Shell Pulls Plug On Rotterdam Biofuels Plant
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Retreat from green energy continues as facility that was earmarked to produce sustainable aviation fuel and renewable diesel will not now be built
These first three paragraphs add some details.
Shell has scrapped construction of one of Europe’s biggest biofuels plants as it continues its retreat from green energy
The move by the FTSE 100 oil and gas group represents a further setback for efforts to cut aviation emissions.
Shell said it would not restart construction of the biofuels facility at its Rotterdam energy and chemicals plant, which was due to produce sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) and renewable diesel.
When I wrote Centrica Secures Investment Stake In Gasrec Helping Boost UK Bio-LNG Ambitions, I took a look at the use of liquified natural gas (LNG) in transport.
This paragraph from the Centrica press release about the stake, gives the thoughts of Chris O’Shea, who is Group Chief Executive, Centrica.
Chris O’Shea, Group Chief Executive, Centrica plc, said: “Demand for bio-LNG for transport is growing fast as more HGV operators make the switch – drawn by a clean, ready-to-use fuel which slashes CO2 emissions by up to 85 per cent in comparison to diesel*. This investment in Gasrec enhances our collaboration with the leading company in the sector, and puts us in a strong position to energise a vital sector of the industry on its journey to net zero.”
Chris O’Shea of Centrica appears to feel that bio-LNG is a good alternative to diesel, so have Shell come to a similar decision, about satisfying the demand for diesel?
I asked Google AI if LNG has advantages over diesel as a truck fuel and received this answer.
Yes, LNG offers advantages over diesel, including significantly lower emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter (PM), which improves local air quality. It can also be more economically efficient, with fuel costs potentially lower than diesel depending on market conditions. However, the overall greenhouse gas (GHG) benefits are mixed; while LNG has a lower carbon content, it can result in higher lifecycle GHG emissions due to energy losses in its production and transport, as well as methane slip.
Note.
- If it drops emissions by up to 85 percent for bio-LNG, surely, it would do the same for LNG.
- I also think with tight regulations, the use of LNG could improve air quality in cities like London.
- LNG would probably be a more affordable fuel than hydrogen.
It should also be noted, that several major diesel engine makers, now make families of engines, which can handle, diesel, hydrogen and natural gas.
LNG would also be a convenient stepping stone between current fuels and hydrogen, that might give a few extra years for the transition.
Could LNG Be Used In Aircraft?
Consider.
- LNG would certainly give some reduction in carbon emissions.
- Handling LNG in aircraft could have similar problems to hydrogen, so companies like Airbus might have already solved them.
- In addition, LNG doesn’t have the fearsome reputation, that hydrogen seems to have gained because of the Hindenburg.
- It would be easier to provide LNG fuel at airports all round the world.
- Airbus have said availability of hydrogen at airports, could be a problem.
Out of curiosity, I asked Google AI if LNG could be used to power an airliner and received this answer.
Yes, liquefied natural gas (LNG) can theoretically be used to power airliners, offering a potential reduction in CO2 emissions compared to conventional jet fuel, but significant challenges exist. These challenges include the need for entirely new, larger, and heavier cryogenic fuel tanks, modifications to aircraft engines and fuel systems, and the development of a new global infrastructure for LNG supply. While experimental tests have been conducted, such as on the Soviet Union’s Tupolev Tu-155 in 1989, LNG is not currently in normal service due to these practical and infrastructural hurdles.
I would prefer it was a purpose-designed Airbus, than a Soviet-era Tupolev.
Could High Speed Two Serve Chester And North Wales?
This diagram shows High Speed Two services, as they were originally envisaged before Phase 2 was discontinued.
Note.
- Trains to the left of the vertical black line are Phase 1 and those to the right are Phase 2.
- Full-Size trains are shown in blue.
- Classic-Compatible trains are shown in yellow.
- Blue circles are shown, where trains stop.
- The dotted circles are where trains split and join.
- In the red boxes routes alternate every hour.
Click on the diagram to enlarge it.
If I look at the trains counting from the left of the diagram, I see the following.
- Train 4 is a pair of Classic-Compatible trains, that split and join at Crewe, with one train going to Lancaster and the other to Liverpool Lime Street.
- Train 5 is a single Classic-Compatible train going to Liverpool Lime Street.
This gives Liverpool Lime Street two trains per hour (tph) and Lancaster one tph
Could train 5 be a a pair of Classic-Compatible trains, that split and join at Crewe, with one train going to Holyhead via Chester and the other to Liverpool Lime Street?
Consider.
- Yesterday, a pair of Class 805 trains, ran between Euston and Holyhead. Each Class 805 train is 130 metres long, so a pair of Class 805 trains is sixty metres longer than a High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train.
- I am certain, that a single High Speed Two Classic-Compatible train will fit the platforms between Crewe and Holyhead.
- Crewe and Holyhead is 105.5 miles and the route is not electrified.
- Crewe and Holyhead is double-track all the way except for the Britannia Bridge over the Menai Strait.
- With the exception of perhaps 2 to 3 miles, half the route between Crewe and Holyhead has a line speed of 90 mph. with the other half being 75 mph.
- Given the countryside and the number of important historic sites, electrification might be difficult, as the heritage Taliban will say no!
- It was promised by the last government that Crewe and Holyhead would be electrified, but I will assume it won’t be!
- Hitachi, who are part of the consortium building the High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains have developed battery-electric high speed train technology, which is likely to be applied to the Current Class 805 trains, that work the route.
- Hitachi’s battery-electric high speed train technology can propel the trains at up to 125 mph, provided the track allows it.
I feel that Crewe and Holyhead can be developed into one of the most iconic high speed railways in the world, by using battery-electric high-speed trains. Tourists would come from all over the world, to experience mouse-quiet battery-electric trains.
High Speed Two should go for it!
These are some thoughts.
It Would Be A Green Route To Ireland
Consider.
The fastest direct Avanti service to Holyhead is scheduled to take three hours and forty-two minutes, with one hour and 46 minutes between Euston and Crewe, and one hour and fifty-seven minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- High Speed Two will knock thirty-four minutes off the time between Euston and Crewe, when the core route between Euston and Crewe is complete, which will reduce the time to three hours eight minutes, with with one hour and 12 minutes between Euston and Crewe, and one hour and fifty-seven minutes between Crewe and Holyhead.
- The Crewe and Holyhead section of the route would still take one hours and fifty-seven minutes, which is an average speed of just 54 mph, along the North Wales Coast.
- An overall time of three hours between Euston and Holyhead, would require an average speed along the North Wales coast, which would be an average speed of just 62 mph.
- The operating speed is an average of around 80 mph between Crewe and Holyhead, and would run the section of the route in 79 minutes, which would mean a Euston and Holyhead time of two hours and 31 minutes.
- A 100 mph average between Crewe and Holyhead, would run the section of the route in 63 minutes, which would mean a Euston and Holyhead time of of two hours and 15 minutes.
I believe that with track improvements, a more efficient stopping pattern and using Hitachi’s battery technology, that battery-electric High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains could run between Euston and Holyhead in under two hours.
A fast ferry would complete the route between Holyhead and Dun Laoghaire.
Could More Than One Train Per Hour Be Sent To Chester And North Wales?
Consider.
- Because of the cancellation of Phase 2 of High Speed 2, there are spare paths on High Speed Two between London and the West Midlands.
- If the core section of High Speed Two is extended Northwards to Crewe, as advocated by Dyan Perry of the High Speed Rail Group, that I wrote about in The Future Of HS2 Could Lie In Its Original Vision, this would create extra paths to Crewe.
- If the West Midlands and Crewe section of the High Speed Two route has the same capacity as London Euston and the West Midlands it could handle seventeen tph.
- At present it looks like with the cancellation of Phase 2, the West Midlands and Crewe section will handle just ten tph.
, So there will be seven spare paths between Euston and Crewe!
In fact it will be better than that, as each train could be a pair of Classic-Compatible trains, that split and joined to serve two destinations.
Could A North Wales Service Call At Hawarden Airport?
Hawarden Airport is where Airbus build wings for their aircraft in the UK.This Google Map shows Hawarden Airport.
Note.
- The large runway.
- The various factory buildings.
- The North Wales Coast Line between Chester and Holyhead, runs along the North side of the Airport.
I doubt if Airbus wanted a station, it would be difficult to arrange.
Conclusion
Because of the vacant paths, it would appear that extra services to North Wales and North West England can be fitted in.
Gatwick’s Hydrogen Advantage Over Heathrow
The Future Of Hydrogen In Aviation
I believe that hydrogen will have a big future in aviation.
Powering Aircraft
It will be some years, but not as many as some people think, before we see hydrogen-powered aircraft in the air.
Airbus have produced this infographic of three possible hydrogen-powered aircraft.

Discover the three zero-emission concept aircraft known as ZEROe in this infographic. These turbofan, turboprop, and blended-wing-body configurations are all hydrogen hybrid aircraft.
I wrote a bit more about these three hydrogen-powered concepts in ZEROe – Towards The World’s First Zero-Emission Commercial Aircraft.
My best estimate is that we’ll see hydrogen-powered aircraft in the air by 2035.
Towing Aircraft Around
Most aircraft are very heavy and towing them around needs a lot of zero-carbon energy.
So I think it is likely, that at some time in the near future,tugs to tow large aircraft around an airport will be hydrogen powered.
If you type “hydrogen-powered aircraft tug” into Google, you get several sensible product developments, including ones from.
- Exeter Airport
- Teesside Airport
- The Royal Air Force.
- The US Air Force
Note.
- The involvement of the military.
- At least two of the tugs are conversions of existing equipment.
- The extra weight of the battery in an electric-powered tug, may make the realisation of a viable electric aircraft-tug difficult.
I suspect we’ll see hydrogen-powered aircraft tugs in use on airports around the world in the near future.
Long-Term Car-Park Buses
I would have thought that using hydrogen-powered or battery-electric buses to serve long-term car-parks at an airport would be an obvious application. But it does appear that airports using zero-carbon buses to serve long-term car-parks are not very common.
- Gatwick uses a large fleet of hydrogen buses to bring passengers and staff to the airport, but these don’t appear to be linked to car parking.
- Incheon Airport in Korea does appear to use hydrogen-powered buses.
Please let me know, if you know of any other uses of hydrogen-powered vehicles at airports.
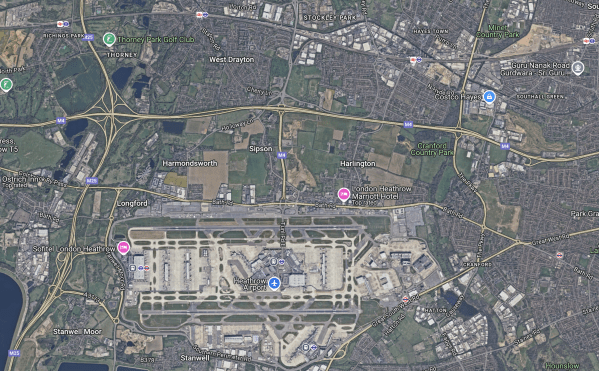
Hydrogen For Heathrow
This Google Map shows Heathrow Airport.
Note.
- The M4 going across the map.
- The two main runways.
- A new third runway would go between the M4 and the Northern runway.
It is likely if the third runway goes ahead, the village of Harmondsworth will be flattened.
It is likely that supplying hydrogen to Heathrow will mean a hydrogen terminal somewhere South of the M4, which could be supplied by rail tankers.
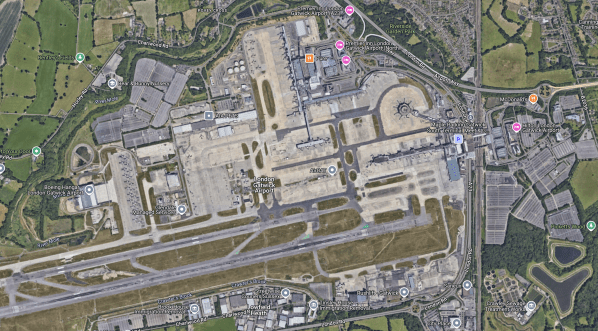
Hydrogen For Gatwick
This Google Map shows Gatwick Airport.
Note.
- The current main runway with the emergency runway to its North.
- Because the runways are too close together they cannot be used simultaneously.
- To create a second runway, the two runways would be moved further apart and the current emergency runway would be enlarged.
- The Brighton Main Line runs North-South past the Eastern end of the main runway.
Gatwick’s expansion plan doesn’t appear to require any properties outside the airport boundaries to be demolished.
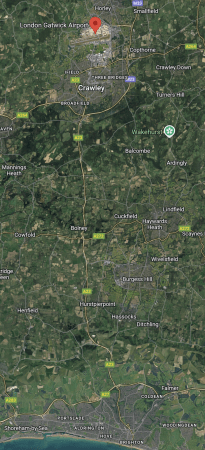
This Google Map shows Sussex between Gatwick Airport and Brighton.
Note.
- Gatwick Airport is indicated by the red arrow at the top of the map.
- Gatwick’s runways can be picked out under the red arrow.
- The South Coast is at the bottom of the map.
- The M23 and the Brighton Main Line connect Gatwick Airport and Brighton.
- Shoreham and Brighton are on the South Coast.
- Click the map to show on a larger scale.
Under current plans, the Ramplion offshore wind farm off the South Coast is going to be increased in size to 1.6 GW.
The simplest plan to provide large amounts of green hydrogen to Gatwick would be to build a large electrolyser in the Port of Shoreham and pipe it along the railway to Gatwick Airport. Hydrogen could also be shipped at night into the Airport using rail tankers.
There’s no doubt in my mind, that it will be much easier to supply large quantities of hydrogen to Gatwick, rather than Heathrow.
In 2023, I wrote Discover How Greater Brighton Is Championing The Transition To Hydrogen, which probably indicates that the locals and their politicians, would welcome the investment in hydrogen in their city.
It should also be noted that world class consultants Ricardo, who are very much involved in the development and promotion of hydrogen technology are based in Shoreham.
Liquid hydrogen could also be imported and distributed from the Port of Shoreham.
Brighton could end up as the South of England’s Hydrogen City.
Never Mind Heathrow: Gatwick Airport Is Close To Getting A New Runway
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Times.
A friend passed through at Gatwick Airport yesterday, so I went to wish him well. For a change , I took a Metrobus from Sutton station to the South terminal – This route is free and doesn’t need a ticket with a Freedom Pass!
The bus was no ordinary bus, but a brand new Wrightbus hydrogen double decker from Ballymena.
It took a round-about route, as its main function is to bring local workers and passengers into the airport and handle traffic to Redhilll, Reigate and East Surrey Hospital.
But if this is the shape of buses to come, then I’m for it. Quality was more coach than bus and performance was sparkling with little or no noise and vibration.
Gatwick and Metrobus are building a network of local hydrogen buses to bring workers and passengers into the airport and I suspect, if the Airport has the fuel, they’ll use it for other purposes, like air-side vehicles, aircraft tow-trucks and car park buses.
Gatwick unlike Heathrow has a close-by source of electricity to produce hydrogen in the soon-to-be-extended 1.6 GW Ramplion offshore wind farm, just off Brighton.
Airbus are talking about bringing hydrogen aircraft into service by 2035 and I believe that by this date we’ll be regularly seeing hydrogen-turboprops on short routes.
As someone, whose software planned the Channel Tunnel, I think it reasonable by 2035, the following projects will be completed.
- Zeroavia are talking of converting aircraft to hydrogen in the next few years.
- A number of short-haul hydrogen aircraft are in service.
- Gatwick’s new runway and terminals are built.
- Ramplion is pumping hydrogen to the airport.
- The station has been updated.
- The Thameslink frequency of trains will have been increased.
Gatwick could be the first major airport to use large amounts of hydrogen, to cut emissions.
Thoughts On The Airbus A 390
Ask Google what she knows about the Airbus A 390 and you get this AI Summary.
The Airbus A390 is a three-deck, six-engine aircraft that can carry around 1,000 passengers. It’s based on the A380, but with a third deck and extra engines. The A390 was custom-built for Qantas to fly between Melbourne and New York.
Google got their summary from this page on steemit.
Search for images of the Airbus A 390 and you get several images of this unusual three-deck aircraft, that looks like a widened Airbus A 380 with six engines.
These are some of my thoughts.
Wikipedia Entries
There is no Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 390.
But.
- There is a Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 380.
- There is also a Wikipedia entry for the six unusual Airbus Beluga XLs, which are used to transport two pairs of Airbus A 350 wings between factories.
The A 390 is supposedly based on the A 380 and the Beluga XL appears to have a fuselage that is a bit like the Airbus A 390.
Will The Airbus A 390 Fly?
After reading the two Wikipedia entries, I am fairly sure that an Airbus A 390 airliner, as shown in the pictures would be able to fly.
Although, I must say, that I was surprised, at seeing an Airbus Beluga XL on video. This is a Beluga XL landing at Heathrow.
So I think we can say, that Airbus know more than a bit about the aerodynamics of three-deck fuselages.
The Antonov An-225 Mriya
This aircraft designed and built in the Soviet Union , does have a Wikipedia entry.
These three paragraphs from the start of the entry, give some details of this unusual and very large aircraft.
The Antonov An-225 Mriya (Ukrainian: Антонов Ан-225 Мрія, lit. ’dream’ or ‘inspiration’) was a strategic airlift cargo aircraft designed and produced by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union.
It was originally developed during the 1980s as an enlarged derivative of the Antonov An-124 airlifter for transporting Buran spacecraft. On 21 December 1988, the An-225 performed its maiden flight; only one aircraft was ever completed, although a second airframe with a slightly different configuration was partially built. After a brief period of use in the Soviet space programme, the aircraft was mothballed during the early 1990s. Towards the turn of the century, it was decided to refurbish the An-225 and reintroduce it for commercial operations, carrying oversized payloads for the operator Antonov Airlines. Multiple announcements were made regarding the potential completion of the second airframe, though its construction largely remained on hold due to a lack of funding. By 2009, it had reportedly been brought up to 60–70% completion.
With a maximum takeoff weight of 640 tonnes (705 short tons), the An-225 held several records, including heaviest aircraft ever built and largest wingspan of any operational aircraft. It was commonly used to transport objects once thought impossible to move by air, such as 130-ton generators, wind turbine blades, and diesel locomotives.
This further paragraph described the destruction of the aircraft.
The only completed An-225 was destroyed in the Battle of Antonov Airport in 2022 during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy announced plans to complete the second An-225 to replace the destroyed aircraft.
I feel that the Mriya is significant for the Airbus A 390 for three reasons.
- Mriya was a six-engine heavy-lift cargo aircraft developed from a certified four-engine transport.
- Mriya was starting to make a name for being able to move over-sized cargo around the world.
- Given the parlous state of parts of the world and the ambitions of some of its so-called leaders, I believe, as I suspect others do, that a heavy-lift cargo aircraft is needed for disaster relief.
So are Airbus looking at the possibilities of converting some unwanted A 380 airliners into the heavy-lift aircraft, that they believe the world needs?
- They may even want some for their own purposes.
- Jeff Bezos or Elon Musk may need a heavy-lift aircraft for their space programs.
Converting some unwanted Airbus A 380s into heavy-lift cargo aircraft could be a more affordable route, than designing and building new aircraft from scratch.
UK Investment Summit Latest: Starmer Announces £1.1bn Expansion Of Stansted Airport
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Times.
The Times has this sub-heading about Stansted
Analysis: Stansted Deal Prioritises Growth Over Climate
There are four paragraphs of analysis.
Over the weekend, Sir Keir Starmer made clear that his commitments to boost workers’ rights would not get in the way of his desire to bring in cash from the owners of P&O. As ministers now trumpet a deal to upgrade Stansted airport, it seems that growth and jobs also trump concerns about emissions.
Louise Haigh, the transport secretary who prompted the row with DP World by calling P&O a “rogue operator”, praised the Stansted deal as a “clear signal that Britain is open for business”. She argued that Stansted could be upgraded “while also meeting our existing environment obligations”, with the airport promising a new solar farm to generate electricity. But environmentalists will be dismayed by the prospect of more plane journeys and associated emissions.
The deal also raises fresh questions about a third runway at Heathrow after years of dithering under the Conservatives. No 10 has previously said it is “not opposed” to expansion if it can meet tests on emissions, climate change, noise pollution — and growth.
Starmer has said he will not duck decisions because they are “too difficult”. A decision on Heathrow offers a very clear test of that promise.
Is Hydrogen The Reason For The Choice Of Stansted?
I wonder if the choice of Stansted for expansion is down to the likelihood, that East Anglia will be a big centre for the generation of zero-carbon green and pink hydrogen, with gigawatts of offshore wind farms for the green and nuclear at Sizewell for the pink.
Aircraft of the future will surely need hydrogen for flying to their destinations.
Already, the massive construction of Sizewell C is going to be performed using zero-construction methods involving electricity and hydrogen, as far as is possible.
Large construction at Stansted Airport could be done in a similar manner, using perhaps a hydrogen pipeline between Sizewell and Stansted running along the A 14. This would probably be built anyway, so that East Anglia’s large numbers of heavy trucks could be converted to hydrogen.
Already the hydrogen buses to bring workers to the Sizewell C site have been ordered from Wrightbus in Ballymena.
Airbus, are planning to have their hydrogen-powered Boeing 737/A 320-size airliner in service by the mid-2030s. From visualisations released by Airbus, the Zeroe hydrogen Turbofan looks very much like a redesigned version of the current A320 neo, with two hydrogen turbofans (hopefully with RR on the side!) Converting an existing proven airliner, only means that the new parts need to be certified, so this would bring the plane into service quicker.
Airbus’s infographic shows the Zeroe hydrogen Turbofan will seat up to 200 passengers and have a range of 2,000 nautical miles or 3,700 km.

Discover the three zero-emission concept aircraft known as ZEROe in this infographic. These turbofan, turboprop, and blended-wing-body configurations are all hydrogen hybrid aircraft.
A typical A 320 neo will fly 165 passengers up to 3,500 nautical miles or 6.500 km.
A few distances from Stansted include.
- Athens – 2,400 km.
- Berlin – 905 km.
- Cairo – 3514 km.
- Copenhagen 913 km.
- Dublin – 470 km.
- Edinburgh – 509 km.
- Gander 3,800 km
- Geneva – 760 km.
- Glasgow – 540 km.
- Istanbul – 2480 km.
- Madrid – 1300 km.
- Milan – 960 km.
- Munich – 909 km.
- Palma de Mallorca – 1,400 km.
- Reykjavík – 1870 km.
- Rome – 1,442 km.
- Stockholm – 1,400 km.
- Tel-Aviv – 3,564 km.
- Tenerife North – 2944 km.
- Tenerife South – 2999 km.
- Warsaw 1,412 km.
These distances would mean, a lot of current European destinations could be reached, if the plane were filled at both airports, but a surprising number of popular places could be reached by only refuelling at Stansted.
It also appears to me, that with refuelling in Iceland and perhaps a stopover, in that delightful and different country, zero-carbon flights across the Atlantic would be possible.
If a hydrogen-powered aircraft has the 3,700 km. range that Airbus are promising, it will be an aircraft with a lot of possibilities!
Short Flights
- Amsterdam – 541 km.
- Cardiff – 253 km.
- Exeter – 284 km.
- Jersey – 344 km.
- Liverpool – 264 km.
- Newcastle – 373 km.
- Newquay – 399 km.
- Ronaldsway – 408 km.
- Southampton – 151 km.
Some of these flights would be competing with trains.
Flights Around The British Isles
One of the longest flights around the British Isles would be between Stansted and Sumburgh Airport in the Shetland Isles.
But this is only 894 kilometres, so a return trip would be possible.
I also feel that arranging hydrogen refuelling on Shetland will not be a difficult task, as the islands are likely to have copious supplies of green hydrogen.
Flights From Stansted To Europe
Applying a ten percent reserve probably means a safe one-way range of around 1,700 km.
This would mean that.
- Amsterdam – 541 km.
- Berlin – 905 km.
- Copenhagen – 913 km.
- Madrid – 1300 km.
- Milan – 960 km.
- Munich – 909 km.
- Palma de Mallorca – 1,400 km.
- Rome – 1,442 km.
- Stockholm – 1,400 km.
- Warsaw 1,412 km.
Should all be in range. of an out-and-back flight, after fully fuelling the plane at Stansted Airport.
Others like.
- Athens – 2,400 km.
- Bucharest – 2070 km.
- Cairo – 3514 km.
- Istanbul – 2480 km.
- Lisbon – 1630 km.
- Malta – 2107 km.
- Marrakech – 2350. km.
- Sofia – 2010 km.
- Tel-Aviv – 3,564 km.
- Tenerife North – 2944 km.
- Tenerife South – 2999 km.
Could be handled by refuelling at the destination.
Hopping Across The Atlantic
Consider.
- My great aunt Beatrice used to fly the Atlantic in the 1950s, although it was usually a succession of small hops between Heathrow Shannon and Gander Airports. I think she regularly used ships like the Queen Mary and Elizabeth, as she found them less stressful.
- Icelandair offer short stopovers in Reykjavik and I suspect they will offer this with hydrogen-fuelled aircraft.
- British Airways used to offer a London City Airport to New York flight via Shannon using an Airbus A 318.
I would certainly be interested to hop across from Stansted to New York in a hydrogen-powered aircraft, and I suspect others would do it for the environmental brownie points.
Legs could be.
- Stansted and Reykjavík – 1870 km.
- Reykjavík and Gander – 2568 km
- Gander and New York – 1767 km.
A stop could possibly be squeezed in at Boston.
It could be an interesting way to cross the Atlantic.
Hydrogen Production In East Anglia
I said earlier that East Anglia could produce a lot of zero-carbon green and prink hydrogen from wind and nuclear and this would be used for the following.
- Aviation out of Stansted and Southend Airports.
- Shipping out of the Port of Felixstowe, London Gateway and other smaller ports.
- Providing energy for heavy transport in East Anglia.
- Providing energy for Freeport East at Felixstowe and Harwich.
- Refuelling passing shipping.
- Supplying off-grid energy to rural properties and businesses in the East of England, which I wrote about in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Any spare hydrogen could always be sold to the Germans.
Decarbonisation Of The Railways In East Anglia
Undoubtedly, some hydrogen will be used to decarbonise some parts of East Anglia’s railways.
Many passenger trains are electrified, but some rural and cross-country services still use diesel. However, the Class 745 trains, that were built by Stadler for these services could be converted to hydrogen or battery-electric.
Similarly, locomotives that haul the freight trains out of the ports of East Anglia will be replaced with hydrogen or battery-electric locomotives.
I am fairly certain, that by 2040, all railways in East Anglia will be zero-carbon.
The East-West Rail Link
It is not known yet, whether the current government will continue to build the East West Rail Link, but it could be invaluable in connecting Stansted Airport to the West of England.
Connecting Stansted Airport To The North Of England and Scotland By Rail
If Stansted is developed as a zero-carbon airport, based on the new hydrogen-powered aircraft, travellers between say the North of England and Scotland, will surely want to travel to Stansted in a carbon-free manner.
So would it be sensible to run rail electric services between the North and Stansted?
Conclusion
Stansted could develop into the UK’s zero-carbon airport.
British Gas Joins Forces With Samsung To Help Customers Power Smarter Energy Use
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This is the sub-heading.
British Gas and Samsung have today announced the exciting first step in a long-term venture – aimed at helping customers better manage their energy use and increase the adoption of low carbon heating technologies in homes across Britain.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The collaboration will see British Gas integrate with Samsung’s SmartThings app to help customers optimise their home appliances to use energy when the cost and demand are lower. This is now possible through the integration of SmartThings Energy and British Gas’ PeakSave demand flexibility scheme informing customers (by sending notifications via their smartphone, TV or other compatible devices) of the best times to use household appliances to save money.
The PeakSave scheme includes PeakSave Sundays, running every Sunday until the end of February with half-price electricity from 11am to 4pm for British Gas customers and PeakSave Winter events which encourages customers to move their electricity use out of peak times when there is high demand on Britain’s energy grid.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I believe that this could make optimising your energy use much easier.
- It would surely be a lot easier to check usage on your phone rather than a smart meter, when you perhaps cook a ready meal, so that you can see if your microwave or traditional cooker is cheapest.
- Suppose you and everybody, who lives with you are out for supper and British Gas want to cut off your gas for a reward, you can make an appropriate decision.
- Hopefully, if you have the right controls, you’ll be able to switch lights and appliances off and on.
The possibilities are endless.
I shall certainly be looking at the reviews of this app.
There is a section in the press release called Scaling Up Low Carbon Heating Opportunities, where this is said.
The collaboration will also help support customers in their journey to decarbonising their homes by introducing smart technologies in a way that is simple and empowering. From early 2024, British Gas will include Samsung heat pumps in its offering to British households to support the UK’s commitment to reach net zero by 2050.
The venture will see specially trained British Gas surveyors and engineers working with consumers to explain the benefits of heat pumps and then conducting the installations on-site. Samsung will be supporting workforce training as part of their efforts to upskill the heating industry to ensure there are enough installers to service the expected growing demand.
British Gas also offers customers the chance to purchase heat pumps through flexible financing methods. This, combined with the recently increased UK Government Boiler Upgrade Scheme grant of £7,500, creates an attractive package of financing options to help people make the transition more affordable.
Various plumbers, who I would trust, have given me different views about heat pumps.
I suspect the Samsung’s SmartThings app might be able to simulate your energy usage with or without the heat pump, as it would know your energy use with your current boiler.
I was doing similar calculations for chemical plants in the early 1970s at ICI, using a PACE 231-R computer.
Consider.
- It may look rather old fashioned, but it could solve a hundred simultaneous differential equations in one go.
- Two similar computers linked together were the analogue half of NASA’s moon mission simulator.
- Without these wonderful machines, NASA would not have been able to re-calculate the dynamics of Apollo 13 and the mission would be remembered as a disaster, rather than the first space rescue.
The average current smart phone has more computing power than a PACE 231-R.
What’s In It For Samsung?
I have a Samsung television, but unfortunately it has a screen fault because of age. So if I had the Samsung app and liked it, I might buy another Samsung TV.
Similarly, the app might give me a financial reason to buy a Samsung heat pump.
Samsung will sell more equipment.
What’s In It For Centrica?
Centrica would appear to be a loser, as bills will fall and they could be paying customers to not use energy.
But they are surely hoping that their market share will increase and I’m sure Samsung will give them a commission.
What’s In It For The Consumer?
Hopefully, they’ll get lower energy bills.
But also they might get a lot of convenience controlling their appliances and heating.
Conclusion
Using energy is becoming a computer game with monetary rewards.
Is the deal between Centrica/British Gas and Samsung another deal that has been brought to fruition by the Korean President’s visit to the UK?
It looks like this is the third recent deal signed between UK and Korean companies, after these two.
- South Korea, UK Strenghten Offshore Wind Ties
- UK And South Korea Help Secure Millions For World’s Largest Monopile Factory
I suspect, there might be a few more deals, if Charles and Camilla really turned on the charm.
In Mersey Tidal Project And Where It Is Up To Now, I wrote about talks between Liverpool City Council and Korea Water about a tidal barrage of the Mersey. This project must surely be a possibility!
This is said in the Wikipedia entry for Korean Air under Fleet Plans.
At the Association of Asia Pacific Airlines Assembly in 2018, Korean Air announced that it was considering a new large widebody aircraft order to replace older Airbus A330, Boeing 747-400, Boeing 777-200ER and Boeing 777-300. Types under consideration for replacement of older widebody aircraft in the fleet include the Boeing 777X and Airbus A350 XWB. At the International Air Transport Association Annual General Meeting (IATA AGM) in Seoul, Chairman Walter Cho said Korean Air’s widebody order is imminent and it is considering an extra order of Airbus A220 Family including developing version, Airbus A220-500.
Note.
- Airbus A350 XWB have Welsh wings and Rolls-Royce engines.
- Airbus A220-500 are made in Canada with wings and composite parts from Belfast. Rolls-Royce may have a suitable engine.
Could a deal have something in it for the UK?
Although Korea has its own SMR program, I wonder, if there could be a link-up between Korean industry and Rolls-Royce over SMRs?
Airport Of The Future
I am fairly sure, that in ten years, there will be a lot of zero-carbon aircraft flying short haul routes. I have been particularly impressed by some of the ideas from Airbus, although Boeing seem to be very quiet on the subject. Perhaps it’s the difference between visionaries and engineers, and accountants.
But you rarely read anything about how airports are preparing for even a low-carbon future.
- Some long-stay car-parks could be made electric vehicles only, so they would become massive grid batteries, whilst owners are travelling.
- Airside vehicles can all be made zero-carbon.
- Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) shouldn’t be a problem, as it would be handled like jet fuel.
- Do airports have a large enough grid connection for all the electrification of vehicles and some planes?
- Do airports have a plan for hydrogen?
The last two points, probably mean we should have built Maplin.
- It could have a cable and a hydrogen pipeline from wind farms and co-located hydrogen electrolysers in the Thames Estuary.
- The Elizabeth Line or a new line could easily be extended or built to the airport, to give a 125 mph connection.
But that enemy of the planet; Harold Wilson cancelled it.
Airbus, Rolls-Royce, EasyJet Headline Formation Of UK Hydrogen Alliance
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article from Future Flight.
These two paragraphs outline the story.
A group of leading companies in the UK aviation and renewable energy sectors including EasyJet, Rolls-Royce, and Airbus has established the Hydrogen in Aviation (HIA) alliance to accelerate the delivery of zero-carbon aviation, the companies said Tuesday. HIA, whose partners also include Ørsted, GKN Aerospace, and Bristol Airport, said decarbonization efforts involving hydrogen should assume more urgency at a time when sustainable aviation fuel and batteries have drawn so much of the sector’s attention.
Working with government, local authorities, and the aviation and hydrogen sectors, the group plans to draw on members’ expertise to propose “a clear and deliverable pathway” to achieving hydrogen-powered aviation. Efforts center on clearing a pathway for preparing the needed infrastructure as well as policy, regulatory, and safety frameworks.
This Airbus infographic describes the aircraft in Airbus’s ZEROe project.

Discover the three zero-emission concept aircraft known as ZEROe in this infographic. These turbofan, turboprop, and blended-wing-body configurations are all hydrogen hybrid aircraft.
These are my thoughts.
Do The ZEROe Turboprop And The ZEROe Turbofan Have Similar Hydrogen Systems?
This is Airbus’s summary of the design of the ZEROe Turboprop
Two hybrid-hydrogen turboprop engines, which drive eight-bladed propellers, provide thrust. The liquid hydrogen storage and distribution system is located behind the rear pressure bulkhead
This screen capture taken from an Airbus video, shows a rear view of the plane.
Note the sizeable cone-shaped rear end to the fuselage with no windows.
This is Airbus’s summary of the design of the ZEROe Turbofan
Two hybrid hydrogen turbofan engines provide thrust. The liquid hydrogen storage and distribution system is located behind the rear pressure bulkhead.
This screen capture taken from an Airbus video, shows the plane.
Note how there are no windows at the back of the fuselage, as the hydrogen tank doesn’t need them.
It looks to me, that similar cone-shaped tanks for hydrogen, customised for each aircraft could be placed behind the rear bulkhead.
There would probably be space for any pumps needed to distribute the hydrogen to the engines.
All the stored hydrogen and its gubbins could be safely sealed behind the rear bulkhead.
I am fairly certain that the ZEROe Turboprop and the ZEROe Turbofan will have similar hydrogen systems.
Do The ZEROe Turboprop And The ZEROe Turbofan Have Auxiliary Power Units?
The auxiliary power unit or APU in an aircraft that provides energy for functions other than propulsion.
In Airbus To Trial In-flight Auxiliary Power Entirely Generated By Hydrogen, I wrote about Airbus’s development of APU’s based on fuel cells and running on hydrogen.
This surely could be a way to go.
- A battery could store power.
- Fuel cells are proving to be reliable.
- The plane would have two independent electrical systems.
Power would always be available for the cockpit, flying controls and to restart the engines, just as it is in any airliner today.
Do The ZEROe Turboprop And The ZEROe Turbofan Have The Same Cockpit?
The cockpits of the A 320 neo and the A 320 ceo seem to have a similar profile, but the cockpit of the ZEROe Turbofan seems to have been reprofiled.
In ZEROe – Towards The World’s First Zero-Emission Commercial Aircraft, I showed these front on views of the cockpits of the ZEROe Turboprop and ZEROe Turbofan.
I questioned if the two cockpits were related.
- A single cockpit for both aircraft would surely ease manufacture, maintenance and pilot training.
- I’m no aerodynamicist, but it certainly looks that the new cockpit will reduce drag and fuel consumption.
This common cockpit concept was used for the Boeing 757 and the Boeing 767 in the 1980s, so it is not a new concept.
Although the cockpit, appears to be being used in the ZEROe for the first time, I would expect it is already under development and might feature in any later version of the A 320 neo.
Do Airbus Have A Preferred Development Order?
Consider.
- My product development experience indicates that the development of the ZEROe Blended-Wing Body will involve more flight testing and aerodynamic checks than the other two aircraft, so I would make it the last aircraft to enter service.
- The ZEROe Turboprop appears to be a development of the ATR 72.
- The ZEROe Turbofan appears to be a development of an A 320 neo.
- The ZEROe Turboprop and ZEROe Turbofan would appear to have similar designs of cockpit, hydrogen systems and auxiliary power units.
- It looks to me that either of the ZEROe Turboprop or ZEROe Turbofan could be developed first.
I would develop the ZEROe Turboprop first, as it is the smaller aircraft.
Why Bristol Airport?
This page on the Airbus web site is entitled Airbus In The United Kingdom, where this is the first paragraph.
Building on a proud 100-year British aviation heritage, Airbus is part of the very fabric of the UK – which is one of the company’s four home markets, alongside France, Germany and Spain. Its 11,000-strong UK workforce is part of a global family of 125,000 employees.
This is said under Commercial Aircraft.
The sites at Filton and Broughton design, test and manufacture the wings for all Airbus’ A320 family, A330 and A350 commercial aircraft, directly sustaining more than 8,000 full-time jobs and hundreds of apprenticeships.
A220 family wings are designed and built by Spirit AeroSystems in Belfast, Northern Ireland.
Broughton has a proud tradition of aerospace manufacturing dating back 80 years, having supplied the RAF with vital aircraft during the Second World War. Employing almost 5,000 people, Broughton is a global centre of excellence for manufacturing and delivers over 500 wing sets per year for the A320 family, A330 and A350. Airbus has invested more than £2 billion in the Broughton plant over the past 10 years.
Core activities at Filton, where an additional 3,000 people work, are the design, engineering and support for Airbus wings, fuel systems and landing gear systems. Teams also work on aerodynamics research, development and test facilities, including our future zero-emissions programme, ZEROe, while wings for the A400M transporter are assembled on site.
It would appear that Filton in Bristol, is a very important part of Airbus’s operations in the UK.
- It appears to have major responsibility for all Airbus wings except the smallest.
- It has a large responsibility with respect to the ZEROe family of aircraft.
- Filton Airfield is now closed.
- Filton can do substantial assembly if required.
So was it just a logical decision to phone up Bristol Airport and ask, if they’d like to join the project?
In addition.
- Bristol Airport has a 2000 metre East West asphalt runway.
- The airport can handle a Boeing 787 Dreamliner and Airbus A330.
- It is the eighth busiest airport in the UK.
- It is a busy general aviation airfield.
- There is plenty of electricity in the area and Hinckley Point C will open down the road in a couple of years.
Bristol Airport is probably typical of many provincial airports around the world.
Why EasyJet?
These paragraphs from the Future Flight article help to explain.
“There is no doubt that the UK has the potential to become a world leader in hydrogen aviation, which could bring with it a £34 billion per annum boost to the country’s economy by 2050, but in order to capture this opportunity, rapid change is needed and the time to act is now,” said Johan Lundgren, CEO of EasyJet and HIA’s first chairman.
“We must work together to deliver the radical solutions required for a hard-to-abate industry like aviation so we can protect and maximize the benefits that it brings to the UK economy and society and that we know British consumers want to be preserved.”
Under its Zero-E program, Airbus aims to bring to market the first hydrogen-powered narrowbody commercial airplane by 2035. Separately, a partnership between Rolls-Royce and EasyJet signed last year saw the companies test hydrogen fuel in gaseous form in an adapted AE2100-A turbine, the engine that powers the Saab 2000 regional airliner. The November 2022 test, which used hydrogen produced in the Orkney Islands by the European Marine Energy Centre using renewable energy, marked the first run of a modern engine using hydrogen.
EasyJet seems to be enthusiastic about hydrogen and their CEO will be the HIA’s first chairman.
EasyJet also has a series of routes from Bristol Airport.
- Alicante – 907 miles
- Amsterdam – 326 miles
- Athens – 1592 miles
- Antalya – 1981 miles
- Barcelona – 733 miles
- Basel/Mulhouse – 530 miles
- Belfast–City – 259 miles
- Belfast–International – 269 miles
- Berlin – 694 miles
- Bilbao – 559 miles
- Bodrum – 1772 miles
- Bordeaux – 462 miles
- Catania – 1295 miles
- Chania – 1719 miles
- Copenhagen – 694 miles
- Corfu – 1356 miles
- Dalaman – 1981 miles
- Dubrovnik – 1155 miles
- Edinburgh – 316 miles
- Enfidha – 1241 miles
- Faro – 1026 miles
- Fuerteventura – 1687 miles
- Funchal – 1473 miles
- Geneva – 536 miles
- Gibraltar – 1060 miles
- Glasgow – 317 miles
- Gran Canaria – 1749 miles
- Grenoble – 556 miles
- Heraklion – 1768 miles
- Hurghada – 2526 miles
- Ibiza – 887 miles
- Innsbruck – 693 miles
- Inverness – 429 miles
- Isle of Man – 203 miles
- Kefalonia – 1451 miles
- Kos – 1770 miles
- Kraków – 991 miles
- La Rochelle – 366 miles
- Lanzarote – 1649 miles
- Larnaca – 2126 miles
- Lisbon – 925 miles
- Lyon – 529 miles
- Madrid – 755 miles
- Málaga – 1020 miles
- Marrakesh – 1393 miles
- Marseille – 662 miles
- Menorca – 863 miles
- Milan–Malpensa – 682 miles
- Murcia – 945 miles
- Mykonos – 1670 miles
- Nantes – 251 miles
- Naples – 1085 miles
- Newcastle upon Tyne – 256 miles
- Nice – 704 miles
- Olbia – 929 miles
- Palma de Mallorca – 859 miles
- Paphos – 2087 miles
- Paris–Charles de Gaulle – 285 miles
- Paris–Orly – 290 miles
- Pisa – 808 miles
- Porto – 755 miles
- Prague – 746 miles
- Preveza/Lefkada – 1421 miles
- Pula – 885 miles
- Reykjavík–Keflavík – 1121 miles
- Rome–Fiumicino – 968 miles
- Rovaniemi – 1436 miles
- Salzburg – 745 miles
- Santorini – 1726 miles
- Sharm El Sheikh – 2507 miles
- Sofia – 1359 miles
- Split – 927 miles
- Tenerife–South – 1766 miles
- Toulouse – 569 miles
- Turin – 645 miles
- Venice – 798 miles
- Zakynthos – 1484 miles
Note.
- There are nine routes under 400 miles, which might enable a round trip without refuelling in a ZEROe Turboprop.
- There are nine routes under 800 miles, which might enable a round trip without refuelling in a ZEROe Turbofan.
- There are only four routes over 2000 miles, which might make a single trip difficult in a ZEROe Turbofan.
- Bristol and Toulouse is a convenient 569 miles for Airbus and its employees, customers and contractors.
It does appear that, EasyJet’s routes fit the 1000 mile range of a ZEROe Turboprop and the 2000 mile range of a ZEROe Turbofan exceedingly well.
Conclusion
Bristol will be important in the development of Airbus’s three ZEROe aircraft.