SSE Thermal Charts Path To Green Hydrogen Future With First-Of-A-Kind Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from SSE Thermal.
This is the sub-heading.
SSE Thermal is developing a first-of-a-kind project in the Humber which would unite hydrogen production, storage and power generation in one location by the middle of this decade.
These paragraphs explain the project.
The Aldbrough Hydrogen Pathfinder project will support the evidence base for wider deployment of flexible hydrogen power in the UK’s net zero journey and is a major enabler of SSE Thermal’s wider Humber ambitions.
Located at SSE Thermal and Equinor’s existing Aldbrough Gas Storage site on the East Yorkshire coast, the project is designed to demonstrate the interactions between hydrogen electrolysis, hydrogen cavern storage and 100% hydrogen dispatchable power.
The concept would see green power sourced from grid through Renewable PPAs, in compliance with the Low Carbon Hydrogen Standard. Hydrogen would then be produced via a 35MW electrolyser before being stored in a converted salt cavern and then used in a 100% hydrogen-fired turbine, exporting flexible green power back to grid at times of system need. In future, hydrogen storage will also benefit offtakers in other sectors, for example in industry, heat or transport.
Note.
- The Aldbrough Gas Storage site currently can store the equivalent of 320 GWh of electricity, It is currently being expanded to be one of the largest hydrogen stores in the world according to this page on the SSE web site.
- SSE Thermal are proposing to build a hydrogen-powered power station at Keadby to the South of the Humber. The press release says this power station could have a peak demand of 1,800MW of hydrogen.
- Aldbrough at its current size could keep the Keadby hydrogen-powered power station going for a week. But Aldbrough will be a lot bigger than the current 320 GWh.
- The Hornsea and Dogger Bank wind farms off the coast of East Yorkshire will have a capacity of at least 13.5 GW.
- A 35 MW electrolyser will produce 15.2 tonnes of hydrogen per day.
SSE and Equinor hope to be storing hydrogen by 2025.
Conclusion
It is an enormous project and it will surely grow with more electrolysers and hydrogen-powered power stations.
Highview Power In The Daily Express
This article in the Daily Express is entitled The Storage Sites Around The UK That Could Provide Cheap Power To Millions Of Homes.
Highview Power gets a large mention for its plan for twenty storage sites around the UK.
This is said about their planned sites at Carrington and on Humberside.
It is hoped that the first plant, a £250million Manchester station, will come online as early as 2024. It will have a 30megawatts capacity, able to store 300megawatt hours of electricity, enough to supply 600,000 homes with clean power for an hour.
The next plants will be even larger in scale, with four a five planned for Humberside with a 200megawatt/2.5gigwatt hour capacity. The CRYOBattery site would be able to store excess energy generated by the Dogger Bank, Hornsea and Sofia wind farms.
There is also a comprehensive map, with sites indicated at places like Aberdeen, Anglesey, Inverness, Liverpool, Montrose, Norfolk and Sizewell.
The sites seem to be following the wind, which is where excess power needs to be stored and released, when the wind is on strike.
Dogger Bank – The Joke That Is Growing Up To Be A Wind Powerhouse
The Wikipedia entry for the Dogger Bank, describes it like this.
Dogger Bank is a large sandbank in a shallow area of the North Sea about 100 kilometres (62 mi) off the east coast of England.
But many of my generation remember it from its use in the Shipping Forecast and as a joke place like the Balls Pond Road, Knotty Ash and East Cheam, in radio and TV comedy from the 1950s and 1960s.
But now it is being turned into one of the largest wind powerhouses!
According to Wikipedia’s list of the UK’s offshore wind farms, these wind farms are being developed on the Dogger Bank.
- Sofia Offshore Wind Farm – 1400 MW – Under Construction – Commissioning in 2023/26 – £39.65/MWh – RWE
- Dogger Bank A – 1235 MW – Under Construction – Commissioning in 2023/24 – £39.65/MWh – SSE/Equinor
- Dogger Bank B – 1235 MW – Pre-Construction – Commissioning in 2024/25 – £41.61/MWh – SSE/Equinor
- Dogger Bank C – 1218 MW – Pre-Construction – Commissioning in 2024/25 – £41.61/MWh – SSE/Equinor
- Dogger Bank D – 1320 MW – Early Planning – SSE/Equinor
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW – Early Planning – RWE
Note.
- These total up to 9408 MW.
- The Dogger Bank wind farms have their own web site.
- The Sofia offshore wind farm has its own web site.
- The Dogger Bank South wind farms have their own web site.
- Dogger Bank A and Dogger Bank B will connect to the National Grid at Creyke Beck to the North of Hull.
- Sofia and Dogger Bank C will connect to the National Grid at Lazenby on Teesside.
But this is only the start on the British section of the Dogger Bank.
This map, which comes courtesy of Energy Network Magazine and 4C Offshore is entitled 2001 UK Offshore Windfarm Map shows all UK offshore wind farms and their status. It looks to my naive mind, that there could be space for more wind farms to the North and West of the cluster of Digger Bank wind farms.
The North Sea Wind Power Hub
The UK doesn’t have full territorial rights to the Dogger Bank we share the bank with the Danes, Dutch and Germans.
In the Wikipedia entry for the Dogger Bank wind farm, this is said about the North Sea Wind Power Hub.
Dutch, German, and Danish electrical grid operators are cooperating in a project to build a North Sea Wind Power Hub complex on one or more artificial islands to be constructed on Dogger Bank as part of a European system for sustainable electricity. The power hub would interconnect the three national power grids with each other and with the Dogger Bank Wind Farm.
A study commissioned by Dutch electrical grid operator TenneT reported in February 2017 that as much as 110 gigawatts of wind energy generating capacity could ultimately be developed at the Dogger Bank location.
Note.
- 110 GW shared equally would be 27.5 GW.
- As we already have 9.4 GW of wind power, under construction or in planning around the Dogger Bank, could we find space for the other 18.1 GW?
- I suspect we could squeeze it in.
If we can and the Danes, Dutch and Germans can generate their share, the four countries would each have a 27.5 GW wind farm.
What would put the icing on the cake, would be if there could be a massive battery on the Dogger Bank. It wouldn’t be possible now and many would consider it a joke. But who knows what the capacity of an underwater battery based on concrete, steel, seawater and masses of ingenuity will be in a few years time.
Where Does Norway Fit In To The North Sea Wind Power Hub?
It could be argued that Norway could also connect to the North Sea Wind Power Hub.
- 110 GW shared equally would be 22 GW.
- Norway can build massive pumped storage hydroelectric power stations close to the landfall of an interconnector to the North Sea Wind Power Hub.
- the British, Danes, Dutch and Germans can’t do that, as they don’t have any handy mountains.
- Norway is a richer country the others involved in the project.
I can see Norway signing up to the North Sea Wind Power Hub.
The North Sea Link
The Wikipedia entry for the North Sea Link, introduces it like this.
The North Sea Link is a 1,400 MW high-voltage direct current submarine power cable between Norway and the United Kingdom.
At 720 km (450 mi) it is the longest subsea interconnector in the world. The cable became operational on 1 October 2021.
It runs between Kvilldal in Norway and Blyth in Northumberland.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see that the North Sea Link is modified, so that it has a connection to the North Sea Wind Power Hub.
Plans Emerge For 8 GW Of Offshore Wind On Dogger Bank
Wikipedia has an entry, which is a List Of Offshore Wind Farms In The United Kingdom.
The totals are worth a look.
- Operational – 13279 MW
- Under Construction – 4125 MW
- Proposed Under The UK Government’s Contracts For Difference Round 3 – 2412 MW
- Proposed Under The UK Government’s Contracts For Difference Round 4 – 7026 MW
- Exploratory Phase, But No Contract for Difference – Scotland – 24,826 MW
- Exploratory Phase, But No Contract for Difference – England – 14,500 MW
Note.
- That gives a Grand Total of 66,168 MW or 66.168 GW.
- The government’s target is 50 GW of offshore wind by 2030.
- The typical UK power need is around 23 GW, so with nuclear and solar, we could be approaching three times the electricity generation capacity that we currently need.
The figures don’t include projects like Berwick Bank, Cerulean Wind, Norfolk Vanguard or Northern Horizons, which are not mentioned in Wikipedia’s list.
I regularly look at the list of wind farms in this Wikipedia entry and noticed that the number of Dogger Bank wind farms had increased.
They are now given as.
- Dogger Bank A – 1200 MW – Completion in 2023/24
- Dogger Bank B – 1200 MW – Completion in 2024/25
- Dogger Bank C – 1200 MW – Completion in 2024/25
- Dogger Bank D – 1320 MW – No Completion Given
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW – No Completion Given
Note, that gives a Grand Total of 7920 MW or 7.920 GW.
This article on offshoreWIND.biz is entitled BREAKING: SSE, Equinor Plan 1.3 GW Dogger Bank D Offshore Wind Project.
It was published on the October 6th, 2022 and starts with this summary.
SSE Renewables and Equinor are looking into building what would be the fourth part of Dogger Bank Wind Farm, the world’s largest offshore wind farm, whose three phases (A, B and C) are currently under construction. Surveys are now underway at an offshore site where the partners want to develop Dogger Bank D, which would bring Dogger Bank Wind Farm’s total capacity to nearly 5 GW if built.
Obviously, there are a few ifs and buts about this development, but it does look like SSE Renewables and Equinor are serious about developing Dogger Bank D.
More Dogger Bank Gigawatts for UK As RWE Moves Forward With Two 1.5 GW Projects
This subheading describes, the 3 GW wind farm, that I listed earlier as Dogger Bank South.
These three paragraphs describe the projects.
RWE is now moving forward with two new offshore wind farms in the Zone, each with a 1.5 GW generation capacity, after the company obtained approval from the UK Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) to enter into an Agreement for Lease with The Crown Estate this Summer, following the Round 4 leasing process.
The wind farms will be built at two adjacent sites located just southwest of the Dogger Bank A offshore wind farm and are dubbed Dogger Bank South (DBS) East and Dogger Bank South (DBS) West.
RWE has also started with geophysical seabed surveys within the wind turbine array areas for its two new projects.
It appears that they have already got the leasing process started.
When Will Dogger Bank D And Dogger Bank South Be Operational?
Consider.
- In How Long Does It Take To Build An Offshore Wind Farm?, showed that a lot of offshore wind farms have gone from planning permission to first operation in six years.
- I don’t think that there will be planning permission problems on the Dogger Bank.
- The two wind farms are a continuation of Dogger Bank A, B and C and the Sofia wind farms.
- A lot of the construction, would be more of the same.
With average luck, I can see Dogger Bank D and Dogger Bank South in full production before the end of 2028.
The Monster In The Mountains That Could Save Europe’s Winter
Ulla-Førre is a complex of five hydroelectric power stations and a massive lake in the Norwegian mountains to the East of Stavanger.
- The power stations have a total generating capacity of 2.1 GW.
- Lake Blåsjø is able to hold enough water to generate 7800 GWh of electricity.
- The complex is at the Norwegian end of the North Sea Link to Blyth in England.
This YouTube video from Statkraft, explains how Ulla-Førre was built.
I have some further explanation and thoughts.
What Is The Operating Philosophy Of The North Sea Link?
This press release from National Grid says this.
The Norwegian power generation is sourced from hydropower plants connected to large reservoirs, which can respond faster to fluctuations in demand compared to other major generation technologies. However, as the water level in reservoirs is subject to weather conditions, production varies throughout seasons and years.
When wind generation is high and electricity demand low in Britain, NSL will enable renewable power to be exported from the UK, conserving water in Norway’s reservoirs. When demand is high in Britain and there is low wind generation, hydro power can be imported from Norway, helping to ensure secure, affordable and sustainable electricity supplies for UK consumers.
It almost seems to me, that the North Sea Link is part of a massive pumped-storage system, where we can bank some of our wind-generated electricity in Norway and draw it out when we need it.
Suppose There Is No Wind In The UK And Norway’s Giant Reservoirs Need Filling?
We could always throw on a substitute, which is the 1,185 MW Hartlepool nuclear power station.
- Unfortunately, this will close in 2024.
- Wikipedia indicates that Hartlepool’s closure has been on and off several years, so I don’t think it will be delayed again.
- A new station probably couldn’t be commissioned until 2029, at the earliest.
But over the next few years these wind farms will be connected to the North-East.
- Sofia wind farm should commission the 1.4 GW Phase 1, which connects to Teesside in 2023.
- Dogger Bank wind farm should commission 3.6 GW, which connects to Teesside and Humberside in 2025.
- The 4.1 GW Berwick Bank wind farm will have a second connection to Blyth by 2030. Say 2 GW!
There’s more than enough wind there to fill up Norway’s reservoirs and replace Hartlepool nuclear station.
Will Ulla-Førre Be Expanded?
It does sound to me that the video does imply that Ulla-Førre could be expanded.
An Update To Will We Run Out Of Power This Winter?
My Methods
Project Timescales For Wind Farms
In How Long Does It Take To Build An Offshore Wind Farm?, I came to these conclusions.
- It will take six years or less from planning consent to commissioning.
- It will take two years or less from the start of construction to commissioning.
I shall use these timescales, as any accelerations by the government, will only reduce them.
Dates
If a date is something like 2024/25, I will use the latest date. i.e. 2025 in this example.
The Update
In Will We Run Out Of Power This Winter?, which I wrote in July this year, I did a calculation of how much renewable energy would come on stream in the next few years.
I summarised the amount of new renewable energy coming on stream like this.
- 2022 – 3200 MW
- 2023 – 1500 MW
- 3024 – 2400 MW
- 2025 – 6576 MW
- 2026 – 1705 MW
- 2027 – 7061 GW
This totals to 22442 MW.
But I had made two omissions.
- Hornsea 3 wind farm will add 2582 MW in 2026/27.
- Hinckley Point C nuclear power station will add 3260 MW in 2027.
Ørsted have also brought forward the completion date of the Sofia wind farm to 2023, which moves 1400 GW from 2024 to 2023.
The new renewables summary figures have now changed to.
- 2022 – 3200 MW
- 2023 – 2925 MW
- 3024 – 1326 MW
- 2025 – 6576 MW
- 2026 – 1705 MW
- 2027 – 13173 MW
This totals to 28554 MW.
Note.
- The early delivery of the Sofia wind farm has increased the amount of wind farms coming onstream next year, which will help the Winter of 2023/2024.
- It will also help the Liz Truss/Kwasi Kwarteng government at the next election, that should take place in early 2025.
- Hornsea 3 and Hinckley Point C make 2027 a big year for new renewable energy commissioning.
By 2027, we have more than doubled our renewable energy generation.
The Growth Plan 2022
In this document from the Treasury, the following groups of wind farms are listed for acceleration.
- Remaining Round 3 Projects
- Round 4 Projects
- Extension Projects
- Scotwind Projects
- INTOG Projects
- Floating Wind Commercialisation Projects
- Celtic Sea Projects
I will look at each in turn.
Remaining Round 3 Projects
In this group are the the 1200 MW Dogger Bank B and Dogger Bank C wind farms, which are due for commissioning in 2024/25.
Suppose that as with the Sofia wind farm in the same area, they were to be able to be brought forward by a year.
The new renewables summary figures would change to.
- 2022 – 3200 MW
- 2023 – 2925 MW
- 3024 – 3726 MW
- 2025 – 5076 MW
- 2026 – 1705 MW
- 2027 – 13173 MW
This totals to 28554 MW.
It looks like if Dogger Bank B and Dogger Bank C can be accelerated by a year, it has four effects.
- The renewables come onstream at a more constant rate.
- SSE and Equinor, who are developing the Dogger Bank wind farms start to get paid earlier.
- The UK gets more electricity earlier, which helps bridge the gap until Hornsea 3 and Hinckley Point C come onstream in 2027.
- The UK Government gets taxes and lease fees from the Dogger Bank wind farms at an earlier date.
Accelerating the remaining Round 3 projects would appear to be a good idea.
Round 4 Projects
According to Wikipedia’s list of proposed wind farms, there are six Round 4 wind farms, which total up to 7026 MW.
Accelerating these projects, is probably a matter of improved government regulations and pressure, and good project management.
But all time savings in delivering the wind farms benefits everybody all round.
This document from the Department of Business, Industry and Industrial Strategy lists all the Contracts for Difference Allocation Round 4 results for the supply of zero-carbon electricity.
Many of these projects are smaller projects and I suspect quite a few are shovel ready.
But as with the big wind farms, there are some projects that can be brought forward to everybody’s benefit.
Norfolk Boreas
Norfolk Boreas wind farm is one of the Round 4 projects.
The wind farm is shown as 1400 MW on Wikipedia.
On the web site, it now says construction will start in 2023, which could mean a completion by 2025, as these projects seem to take about two years from first construction to commissioning, as I showed in How Long Does It Take To Build An Offshore Wind Farm?.
The new renewables summary figures would change to.
- 2022 – 3200 MW
- 2023 – 2925 MW
- 3024 – 3726 MW
- 2025 – 6476 MW
- 2026 – 1705 MW
- 2027 – 11773 MW
This still totals to 28554 MW.
This acceleration of a large field would be beneficial, as the 2025 figure has increased substantially.
I would suspect that Vattenfall are looking hard to accelerate their Norfolk projects.
Extension Projects
I first talked about extension projects in Offshore Wind Extension Projects 2017.
The target was to add 2.85 GW of offshore wind and in the end seven projects were authorised.
- Sheringham Shoal offshore wind farm – 719 MW with Dudgeon
- Dudgeon offshore wind farm – 719 MW with Sheringham Shoal
- Greater Gabbard offshore wind farm
- Galloper offshore wind farm
- Rampion offshore wind farm – 1200 MW
- Gwynt y Môr offshore wind farm – 1100 MW
- Thanet offshore wind farm – 340 MW
These are the best figures I have and they add up to an interim total of 3359 MW.
I suspect that these projects could be easy to accelerate, as the developers have probably been designing these extensions since 2017.
I think it is reasonable to assume that these seven wind farms will add at least 3000 MW, that can be commissioned by 2027.
The new renewables summary figures would change to.
- 2022 – 3200 MW
- 2023 – 2925 MW
- 3024 – 3726 MW
- 2025 – 6476 MW
- 2026 – 1705 MW
- 2027 – 14773 MW
This now totals to 31554 MW.
Accelerating the extension projects would be a good idea, especially, as they were awarded some years ago, so are probably well into the design phase.
ScotWind Projects
I first talked about ScotWind in ScotWind Offshore Wind Leasing Delivers Major Boost To Scotland’s Net Zero Aspirations.
It was planned to do the following.
- Generate 9.7 GW from six wind farms with fixed foundations.
- Generate 14.6 GW from ten floating wind farms.
But since then three more floating wind farms with a total capacity of 2800 MW have been added, as I wrote about in Three Shetland ScotWind Projects Announced.
I suspect that some of these projects are ripe for acceleration and some may well be generating useful electricity by 2030 or even earlier.
INTOG Projects
I wrote about INTOG in What Is INTOG?.
I can see the INTOG Projects contributing significantly to our fleet of offshore wind turbines.
I have already found a 6 GW/£30 billion project to decarbonise oil and gas rigs around our shores, which is proposed by Cerulean Winds and described on this web page.
If the other large INTOG projects are as good as this one, then we’ll be seeing some sensational engineering.
Floating Wind Commercialisation Projects
This page on the Carbon Trust website is entitled Floating Wind Joint Industry Programme (JIP).
They appear to be very much involved in projects like these.
The page has this description.
The Floating Wind Joint Industry Programme is a world leading collaborative research and development (R&D) initiative dedicated to overcoming technological challenges and advancing commercialisation of floating offshore wind.
This graphic shows the partners and advisors.
Most of the big wind farm builders and turbine and electrical gubbins manufacturers are represented.
Celtic Sea Projects
The Celtic Sea lies between South-East Ireland, Pembrokeshire and the Devon and Cornwall peninsular.
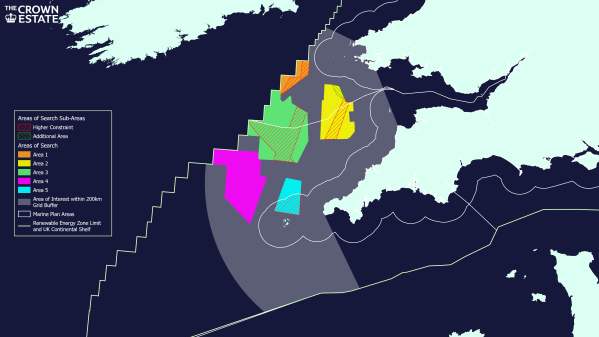
The Crown Estate kicked this off with press release in July 2022, that I wrote about in The Crown Estate Announces Areas Of Search To Support Growth Of Floating Wind In The Celtic Sea.
This map shows the five areas of search.
One Celtic Sea project has already been awarded a Contract for Difference in the Round 4 allocation, which I wrote about in Hexicon Wins UK’s First Ever CfD Auction For Floating Offshore Wind.
Other wind farms have already been proposed for the Celtic Sea.
In DP Energy And Offshore Wind Farms In Ireland, I said this.
They are also developing the Gwynt Glas offshore wind farm in the UK sector of the Celtic Sea.
- In January 2022, EDF Renewables and DP Energy announced a Joint Venture partnership to combine their knowledge and
expertise, in order to participate in the leasing round to secure seabed rights to develop up to 1GW of FLOW in the Celtic Sea. - The wind farm is located between Pembroke and Cornwall.
The addition of Gwynt Glas will increase the total of floating offshore wind in the UK section of the Celtic Sea.
- Blue Gem Wind – Erebus – 100 MW Demonstration project – 27 miles offshore
- Blue Gem Wind – Valorus – 300 MW Early-Commercial project – 31 miles offshore
- Falck Renewables and BlueFloat Energy – Petroc – 300 MW project – 37 miles offshore
- Falck Renewables and BlueFloat Energy – Llywelyn – 300 MW project – 40 miles offshore
- Llŷr Wind – 100 MW Project – 25 miles offshore
- Llŷr Wind – 100 MW Project – 25 miles offshore
- Gwynt Glas – 1000 MW Project – 50 miles offshore
This makes a total of 2.2 GW, with investors from several countries.
It does seem that the Celtic Sea is becoming the next area of offshore wind around the British Isles to be developed.
How do these wind farms fit in with the Crown Estate’s plans for the Celtic Sea?
I certainly, don’t think that the Crown Estate will be short of worthwhile proposals.
Conclusion
More and more wind farms keep rolling in.
Can We Move The Equilibrium Point Of The Energy Market?
Equilibrium In Systems
As a Control Engineer, I believe that most systems eventually end up in a state of equilibrium.
How many football batches have you watched between two evenly-matched teams that have ended, where the statistics are even and the match has ended in a nil-nil draw or a win by one goal.
Now suppose one manager makes an inspired substitution, one important player gets injured or one player gets sent off.
One team will have an advantage, the statistics will no longer be even and one team will probably win.
The equilibrium point will have been shifted.
Zopa’s Stable Peer-to-Peer Lending System
I used Zopa’s peer-to-peer lending system for several years and found it a very stable system, that over the years paid a steady return of between four and five percent before tax.
I even developed a method to maximise my savings income, which I wrote about in The Concept Of Hybrid Banking.
It was a sad day for me, when Zopa closed its ground-breaking peer-to-peer lending system.
As a Control Engineer, I believe that Zopa’s strength was a well-written computerised algorithm, that matched lenders and borrowers and spread the risk.
- There was no bias in the system, introduced by personal prejudices.
- The algorithm was agnostic and judged all borrowers on their profiles and credit ratings alone.
- Money was allocated under fair rules for borrowers.
- I never borrowed from Zopa, but from my experience of owning half of a finance company, their terms were the most customer-friendly I’ve ever seen.
Someone will go back to the basics of peer-to-peer lending and it can’t be soon enough for both savers and borrowers.
Zopa In Troubled Times
Over the years that I invested in Zopa, my returns stayed very much the same, as the algorithm seemed to be able to maintain sufficient difference between lenders’ returns and borrowers’ rates. I also suspect the dynamics of savvy lenders and borrowers helped to stabilise both the system and the difference between rates.
It even worked through the Banking Crisis of 2008 and other mini-hiccups along the way.
My Conclusion About Zopa
As someone, who knows computing well, I would rate Zopa, one of the best computer systems, I’ve ever seen.
But it showed how a large transactional system can work well.
One of the keys to its success and smooth operation was that the computer was totally in control and it took all transaction decisions without direct human intervention.
The Energy Market
The energy market is a network of energy providers and users.
It is controlled by complicated rules and it has settled into an equilibrium, which involves.
- Importation of energy, which I suspect is not at a low price
- Some high priced energy generators, based on gas, which has a high-price, due to Putin’s war.
- Waste of wind energy due to lack of energy storage.
- The intermittency of renewable sources.
- A lack of gas storage, means that we probably get the wrong end of fluctuations in the gas price.
This results in a high price to consumers.
Can We Move The Equilibrium Point Of The Energy Market?
And we also need to move it quickly to a more favourable place, which benefits everybody!
As a Control Engineer, I believe that there are five ways to move the equilibrium point.
- Stop Putin’s war.
- Increase gas storage.
- Generate more low-cost electricity.
- Increase electricity storage.
- Improve the control algorithm.
I will now look at each in more detail.
Stopping Putin’s War
Giving in to Putin’s ambitions, would be an easy way to solve our energy crisis. But at what cost?
My parents generation, watched as Nazi Germany took over Austria and Czechoslovakia, whilst the world did nothing.
- We mustn’t repeat that mistake.
- We must not flinch in our support of the Ukraine.
- We must be ready to support Moldova, Finland and the Baltic States if Putin expands his ambitions.
I do wonder, if Boris will turn up with Churchillian-style anti-Putin rhetoric all over Eastern Europe.
Increasing Gas Storage
The major gas storage facility is Rough, which is handily close to the Easington gas terminal.
The facility needs maintenance and this paragraph from the Wikipedia entry gives the current status.
In May 2022, the Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, Kwasi Kwarteng, began talks with the site’s owners with a view to reopening the site to help ease the ongoing cost-of-living crisis in the United Kingdom. In June 2022, owners Centrica submitted an application to the North Sea Transition Authority (NSTA), the licencing authority for the UK Government, to reopen the facility. Approval was granted in July. Subsequently, Centrica indicated that they are working hard to restore storage operations at Rough which would depend on securing subsidies from the British government. Centrica was aiming to have some capacity available for the winter of 2022/23 against an overall plan to increase storage capacity gradually over time.
Note.
- Rough can store around 2832 million cubic metres of gas.
- This article on Energy Live News is entitled Reopening Of Rough Storage Gets The All-Clear.
Less well-known is SSE and Equinor’s Aldborough Gas Storage.
These three paragraphs from SSE web site, describe the gas storage.
The Aldbrough Gas Storage facility, in East Yorkshire, officially opened in June 2011. The last of the nine caverns entered commercial operation in November 2012.
The facility, which is a joint venture between SSE Thermal (66%) and Equinor, has the capacity to store around 330 million cubic metres (mcm) of gas.
SSE Thermal and Equinor have consent to increase the storage capacity at the Aldbrough site (Aldbrough Phase 2) and during the last couple of years have been working to involve the local community where appropriate to refine aspects of this project, which has not been progressed to date due to market conditions.
Future plans for the facility, may include converting it to one of the world’s largest hydrogen stores.
In the grand scheme of things, Rough and Aldborough, when you consider that the UK uses 211 million cubic metres of gas every day, will only keep us going for a few days.
But it should be noted, that the Easington gas terminal is connected to the Norwegian gas fields, by the Langeled pipeline.
So Yorkshire and Humberside will be alright.
Generating More Low-Cost Electricity
The only low-cost electricity of any size to come on stream will be wind-power.
This article on Renewables Now is entitled UK Hits 25.5 GW Of Wind Power Capacity.
These wind farms seem to be coming on stream soon or have been commissioned recently.
- Dogger Bank A – 1200 MW – Commissioning 2023 expected
- Dogger Bank B – 1200 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
- Dogger Bank C – 1200 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
- Hornsea Two – 1386 MW – Commissioned 2022
- Moray East – 950 MW – Commissioning 2022 expected
- Neart Na Gaoithe – 450 MW – Commissioning 2024 expected
- Seagreen – 1075 MW – Commissioning 2023 expected
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW – Commissioning 2022 expected
That is expected to be over 5 GW of offshore wind by the end of 2023.
In case there is some double counting, I’ll only say that wind power capacity could be near to 30 GW by December 2023, with perhaps another 3 GW by December 2024.
Other large wind farms in the future include.
- Berwick Bank – 4100 MW – Commissioning 2028 expected
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW – Commissioning 2026 expected
- East Anglia Three – 1400 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Inch Cape Phase 1 – 1080 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Hornsea Three – 2800 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Moray West – 294 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Morgan and Mona – 3000 MW – Commissioning for 2028 expected
- Morven – 2900 MW – Commissioning for 2028 expected
- Norfolk Boreas – 1400 MW – Commissioning 2027 expected
- Norfolk Vanguard – 1400 MW – Construction start planned for 2023
- Sofia – 1400 MW – Commissioning 2026 expected
That is over 14 GW of wind power.
I should also take note of solar and onshore wind power detailed in this document from the Department of Business, Industry and Industrial Strategy that lists all the Contracts for Difference Allocation Round 4 results for the supply of zero-carbon electricity.
It gives these figures and dates.
- Solar – 251 MW – Commissioning 2023/24 expected
- Solar – 1958 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
- Onshore Wind – 888 MW – Commissioning 2024/25 expected
I can now build a yearly table of renewables likely to be commissioned in each year.
- 2022 – 3193 MW
- 2023 – 2275 MW
- 2024 – 701 MW
- 2025 – 5246 MW
- 2026 – 2300 MW
- 2027 – 6974 MW
- 2028 – 11400 MW
Note.
- Where a double date has been given, I’m taking the latter date.
- I have assumed that Norfolk Vanguard will be commissioned in 2028.
- I have ignored Hinckley Point C, which should add 3.26 GW in mid-2027.
- I have only taken into account one of the Scotwind wind farms in Scotland, some of which could be commissioned by 2028.
- I have assumed that BP’s Mona, Morgan and Morven will all be commissioned by 2028.
This is a total of 32 GW or an average of nearly 5 GW per year.
Increasing Electricity Storage
Big schemes like the 1.5 GW/ 30 GWh Coire Glas and 600 MW Cruachan 2 will help, but with 32 GW of renewable energy to be installed before 2028 and energy prices rocketing, we need substantial energy storage in the next couple of years.
One feasible plan that has been put forward is that of Highview Power’s CEO; Rupert Pearce,, that I wrote about in Highview Power’s Plan To Add Energy Storage To The UK Power Network.
The plan is to build twenty of Highview Power’s CRYOBatteries around the country.
- Each CRYOBattery will be able to store 30 GWh.
- Each CRYOBattery will be one of the largest batteries in the world.
- They will have three times the storage of the pumped storage hydroelectric power station at Dinorwig.
- They will be able to supply 2.5 GW for twelve hours, which is more output than Sizewell B nuclear power station.
Note.
- The first 30 GWh CRYOBattery is planned to be operational by late 2024.
- 600 GWh distributed around the country would probably be sufficient.
I believe that as these batteries are made from standard proven components, they could be built fairly quickly.
Paying For The Energy Storage
This press release from Highview Power is entitled New Analysis Reveals Extent Of UK Renewable Energy Waste, which makes these three bullet points.
- Enough renewable energy to power 500,000 homes a day wasted since the energy crisis began.
- 8 out of 10 Britons want more investment in boosting Britain’s energy resilience.
- UK spent £390 million turning off wind farms and using gas since September 2021.
Note.
- As the press release was published in July 2022, was the £390 million for ten months.
- Will this level of spend continue, as we’re not creating any electricity storage or building any factories that will start in a year or so, that will need large amounts of electricity?
- The Germans are at least building the NeuConnect interconnector between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven.
- As we’re adding up to 5 GW per year to our renewable energy systems, this problem will surely get worse and we’ll spend more money switching off wind turbines.
We have the money to build a very large amount of energy storage.
Improving The Control Algorithm
A better control algorithm would always help and politicians should only be allowed to set objectives.
Conclusion
There is a chance we’ll have an oversupply of electricity, but this will have effects in the UK.
- Gas-fired power-stations will be retired from front-line service to produce electricity.
- Some will question the need for nuclear power.
- Gas may even be used selectively to provide carbon dioxide for agricultural, scientific and industrial processes.
- Industries that need a lot of electricity may build factories in the UK.
- We will have a large supply of green hydrogen.
But it should bring the price of electricity down.
Where Are The Magnificent Eighteen?
In the two classic Japanese and American films of the fifties, there were seven saviours, who worked together.
This page on the Highview Power web site talks about their proposed CRYOBattery in Yorkshire, where this is said.
Highview Power’s second commercial renewable energy power station in the UK is a 200MW/2.5GWh facility in Yorkshire. This is the first of 18 sites for UK wide deployment strategically located to benefit from the existing transmission infrastructure.
As the UK’s energy problem is much worse than the problems in the films, perhaps we need more saviours.
In this article on the Telegraph, which is entitled Britain Will Soon Have A Glut Of Cheap Power, And World-Leading Batteries To Store It, Rupert Pearce, who is Highview’s chief executive, is quoted as saying the following.
Highview is well beyond the pilot phase and is developing its first large UK plant in Humberside, today Britain’s top hub for North Sea wind. It will offer 2.5GW for over 12 hours, or 0.5GW for over 60 hours, and so forth, and should be up and running by late 2024.
Further projects will be built at a breakneck speed of two to three a year during the 2020s, with a target of 20 sites able to provide almost 6GW of back-up electricity for four days at a time, or whatever time/power mix is optimal.
Is this Humberside CRYOBattery, the one on the web site described as in Yorkshire? It’s certainly in the old East Riding.
In Highview Power’s Plan To Add Energy Storage To The UK Power Network, I came to the conclusion, that the Humberside CRYOBattery will most likely be built near Creyke Beck substation, which is close to Cottingham.
- Dogger Bank A, Dogger Bank B and Hornsea 4 offshore wind farms will all be connected to the Creyke Beck substation.
- These wind farms have a total capacity of 3.4 GW.
- The Humberside CRYOBattery, now looks to have a maximum output of 2.5 GW.
- It looks like the Humberside CRYOBattery would be a well-matched backup to the three planned wind farms and perhaps even a few more turbines.
Building the Humberside CRYOBattery at Creyke Beck substation would appear to be a sensible decision.
We Only Have Half A Story
It looks like we’ve only got half a story, with a lot of detail missing.
- Will there be eighteen or twenty of Highview Power’s CRYOBatteries?
- Will they have a power output of 400 MW or nearly 6 GW for four hours?
- Will they have a storage capacity of 2.5 GWh or 30 GWh?
- Is the web site or the CEO correct?
- Have Highview Power and National Grid signed a deal for the next few CRYOBatteries?
I am expecting to see a big press statement at some time, perhaps even in the next few days, that will clear everything up.
If it was me, I would invite the new Prime Minister to the opening of the Carrington CRYOBattery and make the statement there.
The joint publicity could be equally valuable to both the Prime Minister and Highview Power.
Highview Power’s Second Commercial System In Yorkshire
This is all that Highview Power say about their proposed system in Yorkshire, on their web site.
Highview Power’s second commercial renewable energy power station in the UK is a 200MW/2.5GWh facility in Yorkshire. This is the first of 18 sites for UK wide deployment strategically located to benefit from the existing transmission infrastructure.
I have a few thoughts.
How Does The Size Of This System Fit With Other Systems?
According to the Highview Power web site the Manchester system is a 50MW/300MWh facility, but Wikipedia has this system as a 50MW/250MWh.
In this article on the Telegraph, which is entitled Britain Will Soon Have A Glut Of Cheap Power, And World-Leading Batteries To Store It, it is stated that they are planning a battery with this specification, location and timeline.
- 2.5 GW output
- 30 GWh of storage
- Located on Humberside
- Delivery in late 2024.
This CRYOBattery is an absolute monster.
Will The Humberside CRYOBattery Be Built At Creyke Beck Substation?
In Highview Power’s Plan To Add Energy Storage To The UK Power Network, I came to the conclusion, that the Humberside CRYOBattery will most likely be built near Creyke Beck substation, which is close to Cottingham.
- Dogger Bank A, Dogger Bank B and Hornsea 4 offshore wind farms will all be connected to the Creyke Beck substation.
- These wind farms have a total capacity of 3.4 GW.
- The Humberside CRYOBattery, now looks to have a maximum output of 2.5 GW.
- It looks like the Humberside CRYOBattery would be a well-matched backup to the three planned wind farms and perhaps even a few more turbines.
Building the Humberside CRYOBattery at Creyke Beck substation would appear to be a sensible decision.
Is Cottingham In Humberside, Yorkshire Or Both?
The Wikipedia entry for the village is named Cottingham, East Riding of Yorkshire, says this.
A golf course and leisure club on Wood Hill Way, and a major (400/275 kV AC) electricity substation “Creyke Beck”, lie just outside the formal boundaries of the parish, within Skidby civil parish.
Skidby is definitely in Yorkshire.
Where Are The Other Seventeen Sites?
The Yorkshire facility is indicated to be one of 18 sites on the Highview Power web site. Where are the other seventeen?
All we know is that they will be strategically located to benefit from the existing transmission infrastructure.
This is said in the Wikipedia entry, which is entitled High-Voltage Substations In The United Kingdom.
In 2020 there were 179 400 kV substations and 137 275 kV substations.
He who pays the money, makes the choice!
Has The Company Changed Direction?
I wrote Highview Power Names Rupert Pearce Chief Executive Officer on April 12th, 2022.
- Since then, the Vermont and Chile projects have disappeared from the web site and projects in Yorkshire and Australia have been added.
- The web site has also been improved.
- As new CEOs often do, is Rupert Pearce refocussing the company?
Are they also looking in detail at current projects?
Has The Yorkshire Project Grown Substantially?
Consider.
- National Grid are a company that has improved its image and engineering in recent years.
- It has shown it can obtain finance for infrastructure from the City of London and respected financial institutions.
- National Grid probably have extensive computer models of their electricity network.
- National Grid knows it must add energy storage to their electricity network.
- National Grid pays almost a billion pounds a year to wind farm operators to shut them down.
Eventually saving up to a billion pounds would be a good reason to have a small bet on promising technology.
Did Rupert Pearce ask his engineers to design the largest CRYOBattery they can?
Did National Grid have a count up sand find that twenty CRYOBatteries would cover all the strategic points on their transmission infrastructure?
According to the figures on the Highview Power web site (200 MW/2.5 GWh), eighteen systems like the one proposed for Yorkshire would have.
- A total output of 3.6 GW
- A total storage capacity of 45 GWh
The figures given in the article in the Telegraph (2.5 GW/30 GWh) for the very large system, would mean that twenty systems would have.
- A total output of 50 GW
- A total storage capacity of 600 GWh
These figures are between thirteen and fourteen times larger than those originally proposed.
Building The System
The Highview Power web site, says this about the deployment of eighteen systems.
UK wide deployment strategically located to benefit from the existing transmission infrastructure.
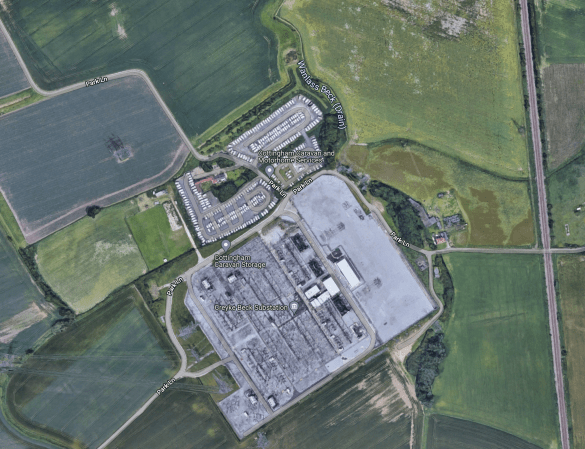
This Google Map shows the Creyke Beck substation.
Could 30 GWh of liquid-air storage be accommodated on the site?
I can see a large insulated sphere, partly buried in the ground being used.
Designing, building and testing the first system will probably be the most difficult part of the project.
- But once the first system is successfully working reliably, the roll-out of other systems can be started.
- The biggest problem will probably be planning permissions, so the systems must be designed to be sympathetic to the local environment.
I can certainly see, twenty of these systems in the UK, but how many others will we see worldwide?
I
Highview Power’s Plan To Add Energy Storage To The UK Power Network
The plan was disclosed in this article on the Telegraph, which is entitled Britain Will Soon Have A Glut Of Cheap Power, And World-Leading Batteries To Store It, by Rupert Pearce, who is Highview’s chief executive.
His plan is to build twenty of Highview Power’s CRYOBatteries around the country.
- Each CRYOBattery will be able to store 30 GWh.
- Each CRYOBattery will be one of the largest batteries in the world.
- They will have three times the storage of the pumped storage hydroelectric power station at Dinorwig.
- They will be able to supply 2.5 GW for twelve hours, which is more output than Sizewell B nuclear power station.
The first 30 GWh CRYOBattery is planned to be operational by late 2024.
- It will be built on Humberside.
- Humberside is or will be closely connected to the Dogger Bank, Hornsea and Sofia wind farms.
- When fully developed, I believe these wind farms could be producing upwards of 8 GW.
The Telegraph quotes Rupert Pearce as saying this.
We can take power when the grid can’t handle it, and fill our tanks with wasted wind (curtailment). At the moment the grid has to pay companies £1bn a year not to produce, which is grotesque.
I certainly agree with what he says about it being a grotesque practice.
It sounds to me, that Rupert’s plan would see Highview Power in the waste electricity management business.
- The wasted wind would just be switched to the Humberside CRYOBattery, if there was too much power in the area.
- The CRYOBattery might be conveniently located, where the wind farm cables join the grid.
- Dogger Bank A and B wind farms are connected to Creyke Beck substation, which is North of the Humber.
- Hornsea 1 and Hornsea 2 wind farm are connected to Killingholme substation, which is South of the Humber.
- Hornsea 3 wind farm will be connected to Norfolk.
- Hornsea 4 wind farms will be connected to Creyke Beck substation
- It looks like the combined capacity of Dogger Bank A, Dogger Bank B and Hornsea 4 could be around 3.4 GW.
- Sofia wind farm will be connected to Lazenby substation near Redcar.
- As the CRYOBattery is buying, selling and storing electricity, I would assume that there’s money to be made.
This Google Map shows Creyke Beck substation.
Note.
- It is a large site.
- Creyke Beck Storage have built a 49.99 MW lithium-ion storage battery on the site.
- The Northern part of the site is used to store caravans.
- It looks like the combined capacity of Dogger Bank A, Dogger Bank B and Hornsea 4 could be around 3.4 GW.
It looks like a 30 GWh CRYOBattery with a maximum output of 2.5 GW would be an ideal companion for the three wind farms connected to Creyke Back substation.
The combination could probably supply upwards of 2.5 GW to the grid at all times to provide a strong baseload for Humberside.
Conclusion
Will the income from the Humberside CRYOBattery be used to fund the next CRYOBattery?
I very much think so as it’s very sensible financial management!