A First Look At SEGRO Logistics Park Radlett – 26th February 2026
The site of SEGRO Logistics Park Radlett can really only be seen from a train on the Midland Main Line going between Radlett and St Albans City stations.
I took these pictures from a Thameslink train going North.
I took these pictures from a Thameslink train going South.
Note.
- Most of the work at present is site clearance and landscaping.
- The Midland Main Line crossed over the M25 and goes under A414.
- Veralum Golf Course is on your left as you approach St Albans.
The Logistics Park is going to cover a large area.
I shall be following this project regularly.
West Ealing Station – 1st February 2026
Because of the confusion of WordPress yesterday, I had to go back to West Ealing station to take more pictures today.
These are the pictures that I took.
These are some of my thoughts.
The High-Density Transport-Hub Cluster
This seems to be coming on with several blocks now visible and the Waitrose site to be developed.
There also seems to be some useful shops, which include a pleasant Italian cafe on the North side of the rail lines.
The Fast-Charge System Contacts
Note.
- These are shown in Pictures 16-17!
- There are two contacts, which are in yellow for safety reasons.
- I wonder how many can be installed?
- Is it one per battery and one battery per car?
I suspect by duplicating cables and putting them underneath and between the tracks, the Fast-Charge system could handle a train like a Class 800 train.
Will Other High-Density Transport-Hub Clusters Be Developed Along The Elizabeth Line?
This is one for the nimbys, planners, politicians and residents, but I don’t see why some councils will try.
UK, French, And Irish Ports Join Hands In Global Floating Wind Collaboration
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s Associated British Ports (ABP) has teamed up with France’s BrestPort and Ireland’s Shannon Foynes Port to establish the Global Floating Offshore Wind Ports Alliance (FLOW Ports Alliance) to help bring together major floating offshore wind ports across the world and unlock the technology’s full potential.
These first two paragraphs add more detail.
The FLOW Ports Alliance aims to recruit ports in Europe to collaborate on FLOW port design, standardisation, and best operational practices.
It plans to strengthen and accelerate compliant knowledge and experience exchange between ports, share best practices as they emerge through demonstration projects, and share innovations to the benefit of the global FLOW network.
Surely, a global network of ports that can handle construction, operation and maintenance of a range of floating wind platforms, is an excellent idea.
Canal Water To Heat Some Of Liverpool’s Most Famous Buildings In Hi-Tech Carbon-Cutting Scheme
The title of this post is the same as that of this press release from Liverpool City Region.
These five bullet-points act as subheadings.
- Energy generated from Leeds and Liverpool canal by one of the UK’s largest water source heat pumps
- Announcement comes as Mersey Heat Energy Centre officially opens
- Scheme to connect Georges Dock, Cunard and the Museum of Liverpool buildings to Mersey Heat Network
- Joint project between Combined Authority, Liverpool City Council and National Museums Liverpool
- Key part of Combined Authority plan to reach net zero by 2035
These introductory paragraphs add more detail.
Three major public buildings on Liverpool’s waterfront are to slash carbon emissions by joining a heat network driven by energy from canal water.
Under the plan, an extended pipeline will connect Georges Dock building, the Cunard building, and the Museum of Liverpool, part of National Museums Liverpool (NML), to the Mersey Heat network.
The newly opened Mersey Heat Energy Centre is already supplying the Liverpool Waters site, the Titanic Hotel and the Tobacco Warehouse apartments.
It uses one of the UK’s largest water source heat pumps to extract energy from the Leeds and Liverpool Canal to power a network of heating pipes.
The project is the latest in the Liverpool City Region’s five-year carbon action plan and journey to reach net zero. The Combined Authority has recently secured an additional £35m to decarbonise dozens of other public buildings from the Department of Energy Security and Net Zero.
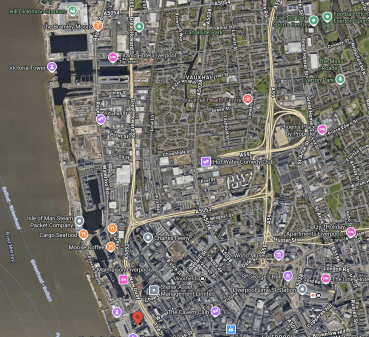
This map of the Liverpool Waterfront shows the canal and some of the buildings mentioned.
Note.
- In the top-left corner is Everton’s new Hill-Dickenson Stadium, which at the time of this map was under construction.
- The pink arrow to its right indicates the Titantic Hotel.
- The Leeds and Liverpool canal passes on the South side of the hotel.
- On the other bank of the canal is the Tobacco Warehouse.
- The canal goes East and then turns North before going all the way to Leeds. The Wikipedia entry gives full details of the canal.
- From the Titanic Hotel, the Leeds and Liverpool Canal also turns South and boats can go along Liverpool’s famous Waterfront to Canning Dock, in front of the Tate Liverpool.
- The red arrow marks the Liver Building.
- Georges Dock building, the Cunard building, and the Museum of Liverpool are just to the South the Liver Building.
- To the East of the Liver building, there is Liverpool City Centre, with beyond it Liverpool Lime Street station, with another collection of important buildings including St. George’s Hall, the Picton Library, World Museum and the Walker Art Gallery.
The Combined Authority will not have a shortage of buildings to decarbonise with the £35m from the Department of Energy Security and Net Zero.
These are my thoughts.
What Is A Water Source Heat Pump?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
A water source heat pump (WSHP) is a highly efficient, low-carbon renewable energy system that extracts heat from a nearby water source like a lake, river, or canal to provide heating and hot water for a building, and can also be used for cooling. It works by using electricity to transfer this thermal energy into the building’s heating system, offering a more efficient alternative to traditional boilers and reducing energy bills. There are two main types: closed-loop systems, which circulate a fluid through pipes submerged in the water, and open-loop systems, which directly pump and then discharge the water.
Is Mersey Heat Energy Centre A Closed Or Open-Loop Water Source Heat Pump?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The Mersey Energy Heat Centre uses an open-loop water source heat pump system. It abstracts water from the Leeds and Liverpool Canal, extracts heat from it, and then returns the water back to the dock system.
As the Leeds and Liverpool Canal is 127 miles long, and there appears from the map to be a lot of water in the docks at the Liverpool end, I would expect that Liverpool will have more than enough water to extract heat from.
Where Exactly Is The Mersey Heat Energy Centre?
In this article on Place North West, which is entitled Work Begins On Peel’s Mersey Heat Energy Centre, has this image, which is labelled as the Mersey Heat Energy Centre.
Note the large building in the foreground with the circular objects on the roof. Could these be fans or vents?
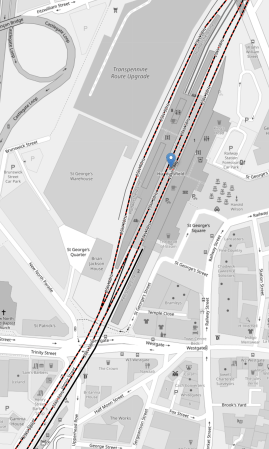
This Google Map shows the area.
Note.
- The two docks at the top of the map can be picked out in the image.
- The main breakwater on the left, which is marked Isle of Man Steam Packet Company, looks very similar to the one shown in the image.
- The bridge between the two docks on the left appears to be the same in both map and image.
I am fairly sure, that the large building on the breakwater with the three circles on the roof, is the Mersey Heat Energy Centre.
It certainly looks to be a building, that could provide a substantial amount of heat and power .
What Is The Output Of The Mersey Heat And Energy Centre?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The Mersey Heat and Energy Centre produces low-carbon heat for up to 6,700 homes and 1.3 million square feet of commercial space, aiming to deliver around 20GWh of heat per year. The project is also planned to expand to supply around 45GWh annually. This heat is delivered to buildings for their heating and hot water needs through the Mersey Heat network.
This article on Place North West, also has this similar answer.
Led by district heat network specialist Ener-Vate, the Mersey Heat Energy Centre will feature two 3MW water source heat pumps that would work on an ‘open loop’ system to take heat from water from the Leeds-Liverpool canal. This heat would be used to warm surrounding homes and businesses within six kilometres.
Plans form the first phase of Peel NRE’s Mersey Heat network. The initial project could supply 20GWh of heat every year, with planning permission secured to expand to supply around 45GWh – the equivalent of supplying heating and hot water to 17,000 homes.
It looks like we’re getting similar answers from different sources.
Does the Merseyside Area Have Enough Green Electricity To Power A Large Water Source Heat Pump?
In Could Liverpool Develop A Massive Zero-Carbon Data Centre?, I calculated the operational and planned offshore wind power in Liverpool Bay and got these results.
- 2509 MW has been commissioned.
- 3980 MW is being planned.
That is a total of 6489 MW or about twice the output of Hinckley Point C nuclear power station.
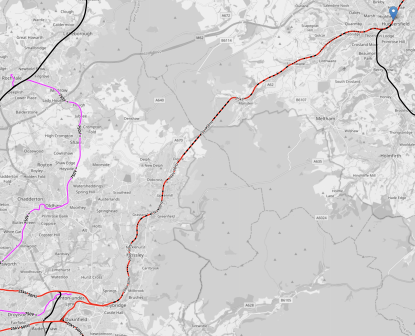
This map shows the existing wind farms in the sea between Liverpool, Lancashire and the Isle of Man.
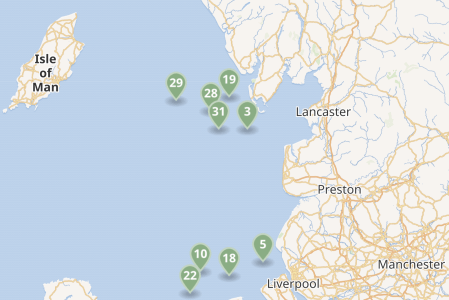
Note.
- Each green arrow is a wind farm.
- There is the 2452 MW Heysham nuclear power complex near Lancaster.
- The Western HVDC Link is a 2250 MW connection between Hunterston in Western Scotland near Glasgow and Connah’s Quay on the Wirral.
- I also suspect more space in Liverpool Bay could be developed with wind farms.
Spinal Tap turned the power up to 11, Liverpool, being Liverpool, they have enough power to go to at least sixteen.
Will Merseyside Have Lots Of Data Centres?
Consider.
- It has the power.
- It has the water.
- The locals speak a form of English.
- Merseyside will be two hours from London by train.
- There are two Premier League football teams.
- The golf courses are good.
- It is a city that is famous all over the world.
I am sure the number of data centres will grow.
Historic Church Tower Suspended On Stilts To Make Way For London Skyscraper
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
The remaining part of the 700-year-old All Hallows Staining, off Fenchurch Street, will be the centrepiece of the public square below Axa’s £1 billion office
These three paragraphs add more details.
A700-year-old church tower is being suspended on 45ft stilts while developers clear the ground beneath to make way for the City of London’s newest skyscraper.
The tower, which is all that remains of All Hallows Staining close to Fenchurch Street station, is being preserved and will be the centrepiece of the public square at the base of 50 Fenchurch Street — the £1 billion office tower being built by the investment arm of Axa, the French insurer.
More than 125,000 tonnes of earth has been cleared from underneath and around the church — which survived the Great Fire of London in 1666 — into which the foundations will be laid and a basement level built.
The Wikipedia entry for All Hallows Staining, starts with this paragraph.
All Hallows Staining was a Church of England church located at the junction of Mark Lane and Dunster Court in the north-eastern corner of Langbourn ward in the City of London, England, close to Fenchurch Street railway station. All that remains of the church is the tower, built around AD 1320 as part of the second church on the site. Use of the grounds around the church is the subject of the Allhallows Staining Church Act 2010 (c. v).
Note.
- The Wikipedia entry gives a lot of history and other details about the tower.
- It was named “Staining”, which means stone, to distinguish it from the other churches of All Hallows in the City of London, which were wooden.
- The old church survived the Great Fire of London in 1666 but collapsed five years later in 1671.
- The church appears to have been cheaply rebuilt in 1674.
- In 1870 the parish of All Hallows Staining was combined with that of St Olave Hart Street and All Hallows was demolished, leaving only the tower.
- All Hallows Staining seems to have survived World War Two, but St Olave Hart Street suffered serious damage.
- Between 1948 and 1954, when the restored St Olave’s was reopened, a prefabricated church stood on the site of All Hallows Staining. The tower of All Hallows Staining was used as the chancel of the temporary church.
- The remains of All Hallows Staining were designated a Grade I listed building on 4 January 1950.
The tower of All Hallows Staining seems to have a very strong survival instinct.
This web page gives more details of Fifty Fenchurch Street,
This morning, I went to take some pictures of the tower and the construction site.
Note.
- I walked around the site from the forecourt of Fenchurch Street station.
- The last three pictures were taken from the top deck of a Westbound 25 bus.
- There appears to be no accessible bar or roof-top from which you can look down on the site.
So for the present time, the 25 bus seems to give the best views.
This afternoon, I took a train to Fenchurch Street station and looked at the Eastern and Northern sides of the site.
Note.
- The first picture was taken through the upper windows of the front of Fenchurch Street station.
- I think I might have got a better view out of the window of Fenchurch Street station, if Great Socialist Railways had cleaned the windows.
- In pictures three to nine, the “Walkie-Talkie” towers over All Hallows Staining.
- Some pictures were better than those I took in the morning, as the truck had moved.
- The last picture shows the sign for the Garden at 120.
The area isn’t short of geometric shapes to photograph.
Gatwick Second Runway Plan Approved By Transport Secretary
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Transport Secretary Heidi Alexander has approved plans for a second runway at London Gatwick Airport, as the government looks for economic growth opportunities.
These four introductory paragraphs add some detail.
The £2.2bn privately-financed project involves in effect moving the current Northern Runway 12 metres to bring it into regular use, as well as other developments, including extending the size of terminals.
The airport says its plans will bring jobs and boost the local economy. But there has long been opposition from campaigners and groups worried about the impact on the surrounding area.
Gatwick currently handles about 280,000 flights a year. It says the plan would enable that number to rise to around 389,000 by the late 2030s.
A government source has described the plans as a “no-brainer for growth,” adding that “it is possible that planes could be taking off from a new full runway at Gatwick before the next general election.”
Over the last fifty years, I’ve been involved in many large projects, as I used to write project management software and at one period in the 1980s, half of all the world’s major projects, were being managed by the Artemis software, that I wrote in a Suffolk attic.
I am starting this post by asking Google AI, when Gatwick’s Northern Runway was built. This was the answer I received.
Gatwick’s Northern Runway was built in 1979 by widening an existing taxiway to serve as an emergency runway. While the main runway is known as 08R/26L, the standby or emergency runway is designated as 08L/26R and is located just to the north of the main runway.
Note.
- 08 means that the runway is aligned at 080 degrees, which is almost due East.
- 26 means that the runway is aligned at 260 degrees, which is almost due West.
- Normally, when landing and taking off at Gatwick, your aircraft will use the Southern runway, which points to the West or Runway 26L.
This Google Map shows the layout of the airport.

Note.
- The longer Southern 08R/26L runway.
- The shorter Northern 08L/26R runway.
- The station in the North-East corner of the map is Horley.
- The station to the East of the runways is Gatwick Airport station.
- Both stations are on the Brighton Main Line, which runs North-South past the Airport.
- As when it was built, the Airport envisaged that the Northern runway would be turned into a runway that would meet all standards, I doubt there will be any problems rebuilding the Northern Runway, the required twelve metres to the North.
It was a cunning plan, when it was executed in the late 1970s and worthy of Baldrick at his best.
I do wonder, if it had been developed using Artemis!
I’ve Just Glimpsed The Future Of Train Travel Across The North Of England And I Like It
Yesterday, I had an appointment at Liverpool Lime Street station at four o’clock, so as I hadn’t seen the works for the TransPennine Upgrade for some time, I decided to go the long way round with a change of train from LNER to TransPennine Express at Leeds.
These sections document my day.
London King’s Cross To Leeds In An InterCity 225
I took these pictures on the journey.
Note.
- The 31 InterCity 225 trains were built around 1990.
- They have a capacity of 535 seats, whereas the newer Hitachi Class 801 trains have a capacity of 611 seats. Both trains are nine cars with both First and Standard seats.
- There is more of a step-up and step-down when entering or leaving the trains, compared to the best of today’s trains.
- They are now being phased out in favour of ten new CAF tri-mode Class 897 trains, which should be entering service in 2027.
- No details are available of the seating capacity of these trains, but they could be between 650 and 700, so they could maximise capacity on any LNER route.
Yesterday, the InterCity 225 performed well, although the windows at the seat where I sat, were rather dirty.
Changing Trains At Leeds Station
I changed to TransPennine Exzpress at Leeds station.
- At least, Leeds station, is one of the few in the UK, with a ticket office behind the barrier. Reading station please note this.
- But, I did have to walk across the bridge from one side of the station to the other.
In the end, I caught the TransPennine Express with about thirty seconds to spare.
Between Leeds And Huddersfield Stations
I took these pictures between Leeds and Huddersfield stations.
Note.
- Dewsbury and Huddersfield stations is about eight miles and takes about eight minutes.
- It is virtually a continuous building site, where extra tracks are being inserted.
- Three stations are being rebuilt.
- Overhead electrification is being installed. But except for approaching Huddersfield, there’s not much to be seen.
- OpenRailwayMap gives the maximum speed between Dewsbury and Huddersfield stations as between 60-75 mph.
The ride on my Class 803 train was very quiet and smooth. Was it on battery power or was I sitting in a coach without a diesel engine underneath?
Huddersfield Station
I took these pictures at Huddersfield station.
Note.
- Huddersfield station is Grade I Listed.
- There is a pub in each wing.
- I had a beer in the West Wing.
- There are currently three main through platforms and three bay platforms.
- Extensive works, which will be part of the TransPennine Upgrade, will include electrification, a new roof, a new footbridge, and two extra through platforms.
Huddersfield station will be the jewel in the Costa del Yorkshire.
The Platforms At Huddersfield Station
This OpenRailwayMap shows the platforms in Huddersfield station.
Note.
- The red and black tracks are being electrified.
- Of the current platforms, Platforms 1, 4 and 8 will be electrified.
- The two bay platforms; 5 and 6, will be converted into through platforms.
- Platform 2 is the bay platform in the South-West corner of the map, that is used by the shuttle train from Sheffield.
I am sure extra platforms could be electrified as required, as there must be a good electrical connection at Huddersfield station.
A Tram-Train Service Between Huddersfield And Sheffield Stations
This OpenRailwayMap shows platform 2 at Huddersfield station.
Note.
- Platform 2 is the black track at the right of the two through tracks, that are being electrified.
- Platform 2 is a bay platform close to the Head of Steam pub.
- I estimate that the platform is about 90 metres long.
- I suspect Platform 2 could be lengthened if required.
- Sheffield’s Class 399 tram/trains are 37.2 metres long, so a pair should fit in Platform 2.
- The Class 398 tram/trains can run on battery power and climb hills in South Wales.
- Platform 2 at Huddersfield station could be electrified to charge the tram/trains.
- There could be a significant height difference between Huddersfield and Sheffield stations of about 40 metres, which could be used to charge tram/trains on the way down.
- I feel with some track improvements, that a four trains per hour (tph) service could be run.
The service would call at Meadowhall, Chapeltown, Elsecar, Wombwell, Barnsley, Dodworth, Silkstone Common, Penistone, Denby Dale, Shepley, Stocksmoor, Brockholes, Honley, Berry Brow and Lockwood
The Pair Of Cranes In Huddersfield Station
These can’t be missed in the pictures. But why two massive cranes?
With an old roof to be taken down and a new roof and a footbridge to be lifted into place, I believe Network Rail have decided to bring in two of largest mobile cranes available in the UK, so that all the lifting doesn’t delay the project.
Between Huddersfield And Stalybridge Stations
I took these pictures between Huddersfield and Stalybridge stations.
Note.
- The Class 802 train was running freely along a well-laid track.
- There are four stations between Huddersfield and Stalybridge; Slaithwaite, Marsden, Greenfield and Mossley(Manchester).
- The stations were in reasonable condition, but some needed new footbridges and a bit of refurbishment.
- There was virtually no signs of any foundations for electrification.
This map shows the route.
Note.
- The pink tracks are the Manchester Metrolink.
- The red tracks are electrified at 25 KVAC overhead.
- The red and black tracks are being electrified.
- Huddersfield is indicated by the blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map.
- Stalybridge station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The pink track in the South-West corner of the map is the Manchester Metrolink branch to Ashton-under-Lyme.
- The route between Huddersfield and Stalybridge is shown as it will will be fully electrified.
- Huddersfield and Stalybridge is 18 miles.
- There are three short tunnels between Huddersfield and Stalybridge.
I wonder, if it would be more affordable to not put up wires between Huddersfield and Stalybridge and use battery-electric passenger trains and hydrogen freight locomotives?
Stalybridge Station
I took these pictures at Stalybridge station.
The station is fully-electrified and has direct services to Huddersfield, Hull, Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester Piccadilly, Manchester Victoria, Newcastlle, Wigan and York.
Will Liverpool Lime Street And Newcastle Be Fully Electrified?
Consider.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Newcastle stations is 180.8 miles.
- Newcastle and Church Fenton stations is 91.4 miles and is fully-electrified.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Stalybridge stations is 39.4 miles and is fully-electrified.
This means that the gap between Church Fenton and Stalybridge stations is just fifty miles.
Real Time Trains indicate that the current Class 802 trains on the route run on diesel between Stalybridge and York stations, which is 60.8 miles.
- Changing power in Stalybridge and York stations means if anything goes wrong passengers can be easily rescued.
- From what I saw on Thursday, it looks like electrification will be completed between Neville Hill depot and Huddersfield.
I wouldn’t be surprised, if they just electrified to the West of Stalybridge and the East of Huddersfield.
That would mean that the 18 miles between Stalybridge and Huddersfield would be run on batteries.
- But it would also avoid electrifying three tunnels.
- How much disruption would be saved, by not electrifying the tunnels?
- Freight trains would use something like a bi-mode Class 99 locomotive, but it would only need a range of 18 miles on diesel.
I can also see improvised bi-mode locomotives being used like this combination of a Class 66 and Class 90 locomotives.
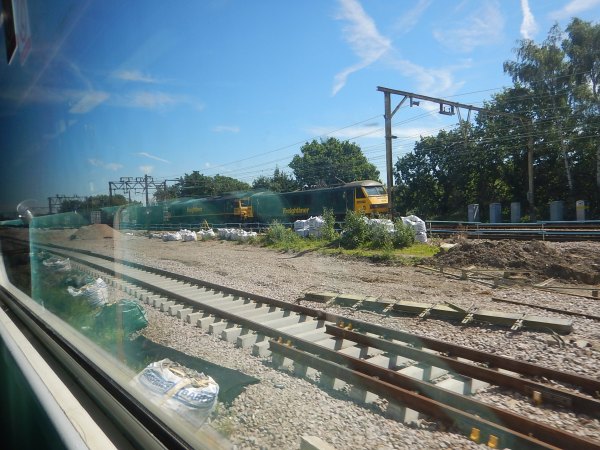

It was certainly doing its job, when I saw the combination at Shenfield.
The Power Of Buildings To Come
I took this picture on Bishopsgate in London.
It’s advertising the building, which is being built behind the hoarding called One Exchange Square.
Heads Of The Valleys Road Upgrade Officially Opens
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on BusinessNewsWales.
This is the sub-heading.
The final phase of the £2 billion Heads of the Valleys Road upgrade programme has officially opened.
These first two paragraphs add detail to the project.
The Welsh Government said it marked the completion of “one of the UK’s largest and most technically challenging road projects”.
The £1.4 billion Section 5&6 Dowlais to Hirwaun final phase links the Valleys, South and West Wales to the English Midlands and beyond, together with ports serving Irish and other European destinations. As well as improving the resilience of the South Wales trunk road network, the road provides a vital link across the top of the South Wales valleys for the Metro project improving links to the Cardiff and Swansea Bay City Regions, the Welsh Government said.
From the statistics of work done and the money involved, it would appear that a comprehensive upgrade has fixed a big gap in the UK’s motorway network in South Wales.
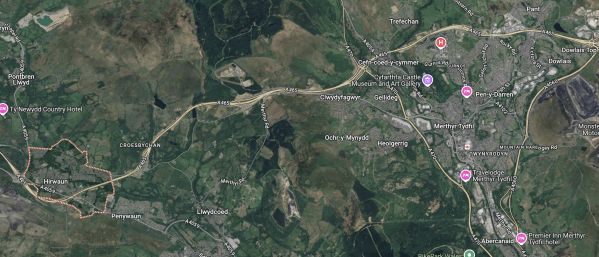
This Google Map shows the locations of Dowlais and Hirwaun.
Note.
- Dowlais is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Hirwaun is in the South-West corner of the map and is outlined in red.
- The Heads of the Valleys Road links Dowlais and Hirwaun.
- Going East from Dowlais leads to Abergavenny, Monmouth, Raglan and the English Midlands.
- Abergavenny has a station, but Monmouth and Raglan don’t!
- Abergavenny station has comprehensive services to stations as far apart as Cardiff, Crewe, Holyhead, Manchester Piccadilly, Swansea and Wrexham General.
Abergavenny station could eventually turn out to be a parkway station for the South Wales Valleys.
I can certainly understand, why Lumo wants to run a service to Hereford.
I also feel that the Welsh government and Transport for Wales would be in favour of the service.
- Three towns in Wales; Cwmbran, Pontypool and Abergavenny get a direct service to Bristol Parkway and London Paddington stations.
- Hereford already has an hourly connection to Birmingham New Street via Worcester and University.
- If a coach were to be provided between Bristol Parkway and Bristol Airport, this could make getting to Bristol Airport easier.
I can see further improvements to services, that terminate at Abergavenny.