TransPennine Express Releases Blueprint For Improving Service And Fleet Upgrade
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Technology Magazine.
This is the sub-heading.
TransPennine Express (TPE), which transferred to the government’s owning group (DOHL) earlier this year, has set out its plans to address many of the issues which have caused problems and disruption for rail customers.
These three paragraphs summarize their plans.
Making Journeys Better: A Prospectus gives clear detail of the issues TPE has faced during the past two years as well as outlining how TPE, under DOHL, will work to make things better, having completed an in-depth review of the business.
Part of the plans involve the operators plans for its new fleet. Its New Trains Programme outlines its long term view for decarbonisation. The report states that TPE will look towards new technology on its fleet to overcome the lack of clarity on the full electrification of the line.
This, it states will help with the cascading and removal of diesel trains faster across its network.
It always looked to me, that TPE under First Group, brought rather a dog’s breakfast of trains, when a unified fleet of Class 802 trains, as per Hull Trains, might have been easier to operate.
- They are already retiring the Class 68 locomotives and their Mark 5 coaches, so surely to decarbonise their services, a number of battery electric high speed trains would be an idea.
- They are already testing Class 802 battery-electric trains for Hitachi and Eversholt Rail.
- I also feel that CAF could offer a suitable battery-electric train, based on the Class 397 train.
TPE say in the example, that they expect a decision later in the month.
TransPennine Express Services And Battery Electric Trains
These are their services and how they would be effected by battery-electric trains.
- Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.
- Liverpool Lime Street And Hull – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.. – 42 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and Micklefield.
- Manchester Airport and Saltburn – Fully-electrified between Manchester Airport and Northallerton after TransPennine Upgrade. – 33.6 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and Northallerton. Would eliminate overnight noise problems at Redcar.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Newcastle – Fully-electrified after TransPennine Upgrade.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Scarborough – Fully-electrified between Manchester Piccadilly and York after TransPennine Upgrade. – 42.1 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric train that charged between Leeds and York.
- York and Scarborough – Electrified at York – 42.1 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at York.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Huddersfield – Electrified at Manchester Piccadilly – 25.5 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at Manchester Piccadilly.
- Leeds and Huddersfield – Electrified at Leeds – 17.2 miles unelectrified – Service could be run by a battery-electric shuttle train that charged at Leeds.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes – 125,6 miles unelectrified – In Electrification Of The Hope Valley Line, I show how this route can be run by battery-electric trains that charged on existing electrification a short new section of electrification at Cleethorpes.
Note.
- If Manchester Victoria and Huddersfield, is not electrified, battery-electric trains would be able to cross the 25.8 miles of unelectrified track on battery power.
- If Leeds and Huddersfield, is not electrified, battery-electric trains would be able to cross the 17.2 miles of unelectrified track on battery power.
- I am assuming that the TransPennine Upgrade between Manchester and Leeds will be completed, so that between Liverpool Lime Street and Leeds is fully-electrified.
- The only new infrastructure needed would be electrification at Cleethorpes to charge the trains.
All services except for Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes could be run using battery-electric trains with a range on a full battery of at least 100 miles and with no additional electrification.
Electrifying Cleethorpes Station
This Google Map shows Cleethorpes station.
These pictures show the station in June 2023, when it appears to be going through a platform refurbishment.
I don’t think it would be the most difficult station to electrify.
- There are four platforms.
- As the station is likely to get more battery-electric services, including one from King’s Cross, I would suspect that at least three out of the four platforms would be electrified.
- Although, the station is Grade II Listed, there doesn’t appear to be any canopies or important architectural details, that would get in the way of electrification.
Once Cleethorpes station had been successfully electrified, similar installations could be applied at other stations like Saltburn, Scarborough and Skegness.
Conclusion
If TransPennine Express were to buy the right number of battery-electric trains with a hundred mile range, they can decarbonise all their routes in a train factory.
World’s Largest Offshore Wind Farm Produces Power For The First Time
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from SSE.
These bullet points sum up the press release.
- UK Prime Minister Rishi Sunak hails Dogger Bank’s role in bolstering energy security, creating jobs, lowering costs, and achieving Net Zero
- First power achieved at UK’s Dogger Bank as the first of 277 turbines installed 130km from UK coast
- Dogger Bank is now connected via HVDC technology to Britain’s national grid and providing renewable power to homes and businesses
- Each rotation of the first turbine’s 107m long Haliade-X blades can produce enough clean energy to power an average home for two days
- When complete Dogger Bank will deliver clean energy to six million homes annually
I will repeat a highlight of important paragraphs from the press release.
The Size Of The Dogger Bank Wind Farms
When fully complete, Dogger Bank’s world-record-beating 3.6GW capacity will comprise 277 giant offshore turbines capable of producing enough clean energy to power the equivalent of six million homes annually and deliver yearly CO2 savings equivalent to removing 1.5 million cars from the road.
Note.
- The first 1.2 GW section is scheduled for completion in the next few months.
- Two more sections of the Dogger Bank wind farm will eventually raise the capacity to 6 GW.
This cluster of wind farms certainly shows what can be achieved with British offshore wind power.
Innovative HVDC Technology
Dogger Bank also marks the first use of HVDC transmission technology to connect a British wind farm to National Grid’s UK energy network. This includes the installation of the world’s first unmanned offshore HVDC substation platform at the site, as well as first use of Hitachi Energy’s HVDC Light® transmission system which was successfully executed in record time of 38 months with the highest safety and quality standards.
Note.
- HVDC technology appears to be a more efficient way of transmitting energy under the sea and is now generally used for interconnectors.
- This page on the Hitachi Energy web site is entitled Dogger Bank HVDC Connection and gives a good description of the connection and its advantages.
The HVDC Technology and its installation looks like a real achievement, that can be applied to lots of other offshore wind farms.
XLCC seem to be doing the right thing in building an HVDC cable factory in Scotland. Check out their web site.
Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle By Battery-Electric Class 802 Train
After my visit to Morley station, which I wrote about in Morley Station – 17th August 2023, in this post, I look at how a battery-electric Class 802 train might run between Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle stations.
These are the various sections of the route.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Victoria – 31.6 miles – 36 minutes – Electrified
- Manchester Victoria and Huddersfield – 25.7 miles – 30 minutes – Not Electrified
- Huddersfield and Dewsbury – 8 miles – 7 minutes – Currently Being Electrified
- Dewsbury and Leeds – 9.1 miles – 14 minutes – Not Electrified
- Leeds and York – 25.8 miles – 30 minutes – Currently Being Electrified
- York and Newcastle – 80.2 miles – 58 minutes – Electrified
Note.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Victoria, Leeds and York and York and Newcastle are all long enough to fully charge a battery-electric train.
- There is electrification of both ends of the route.
- Manchester Victoria and York is a distance of 68.6 miles.
- The total route length is a distance of 180.4 miles.
In the August 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled GWR Seeks Opportunities To Grow.
This is the sub-heading.
Managing Director Mark Hopwood tells Philip Sherratt there is plenty of potential to increase rail’s economic contribution.
This is a paragraph.
Meanwhile, GWR had announced plans with Eversholt Rail to trial the replacement of a diesel generator unit with batteries on a Class 802 IET. However, Mr. Hopwood says this would not be useful for GWR and so the trial is not proceeding; instead, a TransPennine Express Class 802 will be the subject of a battery trial.
Could the trial be conducted on TransPennine Express’s Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle route?
- The total route length is a distance of 180.4 miles.
- The two electrified sections at the ends of the route; Liverpool Lime Street and Manchester Victoria and York and Newcastle are both long enough to fully charge a battery-electric train.
- The central section between Manchester Victoria and York is not overly long at 68.6 miles.
- The route is convenient for Hitachi’s headquarters at Newton Aycliffe.
It looks like, the Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle route would make an ideal test route for battery-electric Class 802 trains.
Manchester Piccadilly And Newcastle By Battery-Electric Class 802 Train
This is a very similar route to the Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle route with a different Western terminal.
These are the various sections of the route.
- Manchester Piccadilly and Huddersfield – 25.5 miles – 42 minutes – Not Electrified
- Huddersfield and Dewsbury – 8 miles – 10 minutes – Currently Being Electrified
- Dewsbury and Leeds – 9.1 miles – 14 minutes – Not Electrified
- Leeds and York – 25.8 miles – 30 minutes – Currently Being Electrified
- York and Newcastle – 80.2 miles – 58 minutes – Electrified
Note.
- Turnround time at Manchester Piccadilly and York and Newcastle are all long enough to fully charge a battery-electric train.
- There is electrification of both ends of the route.
- Manchester Piccadilly and York is a distance of 68.4 miles.
- The total route length is a distance of 148.5 miles.
Like the Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle route, I believe the Manchester Piccadilly And Newcastle route would make an ideal test route for battery-electric Class 802 trains.
National Express Owner Plans To Launch Eurostar Rival
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the Financial Times.
I have documented a few attempts to start a competitor to Eurostar.
- Express London-Amsterdam Eurostar Service Being Explored
- Getlink Pushes Budget Train Service Between London And Paris To Rival Eurostar
- RENFE Aims To Compete With Eurostar On Paris – London Route
- Transmanche Metro
- The Wikipedia entry for Eurostar details German and Italian attempts to start a service.
Note.
- None of the proposals seem to have got past being announced.
- The only useful fact given in the article, is that the service will be called Evolyn.
Searches of the Internet reveal virtually no more facts, rehashes of the FT article and a lot of waffle.
These are my thoughts.
Would Eurostar Give Up And Slots At St. Pancras International?
I use slots deliberately, as British Airways don’t seem keen to ever give up slots at Heathrow or Gatwick.
And I suspect Eurostar would be the same!
St. Pancras International Doesn’t Have Enough Space
This article on Kent & Surrey Bylines, which is entitled Why Are There Such Queues At St Pancras For Eurostar?, is typical of many you can find on the Internet.
This is the sub-heading.
Eurostar no longer stops at Ebbsfleet or Ashford International, and the queues at St Pancras are becoming intolerable
This is the first paragraph.
Passengers are complaining. The queues at St Pancras are now intolerable. The lines stretch back into the main hall. It is like an airport with the slow shuffle towards the security kiosks. Then, once you are through that, you go to the departure lounge. However, there is not enough seating for the waiting passengers (see picture above taken this month). Because you have to check in 90 minutes before the train starts, one can be stuck standing in this waiting room for an hour. Unless, that is, one is white-haired and venerable, in which case one is usually offered a seat by someone younger and fitter.
It was written on the 9th of last month. But the problems have been bad for some years, as St. Pancras station is too small.
Could Ashford International Station Be Used As A Terminal?
The station has platforms on High Speed One, but the Financial Times says the service will be run between London and Paris.
I doubt even Ryanair would stretch it to say that Ashford was in London.
Could Ebbsfleet International Station Be Used As A Terminal?
It might be possible to say that Ebbsfleet was in London, but then it is not well-connected to Central London.
Does That leave Just Stratford International?
In Platforms 1 And 4 At Stratford International Station, I came to this conclusion.
I have come to these conclusions about Platforms 1 And 4 at Stratford International station.
- The platforms are designed to take the longest Eurostar trains.
- The access to Platforms 1 And 4, doesn’t appear to be designed for continuous heavy use.
- The diamond crossover at the Eastern end of the station would allow Stratford International station to be used as an emergency terminus.
The track layout at the London end of High Speed One appears to have been designed for all eventualities.
But I suspect that Stratford International station will need a lot of money spent to provide Customs and Immigration facilities.
Could Victoria Station Be Used As A Terminal?
National Express is primarily a coach company, so could they be planning a service to connect the long distance coach networks of London and Paris?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the link between High Speed One and the Chatham Main Line.
Note.
- Ebbsfleet International and Northfleet stations are at the top of the map.
- High Speed One is the red line going through Ebbsfleet International station.
- The orange line going across the South-West corner of the map is the Chatham Main Line between Victoria station and Chatham.
- The Chatham Main Line is connected to High Speed One, by the Waterloo Connection or the Fawkham Junction Link.
This route was the original route for Eurostar to Waterloo.
But it could just as easily go into Victoria.
- Southeastern’s Victoria and Dover service takes this route.
- The distance between Victoria and Fawkham junction is 22.6 miles.
- Trains take 28 minutes with a stop at Bromley.
- I wrote some more about the Fawkham Junction Link in Kent On The Cusp Of Change – Fawkham Junction Link.
- I also wrote some more about Victoria as a High Speed terminal in Kent On The Cusp Of Change – Victoria As A Highspeed Terminal.
Note that the two Kent On The Cusp Of Change posts were based on an article in the July 2017 Edition of Modern Railways.
I am convinced that Victoria could be used as a terminal for Continental trains.
Where Would The Service Terminate In France?
Everything I said about congestion also applies to Gare Du Nord, so would it be better to use Marne-la-Vallée–Chessy station that serves Disneyland Paris and Charles de Gaulle Airport, which used to be used by Eurostar.
There are certainly possibilities to do something different.
What Trains Would Be Needed?
The FT article says that the consortium have talked to Alstom, who build the Class 373 trains.
The trains would probably need a specification like this.
- Maximum speed of at least 200 mph, like Eurostar’s Class 374 trains.
- Ability to run on tracks with a UK loading gauge.
- Ability to use both 750 VDC third rail and 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- Less than 240 metres long, which are the platform lengths at Victoria.
Would a High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Train be suitable?
- The trains will have a maximum speed of 224 mph.
- It has been designed for a UK loading gauge.
- The two partners in these trains; Alstom and Hitachi, have both built high speed trains capable of running at slower speeds using third rail electrification.
- The standard length of the trains are 200 metres.
I suspect they would do nicely.
Conclusion
I suspect that the National Express service could use High Speed Two Classic-Compatible Trains between Victoria and Marne-la-Vallée–Chessy stations.
- The trains would be standard with the ability to use third rail electrification
- They would use a single International platform at Victoria and Marne-la-Vallée–Chessy.
- Victoria station is well-connected to the Underground.
- Marne-la-Vallée–Chessy station is connected to Charles de Gaulle airport and Disneyland Paris.
I feel that there is a feasible service that can be designed.
Are The Elizabeth Line Trains Ready To Be Lengthened?
When Transport for London updated the North and East London Lines of the London Overground in the early years of this century, they felt that four-car Class 378 trains would have enough capacity for the lines. But the lines proved more popular than, they had expected and the trains were very overcrowded. So it was decided to lengthen the trains to the five cars they are today.
This wasn’t as easy as it seems, as platforms at several stations had to be lengthened, which was disruptive and expensive.
One day last week, I was in Farringdon station and took these pictures of the platform edge doors at the back end of a Class 345 train.
Note how, that when a train is in the station, it doesn’t reach to the end.
But this is not always the case, as this picture from Paddington station shows.
Does this mean that some underground Elizabeth Line platforms are longer than others?
In Bombardier’s Plug-and-Play Train, I discuss the plug-and-play design of Aventras.
- This plug-and-play design allows trains to be lengthened or shortened by adding or removing carriages.
- Class 345 trains are actually two half-trains, with a trailer car in between them.
So is this why Class 345 trains have run services as both seven-car and nine-car trains?
The former have three-car half-trains and the latter have four-car half-trains, with an extra MS car.
Talk Of Eleven-Car Trains
If you search the Internet, you’ll find forums and web pages speculating about. whether the trains will be lengthened to ten-cars or even eleven-cars.
Consider.
- The current trains are 204.73 metres long.
- Extra intermediate cars are all 22.5 metres long.
- The trains also are probably fitted with selective door opening or can be as most modern trains have it.
This would mean, that a ten-car train would be 227.23 metres long and an eleven-car train will be 249.73 metres.
The eleven-car figure is just 27 centimetres short of 250 metres.
I wouldn’t me surprised if the maximum train length was given to Bombardier as 250 metres.
I certainly feel, that if it should be decided to lengthen the trains by adding another carriage or two, that this will not be a problem.
The Elizabeth Line’s Two Problems
These posts talk about the two problems.
In TfL Needs More Elizabeth Line Trains Because Of HS2 Delays At Euston, I talked about what happens, if High Speed Two doesn’t link initially to Euston.
In Elizabeth Line: Commuters Say Service ‘Not What Was Promised’, I talked about problems of overcrowding at the Western end of the line.
The solutions to both problems are either more trains or adding more carriages to existing trains.
In this article on Ian Visits, which has the same title as the first post, Ian says this about ordering more trains.
Although HS2 isn’t expected to open until some point between 2029-33, TfL is warning that it will need to place the orders for the new trains soon, as the cost of doing so later will be significantly more expensive. That’s because the factory lines to build Elizabeth line trains at Alstom’s factory in Derbyshire are still in place, but will be demobilised soon. If the trains aren’t ordered before that happens, then the cost of reactivating the factory lines has to be included in the bill.
I suspect, it probably applies to an order for extra carriages as well.
Problems For Alstom
But will a substantial order for more Class 345 trains or carriages cause problems for Alstom at Derby?
This extract from the Wikipedia entry for High Speed Two rolling stock, describes how the Hitachi-Alstom joint venture will build the Classic-Compatible trains for High Speed Two.
Vehicle body assembly and initial fitting out of the trains will take place at the Hitachi Newton Aycliffe factory, the bogies will be manufactured at the Alstom factory in Crewe, and final assembly and fit-out, including the interiors, electronics and bogies, will take place at Alstom’s factory in Derby.
If more Class 345 trains are to be built at Derby, does it mean a rethink by the joint venture?
In Battery EMUs Envisaged In Southeastern Fleet Procurement, I talked about how Southeastern were looking for new trains. Given that Aventras from Alstom could be in the frame for these new trrains for Southeastern, does that give Alstom more complications?
Thoughts About Electrification Through Devon And Cornwall
Distances
I’ll start by looking at a few distances.
- Penzance and Taunton – 162.3 miles
- Penzance and Exeter St. David’s – 131.5 miles
- Penzance and Plymouth – 79.5 miles
- Taunton and Exeter St. David’s – 30.7 miles
- Plymouth and Exeter St. David’s – 52 miles
- Taunton and Newbury – 89.6 miles
- Plymouth and Taunton – 82.8 miles
- Taunton and Paignton – 59 miles
- Taunton and Patchway – 51.7 miles
Note.
- Patchway and Newbury are already electrified to Cardiff Central and London Paddington respectively.
- Bombardier’s engineer told me eight years ago, that the battery-electric Class 379 had a range of sixty miles.
- Stadler’s FLIRT Akku has a Guinness world record of 139 miles on one battery charge. See this page on the Stadler web site.
- Even Stadler’s Class 777 trains for Merseyrail have a range of 84 miles on battery power. See New Merseyrail Train Runs 135km On Battery.
The rail distances in Devon and Cornwall are getting closer to being within the capability of trains fitted with batteries.
Station Stop Times
These are typical times that trains stop in the more important stations between Taunton and Penzance.
- Taunton – < 2 mins
- Tiverton Parkway – < 2 mins
- Exeter St. Davids – 2 mins
- Newton Abbot – < 2 mins
- Totnes – < 2 mins
- Plymouth – 11 minutes
- Devonport – < 2 mins
- Saltash – < 2 mins
- Menheniot – < 2 mins
- Liskeard – < 3 mins
- Bodmin Parkway – 2 mins
- Lostwithiel – 2 mins
- Par – 2 mins
- St. Austell – 2 mins.
- Truro – 2 mins
- Redruth – 2 mins
- Camborne – 2 mins
Note.
- The timings were for today.
- The Cardiff and Penzance services were being run by five-car Class 802 trains.
- Most station stops are around two minutes or less, but Plymouth on this train was eleven minutes.
I find it interesting that the Plymouth stop takes so much longer.
Train Stops At Plymouth
I looked at about twenty trains stopping at Plymouth, that included these services.
- London Paddington and Penzance
- Penzance and London Paddington
- Cardiff Central and Penzance
- Penzance and Cardiff Central
Note.
- I found an average time of eight minutes.
- Eleven minutes was a common stop.
- Eight minutes could be enough time for the rail equivalent of a Formula One splash and dash.
- CrossCountry services were going through the station in three minutes.
I am led to believe that the timetable used by the GWR trains would allow a quick battery charge at Plymouth station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms at Plymouth station.
Note.
- London is to the East and Penzance is to the West.
- Platform numbers increase from South to North.
- The two East-facing bay platforms are Platforms 1 and 2.
- The West-facing bay platform in the South-West corner is Platform 3.
- Platform 4 shares the island with the bay platforms 1, 2 and 3.
- Most trains going to Penzance use Platform 4.
- Platforms 5 and 6 share the centre island platform.
- Platforms 7 and 8 share the Northernmost island platform.
- Most trains going towards London use Platform 7.
- Wikipedia indicates that the track layout is comprehensive and allows a lot of operational flexibility.
Although the station was completed around forty years ago, it could have been designed for handling modern battery-electric trains.
- There are three bay platforms numbered 1 to 3, to charge local services and send them on their way.
- Trains can arrive and depart in the five through platforms, numbered 4 to 8, from either direction.
- Two days ago, a nine-car London Paddington to Plymouth train terminated in Platform 7. After waiting an hour it returned to London. An hour would be enough time to fully-charge a train.
- As many platforms as needed could be electrified.
I am fairly sure, that most battery-electric trains could be timetabled to leave Plymouth station with full batteries.
Turnround At Penzance
I have found these turnrounds.
- 802113 arrived from Paddington at 1142 and left for London at 1215
- 802022 arrived from Paddington at 1307 and left for London at 1415
- 802103 arrived from Paddington at 1500 and left for London at 1615
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms at Penzance station.
Note.
- The three example trains used Platform 1.
- Platform 1 is the long platform on the landward side of the station.
- Platforms are numbered 1 to 4 from left to right.
- An appropriate number of platforms would be electrified to charge trains terminating at Penzance.
Trains would appear to have plenty enough time to recharge, so they would start their return journey with full batteries.
Engineering Ambition
Several times in my life, I’ve got fired up about engineering or software projects and I like to think, I’ve produced the best and fastest solution.
For this reason, I believe that Hyperdrive Innovation, who are now part of Turntide Technologies, and Hitachi will set themselves three objectives with the design of the the battery packs for the Class 802 train.
- The battery-electric Class 802 will outperform the Stadler FLIRT Akku in terms of speed and distance.
- The battery packs will be plug-compatible with the diesel engines, so there will only be minor software modification to the trains.
- The train will be able to be handle all Great Western Railway’s routes without using diesel.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that on many routes the train will cruise at over 110 mph on batteries.
I also suspect they want the Akku’s Guinness world record, which will mean the range will be in excess of 139 miles.
Battery Range Needed For Routes
These are routes that need to be covered by battery-electric Class 802 trains or similar.
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Chester – 22.2 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Holyhead – 105.5 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Llandudno Junction – 65.5 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Crewe and Wrexham – 34.4 miles
- Avanti West Coast – Shrewsbury and Wolverhampton – 29.7 miles
- Great Western Railway – Penzance and Plymouth – 79.5 miles
- Great Western Railway – Plymouth and Taunton – 82.8 miles
- Great Western Railway – Taunton and Patchway – 51.7 miles
- Great Western Railway – Newbury and Taunton – 89.6 miles
- Great Western Railway – Taunton and Paignton – 59.0 miles
- Great Western Railway – Weston-super-Mare and Chippenham – 43.5 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Great Malvern – 65.6 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Hereford – 86.3 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Worcester Foregate Street – 57.6 miles
- Great Western Railway – Oxford and Worcester Shrub Hill – 57.2 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cheltenham Spa and Swindon – 43.2 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cardiff Central and Carmarthen – 77.4 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cardiff Central and Pembroke Dock – 118.9 miles
- Great Western Railway – Cardiff Central and Swansea – 45.7 miles
- Hull Trains – Beverley and Temple Hirst Junction – 44.3 miles
- Hull Trains – Hull and Temple Hirst Junction – 36.1 miles
- LNER – Hull and Temple Hirst Junction – 36.1 miles
- LNER – Middlesbrough and Longlands Junction – 22.2 miles
- LNER – Sunderland and Longlands Junction – 48.5 miles
- LNER – Lincoln Central and Newark Northgate – 16.6 miles
- LNER – Leeds and Bradford – 13 miles
- LNER – Leeds and Harrogate – 18 miles
- LNER – Leeds and Huddersfield – 17 miles
- LNER – Stirling and Inverness – 146 miles
- LNER – Edinburgh Haymarket and Aberdeen – 130 miles
- LNER – Peterborough and Doncaster via Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line – 93.7 miles
- South Western Railway – Basingstoke and Exeter St. David’s – 124.5 miles
- TransPennine – Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- TransPennine – Longlands Junction and Saltburn – 34.7 miles
- TransPennine – York and Scarborough – 42 miles
- TransPennine – Doncaster and Cleethorpes – 52.1 miles
- TransPennine – Stockport and Doncaster – 55.4 miles
- TransPennine – Stockport and Cleethorpes – 107.5 miles
Note.
- Stirling and Inverness and Edinburgh Haymarket and Aberdeen could be shortened by up to thirty miles, by planned electrification in Scotland.
- I have assumed that the TransPennine Upgrade has been completed.
- It looks like a battery-electric Class 802 train could use the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line diversion via Lincoln.
- I am slightly surprised, that the longest stretch of line without electrification and with a passenger service is Basingstoke and Exeter St. David’s.
Charging will be needed at some places to charge the battery-electric trains. Stations fitted with chargers could include Aberdeen, Carmarthen, Cleethorpes, Exeter St. David’s, Hereford, Holyhead, Hull, Inverness, Paignton, Penzance, Pembroke Dock, Plymouth, Swansea, Taunton, Weston-super-Mare, Worcester.
Most chargers would be a length of electrification in the platform, where the battery-electric trains terminated or passed through.
More On LNER’s Ten New Bi-Modes
I wrote about these trains in LNER Seeks 10 More Bi-Modes.
This was my conclusion.
There is a lot of scope to develop LNER’s services.
I think it is likely that the order will go to Hitachi.
But as I indicated, I do believe that there is scope for a manufacturer to design a zero-carbon train, that was able to serve Aberdeen and Inverness.
-
- I suspect a fleet of ten trains would be sufficient.
- Trains would use the 25 KVAC overhead electrification, where it exists and hydrogen or battery power North of the wires.
The trains would also be capable of being upgraded to higher speeds, should the East Coast Main Line be turned into a High Speed Line.
I also think, that whatever trains are bought, there will be a large upgrading of the existing Hitachi fleet, which will add batteries to a lot of trains.
In the July 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled LNER Embraces Pioneering Spirit, which takes the form of an interview with LNER’s Managing Director; David Horne.
In a section, which is entitled ‘225’ Replacement, this is said.
Meanwhile, Mr Horne is looking to what might replace the InterCity 225 fleet, now smartly repainted in a scheme which pays homage to the original ‘Swallow’ livery. While there were fears this fleet may be withdrawn as an economy measure, the ‘225s’ are now on lease until at least next summer.
But Mr Horne says obsolescence issues are a real challenge and LNER will struggle to maintain the fleet beyond 2025, and from the May 2023 timetable change the number of daily diagrams was reduced from five to four to conserve the fleet’s mileage. Much of the heavy maintenance work had previously been carried out at Wabtec’s Doncaster site, but this facility is no longer available, and while a recent reliability improvement programme is bearing fruit, the challenges remain. The crunch point comes with the transition to ETCS at the southern end of the ECML as part of the East Coast Digital Programme – Mr Horne says LNER does not want to fit cab signalling on the ‘225s’.
The solution to this issue is to procure additional trains to run alongside the 65 Azumas, and LNER went out to tender in October 2020 for a fleet of 10 trains with self-power capability.
While a preferred bidder has been identified, the business case to proceed with the procurement is awaiting approval, but Mr Horne is still hopeful this project can be progressed.
The current plan envisages the new trains broadly replacing the ‘225s’ on Leeds and York diagrams, but a major benefit with the new fleet would be during engineering work – at present LNER has to withdraw services to places such as Harrogate and Hull to concentrate its bi-mode Azumas on services using non-electrified diversionary routes, and having more stock with self-power capability would ease the issue.
Currently, LNER has these Azumas and InterCity 225s in its fleet.
- Five-car bi-mode Class 800 trains – 10
- Nine-car bi-mode Class 800 trains – 13
- Five-car electric Class 801 trains – 12
- Nine-car electric Class 801 trains – 30
- Nine-car electric ImterCity 225 trains – 8
Note.
- There are 23 bi-mode trains and 50 electric trains.
- There are 167 bi-mode carriages and 302 electric carriages.
- Currently 31.5 % of the trains are bi-mode.
- With ten new bi-mode trains and no InterCity 225 trains, 44 % of the fleet will be bi-mode.
Is this increase in the percentage of the fleet, that are bi-mode acceptable?
I wonder, if there is a more affordable and flexible way to increase the fleet size.
In the Wikipedia entry for the Class 800 train, there is a section, which is entitled Traction And Generator Units, where this is said.
The Class 800 and Class 802 bi-mode are equipped with three GU per five-car set and five GU per nine-car set; a five-car set has a GU situated under vehicles 2/3/4 and a nine-car set has a GU situated under vehicles 2/3/5/7/8. In comparison, the electric-orientated Class 801 features a single GU for a five to nine-car set, which provides emergency power for limited traction and auxiliaries if the power supply from the overhead line fails. By adding or removing GUs, a Class 800 can be converted into a Class 801 and vice versa.
Let’s look at LNER’s needs, which are actually two separate sub-needs.
- There is a need for ten new trains to replace the InterCity 225 trains.
- There is a need to increase the size of the bi-mode fleet to be able to use the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line and other non-electrified routes to by-pass engineering works.
Note.
- I suspect that as Mr Horne explained, there are only five or possibly four InterCity 225s diagrammed on a particular day, then perhaps ten five-car bi-mode Class 800 trains, might be able to cover for the retirement of the InterCity 225s.
- These trains would work as pairs to Leeds and York to replace the InterCity 225 capacity.
- If required they could split and join at Leeds and York to serve other destinations.
- The diversion route of the Great Eastern Joint Line has an unelectrified distance of 93.7 miles and the route is electrified at both ends.
- Would a battery-electric Class 800 train handle this distance? I suspect if Stadler can do it, then Hitachi and Turntide Technology will be able to do it too!
LNER will have replaced the InterCity 225s and acquired ten new five-car blockade runners.
As an order for ten new five-car battery-electric trains, is not to be sneezed at, I suspect Hitachi will make sure that their new battery-electric variants have enough range.
So this would mean that the range of a five cat battery-electric Class 800 train, should be in excess of 93.7 miles.
It should be noted that the five-car Class 800 and Class 802 trains have specific advantages when it comes to converting them to battery-electric trains.
- They are modern trains, that are still in production, every bit of information about the train is known down to the last nut, bolt and plastic clip.
- Like most modern trains, hey have a sophisticated computer system controlling the train.
- They have spaces for three, four or maybe even five diesel engines under the floor, which could be used for a battery-pack in every car designed to hold a diesel engine.
- The train has an electric bus between nose and tail.
- As is shown, when the trains change between diesel and electric, the pantograph can go up and down with all the alacrity of a whore’s drawers.
- The trains can be converted between bi-mode and electric, by adding or removing diesel packs. I doubt this feature will be removed, as batteries replace diesels.
With my Electrical and Control Engineer’s hard hat on, I doubt there is anything to stop a Class 800 or Class 802 train being fitted with three or more batteries to create a 125 mph train, with a range approaching two hundred miles on battery power.
The initial name of these Hitachi trains was the Hitachi Super Express. Is this train the Hitachi Super Battery Express?
But it would appear, that for their initial needs, LNER, just need a range to handle the near hundred miles of the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line.
Inverness and Aberdeen will come later.
Hull Trains
This page on the Lumo web site is entitled Greener Travel Between Edinburgh And London.
These are the first three paragraphs.
A new, 100% electric rail service is to start running between London and Edinburgh with fares for as little as £14.90 in a bid to encourage greener and more affordable travel between the capitals.
Called Lumo, it will provide low-carbon, affordable long-distance travel for over 1 million passengers per year. Over 74,500 passengers currently fly between Edinburgh and London each month3.
And with single tickets between the capitals starting from just £14.90, Lumo will be a comfortable, convenient alternative to flying that is affordable for all. Some 60% of all single fares will be available at a cost of £30 or less.
I’m sure Hull Trains, who are owned by First Group like Lumo would like to position themselves in the 100 % electric low-carbon box too!
Currently, Hull Trains’s five-car Class 802 trains, run 88.6 and 72.2 miles using diesel on round-trips to Beverley and Hull respectively from London.
If batteries were fitted to their trains to give a battery range of around a hundred miles, Hull Trains could call themselves 100 % electric.
No new infrastructure would be required, but a short length of overhead electrification in a convenient platform at Hull station would ensure the train left for London and Beverley with a full battery.
The pictures show Hull Trains’s Class 802 train in Platform 7 at Hull station.
Penzance And Taunton
This to me is the key section as if you can run a battery-electric train between these two stations it allows so many of the services to be run using zero-carbon traction.
These are distances from Taunton.
- Exeter St. David’s – 30.7 miles
- Newbury – 89.6 miles
- Okehampton – 55.3 miles
- Paignton – 59.0 miles
- Patchway – 51.7 miles
- Plymouth – 82.8 miles
Note.
- I’ve added Okehampton, as I feel that if Dawlish had another encounter with Poseidon, Okehampton with its proposed Parkway station on the A30 could be the terminus for coaches to and from Cornwall.
- All would be possible with a battery-electric train, with a hundred-mile range, leaving Taunton with a full battery.
- Charging could be needed at Okehampton and Paignton.
What is needed is some form of charging in the Taunton area.
This OpenRailwayMap shows Taunton station.
Note.
- The station has four through platforms.
- All Great Western Railway services to and from Devon and Cornwall stop in the station.
- I feel it would be possible to electrify the station, so that all stopping trains could charge the batteries.
But the problem would be, that as typically trains only stop for a couple of minutes at Taunton, there may not be enough time to take enough charge on board.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the track between Wellington and Collumpton, between Taunton and Exeter.
Note.
- The black line is the railway between Taunton and Exeter.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map indicates the position of the proposed Wellington station.
- Collumpton is in the South-West corner of the map and has also been put forward for a new Collumpton station.
- I talked about the reopening of these two stations in Reopening Of Wellington and Cullompton Stations.
- The M5 to the North of Collumpton runs closely alongside the railway.
- According to Real Time Trains, it takes just under ten minutes to go the thirteen miles between Wellington and Collumpton.
This Google Map shows a section of the M5 North of Collumpton.
And this Google Map shows Tiverton Parkway station.
Note how the railway runs alongside the M5 to the West.
I feel that if the two new stations of Wellington and Collumpton are built between Taunton and Exeter St. David’s, then why not partially electrify the route, so that all trains would leave or pass through Taunton and Collumpton stations with full batteries.
- Going West the trains would reach Exeter St. David’s, Okehampton or Plymouth.
- Going East trains would reach Newbury for Reading and Paddington, and Patchway for Cardiff.
I believe that a battery-electric solution is possible, that would enable the decarbonisation of the Great Western Main Line all the way to Penzance.
Hitachi Rail Names Preferred Supplier For Battery System Development For UK Trial
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Rail Technology Magazine.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Hitachi Rail UK is continuing its commitment to electrification and sustainability as it has teamed with a UK based Technology firm to design and supply its traction and battery systems for its intercity battery train trial which it hopes to run in the future.
Working with the North East England Partnership and Turntide Technologies, Hitachi UK Rail are working towards a UK trial for its battery technology which is engineered to reduce emissions and fuel costs. It is hoped, that if successful, it’ll advance the UK’s position as a global leader in battery train technology.
Note.
- Turntide Technologies took over Hyperdrive Innovation.
- Turntide Technologies have designed and built systems for JCB.
Up until now, we have been told very little about the batteries.
I have the following questions.
Is The Battery System In The Class 803 Trains For Lumo By Turntide Technologies/Hyperdrive Innovation?
The Wikipedia entry for Lumo, says this about the design of the Class 803 train.
Services are operated by a fleet of 125 mph (200 km/h) Class 803 electric multiple unit trains, ordered in March 2019 at a cost of £100 million, financed by the rail leasing company Beacon Rail.[15] While based on the same Hitachi AT300 design as the Class 801 Azuma trains operated on the East Coast Main Line by franchised operator London North Eastern Railway (LNER), they are not fitted with an auxiliary diesel engine, but instead feature batteries intended solely to power onboard facilities in case of overhead line equipment failure.
The maker of the batteries has not been disclosed.
If they have been made by Turntide, then they would certainly have had a good vibration testing.
Is The Battery System In The Class 803 Trains Similar To That Proposed For Class 800/802/805/810 Trains?
It would seem sensible, as this would mean that Hitachi would only be introducing one type of battery into the various fleets.
Supporting structures and wiring harnesses would then be identical in all trains, whether diesel engines or batteries were to be fitted.
Are The Batteries Plug Compatible With Similar Performance To The Diesel Engines?
I have never driven a train, but I have ridden in the cab of an InterCity 125, as I wrote about in Edinburgh to Inverness in the Cab of an HST.
The driver controls the two locomotives individually, just like I controlled the two engines in my Cessna 340 with two separate throttles.
So how does a driver control all the three engines in a five-car Class 800 train or the five engines in a nine-car?
Put simply, the driver just tells the computer, what speed or power is required and the train’s computer adjusts al the engines accordingly.
I believe it would be possible to design battery packs that are plug-compatible with similar performance to the diesel engines.
Hitachi could be playing an old Electrical/Electronic Engineer’s trick.
As a sixteen-year-old, I spent a Summer in a rolling mills, building replacement transistorised control units for the old electronic valve units. They had been designed, so they were plug-compatible and performed identically.
The great advantage of this approach, is that no changes were needed to the rolling mill.
So if Hitachi are using a similar approach, there should be very few or even no changes to the train.
What Range Will A Class 800 Train Have On Batteries?
This article on Focus Transport is entitled 224-kilometre Battery Range For FLIRT Akku – Stadler Sets World Record For Guinness Book Of Records.
I would be very surprised if Hitachi don’t break that record of 224 kilometres or 139 miles.
Conclusion
I belive we’re going to see a real revolution in rail transport.
The Ways First Group, Hitachi, Hyperdrive Innovation and Turntide Technologies Can Enable Electric Trains To Run Between Basingstoke And Exeter
Who Are Turntide Technologies?
The Wikipedia entry for the company starts with this paragraph.
Turntide Technologies is a US-based business that makes intelligent, sustainable motor systems. Turntide applies its Technology for Sustainable Operations across buildings, agriculture, and transportation segments. It maintains operations in the USA, Canada, the United Kingdom, and India.
These three paragraphs from the Technology section of the Wikipedia entry outline their technology.
Turntide’s core product is its Technology for Sustainable Operations, a cloud-based open platform that monitors and automates building and vehicle systems. The platform is powered by its Smart Motor System, a connected hardware-software machine built around a high rotor pole switched reluctance motor.
Southern California Edison utility certified in 2018 that the V01 Smart Motor System reduced energy consumption by 23%-57% compared with a standard AC induction motor, and 11% compared with an induction motor controlled by a variable frequency drive.
In 2019, National Renewable Energy Laboratory certified that Turntide’s motor reduced energy consumption in refrigerator condenser fans by 29%-71%.
Note.
- Turntide’s efficiencies, which appear to have been verified by reputable organisations, if they can be reproduced in traction systems for battery-powered transport could improve range substantially.
- There are also other more efficient electric motors being developed.
- I wrote about Norfolk-based advanced traction motor company; Equipmake in Equipmake Hybrid To Battery Powered LT11.
- Motors like these, are the engineer’s cure for range anxiety.
I have to ask, if Hitachi (, and Stadler) are using more efficient motors to stretch the range of their battery-electric trains.
Initially, Hitachi asked Hyperdrive Innovation to design battery packs for Class 802 and other similar trains.
These three posts give some details about the battery project involving the two companies.
- Hitachi And Eversholt Rail To Develop GWR Intercity Battery Hybrid Train – Offering Fuel Savings Of More Than 20%
- Hitachi Rail And Angel Trains To Create Intercity Battery Hybrid Train On TransPennine Express
- More On Batteries On Class 802 Trains
Consider.
- In June 2021, Turntide acquired Hyperdrive Innovation.
- So did this effectively invite Turntide to the project?
- According to the Internet, Hitachi are one of the largest manufacturers of electric motors.
- Turntide are very-well funded by the likes of Bill Gates, Robert Downey Junior and some big funds.
Has there been some intense design meetings, which have been beneficial to all parties?
In my experience, these groupings don’t often work out how they should!
But this relationship seems to be doing fine.
One of Hitachi’s managers from the battery-train project even appears in the video on Turntide’s home page.
Electrifying Basingstoke And Exeter
Consider these facts about the route.
- Basingstoke and Salisbury is 35.8 miles.
- Salisbury and Exeter is 88.5 miles.
- Basingstoke and Exeter is 124.3 miles.
- There is no electrification.
- There are 14 stops between Salisbury and Exeter.
- There are 4 stops between Basingstoke and Salisbury.
- Trains are up to nine car Class 159 trains.
- Average speeds are not much better than 50 mph.
- Maximum speeds vary between 75 and 90 mph.
To get an estimate of how much energy, a Basingstoke and Exeter train will use, I’ll start with a figure from How Much Power Is Needed To Run A Train At 125 Or 100 mph?.
At 125 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 3.42 kWh per vehicle mile.
As drag is proportional to the square of the speed, which gives
- At 100 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 2.19 kWh per vehicle mile.
- At 80 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 1.40 kWh per vehicle mile.
For this calculation I’ll take the 80 mph figure of 1.40 kWh per vehicle mile.
Assuming a five-car train travelling between Basingstoke and Exeter, which is 124.3 miles gives a figure of 870 kWh.
But this is only one use of energy on the train.
- Every time, the train accelerates it will need power, but it will charge itself using regenerative braking.
- An all-electric Class 803 train has a mass of 228.5 tonnes and carries 400 passengers.
- If I assume that each passenger is 80 Kg including baggage, bikes and buggies, that gives a mass of 32 tonnes or a total mass of 260.5 tonnes.
- Putting these figures into Omni’s Kinetic Energy calculator gives a figure of 46.3 kWh at 80 mph.
As there are eighteen stops along the route and at each stop it could lose up to twenty percent of its energy, this means that the eighteen stops will cost 166.7 KWh.
Adding this to the 870 KWh it takes to maintain speed, it looks like a trip between Basingstoke and Exeter will take 1036.7 kWh.
Could this be a 200 kWh battery in each coach?
Obviously, this is only a rough calculation and with the better figures Hitachi would have, I would suspect much better answers.
But I do believe that it would be possible to run between Basingstoke and Exeter on battery power, if the train was efficient.
Charging The Train
The train would be charged on the third-rail electrification between Waterloo and Basingstoke.
But what would happen at Exeter?
The trains could be bi-modes like Hitachi’s Class 395 trains for Southeastern,
One of Vivarail’s third-rail charging systems, that First Group, acquired from the Receiver of Vivarail could be used.
Getting The Order Right
Would between Basingstoke and Exeter, be a sensible route to convert to battery-electric trains early, as it would release a useful fleet of diesel trains, that might be able to fill in for a couple of years by replacing the Castles!
National Grid Avoids Emissions At London Power Tunnels Substation With Green Grid Technology
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These are the main bullet points.
- £1bn project to rewire London will see the replacement of ageing high-voltage electricity cables and expand network capacity to meet the increasing electricity demand
- A new substation at Bengeworth Road in Lambeth is at the heart of the project and will be built by Linxon using Hitachi Energy’s SF6 free gas insulated switchgear technology in a UK first
- The project forms part of National Grid’s ambition to have no SF6 in electrical assets by 2050
- National Grid is investing a total of £1.3bn every year in electricity network infrastructure needed to help the UK decarbonise and reach net zero emissions
I’ll now expand some of these points.
The London Power Tunnels
This is said about the London Power Tunnels.
National Grid’s London Power Tunnels (LPT) project is a seven-year, £1 billion project, to rewire South London via deep underground tunnels. This vital work to replace ageing high-voltage cables will expand capacity and help keep Londoners connected to secure and reliable electricity supplies.
Note.
- In total, there are 32.5km of 3m diameter tunnels.
- They stretch between Wimbledon and Crayford.
- As part of the project, a new tunnel access shaft, substation and headhouse is being built at Bengeworth Road, Lambeth to connect to our London Power Tunnels (LPT) route.
The London Power Tunnels have their own web site.
Sulphur Hexafluoride
This is said about Sulphur Hexafluoride.
Sulphur Hexafluoride (SF6 ) is used in the electricity industry in substations to prevent short circuits and to keep the network safe and reliable, but it has a high global warming potential. National Grid’s ambition is to reduce its SF6 emissions by 50% by 2030 and remove all SF6 gas from electrical assets by 2050.
Linxon is building Bengeworth Road substation for National Grid and to support the business in its transition to SF6 -free solutions, in a UK first, Hitachi Energy will deliver EconiQ™ 400-kilovolt (kV) gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) and gas-insulated lines (GIL) containing no SF6, to enable the transmission of energy over long distances. Installation is expected to begin in 2023, subject to prior approval of the substation by Lambeth Council.
In the Wikipedia entry for sulphur hexafluoride, this is said.
SF6 is 23,500 times more potent than CO2 as a greenhouse gas but exists in relatively minor concentrations in the atmosphere. Its concentration in Earth’s troposphere reached 10.63 parts per trillion (ppt) in 2021, rising at 0.39 ppt/year.[8] The increase over the prior 40 years was driven in large part by the expanding electric power sector, including fugitive emissions from banks of SF6 gas contained in its medium- and high-voltage switchgear. Uses in magnesium, aluminium, and electronics manufacturing also hastened atmospheric growth.
As I have a lot of experience of HF, my view is that we’re well shot of the SF6, but I’ll be 103, when National Grid eliminate it.
Regulator Approves New Grand Union Train Service From Carmarthen To London Paddington
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from the Office of Rail and Road.
This is the sub-heading of the press release.
The Office of Rail and Road (ORR) has opened up the Great Western Main Line to competition and enabled a significant increase in rail services between London and South Wales.
These points are made in the press release.
- The rail regulator has approved the introduction of new train services between London, Cardiff and South West Wales from the end of 2024.
- The services will be operated by a new open access operator, Grand Union Trains, bringing competition to the Great Western route out of Paddington.
- Passengers travelling between London, Bristol Parkway, Severn Tunnel Junction, Newport, Cardiff, Gowerton, Llanelli and Carmarthen will benefit from an extra five daily return services and greater choice of operator.
- The decision opens up the Great Western Main Line to competition for the first time, with potential benefits in terms of lower fares, improved service quality and innovation for all passengers using the route.
- The application, submitted to ORR in June 2022, was disputed by Network Rail due to concerns about capacity on the network. But following careful consideration and analysis, ORR has directed Network Rail to enter into a contract with Grand Union.
- Grand Union has committed to significant investment in new trains.
- As an ‘open access’ train operator, however, it will not get paid subsidies from public funds, unlike current operators along the route.
ORR supports new open access where it delivers competition for the benefit of passengers. In making this decision, the regulator has weighed this up against the impact on Government funds and effect on other users of the railway, both passengers and freight customers.
These are my thoughts.
The Company
Grand Union Trains have certainly persevered to get this approval.
- The company was created by Ian Yeowart, who previously created open access operators; Alliance Rail Holdings and Grand Central before selling both to Arriva.
- After multiple negotiations with the Office of Road and Rail (ORR), Yeowart must know how to get an acceptable deal.
- Grand Union Trains have a similar application for a service between Euston and Stirling with the ORR.
Grand Union Trains also have a web site.
The home page has a mission statement of Railways To Our Core, with this statement underneath.
At Grand Union we are passionate about Britain’s railways. We are committed to the traditional values of providing a high-quality customer service and a comfortable journey experience at a fair price.
I’ll go with that.
The Financial Backing Of The Company
All the UK’s open access operators are well-financed either by Arriva or First Group.
The ORR would not receive any thanks, if they approved an operator, which duly went bust.
So what is the quality of the financing behind Grand Union Trains?
This article on Railway Gazette is entitled RENFE Looks At Entering UK Rail Market Through Open Access Partnership, which starts with this paragraph.
Open access passenger service developer Grand Union Trains is working with Spain’s national operator RENFE and private equity firm Serena Industrial Partners on a proposed service between London and Wales.
That is fairly clear and would surely help in the financing of Grand Union Trains.
The Route
Trains will run between Carmarthen and London Paddington, with stops at Llanelli, Gowerton, Cardiff, Newport, Severn Tunnel Junction and Bristol Parkway.
A new station at Felindre will replace Gowerton at some time in the future.
There will be five trains per day (tpd).
I have some thoughts and questions about the route
Felindre Station
Felindre station is named in Wikipedia as the West Wales Parkway station, where it is introduced like this.
West Wales Parkway is a proposed railway station north of Swansea, near to the boundaries of the neighbouring principal area of Carmarthenshire, and the villages of Felindre and Llangyfelach. The station is proposed to be situated at the former Felindre steelworks, near Junction 46 of the M4 and A48, and near Felindre Business Park and Penllergaer Business Park. The project is in the planning stages, as part of a wider Department for Transport proposal to re-open the Swansea District line to passenger traffic.
This Google Map shows where, it appears the Felindre station will be built.
Note.
- The Felindre Business Park in the North-West corner of the map, with a Park-and-Ride.
- The M4 running across the bottom of the map.
- The Swansea District Line runs East-West between the motorway and the Business Park.
It looks that the new station could be located on the South side of the Business Park.
When High Speed Two Opens Will Trains Call At Old Oak Common?
When High Speed Two opens, all GWR trains will stop at Old Oak Common station for these connections.
- Chiltern for for Banbury, Bicester, High Wycombe and the West Midlands
- Elizabeth Line for Central and East London and the Thames Valley
- Heathrow Airport
- High Speed Two for Birmingham and the North
- Overground for Outer London
As Old Oak Common will be such an important interchange, I think they should.
Will The Platforms At Carmarthen Station Need Lengthening?
This Google Map shows Carmarthen station.
Note.
- The station has two platforms.
- There are certainly pictures of the station with an InterCity 125 in the station. There is a picture on the Wikipedia entry for Carmarthen station.
These pictures show the station.
I suspect that the station will be upgraded to accommodate Grand Union Trains.
The Trains
An article in the June 2022 Edition of Modern Railways, which is entitled Grand Union Bids For London To Carmarthen, gives these details of the trains.
- Three classes.
- 2023 start for the service.
- Cycle provision.
- Vanload freight will be carried.
- Electric trains could start between London and Cardiff by 2023.
- In 2025, trains could be nine-car bi-modes.
- South Wales-based operation and maintenance.
- 125 full-time jobs created.
It certainly seems to be a comprehensive and well-thought out plan.
I have a few thoughts on the trains.
What Make Of Trains Will Be Procured?
Consider.
- Lumo’s Class 803 trains were ordered from Hitachi in March 2019 and entered service in October 2021.
- So if they ordered their version of the Hitachi trains by the end of 2022, the trains could be in service by July/August 2025.
- It would probably be easier, if the only fast trains on the Great Western Main Line between London and South Wales were all Hitachi trains with identical performance.
But the Spanish backers of Grand Union Trains may prefer Spanish-designed trains assembled in South Wales. So would a bi-mode version of CAF’s Class 397 trains be suitable?
On the other hand, the Carmarthen and Cardiff section of the route without a reverse at Swansea is only seventy-five miles.
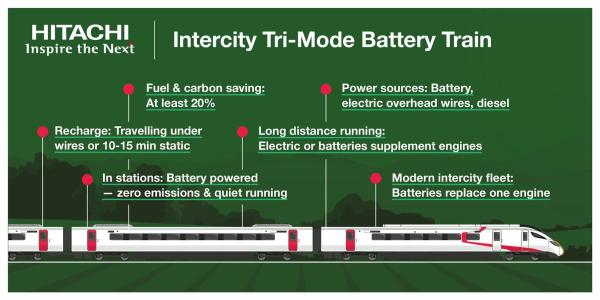
This Hitachi infographic shows the Hitachi Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train.
Consider.
- Charging could be provided at Carmarthen using a short length of electrification or one of Furrer + Frey standard chargers.
- Charging would also use the electrification between London Paddington and Cardiff.
- A nine-car Class 800 or Class 802 train has five engines and a five-car train has three engines.
- The Intercity Tri-Mode Battery Train was announced in December 2022.
- In the intervening two years how far has the project progressed?
- For the last twelve months, Lumo have been running trains with an emergency battery-pack for hotel power. How are the batteries doing, whilst being ferried up and down, the East Coast Main Line?
Can Hitachi configure a train with more than one battery-pack and a number of diesel engines, that has a range of seventy-five miles? I suspect they can.
I suspect that CAF also have similar technology.
There is also a benefit to Great Western Railway (GWR).
If GWR were able to fit out their Class 802 trains in the same way, they would be able to run between Cardiff and Swansea on battery power.
- It is only 45.7 miles.
- Charging would need to be provided at Swansea.
- GWR could still run their one tpd service to Carmarthen.
It looks like both train operating companies could be able to do as Lumo does and advertise all electric services.
What Could Be The Maxmum Range Of A Hitachi Train On Batteries?
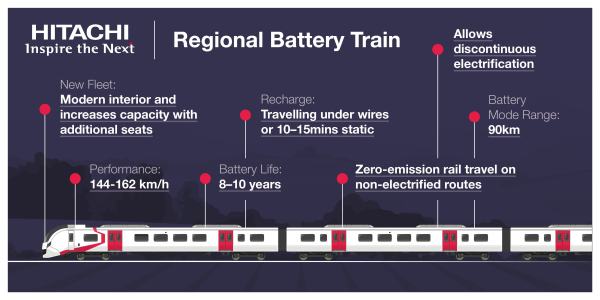
This Hitachi infographic shows the Hitachi Regional Battery Train.
Consider.
- It has a battery range of 90 km or 56 miles on the single battery.
- I would expect that by a regional train, Hitachi mean a five car Class 800 or 802 train, like those that go to Cheltenham, Lincoln or Middlesbrough.
- A five-car Hitachi Regional Battery Train would have a battery that could contain power equivalent to 280 car-miles.
- Five-car Class 800 or 802 trains have three engine positions.
- These Hitachi trains have a very sophisticated control system, which I wrote about in Do Class 800/801/802 Trains Use Batteries For Regenerative Braking?
I believe the engineers at Hyperdrive Innovation have designed the battery-packs that replace the diesel engines as simulations of the diesel engines, so they can be a direct replacement.
This would mean that battery-packs could be additive, so the following could apply to a five-car train.
- Two battery packs could have a range of 112 miles.
- Three battery packs could have a range of 168 miles.
GWR generally runs pairs of five-car trains to Swansea, which would be 90 miles without electrification.
If five-car trains with two battery packs, could be given a range of 112 miles, GWR could run an electric service to Swansea.
They could also run to Carmarthen, if Grand Union Trains would share the charger.
What ranges could be possible with nine-car trains, if one battery pack is good for 280 car-miles?
- One battery-pack, gives a range of 280/9 = 31 miles
- Two battery-packs, give a range of 2*280/9 = 62 miles
- Three battery-packs, give a range of 3*280/9 = 93 miles
- Four battery-packs, give a range of 4*280/9 = 124 miles
- Five battery-packs, give a range of 5*280/9 = 155 miles
- Six battery-packs, give a range of 6*280/9 = 187 miles
- Seven battery-packs, give a range of 7*280/9 = 218 miles
Note.
- I have rounded figures to the nearest mile.
- There are five cars with diesel engines in a nine-car train, which are in cars 2,3,5, 7 and 8.
- Diesel engines are also placed under the driver cars in five-car Class 810 trains.
- For the previous two reasons, I feel that the maximum numbers of diesel engines in a nine-car train could be a maximum of seven.
- I have therefor assumed a maximum of seven battery packs.
These distances seem sensational, but when you consider that Stradler’s Flirt Akku has demonstrated a battery range of 243 kilometres or 150 miles, I don’t think they are out of order.
But, if they are correct, then the ramifications are enormous.
- Large numbers of routes could become electric without any infrastructure works.
- Grand Union Trains would be able to run to Carmarthen and back without a charger at Carmarthen.
- GWR would be able to run to Swansea and back without a charger at Swansea.
Prudence may mean strategic chargers are installed.
Rrenewable Energy Developments In South West Wales
In Enter The Dragon, I talked about renewable energy developments in South West Wales.
I used information from this article on the Engineer, which is entitled Unlocking The Renewables Potential Of The Celtic Sea.
The article on the Engineer finishes with this conclusion.
For now, Wales may be lagging slightly behind its Celtic cousin to the north, but if the true potential of the Celtic Sea can be unleashed – FLOW, tidal stream, lagoon and wave – it looks set to play an even more prominent role in the net zero pursuit.
The Red Dragon is entering the battle to replace Vlad the Mad’s tainted energy.
South West Wales could see a massive renewable energy boom.
Grand Union Trains will increase the capacity to bring in more workers to support the developments from South Wales and Bristol.