Could High Speed Two Serve Chester And North Wales?
This diagram shows High Speed Two services, as they were originally envisaged before Phase 2 was discontinued.
Note.
- Trains to the left of the vertical black line are Phase 1 and those to the right are Phase 2.
- Full-Size trains are shown in blue.
- Classic-Compatible trains are shown in yellow.
- Blue circles are shown, where trains stop.
- The dotted circles are where trains split and join.
- In the red boxes routes alternate every hour.
Click on the diagram to enlarge it.
If I look at the trains counting from the left of the diagram, I see the following.
- Train 4 is a pair of Classic-Compatible trains, that split and join at Crewe, with one train going to Lancaster and the other to Liverpool Lime Street.
- Train 5 is a single Classic-Compatible train going to Liverpool Lime Street.
This gives Liverpool Lime Street two trains per hour (tph) and Lancaster one tph
Could train 5 be a a pair of Classic-Compatible trains, that split and join at Crewe, with one train going to Holyhead via Chester and the other to Liverpool Lime Street?
Consider.
- Yesterday, a pair of Class 805 trains, ran between Euston and Holyhead. Each Class 805 train is 130 metres long, so a pair of Class 805 trains is sixty metres longer than a High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train.
- I am certain, that a single High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train will fit the platforms between Crewe and Holyhead.
- Crewe and Holyhead is 105.5 miles and the route is not electrified.
- Crewe and Holyhead is double-track all the way except for the Britannia Bridge over the Menai Strait.
- With the exception of perhaps 2 to 3 miles, half the route between Crewe and Holyhead has a line speed of 90 mph. with the other half being 75 mph.
- Given the countryside and the number of important historic sites, electrification might be difficult, as the heritage Taliban will say no!
- It was promised by the last government that Crewe and Holyhead would be electrified, but I will assume it won’t be!
- Hitachi, who are part of the consortium building the High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains have developed battery-electric high speed train technology, which is likely to be applied to the Current Class 805 trains, that work the route.
- Hitachi’s battery-electric high speed train technology can propel the trains at up to 125 mph, provided the track allows it.
I feel that Crewe and Holyhead can be developed into one of the most iconic high speed railways in the world, by using battery-electric high-speed trains. Tourists would come from all over the world, to experience mouse-quiet battery-electric trains.
High Speed Two should go for it!
These are some thoughts.
It Would Be A Green Route To Ireland
Consider.
The fastest direct Avanti service to Holyhead is scheduled to take three hours and forty-two minutes, with one hour and 46 minutes between Euston and Crewe, and one hour and fifty-seven minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- High Speed Two will knock thirty-four minutes off the time between Euston and Crewe, when the core route between Euston and Crewe is complete, which will reduce the time to three hours eight minutes, with with one hour and 12 minutes between Euston and Crewe, and one hour and fifty-seven minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- The Crewe and Holyhead section of the route would still take one hours and fifty-seven minutes, which is an average speed of just 54 mph, along the North Wales Coast.
- An overall time of three hours between Euston and Holyhead, would require an average speed along the North Wales coast, which would be an average speed of just 62 mph.
- The operating speed is an average of around 80 mph between Crewe and Holyhead, and would run the section of the route in 79 minutes, which would mean a Euston and Holyhead time of two hours and 31 minutes.
- A 100 mph average between Crewe and Holyhead, would run the section of the route in 63 minutes, which would mean a Euston and Holyhead time of of two hours and 15 minutes.
I believe that with track improvements, a more efficient stopping pattern and using Hitachi’s battery technology, that battery-electric High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains could run between Euston and Holyhead in under two hours.
A fast ferry would complete the route between Holyhead and Dun Laoghaire.
Could More Than One Train Per Hour Be Sent To Chester And North Wales?
Consider.
- Because of the cancellation of Phase 2 of High Speed 2, there are spare paths on High Speed Two between London and the West Midlands.
- If the core section of High Speed Two is extended Northwards to Crewe, as advocated by Dyan Perry of the High Speed Rail Group, that I wrote about in The Future Of HS2 Could Lie In Its Original Vision, this would create extra paths to Crewe.
- If the West Midlands and Crewe section of the High Speed Two route has the same capacity as London Euston and the West Midlands it could handle seventeen tph.
- At present it looks like with the cancellation of Phase 2, the West Midlands and Crewe section will handle just ten tph.
, So there will be seven spare paths between Euston and Crewe!
In fact it will be better than that, as each train could be a pair of Classic-Compatible trains, that split and joined to serve two destinations.
Could A North Wales Service Call At Hawarden Airport?
Hawarden Airport is where Airbus build wings for their aircraft in the UK.This Google Map shows Hawarden Airport.
Note.
- The large runway.
- The various factory buildings.
- The North Wales Coast Line between Chester and Holyhead, runs along the North side of the Airport.
I doubt if Airbus wanted a station, it would be difficult to arrange.
Conclusion
Because of the vacant paths, it would appear that extra services to North Wales and North West England can be fitted in.
Mayors Head To Parliament With Plan For Northern Arc To Deliver Green Growth
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from Liverpool City Region.
These four bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Steve Rotheram and Andy Burnham take case for backing Northern Arc to Treasury – as new data shows North can drive green growth and unlock £90bn for UK economy
- Liverpool City Region and Greater Manchester Mayors will meet with ministers and MPs today, and Andy Burnham will give evidence at Business and Trade Select Committee on the UK’s industrial strategy
- Economic analysis shows that investing in transport infrastructure and a pipeline of projects across the North would benefit the whole UK economy, improving living standards and closing the North-South productivity gap
- Mayors will also address Innovation Zero World Congress in London, showing how city-regions can create high quality jobs by pioneering low-carbon innovation
These two paragraphs add a bit more detail.
The right investment would create a growth corridor, stretching from the Mersey to the Pennines and connecting into West and South Yorkshire, underpinned by transport networks that would include a new railway linking Liverpool and Manchester.
The Northern Arc area spans regions with close economic ties to Lancashire, North Wales, Hull and the North East. With international connections through the Port of Liverpool and Manchester Airport, it’s well positioned for global trade.
If I have a problem with the mayors’ thoughts, the plan outlined in the news item is rather Liverpool/Manchester-based with Hull being the only city outside that area getting a mention. Do Blackburn, Blackpool, Bradford, Burnley, Doncaster, Huddersfield, Leeds, Preston, Rotherham, Scunthorpe, Stockport, Wigan and York exist?
For instance you would expert a report from Liverpool and Manchester’s Mayors to call for a new railway between their two cities. And of course they do!
The current TransPennine Lines has two main routes across the Pennines between East and West.
If ever there was a rail route, designed by Topsy, it is the North TransPennine Route.
- There are six separate services, if you ignore Newcastle and Edinburgh Waverley, which is a shuttle to fill a gap in rail services.
- In the West trains terminate at Huddersfield, Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Airport, Manchester Piccadilly and Manchester Victoria
- In the East trains terminate at Edinburgh Waverley, Hull, Leeds, Newcastle, Redcar Central, Scarborough and York.
- Terminals like Huddersfield, Hull, Liverpool Lime Street, Newcastle and York are some of the best terminal stations in the UK, but others are very second rate.
I suspect, this North TransPennine Route structure brought about the demise of TransPennine Express.
The South TransPennine Route on the other hand, although it was built by several different railway companies, they were all intent on the same thing. An East-West route across the Pennines through Doncaster, Manchester and Sheffield.
- The Western terminal is Liverpool Lime Street, which in my view is the finest grand terminus in the UK, in terms of architecture, onward connections and operation. It is also the oldest still-operating grand terminus mainline station in the world, in that it dates from 1836.
- The Eastern terminal is Cleethorpes, which is an efficient four-platform recently-refurbished station, that is within a hundred metres of some of the best gluten-free fish and chips, I’ve ever tasted on the pier.
- Intermediate stations include Liverpool South Parkway, Warrington Central, Birchwood, Irlam, Urmston, Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester Piccadilly, Stockport, Sheffield, Meadowhall, Doncaster, Scunthorpe, Barnetby, Habrough and Grimsby Town.
- Liverpool South Parkway has a bus connection to Liverpool Airport
- Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Oxford Road, Manchester Piccadilly, Stockport, Sheffield and Doncaster are stations with comprehensive onward connections.
- The route is electrified between Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Piccadilly and at Doncaster.Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes is 148.2 miles
- Hazel Grove and Doncaster is without electrification and is 52.3 miles long.
- Cleethorpes and Doncaster is without electrification and is 52.1 miles long.
- I believe that Hitachi, Siemens and Stadler could supply battery-electric trains, that would be able to work the route, with the addition of a short length of overhead wires at Cleethorpes, so that trains could return to Doncaster.
- Trains go straight through all the intermediate stations, so there are no time-wasting reverses.
- Journey time is just over three and a half hours.
I believe that a mouse-quiet battery-electric train would pack in the punters, if only for the novelty.
But.
A battery-electric train would probably knock perhaps thirty minutes off the journey.
The timetable would be an hourly train at all stations.
The service would pass the mother’s birthday test, in that you could easily visit any station from any other and buy your mother lunch before returning on a convenient train.
There are connections to and from London at Liverpool Lime Street, Manchester Piccadilly, Stockport, Sheffield and Doncaster.
It could be a very useful East-West train service.
Arriva Group Invests In New Battery Hybrid Train Fleet In Boost To UK Rail Industry
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from Arriva Group.
These four bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Order worth around £300 million for fleet of new trains, which will increase seats by 20 per cent, improving capacity and connectivity.
- 45 rail cars to be manufactured at Hitachi Rail in the North East and financed by Angel Trains, helping secure highly skilled jobs and unlocking a new advanced manufacturing opportunity for rail.
- State-of-the-art ‘tri-mode’ train technology has proven its ability to cut emissions and fuel costs by around 30 per cent to support UK Government’s decarbonisation agenda.
- Announcement is made from Hitachi’s Newton Aycliffe factory and attended by the Secretary of State for Transport, Heidi Alexander MP.
These three paragraphs give more details.
Arriva Group announced today an order for nine cutting-edge battery hybrid trains to replace its entire Grand Central fleet, providing a major boost to regional economies and offering passengers more comfortable, greener travel options.
The order for 45 Hitachi Rail ‘tri-mode’ cars, which have the flexibility to run on electrified and non-electrified tracks, along with a 10-year maintenance contract, represents an investment of around £300 million. Tri-mode means the trains can be powered using electricity, battery or diesel.
It follows approval by the rail regulator for extended track access rights for Grand Central’s existing services through to 2038, with the investment underpinning Arriva’s long-term commitment to UK rail and to delivering sustainable public transport solutions to communities up and down the country and across Europe.
The trains will be built by Hitachi at Newton Aycliffe.
I have some further thoughts and questions.
What Distances Will The Trains Run Away From Electrification?
The distances that the various services will run away from electrification are as follows.
- King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange – Doncaster and Bradford Interchange – 52.1 miles.
- King’s Cross and Cleethorpes – Doncaster and Cleethorpes – 52.1 miles.
- King’s Cross and Sunderland – Longlands junction and Sunderland – 48.5 miles.
It would appear that a train with a range away from electrification of 55 miles would be enough, if there were to be charging at all the destinations.
Will The Trains Be Able To Take The Great Northern And Great Eastern Joint Line (GNGE) Diversion Via Lincoln On The East Coast Main Line?
I discussed using this diversion in detail in London And Edinburgh By Lumo Using the Joint Line Diversion.
In that post, I said this.
The January 2024 Edition of Modern Railways says that the diversion is approximately 90 miles or 145 kilometers.
If the trains have a 90 mile capability on batteries and/or diesel, they will be able to use the diversion.
As Hull Trains, LNER and Lumo all need this ability to take the GNGE Diversion, I suspect, it will be a tick-box on the order form for the trains.
When Will The Trains Be In Service?
The news item says this.
The trains will be delivered in 2028 under a 10-year leasing arrangement, in partnership and financed by Angel Trains.
Will The New Trains Be Faster?
They might save a couple of minutes, if Doncaster is the first stop.
Will The New Trains Be Quieter?
The news item says this about noise and emissions.
State-of-the-art ‘tri-mode’ train technology has proven its ability to cut emissions and fuel costs by around 30 per cent to support UK Government’s decarbonisation agenda.
Hitachi have said that the diesel engines will not run in stations.
Could The Trains Run Grand Central’s Routes Carbon-Free?
In The Data Sheet For Hitachi Battery Electric Trains, I came to these conclusions
- The battery pack has a capacity of 750 kWh.
- A five-car train needs three battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- A nine-car train needs five battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- The maximum range of a five-car train with three batteries is 117 miles.
- The maximum range of a nine-car train with five batteries is 121 miles.
As battery technology gets better, these distances will increase.
If I was choosing the trains for Grand Central, the trains would be able to operate these routes without using diesel.
- Doncaster and Bradford Interchange and return.
- Doncaster and Cleethorpes and return.
- Longlands junction and Sunderland and return.
Passengers might not like to have noisy passengers.
Probably, the best insurance policy to avoid running out of battery power, would be to have perhaps fifty metres of electrification at terminal stations. Hitachi claim they can offer a nice line in short lengths of electrification.
Quiet Trains Should Attract Passengers
I’ve seen it before and also with buses.
The Number Of Trains Ordered
The basic order is for nine trains, but Railway Gazette says this.
Arriva welcomed the ‘swift decision-making’ by ORR and the backing of the Department for Transport and Network Rail. It has also submitted applications to run more trains to Bradford and introduce services to Cleethorpes, and has an option to buy more trains if these are approved.
I’ve read somewhere that the option is for three extra trains.
So that’s a total of twelve, which would replace the ten Class 180 trains and two Class 221 trains, that Grand Central Trains currently run.
What About Chiltern Railways And CrossCountry?
Train operating companies Chiltern Railways, CrossCountry and Grand Central Trains are all wholly owned subsidiaries of Arriva Trains UK, who are described like this in the first paragraph of their Wikipedia entry.
Arriva UK Trains Limited is the company that oversees Arriva’s train operating companies in the United Kingdom. It gained its first franchises in February 2000. These were later lost, though several others were gained. In January 2010, with the take-over of Arriva by Deutsche Bahn, Arriva UK Trains also took over the running of those formerly overseen by DB Regio UK Limited
Arriva is ultimately owned by American infrastructure investment company; I Squared Capital.
Both Chiltern Railways and CrossCountry have trains, that are coming to the date, when they will need to be replaced and similar trains to those ordered by Grand Central could be suitable. to replace some.
Chiltern Railways have six rakes of Mark 3 coaches, that are hauled by diesel locomotives between London Marylebone and Birmingham Moor Street stations, These rakes of coaches could be replaced by Hitachi tri-mode trains, of perhaps five or six cars.
Chiltern Railways also have about sixty assorted diesel multiple units totalling up to about 150 carriages.
CrossCountry Trains have twenty-nine two- or three-car Class 170 trains and sixty-one four- or five car Class 220 or 221 trains. All these ninety trains were built this century and are diesel-powered.
The Government’s policy of net-zero by 2050, would probably mean a significant number of these smaller diesel multiple units need to be replaced by 2030.
If the Grand Central Trains new Hitachi trains are a success, then changing the longer four-, five- and six-car trains for similar Hitachi trains, would be a low-risk replacement strategy for I Squared Capital, that could be applied at Chiltern Railways and CrossCountry.
I can also see a need for a two-, three- or four-car tri-mode train for Chiltern Railways and CrossCountry.
Was The Date Of The Announcement Significant?
In October 2020, I wrote Hitachi Targets Export Opportunities From Newton Aycliffe and I believe that tri-mode trains like these that Grand Central have ordered could have export opportunities.
One country for exports has possibilities and that is the United States.
- Hitachi AT-300 trains like these don’t need expensive high-speed tracks and there are probably many lines in the United States, where these trains could fit existing tracks.
- This page on the Hitachi Rail web site is entitled Hitachi Rail in the USA and Canada.
- In the UK, companies like GWR, LNER, Southeastern and TransPennine Express effectively use theHitachi trains as fast commuter trains on some routes.
- Trump’s tariffs would only be 10 % on these trains.
- The Grand Central version looks very stylish!
- Hitachi’s battery technology is owned by Turntide Technology, who are a US company.
- For some routes, the trains would probably only need to be battery-electric.
Has the experience of running Chiltern Railways, CrossCountry and Grand Central Trains convinced I Squared Capital, that running railways is a good investment?
Have I Squared Capital identified some railroads in the United States, that could follow a similar upgrade path to Chiltern Railways?
Was it significant that the order was announced the day after Trump’s tariffs?
.
Changing Trains At Newcastle Station
In the last few weeks, I have changed trains at Newcastle station between the East Coast Main and the Northumberland Line four times.
I took these pictures on Sunday, when I changed twice.
Note.
- On my two train changes yesterday, I needed to buy a ticket for the next leg of my journey and I had to walk miles to the ticket office.
- The walk was rather straining on my dodgy knees.
- There are no signs to the ticket office and I only found it due to a helful human.
- In the morning, I missed my connection and had to wait an hour for the next train.
- A lot of these pictures show diesel multiple units, that were working the Northumberland Line to Ashington in Platform 1, surrounded by happy passengers.
- Platform 1 appears to be able to take at least a pair of Class 158 two-car diesel multiple units.
- Platform 1 appears to be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead wires, even if the Northumberland Line isn’t electrified.
- The staff seem extremely pleased with the success of the Northumberland Line.
The staff were very helpful, but it was all very much organised chaos.
But from what I saw yesterday, it appears that something powerful is stirring along the Northumberland Line.
Perhaps what the BBC predicted in Northumberland Line: Railway ‘Could Create Economic Powerhouse’ is starting to happen?
This was the sub-heading of the BBC article.
An “east coast economic powerhouse” stretching from Edinburgh to Leeds could be created if the Northumberland Line rail scheme goes ahead, a public inquiry has been told.
I’m well aware that one busy weekend doesn’t make a powerhouse.
But Northumberland Council must get ready for the next phases of the project.
Larger Zero-Carbon Trains
In Alstom Hydrogen Aventras And The Reopened Northumberland Line, I suggested that Alstom hydrogen trains might be suitable for the Northumberland Line, but these trains have not been seen in the flesh, so they can probably be discounted.
But this is a picture I took yesterday of Platform 1 at Newcastle station.
Note.
- The wires of the electrification above the Class 158 diesel multiple unit.
- An out and back trip between Newcastle and Ashington is probably less than fifty miles.
In the Wikipedia entry for Merseyrail’s Stadler Class 777 trains, this is said.
In December 2022, a maximum test range of 135 km (84 miles) was achieved, which was “much longer than we expected”.
It would appear that a small fleet of perhaps three trains, that were fitted with pantographs for charging could work the Northumberland Line, without the need for substantial additions to the infrastructure.
In the Wikipedia entry for the new Tyne and Wear Metro’s Stadler Class 555 trains, this is said.
The new trains will be five cars long in fixed formations, with a Jacobs bogie between the inner cars. One centre car will be fitted with a Brecknell Willis pantograph to draw the power from the 1,500 V DC overhead lines. They will also be fitted with regenerative braking technology for greater energy efficiency, and a battery energy storage system that will allow the trains to remain powered and reach the nearest station if the overhead lines fail. This offers the potential to be used on routes that are not fitted with overhead lines that may be added to the network in the future.
As the Class 777 and Class 555 trains appear to be cousins, perhaps those innovative Swiss engineers at Stadler can come up with a 25 KVAC battery-electric Class 555 train, that could charge its batteries in Platform 1 at Newcastle station and then use battery power to get to Ashington and back.
With perhaps a couple of short lengths of 25 KVAC overhead electrification, I feel Stadler could create a battery-electric Class 555 train, that could handle.
- Newcastle and Ashington and on to Newbiggin, as I wrote about in Onward To Newbiggin-by-the-Sea For The Northumberland Line?.
- Newcastle and Carlisle
- Carlisle and Morpeth via Newcastle
- Hexham and Nunthorpe via Newcastle
How many other branches from electrified main lines in the UK, could be handled by such a train?
How about these routes for starters.
- Darlington and Bishop Auckland
- Darlington and Saltburn
- Preston and Blackpool South.
- Skipton and Preston via Colne.
- Lancaster and Morecambe
- Leeds Metro
- Llandudno Junction and Blaenau Ffestiniog
- Middlesbrough and Whitby.
- Sheffield and Huddersfield
- Sheffield and Leeds
- Sheeffield and Manchester Piccaduilly
Sheffield and York
The Class 555 trains would also have other advantages.
- In the Newcastle area, I’m sure the Tyne and Wear Metro could probably service them.
- They have the Stadler steps for easy access.
- Most Stadler trains, tram-trains and trams are good at climbing hills.
Great British Railways could do a lot worse, than buying a reasonable number of Class 555 battery-electric trains.
Grand Central To Submit Application For Direct Services Between Lincolnshire And London
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from Grand Central.
These three bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Grand Central has today launched an application process for direct services between Cleethorpes, Grimsby, Habrough, Scunthorpe and London – plans to bring significant benefits to underserved areas.
- The application will be welcomed by communities, businesses, and organisations, who have been actively campaigning for the introduction of direct rail links to London.
- If approved, the new services could unlock £30.1 million annually for the region.
These three paragraphs add more details.
Grand Central has today notified Network Rail of its plans to operate new direct services between Lincolnshire and London that, if approved by the rail regulator (the ORR), will bring significant benefits to underserved areas across Lincolnshire and the wider region.
Under the proposals, direct services to London will be provided from Cleethorpes, Grimsby, Habrough, and Scunthorpe, with Grand Central planning to operate the services from as early as December 2026.
The plan makes best use of capacity on the rail network by running trains from the proposed new stops before connecting into existing Grand Central services at Doncaster.
The service seems very similar to the proposed King’s Cross and Cleethorpes service described in the this section of the Grand Central Wikipedia entry, where this is said.
In December 2017, Grand Central announced plans to bid for a service from London King’s Cross to Cleethorpes in early 2018 for a date in 2020. It would involve the existing Bradford Interchange service extended to ten coaches from London to Doncaster then dividing with five coaches going to Cleethorpes via Scunthorpe, Barnetby, Habrough and Grimsby. The other five coaches would be the existing service to Bradford Interchange. This proposal would require permission for a split of trains as it has not been used on the East Coast Main Line before. In February 2018, Grand Central announced plans for an additional call at Crow The company planned to operate four trains per day from 2020. However, in July 2018, the Office of Rail and Road announced new access charges which would affect the business case for the new service, leading to Grand Central announcing that it would delay bidding until 2019.
Note.
- It appears that the service is not calling at Crow.
- By splitting and joining at Doncaster, Grand Central will be getting more coaches and passengers, up and down a single path between King’s Cross and Doncaster stations.
- Grand Central run four trains per day (tpd) between King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange, so as four tpd will be running between King’s Cross and Doncaster stations, it appears Grand Central will be running a full service.
It appears that open access applications come to those who wait eight years.
I have some further thoughts.
What Class Of Trains Do Grand Central Currently Use?
According to Real Time Trains on Friday the 21st of March 2025, two Class 180 trains and two Class 221 trains each ran a service between King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange stations.
Both type of train appear to be able to run as a pair of trains.
As Bradford is the UK City of Culture in 2025, that could prove useful.
What Trains Will Grand Central Use For The New Service?
It would appear that either type of train type could run the service,
So it would probably come down to factors like reliability, comfort and what is available.
I Was Mildly Surprised When I Saw This Application Had Gone In
But, circumstances change.
- Grand Central now run two Class 221 trains, in addition to the Class 180 trains.
- There are more Class 221 trains in store, if needed.
- The UK has had several changes of government since the original application in 2017 and track-access charges may have been reduced.
- Cleethorpes station has been refurbished.
Cleethorpes Station – 28th June 2023 shows the station in 2023.
But a new problem has arisen. The new Transport Secretary doesn’t seem keen on open access services, from some of the things she’s said.
Perhaps, she has had a change of heart or as she looks to be a good doer, someone has bought her a decent meal of fish and chips in Cleethorpes? My meal in the town is described in Lunch On The Pier In Cleethorpes.
But would Grand Central put in an application, if they knew they were wasting their money?
Or could this be an application funded by all the open access operators to get a definitive view on the government’s policy?
Could The Cleethorpes Service Be Run By Battery-Electric Trains?
Consider.
- Doncaster and Cleethorpes are 52.1 miles apart.
- Surprisingly Doncaster and Bradford Interchange are 52.1 miles apart.
- King’s Cross and Doncaster are 155.9 miles apart and fully-electrified.
- A battery that had enough capacity to do the return trips from Doncaster to either Cleethorpes or Bradford Interchange, would be easily recharged on the way to and from London.
With careful calculation of the battery size and good capacity management, I also suspect a battery-electric train could be able to take the GNGE Diversion via Lincoln.
Could The Cleethorpes Service Be Run By Hydrogen-Electric Trains?
Consider the daily services will be made up of these runs.
- Eight runs between London and Bradford Interchange each consisting of 155.9 miles on wires and 52.1 miles on hydrogen.
- Eight runs between London and Cleethorpes each consisting of 155.9 miles on wires and 52.1 miles on hydrogen.
Which means there are 833.6 miles per day run on hydrogen.
If there are four trains running the service as now, that is 208.4 miles per train per day on hydrogen.
A hydrogen-powered train with this daily range is very much a possibility.
The German Dimension To Grand Central Trains
Consider.
- Grand Central are owned by Arriva.
- Arriva are owned by Deutche Bahn.
- Siemens have a train factory at Goole close to Doncaster.
- Siemens have built quite a few electric multiple units for various UK railways.
- Siemens have designs for battery-electric and hydrogen-electric multiple units, that would be suitable for Grand Central Trains.
- Jürgen Maier was senior in Siemens UK, when the train factory at Goole was built and is now chair of Great British Energy.
I believe that Siemens at Goole could build trains, that would do nicely for Grand Central Trains.
- It would surely be handy for Grand Central Trains to have their fleet stabled in easy reach of the factory.
- In addition, hydrogen will soon be readily-available in the Doncaster area.
Grand Central trains could do a lot worse than buy trains built or assembled at Siemen’s factory at Goole.
Council Opposes Six Track Plan For East West Rail
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Councillors have voted to oppose part of a major railway line being built through their district.
These four paragraphs add detail to the story
Bedford Borough Council wants the East West Rail (EWR) line to be made up of four tracks, rather than six, in the Poets area north of the town.
Thirty-seven homes would need to be demolished in order to accommodate the two additional tracks.
However, in their full-council meeting on Wednesday, members agreed to support other parts of the project, such as the relocation of Stewartby station and the closure of Kempston Hardwick.
An EWR spokesperson said it was committed to working with local communities.
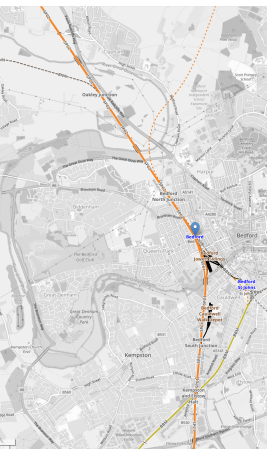
This OpenRailwayMap shows the Midland Main Line and the East-West Rail through Bedford.
Note.
- The solid orange line running from the North-West corner of the map to its Southern edge is the electrified Midland Main Line.
- The blue arrow on this line indicates Bedford station.
- The blue lettering to the South-East of Bedford station, indicates Bedford St. Johns station.
- The yellow line connecting the two stations is the Eastern end of the Marston Vale Line, which connects Bedford and Bletchley stations.
- The Marston Vale Line will be taken over by the East-West Rail.
- Just North of Bedford station is Bedford North junction.
The East-West Rail branches away from Bedford North junction to the North-East on its way to Cambridge. It is shown as a dotted orange line.
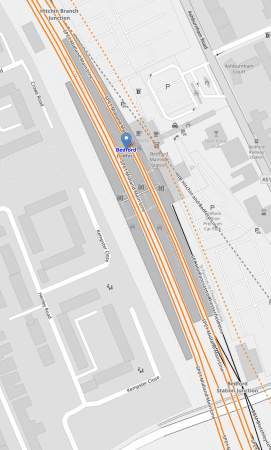
This OpenRailwayMap shows Bedford station to a larger scale.
Note,
- The Western pair of orange lines are the current fast lines of the Midland Main Line.
- The Eastern pair of orange lines are the current slow lines of the Midland Main Line.
- To the East the orange dotted line shows indicates a proposed route of the East-West Rail.
- There appear to be crossovers that allow East-West Rail services to use Platforms 1 and 2 through Bedford station.
Between the Midland Main Line and East-West Rail platforms, the current Platform 1A used by the Marston Vale Line can be seen.
This picture show the current Marston Vale Line platform at Bedford station,
Note.
- The Marston Vale Line platform is on the left.
- It is numbered 1A.
- The platform is electrified, so can it be it used to terminate some Thameslink services.
It could also be used to terminate East-West Rail services from the West and if they were battery-electric trains they could be charged.
Oxford and Bedford is 51 miles or 82 kilometers, which is within range of a modern battery-electric train. Es[ecially, if it did a ‘splash and dash’ at Milton Keynes Central or Bletchley!
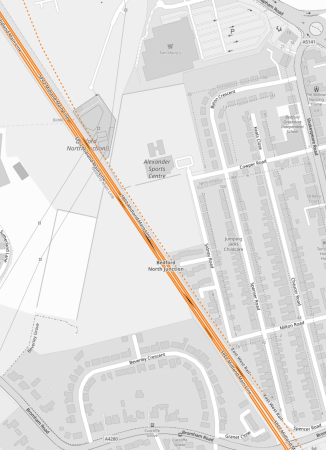
This OpenRailwayMap shows the lines to the North of Bedford station.
Note.
- The current four-track Midland Main Line running diagonally across the map.
- The East-West Rail running along on the East side and branching off to Cambridge.
- Crossovers between the Midland Main Line and East-West Rail.
It looks to me, that operation of East-West Rail trains through Bedford station will be as follows.
- Oxford to Cambridge trains will use the crossovers to call in the existing Platform 2 at Bedford station.
- Cambridge to Oxford to will use the crossovers to call in the existing Platform 1 at Bedford station.
- Trains that are not stopping could use the avoiding line along the East side of the station.
- Oxford to Bedford terminating trains, would stop in Platform 1A.
Because there would be a crossover between the Midland Main Line slow lines and the East-West Rail to the South and North of Bedford station, I suspect for operatuional reasons and safety Network Rail want a double track avoiding line.
Fast Battery-Electric Hitachi Trains Between Paddington And Bristol Temple Mead Stations
It was when I was writing Thoughts On Lumo’s Proposed Paddington And Paignton Service, that I realised how significant Hitachi’s battery-electric high speed trains will be.
This page on the Hitachi web site gives this overview of their Intercity Battery Trains.
A quick and easy application of battery technology is to install it on existing or future Hitachi intercity trains. Hitachi Rail’s modular design means this can be done without the need to re-engineer or rebuild the train and return them to service as quickly as possible for passengers.
Replacing one diesel engine with just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%. Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance.
For the purpose of this exercise, I will assume the following.
- All trains are five-car trains.
- They were all originally manufactured as Class 800, 802 or 805 trains.
- They were all originally manufactured with three 750 kW Rolls-Royce mtu diesel generators.
- One diesel generator in each train has been replaced by a 750 kW battery-pack of the same size, weight and performance.
According to Hitachi’s web page, that I quote above, this gives intercity speeds at the same or increased performance, for 70 km. on non-electrified routes.
I will now look at how a Hitachi battery-electric high speed train would handle the line between London Paddington and Bristol Temple Mead stations.
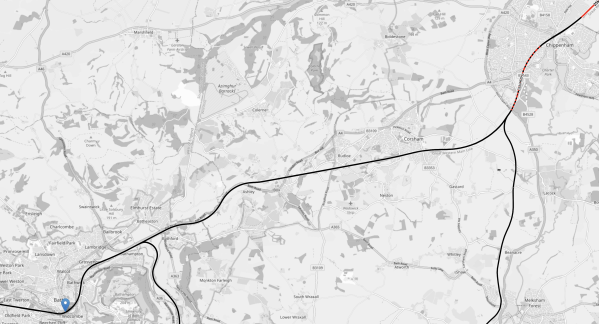
This OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification between Chippenham and Bath Spa stations.
Note.
- London Paddington and Bristol Temple Mead stations are 118.3 miles apart.
- The blue arrow indicates Bath Spa station.
- Bristol Temple Meads station is 11.5 miles to the West of Bath Spa station.
- Chippenham station is in the North East corner of the map.
- Black lines are not electrified.
- Red lines are electrified with 25 KVAC overhead wires.
- The 93.9 miles betweeen London Paddington and Chippenham is fully-electrified.
- Red and black dotted lines are being electrified.
- The 24.4 miles between Chippenham and Bristol Temple Mead stations is not electrified.
- The residents of Bath Spa are not keen for the railway through Bath to be electrified.
The single battery-pack in the train, will have to propel the train between Chippenham and Bristol Temple Mead stations.
- On arrival at Chippenham, the battery will have been fully charged on the 93.9 miles from London Paddington.
- The train will be switched to battery power and proceed through Bath Spa station to Bristol Temple Meads station.
- The 24.4 miles between Chippenham and Bristol Temple Mead stations is only 39.26 km. so it is well within range of a single battery pack.
- The trains will be able to reach Bath, as fast as the track allows, so they could have come much of the way from London Paddington at speeds approaching 125 mph.
Hence my belief that Bath Spa could be reached in around an hour without any stops from London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads in a very fast time.
There may be a need to top up the battery at Bristol Temple Meads station for London trains to return to the electrification at Chippenham or for other trains to continue their journey through Bristol.
This could be handled by some lengths of electrification in platforms in Bristol Temple Meads station, where the Hitachi trains terminate.
However, I feel Network Rail will be able to avoid the sensitive and possibly very challenging electrification through Bath.
Conclusion
London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads via Bath Spa trains would be substantially speeded up. Especially, if the first stop out of London Paddington were to be Bath Spa station.
Great Western Railway would only cut out the stops if they wanted to speed up services.
Who’d have thought, that powering services by batteries, would speed up services?
Thoughts On Lumo’s Proposed Paddington And Paignton Service
Modern Railways says this about Lumo’s proposed new service between Paddington and Paignton.
Under the plans for Paignton, announced on 5 December, there would be five return Lumo trains running between Paddington and Paignton, serving Bath Spa, Bristol Temple Meads, Taunton, Exeter St David’s and Torquay. These could start in May 2028. A sixth path is planned between Highbridge & Burnham and London Paddington.
Modern Railways says that currently there are only three direct trains between Torbay and London and that rail has a 29% modal share on that route compared to 71% for road.
Modern Railways tell us that GWR current run three trains per day to Paignton and these call at Reading, Newbury, Hungerford, Pewsey, Westbury, Castle Cary, Taunton, Tiverton Parkway and Exeter St. David’s and Torquay.
Note.
- Lumo will be taking five stops using a longer route.
- GWR currently take ten stops using a shorter route via Westbury.
- GWR currently take ten stops between London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads.
- The fastest GWR service I can find takes three hours and four minutes between London Paddington and Paignton.
- The fastest GWR service I can find takes one hour and thirty-five minutes between London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads.
- The fastest service I can find takes one hour and thirty-nine minutes with five stops between Bristol Temple Meads and Paignton.
- Lumo’s trains will probably be fitted with traction batteries rather than diesel engines, so it is likely, that the fewer stops they execute will be done quieter and faster.
I would not be at all surprised to find that Lumo’s journey times would be of this order.
- London Paddington and Bath Spa – One hour
- London Paddington and Bristol Temple Meads – One hour and thirty minutes
- London Paddington and Taunton – Two hours
- London Paddington and Exeter St. David’s – Two hours and thirty minutes
- London Paddington and Torquay – Two hours and fifty minutes
- Paddington and Paignton – Three hours
These sections would not be electrified.
- Chippenham and Bristol Temple Meads – 24.4 miles
- Bristol Temple Meads and Paignton – 103.8 miles
In Fast Battery-Electric Hitachi Trains Between Paddington And Bristol Temple Mead Stations, I discuss how Lumo and Great Western Railway will speed trains to Bristol Temple Meads via Bath Spa and Chippenham.
If 128.2 miles on batteries sounds a tough ask, remember that a similar-sized Stadler Addu ran 139 miles on one charge in 2021. Lumo, Hitachi and their battery makers from Sunderland didn’t enter this contest to come a distant second.
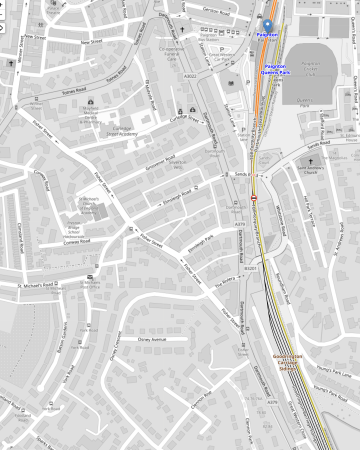
Paignton has a big advantage, as this OpenRailwayMap shows.
Note.
- Paignton station is marked by the blue arrow and writing at the top of the map.
- There are two platforms, one of which normally handles arrivals and the other departures.
- There are the Goodrington Carriage sidings to the South of the station.
I’m sure Hitachi will electrify some of the sidings, so that Lumo’s trains can leave Paignton with full batteries. But they only need enough charge to cover the 128.2 miles to Chippenham!
I have a few extra thoughts.
The Train’s Batteries Will Get Bigger
Hitachi must have access to the best battery chemistry, that the world and especially Japan can offer.
I feel very strongly, that the performance of Hitachi’s trains will get better, as the years progress.
Pairs Of Trains Could Be Used
I suspect all the stations that will be used by the service ; Paddington, Bath Spa, Bristol Temple Meads, Taunton, Exeter St David’s, Torquay and Paignton can handle a pair of five-car Hitachi trains on a busy day.
The Goodrington Carriage sidings at Paignton station would certainly appear to be long enough.
This could be useful.
An Early Bath
Consider.
- Currently, the fastest trains to Bath Spa take one hour and fourteen minutes from London Paddington.
- But the trains do make as many as three stops at Reading, Swindon and Chippenham, before they stop at Bath Spa.
- London Paddington and Bath Spa are 106.8 miles apart.
- The route is fully electrified between London Paddington and Chippenham.
This is an average speed of 86.6 mph.
Lumo will have two advantages
- They will be making Bath Spa the first stop.
- They will be able to maintain at least 100 mph for a large part of the route between London Paddington and Bath Spa, by the use of traction batteries, where there are no wires.
- To go between London Paddington and Bath Spa in an hour, requires an average speed of 106.8 mph
If they could average 100 mph, the time would be 66 minutes.
Bath Spa may not be an hour from Paddington, but it will be very close to it.
I would expect that a fast service to Bath could fill up with day-trippers.
How Long Will A Round Trip Take?
If I’m right that Lumo’s battery-electric high speed trains will be able to do one-way in three hours, then adding in half-an-hour to turn and charge the train at Paignton would suggest a six-an-a-half hour round trip.
How Many Trains Will Be Needed For A Full Service?
Lumo are talking of five round trips per day to Paignton and one to Highbridge & Burnham, so this would probably need two trains to run the service.
The Wikipedia entry for Highbridge & Burnham station says this.
A loop on the west side of the line south of the station can be used by goods trains in either direction, southbound trains crossing over to run wrong line through the northbound No.2 platform to do so. This crossing also allows terminating passenger trains from the north to reverse here if required.
Perhaps this loop will be used to allow one train to start from here in the morning and at the end of the day stable here overnight.
The loop could be electrified to make sure that the first train of the day gets to Chippenham.
Trains could follow a schedule like this.
- Train 1 – Leaves Highbridge & Burnham – 06:00
- Train 1 – Arrives London Paddington – 08:00
- Train 1 – Leaves London Paddington – 08:30
- Train 1 – Arrives Paignton – 11:30
- Train 1 – Leaves Paignton – 12:00
- Train 1 – Arrives London Paddington – 15:00
- Train 1 – Leaves London Paddington – 15:30
- Train 1 – Arrives Paignton – 18:30
- Train 1 – Leaves Paignton – 19:00
- Train 1 – Arrives London Paddington – 22:00
- Train 2 – Leaves London Paddington – 06:30
- Train 2 – Arrives Paignton – 09:30
- Train 2 – Leaves Paignton – 10:00
- Train 2 – Arrives London Paddington – 13:00
- Train 2 – Leaves London Paddington – 13:30
- Train 2 – Arrives Paignton – 16:30
- Train 2 – Leaves Paignton – 17:00
- Train 2 – Arrives London Paddington – 20:00
- Train 2 – Leaves London Paddington – 20:30
- Train 2 – Arrives Highbridge & Burnham – 22:30
Someone with more experience of writing timetables could make this work.
But it does appear to me, that using Highbridge & Burnham station for an early start and an overnight charge of one of the trains could mae the whole service work.
Fourteen New Trains To Drive First Rail Open Access Growth
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from First Group.
These four bullet points are sub-headings.
- The Group has signed an agreement with Angel Trains and Hitachi to lease 14 new five-car class 80X Hitachi electric, battery electric or bi-mode trains (70 cars in total) at a cost of c.£500m including maintenance, over a ten year lease period
- The trains will be manufactured by Hitachi in County Durham, securing the skills base and jobs in the local area
- The new trains will enable FirstGroup to significantly expand its open access portfolio and will be used on the newly announced London-Carmarthen route and to increase the number of cars on the existing Lumo and Hull Trains services
- The agreement also contains an option for FirstGroup to lease up to an additional 13 trains on the same terms if the Group’s open access applications are granted by the Office of Rail and Road (‘ORR’)
These first three paragraphs add a bit more detail.
Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer is visiting Newton Aycliffe, County Durham, today to celebrate a significant agreement for the Hitachi factory which has secured an order to manufacture 70 new rail cars for FirstGroup’s growing open access business, creating certainty for the manufacturing skills base, and the factory’s future.
The Lease Agreement will deliver 14 new trains, which will not only give the Group a homogenous fleet across its open access operations, ensuring flexibility and reliability for customers, but also facilitates the Group’s strategic objective of materially increasing its open access capacity. Delivery of the new trains is expected to commence in late 2027. The lease will be financed by Angel Trains, adding to their portfolio of Hitachi assets. The trains will be maintained by Hitachi at their facilities around the country.
The trains will be used on the Group’s open access rail services, including the Carmarthen-London route announced on 5 December, and the existing Hull Trains and Lumo services on the East Coast Mainline.
Note.
- Does the presence of Keir Starmer indicate any approval for open access?
- Trains could be electric, battery electric or bi-mode.
- Bi-mode trains should only be purchased these days, if they are convertible to battery-electric trains. Hitachi’s can.
- Delivery is expected to commence in late 2027.
- The first fourteen trains will be deployed on the London to Carmarthen, Edinburgh and Hull routes.
This table shows the trains needed initially for each route.
- Carmarthen – Class 802 trains – 5 tpd – 5 trains – 75.3 miles unelectrified
- Edinburgh – Class 803 trains – 5 tpd – 5 trains – electrified
- Hull – Class 802 trains – 5 tpd – 5 trains – 44.3 miles unelectrified
Note.
- tpd is trains per day.
- I’m assuming that as unelectrified distances to Carmarthen and Hull are not that far apart, the number of trains needed is the same.
- Class 802 trains are bi-mode.
- Class 803 trains are electric.
After the fourteen new trains are delivered, there will be a combined fleet of 29 trains.
Consider.
- Hull Trains have started running some services as pairs of trains. I wrote about this in Ten-Car Hull Trains.
- Lumo has been a success and perhaps needs more capacity.
The Wikipedia entry for Grand Union says this.
Grand Union proposed to operate with ex-LNER Class 91s and Rail Operations Group Class 93s hauling nine-car Mark 4s and a Driving Van Trailer.
So perhaps the Carmarthen service needs ten-car trains.
That would mean that the number of routes needed for the three routes would be as follows.
- Carmarthen – Class 802 trains – 5 tpd -10 trains
- Edinburgh – Class 803 trains – 5 tpd -10 trains
- Hull – Class 802 trains – 7 tpd – 10 trains
It would appear that we’re a train short with 29 in the combined fleet against a need of 30 trains.
But then it would also appear that Hull Trains can provide the required five/ten car service with only four trains.
I would assume that the extra train, goes to make up the numbers for Lumo’s Carmarthen service.
FirstGroup Acquires London – South Wales Open Access Business And Plans Lumo To Devon
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
This is the sub-heading.
‘Growing our open access rail portfolio is a key priority’, FirstGroup CEO Graham Sutherland said on December 5 when the company announced that it had acquired Grand Union Trains GWML Holdings Ltd. GUT holds track access rights to launch an open access passenger service between London and Carmarthen. FirstGroup has also applied for paths to launch a London to Paignton service.
FirstGroup seem to have acted quickly to replace the business that they have lost to the Government.
This is said about the London Paddington and Carmarthen route.
The London Paddington to Carmarthen service is now expected to launch in December 2027, with GUT having secured track access rights to the end of 2037.
There will be five services each way per day, calling at stations including Bristol Parkway, Newport, Severn Tunnel Junction, Cardiff Central, Gowerton and Llanelli. FirstGroup said it would provide low fares, ‘more customer choice and much-needed additional capacity’.
It is still considering rolling stock options, and ’updates will be provided in due course’. The trains would have one class, free wi-fi and onboard catering.
After the successful trial of battery-powered high speed trains that I wrote about in ‘UK-First’ Intercity Battery Trial Exceeds Expectations, I would suspect that the train would run between London Paddington and Carmarthen like this.
- Run between London Paddington and Cardiff Central using the 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- Whilst running between Paddington and Cardiff Central, the train’s batteries will be fully charged using the overhead electrification.
- Run between Cardiff Central and Carmarthen using the onboard battery power.
- Charge the train as required at Carmarthen.
Note.
- London Paddington and Cardiff Central is 145.2 miles or 233.7 km.
- Cardiff Central and Carmarthen via Gowerton is 75.3 miles or 121.2 km.
- In case of disruption, trains could wait at Cardiff Central, until the batteries had enough charge.
A battery capability of 121.2 km will be needed.
This is said about the London Paddington and Paignton route.
An application has been submitted to the Office of Rail & Road for the service to incorporate five return trips per day between London Paddington and Paignton via stations including Bath Spa, Bristol Temple Meads, Taunton, Exeter St David’s and Torquay from May 2028, as well as a sixth path between Highbridge & Burnham and London.
I suspect that the Paignton route will use a similar profile to the Carmarthen route.
- Run between London Paddington and Chippenham using the 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- Whilst running between Paddington and Chippenham, the train’s batteries will be fully charged using the overhead electrification.
- Run between Chippenham and Paignton using the onboard battery power.
- Charge the train as required at Paignton .
Note.
- London Paddington and Chippenham is 93.5 miles or 233.7 km.
- Chippenham and Paignton is 128.6 miles or 207 km.
- In case of disruption, trains could wait at Chippenham , until the batteries had enough charge.
A battery capability of 207 km will be needed.
This page on the Hitachi Rail web site is entitled Intercity Battery Trains, where this is a paragraph.
Replacing one diesel engine with just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%. Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance.
I am a Graduate Control and Electrical Engineer and I believe that, if you have a train with two batteries, then by sequencing and managing the power, a range of 140 km. should be possible. As a typical Class 802 train, as used by Hull Trains has three diesel engines, would the train have a range of 210 km., if all three were swapped for batteries?
One fact, that has been disclosed by Hitachi, is that diesel engines and battery packs are identical in weight and power, so train performance and handling is unaffected, by the number of batteries.
If we look at the routes of First Group present and future subsidiaries and how much is on unelectrified track, we can create the following table.
- Beverley – Hull Trains – 71.3 km.
- Carmarthen – Lumo – 121.2 km.
- Hull – Hull Trains – 58,1 km.
- Paignton – Lumo – 207 km.
- Rochdale – Lumo – 16.7 km.
- Sheffield – Hull Trains – 37.5 km.
- Worksop – Hull Trains – 12.2 km.
Note,
- One two or three batteries could be fitted.
- Some destinations could be served without any charging at the destination.
- Hitachi have proposed short lengths of 25 KVAC overhead line to charge trains.
- For some destinations, it may be a more affordable to add another battery than add a charger.
It’s all very modular.