would all depend on where extra rail services are needed.
Could Cleethorpes And Grimsby Town Have A Service From King’s Cross?
In Azuma Test Train Takes To The Tracks As LNER Trials Possible New Route, I discuss how in June 2023, LNER ran a test train to Cleethorpes and Grimsby Town.
- With all the energy development going on in North-East Lincolnshire, I suspect that a service between King’s Cross and Cleethorpes via Lincoln, Market Rasen, Barnetby and Grimsby Town could be viable.
- I suspect that the energy developments could find recruitment difficult and say a one tp2h service to Peterborough might ease the problem.
- Whether it ran to Lincoln via Newark and the East Coast Main Line or via Spalding and Sleaford would be down to predicted traffic.
- The distance via Newark would be 64 miles or 128 miles return.
- The distance via Peterborough would be 92 miles or 184 miles return.
- These distances would probably mean that a battery-electric train would need charging at Cleethorpes.
So would it be better if the Cleethorpes trains were to be run by CAF tri-mode trains.
Could Cleethorpes Services Be Paired With The York Service?
The current King’s Cross and Lincoln service uses the same path as a York service.
- Both services leave King’s Cross at six minutes past the hour.
- York trains leave at odd hours.
- Lincoln trains leave at even hours.
If the York service used the Joint Line and the Lincoln service were to be extended to Cleethorpes, Lincoln would receive an hourly service.
- One service could go via Newark and the other via Peterborough, Spalding and Sleaford.
- A path on the East Coast Main Line would be saved.
- The service to York could go via Leeds.
- The York service could be extended to Middlesbrough, Scarborough or Sunderland.
- I suspect that timings to Cleethorpes and York could be a similar six-hour round trip.
- CAF tri-mode trains would be needed for the Cleethorpes services.
- Either train type could work the York services.
There are various possibilities to improve the train service been London and Lincolnshire.
What Will Be The Maximum Range Of The CAF Tri-Mode Trains?
When determining this, LNER would probably have taken into account all current and every possible service, that they might run in the future, which was not fully electrified.
These would include.
- London King’s Cross and Aberdeen – 91.4 miles
- London King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange via Shaftholme junction – 47.8 miles
- London King’s Cross and Cleethorpes via Newark and Lincoln – 64 miles
- London King’s Cross and Cleethorpes via Peterborough, Spalding and Lincoln – 92 miles
- London King’s Cross and Harrogate via Leeds – 18.3 miles
- London King’s Cross and Inverness– 151.1 miles
- London King’s Cross and Hull via Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- London King’s Cross and Lincoln – 16.8 miles
- London King’s Cross and Middlesbrough via Northallerton – 20.3 miles
- London King’s Cross and Scarborough via York – 42.1 miles
- London King’s Cross and Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles
They would also have taken in possible diversion routes.
- London King’s Cross and Carlisle via Leeds – 86.8 miles
- London and Edinburgh – 400 miles
- London King’s Cross and Newcastle via Northallerton and Durham Coast Line – 59.6 miles
Note.
- The distance is the length without electrification.
- London King’s Cross and Carlisle is a possible diversion route, if between Leeds and Edinburgh is blocked.
- A London King’s Cross and Edinburgh capability might be needed, if there was something like a serious weather problem, bringing down the overhead wires.
- London King’s Cross and Newcastle via Northallerton and Durham Coast Line is a possible diversion route, if between Northallerton and Newcastle is blocked.
LNER’s longest route without electrification is to Inverness and it is 151.1 miles between Stirling and Inverness.
London King’s Cross and Cleethorpes via Peterborough, Spalding and Lincoln could be longer, if it were to be run as a return trip of 184 miles.
LNER will probably have specified the range they need on the longest route they run or might run in the future, as there is no point in buying a fleet of trains and then finding that they can’t handle all your routes. They would also include all possible emergency routes, just as they’ve already included the Joint Line.
Out of curiosity I asked Professor Google how far a diesel train could run on a full tank of diesel and got this answer.
According to the traction manual for 158/159 stock each coach has a 400 gallon tank or 1818 Ltr. £2500 at the filling station.
The manual also says that that is enough fuel to travel Waterloo to Exeter and back twice over. Which is 688 miles exactly. Guess there is spare in there for shunting and idling at terminus. Still an mpg of 1.7.
It looks to me, that if a humble Class 158/159 train has a range of nearly 700 miles, then LNER can probably have virtually any distance they want for their new trains.
These journeys will probably all be possible.
- Between London King’s Cross and Edinburgh – 400 miles
- A round trip between Stirling and Inverness – 302.2 miles
- A round trip between Peterborough and Cleethorpes – 184 miles
Professor Google also gives the diesel range of a Class 800 train as 650 miles.
Conclusion
It looks to me, that LNER, Lumo and FirstGroup have a serious plan to decarbonise their network.
All services, that can be decarbonised by replacing diesel generator units, with electrical battery packs.
LNER’s longer routes will use the new CAF trains.
These will be fully decarbonised at a later date.
Great Western Railway Updates EHRT On Its Upcoming Operational Trial Of Fast Charge Tech
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Electric and Hybrid Rail Technology.
This is the sub-heading.
Great Western Railway’s senior program manager, Sonya Johns, speaks to Electric & Hybrid Rail Technology about the firm’s progress on developing ex-Vivarail Fast Charge technology for battery-powered trains, ahead of operational trials due to commence in 2024.
The article is a must-read as it describes the progress since First Group, acquired the assets and intellectual property of Vivarail and its Fast Charge battery train technology.
This paragraph describes the components of the Fast Charge technology.
The Fast Charge system consists of three key components: retractable charging shoe gear, which is mounted to the underframe of the train; short (4m) charging rails mounted between the underframe of the train; and the Fast Charge Battery Bank (FCBB) installed beside the track, acting as an energy buffer between the train and the grid.
This paragraph outlines the benefits of the system.
The Fast Charge system has several benefits, according to Johns, including high charging power, enabling the train to be recharged in around 10 minutes; a standard DNO connection, avoiding costly power supply upgrades; full automation, with no driver interaction required; low safety risk (the charging rails are never live unless fully covered by the train); and minimal disruption during installation, as the FCBB is manufactured offsite and the charging rails are attached to existing sleepers.
This sounds like a system, that has been designed by someone fed up with regulators saying no to innovative ideas.
Other points from the article include.
- The shoe gear has been designed to be easily installed on any rolling stock.
- The one-year trial of the Fast Charge technology and the Class 230 battery train on the West Ealing and Greenford line will commence in spring 2024.
- GWR will capture and analyze data during the trial to understand how the technology performs in different conditions.
The article finishes with this paragraph.
The work, according to GWR, is part of its commitment to reduce the carbon emissions of its train fleet with a view to removing all diesel-only traction from the network by 2040, in line with the Government’s Transport Decarbonisation Plan.
Adrian Shooter would have been pleased if he was here to see it.
May The Maths Be With You!
It was a bit of a surprise, when in the November 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, in an article, which was entitled Extra Luggage Racks For Lumo, I read this closing paragraph.
Lumo celebrated its second birthday in late October and was also set to mark the carriage of its two-millionth passenger. It is understood Lumo is interested in augmenting its fleet, such has been the success of the service; while many operators favour bi-mode units, Lumo is proud of its all-electric credentials so straight EMUs are still preferred, although the possibilities of including batteries which could power the trains may be pursued (the ‘803s’ have on-board batteries, but only to provide power to on-board systems if the electricity supply fails).
I find this development very interesting.
Surely the obvious way to increase capacity would be to acquire some extra identical trains and run the busiest services as ten-car trains. I talked about Hull Trains running ten-car trains in Ten-Car Hull Trains. Both companies have five trains, so I suspect that this number would allow for occasional ten-car trains.
If not, then add a few identical trains to the fleet, so capacity can be matched to the demand.
- Some services would be ten-car instead of five-car.
- Platforms at Edinburgh, King’s Cross and Newcastle already handle nine and ten-car trains, so infrastructure costs would be minimal.
- No extra paths would be needed, as a ten-car train can run in a path, that normally has five-car trains, as Hull Trains have shown.
A simple spreadsheet should probably predict, when and how many extra trains need to be added to the fleet.
Lumo And Traction Batteries
But why does the Modern Railways’s article talk about traction batteries?
In the two years since Lumo started their service, there have been days, when the East Coast Main Line has been closed for engineering works, bad weather or an incident. I wrote about an incident in Azumas Everywhere!.
Some of these engineering works have been able to be by-passed by using diversions. But not all of these diversion routes are fully-electrified, so are not available for Lumo.
There would appear to be three viable diversions for the East Coast Main Line.
- Werrington Junction and Doncaster via Lincoln – Not Electrified – 85.4 miles
- Doncaster and York via Leeds – Being Electrified – 55.5 miles
- Northallerton and Newcastle – Not Electrified – 56.8 miles
If all or some of Lumo’s five-car trains had a battery-range of a hundred miles, they would be able to divert around some blockades.
Note.
- A traction battery could also provide power to on-board systems if the electricity supply fails.
- A traction battery would allow the train to skip past some catenary problems.
- I would be interested to know how much diversions, bad weather and incidents have cost Lumo in lost sales and refunds.
As an electrical engineer, I believe, that the emergency-only and the traction batteries could be the same design, but with different software and capacity.
The extra cost of the larger capacity traction battery, might deliver a better service and also pay for itself in the long term.
Extending Lumo’s Route
Lumo will want to maximise revenue and profits, so would it be possible to extend the route North of Edinburgh?
Consider.
- Edinburgh and Aberdeen is 131.4 miles
- Ladybank is a station to the North of the Forth Bridge, which is under 40 miles from Edinburgh.
- The line between Edinburgh and Ladybank is being electrified.
- Ladybank is just 91.4 miles South of Aberdeen.
At some point in the next few years, I believe that one of Lumo’s trains fitted with a hundred mile traction battery could reach Aberdeen on electric power.
The train would need to be charged at Aberdeen before returning South.
How would Aberdonians like that?
Unfortunately, Inverness is 146.1 miles from the nearest electrification at Dunblane, so it is probably too far for a hundred mile traction battery.
It does appear to me that if Lumo’s trains were fitted with a hundred mile traction battery, this would enable them to take some non-electrified diversions and provide a service to Aberdeen.
How Useful Would A Hundred Mile Range Battery-Electric Train Be To Other Operators?
I take each operator in turn.
Hull Trains
Consider.
- It appears that Hull Trains change between diesel and electric power at Temple Hirst junction, which is between Doncaster and Selby, on their route between King’s Cross and Hull/Beverley.
- The distance between Temple Hirst junction and Beverley is 44.3 miles.
- It would appear that an out-and-return journey could be possible on a hundred mile traction battery.
- The hundred mile traction battery would also allow Hull Trains to use the Lincoln diversion, either when necessary or by design.
To ensure enough range, a short length of overhead electrification could be erected at Hull station to combat range anxiety.
The Modern Railways article also says this.
The co-operation between sister East Coast Main Line open access operators Lumo and Hull Trains continues, with one recent move being the use of Hull Trains ‘802’ on Lumo services to cover for a shortage of the dedicated ‘803s’ while one was out of action for repairs following a fatality. although the two types are similar, there are notable differences, most obviously that the Hull Trains units are bi-modes while the Lumo sets are straight EMUs, and a training conversion course is required for Lumo drivers on the ‘802s’. There are also challenges from a passenger-facing perspective – the Hull trains units have around 20 % fewer seats and a First Class area.
If Hull Trains used traction batteries rather than diesel engines could the trains be identical to Lumo’s trains from the driver’s perspective?
This would surely appeal to First Group, who are the owner of both Hull Trains and Lumo.
TransPennine Express
These are TransPennine Express services.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Newcastle – Fully Electrified
- Liverpool Lime Street and Hull – Part Electrified – Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- Manchester Airport and Saltburn – Part Electrified – Saltburn and Northallerton – 33.6 miles
- Manchester Piccadilly and Newcastle – Fully Electrified
- Manchester Piccadilly and Scarborough – Part Electrified – York and Scarborough – 42.1 miles
- York and Scarborough – Not Electrified – 42.1 miles
- Manchester Piccadilly and Huddersfield – Fully Electrified
- Huddersfield and Leeds – Fully Electrified
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes – Part Electrified – Hazel Grove and Cleethorpes – 104.6 miles
Note.
- I am assuming that the TransPennine Upgrade has been completed and Manchester and Leeds is electrified.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes will need some form of charging at Cleethorpes and a slightly larger battery.
All of these TransPennine Rxpress routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
LNER
These are distances from the electrification of the East Coast Main Line.
- Aberdeen via Ladybank – 91.4 miles – Charge before return
- Bradford Forster Square – Electrified
- Carlisle via Skipton – 86.8 miles – Charge before return
- Cleethorpes via Newark and Lincoln – 63.9 miles – Charge before return
- Harrogate via Leeds – 18.3 miles
- Huddersfield via Leeds – 17.2 miles
- Hull via Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- Lincoln via Newark – 16.7 miles
- Middlesbrough via Northallerton – 22.2 miles
- Scarborough via York – 42.1 miles
- Skipton – Electrified
- Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Carlisle could be a possibility during High Speed Two upgrading of the West Coast Main Line or for an enthusiasts’ special or tourist train.
- Cleethorpes is a possible new service for LNER. I wrote about this in LNER To Serve Cleethorpes.
- Scarborough must be a possible new service for LNER.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return. Carlisle is electrified, but Cleethorpes is not.
- The only new infrastructure would be the charging at Cleethorpes.
All of these LNER routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
The hundred mile traction battery would also allow LNER to use the Lincoln diversion.
Grand Central
These are distances from the electrification of the East Coast Main Line for Grand Central’s services.
- Bradford Interchange via Shaftholme junction – 47.8 miles
- Cleethorpes via Doncaster – 52.1 miles – Charge before return
- Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Cleethorpes is a possible new service for Grand Central.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return.
All of these routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
The hundred mile traction battery would also allow Grand Central to use the Lincoln diversion.
Avanti West Coast
These are distances from the electrification of the West Coast Main Line for Avanti West Coast’s services.
- Chester via Crewe – 21.1 miles
- Gobowen via Wolverhampton – 47.7 miles
- Holyhead via Crewe – 105.5 miles – Charge before return
- Shrewsbury via Wolverhampton – 29.7 miles
- Wrexham via Crewe – 33.3 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Gobowen is a possible new service for Avanti West Coast.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return.
All of these routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
Great Western Railway
These are distances from the electrification of the Great Western Main Line for Great Western Railway’s services.
- Bristol Temple Meads via Chippenham – 24.4 miles
- Carmarthen via Cardiff Central – 77.4 miles – Charge before return
- Cheltenham Spa via Swindon – 43.2 miles
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – 120.4 miles – Charge before return
- Great Malvern via Didcot East junction – 76.1 miles – Charge before return
- Hereford via Didcot East junction – 96.9 miles – Charge before return
- Oxford via Didcot Parkway – 10.3 miles
- Paignton via Newbury – 148.7 miles – Charge before return
- Pembroke Dock via Cardiff Central – 121.6 miles – Charge before return
- Penzance via Newbury – 172.6 miles – Charge before return
- Plymouth via Newbury – 120.4 miles – Charge before return
- Swansea via Cardiff Central – 53 miles – Charge before return
- Weston-super-Mare via Chippenham – 43.8 miles
- Worcester Foregate Street via Didcot East junction – 68.2 miles – Charge before return
- Worcester Shrub Hill via Didcot East junction – 67.6 miles – Charge before return
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return.
- Partial electrification through Hereford, Great Malvern, Worcester Foregate Street and Worcester Shrub Hill, could possibly be used to charge services from Hereford and Worcester.
- Partial electrification through Penzance, Plymouth and Exeter St. Davids, could possibly be used to charge services from the South West.
- Partial electrification West of Swansea, could possibly be used to charge services from West Wales.
All routes, except for Hereford and Worcester, the South-West and West Wales, would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
I’ll now look at the three groups of services in more detail.
Services To Hereford And Worcester
These are distances from the electrification of the Great Western Main Line for Great Western Railway’s Hereford and Worcester services.
- Great Malvern via Didcot East junction – 76.1 miles
- Hereford via Didcot East junction – 96.9 miles
- Worcester Foregate Street via Didcot East junction – 68.2 miles
- Worcester Shrub Hill via Didcot East junction – 67.6 miles
Note.
- All services join the Great Western Main Line at Didcot East junction.
- Some services will be probably need to have, their batteries charged at the Hereford and Worcester end.
At the present time, the electrification finishes at Didcot East junction, but if it were to be extended to Charlbury station, these would be the distances without electrification.
- Great Malvern via Charlbury – 52.3 miles
- Hereford via Charlbury – 73.1 miles
- Worcester Foregate Street via Charlbury – 44.4 miles
- Worcester Shrub Hill via Charlbury – 43.8 miles
Note.
- Some of the track between Oxford and Charlbury is only single track, which may give advantages, when it is electrified.
- It might be possible with a hundred mile traction battery for all Worcester services to charge their batteries between Charlbury and London Paddington and not need a charge at Worcester to return.
- A larger traction battery or extending the electrification to perhaps Morton-in-Marsh could see Great Malvern in range of battery-electric trains from London Paddington without a charge.
- Hereford would probably be too far to get away without charging at Hereford.
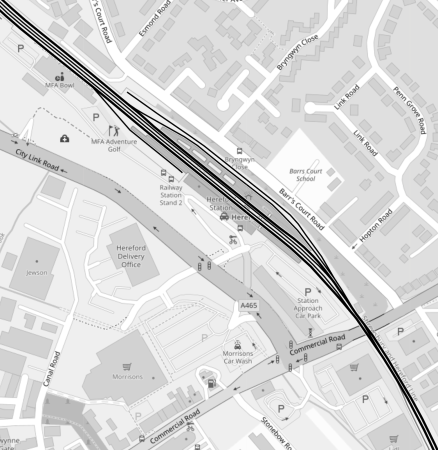
This OpenRailwayMap shows the layout of Hereford station.
I’m certain that a platform can be found, where there is space for a charger, which could also be used for other trains serving the station.
Services To The South West
In the August 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled GWR Seeks Opportunities To Grow.
This is the sub-heading.
Managing Director Mark Hopwood tells Philip Sherratt there is plenty of potential to increase rail’s economic contribution.
This is two paragraphs.
The desire to provide electrification to support aggregates traffic from the Mendip quarries could also benefit GWR , says Mr. Hopwood. ‘Having an electric loco would massively help with pathing heavy freight trains through the Thames Valley. If you could electrify from Newbury to East Somerset Junction, a big chunk of the Berks and Hants route would be wired.
Then you can ask how much further you could get on battery power on an IET without running out of juice.’
Newbury to East Somerset Junction would be 53.5 miles of electrification, so I can build this table of services to the South-West
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – 120.4 miles – 66.9 miles
- Paignton via Newbury – 148.7 miles – 95.2 miles
- Penzance via Newbury – 251.9 miles – 198.5 miles
- Plymouth via Newbury – 172.6 miles – 119 miles
Note.
- The distance between Penzance and Plymouth is 79.5 miles.
- The first figure in the table is the distance to Newbury.
- The second figure in the table is the distance to East Somerset junction.
A possible way of running these four services to London on battery power is emerging.
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – Charge before return – Run on battery for 66.9 miles to East Somerset junction.
- Paignton via Newbury – Charge before return – Run on battery for 95.2 miles to East Somerset junction.
- Penzance via Newbury- Charge before return – Run on battery for 79.5 miles to Plymouth – Charge at Plymouth – Run on battery for 119 miles to East Somerset junction.
- Plymouth via Newbury – Charge before return – Run on battery for 119 miles to East Somerset junction.
Once at East Somerset junction, it’s electrification all the way to Paddington.
This is the corresponding way to run services from London.
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 66.9 miles to Exeter St. Davids.
- Paignton via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 95.2 miles to Paignton.
- Penzance via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 119 miles to Plymouth – Charge at Plymouth – Run on battery for 79.5 miles to Penzance.
- Plymouth via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 119 miles to Plymouth.
More electrification or a larger than a hundred mile traction battery would be needed, as Plymouth and East Somerset junction is 119 miles.
But if a Stadler Akku can do 139 miles on a charge, why shouldn’t a Hitachi battery-electric train?
Services To West Wales
It seems that the current timetable is already setup for battery-electric trains to run to and beyond Swansea.
- Carmarthen and Swansea is almost exactly 32 miles.
- Pembroke Dock and Swansea is 73.4 miles.
- Swansea and Cardiff Central is 45.7 miles.
Note
- All these sections could be run by a battery-electric train, with a fully-charged hundred mile traction battery.
- All trains going to or from Carmarthen or Pembroke Dock reverse at Swansea, where a generous time of more than eleven minutes is allowed for the manoeuvre.
- During the reverse at Swansea, there is sufficient time to charge the batteries, if overhead wires were present.
Battery-electric services could serve Wales Wales with overhead electrification at Carmarthen, Pembroke Dock and Swansea.
Conclusion
We will go a long way, if we embrace battery-electric trains.
Most routes can be handled with a train with a traction battery range of 100 miles.
Exceptions are.
- Hazel Grove and Cleethorpes – 104.6 miles
- Plymouth and East Somerset junction – 119 miles
But if a Stadler Akku can do 139 miles on a charge, why shouldn’t a Hitachi battery-electric train?
TransPennine Express Releases Blueprint For Improving Service And Fleet Upgrade
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Technology Magazine.
This is the sub-heading.
TransPennine Express (TPE), which transferred to the government’s owning group (DOHL) earlier this year, has set out its plans to address many of the issues which have caused problems and disruption for rail customers.
These three paragraphs summarize their plans.
Making Journeys Better: A Prospectus gives clear detail of the issues TPE has faced during the past two years as well as outlining how TPE, under DOHL, will work to make things better, having completed an in-depth review of the business.
Part of the plans involve the operators plans for its new fleet. Its New Trains Programme outlines its long term view for decarbonisation. The report states that TPE will look towards new technology on its fleet to overcome the lack of clarity on the full electrification of the line.
This, it states will help with the cascading and removal of diesel trains faster across its network.
It always looked to me, that TPE under First Group, brought rather a dog’s breakfast of trains, when a unified fleet of Class 802 trains, as per Hull Trains, might have been easier to operate.
- They are already retiring the Class 68 locomotives and their Mark 5 coaches, so surely to decarbonise their services, a number of battery electric high speed trains would be an idea.
- They are already testing Class 802 battery-electric trains for Hitachi and Eversholt Rail.
- I also feel that CAF could offer a suitable battery-electric train, based on the Class 397 train.
TPE say in the example, that they expect a decision later in the month.
TransPennine Express Services And Battery Electric Trains
These are their services and how they would be effected by battery-electric trains.
- Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.
- Liverpool Lime Street And Hull – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.. – 42 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and Micklefield.
- Manchester Airport and Saltburn – Fully-electrified between Manchester Airport and Northallerton after TransPennine Upgrade. – 33.6 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and Northallerton. Would eliminate overnight noise problems at Redcar.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Newcastle – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Scarborough – Fully-electrified between Manchester Piccadilly and York after TransPennine Upgrade. – 42.1 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and York.
- York and Scarborough – Electrified at York – 42.1 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at York.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Huddersfield – Electrified at Manchester Piccadilly – 25.5 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at Manchester Piccadilly.
- Leeds and Huddersfield – Electrified at Leeds – 17.2 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at Leeds.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes – 125,6 miles unelectrified – In Electrification Of The Hope Valley Line, I show how this route can be run by battery-electric trains that charged on existing electrification a short new section of electrification at Cleethorpes.
Note.
- If Manchester Victoria and Huddersfield, is not electrified, battery-electric trains would be able to cross the 25.8 miles of unelectrified track on battery power.
- If Leeds and Huddersfield, is not electrified, battery-electric trains would be able to cross the 17.2 miles of unelectrified track on battery power.
- I am assuming that the TransPennine Upgrade between Manchester and Leeds will be completed, so that between Liverpool Lime Street and Leeds is fully-electrified.
- The only new infrastructure needed would be electrification at Cleethorpes to charge the trains.
All services except for Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes could be run using battery-electric trains with a range on a full battery of at least 100 miles and with no additional electrification.
Electrifying Cleethorpes Station
This Google Map shows Cleethorpes station.
These pictures show the station in June 2023, when it appears to be going through a platform refurbishment.
I don’t think it would be the most difficult station to electrify.
- There are four platforms.
- As the station is likely to get more battery-electric services, including one from King’s Cross, I would suspect that at least three out of the four platforms would be electrified.
- Although, the station is Grade II Listed, there doesn’t appear to be any canopies or important architectural details, that would get in the way of electrification.
Once Cleethorpes station had been successfully electrified, similar installations could be applied at other stations like Saltburn, Scarborough and Skegness.
Conclusion
If TransPennine Express were to buy the right number of battery-electric trains with a hundred mile range, they can decarbonise all their routes in a train factory.
Elizabeth Line Takes Fliers Away From Heathrow Express
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Times.
These three paragraphs add details to the story.
The opening of the Elizabeth Line has eaten into the revenues of Heathrow Express, the country’s most expensive railway service per mile travelled.
Filings reveal that Heathrow Express, which offers a 15-minute service between London Paddington and Heathrow, has failed to recover to pre-pandemic levels despite flight volumes at the airport returning to near-normal. Heathrow said revenues from Heathrow Express in the first three months of the year were £22 million.
While that is 50 per cent more than in the same period last year, when Covid-19 travel restrictions were beginning to be relaxed, it is almost a third down on the £31 million of revenues in the first quarter of 2019.
Considering how air travel is on the upturn, Heathrow Express would not appear to be performing as the airport expects.
Remember, that First Group are paid by Heathrow Airport to run the service, which is owned by the airport.
In So Many Cases On A Train!, I wrote about a trip from West Ealing to Moorgate station. These were my opening sentences.
This afternoon about three, I went to West Ealing station to see what it was like to transfer between the Elizabeth Line Central Tunnel and the Western Branch at Paddington.
Coming back, I took an Elizabeth Line service that had started from Heathrow Airport and it was one of the busiest Lizzies, I’d ever ridden!
To get on the train at West Ealing station, I got in to probably coach 4 of 9, as that was in the dry and the back end of the train I needed for Moorgate station was certainly in the wet.
I then had to walk half the length of the train to get to the back of the train.
It was not easy, as the train was full of scores of passengers with large wheelie cases.
It certainly got me thinking about how passengers were getting to and from Heathrow and I came to this conclusion.
Lizzie will start a revolution in travel to and from Heathrow.
Judging by the title of the article in The Times, the revolution has already started.
Consider these reasons.
- Heathrow Express is overpriced.
- It doesn’t go where many passengers want to go.
- It’s not the best way to get workers to and from the airport.
- The ULEZ will discourage passengers and staff from driving to the airport.
In Effects Of The ULEZ In West London, I said this about journeys to and from the airport.
Heathrow Airport is one of the world’s busiest airports and 76,000 people work at the airport, with many more employed nearby.
The airport handled 61.6 million passengers in 2022, which is a few short of 170,000 per day.
If you consider that those that work at the airport do two trips per day and passengers generally do one, that means there are 322,000 trips per day to or from the airport.
But as it now so easy to get to the Airport using the Elizabeth Line will more people use the new line to meet and greet and say goodbye to loved ones or business associates. Since the Elizabeth Line opened, I’ve met a couple of friends at Heathrow, who were passing through.
I wonder, if that daily journey total of 322,000 could be nearer to 350,000 or even 400,000.
If the ULEZ charge makes some passengers and staff switch from their car to using a bus or train, this probably means that public transport to and from the airport, will need to be boosted by a substantial amount.
I can see airport workers lobbying for free tickets on Heathrow Express, but they probably live closer to the airport than Paddington or perhaps even in the Eastern areas of London served by the Elizabeth Line.
The Elizabeth Line Is Showing Signs Of Running Out Of Capacity
In the last few weeks, I’ve been on some very full Elizabeth Line trains.
Articles, like this one on Rail Advent, which is entitled Transport for London Looks Into Funding For Additional Elizabeth Line Trains, are also starting to appear.
These three paragraphs explain the problem.
Transport for London has announced that they are looking for confirmation from the Government regarding funding so that they can look into the possibility of purchasing additional Elizabeth Line trains.
The news from TfL comes after the recent announcement of delays to HS2 terminating at London Euston.
TfL says that without the extra trains, there is insufficient capacity on the Elizabeth Line (until HS2 is extended to Euston in the 2040s) for passengers looking to use HS2 and the Elizabeth Line to get into Central London.
Alstom also appear to want the space in the factory to build other trains.
So it appears that Transport for London must act soon.
Heathrow Express Needs To Be Repurposed
In Extending The Elizabeth Line – High Speed Trains On The Elizabeth Line, I talked about running faster trains through the Central Tunnel of the Elizabeth Line.
As any train would have to be compatible with the platform-edge doors in the central tunnel of the Elizabeth Line, the trains would have to be dimensionally identical to the current Class 345 trains.
- Nine cars
- Possibility of lengthening to ten cars.
- 204.73 metres long.
- 6 sets of doors per carriage
- Ability to run under full digital signalling.
- The trains would be designed for a higher speed of at least 110 or 125 mph, to enable running on the fast lines of the Great Western Main Line.
- The trains would have Heathrow Express branding and interior.
Services could be as follows.
- Heathrow Terminal 4 and Southend Victoria via Bond Street and Liverpool Street for the City and Stratford.
- Heathrow Terminal 5 and Ebbsfleet International via Bond Street and Liverpool Street for the City and Canary Wharf.
Note.
- Both services would be two trains per hour (tph)
- Traffic would determine, which Eastern terminal is paired with which Western terminal.
- Each route would also have two Elizabeth Line tph on the same route.
The Heathrow Express services would run as follows.
- Between Heathrow Airport and Paddington, they would run as now.
- I believe that by using the power of the digital signalling, they could be slotted into the queue of Elizabeth Line trains taking the Central Tunnel.
- They would run through the Central Tunnel, as just another Elizabeth Line train, stopping at all stations.
- Southend Victoria trains would stop at Stratford, take the fast lines to Shenfield, after which they would stop at all stations to Southend Victoria.
- Ebbsfleet International trains would stop at all stations from Abbey Wood to Ebbsfleet International.
Note.
- Trains would stop at Old Oak Common after it opened for High Speed Two and GWR.
- All ticketing would be contactless.
- Passengers using Heathrow Express to the West of Paddington, would pay an extra fee, but nothing like today’s price.
These Heathrow Express routes would have advantages.
- Southend Airport and Southend Victoria would get a direct fast train to Central London and High Speed Two.
- Heathrow would have a direct connection with Continental train services at Ebbsfleet International.
- Capacity could be increased by going to ten-car trains.
- Heathrow Express could release their platforms at Paddington.
- There would be two fast tph between Heathrow and Stratford.
- There would be two fast tph between Heathrow and Canary Wharf.
- There would be four fast tph between Heathrow and Bond Street for the shopping and Liverpool Street for the City of London.
- There would be four fast tph between Heathrow and Farringdon for Thameslink, Gatwick and Luton Airports.
Heathrow Express trains will be fifteen minutes faster to all destinations.
I don’t think there would be any major disadvantages.
The Ways First Group, Hitachi, Hyperdrive Innovation and Turntide Technologies Can Enable Electric Trains To Run Between Basingstoke And Exeter
Who Are Turntide Technologies?
The Wikipedia entry for the company starts with this paragraph.
Turntide Technologies is a US-based business that makes intelligent, sustainable motor systems. Turntide applies its Technology for Sustainable Operations across buildings, agriculture, and transportation segments. It maintains operations in the USA, Canada, the United Kingdom, and India.
These three paragraphs from the Technology section of the Wikipedia entry outline their technology.
Turntide’s core product is its Technology for Sustainable Operations, a cloud-based open platform that monitors and automates building and vehicle systems. The platform is powered by its Smart Motor System, a connected hardware-software machine built around a high rotor pole switched reluctance motor.
Southern California Edison utility certified in 2018 that the V01 Smart Motor System reduced energy consumption by 23%-57% compared with a standard AC induction motor, and 11% compared with an induction motor controlled by a variable frequency drive.
In 2019, National Renewable Energy Laboratory certified that Turntide’s motor reduced energy consumption in refrigerator condenser fans by 29%-71%.
Note.
- Turntide’s efficiencies, which appear to have been verified by reputable organisations, if they can be reproduced in traction systems for battery-powered transport could improve range substantially.
- There are also other more efficient electric motors being developed.
- I wrote about Norfolk-based advanced traction motor company; Equipmake in Equipmake Hybrid To Battery Powered LT11.
- Motors like these, are the engineer’s cure for range anxiety.
I have to ask, if Hitachi (, and Stadler) are using more efficient motors to stretch the range of their battery-electric trains.
Initially, Hitachi asked Hyperdrive Innovation to design battery packs for Class 802 and other similar trains.
These three posts give some details about the battery project involving the two companies.
- Hitachi And Eversholt Rail To Develop GWR Intercity Battery Hybrid Train – Offering Fuel Savings Of More Than 20%
- Hitachi Rail And Angel Trains To Create Intercity Battery Hybrid Train On TransPennine Express
- More On Batteries On Class 802 Trains
Consider.
- In June 2021, Turntide acquired Hyperdrive Innovation.
- So did this effectively invite Turntide to the project?
- According to the Internet, Hitachi are one of the largest manufacturers of electric motors.
- Turntide are very-well funded by the likes of Bill Gates, Robert Downey Junior and some big funds.
Has there been some intense design meetings, which have been beneficial to all parties?
In my experience, these groupings don’t often work out how they should!
But this relationship seems to be doing fine.
One of Hitachi’s managers from the battery-train project even appears in the video on Turntide’s home page.
Electrifying Basingstoke And Exeter
Consider these facts about the route.
- Basingstoke and Salisbury is 35.8 miles.
- Salisbury and Exeter is 88.5 miles.
- Basingstoke and Exeter is 124.3 miles.
- There is no electrification.
- There are 14 stops between Salisbury and Exeter.
- There are 4 stops between Basingstoke and Salisbury.
- Trains are up to nine car Class 159 trains.
- Average speeds are not much better than 50 mph.
- Maximum speeds vary between 75 and 90 mph.
To get an estimate of how much energy, a Basingstoke and Exeter train will use, I’ll start with a figure from How Much Power Is Needed To Run A Train At 125 Or 100 mph?.
At 125 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 3.42 kWh per vehicle mile.
As drag is proportional to the square of the speed, which gives
- At 100 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 2.19 kWh per vehicle mile.
- At 80 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 1.40 kWh per vehicle mile.
For this calculation I’ll take the 80 mph figure of 1.40 kWh per vehicle mile.
Assuming a five-car train travelling between Basingstoke and Exeter, which is 124.3 miles gives a figure of 870 kWh.
But this is only one use of energy on the train.
- Every time, the train accelerates it will need power, but it will charge itself using regenerative braking.
- An all-electric Class 803 train has a mass of 228.5 tonnes and carries 400 passengers.
- If I assume that each passenger is 80 Kg including baggage, bikes and buggies, that gives a mass of 32 tonnes or a total mass of 260.5 tonnes.
- Putting these figures into Omni’s Kinetic Energy calculator gives a figure of 46.3 kWh at 80 mph.
As there are eighteen stops along the route and at each stop it could lose up to twenty percent of its energy, this means that the eighteen stops will cost 166.7 KWh.
Adding this to the 870 KWh it takes to maintain speed, it looks like a trip between Basingstoke and Exeter will take 1036.7 kWh.
Could this be a 200 kWh battery in each coach?
Obviously, this is only a rough calculation and with the better figures Hitachi would have, I would suspect much better answers.
But I do believe that it would be possible to run between Basingstoke and Exeter on battery power, if the train was efficient.
Charging The Train
The train would be charged on the third-rail electrification between Waterloo and Basingstoke.
But what would happen at Exeter?
The trains could be bi-modes like Hitachi’s Class 395 trains for Southeastern,
One of Vivarail’s third-rail charging systems, that First Group, acquired from the Receiver of Vivarail could be used.
Getting The Order Right
Would between Basingstoke and Exeter, be a sensible route to convert to battery-electric trains early, as it would release a useful fleet of diesel trains, that might be able to fill in for a couple of years by replacing the Castles!
Wrightbus: Ballymena Company Gets Order For 117 Buses
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
County Antrim firm Wrightbus has secured a £25.3m order to build 117 zero-emission buses for use in England
And this is the first paragraph.
Operated by First Bus, the vehicles will be used in Yorkshire, Norfolk, Portsmouth and Hampshire.
They don’t say, whether the buses are battery or hydrogen powered.
GWR And Vivarail
This is an attempt to make some sense about what is happening between GWR and the assets of Vivarail.
These are some random thoughts.
Ongoing Maintenance Of Existing Trains
Currently, there are four operators in the UK, with various types of Vivarail‘s Class 230 trains.
- Great Western Railway – 1 – Infrastructure under construction for trial on the Greenford Branch.
- Island Line – 5 – In operation.
- Transport for Wales – 5 – Undergoing testing prior to entering service.
- West Midlands Trains – 3 – Withdrawn from service indefinitely in December 2022.
Note.
- West Midlands Trains withdrew the trains because of uncertainty about the servicing of the trains.
- West Midlands Trains are getting complaints about the bus replacement service.
- All operators will probably need assistance to service the trains.
- Great Western Railway and Island Line are First Group companies.
Could First Group have got in first, so they can protect their interests with a professional Vivarail train maintenance organisation?
Mark Hopwood
In Special Train Offers A Strong Case For Reopening Fawley Line, I said this.
This is another quote from the Rail Magazine article.
However, SWR’s Mark Hopwood favours a much bolder plan. “We’d have to take a decision, once we knew the line was going ahead. But my personal belief is that we should be looking for a modern environmentally-friendly train that can use third-rail electricity between Southampton and Totton and maybe operate on batteries down the branch line.”
Pressed on whether that would mean Vivarail-converted former-London Underground stock, Hopwood adds. “It could be. Or it could be a conversion of our own Class 456, which will be replaced by new rolling stock very shortly. But I don’t think this is the time to use old diesels.
Mark Hopwood is now the Managing Director of Great Western Railway and he seems to be in favour of battery-electric trains. I agree totally with his statement about old diesels.
Mark Hopwood And The Cholsey And Wallingford Branch
According to LinkedIn, Mark Hopwood is also the President at the Cholsey and Wallingford Railway
- This is a two-and-a-half mile long standard gauge heritage railway.
- It used to be a branch line, that served the town of Wallingford.
- It connects to the Great Western Main Line in a bay platform at Cholsey station.
- Wallingford station has now been demolished.
- The heritage railway uses a new site on the south side of St. Johns Road.
This map from OpenRailwayMap shows the branch line.
Note.
- Cholsey station and the Great Western Main Line is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- The current Wallingford station is in the North-Eastern corner.
- The Cholsey and Wallingford Railway is shown in yellow.
This Google Map shows Cholsey station.
Note.
- There are four through platforms for Great Western Railway services.
- Platforms 1 and 2 for the fast services are on the Western side.
- Platforms 3 and 4 for the slow services are on the Eastern side.
- Bay Platform 5 is tucked in the North-East corner of the station and is the terminus for services on the Cholsey and Wallingford Railway.
- There are only 55 parking spaces.
Is the number of parking spaces sufficient for the station, if a lot of passengers drive from Wallingford?
Could a commercial service run between Cholsey and Wallingford?
Consider.
- Wallingford is a town of nearly twelve thousand people.
- Cholsey station has two trains per hour (tph) between Paddington and Didcot Parkway stations, with extra services between Oxford and Reading stations in the Peaks.
- There is only limited parking at Cholsey station.
- Most GWR branch lines are run by an hourly service.
- I feel that two-car battery-electric train could provide one or two tph on the branch.
- Charging would probably be needed at only one end of the branch line.
- As all the through lines at Cholsey station are electrified with 25 KVAC overhead wires, I suspect that charging would be provided at that station.
A two-car battery-electric train could probably provide a commercial service on this branch, if the Cholsey and Wallingford Railway wanted a revenue stream.
First Group Services That Could Be Run By Battery-Electric Trains
These Great Western Railway and South Western Railway services might be suitable for battery-electric services.
- Newbury and Bedwyn – Newbury is electrified.
- West Ealing and Greenford – West Ealing is electrified.
- Slough and Windsor and Eton Central – Slough is electrified.
- Maidenhead and Marlow – Maidenhead is electrified.
- Twyford and Henley-on-Thames – Twyford is electrified.
- Reading and Gatwick Airport – Partially electrified.
- Reading and Redhill – Partially electrified.
- Reading and Basingstoke – Partially electrified.
- Didcot Parkway and Oxford – Didcot Parkway is electrified.
- Weston-super-Mare and Severn Beach – No electrification.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Avonmouth – No electrification.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Filton Abbey Wood – No electrification.
- Bristol Temple Meads and Portishead – Proposed – No electrification.
- Swindon and Westbury – Swindon is electrified.
- Exmouth and Paignton – No electrification.
- Exeter Central and Okehampton – No electrification.
- Exeter Central and Barnstaple – No electrification.
- Plymouth and Gunnislake – No electrification.
- Liskeard and Looe – No electrification.
- Par and Newquay – No electrification.
- Truro and Falmouth Docks – No electrification.
- St. Erth and St. Ives- No electrification.
- Romsey and Salisbury – Partially electrified.
- Southampton Central and Fawley – Proposed – Partially electrified.
Note.
- Most services are one or two tph or less.
- Reading and Basingstoke, Didcot Parkway and Oxford, Exmouth and Paignton, and Romsey and Salisbury are 2 tph.
- I have included the proposed Bristol Temple Meads and Portishead and Southampton Central and Fawley services.
- All electrification is 25 KVAC overhead except for the North Downs Line between Reading and Gatwick Airport via Redhill, and Romsey and Salisbury, which are 750 VDC third rail.
There are a total of 24 services. As each 2 tph service will need two trains and the North Downs services probably six, a rough calculation, indicates there would need to be a minimum of over thirty trains, to convert all these services to battery-electric operation.
This simple analysis makes Mark Hopwood’s enthusiasm, that I quoted earlier understandable.
The Requirement For First Group Battery-Electric Trains
Consider.
- Most of the services can accommodate three or four-car trains.
- A few services can only be run with two-car trains.
- Some services will need running with 25 KVAC overhead electrification for operation or deploying to and from the depot.
- Some services will need running with 750 VDC third-rail electrification for operation or deploying to and from the depot.
- A modern interior with or without a fully-accessible toilet is needed.
- Ability to recharge in a platform fitted with electrification or a charging system in under ten minutes.
- A reasonable cruising speed where electrification is needed for deployment.
This suggests to me, that two train types will be needed.
- A Vivarail-style two-car train for branches like West Ealing and Greenford and Southampton Central and Fawley.
- A three- or four-car dual-voltage electric multiple unit, based on something like an Alstom Aventra, a Bombardier Electrostar or a British Rail-era Class 321 train.
The Class 321 train could be ideal.
- It is a 100 mph train.
- It is a four-car train, that can be shortened to three-cars.
- Versions are available for both 25 KVAC overhead and 750 VDC third-rail electrification.
- Some have been converted to a modern Renatus interior, with a fully-accessible toilet.
- Greater Anglia have run Class 321 Renatus trains between London and Norwich.
- The Class 321 Renatus trains are fitted with a modern AC-based traction system.
- Eversholt Rail and Vivarail were working on a Class 321 BEMU, which I wrote about in Eversholt Rail And Vivarail To Develop Class 321 BEMU.
- Other operators like Northern, Scotrail and Transport for Wales might like a Class 321 BEMU.
Could First Group convert the Class 321 trains?
In What Train Is This?, I talk about a refurbishment of a GWR Class 150 train, that was one of the best I’ve seen.
I suspect that First Group could do the conversion, with a little help from their friends, like Wabtec and the ex-Vivarail employees, that they’ve hired.
Could The Class 387 Trains Be Converted To Battery-Electric Operation?
It was in February 2015, that I wrote Is The Battery Electric Multiple Unit (BEMU) A Big Innovation In Train Design?, after a ride in public service on Bombardier’s test battery-electric train based on a Class 379 train.
The Class 387 and Class 379 trains are very similar and with Vivarail’s battery and charging expertise, I believe that both Class 379 and Class 387 trains could be converted into modern four-car battery-electric trains.
- They would have a 100 mph or possibly a 110 mph operating speed, so could work routes like the Great Western Main Line amongst the thundering herds of Hitachis.
- The interiors would be suitable for longer routes like Cardiff Central and Exeter or Waterloo and Exeter via Salisbury.
- Great Western Railway have 33 Class 387 trains.
- Thirty Class 379 trains are wasting space in sidings.
I believe that with modern battery technology, these trains could have a battery range in excess of ninety miles.
This would enable services like Cardiff Central and Exeter St. Davids and Exeter St. Davids and Salisbury.
With judicious use of charging stations in stations like Bristol Temple Meads, Exeter St. Davids and Salisbury, all First Group main line services, that are not run by the Hitachi trains could be converted to battery-electric operation.
Conclusion
I believe a well-thought out plan is emerging.
GWR Takes Over Battery Train Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail News.
This paragraph outlines the takeover.
Great Western Railway has bought equipment from battery train manufacturer Vivarail, which went into administration in December. The purchase has included rolling stock, FastCharge systems and other items. Nine former Vivarail staff have also joined GWR, as it continues to prepare for using a battery unit on the West Ealing to Greenford branch. GWR engineering director Simon Green said: ‘There have clearly been some setbacks that mean we will need to review the existing plans and timescales, but we will continue to work with Network Rail and the Department for Transport to get the project back on track.’
This sounds a very sensible action to me.
- GWR take control of the West Ealing project.
- GWR’s sister company; South Western Railway, probably will get the support they need for the Vivarail trains on the Island Line.
- It may lead to First Group companies using more Vivarail trains on other lines.
I also suspect the deal will mean that the remains of Vivarail has more of a future and someone will buy it, to continue development.
The original press release is on the First Group web site and it is entitled Fast-Charging Battery Trial To Resume After GWR Agrees Deal To Purchase Vivarail Assets.