Development Consent Decision On 3 GW Dogger Bank South Project Postponed
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK Secretary of State for Energy Security and Net Zero has set a new deadline for the decision on the Development Consent Order (DCO) for Dogger Bank South, a 3 GW offshore wind project developed by RWE, which the company owns in partnership with Masdar.
These two paragraphs add more detail to the project.
The statutory deadline for the decision on the project was 10 January 2026. This has now been moved to 30 April.
According to a statement from the Minister for Energy Consumers, Martin McCluskey, the extension will allow time to request further information that was not provided for consideration during the examination period and to give all interested parties the opportunity to review and comment on such information.
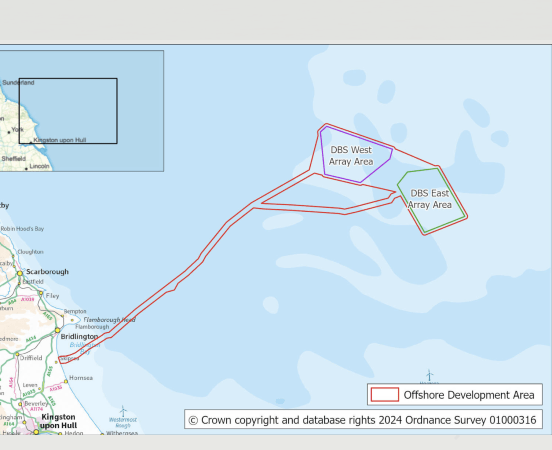
I clipped this map from the Dogger Bank South web site.
Note.
- Bridlington, Kingston-Upon-Hull and Scarborough can be picked out on the coast of East Yorkshire.
- The two wind farms and the route of the cables to the shore can be clearly seen.
I just wonder, whether the nature of the project is changing.
Consider.
- Three GW is a lot of power to move across Yorkshire to where it can be connected to the grid.
- In Consultation On Offshore Wind Reform: Hydrogen Sector Calls For Hybrid Connection Concepts And Warns Of Compensation Risks, German companies involved in the AquaVentus project are calling for more hydrogen to be produced offshore and piped to the shore.
- Could hydrogen produced in the Dogger Bank Wind farms be piped to the Northern end of the AquaVentus pipeline on the German sector of the Dogger Bank?
- A pipeline or cable could still bring energy to Yorkshire.
- The hydrogen could go to the hydrogen stores at Aldbrough and Rough.
- SSE and Centrica could play hydrogen-bankers to the Germans, as Germany is short of hydrogen storage.
- East Yorkshire is building two hydrogen power stations at Keadby and Ferrybridge.
- Support for the Dogger Bank South wind farms will probably be from RWE’S Grimsby hub.
Is this the Anglo-German co-operation, I talked about in UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties at work?
I can see benefits for this arrangement for the UK.
- Hydrogen production is offshore.
- A lot of the onshore employment is in the UK.
- There will be a hydrogen pipeline between Germany and the vast hydrogen storage of Humberside via the German Dogger Bank and Dogger Bank South wind farms.
- Will there be a hydrogen pipeline between the North of Scotland and Humberside via the AquaVentus pipeline?
- There will also be a substantial cash flow to the UK Treasury because of all the hydrogen production in UK waters.
RWE may also be able to use a standard hydrogen production platform in German and UK waters.
This is the sort of plan, that the money men will like.
Consultation On Offshore Wind Reform: Hydrogen Sector Calls For Hybrid Connection Concepts And Warns Of Compensation Risks
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the AquaVentus web site.
There is this statement on the home page.
Berlin, January 02 2026. In the context of the consultation launched by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWE) on the reform of the Wind Energy at Sea Act (WindSeeG), the hydrogen initiative AquaVentus is calling for clear legislative action to enable a cost-efficient and system-friendly development of offshore wind energy. At the heart of its position is the timely legal establishment of hybrid connection concepts, allowing offshore wind farms to be connected via both electricity cables and hydrogen pipelines.
Note.
- I’ve always felt that copying proven technologies from the offshore oil and gas industry is good practice.
- It may be easier to recycle infrastructure like pipelines, platforms and storage by creating the hydrogen offshore.
- In the UK, Centrica and SSE are already re-purposing natural gas storage for hydrogen.
It may feel safer to some for the hydrogen to be produced a distance offshore.
EDF Developing Offshore Wind-Powered Hydrogen Production Project In French EEZ
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
EDF Power Solutions has invited applications for a tender for Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) services and hazard studies as part of a project to develop an offshore hydrogen production station in France’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
This is the first paragraph.
The project, dubbed HYODE (HYdrogen Offshore DunkerquE), will produce green hydrogen by coupling offshore wind farms with an offshore electrolyser near Dunkirk, France, and is planned to also include storage and transport by ship to port, forming what EDF describes as an “innovative solution” to help scale green hydrogen production.
I asked Google AI, if there are any operational offshore hydrogen electrolysers and received this answer.
Yes, there are operational offshore electrolyser projects, though large-scale, dedicated offshore hydrogen platforms are still in development. The first operational offshore production on an existing gas platform is planned for late 2024 with the PosHYdon project. Additionally, a pilot project in the UK is testing the full integration of a hydrogen electrolyser onto an existing offshore wind turbine, with another project in the Netherlands installing an offshore hydrogen production and storage platform.
But, I did get this page on page on the Ramboll web site, which is entitled The Rise Of Offshore Hydrogen Production At Scale, which has this introductory paragraph.
The stage is set for producing green hydrogen from offshore wind and desalinated seawater. Building on existing and proven technology, offshore wind farms have the potential to become future production hubs for green hydrogen production at scale to meet increasing demand.
That sounds very promising, especially, if proven technology is borrowed from the offshore oil and gas industry.
It’s
The Monster That Is AquaVentus Is Waking Up
I have written about AquaVentus for some time, but inh the last couple of days, ten references have been found to the project by my Google Alert.
What Is AquaVentus?
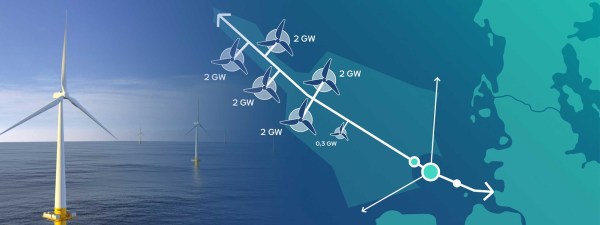
AquaVentus has a web page on the RWE web site, from where I clipped this image.
Note.
- The spine of AquaVentus is a pipeline called AquaDuctus to bring hydrogen to Germany.
- This image shows 10.3 GW of hydrogen will be generated and brought to near Wilhelmshaven in North-West Germany.
These two paragraphs introduce AquaVentus.
Hydrogen is considered the great hope of decarbonisation in all sectors that cannot be electrified, e.g. industrial manufacturing, aviation and shipping. Massive investments in the expansion of renewable energy are needed to enable carbon-neutral hydrogen production. After all, wind, solar and hydroelectric power form the basis of climate-friendly hydrogen.
In its quest for climate-friendly hydrogen production, the AquaVentus initiative has set its sights on one renewable energy generation technology: offshore wind. The initiative aims to use electricity from offshore wind farms to operate electrolysers also installed at sea on an industrial scale. Plans envisage setting up electrolysis units in the North Sea with a total capacity of 10 gigawatts, enough to produce 1 million metric tons of green hydrogen.
It is not an unambitious project.
North Sea Hydrogen Co-operation: AquaVentus And Hydrogen Scotland
The title of this section is the same as that of this page on the Hydrogen Scotland web site.
This is the introduction.
Hydrogen Scotland signed a comprehensive Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with AquaVentus at Offshore Europe in Aberdeen. The partnership aims to unlock the North Sea’s vast potential for hydrogen production and establish Scotland as a key supplier to European markets through the development of shared infrastructure.
Both partners are committed to intensifying research activities and advocating for the rapid scale-up of a European hydrogen economy.
By joining forces, members of AquaVentus and Hydrogen Scotland can help advance the development and deployment of technologies along the entire value chain – from production through transport and storage to the use of hydrogen for decarbonising the energy system. In addition, both organisations intend to intensify their supporting activities and jointly advocate for the accelerated ramp-up of a European hydrogen economy.
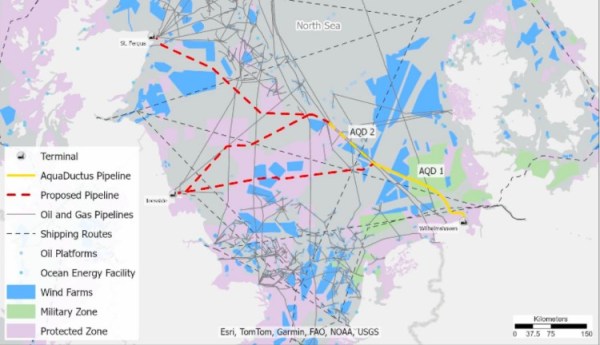
This map of the North Sea, which I downloaded from the Hydrogen Scotland web site, shows the co-operation.
Note.
- The yellow AquaDuctus pipeline connected to the German coast near Wilhelmshaven.
- There appear to be two AquaDuctus sections ; AQD 1 and AQD 2.
- There are appear to be three proposed pipelines, which are shown in a dotted red, that connect the UK to AquaDuctus.
- The Northern proposed pipeline appears to connect to the St. Fergus gas terminal on the North-East tip of Scotland.
- The two Southern proposed pipelines appear to connect to the Easington gas terminal in East Yorkshire.
- Easington gas terminal is within easy reach of the massive gas stores, which are being converted to hold hydrogen at Aldbrough and Rough.
- The blue areas are offshore wind farms.
- The blue area straddling the Southernmost proposed pipe line is the Dogger Bank wind farm, is the world’s largest offshore wind farm and could evebtually total over 6 GW.
- RWE are developing 7.2 GW of wind farms between Dogger Bank and Norfolk in UK waters, which could generate hydrogen for AquaDuctus.
This cooperation seems to be getting the hydrogen Germany needs to its industry.
These five paragraphs outline a position paper by AquaVentus.
This opportunity for German-British cooperation on hydrogen is highlighted in a position paper presented by AquaVentus alongside the signing of the MoU. This paper addresses how the requirements of German-British cooperation – as outlined, for example, in the July 2025 Kensington Treaty between the UK and Germany and the European Commission’s Common Understanding published in May 2025 – can be met.
The position paper highlights the significant potential of hydrogen production in Scotland, the necessity of imports for Germany, and references transport infrastructure already under planning. It thus lays the foundation for cross-border hydrogen trade between Germany and the United Kingdom, and for deeper European cooperation in the hydrogen sector, with three essential prerequisites:
Firstly, the networking of producers and consumers across national borders is critical for a successful market ramp-up
Secondly, beyond this synchronised production and transport infrastructure, regulatory frameworks must also be harmonised. Hybrid connection concepts (pipes & wires) that integrate both electricity and hydrogen networks provide the necessary flexibility for future energy needs, enable efficient use of renewable energy and ensure cost-effective grid expansion
Thirdly, the development from a national core network to a European Hydrogen Backbone is emphasised. Projects such as AquaDuctus can serve as a nucleus for building a pan-European hydrogen network that will shape Europe’s energy infrastructure in the long term. For the authors, strengthened cooperation with the United Kingdom is not only a sound energy policy and economic decision, but also a key contribution to European energy resilience.
Note.
Scotland And AquaVentus Partner On North Sea Hydrogen Pipeline Plans
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on H2-View.
These four paragraphs introduce the deal and add some detail.
Hydrogen Scotland has committed to working with the AquaDuctus consortium on cross-border infrastructure concepts to connect Scotland’s offshore wind power to hydrogen production in the North Sea.
Under a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), the two organisations plan to combine Scotland’s offshore wind with AquaVentus’ offshore electrolysis expertise, linking export and import goals across the North Sea.
The AquaDuctus pipeline is a planned offshore hydrogen link designed to carry green hydrogen through the North Sea, using a pipes and wires hybrid approach. The German consortium plans 10GW of offshore electrolysers in the North Sea, producing around one million tonnes of green hydrogen.
The pipeline design allows offshore wind farms to deliver electricity when the grid needs it, or convert power into hydrogen via electrolysis and transport it through pipelines.
Germany is embracing hydrogen in a big way.
- I introduce AquaVentus in AquaVentus, which I suggest you read.
- AquaVentus is being developed by RWE.
- AquaVentus connects to a German hydrogen network called H2ercules to actually distribute the hydrogen.
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that will deliver hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Esbjerg in Denmark, that is marked DK.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway, which goes North,
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland, that is marked UK.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England, that is marked UK.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Rough owned by Centrica.
- Aldbrough and Rough gas storage sites are being converted into two of the largest hydrogen storage sites in the world!
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
When it is completed, AquaVentus will be a very comprehensive hydrogen network.
I believe that offshore electrolysers could be built in the area of the Hornsea 4, Dogger Bank South and other wind farms and the hydrogen generated would be taken by AquaVentus to either Germany or the UK.
- Both countries get the hydrogen they need.
- Excess hydrogen would be stored in Aldbrough and Rough.
- British Steel at Scunthorpe gets decarbonised.
- A 1.8 GW hydrogen-fired powerstation at Keadby gets the hydrogen it needs to backup the wind farms.
Germany and the UK get security in the supply of hydrogen.
Conclusion
This should be a massive deal for Germany and the UK.
Centrica Secures Investment Stake In Gasrec Helping Boost UK Bio-LNG Ambitions
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica has secured a minority stake in Gasrec, the UK’s largest dual provider of bio-LNG (bio-Liquified Natural Gas) and bio-CNG (bio-Compressed Natural Gas) to the road transport sector,
These first two paragraphs give more details.
Gasrec says the investment will drive the next phase of its infrastructure ambitions, with plans to open a UK wide network of open-access refuelling stations supplying renewable bio-LNG for the decarbonisation of heavy goods vehicles.
Centrica is taking a 16% stake and becomes one of three major shareholders in Gasrec, alongside global integrated energy company bp and private family office 44 North.
I have some thoughts.
Does Running A Truck On bio-LNG or bio-CNG. Reduce Carbon Emissions?
This paragraph from the press release, gives the thoughts of Chris O’Shea, who is Group Chief Executive, Centrica.
Chris O’Shea, Group Chief Executive, Centrica plc, said: “Demand for bio-LNG for transport is growing fast as more HGV operators make the switch – drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel*. This investment in Gasrec enhances our collaboration with the leading company in the sector, and puts us in a strong position to energise a vital sector of the industry on its journey to net zero.”
As Centrica is a public company, with shareholders, who would take a dim view of Mr. O’Shea telling porkies, I suspect we can assume that the following is true.
Drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel.
The asterisk in the full quote, refers to this note.
Low Carbon Vehicle Partnership, Innovate UK and Office for Low Emission Vehicles, Low Emission Freight & Logistics Trial (LEFT), Key Findings, November 2020. Using specific feedstocks CO2 reductions of 200% are achievable.
Centrica could be being conservative with their claims.
Decarbonising Buses, Locomotives And Trucks
Despite what Elon Musk, would have us believe, electric trucks will not dominate the future of freight transport.
An electric truck would be the vehicle equivalent of asking Usain Bolt to run a hundred metres with a large refrigerator on his back.
Trucks are going to need a fuel without a weight penalty and with a long range.
I asked Google for information about Cummins diesel, natural gas and hydrogen engines and received this AI Overview.
Cummins offers engines powered by diesel, natural gas, and hydrogen. While diesel engines are well-established, Cummins is also developing both natural gas and hydrogen engines, particularly focusing on hydrogen as a pathway to zero-carbon solutions for various applications. Cummins utilizes a fuel-agnostic platform, meaning a common base engine can be adapted for different fuel types, including diesel, natural gas, and hydrogen.
Recently, GB Railfreight purchased thirty Class 99 locomotives from Stadler.
- They can use electrification, where it exists.
- Where electrification doesn’t exist, they can use an onboard Cummins diesel engine, which is built in Darlington.
- In electric-mode, they have 6.2 MW of power, and are the most powerful locomotives ever to run on UK railways.
- In diesel-mode, they have 1.8 MW of power, which is more than enough to haul a large container train in and out of Felixstowe.
I had thought that at some future date, Cummins would convert these locomotives to electro-hydrogen.
But now that Gasrec is providing bio-LNG and bio-CNG, GB Railfreight, have the option of converting both hydrogen and biomethane.
Similar logic can be applied to Wrightbus’s Streetdeck Ultroliner, one version of which is fitted with a Cummins engine, that can be converted to electric, hydrogen or natural gas, which of course includes biomethane. This page on the Wrightbus web site describes the bus.
Wrightbus are also going back into coach manufacture, as I wrote about in Wrightbus Goes Back To The Future As It Relaunches The Contour Coach. As with the Streetdeck Ultroliner, Cummins seem to be providing one of the power units.
It seems to me, that the zero- and low-carbon revolution in transport will generate a need for the availability of biomethane, hydrogen and natural gas fuel for transport all over the country.
Gasrec with around twenty biomethane fuelling points around the country, seem well-placed to supply the biomethane in bio-LNG or bio-CNG form.
Could Gasrec Deliver Hydrogen?
Various bus companies in the UK, have had difficulty getting the fuel for their hydrogen buses.
I believe that delivering hydrogen would be very similar to delivering LNG and if Gasrec can deliver LNG successfully and safely, they probably have the technology to do the same for hydrogen.
Centrica Seem To Be Assembling An Interesting Consortium
These are some deals, that I have reported on this blog, that involve Centrica.
- Centrica, along with Hyundai, Kia, Siemens and others have backed Hull-based hydrogen start-up; HiiROC, who can produce affordable hydrogen from any hydrocarbon gas including natural gas, where it is needed.
- Centrica have invested in Sizewell C. Will they be using their share of the electricity to make affordable pink hydrogen using HiiROC?
- In Centrica And Ryze Agree To Develop Hydrogen Pathway, I talked about how Centrica and Ryse were aiming to bring hydrogen to the masses.
- In Recurrent Energy’s Middle Road Project Sold To Centrica, I talked about a Centrica investment in solar power.
- In Aberdeen’s Exceed Secures Centrica Rough Contract, I talked about how Centrica were redeveloping the Rough gas storage site for hydrogen.
- In Lhyfe And Centrica To Develop Offshore Renewable Green Hydrogen In The UK, I talked about developing offshore hydrogen.
- In Centrica Announces Hydrogen Ready Combined Heat And Power Partnership With 2G, the title says it all.
- In Centrica Signs UK Biomethane Agreement With Yorkshire Water And SGN Commercial Services, Centrica appear to be sourcing biomethane from Yorkshire Water.
- In Centrica Invests In Renewable Energy Storage Capabilities To Boost UK’s Energy Security And Accelerate Transition To Net Zero, I talk about Centrica, Goldman Sachs and others, investment in liquid-air energy storage company; Highview Power.
- In British Gas Owner Mulls Mini-Nuke Challenge To Rolls-Royce, I talk about rumours that Centrica might invest in SMRs.
Note.
- A lot of these deals are are about hydrogen production.
- Some of these deals are about biomethane production.
- None of these deals talk about getting hydrogen and biomethane to customers.
It appears to me, that Gasrec have a model that works to get hydrogen, methane and biomethane from production and storage to the end customers.
Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network
In Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network, I talked about supplying all those millions of off-gas grid properties with hydrogen for heating, agricultural and industrial purposes, in the countryside of the UK.
Gasrec have the technology to decarbonise the countryside.
Conclusion
Gasrec would appear to be a very useful partner for Centrica.
mtu Engines From Rolls-Royce Provide Emergency Power On Offshore Wind Platforms In The UK
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
These two bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Four engines from the mtu Series 4000 provide emergency power for two converter platforms
- Norfolk wind farm will generate electricity for demand from more than four million households
This opening paragraph adds more detail.
Rolls-Royce has received a second order from Eureka Pumps AS to supply mtu Series 4000 engines to power emergency power generators for the Norfolk Offshore Wind Farm on the east coast of the United Kingdom. Rolls-Royce will thus supply a total of four mtu engines for the first and second phases of the large wind farm, which is operated by energy supplier RWE. The engines will be installed on two converter platforms at sea and onshore, which are the heart of the offshore grid connection: they ensure that the electricity generated at sea can be fed into the power grid. With a total capacity of 4.2 GW, the wind farm is expected to generate electricity for more than four million households during the course of this decade. It is located 50 to 80 kilometers off the east coast of the UK.
In some ways I find it strange, that a diesel generator is used to provide the necessary emergency power.
But when I asked Google if mtu 4000 generators can operate on hydrogen. I got this answer.
Yes, mtu Series 4000 engines, specifically the gas variants, can be adapted to run on hydrogen fuel. Rolls-Royce has successfully tested a 12-cylinder mtu Series 4000 L64 engine with 100% hydrogen fuel and reported positive results. Furthermore, mtu gas engines are designed to be “H2-ready,” meaning they can be converted to operate with hydrogen, either as a blend or with 100% hydrogen fuel.
That seems very much to be a definite affirmative answer.
So will these mtu Series 4000 engines for the Norfolk wind farms be “H2 ready”? The hydrogen needed, could be generated on the platform, using some form of electrolyser and some megawatts of electricity from the wind farms.
Will The Norfolk Wind Farms Generate Hydrogen For Germany?
Consider.
- Germany needs to replace Russian gas and their own coal, with a zero-carbon fuel.
- Germany is developing H2ercules to distribute hydrogen to Southern Germany.
- Germany is developing AquaVentus to collect 10 GW of hydrogen from wind-powered offshore electrolysers in the North Sea.
- The AquaVentus web site shows connections in the UK to Humberside and Peterhead, both of which are areas, where large hydrogen electrolysers are bing built.
- In addition Humberside has two of the world’s largest hydrogen stores and is building a 1.8 GW hydrogen-fired powerstation.
- The Norfolk wind farms with a capacity of 4.2 GW, are not far from the border between British and German waters.
- To the North of the Norfolk wind farm, RWE are developing the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm.
- 7.2 GW of British hydrogen would make a large proportion of the hydrogen Germany needs.
I clipped this map from a video about Aquaventus.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that will deliver hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Esbjerg in Denmark, that is marked DK.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway, which goes North,
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland, that is marked UK.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England, that is marked UK.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- Aldbrough and Rough gas storage sites are being converted into two of the largest hydrogen storage sites in the world!
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
When it is completed, AquaVentus will be a very comprehensive hydrogen network.
It will also be a massive Magic Money Tree for the UK Treasury.
So why is this vast hydrogen system never mentioned?
It was negotiated by Clair Coutinho and Robert Habeck, back in the days, when Boris was Prime Minister.
Centrica And Equinor Agree Major New Deal To Bolster UK Energy Security
The title of this post, is the same as that as this news item from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica and Equinor have today announced a £20 billion plus agreement to deliver gas to the UK. The new deal will see Centrica take delivery of five billion cubic meters (bcm) of gas per year to 2035.
These three paragraphs add more detail to the deal.
The expansive ten-year deal continues a long-term relationship with Equinor that dates back to 2005 bringing gas from Norway to the UK.
In 2024, the UK imported almost two-thirds (66.2%) of its gas demand, with 50.2% of the total imports coming from Norway1. This is an increase from the UK importing around a third of its gas requirements from Norway in 20222 and underlines the strategic importance of the Norwegian relationship to UK energy and price security.
The contract also allows for natural gas sales to be replaced with hydrogen in the future, providing further support to the UK’s hydrogen economy.
I believe there is more to this deal than, is stated in the news item.
These are my thoughts.
Where Does AquaVentus Fit In?
The AquaVentus web site has a sub heading of Hydrogen Production In The North Sea.
This video on the web site shows the structure of the project.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that will deliver hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Esbjerg in Denmark, that is marked DK.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway, which goes North,
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland, that is marked UK.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England, that is marked UK.
- There appears to be an extra link, that would create a hydrogen link between Norway and Humberside.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- Aldbrough and Rough gas storage sites are being converted into two of the largest hydrogen storage sites in the world!
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
When it is completed, AquaVentus will be a very comprehensive hydrogen network.
RWE
I should add that AquaVentus is a project of German energy company; RWE.
It should be noted that RWE are the largest generator of electricity in the UK.
They will soon be even larger as they are developing these offshore wind farms in British waters.
- Dogger Bank South – 3 GW
- Norfolk Boreas – 1.4 GW
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1.4 GW
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1.4 GW
Note.
- This is 7.2 GW of electricity.
- The three Norfolk wind farms wwere possibly acquired at a bargain price from Vattenfall.
- None of these wind farms have Contracts for Difference.
- RWE are developing large offshore electrolysers.
- East Anglia is in revolt over pylons marching across the landscape.
I wonder, if RWE will convert the electricity to hydrogen and bring it ashore using AquaVentus, coastal tankers or pipelines to existing gas terminals like Bacton.
The revenue from all this hydrogen going to Germany could explain the rise in Government spending, as it could be a Magic Money Tree like no other.
HiiROC
HiiROC is a Hull-based start-up company backed by Centrica, that can turn any hydrocarbon gas, like chemical plant waste gas, biomethane or natural gas into turquoise hydrogen and carbon black.
I asked Google about the size of Norway’s chemical industry and got this reply.
Norway’s chemical industry, including oil refining and pharmaceuticals, is a significant part of the country’s economy. In 2023, this sector generated sales of NOK 175 billion (approximately €15.2 billion), with 83% of those sales being exports. The industry employed 13,800 full-time equivalents and added NOK 454 billion (approximately €3.9 billion) in value.
Isn’t AI wonderful!
So will Norway use HiiROC or something similar to convert their natural gas and chemical off-gas into valuable hydrogen?
If AquaVentus were to be extended to Norway, then the hydrogen could be sold to both the UK and Germany.
A scenario like this would explain the option to switch to hydrogen in the contract.
Aldbrough And Brough
Earlier, I said that just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
I have read somewhere, that Germany is short of hydrogen storage, but I’m sure Centrica and SSE will help them out for a suitable fee. Centrica are also thought to be experts at buying energy at one price and selling it later at a profit.
Conclusion
I have felt for some time, that selling hydrogen to the Germans was going to be the Conservative government’s Magic Money Tree.
Has this Labour government decided to bring it back to life?
Ørsted Pulls Plug On 2.4 GW Hornsea 4 Offshore Wind Project In UK
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Ørsted has discontinued the development of the UK’s Hornsea 4 offshore wind farm in its current form. The developer said the 2.4 GW project has faced rising supply chain costs, higher interest rates, and increased construction and delivery risks since the Contract for Difference (CfD) award in Allocation Round 6 (AR6) in September 2024.
This introductory paragraph adds more detail.
In combination, these developments have increased the execution risk and deteriorated the value creation of the project, which led to Ørsted stopping further spending on the project at this time and terminating the project’s supply chain contracts, according to the Danish company. This means that the firm will not deliver Hornsea 4 under the CfD awarded in AR6.
Consider.
- Hornsea 4 will be connected to the grid at a new Wanless Beck substation, which will also include a battery and solar farm, which will be South West of the current Creyke Beck substation. Are Ørsted frightened of opposition from the Nimbies to their plans?
- I also wonder if political uncertainty in the UK, and the possibility of a Reform UK government, led by Nigel Farage is worrying companies like Ørsted.
So will factors like these prompt companies like Ørsted to move investment to countries, where they welcome wind turbines like Denmark, Germany and The Netherlands.
Could Ørsted Be Looking At An Alternative?
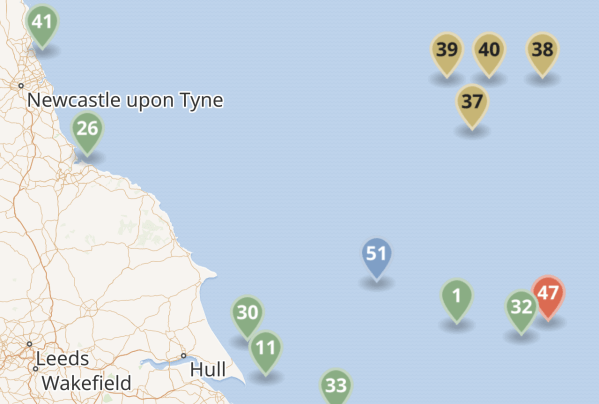
This is a map of wind farms in the North Sea in the Dogger Bank and Hornsea wind farms, that I clipped from Wikipedia..
These are the Dogger Bank and Hornsea wind farms and their developers and size
- 37 – Dogger Bank A – SSE Renewables/Equinor – 1,235 MW
- 39 – Dogger Bank B – SSE Renewables/Equinor – 1,235 MW
- 38 – Dogger Bank C – SSE Renewables/Equinor – 1,218 MW
- 40 – Sofia – RWE – 1,400 MW
- 1 – Hornsea 1 – Ørsted/Global Infrstructure Partners – 1,218 MW
- 32 – Hornsea 2 – Ørsted/Global Infrstructure Partners – 1,386 MW
- 47 – Hornsea 3 – Ørsted – 2,852 MW
- 51 – Hornsea 4 – Ørsted – 2,400 MW
Note.
- That is a total of 12, 944 MW, which is probably enough electricity to power all of England and a large part of Wales.
- Wikipedia’s List of offshore wind farms in the United Kingdom, also lists a 3,000 MW wind farm, that is being developed by German company ; RWE called Dogger Bank South,
- The Dogger Bank South wind farm is not shown on the map, but would surely be South of wind farms 37 to 40 and East of 51.
- The Dogger Bank South wind farm will raise the total of electricity in the Dogger Bank and Hornsea wind farms to just short of 16 GW.
Connecting 16 GW of new electricity into the grid, carrying it away to where it is needed and backing it up, so that power is provided, when the wind doesn’t blow, will not be a nightmare, it will be impossible.
An alternative plan is needed!
AquaVentus To The Rescue!
AquaVentus is a German plan to bring 10 GW of green hydrogen to the German mainland from the North Sea, so they can decarbonise German industry and retire their coal-fired power stations.
- I introduce AquaVentus in AquaVentus, which I suggest you read.
- AquaVentus is being developed by RWE.
- AquaVentus connects to a German hydrogen network called H2ercules to actually distribute the hydrogen.
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that will deliver hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Esbjerg in Denmark, that is marked DK.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway, which goes North,
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland, that is marked UK.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England, that is marked UK.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- Aldbrough and Rough gas storage sites are being converted into two of the largest hydrogen storage sites in the world!
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
When it is completed, AquaVentus will be a very comprehensive hydrogen network.
I believe that offshore electrolysers could be built in the area of the Hornsea 4 and Dogger Bank South wind farms and the hydrogen generated would be taken by AquaVentus to either Germany or the UK.
- Both countries get the hydrogen they need.
- Excess hydrogen would be stored in Aldbrough and Rough.
- British Steel gets decarbonised.
- A 1.8 GW hydrogen-fired powerstation at Keadby gets the hydrogen it needs to backup the wind farms.
Germany and the UK get security in the supply of hydrogen.
These may be my best guesses, but they are based on published plans.
ScottishPower Renewables Picks Port For East Anglia Two Pre-Assembly
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
ScottishPower Renewables, Iberdrola’s UK arm, has selected Peel Ports Great Yarmouth as the staging ground for pre-assembly works for its 960 MW East Anglia Two offshore wind project.
This is the introductory paragraph.
The companies have signed a reservation agreement that will see the Siemens Gamesa turbine components and sections come together for assembly at the Norfolk site before installation in the southern North Sea in 2028.
Note.
- The Port of Great Yarmouth was used for this task with East Anglia One.
- The turbine blades will be manufactured at Siemens Gamesa’s offshore wind blade factory in Hull.
- The monopiles will come from Sif in Rotterdam.
This is the first sentence of the Wikipedia entry for the East5 Anglia Array.
The East Anglia Array is a proposed series of offshore wind farms located around 30 miles off the east coast of East Anglia, in the North Sea, England. It has begun with the currently operational East Anglia ONE, that has been developed in partnership by ScottishPower Renewables and Vattenfall. Up to six individual projects could be set up in the area with a maximum capacity of up to 7.2 GW.
These articles on offshoreWIND.biz indicate that ScottishPower Renewables has been busy signing contracts for East Anglia Two.
- December 4th, 2024 – Nexans Lands Export Cable Contract For East Anglia Two Offshore Wind Farm.
- November 28th, 2024 – Hitachi Energy to Integrate 960 MW East Anglia Two Wind Farm into UK Grid.
- November 12th, 2024 – Siemens Gamesa Bags GBP 1 Billion Turbine Contract For East Anglia Two.
- November 6th, 2024 – Seaway7 Wins East Anglia Two Inter-Array Cable Contract.
- October 31st, 2024 – Sif, Smulders to Deliver Monopiles and TPs For ScottishPower’s East Anglia Two Offshore Wind Farm.
They must have employed lawyers on roller skates to get five contracts signed in just over a month.
Conclusion
East Anglia Two appears to be definitely under way and the Wikipedia extract says there could be a lot more, if all the other wind farms are developed in the same way using the Port of Great Yarmouth.
A total capacity in the East Anglia Array of 7.2 GW will surely be good for both East Anglia and the UK as a whole, but will the natives be happy with all the onshore infrastructure?
I wouldn’t be surprised to see further wind farm developed to generate hydrogen offshore, which will be either brought ashore to the Bacton gas terminal, using existing or new pipelines or distributed using tanker ships to where it is needed.