Backing Up The Wind With The Keadby Power Stations
I went to Cleethorpes from Doncaster by train yesterday. You pass the Keadby site, where there are two large gas–fired power stations of 734 MW and 710 MW. A third one ; Keadby 3 of 910 MW complete with carbon capture and storage should join them by 2027.
So that will be nearly 2.5 GW of reliable electricity.
I find it interesting that one of our first gas-fired power stations with carbon capture will be in Lincolnshire, which is famous for growing plants of all shapes, types and sizes. So will we be seeing lots of greenhouses on the flat lands I saw yesterday, growing plants in an atmosphere they like, so that we can generate our carbon dioxide and eat it.
The next power station at Keadby is called the Keadby Next Generation power station, which is intended to be complete by 2030. It is a bit of a puzzle in that it will run on up to 1800 MW of hydrogen and only produce up to 910 MW of electricity.
Note.
- The hydrogen will come from SSE’s hydrogen store at Aldbrough and Centrica’s store at Rough.
- Surely, the amount of hydrogen and electricity should balance.
When I worked in ICI’s hydrogen plant in the 1960s, ICI had no use for the hydrogen, so they sent it to their power station, blended it with coal gas and used it to make steam for other processes.
Could Keadby Next Generation power station be providing zero-carbon steam for the chemical and other processes on Humberside?
Adding the 910 MW of electricity to Keadby’s gas-fired total of 2.5 GW gives 3.4 GW of electricity from Keadby to back up the wind farms.
3.4 GW at Keadby is what I call backup!
It also should be noted, that one of the reasons for building the Mersey Tidal Barrage is to provide backup for all the wind farms in Liverpool Bay.
Conclusion
I believe that SSE could be supplying zero-carbon steam in addition to electricity from the Keadby Hydrogen power station.
From Doncaster To Cleethorpes
These pictures were taken on my journey between Doncaster and Cleethorpes.
The area is best summed up as flat and decorated with these features.
- A few hedges.
- Some trees and some woodland.
- dozens of wind turbines.
- Lots of pylons carrying electricity.
- Scunthorpe steelworks
- A few stations and railway sidings.
- A couple of waterways.
- Estates of new housing as you approach Grimsby.
When I returned there was more of the same on the other side of the tracks.
With the addition of all the power stations at Keadby and a couple of wind farms.
These are my thoughts on how this landscape will look at some time after 2030.
More Onshore Wind Farms
There will be a lot more wind farms lining the Doncaster and Cleethorpes railway.
The government has said it might pay for turbines and transmission lines to spoil views.
I feel they will have to, to meet their net-zero targets.
There Will Be Massive Hydrogen Storage On The Other Side Of The Humber
SSE are developing Albrough and Centrica are developing Rough into two of the largest hydrogen stores in the world.
The wind farms of the North Sea will provide them with hydrogen.
More Housing
If the government has its wish there will be a lot more new housing.
And as the newer houses show in my pictures, many of them will have solar panels.
More Power Stations At Keadby
Consider.
- The main purpose of the power stations at Keadby will be to provide backup to the wind and solar power in the area and far out to sea.
- The power stations will use hydrogen stored at Albrough and Rough.
- Some of the gas-fired power stations at Keadby will be fitted with carbon capture.
- One hydrogen-fired power station is already being planned.
The power stations at Keadby will probably be capable of supplying several GW of zero-carbon energy.
There Will Be Energy-Hungry Industries Along The South Bank Of The Humber
Just as in the Victorian era, coal attracted steel-making, chemicals and refining to the area, a South Humberside with large amounts of energy will attract heavy industry again.
Already, Siemens have built a train factory at Goole.
There Will Also Be Large Greenhouses In Lincolnshire
Greenhouses are a wonderful green way of absorbing waste heat and carbon dioxide.
Where Have I Seen This Blend Of Offshore Energy, Hydrogen, Heavy Industry And Agriculture Before?
After I visited Eemshaven in the Northern Netherlands, I wrote The Dutch Plan For Hydrogen.
We are not doing something similar, but something much bigger, based on the hydrogen stores at Aldbrough and Brough, the massive offshore wind farms and Lincolnshire’s traditional heavy industry and agriculture.
The Railway Between Doncaster and Cleethorpes Will Be Developed
Just as the Dutch have developed the railways between Groningen and Eemshaven.
The Future Of Drax Power Station
Drax power station is not liked by a lot of environmentalists.
I have been thinking about the future of the power station and the public company that owns it.
Drax power station has a nameplate capacity of around 2.5 GW running on biomass.
It also will be the Southern end of EGL2, which will be an undersea electricity 2 GW superhighway distributing Scottish wind power from Peterhead in Scotland. So the dreaded biomass hated by certain groups will be relegated from the Premier League of electricity generation and replaced by Scottish wind.
As reported in various publications, Drax has signed a deal in the US, so that the biomass can be used for the production of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF)
To my mind, the Drax site could be an ideal one for one or more small modular nuclear reactors.
- The large Drax site has been producing electricity for 52 years.
- In 1986, the site produced nearly 4 GW of electricity.
- I would suspect that the substations on the site could be enlarged to distribute 4 GW of electricity.
- EGL2 will bring in 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity.
- The site has excellent rail connections.
- The site has twelve cooling towers and is encircled by the River Ouse.
- Could all this water be used for cooling the small modular nuclear reactors.
I believe that perhaps three small modular nuclear reactors could be built on the Drax site to backup EGL2 and bring a reliable source of sustainable power to Yorkshire.
Drax is also only about forty miles from the vast hydrogen stores at Aldbrough and Rough, so if Drax needed, if could use excess electricity to create hydrogen for storage.
SSE is consulting on a 1+ GW hydrogen power station at Keadby, so perhaps Drax should have a similar hydrogen power station on its site?
I’ve Just Come Across Avnos
I feel we should take into account any possibilities of second use of oil or gas structures, that once held hydrocarbons.
An article in a magazine called Carbon Herald pointed me to a company called Avnos, who are developing Direct Air Capture of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. If systems like that of Avnos do work, we may need somewhere to put the carbon dioxide.
Centrica are storing the hydrogen in the Rough gas field, which was previously used for storing natural gas and now some depleted gas fields are being used to store captured carbon dioxide.
On the subject of carbon capture, Avnos do it differently, in that for every tonne of CO2, they capture from the air, they capture five tonnes of distilled water. And they do it without using any heat.
This is their web site.
This is their mission statement on the front page of the web site. There is also a video.
Carbon Negative. Water Positive
Avnos is commercializing the most advanced technology in the Direct Air Capture of CO2
Our proprietary Hybrid Direct Air Capture (HDAC) solution inverts the water paradigm in DAC, producing water, eliminating heat consumption and reducing costs compared to other forms of DAC.
It sounds too good to be true!
But I have experience of the positive financial results of fluid dynamics in this area.
Thirty years ago, two guys approached me with an idea for an aerosol valve that used nitrogen as a propellant.
At the time, I lived in the house, where Osborne Reynolds, the great Victorian fluid dynamicist of Reynold’s number fame had been brought up.
The guys succeeded and the device was sold on to J & J.
They were then asked to develop a metered dose inhaler for asthma drugs, which is now sold as Respimat, which is sold by Boehringer Ingelheim.
Afterwards, I researched Reynolds at Manchester University, where he was the first Professor of Engineering and I found that he had done some marvelous things with fluids. He was a true genius and undergraduates are still taught on his Victorian apparatus.
I suspect that Avnos may have been exploring in the same area and are using another of Reynold’s useful properties.
Large Scale Hydrogen Storage Sites Could Reduce Customer Energy Costs By £1bn Per Year
The title of this post, is the same as this press release from Centrica.
These four paragraphs summarise the report.
Centrica and FTI report finds that hydrogen storage would help balance the UK’s energy system and reduce bills.
A net zero scenario including large scale hydrogen storage – specifically, a redeveloped Rough gas storage facility – would reduce energy costs by an additional £1bn per year by 2050.
Report also finds that a UK energy system focused on renewable generation risks high levels of intermittency without an established hydrogen market. By 2050, electricity generation from renewables could exceed total demand around 15% of the time.
Electricity generation from renewables could also rise or fall by as much as 100GW over the course of a single day. More than twice current levels of peak demand on winter evenings and the equivalent energy output from over 30 Hinkley Point C nuclear power stations.
Note.
- Hydrogen Central entitles their article about the Centrica press release Centrica Says Hydrogen Can Reduce Household Bills by £35 a Year. That’s almost a bottle of my favourite Adnams beer a week!
- I talked about the redevelopment of the Rough facility into hydrogen storage in Aberdeen’s Exceed Secures Centrica Rough Contract.
- Generating hydrogen from excess electricity and storing it until it is needed, must be an efficient way of storing electricity or powering industrial processes that need a lot of energy, if storing hydrogen makes £1bn per year!
- It should be noted that Centrica have a large interest in HiiROC, who are developing an efficient way to generate hydrogen from any hydrocarbon gas from chemical plant off-gas through biomethane to natural gas. In a perfect world a HiiROC system in a sewage works could capture the biomethane and split it into hydrogen and carbon black. The hydrogen could be used to refuel vehicles and the carbon black would be taken away to someone, who has need of it.
In some ways, it is surely sensible to have enough energy in a store, if the renewables fail. As Rough is already there and functioning, it is surely one of the easiest routes to redevelop Rough, so that it is in top-quality condition.
It should also be noted, that Rough is not far from the Aldbrough Gas Storage, which SSE are converting to a second massive hydrogen store.
So Humberside will have two of the largest hydrogen stores in the world, which Centrica and SSE will use to maxise energy security in the wider Humberside and East Yorkshire area, and I suspect to maximise their profits as well.
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus, which is a pipeline system, that the Germans are building to bring much-needed hydrogen to German industry from electrolysers in the North Sea and other countries like Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands and the UK.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note how a branch of AquaVentus makes landfall around the Humber estuary at a UK label.
Will Centrica and SSE be trading hydrogen from Rough and Aldbrough with the Germans through AquaVentus? You bet they will, as the Germans are short of both hydrogen and hydrogen storage.
Aberdeen’s Exceed Secures Centrica Rough Contract
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Energy Voice.
This is the sub-heading.
Well and reservoir management firm Exceed has secured a contract with Centrica Energy Storage for the redevelopment of the Rough gas storage field.
This is the introductory paragraph.
Exceed said its role in the initial stages of the project, which is exploring converting the Rough field into a hydrogen storage facility, could create more than 30 jobs.
In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I talked about changing Rough from a gas to a hydrogen store, so it looks like Centrica are going to create a vast hydrogen storage facility.
This all fits with my belief, that Centrica’s Rough facility and SSE’s nearby Aldbrough storage facility, will at sometime in the future be connected to the Germany hydrogen pipeline; AquaVentus to perform backup to hydrogen produced in the North Sea.
I also feel that the hydrogen trading will be of benefit to Centrica and SSE.
The last section of the Energy Voice article is entitled Rough Hydrogen Storage Concerns.
The following facts are given.
There are currently eight geological gas storage sites across Great Britain, containing approximately 3.1bcm in capacity and maximum deliverability rates of 124mcm/day.
Five of these gas storage sites are in salt caverns while the remaining three are depleted oil and gas fields, with the Centrica’s Rough field in the North Sea the only site located offshore.
The British Geological Survey estimates the UK could store up to 3,000 TWh of hydrogen.
Currently, we use the following energy in a year.
- 263 TWh of electricity
- 705 TWh of natural gas
So we use a total of 968 TWh of energy.
3,000 TWh of hydrogen would keep the UK going for three years. So we should be fine!
Energy In – Hydrogen And Carbon Dioxide Out
This article was inspired by this article in the Sunday Times, which is entitled ‘It’s A Slog’: Life Inside Britain’s Last Coal Power Station.
The article is about Ratcliffe-on-Soar power station, which is next to East Midlands Parkway station.
This is the first paragraph of the station’s Wikipedia entry.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar Power Station is a coal-fired power station owned and operated by Uniper at Ratcliffe-on-Soar in Nottinghamshire, England. Commissioned in 1968 by the Central Electricity Generating Board, the station has a capacity of 2,000 MW. It is the last remaining operational coal-fired power station in the UK, and is scheduled to close in September 2024.
I took these pictures of the power station in 2019.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar is the last of a number of large coal-fired power stations, that were built in the area, mainly along the River Trent.
- Rugeley – 600 MW – 1961
- Drakelow – 1630 MW – 1964
- Willington – 800 MW – 1962
- Castle Donington – 600 MW – 1958
- Ratcliffe-on-Soar – 2000 MW – 1968
- High Marnham – 1000 MW – 1959
- Cottam – 2000 MW – 1968
- West Burton – 2000 MW – 1968
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 10,630 MW of electricity.
- There are also a few large gas-fired power stations along the river, that are still operating.
- Both coal and gas-fired stations use the water from the River Trent for cooling.
At the mouth of the river, there is the Keadby cluster of gas-fired power stations.
- Keadby 1 – 734 MW – 1996
- Keadby 2 – 849 MW – 2023
- Keadby 3 – 910 MW – 2027
- Keadby Hydrogen – 900 MW – 2030
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 3,393 MW of electricity.
- Keadby 2 is the most efficient CCGT in the world.
- Keadby 3 will be fitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby 2 has been designed to be retrofitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby Hydrogen will be fuelled by zero-carbon hydrogen.
As the years progress, I can see the Keadby cluster of power stations becoming a large zero-carbon power station to back-up wind farms in the North Sea.
- Hydrogen power stations will emit no carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide from all gas-fired stations will be captured.
- Some carbon dioxide will be sold on, to companies who can use it, in industries like construction, agriculture and chemical manufacture.
- The remaining carbon dioxide will be stored in depleted gas fields.
As technology improves, more carbon dioxide will be used rather than stored.
Other Power Sources In The Humberside Area
In the next few sub-sections, I will list the other major power sources in the Humberside area.
Drax Power Station
Drax power station is a shadow of its former self, when it was one of the power stations fed by the newly discovered Selby coalfield.
These days it is a 2,595 MW biomass-fired power station.
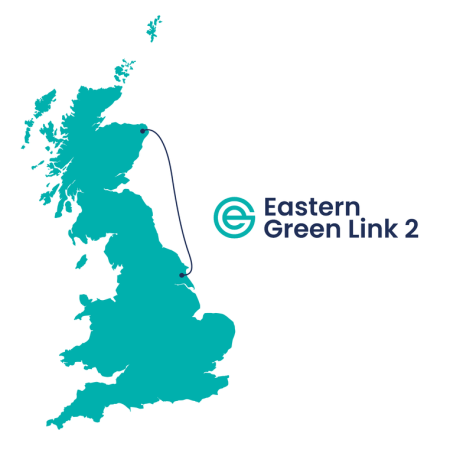
Eastern Green Link 2
Eastern Green Link 2 will be a 2 GW interconnector between Peterhead in Scotland and Drax.
It is shown in this map.
Note.
- Most of the route is underwater.
- It is funded by National Grid.
- Contracts have been signed, as I talk about in Contracts Signed For Eastern Green Link 2 Cable And Converter Stations.
- It is scheduled to be completed by 2029.
This interconnector will bring up to 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity to Drax and Humberside.
Drax has the substations and other electrical gubbins to distribute the electricity efficiently to where it is needed.
2 GW could also reduce the amount of biomass used at Drax.
In the long term, if the concept of the four Eastern Green Links is successful, I could see another Eastern Green Link to Drax to replace imported biomass at Drax.
I also, don’t see why a smaller Drax can’t be run on locally-sourced biomass.
Solar Farms And Batteries Along The River Trent
As the coal-fired power stations along the River Trent are demolished, solar farm developers have moved in to develop large solar farms.
Salt End Power Station And Chemical Works
These two paragraphs from the Wikipedia entry for Salt End describes the hamlet and its power station and chemical works.
Salt End or Saltend is a hamlet in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, in an area known as Holderness. It is situated on the north bank of the Humber Estuary just outside the Hull eastern boundary on the A1033 road. It forms part of the civil parish of Preston.
Salt End is dominated by a chemical park owned by PX group, and a gas-fired power station owned by Triton Power. Chemicals produced at Salt End include acetic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonia, bio-butanol, bio-ethanol, ethyl acetate (ETAC) and ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) with animal feed also being produced on site.
I wonder, if running the complex on hydrogen would give cost and marketing advantages.
Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage Facility
This page on the SSE Thermal web site is entitled Plans For World-Leading Hydrogen Storage Facility At Aldbrough.
This is the most significant paragraph of the page, that is definitely a must-read.
With an initial expected capacity of at least 320GWh, Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage would be significantly larger than any hydrogen storage facility in operation in the world today. The Aldbrough site is ideally located to store the low-carbon hydrogen set to be produced and used in the Humber region.
This is a hydrogen storage facility for a much wider area than Humberside.
Rough Gas Storage Facility
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Rough Gas Storage Facility.
Rough is a natural gas storage facility under the North Sea off the east coast of England. It is capable of storing 100 billion cubic feet of gas, nearly double the storage capacities in operation in Great Britain in 2021.
In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to convert the Rough gas storage into a massive hydrogen storage.
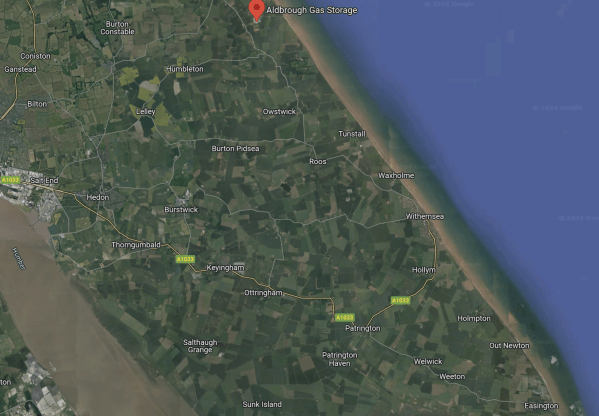
The Location Of Aldbrough Gas Storage, Rough Gas Storage, Salt End And Easington Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows between Salt End and the coast.
Note.
- The river crossing the South-West corner of the map is the Humber.
- Salt End with its power station and chemical works is on the North Bank of the Humber, where the river leaves the map.
- Aldbrough Gas Storage is marked by the red arrow at the top of the map.
- Easington Gas Terminal is in the South-East corner of the map.
- According to Wikipedia, gas flows into and out of the Rough Gas Storage are managed from Easington.
Looking at the map, I feel that the following should be possible.
- The two gas storage sites could be run together.
- Salt End power station and the related chemical works could run on hydrogen.
- Salt End will always have a reliable source of hydrogen.
- This hydrogen could be green if required.
All the chemical works at Salt End, could be run on a zero-carbon basis. Would this mean premium product prices? Just like organic does?
Enter The Germans
The Germans have a huge decarbonisation problem, with all their coal-fired power stations and other industry.
Three massive projects will convert much of the country and industry to hydrogen.
- H2ercules, which is a project of OGE and RWE, will create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen, to where it is needed.
- In Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal, I describe how Uniper are going to build a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhelmshaven.
- AquaVentus is an RWE project that will use 10.3 GW of offshore wind power in German territorial waters to create a million tonnes per year of green hydrogen.
These would appear to be three of Europe’s largest hydrogen projects, that few have ever heard of.
AquaVentus And The UK
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that delivers hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea.
It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network in the North Sea.
These are my thoughts about development of the AquaVentus network.
Hydrogen Production And AquaVentus
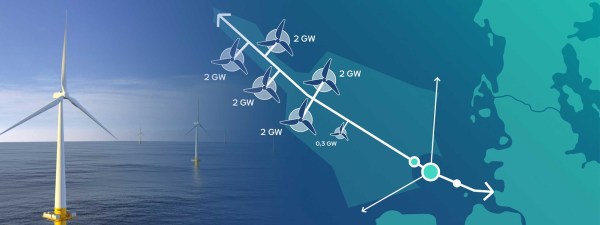
This RWE graphic shows the layout of the wind farms feeding AquaVentus.
Note.
- There is a total of 10.3 GW.
- Is one of the 2 GW web sites on the UK-side of AquaVentus, the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm, which is being developed by RWE?
- Is the 0.3 GW wind farm, RWE’s Norfolk wind farm cluster, which is also being developed by RWE?
Connecting wind farms using hydrogen pipelines to Europe, must surely mitigate the pylon opposition problem from Nimbys in the East of England.
As the AquaVentus spine pipeline could eventually connect to Peterhead, there will be other opportunities to add more hydrogen to AquaVentus.
Hydrogen Storage And AquaVentus
For AquaVentus to work efficiently and supply a large continuous flow of hydrogen to all users, there would need to be storage built into the system.
As AquaVentus is around 200 kilometres in length and natural gas pipelines can be up to 150 centimetres in diameter, don’t underestimate how much hydrogen can be stored in the pipeline system itself.
This page on the Uniper web site is entitled Green Wilhelmshaven: To New Horizons.
This is a sentence on the page.
Access to local hydrogen underground storage at the Etzel salt cavern site.
An Internet search gives the information, that Etzel gas storage could be developed to hold 1 TWh of hydrogen.
That would be enough hydrogen to supply 10 GW for a hundred hours.
Note that the UK branch of AquaVentus reaches the UK, just to the South of the massive hydrogen storage facilities at Aldbrough and Rough.
It would appear that both Germany and the UK are connected to AquaVentus through substantial storage.
I am certain, that all country connections to AquaVentus will have substantial storage at the country’s hydrogen terminal.
AquaDuctus
This would appear to be the first part of the AquaVentus network and has its own web site.
The web site is entitled Nucleus Of A Offshore Hydrogen Backbone.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The project partners are focusing on a scalable, demand-driven infrastructure: By 2030, AquaDuctus will connect the first large hydrogen wind farm site, SEN-1, with a generation capacity of approximately one gigawatt. SEN-1 is located in the German EEZ in the northwest of Helgoland. The pipeline will transport at a length of approx. 200 km green hydrogen produced from offshore wind to the German mainland and from there to European consumers via the onshore hydrogen infrastructure.
In the next project stage, AquaDuctus will be extended to the remote areas of the German exclusive economic zone towards the tip of the so-called duck’s bill. By that, additional future hydrogen wind farm sites will be connected. Along its way AquaDuctus will provide interconnection points with the opportunity for linking of adjacent national offshore hydrogen infrastructures originating from Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium and United Kingdom which opens the door for Europe-wide offshore hydrogen transport by pipeline.
There is also an interactive map, that gives more details.
This paragraph explains, why the Germans have chosen to bring the energy ashore using hydrogen, rather than traditional cables.
Recent studies show that offshore hydrogen production and transport via pipelines is faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly than onshore electrolysis with a corresponding connection of offshore wind turbines via power cables. The German federal government has also recognized this advantage and has clearly expressed its intention to promote offshore hydrogen production in the North Sea.
I suspect, that some UK offshore wind farms will use the same techniques.
Hydrogen Production For The UK
Electrolysers will probably be built along the East Coast between Peterhead and Humberside and these will feed hydrogen into the network.
- Some electrolysers will be offshore and others onshore.
- Turning off windfarms will become a thing of the past, as all surplus electricity will be used to make hydrogen for the UK or export to Europe.
- Until needed the hydrogen will be stored in Albrough and Rough.
Backup for wind farms, will be provided using hydrogen-fired power stations like Keadby Hydrogen power station.
Financial Implications
I reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there would be winners all round.
Rishi Sunak had the cards and he played them very badly.
It is now up to Keir Starmer, Great British Energy and Jürgen Maier to play those cards to link the energy systems of the UK and Germany to ensure security and prosperity for Europe.
Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Wood plc.
These are the first three paragraphs.
Wood, a global leader in consulting and engineering, has been awarded a contract by Centrica Energy Storage (CES) for the redevelopment of the UK’s Rough field in readiness for future hydrogen storage.
The Rough reservoir, located in the Southern North Sea, has been used to store natural gas safely for over thirty years and has the potential to provide over half of the UK’s hydrogen storage requirements.
The front-end engineering design (FEED) contract, awarded to Wood, entails new pipelines, a new unmanned installation, as well as onshore injection facilities at the Easington Gas Terminal, is the first step in making the field hydrogen ready.
Offshore Magazine has this article about the deal, which is entitled Wood Assessing Hydrogen Storage Needs For North Sea Rough Reservoir.
This is a paragraph from the Offshore Magazine article.
Centrica aims to position the Rough Field as the world’s largest long-duration hydrogen storage facility, although FID on the redevelopment project would depend on government support.
It would be a very important project.
Why would Centrica be planning for this massive increase in hydrogen storage?
There could only be one reason.
There is going to be a massive increase in hydrogen production and use.
In Where’s The Plan, Rishi?, I laid out what I believe will happen in the next few years.
- In RWE Goes For An Additional 10 GW Of Offshore Wind In UK Waters In 2030, I detailed how RWE intended to add an extra 10 GW of offshore wind to the seas around the UK.
- As our current offshore wind capacity is around 15 GW, so another 10 GW would surely be very welcome.
- The Germans will develop H2ercules, which is their massive project to create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen to Southern Germany.
- A hydrogen hub at Wilhelmshaven is being built by Uniper to feed H2ercules with green hydrogen from around the world.
But would it not be better, if instead of feeding H2ercules with hydrogen from around the world, some came from the UK, a few hundred miles across the North Sea?
- RWE are developing the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm, which is not in the best place for a cable to the UK. So could this wind farm have an offshore electrolyser and send the hydrogen to Wilhelmshaven, by pipeline or coastal tanker?
- RWE are also developing the 4.2 GW Norfolk cluster of wind farms to the North-East of Great Yarmouth. It might be better, if the output of these wind farms took a hydrogen route to Wilhelmshaven.
- I also believe that a third offshore electrolyser might be situated North of the Wash to bring more hydrogen to Germany.
- Hydrogen could also be sent from the Rough facility to Wilhelmshaven.
The coastal tanker route gives flexibility, so green hydrogen could be sent as required to the UK mainland.
Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech – June 11
I also reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
It is now nineteen days since Rishi made that speech and I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He particularly mentioned.
- New gas-powered stations
- Trebling our offshore wind capacity
- Having new fleets of small modular reactors.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there will be winners all round.
Conclusion
Centrica’s plan for a massive hydrogen store at Rough, close to SSE’s existing gas storage in the salt caverns at Aldbrough, would appear to make sense, if the UK’s excess of offshore wind is converted into green hydrogen, which is then stored and distributed as needed.
Consultation On Plans For Keadby Hydrogen Power Station To Begin
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from SSE.
These four paragraphs outline the project
SSE and Equinor will consult on plans for a new hydrogen-fired power station in North Lincolnshire which would provide vital new reliable and flexible capacity to the electricity system.
Keadby Hydrogen Power Station is a proposed 900MW plant which could be operational from 2030 – bolstering security of supply and supporting the UK’s long-term decarbonisation by providing back-up low-carbon power to variable renewable generation.
The project will enter environmental scoping in April before SSE and Equinor launch a public consultation ahead of a full planning application being made in due course.
Under plans, the new power station will be designed to run on 100% hydrogen. The ambition is that this would be the case from inception, with Government already committed to deploying low-carbon infrastructure in the Humber – the UK’s most carbon intensive cluster.
Note.
- The hydrogen for this power station will be produced by electrolysis or one of the new turquoise methods.
- It will be stored in Aldborough or Rough gas storage.
- This will be the fourth power station at Keadby after Keadby 1 (734 MW), Keadby 2 (893 MW) and Keadby 3 (910 MW)
- Keadby 3 will be fitted with carbon capture.
- These total up to 3.4 GW.
The Keadby cluster of power stations will make good backup to the wind farms in the North Sea.
Energy Security Boost After Centrica And Repsol Agree LNG Supply Deal
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica Energy and Repsol today announced the signing of a deal that will improve the UK’s energy security in the coming years.
These two paragraphs give more details of the deal.
The deal will see Centrica purchase 1 million tonnes of Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) shipments between 2025 and 2027. All of these cargoes are expected to be delivered to the Grain LNG import terminal in Kent.
The deal marks an additional move by Centrica to build further resilience in the UK’s energy security. It follows a 15 year, $8bn deal with Delfin Midstream in July 2023, a three-year supply agreement with Equinor that will heat 4.5m UK homes through to 2024 and the reopening and expansion of the Rough gas storage facility in October 2022 and June 2023 respectively. Rough now provides half of the UK’s total gas storage capacity with the potential to store over 50 billion cubic feet (bcf) of gas, enough to heat almost 10% of UK homes throughout winter.
Centrica do seem to be keeping us supplied with gas.
Two days ago, National Grid published this press release, which is entitled Grain LNG Signs New Deal With Venture Global Further Strengthening The Security Of Supply Of LNG To The United Kingdom.
This is the sub-heading.
Today (5 February), Grain LNG and Venture Global have announced the execution of a binding long-term terminal use agreement (TUA) enabling the regasification and sale of LNG from all of Venture Global’s LNG terminals in Louisiana, including CP2 LNG, subject to obtaining necessary federal permits.
These two paragraphs give more details of the deal.
Under the agreement, Venture Global will have the ability to access 3 million tonnes per annum (3MTPA) of LNG storage and regasification capacity at the Isle of Grain LNG receiving terminal for sixteen years beginning in 2029, equivalent of up to 5% of average UK gas demand.
This is the second agreement from Grain LNG’s competitive auction process which was launched in September 2023. The successful outcome of the auction further secures the future of Europe’s largest LNG import terminal into the mid 2040s.
Two big deals in the same week is not to be sneezed at and must be good for the UK’s energy security.
Grain LNG
The Grain LNG web site, greets you with this message.
Welcome To Europe’s Largest Liquified Natural Gas Terminal, Grain LNG
Grain LNG is the gateway connecting worldwide LNG to the European energy market, making a genuine difference to people’s lives. Find out all about our cutting-edge operations – showcasing our leadership in powering the future – and why Grain LNG is at the forefront of energy as we move towards net zero.
There is also a video.
This Google Map shows the location of Grain LNG on the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- The River Medway flows into the River Thames between the Isle of Grain on the left and the Isle of Sheppey on the right.
- From South to North, the red arrows indicate, the National Grid – Grain Terminal, National Grid L N G and Grain LNG.
There would appear to be space for expansion.