National Grid Launches Viking Link, The Next Step Towards A North Sea Super-Grid
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These four bullet points act as sub-headings.
- The £1.8bn project connecting the UK with Denmark was launched today.
- With a capacity of 1.4GW, Viking Link will be able to power up to 2.5 million UK homes and is the longest land and subsea cable in the world.
- Viking Link will deliver £5.2bn in benefits to UK consumers.
- As the UK’s first connection with renewable energy-rich Denmark, Viking Link will be instrumental in both countries achieving net zero carbon emissions.
The press release then gives all the details of the latest of National Grid’s sixth interconnector.
As a Control Engineer, I like this interconnector.
- Denmark and the UK are both importers of electricity.
- The UK has 30 GW of wind power and Denmark has 7 GW.
- The UK has almost 15 GW of solar power and Denmark has 3.5 GW.
- The UK has 6 GW of nuclear and Denmark banned nuclear in 1985.
- Both the UK and Denmark use large amounts of biomass to generate electricity.
- As the sun goes East to West, Denmark will produce its daily peak solar before the UK.
- If the prevailing winds go West to East, the UK will produce its daily peak wind before Denmark.
It looks to me that a UK-Denmark interconnector could perform a valuable job, by balancing the UK’s electricity peaks and troughs with those of Denmark.
The system could be improved in two ways.
- If Southern England has a sunny, windy day, there may be need for substantial energy storage.
- The route between the UK and Denmark could be via a large offshore wind farm in the North Sea.
Vind∅ is a proposed Danish energy island in the North Sea.
There’s more about the Viking Link on its web site.
This is the introduction on the home page.
Viking Link is a 1400 MW high voltage direct current (DC) electricity link between the British and Danish transmission systems connecting at Bicker Fen substation in Lincolnshire and Revsing substation in southern Jutland, Denmark.
The project involves the construction of converter sites and installation of onshore and offshore cable in each country. These are then connected to the substations.
Viking Link is approximately 765 km long and allows electricity to be exchanged between Great Britain and Denmark.
The interconnector enables the more effective use of renewable energy, access to sustainable electricity generation and improved security of electricity supplies. It also benefits the socio economy of both countries.
This is going to be a very valuable interconnector for the UK, Denmark and those that own it.
Application Of Control Engineering Principles To The Calculation Of Pharmaceutical Drug Doses
Today, I was asked by an eminent cardiologist to give my opinion on this scientific paper in the Journal of the American Heart Association, which was entitled Personalized Antihypertensive Treatment Optimization With Smartphone‐Enabled Remote Precision Dosing of Amlodipine During the COVID‐19 Pandemic (PERSONAL‐CovidBP Trial).
This was the background to the study.
The objective of the PERSONAL‐CovidBP (Personalised Electronic Record Supported Optimisation When Alone for Patients With Hypertension: Pilot Study for Remote Medical Management of Hypertension During the COVID‐19 Pandemic) trial was to assess the efficacy and safety of smartphone‐enabled remote precision dosing of amlodipine to control blood pressure (BP) in participants with primary hypertension during the COVID‐19 pandemic.
These were the methods and the results.
This was an open‐label, remote, dose titration trial using daily home self‐monitoring of BP, drug dose, and side effects with linked smartphone app and telemonitoring. Participants aged ≥18 years with uncontrolled hypertension (5–7 day baseline mean ≥135 mm Hg systolic BP or ≥85 mm Hg diastolic BP) received personalized amlodipine dose titration using novel (1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 mg) and standard (5 and 10 mg) doses daily over 14 weeks. The primary outcome of the trial was mean change in systolic BP from baseline to end of treatment. A total of 205 participants were enrolled and mean BP fell from 142/87 (systolic BP/diastolic BP) to 131/81 mm Hg (a reduction of 11 (95% CI, 10–12)/7 (95% CI, 6–7) mm Hg, P<0.001). The majority of participants achieved BP control on novel doses (84%); of those participants, 35% were controlled by 1 mg daily. The majority (88%) controlled on novel doses had no peripheral edema. Adherence to BP recording and reported adherence to medication was 84% and 94%, respectively. Patient retention was 96% (196/205). Treatment was well tolerated with no withdrawals from adverse events.
These were the conclusions.
Personalized dose titration with amlodipine was safe, well tolerated, and efficacious in treating primary hypertension. The majority of participants achieved BP control on novel doses, and with personalization of dose there were no trial discontinuations due to drug intolerance. App‐assisted remote clinician dose titration may better balance BP control and adverse effects and help optimize long‐term care.
About Myself
I am a Graduate Control Engineer, who graduated from the University of Liverpool in 1968.
I then worked at ICI in Runcorn for eighteen months, before moving to ICI Plastics Division, because of the untimely death of my father-in-law.
One of my tasks at Welwyn, was to look at control algorithms for chemical plants. For this I often used a PACE 231-R analogue computer.
Note.
- These computers could solve up to a hundred simultaneous differential equations at one time.
- They were programmed by wiring the various amplifiers and potentiometers together to simulate the equations.
- There were only a few transistors in these powerful machines, as all electronics were thermionic valves.
- Two of these machines wired together, were used to calculate the trajectories of the Apollo missions.
They were the unsung heroes of bringing Jim Lovell and Apollo 13 home safely.
Determining Control Algorithms
In a typical problem, I would model the a section of a chemical plant and the control system around it.
This would then lead to recommendations, as to the design and operation of the plant, so that it performed as required.
It could be argued that the body of an animal, is a very complicated integrated chemical plant, with a sophisticated control system.
For instance, if sensors around the body, say you are slightly low on fluids, your brain determines you should have a drink.
Many control loops on a chemical plant are controlled by proportional–integral–derivative controllers, which are commonly known as three-term controllers.
This is the first two paragraphs of the Wikipedia entry for three-term controllers.
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a control loop mechanism employing feedback that is widely used in industrial control systems and a variety of other applications requiring continuously modulated control. A PID controller continuously calculates an error value
PID systems automatically apply accurate and responsive correction to a control function. An everyday example is the cruise control on a car, where ascending a hill would lower speed if constant engine power were applied. The controller’s PID algorithm restores the measured speed to the desired speed with minimal delay and overshoot by increasing the power output of the engine in a controlled manner.
I wouldn’t be surprised that the app in the smartphone used in the PERSONAL‐CovidBP Trial contained a form of three-term controller.
These are some points about three-term control algorithms.
Changing Of External Factors
One that was the villain in a problem, I dealt with, also affects my body – the weather.
I was asked to look at the problem of a chemical reaction, that overheated in hot weather. But the plant operators solved it by better insulation and ventilation of the plant and the standard three-term controller adjusted itself automatically to the new conditions.
After my stroke, I am on Warfarin for life. I test my own INR with a Roche meter and I have noticed that atmospheric pressure affects my INR. I change my deose accordingly, using a simple algorithm, of my own design.
The More You Test The More Precise The Control
If you take the cruise control example used by Wikipedia, speed is monitored continuously, as I hope, it would be if you were driving yourself.
But obviously, in many systems, where you are using an input with discrete values to control a system, you can’t be as precise as the data you collect.
When my son was dying from pancreatic cancer, he was fitted with a morphine pump, that he could adjust himself to dull the immense pain he was enduring.
- His nerves and his brain ascertained the pain level.
- He then adjusted the morphine level.
- He could get very precise control of his pain, because he was measuring it continuously.
But he was only using simple one-term control (proportional).
Derivative Control Can Be Difficult To Get Right And Can Even Go Unstable
Derivative control is mainly to stop overshoot, but sometimes you will find that it can go unstable, so two-term(proportional+integral) controllers will be used.
How I Control My INR
As I said earlier, I am on Warfarin for life and test my INR with a Roche meter.
The NHS typically tests patients about once every six weeks, which in my opinion as a Control Engineer is too infrequent.
I usually test myself a couple of times a week.
But every so often, I evaluate what daily dose gives me an equilibrium INR level of 2.5.
For the last three years, I have found a dose of 3.75 mg keeps me more or less on 2.5.
- As Warfarin comes in 1, 3, 5 and 10 mg. tablets, I alternate 3.5 and 4 mg.
- Warfarin tablets are easily cut in half using a sharp knife.
- I record INR and dose in a spreadsheet.
I have been doing this now for over ten years.
Is This A Unique Property Of Warfarin?
In this time, I have had five medical procedures, where surgeons were worried, that as I was on Warfarin, I might bleed too much.
For the first, which was to remove a lump from my mouth, the private surgeon wanted to charge extra for an anaesthetist. In the end, I asked what INR he wanted and he said 2.1 should be OK!
- So I reduced the Warfarin level and tested every day.
- I judged it correctly and had an INR of 2.1 on the day of the operation.
- The operation went incredibly well and I went home on public transport.
- The lump turned out to be benign.
- I’ve not had another lump.
After the operation, I increased the Warfarin level and tested every day, until it regained a level of 2.5.
On analysing my doses through the date of the operation, I found that the total amount of Warfarin, I didn’t take to reduce my INR to 2.1, was the same as I took to bring it back up again to 2.5.
Is this a unique property of Warfarin?
Since then I’ve had two cataract operations performed in a private hospital, where the NHS paid. Interestingly, they wouldn’t trust my own INR readings, so I had to get my GP to take the measurement.
I’ve also had gallstones removed by endoscopy at the local Homerton NHS hospital.
- For cases like mine, the hospital hire in a surgeon from the posh Wellington private hospital for one day a week, who brings the specialist tools needed.
- I wrote about this in Goodbye To My Gallstones.
- As it was a more serious procedure, I reduced my INR to a requested 1.0.
Interestingly, I still have my gall bladder, but the surgeon put it on notice to behave.
Conclusion
I would totally agree with the conclusion given in the PERSONAL‐CovidBP Trial.
Personalized dose titration with amlodipine was safe, well tolerated, and efficacious in treating primary hypertension. The majority of participants achieved BP control on novel doses, and with personalization of dose there were no trial discontinuations due to drug intolerance. App‐assisted remote clinician dose titration may better balance BP control and adverse effects and help optimize long‐term care.
I would add some conclusions of my own.
- The app used in the PERSONAL‐CovidBP Trial, seems to have had a good algorithm.
- I suspect the app could also be Internet-based.
These are some general conclusions.
- If you are on Warfarin and have access to a Roche meter, it is possible to lower your INR to the value required by a surgeon for an operation or a procedure.
- Since starting to take Warfarin, I have had four operations or procedures, where others would have had anaesthetic or a sedative.
- In those four operations, I was able to go home on public transport. If I still drove a car, I could have driven home afterwards.
- Private hospitals like to use an anesthetist, as it pumps up the bill.
- Avoiding anaesthesia must save hospitals money.
Well designed apps, based on Control Engineering principles, that help the patient take the best dose of a drug will become more common.
Thoughts On Alstom At Derby
In the 1970s, I worked at ICI Plastics in Welwyn Garden City in a section called Computer Techniques.
We had a unique mandate from the Divisional Board, that allowed us to stick our nose into anybody’s business.
We certainly weren’t short of computing power, as in addition to the Division’s IBM 360 and dial-up services to GEISco, we had one of the handful of PACE 231R analogue computers in the UK.
Note.
- These machines didn’t use many semiconductors.
- These beasts could solve up to a hundred simultaneous differential equations and display the answers as graphs on the printers.
- Other UK companies and institutions with a PACE 231 R, included BMC, British Rail Research and Cambridge University.
- Two were linked together and these did the calculations for the Apollo flights.
- Their finest hour would surely have been to use their flexibility and power to bring home the stricken Apollo 13.
I got an interesting introduction to the industrial world in my three years at Welwyn.
One of our problems, was recruiting enough specialist engineers and programming staff.
So in the end, at one of our Monday morning meetings, we wrote our own advert for the Sunday Times.
We got all the staff we needed, but they weren’t the sort of recruits, you’d normally expect in the 1970s. Two were Indian and two were American, but all were recent immigrants. But they were certainly good enough to solve our problems.
I don’t think the Personnel Department were amused at our independent recruitment exercise.
I sometimes wonder if Bombardier (now Alstom) in Derby has a similar recruitment problem.
I am a Control Engineer and all these hybrid systems, that will power the transport of the future, be they trains, planes or automobiles, need lots of engineers with similar skills to myself and those of computer programmers. So do local companies; Rolls-Royce, JCB and Toyota, who probably have their own skill shortages in these areas, nick the best from Alstom.
It should be noted that in the railway press, it has been said that the Aventras from Derby were late because of software problems.
UK ESO Unveils GBP 58 Billion Grid Investment Plan To Reach 86 GW of Offshore Wind By 2035
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Great Britain’s electricity system operator (ESO) has proposed a GBP 58 billion (approximately EUR 68 billion) investment in the electricity grid. The proposal outlines a vision for incorporating an additional 21 GW of offshore wind into the grid by 2035, which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
These three paragraphs add more details to what the investment in the grid means for offshore wind.
The ESO released on 19 March the first Beyond 2030 report. The plan sets up the necessary infrastructure to transfer power to and from future industries, as electricity demand is expected to rise by 64 per cent by 2035, according to the ESO.
The grid operator said that the plan connects a further 21 GW of offshore wind in development off the coast of Scotland to the grid in an efficient and coordinated way which would bring the country’s total offshore wind capacity to a potential 86 GW.
The proposals could assist the UK government in meeting the sixth Carbon Budget and allow for the connection of Crown Estate Scotland’s ScotWind leasing round.
These are my thoughts.
How Much Offshore Wind Is In The Pipeline?
This Wikipedia entry is a List Of Offshore Wind Farms In The United Kingdom.
It gives these figures for wind farms in various operational an development states.
- Operational – 14,703 MW
- Under Construction – 5,202 MW
- Pre-Construction – 6,522 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 3 – 12 MW
- Contracts for Difference – Round 4 – 1,428 MW
- Early Planning – England – 18,423 MW
- Early Planning – Wales – 700 MW
- Early Planning – Scotland – 30,326 MW
Note.
- These add up to a total of 77,316 MW.
- If all the wind farms in the Wikipedia entry are commissioned, the UK will be short of the 86,000 MW total by 8,664 MW.
- Some wind farms like Ossian could be increased in size by a few GW, as I reported in Ossian Floating Wind Farm Could Have Capacity Of 3.6 GW.
It looks like only another 7,164 MW of offshore wind needs to be proposed to meet the required total.
This article on offshoreWIND.biz is entitled The Crown Estate Opens 4.5 GW Celtic Sea Floating Wind Seabed Leasing Round, will add another 4,500 MW to the total, which will raise the total to 81,816 MW.
The article also finishes with this paragraph.
Round 5 is expected to be the first phase of development in the Celtic Sea. In November 2023, the UK Government confirmed its intention to unlock space for up to a further 12 GW of capacity in the Celtic Sea.
A further 12 GW of capacity will take the total to 93,816 MW.
In Three Shetland ScotWind Projects Announced, I talked about three extra Scotwind wind farms, that were to be developed to the East of Shetland.
These will add 2.8 GW, bringing the total to 96,616 MW.
I don’t think the UK has a problem with installing 86 GW of offshore wind by 2035, so we must create the electricity network to support it.
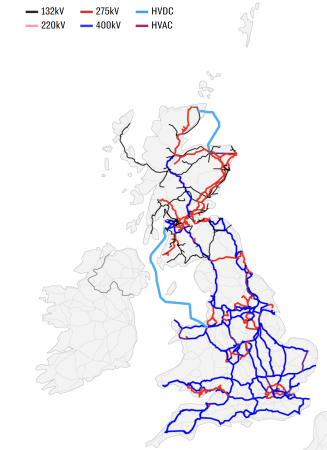
The Electricity Network In 2024
I clipped this map from this article in The Telegraph, which is entitled Britain’s Energy System Will Not Hit Net Zero Until 2035, National Grid Tells Labour.
The dark blue lines are the 400 kV transmission lines.
- The one furthest East in East Anglia serves the Sizewell site, which hosts the Sizewell B nuclear power station and will be the home of Sizewell C nuclear power station, unless the Green or LibDem Parties are a member of a coalition government.
- Kent and Sussex seem to be encircled by 400 kV lines, with small spurs to the interconnectors to Europe.
- Two 400 kV lines appear to serve the South-West peninsular, with one going along the South Coast and the other further North. I suspect these two motorways for electricity explain, why the Morocco-UK Power Project terminates in Devon.
- London seems to have its own M25 for electricity.
- There also appears to be an East-West link to the North of London linking Sizewell in the East and Pembroke in the West. Both ends have large power stations.
- There also appear to be two 400 kV lines from Keadby by the Humber Estuary to North Wales with the pumped storage hydro power station at Dinorwig.
- Two more 400 kV lines link Yorkshire to the South of Scotland.
- A lonely Northern cable connects Edinburgh and the North of Scotland.
The red lines, like the one encircling central London are the 275 kV transmission lines.
- Think of these as the A roads of the electricity network.
- They encircle London often deep underground or under canal towpaths.
- They reinforce the electricity network in South Wales.
- Liverpool appears to have its own local network.
- They also seem to provide most of the capacity North of and between Edinburgh and Glasgow.
Newer cables are starting to appear on this map.
There are two light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- The 1.2 GW Caithness – Moray Link does what it says in the name and it connects the far North of Scotland direct towards Aberdeen.
- The much larger 2.25 GW Western HVDC Link connects Hunterston near Glasgow to Flintshire Bridge near Liverpool. Note how it passes to the West of the Isle of Man.
Not shown on the map are the smaller 500 MW Moyle Interconnector and the recently-opened 600 MW Shetland HVDC Connection.
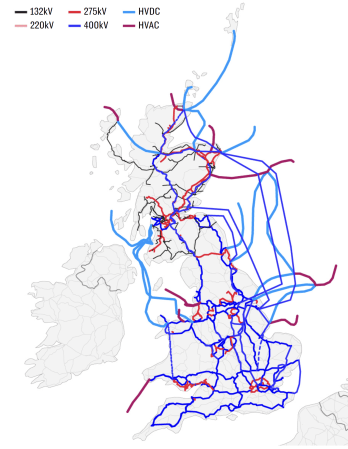
The Electricity Network In 2050
This second map shows how the network will look in 2050.
Note.
- The colours are the same, as the previous map.
- Although, I do think there are some errors in which have been used.
- There are a lot more cables.
There are several more light blue cables and these are HVDC cables that run underwater.
- Shetland is now linked to the North of Scotland by the Shetland HVDC Connection.
- There appears to be a cluster of HVDC interconnectors at Caithness HVDC switching station, near Wick, including a new one to Orkney, to go with the others to Moray and Shetland.
- The 2 GW Scotland England Green Link 1 will run from Torness in Southeast Scotland to Hawthorn Pit substation in Northeast England.
- The 2 GW Eastern Green Link 2 will run from Sandford Bay, at Peterhead in Scotland, to the Drax Power Station in Yorkshire, England.
- There also appear to be two or possibly three other offshore cables linking the East Coast of Scotland with the East Coast of England.
- If the Eastern cables are all 2 GW, that means there is a trunk route for at least 8 GW between Scotland’s wind farms in the North-East and Eastern England, which has the high capacity wind farms of Dogger Bank, Hornsea and around the Lincolnshire and East Angliam coasts.
- Turning to the Western side of Scotland, there appears to be a HVDC connection between the Scottish mainland and the Outer Hebrides.
- South-West of Glasgow, the Western HVDC Link appears to have been duplicated, with a second branch connecting Anglesey and North-West Wales to Scotland.
- The Moyle Interconnector must be in there somewhere.
- Finally, in the South a link is shown between Sizewell and Kent. It’s shown as 400 kV link but surely it would be a HVDC underwater cable.
There are also seven stubs reaching out into the sea, which are probably the power cables to the wind farms.
- The red one leading from South Wales could connect the wind farms of the Celtic Sea.
- The blue link North of Northern Ireland could link the MachairWind wind farm to the grid.
- The other two red links on the West Coast of Scotland could link to other ScotWind wind farms.
- The red link to the North of East Anglia could link RWE’s Norfolk wind farms to the grid.
- The other stubs in the East could either connect wind farms to the grid or be multi-purpose interconnectors linking to Germany and the Netherlands.
It looks to me, that National Grid ESO will be taking tight control of the grid and the connected wind farms, as an integrated entity.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I can’t disagree with that philosophy.
Hydrogen Production
In How Germany Is Dominating Hydrogen Market, I talked about how Germany’s plans to use a lot of hydrogen, will create a large world-wide demand, that the UK because of geography and large amounts of renewable energy is in an ideal place to fulfil.
I can see several large electrolysers being built around the UK coastline and I would expect that National Grid ESO have made provision to ensure that the electrolysers have enough electricity.
Would I Do Anything Different?
Consider.
- If it is built the Morocco-UK Power Project will terminates in Devon.
- There could be more wind farms in the Celtic Sea.
- It is likely, that the wind farms in the Celtic Sea will connect to both Pembroke and Devon.
- Kent has interconnectors to the Continent.
Would a Southern HVDC link along the South Coast between Devon and Kent be a good idea?
Conclusion
Looking at the proposed list of wind farms, a total in excess of 96 GW could be possible, which is ten GW more than needed.
The network not only serves the UK in a comprehensive manner, but also tees up electricity for export to Europe.
UK Set To Provide Record GBP 800 Million Support For Offshore Wind Projects
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK government has revealed the budget of over GBP 1 billion (approximately EUR 1.2 billion) for this year’s Contracts for Difference (CfD) Allocation Round 6 (AR6) with the majority of it, GBP 800 million (around EUR 936 million), earmarked for offshore wind.
These three paragraphs explain the three pots.
The Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) confirmed that over GBP 1 billion will be set aside for the budget, divided into three pots.
Within the overall budget, GBP 120 million is designated for established technologies like solar and onshore wind in Pot 1, while GBP 105 million is set aside for emerging technologies such as floating offshore wind and geothermal in Pot 2.
According to DESNZ, following an extensive review of the latest evidence, including the impact of global events on supply chains, the government has allocated a record GBP 800 million for offshore wind, making this the largest round yet, with four times more budget available to offshore wind than in the previous round.
I am glad to see the support for geothermal energy.
Whilst, these three paragraphs explain the pricing.
This follows the increase in the maximum price for offshore wind and floating offshore wind in November and will help to deliver the UK’s ambition of up to 50 GW of offshore wind by 2030, including up to 5 GW of floating offshore wind, according to the government.
Last year, CfD Round 5 attracted no investors with the former maximum strike prices set at GBP 44/MWh for offshore wind with fixed-bottom foundations, which was too low for the developers who were facing the consequences of inflation and supply chain challenges. The maximum bid price for floating wind was GBP 114/MWh.
Now, the maximum price available for offshore wind projects with fixed-bottom foundations has risen by 66 per cent, from GBP 44/MWh to GBP 73/MWh. The maximum strike price for floating offshore wind projects increased by 52 per cent, from GBP 116/MWh to GBP 176/MWh ahead of AR6 which will open on 27 March.
Prices have certainly risen, but this paragraph explains a limiting mechanism, which is straight out of the Control Engineer’s Toolbox.
The funding for the support will be sourced from energy bills rather than taxation. However, if the price of electricity surpasses the predetermined rate, additional charges will be applied to wind power, with the excess funds returned to consumers.
I would hope that extensive mathematical modelling has been applied to test the new pricing structure.
British Gas Joins Forces With Samsung To Help Customers Power Smarter Energy Use
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
British Gas and Samsung have today announced the exciting first step in a long-term venture – aimed at helping customers better manage their energy use and increase the adoption of low carbon heating technologies in homes across Britain.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The collaboration will see British Gas integrate with Samsung’s SmartThings app to help customers optimise their home appliances to use energy when the cost and demand are lower. This is now possible through the integration of SmartThings Energy and British Gas’ PeakSave demand flexibility scheme informing customers (by sending notifications via their smartphone, TV or other compatible devices) of the best times to use household appliances to save money.
The PeakSave scheme includes PeakSave Sundays, running every Sunday until the end of February with half-price electricity from 11am to 4pm for British Gas customers and PeakSave Winter events which encourages customers to move their electricity use out of peak times when there is high demand on Britain’s energy grid.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I believe that this could make optimising your energy use much easier.
- It would surely be a lot easier to check usage on your phone rather than a smart meter, when you perhaps cook a ready meal, so that you can see if your microwave or traditional cooker is cheapest.
- Suppose you and everybody, who lives with you are out for supper and British Gas want to cut off your gas for a reward, you can make an appropriate decision.
- Hopefully, if you have the right controls, you’ll be able to switch lights and appliances off and on.
The possibilities are endless.
I shall certainly be looking at the reviews of this app.
There is a section in the press release called Scaling Up Low Carbon Heating Opportunities, where this is said.
The collaboration will also help support customers in their journey to decarbonising their homes by introducing smart technologies in a way that is simple and empowering. From early 2024, British Gas will include Samsung heat pumps in its offering to British households to support the UK’s commitment to reach net zero by 2050.
The venture will see specially trained British Gas surveyors and engineers working with consumers to explain the benefits of heat pumps and then conducting the installations on-site. Samsung will be supporting workforce training as part of their efforts to upskill the heating industry to ensure there are enough installers to service the expected growing demand.
British Gas also offers customers the chance to purchase heat pumps through flexible financing methods. This, combined with the recently increased UK Government Boiler Upgrade Scheme grant of £7,500, creates an attractive package of financing options to help people make the transition more affordable.
Various plumbers, who I would trust, have given me different views about heat pumps.
I suspect the Samsung’s SmartThings app might be able to simulate your energy usage with or without the heat pump, as it would know your energy use with your current boiler.
I was doing similar calculations for chemical plants in the early 1970s at ICI, using a PACE 231-R computer.
Consider.
- It may look rather old fashioned, but it could solve a hundred simultaneous differential equations in one go.
- Two similar computers linked together were the analogue half of NASA’s moon mission simulator.
- Without these wonderful machines, NASA would not have been able to re-calculate the dynamics of Apollo 13 and the mission would be remembered as a disaster, rather than the first space rescue.
The average current smart phone has more computing power than a PACE 231-R.
What’s In It For Samsung?
I have a Samsung television, but unfortunately it has a screen fault because of age. So if I had the Samsung app and liked it, I might buy another Samsung TV.
Similarly, the app might give me a financial reason to buy a Samsung heat pump.
Samsung will sell more equipment.
What’s In It For Centrica?
Centrica would appear to be a loser, as bills will fall and they could be paying customers to not use energy.
But they are surely hoping that their market share will increase and I’m sure Samsung will give them a commission.
What’s In It For The Consumer?
Hopefully, they’ll get lower energy bills.
But also they might get a lot of convenience controlling their appliances and heating.
Conclusion
Using energy is becoming a computer game with monetary rewards.
Is the deal between Centrica/British Gas and Samsung another deal that has been brought to fruition by the Korean President’s visit to the UK?
It looks like this is the third recent deal signed between UK and Korean companies, after these two.
- South Korea, UK Strenghten Offshore Wind Ties
- UK And South Korea Help Secure Millions For World’s Largest Monopile Factory
I suspect, there might be a few more deals, if Charles and Camilla really turned on the charm.
In Mersey Tidal Project And Where It Is Up To Now, I wrote about talks between Liverpool City Council and Korea Water about a tidal barrage of the Mersey. This project must surely be a possibility!
This is said in the Wikipedia entry for Korean Air under Fleet Plans.
At the Association of Asia Pacific Airlines Assembly in 2018, Korean Air announced that it was considering a new large widebody aircraft order to replace older Airbus A330, Boeing 747-400, Boeing 777-200ER and Boeing 777-300. Types under consideration for replacement of older widebody aircraft in the fleet include the Boeing 777X and Airbus A350 XWB. At the International Air Transport Association Annual General Meeting (IATA AGM) in Seoul, Chairman Walter Cho said Korean Air’s widebody order is imminent and it is considering an extra order of Airbus A220 Family including developing version, Airbus A220-500.
Note.
- Airbus A350 XWB have Welsh wings and Rolls-Royce engines.
- Airbus A220-500 are made in Canada with wings and composite parts from Belfast. Rolls-Royce may have a suitable engine.
Could a deal have something in it for the UK?
Although Korea has its own SMR program, I wonder, if there could be a link-up between Korean industry and Rolls-Royce over SMRs?
Japanese Offshore Wind And Battery Storage Project Begins Commercial Operation
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
On 1 January 2024, JERA and Green Power Investment Corporation (GPI) began commercial operations at the 112 MW Ishikari Bay New Port Offshore Wind Farm in Japan, which they own through Green Power Ishikari GK, a special-purpose corporation (SPC).
The most significant thing about this wind farm, is that it has been designed from Day One to operate with a battery, which is detailed in the last paragraph.
The project also features a battery storage component with 100 MW x 180 MWh of capacity.
Note that the output of the battery is 89 % of that of the wind farm. Is that the ideal ratio between battery and wind farm capacities?
Conclusion
Because of my training, as an Electronics and Control Engineer, I belief that most renewable energy can be smoothed with the adding of a battery.
Would You Buy A Battery Energy Storage System From Rolls-Royce?
I don’t often click on adverts that appear in web pages.
But I had to click on one from Rolls-Royce mtu, which advertised Battery Energy Storage Systems.
I wonder what the Honourable Charles Rolls would have thought of adverts on the Internet for the company he jointly founded?
I suspect he would have liked the idea, as Rolls was very much a promoter of motoring and aviation and opened one of the first car dealerships in the UK, according to his Wikipedia entry.
The Wikipedia entry for his business partner; Sir Henry Royce starts with this sentence.
Sir Frederick Henry Royce, 1st Baronet, OBE (27 March 1863 – 22 April 1933) was an English engineer famous for his designs of car and aeroplane engines with a reputation for reliability and longevity.
He is also described as a perfectionist.
This sentence from the Wikipedia entry, describes how he started the design of the legendary “R” engine.
In October 1928, he began design of the “R” engine while walking with some of his leading engineers on the beach at West Wittering, sketching ideas in the sand. Less than a year later, the “R” engine, designed in his studio in the village, set a new world air speed record of 357.7 miles per hour and won the Schneider Trophy of 1929.
Later with help from the maddest person my father ever met (his words, not mine!) ; Lady Houston, the Supermarine S.6B won the trophy in 1931 and then broke the world speed record at over 400 mph. Not bad for a seaplane. Take the floats off an S.6B and you almost have a Spitfire.
The Wikipedia entry also describes how the “R” engine was developed into what many engineers believe was the finest internal combustion engine of all time; the Rolls-Royce Merlin.
Following the success of the “R” engine, it was clear that they had an engine that would be of use to the Royal Air Force. As no Government assistance was forthcoming at first, in the national interest they went ahead with development of what was called the “PV-12” engine (standing for Private Venture, 12-cylinder). The idea was to produce an engine of about the same performance as the “R”, albeit with a much longer life. Rolls-Royce launched the PV-12 in October 1933 and the engine completed its first test in 1934, the year after Royce died. The PV-12 became the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine.
Where would we have been in the Battle of Britain without the Merlin engine?
Since 1969, the engineers at Rolls-Royce have followed Sir Henry’s example of perfection and developed the revolutionary RB-211 into the modern day Trent, which is now about to take a big leap into a low-carbon future with the UltraFan.
If the quality of Rolls-Royce mtu’s Battery Energy Storage System matches the levels of perfection Rolls-Royce achieved with the Merlin and the Trent, then I suspect that Sir Henry would have given his approval.
This picture is shown on the web page for the Battery Energy Storage System.
These two paragraphs introduce, what Rolls-Royce mtu are calling the mtuEnergyPack.
In today’s world of economic growth and increasing populations, the demand for electricity is soaring. Governments and industries globally shift to distributed renewable energy, challenging centralized grids. To adapt to this changing energy landscape, the mtuEnergyPack offers an ideal solution.
It integrates renewable sources like solar and wind power, paving the way for future-ready sustainable power systems. The mtu EnergyPack is a scalable, all-in-one solution for autonomous off-grid facilities. It ensures reliable power through peak shaving, load-shifting, and grid stabilization, making it suitable for various applications.
These are my thoughts.
What Is The Output And The Storage Capacity?
This paragraph on this page gives this answer.
It efficiently stores electricity from distributed sources and delivers on demand. The mtu EnergyPack is available in different sizes: The QS and the QL, ranging from 200 kVA to 2,000 kVA, and from 312 kWh to 2,084 kWh, and the QG for grid scale storage needs, ranging from 4,400 kVA and 4,470 kWh to virtually any size.
It seems that you specify your requirements and Rolls-Royce mtu should be able to satisfy it.
What Devices Can Be Connected?
This paragraph on this page gives this answer.
The mtu EnergyPack serves as a key component in enhancing the reliability and profitability of microgrids and energy systems. It stores electricity generated by distributed power sources, including gensets, wind turbines, or solar panels, and delivers it when needed.
In the 1970s, when I was working at ICI, others in the section were working on a system called MEDIA, where every sensor on a chemical plant was connected to the central computer, through its own analog-to-digital computer. It would now be called plug-and-play by some.
I believe that Rolls-Royce mtu are using similar ideas to connect equipment to the control computer.
These are my thoughts about connecting various equipment.
- Hydrogen-powered generators and electrolysers as Rolls-Royce mtu are using at Duisburg, which I wrote about in Rolls-Royce Makes Duisburg Container Terminal Climate Neutral With MTU Hydrogen Technology.
- Could Rolls-Royce’s beer keg-sized 2.5 MW electrical generator based on a Super Hercules engine, be connected?
- Could a Rolls-Royce Trent be connected?
- Could one of Rolls-Royce’s small modular nuclear reactors be connected?
- In Rolls-Royce To Play Key Role In US Department Of Defense Nuclear Microreactor Program, I talk about developing a 1-5 MW nuclear reactor for US Department of Defense. Could these be connected?
I don’t see why every device can’t work to the same protocol.
What Is The Power Density Like?
This paragraph on this page gives this answer.
The mtu EnergyPack’s compact battery system designs suit projects with limited space and logistical restrictions.
In ‘Spirit of Innovation’ Stakes Claim To Be The World’s Fastest All-Electric Vehicle, I talked about Rolls-Royce’s record-breaking electric plane called Spirit of Innovation.
Has what has been learned about energy storage in the confined spaces of an aeroplane been applied to a Battery Energy Storage System?
What Do Rolls-Royce mtu Consider To Be Important Features?
On this page, they list these features.
- Power Density
- Digitally Connected
- Multilevel Safety
- Black Start Capability
- Scalability
- Ultra-Fast Response
- Flexible Use
- Plug-And-Play Installation
The design seems to have everything covered.
Can Similar Systems Be Designed By Others?
I would expect that similar systems can be designed, as technology like batteries is available to all and the operation is only as good as the software controlling the various components of the system.
But similar systems will be without the famous Rolls-Royce logo.
Could One Of These Systems Decarbonise A Village?
I once lived in a village with about fifty houses and perhaps a hundred inhabitants.
- There was an old World War Two airfield, that could probably accommodate a small wind farm of perhaps 20 MW.
- There were a couple of barns and large sheds, that could have solar panels similar to those I described in Bedford Depot’s Massive Solar Roof Helps Thameslink On Way To Net Zero.
I suspect an mtuEnergyPack could control all these inputs and provide the village with the following.
- Enough electricity to power all the needs of the inhabitants, businesses and their vehicles.
- If an electrolyser were to be provided, it could probably produce enough hydrogen to power every boiler and hydrogen-powered vehicle.
Note.
- Farmers would like the local availability of hydrogen, as it will be ideal for tractors and agricultural machinery.
- I actually believe that if a village had a reliable and affordable hydrogen supply, that a large proportion of the inhabitants would switch to hydrogen-powered vehicles.
There would still be the National Grid there for backup.
Conclusion
If I needed an mtuEnergyPack, I’d certainly give one a close look.
Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners Takes FID On 1,000 MWh Battery Energy Storage Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners.
This is the sub-heading.
The battery energy storage system Coalburn 1 will be one of the largest battery storage projects in Europe. Construction has commenced in November 2023 and the project will be 500 MW / 1,000 MWh once complete.
These two paragraphs outline the project.
Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP) through its Flagship Funds has taken final investment decision and commenced construction on a 500 MW / 1,000 MWh energy storage system in Coalburn, Scotland, which will be one of the largest of its kind in Europe.
The facility is the first project to be developed from the partnership between CIP and Alcemi to deploy 4 GW of energy storage assets across the UK. CIP aims to take final investment decision on two other projects next year with a combined capacity above 1 GW. The portfolio will provide vital support to the UK’s energy network, accelerating the integration of renewable energy and the transition to net zero by 2050.
Note.
- FID means final investment decision.
- 500 MW / 1,000 MWh could become a common size as it is two hours of power and easy for politicians to add up.
- CIP and Alcemi seem to be planning a total amount of energy storage, eight times bigger than Coalburn 1.
This battery could be the largest in the UK, when it is commissioned.
Who Are Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP)?
Their About CIP web page gives a lot of details.
Who Are Alcemi?
Their Who We Are web page gives a lot of details.
Environmental Considerations
The press release says this about environmental considerations.
The Coalburn 1 facility has been developed with extensive landscaping and ecological mitigation measures, including the maintenance of peat reserves, tree and wildflower planting, and new habitats, promoting biodiversity across the site.
I’ll agree with that, but add that I hope that they look after the hares. It will be interesting to see how big batteries and big bunnies co-exist. As co-exist they will!
Operation
The press release says this about operation.
The scheme will reduce the need for fossil fuel power generation during periods of peak demand leading to a decrease in CO2 emissions but also provide balancing services to help lower the costs for end consumers to manage the UK Power system.
As a Control Engineer, I suspect, it will act in a little-and-large mode with Scotland’s pumped storage.
Location
This page on the SP Energy Networks web site is entitled Coalburn Connection – South Lanarkshire.
There is this introductory paragraph.
SP Energy Networks own and maintain the electricity network in central and southern Scotland. As part of our infrastructure, Coalburn Grid Substation is a key installation in the transmission network situated to the south of Lesmahagow in South Lanarkshire.
Underneath is this map.
Note.
- The orange arrows are wind farms and there appear to be around a dozen of them.
- The blue arrow is Coalburn Grid Substation.
- Running through the area is the M74 between Glasgow and Carlisle.
- There are some remains of opencast coal-mines in the area, which have been restored and turned into wind farms.
- I have found the capacity of fourteen of the existing wind farms and it totals 946 MW, which is an average capacity for each wind farm of 67 MW.
- During my search for capacity, I found a couple of wind farms that were being upgraded with larger turbines.
- The SP Energy Networks page gives a date of Q3 2025 for connection of the Coalburn battery to the sub-station.
With the 500 MW/1000 MWh Coalburn 1 battery, I wouldn’t be surprised that this massive onshore wind farm complex has been designed to provide a guaranteed 1000 MW to the grid.
Gresham House Energy Storage Sets GBP80 Million Fundraise
Gresham House Energy Storage Fund must be doing something right, as similar headlines are used in half-a-dozen places on the Internet and they regularly seem to be raising more money.
But then, as a Graduate Control Engineer and a previous owner of half a finance company, I’ve always thought raising money to build batteries was a good idea.
My only niggle with Gresham House, is that I would have thought by now, they would have put some money into building one of the excellent new technology batteries that are coming through.
The storage fund or some of its employees, may of course have contributed to some of the crowdfunding for these new technologies, all of which I feel have a good chance of being a success.
Note.
- Energy Dome is Italian and all the others are at least fifty percent British.
- Most of the British batteries have had backing from the UK government.
- All these batteries are environmentally-friendly.
- None of these batteries use large quantities of rare and expensive materials.
- Energy Dome even uses carbon dioxide as the energy storage medium.
In addition, in Scotland, there is traditional pumped storage hydro-electricity.
Project Iliad
This article on renews.biz has a slightly different headline of Gresham House To Raise £80m For US Battery Buildout.
This is the first two paragraphs.
Gresham House Energy Storage Fund is seeking to raise £80m through a share placing.
The new equity raised will primarily be used to finance 160MW of solar with co-located four-hour battery projects in California, US, known as Project Iliad.
The article then gives a lot of financial details of Project Iliad and Gresham House.
Will Gresham House be backing co-located solar/battery projects in the UK?
- In Cleve Hill Solar Park, I write about a co-located solar/battery project in Kent.
- This press release from National Grid is entitled UK’s First Transmission-Connected Solar Farm Goes Live, which also describes a co-located solar/battery project, being built near Bristol.
These two projects are certainly serious and could be pathfinders for a whole host of co-located solar/battery projects.
WillGresham House back some of this new generation?