The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
A floating solar farm described as the UK’s largest is to be built in the north of England after planning permission was approved.
These three paragraphs add more details.
The 46,500-panel array will be installed at the Port of Barrow’s Cavendish Dock in Cumbria and will be capable of producing enough energy to power 14,000 homes a year.
It will be built by Associated British Ports (ABP) and will be used to power the area’s advanced manufacturing sector, including submarine-maker BAE Systems.
The company’s divisional port manager Bryan Davies said the solar farm would “drive economic growth” and was a major milestone in the company’s plans to develop Port of Barrow.
This Google Map shows Cavendish Dock in the centre of Barrow-in-Furness.
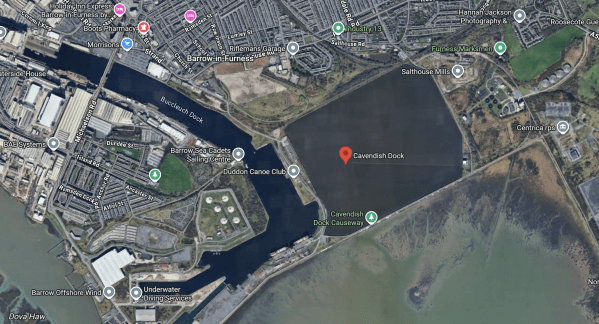
Note.
- BAe Systems are in the West side of the map.
- It looks like the picture on the BBC article was taken from the East.
- In the picture the Cavendish Causeway runs across the bottom-left Corner.
- The solar array appears to be in the North side of the dock.
The solar array will be an impressive structure, when it is complete.
November 30, 2025
Posted by AnonW |
Energy | ABP, BAe Systems, Barrow-in-Furness, Floating Solar Power, Port Of Barrow, Shipbuilding, Solar Power, Submarine |
Leave a comment
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
RWE officially opened its ‘Grimsby Hub’ offshore wind operations and maintenance (O&M) facility in the UK on 9 July. From the new O&M base, located at Associated British Ports’ (ABP) Port of Grimsby, RWE’s teams will maintain and operate the Triton Knoll and Sofia offshore wind farms.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The Grimsby Hub also houses RWE’s new UK Centralised Control Room (CCR), which has been set up to provide 24/7 monitoring of the company’s UK offshore wind farms and can provide services such as marine coordination, turbine operations, alarm management, high voltage monitoring and Emergency Response services with a team of twelve operatives, the developer says.
The O&M facility is already employing over 90 Full-Time Equivalents (FTEs), according to RWE, and is expected to employ around 140 RWE staff by 2027, as well as create approximately 60 new locally sourced jobs through the development of the CCR and ongoing offshore operations.
Note.
- Does RWE’s new UK Centralised Control Room control all their UK offshore wind farms?
- I have added them all up and there are almost 12 GW around our shores.
- I’ve read somewhere, that RWE are the UK’s largest power generator. From these figures, that would not surprise me.
This Google Map shows the location of RWE’s facilities in Grimsby.
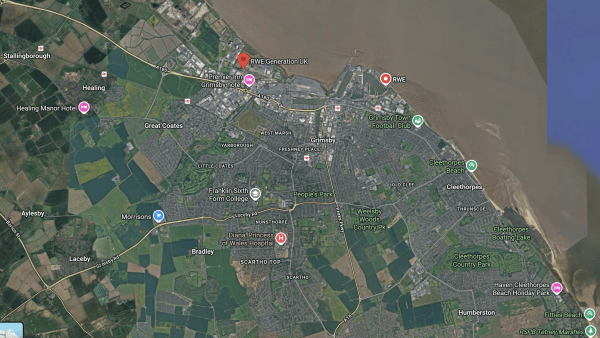
Note.
- The bright red arrow at the top of the map indicates RWE Generation UK in Grimsby Docks.
- There is another RWE location to the right of the bright red arrow.
- There is a line of stations along the coast, which from left-to-right are Stallingborough, Healing, Great Coates, Grimsby Town, Grimsby Docks, New Clee and Cleethorpes.
- Cleethorpes is not shown on the map.
- Doncaster and Cleethorpes are 52.1 mile apart, which is within the range of a battery-electric Hitachi and other trains.
- Charging would be at Doncaster, which is fully electrified and at Cleethorpes, by a short length of electrification.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the layout of and the railways around Grimsby Dock.
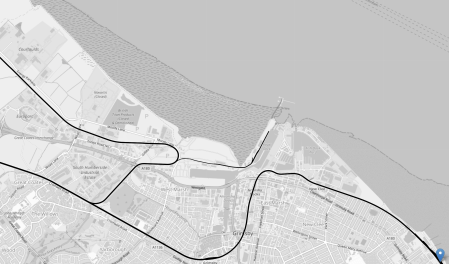
Note.
- Cleethorpes station is indicated by the blue arrow, in the South-East corner of the map.
- Cleethorpes station has four platforms, but no electrification.
- Grimsby Docks are to the North of the railway to Cleethorpes.
- This Wikipedia entry for Cleethorpes station, shows other railways and light railways served the area. Some were even electric.
These are a few of my thoughts on the development of railways between Sheffield and Cleethorpes.
RWE Will Be A Large Driver Of Employment In Grimsby
Earlier I wrote.
- Does RWE’s new UK Centralised Control Room control all their UK offshore wind farms?
- I have added them all up and there are almost 12 GW around our shores.
- I’ve read somewhere, that RWE are the UK’s largest power generator. From these figures, that would not surprise me.
It’s a long time, since I’ve added resources to a large project, so I asked Google AI, “How many people are needed to support a 1 GW offshore wind farm in the UK?”, and received this answer.
Based on data from large-scale UK offshore wind projects, a 1 GW (1,000 MW) offshore wind farm generally requires between 300 and 600+ people to operate and maintain, depending on whether the staff count includes direct operations, service vessel crews, and long-term supply chain partners.
Operational Staffing: Ørsted’s 1.2 GW Hornsea 1 and 1.3 GW Hornsea 2 projects are supported by an East Coast Hub in Grimsby, which maintains a workforce of over 600 people.
Direct & Indirect Support: For a large-scale project, this often breaks down into approximately 100–150 direct, permanent, high-skilled roles (technicians, engineers, management) and hundreds more in indirect, contracted, or supply chain roles (vessel crews, port operations, logistics).
Industry Average: Studies suggest that for operations and maintenance (O&M), around 50–100 full-time equivalent (FTE) jobs are generated per GW of installed capacity in terms of direct, permanent staff.
Key Takeaways for a 1 GW Farm:
- Direct Technicians/Operators: ~100–200+ (working on-site, turbines, or in control rooms).
- O&M Support Services: ~300–400+ (vessel operators, port logistics, supply chain).
- Total Operations Personnel: 300–600+ people.
Google AI appeared to have borrowed the figure from Ørsted and Hornsea 1 and 2.
So if it’s correct, there will be a total of 7,200 personnel supporting RWE’s wind farms in the UK. Even if only a third were employed in Grimsby, that is still a lot of people to accommodate and who will need to travel to work.
I also think a lot of personnel will come in by train, as the station is close to RWE’s locations.
Will Grimsby Have An Aberdeen-Sized Office-Shortage Problem?
One of the biggest problems, I was always hearing in the 1970s, was the shortage of offices in Aberdeen for the use of the oilmen.
In RWE Goes For An Additional 10 GW Of Offshore Wind In UK Waters In 2030, I talked about RWE’s plans for the future and published this table of new wind farms.
- Sofia – 1,400 MW
- Norfolk Boreas – 1380 MW
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW
- Dogger Bank South – 3000 MW
- Awel y Môr – 500 MW
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW
- North Falls – 504 MW
Note.
- Sofia is nearly complete.
- Only the three Norfolk and the Dogger Bank South wind farms are on the East side of England and suitable to be serviced from Grimsby., but they still total 7,140 MW.
Has Grimsby got the office-space for all the people needed?
Could The Cleethorpes And Liverpool Lime Street Service Be Run By Battery-Electric Rolling Stock?
The various sections of this route are as follows.
- Cleethorpes and Doncaster – No Electrification – 52.1 miles
- Doncaster and Meadowhall – No Electrification – 15.2 miles
- Meadowhall and Sheffield – No Electrification – 3.4 miles
- Sheffield and Dore & Totley – No Electrification – 4.2 miles
- Dore & Totley and Hazel Grove – No Electrification – 29.2 miles
- Hazel Grove and Stockport – Electrification – 3.3 miles
- Stockport and Manchester Piccadilly – Electrification – 5.9 miles
- Manchester Piccadilly and Deansgate – Electrification – 0.8 miles
- Deansgate and Liverpool South Parkway -Not Electrified – 28.2 miles
- Liverpool South Parkway and Liverpool Lime Street – Electrified – 5.7 miles
Adding the sections together gives.
- Cleethorpes and Hazel Grove – No Electrification – 104.1 miles
- Hazel Grove and Deansgate – Electrification – 10 miles
- Deansgate and Liverpool South Parkway -Not Electrified – 28.2 miles
- Liverpool South Parkway and Liverpool Lime Street – Electrified – 5.7 miles
Note.
- To cover the 104.1 miles to Hazel Grove battery-electric trains would probably need to leave Cleethorpes with full batteries.
- Doncaster is a fully-electrified station and passing trains may be able to have a quick top-up.
- In South Yorkshire Now Has Better North-South Connections, I calculated that Doncaster is a very busy station with 173 express trains per day calling at the station or one every 8.5 minutes.
- Will trains be able to stop for a long period to charge batteries?
- It may be prudent to electrify between Meadowhall and Sheffield, under the Midland Mainline Electrification.
- Sheffield and Dore & Totley is shown that it will be electrified, under the Midland Mainline Electrification.
- Do we really want to have electrification marching along the Hope Valley Line?
- I believe that hydrogen-hybrid locomotives will be a better solution for freight trains on scenic lines like the Hope Valley, as they are zero-carbon, powerful and with a range comparable to diesel.
I believe CAF, Hitachi and Siemens have off the shelf rolling stock and factories in this country, who could build trains for the Cleethorpes and Liverpool Lime Street route.
How Would You Charge Battery-Electric Trains At Cleethorpes?
This picture shows Cleethorpes station
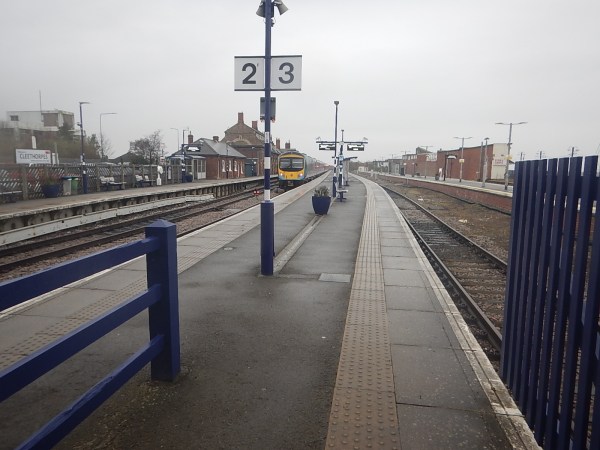

Note.
- The four long platforms without electrification.
- The platforms have recently been refurbished.
- The train in Platform 2 is a TransPennine Express Class 185 Siemens Desiro diesel train.
The simplest way to electrify the station would be to put up enough 25 KVAC overhead wires, so that battery-electric trains needing a charge could put up a pantograph and have a refreshing drink.
In Technology Behind Siemens Mobility’s British Battery Trains Hits The Tracks, I wrote about Siemens Rail Charging Converter.
This is a visualisation of a Siemens Rail Charging Converter in action.

Note.
- The track is electrified with standard 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- The train is a standard Siemens electric or battery-electric train.
- Siemens Rail Charging Converter, which is the shed in the compound on the left is providing the electricity to energise the catenary.
- I suspect, it could power third rail electrification, if the Office of Rail and Road ever allowed it to be still installed.
- The Siemens Rail Charging Converter does have one piece of magic in the shed. I suspect it uses a battery or a large capacitor to help power the electrification, as it can be powered from any typical domestic grid supply.
- I also wonder, if it has safety devices that cut the power outside the shed if track workers or intruders are detected, where they shouldn’t be?
- It could even cut the power, when trains are not running to save power and increase safety.
This looks to me, that a Siemens Rail Charging Converter could be a superb example of out-of-the-box thinking.
Could The Cleethorpes And Barton-on-Humber Service Be Run By Battery-Electric Rolling Stock?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the railways of North-East Lincolnshire.
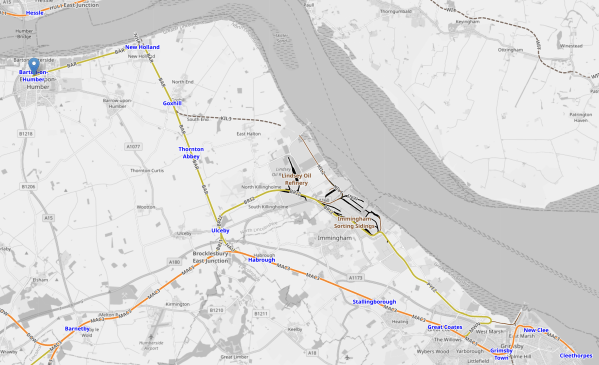
Note.
- Cleethorpes is in the South-East Corner of the map.
- Barton-on-Humber is in the North-West corner of the map and marked by a blue-arrow.
- Stations from South to North would be New Clee, Grimsby Docks, Grimsby Town, Great Coates, Healing, Stallingborough, Habrough, Ulceby, Thornton Abbey, Goxhill, New Holland and Barrow Haven.
- The line is double track.
- Cleethorpes and Barton-on-Humber is just 22.8 miles.
- A round trip would be under fifty miles, which would be well within range of a full-charge at one end.
- Service is one train per two hours (tp2h), which would only need a single train, shuttling between Cleethorpes and Barton-on-Humber.
- Two trains could provide an hourly service.
I would expect, that well-designed, solid and reliable German engineering could build a Siemens’ Rail Charging Connector that could charge four trains per hour (tph) at Cleethorpes station.
At present services are.
- TransPennineExpress – 1 tph to Liverpool Lime Street.
- East Midlands Railway – 1 tp2h to Barton-on-Humber
- East Midlands Railway – 1 tp2h to Matlock via Lincoln and Nottingham
- Northern Trains – 1 train per day (tpd) Sheffield via Brigg.
That is probably only about two tph.
Could The Cleethorpes And Sheffield Service Be Run By Battery-Electric Rolling Stock?
This is a description of the current Cleethorpes and Sheffield service.
- It is run by Northern Trains.
- The morning train leaves Sheffield at 09:54 and arrives in Cleethorpes at 11:40.
- The afternoon train leaves Cleethorpes at 13:20 and arrives in Sheffield at 15:10.
- The train is a Class 150 diesel train, which is a bit of a Joan Collins of a train – Of a certain age, but still scrubs up extremely well!
- Intermediate stations are Worksop, Retford, Gainsborough Central, Kirton Lindsey, Brigg, Barnetby and Grimsby Town
- The route length is 71.6 miles
- Trains take about 45-50 minutes.
It is also a parliamentary train.
The Wikipedia entry for parliamentary train gives this description of the Cleethorpes and Sheffield service.
Via Kirton Lindsey & Brigg. Became a parliamentary service when weekday services were withdrawn in 1993. Regular trains have operated between Gainsborough and Sheffield for most timetable periods since. Suspended January 2022 by Northern, who cited COVID-19 and staffing issues , but the service was reinstated in December 2022. Changed in May 2023 to be one return journey on weekdays only.
In the 1950s and 1960s I lived in Felixstowe part of the time and in the 1970s and 1980s I lived near Woodbridge and I observed first hand the development of the Port of Felixstowe and the effects it had on the surrounding countryside.
The development of the Port of Felixstowe, has brought the following.
- Improved roads and railways.
- Ipswich is now an hour from London by train.
- Ipswich is now a University town.
- New housing and other developments, both in Ipswich and Felixstowe and the surrounding countryside.
- Employment also has increased considerably, both in the Port and in surrounding towns.
- Ipswich’s football team is very much respected all over Europe and has won the English top division, the FA Cup and the UEFA Cup.
When you consider the jobs that RWE could create in the Port of Grimsby, I believe that this could have similar effects in Grimsby and Cleethorpes, as the Port of Felixstowe had in East Suffolk.
Already, the following are being talked about.
- A direct rail link between Cleethorpes and Grimsby to London.
- Battery-electric trains between Cleethorpes and Grimsby and Doncaster, Manchester and Liverpool Lime Street.
I believe that an improved rail link between Cleethorpes and Sheffield could be the catalyst for much needed housing along the route, which would be to the benefit of Cleethorpres, Grimsby, Sheffield and all the intermediate towns and villages on the route.
and the affects this will have on the countryside around the town, I believe that a strong case can be made out for a more frequent service between Cleethorpes and Sheffield.
July 16, 2025
Posted by AnonW |
Artificial Intelligence, Design, Energy, Sport, Transport/Travel | ABP, Ørsted, Barton Line, Battery-Electric Trains, Class 185 Train, Cleethorpes Station, Development, Dore and Totley Station, East Midlands Railway, Football, Google AI, Grimsby, Grimsby Town, Hitachi Intercity Battery Train, Hope Valley Line, Housing, Innovation, Ipswich Town, Lincoln Station, Liverpool Lime Street Station, Matlock Station, Midland Main Line, Midland Main Line Electrification, North Sea Oil And Gas, Northern Trains, Nottingham Station, Office Of Rail And Road, Offshore Wind Power, Port of Felixstowe, Port Of Grimsby, RWE, RWE Grimsby Hub, Sheffield Station, Siemens Desiro, Siemens' Rail Charging Converter, Sofia Wind Farm, Triton Knoll Wind Farm, UK Port Development, University Of Suffolk, Wind Power |
2 Comments
The title of this post, is the same as this article in Ground Engineering.
This is the sub-heading.
Port Talbot in Wales and Port of Cromarty Firth in Scotland have advanced to the next stage of a government funding scheme to develop port infrastructure that will facilitate floating offshore wind.
These three paragraphs introduce the developments.
The UK Government has agreed that the port expansion projects should progress to the next stage of its floating offshore wind manufacturing investment scheme (FLOWMIS) known as the primary list phase.
Up to £160M of grant funding will be allocated to certain investments in the floating offshore wind sector under the scheme.
The money will go towards funding the basic infrastructure necessary to support the assembly of floating offshore wind turbines. This includes the construction, replacement and upgrade of port infrastructure to accommodate large components such as towers and blades, as well as steel and concrete foundations and mooring cables required for floating offshore wind.
The article also says this about Port Talbot.
The Future Port Talbot project in south Wales would see the port transformed into a major hub for the manufacturing, assembly, and integration of floating offshore wind components for projects in the Celtic Sea.
Associated British Ports (ABP), which owns and operates the port, welcomed the government’s decision.
Note.
- Port Talbot will almost certainly use locally produced steel.
- There appears to be at least 4,832 MW of floating wind to be developed in the Celtic Sea in the next few years.
Port Talbot would be ideally placed to handle both English and Welsh coasts and waters in the Celtic Sea.
The article also says this about the Port of Cromarty Firth.
The Port of Cromarty Firth (PoCF) on the east coast of the Scottish Highlands will undergo a fifth phase of expansion work. This will develop the facilities and infrastructure necessary to enable the port to support offshore wind infrastructure projects off the coast of Scotland.
Over £50M has also been earmarked for the port’s expansion.
There appears to be at least 15,216 MW of floating wind to be developed in Scotland in the next few years.
Both ports seem to have welcomed the funding.
Adding the plans for Scotland and the Celtic Sea together gives a figure of just over 20 GW of floating wind to be developed in the next few years.
Conclusion
Surely, the award of funding for floating wind, is a good way to create a new industry and jobs in these two areas and also perform some sensible levelling-up.
I also suspect that spending £160 million to enable the construction of 20 GW of floating wind farm is a good return on the investment.
March 25, 2024
Posted by AnonW |
Energy | ABP, Celtic Sea, Development, Floating Wind Power, FLOWMIS, Inverness & Cromarty Firth Green Freeport, Levelling Up, Offshore Wind Power, Port Talbot, UK Port Development |
5 Comments
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
BW Ideol and Associated British Ports (ABP) have signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) that will see the manufacturer of concrete floating wind foundations and ABP investigating the feasibility of serial production at Port Talbot. The MOU has been signed in preparation for the Celtic Sea leasing round, BW Ideol said on Monday (11 December).
These two paragraphs outline the plans of BW Ideol and ABP have for Port Talbot.
According to the company, Port Talbot is the only Celtic Sea port with the scale and technical capabilities to fully maximise the Celtic Sea supply chain opportunity and is ideally located as a manufacturing base since it lies 120-140 kilometres from the floating offshore wind areas outlined by The Crown Estate for the upcoming leasing round.
The news on the MOU between ABP and BW Ideol comes shortly after ABP announced plans to invest around GBP 500 million (approximately EUR 573 million) to upgrade a site in Port Talbot and turn it into a major floating offshore wind hub.
This Google Map shows Port Talbot Port.

Note.
- It also looks like there is a Heidelberg Cement facility at the South side of the port.
- Port Talbot also has a Tata steelworks.
- The railway and the M4 Motorway are nearby.
- There’s certainly a lot of water.
The port appears well-placed for raw materials and there is quite a bit of free space to build and launch the concrete floaters.
This page on the BW Ideol web site describes their Floatgen demonstrator.
The first section is headed by BW Ideol’s First Floater In Operation, where this is said.
Built around a European consortium of 7 partners, Floatgen is a 2MW floating wind turbine demonstrator installed off the coast of Le Croisic on the offshore experimentation site of the Ecole Centrale de Nantes (SEM-REV). This project is being supported by the European Union as part of the FP7 programme. Floatgen is France’s first offshore wind turbine. 5 000 inhabitants are supplied with its electricity.
It looks like it is or almost is a proven system.
The page talks of two large benefits.
- Innovation at all levels.
- The highest local content of any floating wind turbine.
For the second, the following is said
In comparison to other steel floating foundations, which are imported from abroad, the use of concrete for BW Ideol’s floating foundation allows the construction to be located as close as possible to the deployment site. Construction at the Saint-Nazaire port was therefore a natural and optimal solution and has created a lot of local content. Additionally, the mooring system was manufactured by LeBéon Manufacturing in Brittany. For the majority of all other components or logistical activities, the Floatgen partners have also opted for suppliers within the Saint-Nazaire region.
Note.
- Will ABP and BW Ideol use a similar philosophy at Port Talbot?
- Will low-carbon concrete be used to construct the floaters?
I can certainly see the logic of BW Ideol and ABP getting together at Port Talbot.
December 12, 2023
Posted by AnonW |
Energy | ABP, BW Ideol, Celtic Sea, Concrete, Crown Estate, Floatgen, Floating Wind Power, Offshore Wind Power, Port Talbot, Tata Steel, Wind Power |
1 Comment
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
A consortium led by the Offshore Renewable Energy (ORE) Catapult has launched a project that will create the biggest offshore wind “living lab” in the world in the UK through the development of a 5G Testbed that includes Grimsby Port and the Lynn and Inner Dowsing offshore wind farm.
These two paragraphs outline the project, its aims and partners.
The GBP 2.8 million (approximately EUR 3.2 million) project, which will run until March 2024, involves setting up a 5G Testbed to allow technology providers to test and demonstrate their equipment in real-world conditions, with access to reliable, high-speed communications.
The aim is to kickstart a digital revolution in offshore wind operations and maintenance (O&M) and accelerate the development of a new generation of digital technologies essential for the expansion of offshore wind generation, according to ORE Catapult, which partnered with Microsoft, Vilicom, JET Connectivity, XceCo, Associated British Ports (ABP), Acceleran and Satellite Applications Catapult to realise the project.
This seems to me to be a very good idea and it is certainly well-backed.
April 4, 2023
Posted by AnonW |
Design | 5G, ABP, Grimsby, Microsoft, Mobile Phone, Ports, Research |
Leave a comment
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from RWE.
These are the three bullet points.
- Offshore floating wind in the Celtic Sea could unlock 3,000 jobs and £682 million in supply chain opportunities by 2030
- RWE is targeting the development at least 1GW of floating wind in the region
- Using experience from demonstrator projects and partnerships with local supply chain to strengthen ambitions
These opening three paragraphs outline more of RWE’s vision.
RWE, the world’s second largest offshore wind player and largest generator of clean power in Wales, has unveiled its vision for the future of floating offshore wind in the Celtic Sea region and the opportunities it presents from new large-scale, commercial projects. Entitled “RWE’s Vision for the Celtic Sea”, the document was unveiled during day one of the Marine Energy Wales conference, in Swansea, where RWE is the Platinum Sponsor.
RWE sees floating wind technology as the next frontier in the development of the offshore wind sector, and which could potentially unlock a multi-billion pound opportunity for the broader Celtic Sea region and the UK.
Studies anticipate the first GW of floating wind to be developed in the Celtic Sea could potentially deliver around 3,000 jobs and £682 million in supply chain opportunities for Wales and the south west of England. Against this backdrop, it’s anticipated the technology could unlock a resurgence in Welsh industry, helping to decarbonise industry and transport, spur on academic innovation, and spearhead the growth of a new, highly skilled workforce.
Reading further down, there are these statements.
- RWE will be bidding in the upcoming Celtic Sea auction with the aim of securing at least 1 gigawatt (GW) of installed capacity, to be developed throughout the 2020’s.
- The Celtic Sea region is pivotal to RWE’s ‘Growing Green’ strategy in the UK, where we expect to invest £15 billion in clean energy infrastructure by 2030.
- A cooperation agreement with Tata SteelUK to understand and explore the production of steel components that could be used in high-tech floating wind foundations and structures for projects in the Celtic Sea.
- The company has also signed agreements with ABP Port Talbot, the Port of Milford Haven and Marine Power Systems of Swansea, to explore opportunities for building the supply chain for floating wind.
- RWE is the largest power producer and renewable energy generator in Wales with more than 3GW of energy across 11 sites.
- If successful in the leasing round, RWE’s Celtic Sea projects will also play a key role in the development of RWE’s Pembroke Net Zero Centre, as well as decarbonizing wider industrial processes and transportation across South Wales.
It looks like RWE are very serious about the Celtic Sea and Pembrokeshire.
Pembroke Net Zero Centre
The Pembroke Net Zero Centre looks to be a powerful beast.
It will be located at the 2200 MW Pembroke power station, which is the largest gas-fired power station in Europe.
These are the first two paragraphs on its web page.
RWE is a world leader in renewables, a market leader in the development of offshore wind and a key driver of the global energy transition. In turn, Pembroke is looking to continue its transformation as part of a decarbonisation hub under the title of the PNZC, linking-up with new innovative technologies needed for a low carbon future, including hydrogen production, Carbon Capture and Storage and floating offshore wind.
The PNZC will bring together all areas of the company’s decarbonisation expertise, including innovation, offshore wind, power engineering, trading and the development/operation of highly technical plants.
The page also talks of burning hydrogen in the power station and an initial 100-300 MW ‘pathfinder’ electrolyser on the Pembroke site.
Conclusion
In some ways, RWE are following a similar philosophy in the area, to that being pursued by SSE at Keadby on Humberside.
As The Crown Estate is talking of 4 GW in the Celtic Sea, it looks like RWE are positioning Pembroke to be the backup, when the wind doesn’t blow.
March 22, 2023
Posted by AnonW |
Energy, Hydrogen | ABP, Celtic Sea, Electrolysis, Floating Wind Power, Green Hydrogen, Keadby Power Stations, Offshore Wind Power, Pembroke Net Zero Centre, Pembroke Power Station, RWE |
1 Comment
I listened to Grant Shapps announcement on Friday, when he gave the daily COVID-19 Press Conference.
This article on the Velocys web site is entitled Government Announces Jet Zero Council And Confirms Support For Velocys Waste-To-Jet-Fuel Project.
The article shows a video of the speech and this summary paragraph.
At this afternoon’s COVID-19 press conference, Secretary of State for Transport, Grant Shapps, announced the establishment of a new Jet Zero Council and confirmed Government support for Velocys.
So who are the company with the strange name of Velocys?
This is a quote from the Velocys CEO; Henrik Wareborn.
Today’s announcement on the formation of a Jet Zero Council shows that a new era of net zero carbon flying is on a credible path, at a time when we need it more than ever. This follows news earlier today that our Altalto waste-to-jet fuel facility – the first of its kind in the UK – has received additional funding from Government and formally received planning permission, meaning it could be producing sustainable aviation fuel in commercial scale by the middle of this decade.
Is a new era of net zero carbon flying a possibility or is this a dream too far?
The AltAlto Project
Yhe project is called AltAlto and it has its own web site.
It is backed by British Airways and Shell, and uses technology from Velocys.
This description of the project is on the home page.
Altalto turns household and commercial waste into clean-burning fuels with reduced greenhouse gas emissions for air and road transport.
A page called Technology describes how it is done.
This is the initial summary.
Our process can accept a wide variety of waste, while delivering a clean product. There are very limited emissions to atmosphere from the plant except water and carbon dioxide. Components of the waste which do not get turned into fuel, such as metals and stones, are recycled; a small amount of it (less than 3%) goes to landfill.
This diagram from the Velocys web site illustrates the process.

The then goes through the stages of the process.
- Stage 1 – Preparation – First the waste is treceived, sorted and prepared.
- Stage 2 – Gasification – Next the solid waste is gasified; heated to a high temperature to break it down and convert it into synthesis gas or syngas (carbon monoxide and hydrogen).
- Stage 3 – Synthesis – After cleaning, the syngas is used to synthesis hydrocarbons using the Fischer-Tropsch technology provided by Velocys.
- Stage 4 – Finishing – These hydrocarbons are then refined into the final products; renewable jet fuel (in the form of SPK) and naphtha.
They add this final summary.
The process is fundamentally different to incineration: instead of being burnt, the carbon in the waste is converted into a fuel for use in aircraft or vehicles.
There are many clean ways of making electricity, but it is really difficult to make sustainable jet fuel – this is one of the very few economic ways of doing so. It’s therefore a far better use of household waste than incineration, creating a much more valuable and environmentally beneficial product.
Could the process be considered a sophisticated waste incineration process, where the actual incineration is performed in the turbofan engine in the aircraft or the diesel engine in the truck to provide power?
I have a few questions.
What is Fischer-Tropsch Technology?
This is the first sentence for the Wikipedia entry for the Fischer-Tropsch Process.
The Fischer-Tropsch process is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatures of 150-300 °C (302-572 °F) and pressures of one to several tens of atmospheres. The process was first developed by Franz Fischer and Hans Tropsch at the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut fur Kohlenforschung in Mulheim an der Ruhr, Germany, in 1925.
One of the companies involved in using the Fischer-Tropsch process is the South African company; Sasol. Wikipedia gives this summary about Sasol’s use of the process.
Another large scale implementation of Fischer-Tropsch technology is a series of plants operated by Sasol in South Africa, a country with large coal reserves, but little oil. The first commercial plant opened in 1952. Sasol uses coal and now natural gas as feedstocks and produces a variety of synthetic petroleum products, including most of the country’s diesel fuel.
The involvement with the apartheid regime in South Africa probably wasn’t the best of publicity for the process.
But have Oxford University and Velocys created a way of making net zero carbon aviation and diesel fuels?
What Is SPK?
SPK is Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene and it is an aviation biofuel.
The Wikipedia entry for aviation biofuel has a sub-section called FT-SPK, where this is said.
The second route involves processing solid biomass using pyrolysis to produce pyrolysis oil or gasification to produce a syngas which is then processed into FT SPK (Fischer-Tropsch Synthetic Paraffinic Kerosene)
This sounds like the Velocys process.
What Are The Environmental Effects?
In the Wikipedia entry for aviation biofuel, there is a section called Environmental Effects. This is the first sentence.
A life cycle assessment by the Yale School of Forestry on jatropha, one source of potential biofuels, estimated using it could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 85% if former agro-pastoral land is used, or increase emissions by up to 60% if natural woodland is converted to use. In addition, biofuels do not contain sulphur compounds and thus do not emit sulphur dioxide.
As Velocys produce their SPK from household waste, their fuel will have a different and more positive effect on greenhouse gas emissions.
This press release on the Velocys web site is entitled Plans Submitted For The First Waste To Jet Fuel Plant In The UK And Europe.
This is a paragraph.
The proposed plant will take hundreds of thousands of tonnes of household and commercial solid waste and turn it into clean burning sustainable aviation fuel, reducing net greenhouse gases by 70% compared to the fossil fuel equivalent – equal to taking up to 40,000 cars per year off the road.
Earlier, I quoted this about the process.
There are very limited emissions to atmosphere from the plant except water and carbon dioxide.
A lot depends on where the carbon dioxide is produced, but if it is produced by a well-designed process plant, it should be possible to capture it for storage.
There are also possibilities to reuse carbon-dioxide in the Fischer-Tropsch process.
Could Diesel Be Produced By The Process?
In the United States, Velocys are developing a project called Bayou Fuels.
This is said on the home page.
We are developing a plant in Mississippi that will create diesel fuel for road transportation in the U.S. It will process waste from the paper and lumber industries – woody biomass forest residue that would otherwise rot on the forest floor or contribute to forest fires.
It should be noted that this is said in the Wikipedia entry for the Port of Immingham.
In 2013 ABP began the development of the “Immingham Renewable Fuels Terminal” on the Humber International Terminal site, as part of a 15-year contract with Drax Power Station to supply biomass (wood pellet) to the powerplant. ABP’s total investment in biomass handling facilities, including installations at Hull and Goole was to be around £100 million.
As Velocys’s new plant will be at Immingham, close to the biomass port, I suspect the answer is yes.
Where Is The Plant Located?
This Google Map shows Immingham Port and the area to the South.

Note.
- Immingham Port is towards the North West corner of the map.
- South Humber Bank Power Station is towards the South East corner of the map.
It would appear that the Altalto plant, will be located on an 80 acre site between the port and the power station.
There would also appear from Google Maps that the Barton Line runs through the area, which would surely be handy for bringing in the waste and taking out the fuel.
This picture from the Altalto web site, shows a visualisation of the plant, looking North East.

INote, what looks to be the railway, through the site in the foreground.
There are also a couple of informative videos, including one from the BBC, on this page of the Velocys web site.
t looks to be the ideal site.
How Much Fuel Will The Plant Produce?
According to the video on the web site, the plant will convert 500,000 tonnes of waste into 60,000,000 litres of fuel. I estimate that would be about 48,000 tonnes of jet fuel.
Could The Diesel Fuel Be Used To Decarbonise The Railways In The UK?
I believe that a substantial amount of the use of diesel on the UK’s railways will be cut by the use of battery and hydrogen power in multiple units and locomotives.
But some services like the heavy stone trains moving aggregates from the Mendips and the Peak District to London will be difficult to decarbonise, unless a locomotive manufacturer produces a hydrogen-powered locomotive with upwards of five megawatts of power. And that is a tough design challenge.
Low sulpur diesel produced from waste would be one way to reduce the carbon footprint.
Conclusion
It sounds a crazy idea to create aviation fuel and diesel from household waste!
Will It Work?
Consider.
- It appears that most of the technology used to produce this fuel has been around for decades.
- Sasol opened their first commercial plant in South Africa, using the Fischer-Tropsch process in 1952 and still use the technique today.
- Oxford University have added magic ingredients to the Fischer-Tropsch process.
- Velocys seem to have put in a lot of serious thought to get the Altalto project ticking all the right boxes.
The project could be late, but I feel it will deliver the main objective of converting household and commercial waste to jet fuel and diesel.
June 14, 2020
Posted by AnonW |
Transport/Travel, World | ABP, Altalto, Diesel, Energy From Waste, Flying, Freight, Global Warming/Zero-Carbon, Landfill, Port Of Immingham, Sustainable Aviation Fuel, Velocys |
7 Comments









