Gwynt Glas And South Wales Ports Combine Strength In Preparation For Multi-Billion Floating Wind Industry
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from the Gwynt Glas wind farm.
The news item starts with a spectacular image of a port, that is assembling floating wind turbines and these three paragraphs.
Gwynt Glas Offshore Wind Farm has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the UK’s largest port operator, Associated British Ports, and Wales’ largest energy port, the Port of Milford Haven, to ready the ports for the future needs of floating offshore wind in the Celtic Sea.
Gwynt Glas is a joint venture partnership between EDF Renewables UK and DP Energy. The proposed floating offshore wind farm would generate 1GW of low carbon green energy in the Celtic Sea.
Under the MoU, information and industry knowledge will be shared to investigate the potential opportunities for manufacture, assembly, load-out and servicing for the Gwynt Glas project from the key South Wales Ports of Port Talbot and Milford Haven. This collaborative approach demonstrates a major commitment to supporting economic growth, investment and maximising social value in the region.
UK Port Unveils GBP 150 Million Offshore Wind Expansion Plan
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The Port of Tyne, located in the northeast of England, has unveiled its plans to add 400 metres of deep-water quayside to support offshore renewables, clean energy, and advanced manufacturing.
These two paragraphs add details.
The Port of Tyne is investing GBP 150 million (approximately EUR 173 million) to transform 230 acres into the Tyne Clean Energy Park, a move that could create up to 12,000 jobs, deliver GBP 5.6 billion (about EUR 6.5 billion) to the economy, and establish the North East as a hub for the UK’s green energy revolution, according to an independent study by WSP.
The plan for Tyne Clean Energy Park includes a kilometre of both new and redeveloped deep-water, heavy-lift quay to facilitate the use of a 230-acre footprint located within an Industrial Strategy Zone.
The Wikipedia entry for the Port of Tyne has this opening paragraph.
The Port of Tyne comprises the commercial docks on and around the River Tyne in Tyne and Wear in the northeast of England.
This Google Map shows the River Tyne Through Newcastle.
I estimate that this map is around twenty kilometres from East to West.
This news item from the Port of Tyne is entitled Port of Tyne Unviels 230 Acre Green Development Terminal and gives full details.
This summary is given.
The Port of Tyne is investing £150 million to transform 230 acres into the Tyne Clean Energy Park, adding 400 metres of deep-water quayside to support offshore renewables, clean energy, and advanced manufacturing. The redevelopment could create up to 12,000 jobs, deliver £5.6 billion to the economy, and establish the North East as a hub for the UK’s green energy revolution.
This is not a small development.
In future I shall tag developments like this with a tag of UK Port Development.
.
Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
A major port is set to expand to prepare for construction work linked to several national infrastructure projects.
These first two paragraphs, which give more details.
Peel Ports said it would invest between £50m and £60m in Great Yarmouth’s Outer Harbour by developing the southern terminal, creating a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
Port director Richard Goffin said the construction work, which is set to begin in 2026, would “complete” the port as laid out in a business case in the early 2000s.
This image from Peel Ports Group shows how the Port of Great Yarmouth will look after the the proposed development.
And this Google Map shows the port as it is today.
Note.
- The large triple shed, with the cross-wise middle section can be picked out in both the image and the map.
- The label by the shed says Origin Fertilisers, so I suspect the three objects on the quayside, which are visible in both the image and the map could be conveyors for loading and unloading ships with fertiliser.
- The two breakwaters are visible in both the image and the map.
It looks like the development would mainly involve filling in the Southern part of the current harbour.
With only a quick look and scant details, it looks to me, that it is a development that could be easily realised.
I have some thoughts.
Rail Access To The Port
There is no rail access to the port and I couldn’t see how it could be provided, without demolishing half of the town.
But there are carriage sidings at Great Yarmouth station, which are described in this Wikipedia entry like this.
New sidings were provided at the western end of the station to cope with the additional services operating into the station, following the closure of the M&GN system. It is a crescent-shaped site between the A47 road and Wherryman’s Way at the northernmost point of the River Yare, about 1⁄4 mi (400 m) north-west of the station. It had fallen out of use in the 1980s when Norwich Crown Point depot was built.
In 2010, the unused sidings were purchased by Great Yarmouth Borough Council; they were intended for use as a freight terminal, despite the lack of rail connection to the town’s port. It was hoped that 10,000 tonnes of sugar cane per week would be carried from Yarmouth to Cantley. The need to use a lorry shuttle between the docks and the rail yard, along with a £3.2 million quote for replacing the sidings at Cantley, saw the plan dropped.[19]
In May 2020, Eastern Rail Services commenced a lease with Norfolk County Council and Network Rail for Yarmouth Vauxhall sidings. Managing director James Steward said the siding “matched ERS’s requirement for an East Anglian site to base its rolling stock.” Following extensive de-vegetation works, Direct Rail Services 37402 became the first locomotive in 19 years to run into the sidings on 26 May 2020, followed the next day by it delivering five former Greater Anglia Mark 3 coaches for storage. On 6 July 2020, ERS was authorised a licence exemption permitting them to operate trains within the site
The Port of Great Yarmouth appears to be keen to do its part in the construction of Sizewell C. Could components for the power station, be brought into the port through the new roll-on/roll-off berth and then transferred to rail in the former carriage sidings?
This 3D Google Map shows the carriage sidings.
Most of the rolling stock appears to be retired Mark 2 and M3 coaches.
Road Access To The Port
This Google Map shows Great Yarmouth and the Port and roads in the area.
Note.
- The red arrow indicates Great Yarmouth station.
- The Port of Great Yarmouth is in the South-East corner of the map.
- The A 47 runs down the West side of the town.
- The River Yare runs from the railway station to the sea, just below the port.
There is a road on the East bank of the River Yare, that connects to the A 47 and could easily connect to a rail cargo terminal to the North-West of the station in the derelict carriage sidings.
I can certainly see Nimbies not liking the new roll-on/roll-off ferry creating traffic in the town.
The Construction Of Sizewell C
Sizewell C is very similar to Hinckley Point C and this extract from the Wikipedia entry for Hinckley Point C describes some of that power station’s construction.
In March 2017, EDF, after the Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) gave approval to start building, the building of the first parts of the plant proper began with a network of tunnels to carry cabling and piping. Work was also under way on a jetty to land building materials, a seawall, and accommodation blocks.
In January 2018, EDF said that they were on track to start generating electricity by 2025 and that they planned to start constructing above-ground structures for the power station by June 2019.
The approximate 2,000 cubic metres (71,000 cu ft) concrete pour for the first reactor started on 11 December 2018. It was completed over a 30-hour period, creating the first part of the unit one 4,500 tonne base, a platform 3.2 metres (10 ft 6 in) thick. The reactor building will be built on the (to be completed) platform. This construction start marks the first new reactor build in the UK after a 30-year break, and the second PWR in the UK, after Sizewell B.
Completion of the base for the first reactor, the final 8,954 cubic metres (316,200 cu ft) of concrete, was achieved in June 2019. Completion of the base for the second reactor, 8,991 cubic metres (317,500 cu ft) of concrete, was achieved in June 2020.
Construction utilises the world’s largest crane, the Sarens SGC-250 double ring crane, which is responsible for lifting Hinkley Point C’s heaviest components. More than 600 heavy fabrications, including the five major parts of each unit’s steel containment liner and dome, are positioned by the SGC-250. The crane, named Big Carl, was delivered in modular form, consisting of over 400 deliveries.
In February 2023, the first nuclear reactor pressure vessel was delivered to site via the Bristol Channel Hinkley-dedicated wharf at Combwich. The pressure vessel was built in France in 2022 by Framatome.
In May 2024, the first of the 520 tonne steam generators was delivered to site in the same manner as the reactor pressure vessel.
Note.
- A good proportion of the power station and the materials to build it were brought in by sea.
- The size of everything is huge.
- Big Carl seems to make appearances in all big projects.
- According to the BBC, Peel Ports are spending £60million on a new roll-on/roll-off terminal, 350 metres of quay and ten hectares of high quality storage space.
I wouldn’t be surprised, if they have the contract for Sizewell C’s logistics, that Peel Ports will be laughing all the way to the bank.
If nothing else, after Sizewell C is completed, they will have a high-class port facility at the end of the A 47 from Birmingham, Leicester, Peterborough and Norwich, which could open up possible ferry routes to Europe.
Between Great Yarmouth And Sizewell
If the components come in to Great Yarmouth on trailers on the RORO ferries from France, they could be taken to Sizewell on the A 12 road.
Smaller components may be taken by road, but I wouldn’t rule out a transfer to rail in the carriage sidings at Great Yarmough, as I indicated earlier.
Permission Granted For Ayrshire Renewables Hub
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Scottish Construction Now.
This is the sub-heading.
Planning consent has been granted for a £150 million upgrade to an Ayrshire marine yard, paving the way for increased offshore wind power off the UK’s west coast.
These are the first three paragraphs.
Peel Ports Clydeport has secured permission for the complete redevelopment of the Hunterston marine yard as it prepares the site for major renewables infrastructure. The redevelopment works – which are expected to start in early 2025 and last for around two years – will include substantial upgrades to the marine yard, including infilling the current dry-dock basin and the creation of a new quay wall.
Highview Power recently announced it is to construct the world’s largest Liquid Air Energy Storage (LAES) facility at Hunterston, the latest in a string of renewables projects that are either underway, or in the pipeline, at the site.
The overall redevelopment of Hunterston is expected to attract £3.5 billion in inward investment and create over 5,000 jobs.
Note.
- The Highview Power battery will be 200 MW/3.25 GWh.
- There is also a 400 MW/400 MWh BESS being built at Hunterston.
- The 2 GW MacHairWind project is planned off the coast of Islay.
- According to their web site, MacHairWind will export its first power in the early 2030s.
More renewable infrastructure will surely follow.
Two Ports Advance To Next Stage Of UK Gov Funding For Floating Wind
The title of this post, is the same as this article in Ground Engineering.
This is the sub-heading.
Port Talbot in Wales and Port of Cromarty Firth in Scotland have advanced to the next stage of a government funding scheme to develop port infrastructure that will facilitate floating offshore wind.
These three paragraphs introduce the developments.
The UK Government has agreed that the port expansion projects should progress to the next stage of its floating offshore wind manufacturing investment scheme (FLOWMIS) known as the primary list phase.
Up to £160M of grant funding will be allocated to certain investments in the floating offshore wind sector under the scheme.
The money will go towards funding the basic infrastructure necessary to support the assembly of floating offshore wind turbines. This includes the construction, replacement and upgrade of port infrastructure to accommodate large components such as towers and blades, as well as steel and concrete foundations and mooring cables required for floating offshore wind.
The article also says this about Port Talbot.
The Future Port Talbot project in south Wales would see the port transformed into a major hub for the manufacturing, assembly, and integration of floating offshore wind components for projects in the Celtic Sea.
Associated British Ports (ABP), which owns and operates the port, welcomed the government’s decision.
Note.
- Port Talbot will almost certainly use locally produced steel.
- There appears to be at least 4,832 MW of floating wind to be developed in the Celtic Sea in the next few years.
Port Talbot would be ideally placed to handle both English and Welsh coasts and waters in the Celtic Sea.
The article also says this about the Port of Cromarty Firth.
The Port of Cromarty Firth (PoCF) on the east coast of the Scottish Highlands will undergo a fifth phase of expansion work. This will develop the facilities and infrastructure necessary to enable the port to support offshore wind infrastructure projects off the coast of Scotland.
Over £50M has also been earmarked for the port’s expansion.
There appears to be at least 15,216 MW of floating wind to be developed in Scotland in the next few years.
Both ports seem to have welcomed the funding.
Adding the plans for Scotland and the Celtic Sea together gives a figure of just over 20 GW of floating wind to be developed in the next few years.
Conclusion
Surely, the award of funding for floating wind, is a good way to create a new industry and jobs in these two areas and also perform some sensible levelling-up.
I also suspect that spending £160 million to enable the construction of 20 GW of floating wind farm is a good return on the investment.
ABP To Explore Opportunities For Offshore Wind Port In Scotland
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Associated British Ports (ABP) has signed an agreement to investigate an area for the development of infrastructure to support offshore wind manufacturing, assembly, and marshalling and green energy on the Cromarty Firth in Scotland, within the Inverness Cromarty Firth Green Freeport.
This first paragraph gives a bit more information including the possible location.
The area, located within the proposed Nigg and Pitcalzean area of the Green Freeport, could support both fixed-bottom and floating offshore wind projects and play a major role in the development of current and future ScotWind leasing rounds, said ABP.
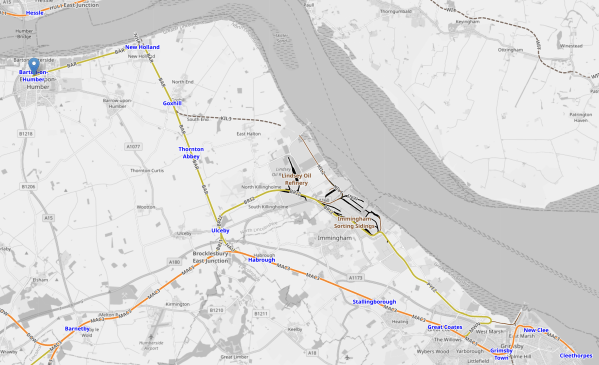
This Google Map shows the location of the Port of Nigg.
Note.
- The Moray Firth with Inverness at its Southern end is the large body of water in the centre of the Southern half of the map.
- The Port of Nigg is on Cromarty Firth and marked by a red arrow.
- Nigg and Pitcalzean are to the North of the port.
This second Google Map shows an enlarged view of the port.
Note.
- Pitcalzean House is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The Port of Nigg is in the centre of the map.
- The water to the West and South of the port is Cromarty Firth.
- The yellow structures in the port are fixed-bottom foundations for wind farms.
Inverness & Cromarty Firth Green Freeport has a web site.
A Quote From Henrik Pedersen
Henrik Pedersen is CEO of ABP and the article quotes him as saying this.
We’re excited to explore the potential of Nigg, applying our experience across the UK, including at our Ports of Grimsby, Hull, Lowestoft and Barrow which already host significant offshore wind activity and at Port Talbot, where we are developing a Floating Offshore Wind port project. We look forward to working with key local partners, the community, and public sector stakeholders.
The article also has this final paragraph.
The Floating Offshore Wind Taskforce’s recently published “Industry Roadmap 2040”, estimated that planed floating offshore wind projects in Scottish waters alone will require three to five integration ports.
There is certainly going to be a significant number of ports, that will be supporting offshore wind activity.
UK Ports Need GBP 4 Billion Investment To Help Unleash Floating Offshore Wind Industry – Report
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
A new report by the Floating Wind Offshore Wind Taskforce says up to eleven ports around the UK will need to be transformed as fast as possible into new industrial hubs to enable the roll-out of floating offshore wind at scale
This is the first paragraph.
The report contains a series of recommendations which could see 34 GW of floating wind installed in UK waters by 2040 if the country’s government takes swift and decisive action. At present Ministers have set a target of 5 GW by 2030.
What a lorra lorra lot of wind! (With apologies to Cilla!)
Cromarty Firth And Forth To Host First Green Freeports
The title of this post, is the same as that, of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Sites at Cromarty Firth and the Forth have been selected to host Scotland’s first green freeports.
These three paragraphs outline the deal.
The winning bids were revealed in a joint announcement by the UK and Scottish governments.
The special economic zones north of the border are being created under a scheme agreed by the two governments.
The successful applicants will be able to offer tax incentives and lower tariffs in the zones.
At least it seems that Westminster and Holyrood are in agreement.
What Is A Green Freeport?
This article on the BBC, is entitled Freeports: What Are They And Will They Help The Economy?.
It is a good summary of freeports in the UK.
This press release from the UK Government is entitled Joint Cooperation To Deliver Two New Green Freeports In Firth Of Forth And Inverness And Cromarty Firth, contains this statement from Deputy Scottish First Minister; John Swinney.
This is a milestone achievement in the process to deliver Green Freeports for Scotland. Inverness and Cromarty Firth Green Freeport and Forth Green Freeport will support businesses to create high-quality, well-paid new jobs, promote growth and regeneration, and make a significant contribution to achieving our net zero ambitions.
A rigorous joint selection process has been followed. The successful applicants showed a strong determination to embed fair work practices, including payment of the Real Living Wage, and to enshrine net zero initiatives in their work.
We look forward to working closely with them to ensure they deliver maximum positive impact and become operational as soon as possible. We will also work with the unsuccessful bidders to consider how they can build on the plans set out in their bids to deliver jobs and growth in their regions outside the Green Freeports programme.
Scotland has a rich history of innovation, trade and manufacturing and as we look to seize the many opportunities achieving net zero offers, the creation of these internationally competitive clusters of excellence will help us to create new green jobs, deliver a just transition and support our economic transformation.
This statement may be a lot more about aspiration, than hard directions, but having in my lifetime seen Scotland rally round their newborn oil and gas industry, I am very hopeful that the concept of a green freeport will be successful.
Unless anyone can correct me, I do feel that Scotland’s two green freeports are a world first.
Forth Green Freeport
This is the home page of the Forth Green Freeport.
- It talks about being Central to Scotland’s green ambitions.
- Places shown on a map of the freeport are Burntisland, Edinburgh Airport, Grangemouth, Leith and Rosyth.
- The freeport has a long list of partners.
It appears to be a well-backed ambitious plan.
Cromarty Green Freeport
Opportunity Cromarty Firth are leading the development of the Cromarty Green Freeport and they have this web site.
This is the sub-heading on the home page.
Opportunity Cromarty Firth (OCF), is a consortium leading a bid in the current competition for Green Freeport status, which could “revolutionise” the Highland economy and stimulate major new manufacturing activity locally and elsewhere in Scotland and the UK.
It is following by these two paragraphs.
The consortium is backed by port owners Port of Cromarty Firth, Global Energy Group, Port of Inverness and The Highland Council alongside a dozen regional businesses, public sector organisations and academic bodies.
OCF believes the creation of such a zone on the Firth would maximise local and Scotland-wide benefits from a pipeline of renewable energy projects placing the Highlands at the heart of the drive towards net-zero and create tens of thousands of jobs.
There would appear to be a lot of aspiration and a good list of partners, but the plans for the freeport don’t seem to be as advanced as those for the Forth Green Freeport.
No Shortage Of Electricity
One thing, that will not be a problem for either freeport, is going to be a poor electricity supply, as both the Forth Estuary and Cromarty Form will be the home to several gigawatts of offshore wind.
In addition, it is likely that the wind farms in the Cromarty Firth will be backed by large amounts of pumped storage hydroelectricity in the Great Glen.
Wind Farms Close To The Cromarty Firth Green Freeport
These wind farms are currently close to the Cromarty Firth Green Freeport.
- Beatrice – 10 MW – Operational
- Beatrice Extension – 588 MW – Operational
- Moray East – 950 MW – Operational
- Moray West – 862 MW – Operational in 2025
- Caldeonia – 2000 MW – Operational in 2030
This is a grand total of 4410 MW. Hinckley Point C will be 3260 MW.
Wind Farms Close To The Forth Green Freeport
These wind farms are currently close to the Forth Green Freeport.
- Seagreen – 862 MW – Operational in 2023
- Inch Cape – 1080 MW – Operational in 2026/27
- Neart Na Gaoithe – 450 MW – Operational in 2024
- Forthwind – 12 MW – Operational in 2023/24
- Berwick Bank 4100 MW – Operational in 2030
This is a grand total of 6504 MW.
North of Scotland Hydrogen Programme
One plan that seems to be being developed by OCF is the North of Scotland Hydrogen Programme, which has this web page on the OCF web site.
These paragraphs outline the plan.
The North of Scotland Hydrogen Programme was established through Opportunity Cromarty Firth and brings together key partners who share ambitions for the region’s renewable, low carbon future. The programme aims to develop a state-of-the-art hub in the Cromarty Firth to produce, store and distribute green hydrogen at scale to the region, Scotland, other parts of the UK and Europe.
The Highlands will be at the centre of future large-scale production of green hydrogen if the Cromarty Firth wins Green Freeport status.
ScottishPower and Storegga have expressed their support for the Green Freeport bid by Opportunity Cromarty Firth (OCF), which could attract more than £1 billion investment to the area and create thousands of jobs and local supply chain opportunities during construction.The joint developers recently announced plans to develop one of the UK’s largest green hydrogen electrolyser plants on the Cromarty Firth. The project’s initial phase would see the facility produce up to 30 megawatts (MW) of green hydrogen to be used in heating processes in nearby whisky distilleries.
Achieving Green Freeport status would have the potential to bring forward significant investment in a larger-scale plant by up to 10 years and would place the Highlands firmly at the centre of future large-scale production of green hydrogen, because of the region’s enormous growth potential of offshore wind, which is critical to the industry’s development.
Note.
- The hydrogen from the first phase of the electrolyser will be used in the whisky industry.
- Gradually, hydrogen use will widen throughout the region.
- I suspect that as hydrogen production grows, it will be exported from the freeport.
This map from the web site shows all the energy flows.
Note.
- Aquaculture is a use for the oxygen produced by the electrolyser.
- Everybody is promoting spaceports. Both hydrogen and oxygen can be used as rocket fuel.
- Hydrogen or electricity is shown powering all sorts of transport, including buses, a cruise ship, trains and trucks.
It certainly is a comprehensive plan.
Hydrogen At The Forth Green Freeport
Hydrogen is mentioned on the About page of the Forth Green Freeport web site in this general statement.
Investments will stimulate growth in trade, providing expanded logistics and trade capacity for existing and emerging industries including advanced modular systems, biofuels, hydrogen and carbon capture and storage, as well as support additional R&D capability and green incubator space to drive SME and start-up business growth.
But as INEOS are a partner, I would expect some hydrogen production from all that green offshore electricity.
Holyhead Hydrogen Hub Planned For Wales
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on H2 View.
This is the introductory paragraph.
Plans for a new hydrogen production plant, refuelling and distribution hub have been unveiled for Holyhead, North Wales.
Some other points from the article.
- Unsurprisingly, it will be called the Holyhead Hydrogen Hub.
- Holyhead is the second largest roll-on, roll-off port in the UK.
- There is plenty of potential for renewable energy in the area.
- It will support the port and large scale movements of HGVs.
- There is plenty of potential for renewable energy in the area.
- The hydrogen in future could support trains, ships, public transport and other uses.
In the last year, I’ve read about hydrogen hubs in ports, including Portsmouth and Antwerp, so Holyhead is just following a trend.