Canal Water To Heat Some Of Liverpool’s Most Famous Buildings In Hi-Tech Carbon-Cutting Scheme
The title of this post is the same as that of this press release from Liverpool City Region.
These five bullet-points act as subheadings.
- Energy generated from Leeds and Liverpool canal by one of the UK’s largest water source heat pumps
- Announcement comes as Mersey Heat Energy Centre officially opens
- Scheme to connect Georges Dock, Cunard and the Museum of Liverpool buildings to Mersey Heat Network
- Joint project between Combined Authority, Liverpool City Council and National Museums Liverpool
- Key part of Combined Authority plan to reach net zero by 2035
These introductory paragraphs add more detail.
Three major public buildings on Liverpool’s waterfront are to slash carbon emissions by joining a heat network driven by energy from canal water.
Under the plan, an extended pipeline will connect Georges Dock building, the Cunard building, and the Museum of Liverpool, part of National Museums Liverpool (NML), to the Mersey Heat network.
The newly opened Mersey Heat Energy Centre is already supplying the Liverpool Waters site, the Titanic Hotel and the Tobacco Warehouse apartments.
It uses one of the UK’s largest water source heat pumps to extract energy from the Leeds and Liverpool Canal to power a network of heating pipes.
The project is the latest in the Liverpool City Region’s five-year carbon action plan and journey to reach net zero. The Combined Authority has recently secured an additional £35m to decarbonise dozens of other public buildings from the Department of Energy Security and Net Zero.
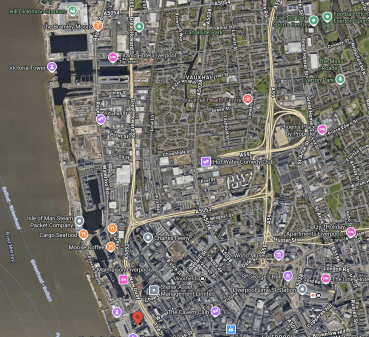
This map of the Liverpool Waterfront shows the canal and some of the buildings mentioned.
Note.
- In the top-left corner is Everton’s new Hill-Dickenson Stadium, which at the time of this map was under construction.
- The pink arrow to its right indicates the Titantic Hotel.
- The Leeds and Liverpool canal passes on the South side of the hotel.
- On the other bank of the canal is the Tobacco Warehouse.
- The canal goes East and then turns North before going all the way to Leeds. The Wikipedia entry gives full details of the canal.
- From the Titanic Hotel, the Leeds and Liverpool Canal also turns South and boats can go along Liverpool’s famous Waterfront to Canning Dock, in front of the Tate Liverpool.
- The red arrow marks the Liver Building.
- Georges Dock building, the Cunard building, and the Museum of Liverpool are just to the South the Liver Building.
- To the East of the Liver building, there is Liverpool City Centre, with beyond it Liverpool Lime Street station, with another collection of important buildings including St. George’s Hall, the Picton Library, World Museum and the Walker Art Gallery.
The Combined Authority will not have a shortage of buildings to decarbonise with the £35m from the Department of Energy Security and Net Zero.
These are my thoughts.
What Is A Water Source Heat Pump?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
A water source heat pump (WSHP) is a highly efficient, low-carbon renewable energy system that extracts heat from a nearby water source like a lake, river, or canal to provide heating and hot water for a building, and can also be used for cooling. It works by using electricity to transfer this thermal energy into the building’s heating system, offering a more efficient alternative to traditional boilers and reducing energy bills. There are two main types: closed-loop systems, which circulate a fluid through pipes submerged in the water, and open-loop systems, which directly pump and then discharge the water.
Is Mersey Heat Energy Centre A Closed Or Open-Loop Water Source Heat Pump?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The Mersey Energy Heat Centre uses an open-loop water source heat pump system. It abstracts water from the Leeds and Liverpool Canal, extracts heat from it, and then returns the water back to the dock system.
As the Leeds and Liverpool Canal is 127 miles long, and there appears from the map to be a lot of water in the docks at the Liverpool end, I would expect that Liverpool will have more than enough water to extract heat from.
Where Exactly Is The Mersey Heat Energy Centre?
In this article on Place North West, which is entitled Work Begins On Peel’s Mersey Heat Energy Centre, has this image, which is labelled as the Mersey Heat Energy Centre.
Note the large building in the foreground with the circular objects on the roof. Could these be fans or vents?
This Google Map shows the area.
Note.
- The two docks at the top of the map can be picked out in the image.
- The main breakwater on the left, which is marked Isle of Man Steam Packet Company, looks very similar to the one shown in the image.
- The bridge between the two docks on the left appears to be the same in both map and image.
I am fairly sure, that the large building on the breakwater with the three circles on the roof, is the Mersey Heat Energy Centre.
It certainly looks to be a building, that could provide a substantial amount of heat and power .
What Is The Output Of The Mersey Heat And Energy Centre?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The Mersey Heat and Energy Centre produces low-carbon heat for up to 6,700 homes and 1.3 million square feet of commercial space, aiming to deliver around 20GWh of heat per year. The project is also planned to expand to supply around 45GWh annually. This heat is delivered to buildings for their heating and hot water needs through the Mersey Heat network.
This article on Place North West, also has this similar answer.
Led by district heat network specialist Ener-Vate, the Mersey Heat Energy Centre will feature two 3MW water source heat pumps that would work on an ‘open loop’ system to take heat from water from the Leeds-Liverpool canal. This heat would be used to warm surrounding homes and businesses within six kilometres.
Plans form the first phase of Peel NRE’s Mersey Heat network. The initial project could supply 20GWh of heat every year, with planning permission secured to expand to supply around 45GWh – the equivalent of supplying heating and hot water to 17,000 homes.
It looks like we’re getting similar answers from different sources.
Does the Merseyside Area Have Enough Green Electricity To Power A Large Water Source Heat Pump?
In Could Liverpool Develop A Massive Zero-Carbon Data Centre?, I calculated the operational and planned offshore wind power in Liverpool Bay and got these results.
- 2509 MW has been commissioned.
- 3980 MW is being planned.
That is a total of 6489 MW or about twice the output of Hinckley Point C nuclear power station.
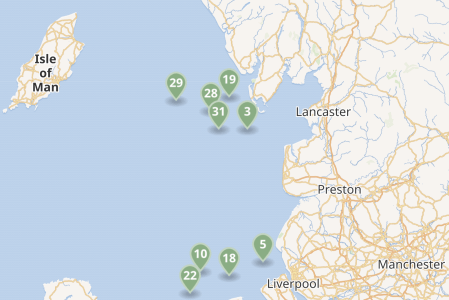
This map shows the existing wind farms in the sea between Liverpool, Lancashire and the Isle of Man.
Note.
- Each green arrow is a wind farm.
- There is the 2452 MW Heysham nuclear power complex near Lancaster.
- The Western HVDC Link is a 2250 MW connection between Hunterston in Western Scotland near Glasgow and Connah’s Quay on the Wirral.
- I also suspect more space in Liverpool Bay could be developed with wind farms.
Spinal Tap turned the power up to 11, Liverpool, being Liverpool, they have enough power to go to at least sixteen.
Will Merseyside Have Lots Of Data Centres?
Consider.
- It has the power.
- It has the water.
- The locals speak a form of English.
- Merseyside will be two hours from London by train.
- There are two Premier League football teams.
- The golf courses are good.
- It is a city that is famous all over the world.
I am sure the number of data centres will grow.
enfinium Announces Proposal For £200m Investment In Carbon Capture Project In North Wales
The title of this post is the same as that of this press release from enfinium.
This is the sub-heading.
The project could be capable of capturing up to 235,000 tonnes of CO2 every year, accelerating efforts to achieve net zero.
The first two paragraphs outline the project.
Today, enfinium, a leading UK energy from waste operator, announces it is progressing plans to invest around £200 million in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology at the Parc Adfer energy from waste facility in Deeside, North Wales, providing vital carbon removals and boosting the green economy.
The project could capture up to 235,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) every year. As over half of the waste processed at the facility is organic, installing CCS would enable the plant to take more CO2 out of the atmosphere than it produces. The Welsh Government’s Carbon Budget makes clear that Wales needs carbon removal solutions to mitigate other polluting parts of the economy to achieve a Net Zero economy.
The press release also says this about Paec Adfer.
Opened in 2019 in partnership with the five local authorities that make up the North Wales Residual Waste Treatment Partnership (NWRWTP), Parc Adfer currently diverts up to 232,000 tonnes of unrecyclable waste from climate damaging landfill. As recognised by the National Infrastructure Commission, emissions from energy from waste plants are lower per tonne of waste compared to landfill.
With CCS installed, Parc Adfer will support the Welsh Government’s ambition to have 100% zero carbon power by 2035 and support over 1,000 jobs in the green economy during the construction phase.
This Google Map shows the location of Parc Adfer, with respect to Liverpool and the River Dee.
Note.
- Liverpool is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Chester is in the South-East corner of the map.
- The Dee Estuary is in the North-West corner of the map.
- The red arrow indicates the location of Parc Adfer.
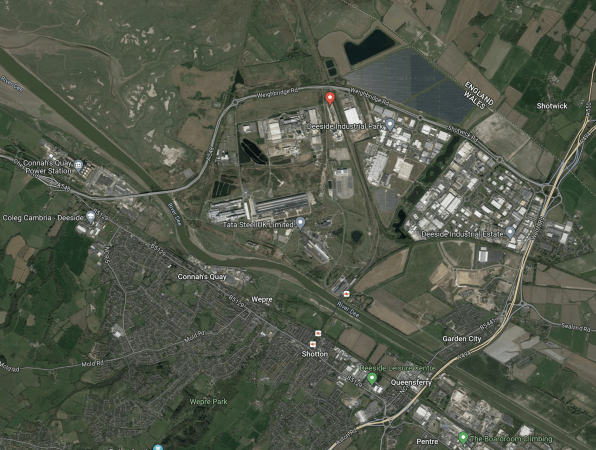
This second Google Map shows the location of Parc Adfer in Deeside Industrial Park, which is just over the England-Wales border.
As before, the red arrow indicates the location of Parc Adfer.
This third Google Map shows the detailed area of Parc Adfer.
Note.
- The red arrow indicates the location of Parc Adfer.
- The Borderlands Line between Liverpool and Wrexham runs alongside the site.
- Around Parc Adfer are assorted steel works and the Flintshire Bridge HVDC Convertor Station for the Western HVDC Link to Hunterston in Scotland.
- On the other side of the tracks are Amazon, Great Bear Distribution, Toyota, Unilever and the Toyota Deeside Solar Park.
These are my thoughts.
Parc Adfer Has Excellent Electrical Connections
In addition to the 2.25 GW Western HVDC Link to Hunterston, there are following power sources in the area.
- The wind farms of Liverpool Bay.
- The 1.4 GW Connah’s Quay power station.
- The 498 MW Deeside power station.
From the enfinium web site, it looks like Parc Adfer will generate 21 MW of zero-carbon energy from waste.
Will Parc Adfer Have A Rail Connection?
According to the enfinium web site, Parc Adfer will process waste from Flintshire County Council, Denbighshire County Council, Conwy County Borough Council, Gwynedd Council and the Isle of Anglesey County Council.
I have arranged these councils in order from East to West and all are served by the North Wales Coast Line.
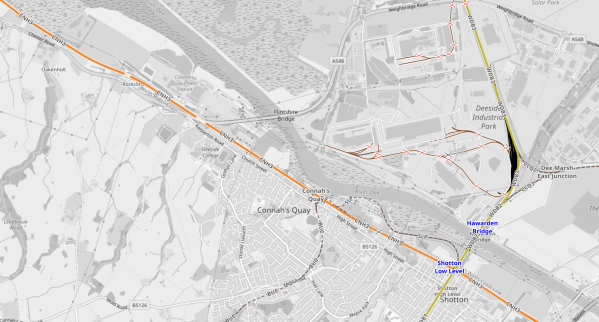
This OpenRailMap shows the rail connection between Parc Adfer and the North Wales Coast Line.
Note.
- The Borderlands Line is shown in yellow and runs between Liverpool and Wrexham.
- The Borderlands Line runs past Parc Adfer just off the North of the map.
- The North Wales Coast Line is shown in orange and runs between North Wales and Chester.
- There are two stations at Shotton; High and Low Levels, which allow a passenger connection.
Unfortunately, there is no rail connection for trains which would allow freight services between Parc Adfer and North Wales.
A section called Future, in the Wikipedia entry for Shotton station, says this about upgrading the station.
In March 2015 Network Rail published the draft version of their Welsh Route Study. It contained a proposal to build a new interchange station that would replace the existing High and Low Level stations, allowing for greater connectivity between the North Wales Coast Main Line and the Borderlands Line. The document recommended a transport planning study to establish the cost, feasibility and benefits of the proposed scheme.
It appears to be likely, that no rail route will be created to allow freight services between Parc Adfer and North Wales.
Deeside Parkway Railway Station
It does appear that a parkway station at Deeside Parkway is a possibility.
This is the opening paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for Deeside Parkway station.
Deeside Parkway is a proposed railway station situated between Neston and Hawarden Bridge on the Borderlands Line. The station is intended to serve the Deeside area of Flintshire, North Wales, particularly the Deeside Industrial Park.
The station is proposed to be park of the North Wales Metro, which is described in this Wikipedia entry.
MacHairWind Wind Farm
MachairWind wind farm has its own page on the ScottishPower Renewables web site.
These are the two introductory paragraphs.
The MacHairWind project off the coast of Islay, which could deliver 2GW of cleaner renewable energy, will make a significant contribution to tackling climate change and achieving Net Zero, with the potential to generate enough clean electricity to power over 2 million homes in Scotland.
It will also build on ScottishPower’s long-standing presence and positive track record of investing in and working with local communities and businesses across Argyll & Bute to realise the benefits of renewable energy developments.
This Google Map shows the area of the wind farm, which is to the North West of the island of Islay.
Note.
- There certainly is a large space of empty sea to the North-West of Islay.
- Glasgow is not far away.
This second Google Map shows the area to the North-East of Islay.
Note.
- Islay is in the South-West corner of the map.
- Colonsay is the smaller island to the North.
- In the North-East corner of the map the red arrow indicate Cruachan pumped hydro power station.
- In the South-East corner of the map is the Clyde Estuary, where the two nuclear power stations at Hunterston were located.
- Hunterston is also the Northern end of Western HVDC Link to North Wales.
Wikipedia says this about the relationship of the Cruachan power station and Hunterston’s nuclear stations.
Construction began in 1959 to coincide with the Hunterston A nuclear power station in Ayrshire. Cruachan uses cheap off-peak electricity generated at night to pump water to the higher reservoir, which can then be released during the day to provide power as necessary.
Now that the two nuclear stations are being decommissioned, will the MacHairWind wind farm be used to pump water to Cruachan’s higher reservoir?
Conclusion
The MacHairWind wind farm seems a well-positioned wind farm.
- It is close to Glasgow.
- It can be used in tandem with the Cruachan pumped hydro power station.
- It will have access to the Western HVDC Link to send power to the North-West of England.
Is Scotland replacing the 1.2 GW Hunterston B nuclear power station with a 2 GW wind farm, with help from Cruachan and other proposed pumped storage hydro schemes to the North of Glasgow?
It also looks like increasing the power at Cruachan from the current 440 MW to a GW, by the building of Cruachan 2 would give the area even more energy security.
Is There A Need For A Norfolk-Suffolk Interconnector?
The coast of East Anglia from the Wash to the Haven Ports of Felixstowe, Harwich and Ipswich is becoming the Energy Coast of England.
Starting at the Wash and going East and then South, the following energy-related sites or large energy users are passed.
Bicker Fen Substation
Bicker may only be a small hamlet in Lincolnshire, but it is becoming increasingly important in supplying energy to the UK.
Nearby is Bicker Fen substation, which connects or will connect the following to the National Grid.
- The 26 MW Bicker Fen onshore windfarm.
- The 1,400 MW interconnector from Denmark called Viking Link.
- The proposed 857 MW offshore wind farm Triton Knoll.
This Google Map shows the location of Bicker Fen with respect to The Wash.
Bicker Fen is marked by the red arrow.
The Google Map shows the substation.
It must be sized to handle over 2 GW, but is it large enough?
Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm
The Dudgeon offshore wind farm is a 402 MW wind farm, which is twenty miles off the North Norfolk coast.
- It has 67 turbines and an offshore substation.
- It is connected to the shore at Weybourne on the coast from where an underground cable is connected to the National Grid at Necton.
- It became operational in Oct 2017.
- Equinor and Statkraft are part owners of the windfarm and this is the home page of the wind farm’s web site.
- Equinor is the operator of the wind farm.
This Google Map shows the location of Weybourne on the coast.
Note.
- Weybourne is in the middle on the coast.
- Sheringham is on the coast in the East.
- Holt is on the Southern edge of the map almost South of Weybourne.
This second map shows the location of the onshore substation at Necton, with respect to the coast.
Note.
- The Necton substation is marked by a red arrow.
- Holt and Sheringham can be picked out by the coast in the middle.
- Weybourne is to the West of Sheringham.
- Necton and Weybourne are 35 miles apart.
Digging in the underground cable between Necton and Weybourne might have caused some disruption.
Looking at Weybourne in detail, I can’t find anything that looks like a substation. So is the Necton substation connected directly to Dudgeon’s offshore substation?
Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm
The Sheringham Shoal offshore wind farm is a 316.8 MW wind farm, which is eleven miles off the North Norfolk coast.
- It has 88 turbines and two offshore substations.
- As with Dudgeon, it is connected to the shore at Weybourne on the coast.
- But the underground cable is connected to an onshore substation at Salle and that is connected to the National Grid at Norwich.
- It became operational in Sept 2012.
- Equinor and Statkraft are part owners of the windfarm and this is the home page of the wind farm’s web site.
- Equinor is the operator of the wind farm.
This second map shows the location of the onshore substation at Salle, with respect to the coast.
Note.
- The Salle substation is marked by a red arrow.
- Holt, Weybourne and Sheringham can be picked out by the coast in the middle.
- Weybourne is to the West of Sheringham.
- Salle and Weybourne are 13.5 miles apart.
Could the following two statements be true?
- As the Sheringham Shoal wind farm was built first, that wind farm was able to use the shorter route.
- It wasn’t built large enough to be able to handle the Dudgeon wind farm.
The statements would certainly explain, why Dudgeon used a second cable.
Extending The Dudgeon And Sheringham Shoal Wind Farms
Both the Dudgeon And Sheringham Shoal web sites have details of the proposed join extension of both wind farms.
This is the main statement on the Overview page.
Equinor has been awarded an Agreement for Lease by the Crown Estate, the intention being to seek consents to increase the generating capacity of both the Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm and the Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm.
They then make three points about the development.
- Equinor is proposing a joint development of the two projects with a common transmission infrastructure.
- As part of the common DCO application, the Extension Projects have a shared point of connection at the National Grid Norwich Main substation.
- These extension projects will have a combined generating capacity of 719MW which will make an important contribution to the UK’s target of 30GW of electricity generated by offshore wind by 2030.
This statement on the Offshore Location page, describes the layout of the wind farms.
The Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm extension is to the north and the east of the existing wind farm, while its Dudgeon counterpart is to the north and south east of the existing Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm site. The proposed extension areas share the boundaries with its existing wind farm site.
They then make these two important points about the development.
- Equinor is seeking to develop the extension project with a joint transmission infrastructure. A common offshore substation infrastructure is planned to be located in the Sheringham Shoal wind farm site.
- The seabed export cable which will transmit the power generated by both wind farm extensions will make landfall at Weybourne.
There is also this map.
Note.
- The purple line appears to be the UK’s ten mile limit.
- The Sheringham Shoal Extension is outlined in red.
- The Dudgeon Extension is outlined in blue.
- The black lines appear to be the power cables.
I suspect the dotted blue lines are shipping routes sneaking their way through the turbines.
This statement on the Onshore Location page, describes the layout of the offshore and onshore cables.
A new seabed export cable will bring the electricity generated by both the Sheringham Shoal and Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm extensions to shore at Weybourne, on the coast of Norfolk.
They then make these two important points about the development.
- From there a new underground cable will be installed to transmit that power to a new purpose built onshore substation, which will be located within a 3km radius of the existing Norwich main substation, south of Norwich. This will be the National Grid network connection point for the electricity from both wind farm extensions.
- The power will be transmitted from landfall to the substation using an HVAC system which eliminates the need for any relay stations along the onshore cable route.
There is also this map.
It will be a substantial undertaking to build the underground cable between Weybourne and South of Norwich.
Bacton Gas Terminal
The Bacton gas terminal is a complex of six gas terminals about ten miles East of Cromer.
- It lands and processes gas from a number of fields in the North Sea.
- It hosts the UK end of the BBL pipeline to The Netherlands.
- It hosts the UK end of the Interconnector to Zeebrugge in Belgium.
- The Baird and Deborah fields, which have been developed as gas storage, are connected to the gas terminal. They are both mothballed.
This Google Map shows the location of the terminal.
Note.
- The Bacton gas terminal is marked by a red arrow.
- Sheringham is in the North West corner of the map.
- Cromer, Overstrand, Trimingham and Mundesley are resort towns and villages along the coast North of Bacton.
This second map shows the Bacton gas terminal in more detail.
Would you want to have a seaside holiday, by a gas terminal?
Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Vanguard
Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard are two wind farms under development by Vattenfall.
- Norfolk Boreas is a proposed 1.8 GW wind farm, that will be 45 miles offshore.
- Norfolk Vanguard is a proposed 1.8 GW wind farm, that will be 29 miles offshore.
This map shows the two fields in relation to the coast.
Note.
- The purple line appears to be the UK’s ten mile limit.
- Norfolk Boreas is outlined in blue.
- Norfolk Vsnguard is outlined in orange.
- Cables will be run in the grey areas.
This second map shows the onshore cable.
Note.
- The cables are planned to come ashore between Happisburgh and Eccles-on-Sea.
- Bacton gas terminal is only a short distance up the coast.
- The onshore cable is planned to go from here across Norfolk to the Necton substation.
But all of this has been overturned by a legal ruling.
This article on the BBC is entitled Norfolk Vanguard: Ministers Wrong Over Wind Farm Go-Ahead, Says Judge.
These are the first four paragraphs.
A High Court judge has quashed permission for one of the world’s largest offshore wind farms to be built off the east coast of England.
The Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Farm was granted development consent in July by the Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS).
But Mr Justice Holgate overturned the decision following legal action from a man living near a planned cable route.
A Department for BEIS spokeswoman said it was “disappointed by the outcome”.
I bet the spokeswoman was disappointed.
Vattenfall and the BEIS will go back to the drawing board.
But seriously, is it a good idea to dig an underground cable all the way across Norfolk or in these times build a massive overhead cable either?
Perhaps the solution is to connect the Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Vanguard wind farms to a giant electrolyser at Bacton, which creates hydrogen.
- The underground electricity cable across Norfolk would not be needed.
- Bacton gas terminal is only a few miles up the coast from the cable’s landfall.
- The UK gets another supply of gas.
- The hydrogen is blended with natural gas for consumption in the UK or Europe.
- A pure hydrogen feed can be used to supply hydrogen buses, trucks and other vehicles, either by tanker or pipeline.
- Excess hydrogen could be stored in depleted gas fields.
The main benefit though, would be that it would transform Bacton gas terminal from a declining asset into Norfolk’s Hydrogen Powerhouse.
Great Yarmouth And Lowestoft
Great Yarmouth Outer Harbour and the Port of Lowestoft have not been the most successful of ports in recent years, but with the building of large numbers of wind farms, they are both likely to receive collateral benefits.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see the support ships for the wind farms switching to zero-carbon power, which would require good electrical connections to the ports to either charge batteries or power electrolysers to generate hydrogen.
Sizewell
Sizewell has only one nuclear power station at present; Sizewell B, but it could be joined by Sizewell C or a fleet of Small Modular Reactors (SMR).
The Sizewell Overhead Transmission Line
Sizewell also has a very high capacity overhead power line to Ipswich and the West.
I doubt, it would be possible to build an overhead transmission line like this today.
Sizewell And Hydrogen
EdF, who own the site are involved with Freeport East and may choose to build a large electrolyser in the area to create hydrogen for the Freeport.
East Anglia Array
The East Anglia Array will be an enormous wind farm., comprising up to six separate projects.
It will be thirty miles offshore.
It could generate up to 7.2 GW.
The first project East Anglia One is in operation and delivers 714 MW to a substation in the Deben Estuary, which connects to the Sizewell high-capacity overhead power line.
Most projects will be in operation by 2026.
Freeport East
As the Freeport develops, it will surely be a massive user of both electricity and hydrogen.
Problems With The Current Electricity Network
I don’t believe that the current electricity network, that serves the wind farms and the large energy users has been designed with the number of wind farms we are seeing in the North Sea in mind.
Every new windfarm seems to need a new connection across Norfolk or Suffolk and in Norfolk, where no high-capacity cables exist, this is stirring up the locals.
There is also no energy storage in the current electricity network, so at times, the network must be less than efficient and wind turbines have to be shut down.
Objections To The Current Policies
It is not difficult to find stories on the Internet about objections to the current policies of building large numbers of wind farms and the Sizewell C nuclear power station.
This article on the East Anglia Daily Times, which is entitled Campaigners Unite In Calling For A Pause Before ‘Onslaught’ Of Energy Projects ‘Devastates’ Region is typical.
This is the first paragraph.
Campaigners and politicians have called on the Government to pause the expansion of the energy industry in Suffolk, which they fear will turn the countryside into an “industrial wasteland” and hit tourism.
The group also appear to be against the construction of Sizewell C.
I feel they have a point about too much development onshore, but I feel that if the UK is to thrive in the future we need an independent zero carbon energy source.
I also believe that thousands of wind farms in the seas around the UK and Ireland are the best way to obtain that energy.
Blending Hydrogen With Natural Gas
Blending green hydrogen produced in an electrolyser with natural gas is an interesting possibility.
- HyDeploy is a project to investigate blending up to 20 % of green hydrogen in the natural gas supply to industrial and domestic users.
- Partners include Cadent, ITM Power, Keele University and the Health and Safety Executive.
- Natural gas naturally contains a small amount of hydrogen anyway.
- The hydrogen gas would be distributed to users in the existing gas delivery network.
I wrote about HyDeploy in a post called HyDeploy.
Thje only loser, if hydrogen were to be blended with natural gas would be Vlad the Poisoner, as he’d sell less of his tainted gas.
An Interconnector Between Bicker Fen And Freeport East
I believe that an electricity interconnector between at least Bicker Fen and Freeport East could solve some of the problems.
My objectives would be.
- Avoid as much disruption on the land as possible.
- Create the capacity to deliver all the energy generated to customers, either as electricity or hydrogen.
- Create an expandable framework, that would support all the wind farms that could be built in the future.
The interconnector would be a few miles offshore and run along the sea-bed.
- This method of construction is well proven.
- It was used for the Western HVDC Link between Hunterston in Scotland and Connah’s Quay in Wales.
- Most wind farms seem to have existing substations and these would be upgraded to host the interconnector.
Connections en route would include.
Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm
The interconnector would connect to the existing offshore substation.
Sheringham Shoal Wind Farm
The interconnector would connect to the existing offshore substation.
Dudgeon and Sheringham Shoal Extension Offshore Wind Farms
These two wind farms could be connected directly to the interconnector, if as planned, they shared an offshore substation in the Sheringham Shoal Extension offshore wind farm.
Bacton Gas Terminal
I would connect to the Bacton Gas Terminal, so that a large electrolyser could be installed at the terminal.
The hydrogen produced could be.
- Stored in depleted gas fields connected to the terminal.
- Blended with natural gas.
- Exported to Europe through an interconnector.
- Supplied to local users by truck or pipeline.
After all, the terminal has been handling gas for over fifty years, so they have a lot of experience of safe gas handling.
Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Vanguard
These two wind farms could be connected directly to the interconnector, if they shared an offshore substation.
It would also help to appease and silence the objectors, if there was no need to dig up half of Norfolk.
Great Yarmouth And Lowestoft
It might be better, if these ports were supplied from the interconnector.
- Either port could have its own electrolyser to generate hydrogen, which could be.
- Used to power ships, trucks and port equipment.
- Liquefied and exported in tankers.
- Used to supply local gas users.
- Hydrogen could be supplied to a converted Great Yarmouth power station.
Both Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft could become hydrogen hub towns.
Sizewell
This site has a high-capacity connection to the National Grid. This connection is a big eyesore, but it needs to run at full capacity to take electricity from the Energy Coast to the interior of England.
That electricity can come from Sizewell B and/or Sizewell C nuclear power stations or the offshore wind farms.
East Anglia Array
There would probably need to be a joint offshore substation to control the massive amounts of electricity generated by the array.
Currently, the only wind farm in operation of this group is East Anglia One, which uses an underground cable connection to the Sizewell high-capacity connection to the Bullen Lane substation at Bramford.
Freeport East, Ipswich And Bullen Lane Substation
This Google Map shows the area between Ipswich and the coast.
Note.
- Sizewell is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Felixstowe, Harwich and Freeport East are at the mouth of the rivers Orwell and Stour.
- The Bullen Lane substation is to the West of Ipswich and shown by the red arrow.
I would certainly investigate the possibility of running an underwater cable up the River Orwell to connect the Southern end of the interconnector Between Bicker Fen And Freeport East.
This Google Map shows the Bullen Lane Substation.
It looks impressive, but is it big enough to handle all the electricity coming ashore from the offshore wind farms to the East of Suffolk and the electricity from the power stations at Sizewell?
Conclusion
I believe there are a lot of possibilities, that would meet the threeobjectives, I stated earlier.
- Avoid as much disruption on the land as possible.
- Create the capacity to deliver all the energy generated to customers, either as electricity or hydrogen.
- Create an expandable framework, that would support all the wind farms that could be built in the future.
In addition, simple mathematics says to me, that either there will need to be extra capacity at both Bicker Fen and Bullen Lane substations and onward to the rest of the country, or a large electrolyser to convert several gigawatts of electricity into hydrogen for distribution, through the gas network.
Expansion Plan To Take World’s Biggest Battery Storage Project To 3GWh Capacity
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Energy Storage News.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Plans to nearly double the output and capacity of the world’s biggest battery energy storage system (BESS) project to date have been announced by its owner, Vistra Energy.
The Texas-headquartered integrated utility and power generation company said it wants to add another 350MW/1,400MWh BESS to the Moss Landing Energy Storage Facility in California’s Monterey Bay.
The project is based at the Moss Landing Power Plant, which was once the largest power plant in the state of California, with a generation capacity of 2560 MW.
There appear to be three phases.
- Phase 1 is 300MW/1,200MWh and went online at the end of 2020
- Phase 2 is 100MW/400MWh and went online in August 2021.
- Phase 3 will be 350MW/1,400MWh.
This gives a maximum power output of 750 MW and prospective total capacity of 3 GWh. At full power, the battery could supply 750 MW for four hours.
For comparison, the two Scottish batteries I talked about in Amp Wins Consent For 800MW Scots Battery Complex, have a combined output of 800 MW and a total capacity of 1600 MWh, which would give a full power run of two hours.
Could the difference be that Scotland has 9.3 GW of installed windpower, whereas the much larger California has only 6 GW?
Both Scotland and California also have some pumped storage power stations.
- Drax Group who own the 7.1 GWh Cruachan power station, plan to increase its generating capacity from 440MW to 1040MW.
- California has two larger stations at Castaic and Helms.
- After writing about the Western HVDC Link in Amp Wins Consent For 800MW Scots Battery Complex, I wonder if when the wind is blowing in Scotland and it isn’t in Wales, that electricity can be exported from Scotland to Wales for storage.
This all shows the complex integrated nature of electricity networks.
Amp Wins Consent For 800MW Scots Battery Complex
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on renews.biz.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Canadian storage player Amp Energy has revealed that its 800MW battery portfolio in Scotland has secured planning consent.
The portfolio is due to be operational in April 2024 and will comprise two 400MW battery facilities, each providing 800 megawatt-hours of energy storage capacity.
Some other points from the article.
- The two facilities will be located at Hunterston and Kincardine.
- They will be the two largest grid-connected battery storage facilities in Europe.
- The two batteries will be optimised by Amp Energy‘s proprietary software.
This Google Map shows the Hunterston area.
Note.
- The Hunterston A and Hunterston B nuclear power stations, which are both being decommissioned.
- Hunterston B only shut down on the 7th of January, this year.
- There is also a large brownfield site in the North-East corner of the map.
This second Google Map shows the South-East corner of the nuclear power station site.
It’s certainly got a good grid connection.
But then it had to support.
- The Hunterston A nuclear power station rated at 360 MW.
- The Hunterston B nuclear power station rated at 1.2 GW.
- The Western HVDC Link, which is an interconnector to Connah’s Quay in North Wales, that is rated at 2.2 GW.
I’m sure that National Grid has a suitable socket for a 400 MW battery.
This Google Map shows the Kincardine area.
Note.
- The Clackmannanshire Bridge down the Western side of the map.
- The Kincardine Substation to the East of the bridge close to the shore of the River Forth.
- The 760 MW Kincardine power station used to be by the substation, but was demolished by 2001.
As at Hunterston, I’m sure that National Grid could find a suitable socket for a 400 MW battery.
Amp Energy’s Philosophy
As a trained Control Engineer I like it.
- Find a well-connected site, that can handle upwards of 400 MW in and out.
- Put in a 800 MWh battery, that can handle 400 MW in and out.
- Optimise the battery, so that it stores and supplies electricity as appropriate.
- Throw in a bit of artificial intelligence.
Old power station sites would seem an ideal place to site a battery. Especially, as many demolished coal, gas and nuclear stations are around 400-600 MW.
It should be noted that Highview Power are building a 50 MW/400 MWh CRYOBattery on an old coal-fired power station site in Vermont.
The Western HVDC Link
I mentioned earlier that the Northern end of the Western HVDC Link, is at Hunterston.
The Wikipedia entry for the Western HVDC Link, says this about the link.
The Western HVDC Link is a high-voltage direct current (HVDC) undersea electrical link in the United Kingdom, between Hunterston in Western Scotland and Flintshire Bridge (Connah’s Quay) in North Wales, routed to the west of the Isle of Man.[2] It has a transmission capacity of 2,250 MW and became fully operational in 2019.
The link is 262 miles long.
This Google Map shows the Connah’s Quay area in North Wales.
Note.
- The red arrow indicates the Flintshire Bridge HVDC converter station, which is the Southern end of the Western HVDC Link.
- The Borderlands Line between Liverpool and Chester, runs North-South to the East of the convertor station.
- To the East of the railway are two solar farms. The Northern one is Shotwick Solar Park, which at 72 MW is the largest solar farm in the UK.
- To the West of the converter station, just to the East of the A 548 road, is the 498 MW Deeside power station.
- Follow the A548 road to the West and over the River Dee, the road passes South of the 1420 MW Connah’s Quay Power station.
- The two power stations burn gas from Liverpool Bay.
- There are a lot of wind turbines along the North Wales Coast and Liverpool Bay.
The map also shows a lot of high electricity users like Tata Steel.
I can certainly see why the Western HVDC Link was built to connect Scotland and North Wales.
- There is a lot of renewable energy generation at both ends.
- There are heavy electricity users at both ends.
- The Scottish Central Belt is at the North.
- Greater Merseyside is at the South.
The Western HVDC Link is an electricity by-pass, that must have avoided expensive and controversial construction on land.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see another 400 MW/800 MWh battery at the Southern end.
Conclusion
The Canadians seem to have bagged two of the best battery sites in Europe.
- Both sites would appear to be able to handle 400 MW, based on past capabilities.
- There is lots of space and extra and/or bigger batteries can probably be connected.
- Scotland is developing several GW of wind power.
I can see Amp Energy building a series of these 400 MW sites in the UK and around Europe.
This is the big news of the day!