CO2 to SAF: A One-Step Solution
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on the Chemical Engineer.
This is the sub-heading,
Oxford spinout OXCCU has launched a demonstration plant at London Oxford Airport to trial its one-step process of turning CO2 into sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). Aniqah Majid visited the plant to investigate the benefits of its “novel” catalyst
One word in this sub-heading caught my eye.
When I was a young engineer in the Computer Techniques section in the Engineering Department at ICI Plastics Division, I did a small mathematical modelling project for this chemical engineer, using the section’s PACE 231-R analogue computer.

He was impressed and gave the 23-year-old self some advice. “You should apply that beast to catalysts.”
I have never had the chance to do any mathematically modelling of catalysts either at ICI Plastics or since, but I have invested small amounts of my own money in companies working with advanced catalysts.
So when OXCCU was picked up by one of my Google Alerts, I investigated.
I like what I found.
The three raw ingredients are.
- Green Hydrogen
- Carbon dioxide perhaps captured from a large gas-fired powerstation like those in the cluster at Keadby.
- OXCCU’s ‘novel’ catalyst, which appears to be an iron-based catalyst containing manganese, potassium, and organic fuel compounds.
I also suspect, that the process needs a fair bit of energy. These processes always seem to, in my experience.
This paragraph outlines how sustainable aviation fuel or (SAF) is created directly.
This catalyst reduces CO2 and H2 into CO and H2 via a reverse water gas shift (RWGS) process, and then subsequently turns it into jet fuel and water via Fischer-Tropsch (FT).
The Wikipedia entry for Fischer-Tropsch process has this first paragraph.
The Fischer–Tropsch process (FT) is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatures of 150–300 °C (302–572 °F) and pressures of one to several tens of atmospheres. The Fischer–Tropsch process is an important reaction in both coal liquefaction and gas to liquids technology for producing liquid hydrocarbons.
Note.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that to obtain the carbon monoxide and hydrogen or syngas for the Fischer-Tropsch process, excess hydrogen is used, so the OXCCU process may need a lot of affordable hydrogen, some of which will be converted to water in the RWGS process.
- The high temperatures and pressures for the Fischer-Tropsch process will need a lot of energy, as I predicted earlier.
But I don’t see why it won’t work with the right catalyst.
The Wikipedia entry for the Fischer-Tropsch process also says this.
Fischer–Tropsch process is discussed as a step of producing carbon-neutral liquid hydrocarbon fuels from CO2 and hydrogen.
Three references are given, but none seem to relate to OXCCU.
OXCCU have a web site, with this title.
Jet Fuel From Waste Carbon
And this mission statement underneath.
OXCCU’s mission is to develop the world’s lowest cost, lowest emission pathways to make SAF from waste carbon, enabling people to continue to fly and use hydrocarbon products but with a reduced climate impact.
It looks like they intend to boldly go.
Conclusion
My 23-year-old self may have been given some good advice.
Great Yarmouth Terminal Set For Redevelopment Under Port Of East Anglia Name
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s Peel Ports Group has decided to invest a further GBP 10 million (approximately EUR 11.3 million) into its Great Yarmouth site, which is being rebranded as the Port of East Anglia.
These four paragraphs add details to the story.
The newly announced GBP 10 million brings this year’s total investment to GBP 70 million across the site and will be used to redevelop the port’s Northern Terminal, helping to accommodate the next generation of offshore wind projects across the region, according to Peel Ports.
Earlier this year, a substantial investment into its Southern Terminal was announced by the port, which has earmarked GBP 60 million to transform capacity and improve efficiencies.
This involves ensuring the port can support multiple hydrogen, carbon capture, offshore wind, and nuclear projects for decades to come.
Its existing terminals service a variety of construction customers, including infrastructure projects such as Sizewell C and offshore energy projects based in the southern North Sea.
Note.
- In Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project, I talk about the work to be done on the Southern Terminal.
- The work on the Southern Terminal includes a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
- Start on the work on the Southern Terminal will start in 2026.
With all the construction work mentioned in the last two paragraphs, I suspect that the Port of Great Yarmouth will be busy?
These are some further thoughts.
Why Is The Port Of Great Yarmouth Being Renamed?
The article says this.
The new name, which will come into effect in early 2026, also aligns with the creation of a new combined authority for Suffolk and Norfolk, according to Peel Ports.
Peel Ports name change is fairly sensible, but as I was conceived in Suffolk and I’m an Ipswich Town supporter, I don’t feel that the two counties should be merged.
Does The Mention Of Hydrogen Mean That The Port Of Great Yarmouth Will Be Hosting A Hydrogen Electrolyser, To Fuel Trucks And Ships?
I asked Google AI, “If A Hydrogen Electrolyser is To Be Built In The Port Of Great Yarmouth?”, and received this answer.
While there are no current public plans for an immediate construction of a large-scale hydrogen electrolyser within the Port of Great Yarmouth, significant port expansion and infrastructure upgrades are underway to ensure it can support future hydrogen projects and related clean energy initiatives.
Note.
- If technology to handle hydrogen, is copied from North Sea gas, there is certainly a lot of proven technology that can be used again.
- There may even be depleted gas fields, where captured carbon dioxide, hydrogen or North Sea gas can be stored.
I find the most exciting thing, would be to send hydrogen to Germany.
Why Would Anybody Export Hydrogen To Germany?
I asked Google AI, the question in the title of this section and received this answer.
Countries would export hydrogen to Germany because Germany has a large, growing demand for hydrogen to power its heavily industrialised economy and achieve its decarbonisation goals, but lacks sufficient domestic renewable energy capacity to produce the required amounts.
Germany also, uses a lot of bloodstained Russian gas and indigenous polluting coal.
How Could Anybody Export Hydrogen To Germany?
- Wilhelmshaven is one of the main import ports for hydrogen in North West Germany.
- Great Yarmouth is probably the closest larger port to Germany.
- Great Yarmouth and Wilhelmshaven are probably about 300 miles apart, by the shortest route.
- Great Yarmouth would need to build infrastructure to export hydrogen.
The easiest way to transport the hydrogen from Great Yarmouth to Wilhelmshaven, is probably to use a gas tanker built especially for the route.
This Google Map shows the route between Great Yarmouth and Wilhelmshaven.
Note.
- The North-East corner of East Anglia with Great Yarmouth to the North of Lowestoft, is in the bottom-left corner of the map.
- Wilhelmshaven is a few miles inland in the top-right corner of the map.
- Could a coastal tanker go along the Dutch and German coasts to Wilhelmshaven?
I have no skills in boats, but would Great Yarmouth to Wilhelmshaven to take hydrogen to Germany?
RWE Are Developing Three Wind Farms To The North-East of Great Yarmouth
RWE are a large German Electricity company and the UK’s largest generator of electricity.
The company is developing three wind farms to the North-East of Great Yarmouth.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1.2 GW – 45 miles offshore
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1.2 GW – 29 miles offshore
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1.2 GW – 28 miles offshore
Note.
- The electricity for all three wind farms is to be brought ashore at Happisburgh South, which is about 22 miles North of Great Yarmouth.
- The original plan was to take the electricity halfway across Norfolk to the Necton substation to connect to the grid.
- The natives will not be happy about a 4.2 GW overhead line between Happisburgh and Necton.
- RWE have built offshore electrolysers before in German waters.
- Could an electrical cable or a hydrogen pipe be laid in the sea between Happisburgh South and the Port of Great Yarmouth?
- The electrolyser could either be offshore at Happisburgh or onshore in the Port of Great Yarmouth.
As I don’t suspect these three wind farms will be the last connected to the Port of Great Yarmouth, I would expect that RWE will put the electrolyser offshore at Happisburgh and connect it by a hydrogen pipeline to the Port of Great Yarmouth.
Could There Be A Connection To The Bacton Gas Terminal?
Consider.
The Bacton Gas Terminal, which feeds gas into the UK Gas Network, is only 4.2 miles up the coast from Happisburgh South.
Some climate scientists advocate blending hydrogen into the gas supply to reduce carbon emissions.
In Better Than A Kick In The Teeth – As C Would Say!, I disclosed that I now have a new hydrogen-ready boiler, so I’m not bothered, if I get changed to a hydrogen blend.
So could hydrogen from the Norfolk wind farms be fed into the grid to reduce carbon emissions?
Could The Port Of Great Yarmouth Become A Hydrogen Distribution Centre?
Thinking about it, the port could also become a distribution centre for green hydrogen.
Consider.
- Hydrogen-powered ships, tugs and workboats could be refuelled.
- Hydrogen-powered trucks could also be refuelled.
- Tanker-trucks could distribute hydrogen, to truck and bus operators, farms and factories, that need it for their transport and operations.
- I believe, that construction equipment will be increasingly hydrogen-powered.
In my life, I have lived at times in two country houses, that were heated by propane and there are about 200,000 off-grid houses in the UK, that are heated this way.
The two houses, where I lived would have been a nightmare to convert to heat pumps, but it would have been very easy to convert them to a hydrogen boiler and power it from a tank in the garden.
It should be noted, that the new boiler in my house in London is hydrogen-ready.
So the Port of Great Yarmouth could be the major centre for hydrogen distribution in Norfolk.
In the 1960s, I used to work in ICI’s hydrogen plant at Runcorn. If you ride in a hydrogen bus in England, it is likely that the hydrogen came from the same plant. Handled correctly, hydrogen is no less safe and reliable than natural gas or propane.
Berkeley Scientists Finally Solve 10-Year Puzzle Enabling Efficient CO2-to-Fuel Conversion With Major Climate Impact Potential
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Sustainability Times.
This is the sub-heading.
In a groundbreaking advancement, scientists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have unveiled the critical mechanisms behind the degradation of copper catalysts, a revelation that promises to revolutionize the production of sustainable fuels by enhancing the efficiency and stability of CO2 conversion processes.
This paragraph gives more details.
Scientists from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory have made a groundbreaking discovery in the field of artificial photosynthesis. By utilizing advanced X-ray techniques, they have uncovered the critical factors that limit the performance of copper catalysts in converting carbon dioxide and water into useful fuels. This revolutionary insight could significantly enhance the stability and efficiency of catalysts in CO2 conversion processes, potentially accelerating the production of ethanol and ethylene. The research, which tackles a decades-old puzzle, offers promising avenues for the development of more durable catalyst systems, paving the way for future advancements in sustainable energy solutions.
I first came across catalysts in my working life, when I was working at ICI. I was modelling a chemical process called sulphonation for a guy who was trying to find an efficient way to create the monomer of building block for a new engineering plastic.
Some feel that all plastics are bad for the environment, but I think that, if the plastic is designed to replace another material in a long-lasting application, then plastic is good for the environment.
This picture shows my wonderful Sheba cutlery.

Note.
- C and I bought it in the 1960s, when we got married.
- Some have been used every day for over fifty years.
- The important bits are Sheffield stainless steel, with the handles formed of black Delrin plastic.
- Some of the handles have been in the dishwasher too many times and have faded.
- From what I have seen on the Internet, the average worth of pieces could be as much as a tenner.
Perhaps, when I pass on, all the pieces should be divided between my grandchildren.
I have digressed and I will return to my modelling project with one of ICI’s catalyst experts.
I remember him telling me, that if you could improve the way catalysts worked, you would open up whole new areas of chemistry.
It looks to me, that the scientists at Berkeley may have opened up a route to turn carbon dioxide into fuel.
Whether that is a good route to decarbonisation is another long discussion.
I’ve Just Come Across Avnos
I feel we should take into account any possibilities of second use of oil or gas structures, that once held hydrocarbons.
An article in a magazine called Carbon Herald pointed me to a company called Avnos, who are developing Direct Air Capture of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere. If systems like that of Avnos do work, we may need somewhere to put the carbon dioxide.
Centrica are storing the hydrogen in the Rough gas field, which was previously used for storing natural gas and now some depleted gas fields are being used to store captured carbon dioxide.
On the subject of carbon capture, Avnos do it differently, in that for every tonne of CO2, they capture from the air, they capture five tonnes of distilled water. And they do it without using any heat.
This is their web site.
This is their mission statement on the front page of the web site. There is also a video.
Carbon Negative. Water Positive
Avnos is commercializing the most advanced technology in the Direct Air Capture of CO2
Our proprietary Hybrid Direct Air Capture (HDAC) solution inverts the water paradigm in DAC, producing water, eliminating heat consumption and reducing costs compared to other forms of DAC.
It sounds too good to be true!
But I have experience of the positive financial results of fluid dynamics in this area.
Thirty years ago, two guys approached me with an idea for an aerosol valve that used nitrogen as a propellant.
At the time, I lived in the house, where Osborne Reynolds, the great Victorian fluid dynamicist of Reynold’s number fame had been brought up.
The guys succeeded and the device was sold on to J & J.
They were then asked to develop a metered dose inhaler for asthma drugs, which is now sold as Respimat, which is sold by Boehringer Ingelheim.
Afterwards, I researched Reynolds at Manchester University, where he was the first Professor of Engineering and I found that he had done some marvelous things with fluids. He was a true genius and undergraduates are still taught on his Victorian apparatus.
I suspect that Avnos may have been exploring in the same area and are using another of Reynold’s useful properties.
Energy Dome Pens Contract For First US Project
The title of this post is the same as that as this article on Energy Storage News.
I like Energy Dome, as it makes one of the causes of global warming; carbon dioxide help with the storage of energy, which many argue is part of the solution of the problem.
This press release gives more details.
- The project is a 20MW/200MWh Battery.
- The battery will be located in Wisconsin.
- In parallel, the construction of Energy Dome’s first-of-a-kind standard CO2 Battery plant in Sardinia, Italy, is also proceeding at full speed.
As Energy Dome is an Italian company, the solution is also more about finesse than brute force.
Energy In – Hydrogen And Carbon Dioxide Out
This article was inspired by this article in the Sunday Times, which is entitled ‘It’s A Slog’: Life Inside Britain’s Last Coal Power Station.
The article is about Ratcliffe-on-Soar power station, which is next to East Midlands Parkway station.
This is the first paragraph of the station’s Wikipedia entry.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar Power Station is a coal-fired power station owned and operated by Uniper at Ratcliffe-on-Soar in Nottinghamshire, England. Commissioned in 1968 by the Central Electricity Generating Board, the station has a capacity of 2,000 MW. It is the last remaining operational coal-fired power station in the UK, and is scheduled to close in September 2024.
I took these pictures of the power station in 2019.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar is the last of a number of large coal-fired power stations, that were built in the area, mainly along the River Trent.
- Rugeley – 600 MW – 1961
- Drakelow – 1630 MW – 1964
- Willington – 800 MW – 1962
- Castle Donington – 600 MW – 1958
- Ratcliffe-on-Soar – 2000 MW – 1968
- High Marnham – 1000 MW – 1959
- Cottam – 2000 MW – 1968
- West Burton – 2000 MW – 1968
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 10,630 MW of electricity.
- There are also a few large gas-fired power stations along the river, that are still operating.
- Both coal and gas-fired stations use the water from the River Trent for cooling.
At the mouth of the river, there is the Keadby cluster of gas-fired power stations.
- Keadby 1 – 734 MW – 1996
- Keadby 2 – 849 MW – 2023
- Keadby 3 – 910 MW – 2027
- Keadby Hydrogen – 900 MW – 2030
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 3,393 MW of electricity.
- Keadby 2 is the most efficient CCGT in the world.
- Keadby 3 will be fitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby 2 has been designed to be retrofitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby Hydrogen will be fuelled by zero-carbon hydrogen.
As the years progress, I can see the Keadby cluster of power stations becoming a large zero-carbon power station to back-up wind farms in the North Sea.
- Hydrogen power stations will emit no carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide from all gas-fired stations will be captured.
- Some carbon dioxide will be sold on, to companies who can use it, in industries like construction, agriculture and chemical manufacture.
- The remaining carbon dioxide will be stored in depleted gas fields.
As technology improves, more carbon dioxide will be used rather than stored.
Other Power Sources In The Humberside Area
In the next few sub-sections, I will list the other major power sources in the Humberside area.
Drax Power Station
Drax power station is a shadow of its former self, when it was one of the power stations fed by the newly discovered Selby coalfield.
These days it is a 2,595 MW biomass-fired power station.
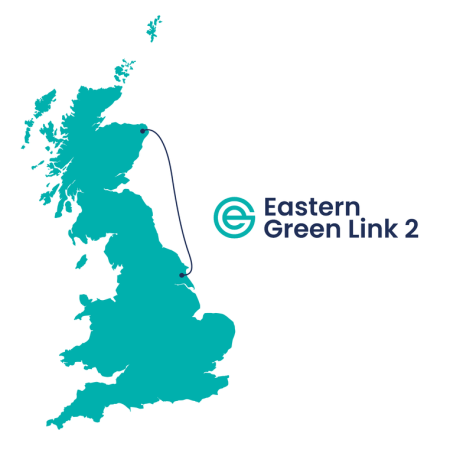
Eastern Green Link 2
Eastern Green Link 2 will be a 2 GW interconnector between Peterhead in Scotland and Drax.
It is shown in this map.
Note.
- Most of the route is underwater.
- It is funded by National Grid.
- Contracts have been signed, as I talk about in Contracts Signed For Eastern Green Link 2 Cable And Converter Stations.
- It is scheduled to be completed by 2029.
This interconnector will bring up to 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity to Drax and Humberside.
Drax has the substations and other electrical gubbins to distribute the electricity efficiently to where it is needed.
2 GW could also reduce the amount of biomass used at Drax.
In the long term, if the concept of the four Eastern Green Links is successful, I could see another Eastern Green Link to Drax to replace imported biomass at Drax.
I also, don’t see why a smaller Drax can’t be run on locally-sourced biomass.
Solar Farms And Batteries Along The River Trent
As the coal-fired power stations along the River Trent are demolished, solar farm developers have moved in to develop large solar farms.
Salt End Power Station And Chemical Works
These two paragraphs from the Wikipedia entry for Salt End describes the hamlet and its power station and chemical works.
Salt End or Saltend is a hamlet in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, in an area known as Holderness. It is situated on the north bank of the Humber Estuary just outside the Hull eastern boundary on the A1033 road. It forms part of the civil parish of Preston.
Salt End is dominated by a chemical park owned by PX group, and a gas-fired power station owned by Triton Power. Chemicals produced at Salt End include acetic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonia, bio-butanol, bio-ethanol, ethyl acetate (ETAC) and ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) with animal feed also being produced on site.
I wonder, if running the complex on hydrogen would give cost and marketing advantages.
Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage Facility
This page on the SSE Thermal web site is entitled Plans For World-Leading Hydrogen Storage Facility At Aldbrough.
This is the most significant paragraph of the page, that is definitely a must-read.
With an initial expected capacity of at least 320GWh, Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage would be significantly larger than any hydrogen storage facility in operation in the world today. The Aldbrough site is ideally located to store the low-carbon hydrogen set to be produced and used in the Humber region.
This is a hydrogen storage facility for a much wider area than Humberside.
Rough Gas Storage Facility
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Rough Gas Storage Facility.
Rough is a natural gas storage facility under the North Sea off the east coast of England. It is capable of storing 100 billion cubic feet of gas, nearly double the storage capacities in operation in Great Britain in 2021.
In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to convert the Rough gas storage into a massive hydrogen storage.
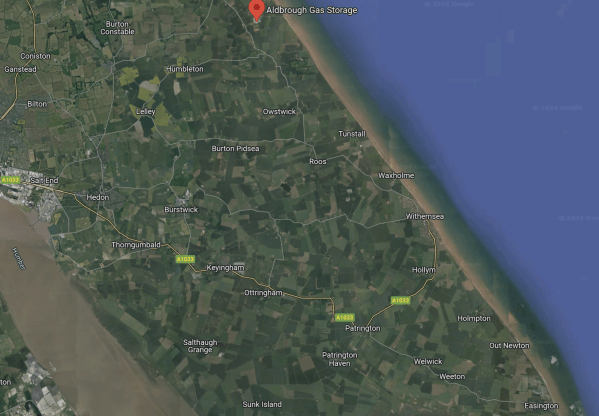
The Location Of Aldbrough Gas Storage, Rough Gas Storage, Salt End And Easington Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows between Salt End and the coast.
Note.
- The river crossing the South-West corner of the map is the Humber.
- Salt End with its power station and chemical works is on the North Bank of the Humber, where the river leaves the map.
- Aldbrough Gas Storage is marked by the red arrow at the top of the map.
- Easington Gas Terminal is in the South-East corner of the map.
- According to Wikipedia, gas flows into and out of the Rough Gas Storage are managed from Easington.
Looking at the map, I feel that the following should be possible.
- The two gas storage sites could be run together.
- Salt End power station and the related chemical works could run on hydrogen.
- Salt End will always have a reliable source of hydrogen.
- This hydrogen could be green if required.
All the chemical works at Salt End, could be run on a zero-carbon basis. Would this mean premium product prices? Just like organic does?
Enter The Germans
The Germans have a huge decarbonisation problem, with all their coal-fired power stations and other industry.
Three massive projects will convert much of the country and industry to hydrogen.
- H2ercules, which is a project of OGE and RWE, will create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen, to where it is needed.
- In Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal, I describe how Uniper are going to build a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhelmshaven.
- AquaVentus is an RWE project that will use 10.3 GW of offshore wind power in German territorial waters to create a million tonnes per year of green hydrogen.
These would appear to be three of Europe’s largest hydrogen projects, that few have ever heard of.
AquaVentus And The UK
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that delivers hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea.
It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network in the North Sea.
These are my thoughts about development of the AquaVentus network.
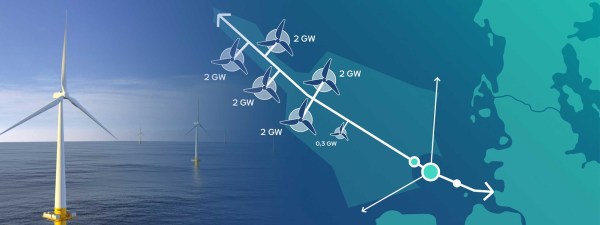
Hydrogen Production And AquaVentus
This RWE graphic shows the layout of the wind farms feeding AquaVentus.
Note.
- There is a total of 10.3 GW.
- Is one of the 2 GW web sites on the UK-side of AquaVentus, the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm, which is being developed by RWE?
- Is the 0.3 GW wind farm, RWE’s Norfolk wind farm cluster, which is also being developed by RWE?
Connecting wind farms using hydrogen pipelines to Europe, must surely mitigate the pylon opposition problem from Nimbys in the East of England.
As the AquaVentus spine pipeline could eventually connect to Peterhead, there will be other opportunities to add more hydrogen to AquaVentus.
Hydrogen Storage And AquaVentus
For AquaVentus to work efficiently and supply a large continuous flow of hydrogen to all users, there would need to be storage built into the system.
As AquaVentus is around 200 kilometres in length and natural gas pipelines can be up to 150 centimetres in diameter, don’t underestimate how much hydrogen can be stored in the pipeline system itself.
This page on the Uniper web site is entitled Green Wilhelmshaven: To New Horizons.
This is a sentence on the page.
Access to local hydrogen underground storage at the Etzel salt cavern site.
An Internet search gives the information, that Etzel gas storage could be developed to hold 1 TWh of hydrogen.
That would be enough hydrogen to supply 10 GW for a hundred hours.
Note that the UK branch of AquaVentus reaches the UK, just to the South of the massive hydrogen storage facilities at Aldbrough and Rough.
It would appear that both Germany and the UK are connected to AquaVentus through substantial storage.
I am certain, that all country connections to AquaVentus will have substantial storage at the country’s hydrogen terminal.
AquaDuctus
This would appear to be the first part of the AquaVentus network and has its own web site.
The web site is entitled Nucleus Of A Offshore Hydrogen Backbone.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The project partners are focusing on a scalable, demand-driven infrastructure: By 2030, AquaDuctus will connect the first large hydrogen wind farm site, SEN-1, with a generation capacity of approximately one gigawatt. SEN-1 is located in the German EEZ in the northwest of Helgoland. The pipeline will transport at a length of approx. 200 km green hydrogen produced from offshore wind to the German mainland and from there to European consumers via the onshore hydrogen infrastructure.
In the next project stage, AquaDuctus will be extended to the remote areas of the German exclusive economic zone towards the tip of the so-called duck’s bill. By that, additional future hydrogen wind farm sites will be connected. Along its way AquaDuctus will provide interconnection points with the opportunity for linking of adjacent national offshore hydrogen infrastructures originating from Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium and United Kingdom which opens the door for Europe-wide offshore hydrogen transport by pipeline.
There is also an interactive map, that gives more details.
This paragraph explains, why the Germans have chosen to bring the energy ashore using hydrogen, rather than traditional cables.
Recent studies show that offshore hydrogen production and transport via pipelines is faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly than onshore electrolysis with a corresponding connection of offshore wind turbines via power cables. The German federal government has also recognized this advantage and has clearly expressed its intention to promote offshore hydrogen production in the North Sea.
I suspect, that some UK offshore wind farms will use the same techniques.
Hydrogen Production For The UK
Electrolysers will probably be built along the East Coast between Peterhead and Humberside and these will feed hydrogen into the network.
- Some electrolysers will be offshore and others onshore.
- Turning off windfarms will become a thing of the past, as all surplus electricity will be used to make hydrogen for the UK or export to Europe.
- Until needed the hydrogen will be stored in Albrough and Rough.
Backup for wind farms, will be provided using hydrogen-fired power stations like Keadby Hydrogen power station.
Financial Implications
I reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there would be winners all round.
Rishi Sunak had the cards and he played them very badly.
It is now up to Keir Starmer, Great British Energy and Jürgen Maier to play those cards to link the energy systems of the UK and Germany to ensure security and prosperity for Europe.
Rolls-Royce To Be A Partner In Zero-Carbon Gas-Fired Power Station In Rhodesia
This press release from Rolls-Royce is entitled Rolls-Royce, Landmark And ASCO Collaborate On CO2 Recovery Power Generation Solutions.
These three bullet points serve as sub-headings.
- Cooperation plans to develop solutions for clean power generation with carbon capture from gas reciprocating engines
- Captured CO2 will be available for use in industries such as food, Efuels, sustainable aviation fuels (SAF), cement and plastic production
- First of-its-kind flexible power generation and carbon capture plant currently under construction in Nottinghamshire, UK
This image shows a Rolls-Royce mtu Series 4000 gas genset.
Note.
- Power is up to 2.5 MW.
- The engine is labelled H2-ready on its web page.
These two paragraphs add some detail to the project.
Rolls-Royce, ASCO Carbon Dioxide Ltd (ASCO), and Landmark Power Holdings Limited (LMPH), have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) aimed at developing scalable solutions for clean power generation with carbon capture from mtu gas reciprocating engines. This strategic partnership will help enable power generation customers to achieve their net zero ambitions and marks a significant step towards addressing climate change.
“Power generation is a highly attractive, growing market segment and an area of strategic focus for Rolls-Royce, where partnerships can help further grow market position and broaden its power generation offering, as set out at last November’s Capital Markets Day”, said Tobias Ostermaier, President Stationary Power Solutions at Rolls-Royce Power Systems. Rolls-Royce is committed to becoming a net zero company by 2050 and supporting customers to do the same.
These are my thoughts.
Uses Of Carbon Dioxide
The press release from Rolls-Royce lists a few uses of carbon dioxide.
The plan is to make the captured CO2 available (utilisation) for use in various industries such as food production, Efuels, sustainable aviation fuel (SAF), cement and plastic production (utilisation). The captured CO2 will also be ready for transportation should permanent sequestration be preferred (storage).
Carbon dioxide can also be added to the air in greenhouses, that are producing flowers, herbs, salad vegetables, soft fruit and tomatoes.
ASCO Carbon Dioxide
ASCO Carbon Dioxide is a subsidiary of French company; Schneider Electric.
The home page on their web site, describes ASCO Carbon Dioxide like this.
The Swiss ASCO CARBON DIOXIDE LTD is a globally operating company that offers complete solutions for CO2 and dry ice. The range of services includes carbon capture plants, CO2 recovery systems, ASCOJET dry ice blasting machines, dry ice production machines, CO2 cylinder filling systems, CO2 vaporisers, CO2 storage tanks, CO2 dosing systems for water neutralization and various other CO2 and dry ice equipment.
Thanks to this broad product range and more than 130 years of practical experience in the comprehensive CO2 and dry ice sector, the customer benefits from individual, complete CO2 solutions from a single source. ASCO has been part of the international industrial gases company Messer Group since 2007 and is its centre of competence for CO2.
In other words, the world and especially the climate change activists may hate carbon dioxide with a vengeance, but ASCO Carbon Dioxide see it as a way to make money and something that needs love.
It also seems, that if you want to do something with or to carbon dioxide, then ASCO Carbon Dioxide could be one of the first companies that you call.
Landmark Power Holdings Limited
The About page on their web site, describes the mission of Landmark Power Holdings Limited like this.
LMPH was established in 2019 with the purpose to help to build a circular economy, by applying new methodologies to proven technologies in energy production.
We support the transition to net zero by supplying dispatchable, low carbon energy that enables more renewable energy production while contributing to a circular economy, by eliminating inefficiencies in production, ensuring that every input is used to its maximum potential and treating all production waste as a profitable resource.
This Solutions page on their web site, describes their FlexPower Plus system.
These are the two introductory paragraphs.
FLEXPOWER PLUS® is LMPH’s modular approach to optimising the generation of clean flexible power. It is a combination of High Efficiency Flexible Power Generation modules and Carbon Capture Utilisation (CCU) modules.
Each of the modules can be added to the production processes depending on the site and production needs.
This last paragraph describes the result.
When you combine the the High Efficiency Flexible Power Generation modules with the Carbon Capture Utilisation (CCU) modules, the power generation is classified as low carbon and considered to be as clean as wind power but with the capacity to provide baseload power.
They certainly sound like my kind of company, as I was simulating processes like this for ICI in the 1970s.
ICI taught me that only four things should leave a chemical or other process plant.
- Product, that is sold at an advantageous price.
- Pure water
- Clean air
- Everybody who worked there.
It appears a FlexPower Plus system produces three valuable products; electricity, heat and pure food-grade carbon-dioxide.
The Rhodesia Project
The Rhodesia project has its own page on the Landmark Power Holdings web site, where these four paragraphs describe the project.
The Rhodesia project is a joint venture with Victory Hill, a specialist investment firm targeting direct investments in global energy infrastructure that support the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
The Rhodesia project is located in north Nottinghamshire near Worksop and has an electrical capacity of 10MW.
Additional capacity is to be sold through a private wire power supply for local businesses with the intent to facilitate vehicle charging stations.
Construction started in March 2022 and the start of power production is projected for Q3 2024 with the full CO2 capture from Q4 2024.
There is also this paragraph, that lists the partners in the Rhodesia project.
For the development of the Rhodesia project LMPH and Victory Hill have partnered with global industrial groups such as Mitsubishi Turboden S.p.A., MTU Rolls-Royce Solutions UK, ASCO CARBON DIOXIDE LTD, Climeon.
With three of the world’s largest companies amongst the partners, this partnership must have a high chance of success.
Victory Hill Capital Hill Partners
Victory Hill Capital Partners are partners in the Rhodesia project.
Their joint philosophy with Landmark Power Holdings is summed up on this video.
Working Together
The press release from Rolls-Royce says this about the partnership.
Rolls-Royce is contributing its extensive experience and global network in the field of decentralized power generation to the cooperation through its Power Systems division with the mtu product portfolio. The contribution of LMPH, a developer of high-efficiency Combined Heat and Power (CHP) projects, is its patented FLEXPOWER PLUS® concept, combined with technical expertise and patented technologies. ASCO has over 50 years of experience in developing and building carbon capture (or CO2-Recovery) plants and will be providing valuable insights and solutions from the carbon capture industry.
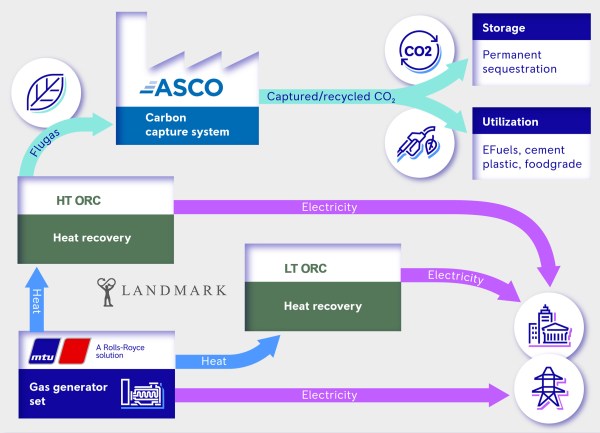
There is also this diagram of the system.
Note.
- The 4000 gas genset is in the bottom-left corner.
- The HT PRC and LT ORC are two Mitsubishi turbo-generators generating electricity from waste heat.
- The ASCO carbon capture system is in the top-left corner.
- Carbon dioxide can either be stored or used.
This system should be zero-carbon, once the design is fully tested.
A View From The Top
This paragraph from the Rolls-Royce press release gives the view of the President Stationary Power Solutions at Rolls-Royce Power Systems.
Tobias Ostermaier, President Stationary Power Solutions at Rolls-Royce Power Systems, said: “We are convinced that CO2 capture and storage systems in combination with our mtu gas gensets are an important building block on the way to Net Zero. As a complement to renewable energy sources, internal combustion engines can already provide clean, cost-effective and extremely reliable power generation.”
I suspect he’s rather pleased.
Google Starts Building £790m Site In Hertfordshire
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Google has invested $1bn (£790m) to build its first UK data centre
These are the first four paragraphs.
The tech giant said construction had started at a 33-acre site in Waltham Cross, Hertfordshire, and hoped it would be completed by 2025.
Google stressed it was too early to say how many jobs would be created but it would need engineers, project managers, data centre technicians, electricians, catering and security personnel.
The prime minister said it showed the UK had “huge potential for growth”.
The project marked the latest investment by a major US tech firm in Britain, after Microsoft announced it would invest £2.5bn to expand data centres for artificial intelligence (AI) across the UK.
Note.
- By “completed by 2025” do they mean completed before 2025 or completed by the end of 2025. Judging by the time they took to build their London HQ, its the latter.
- Rishi is right about the UK having a huge potential for growth! Especially, if the nihilists of the United States vote in the Big Orange!
- Judging by the total spend of £2.5 billion on data centres and the £790 million for this one, this looks to be the first of three.
But where is this data centre going to be built?
This article on EssexLive is entitled Google To Move Into Waltham Cross With £788m Data Centre To Support ‘AI Innovation’, where this is said.
The new data centre will go on land at Maxwell’s Farm, next to the A10 Great Cambridge Road and around one mile from the M25 junction 25. Debbie Weinstein, Google vice president and managing director in the UK and Ireland, set out the decision in a blog post on Thursday, January 18 – the fourth day of the World Economic Forum’s Davos 2024 in Switzerland.
This is a Goggle Map of that area, when I searched for Maxwell’s Farm.
Note.
- The red arrow indicates the result of my search, which Google interpreted as A.J. Maxwell.
- The dual-carriageway road running down the East side of the map is the A10 between London and Cambridge.
- The A10 road joins the M25 at Junction 25.
- The arrow to the South-West of the roundabout indicates the new studios; Sunset Waltham Cross, which is being built.
- At the other side of the studio site, there is a label saying New River and this important piece of London’s water infrastructure can be traced to the top of the map.
- The other dual-carriageway road is the B198 or Lieutenant Ellis Way.
- A quick calculation shows that 33 acres is roughly a 365 metre square.
I would suspect that the data centre will lie somewhere between the A10, the B198 and the New River.
This Google Map shows the South-East corner of the site.
Note.
- There appears to be a lane running East-West, that crosses over both the A10 and the New River.
- Theobalds Lane appears to have some housing and possibly a farm.
- The smaller field by the roundabout appears to have some animals using it as grazing.
- The field between the East-West lane and Theobalds Lane appears to have a good crop of cereal.
The East-West lane would appear to be a possible Southern border of the site.
This Google Map shows where the East-West lane goes.
Note.
- The lane leads to Queen Mary’s High School.
- The school also has access from Lieutenant Ellis Way.
- The New River appears to form, the Eastern boundary of the school site.
- There are sports pitches between the New River and the school.
The New River looks to be the Western boundary of the Google site.
This Google Map shows around the red arrow from the Google search that led me to this area.
Note.
- A.J. Maxwell is identified by the red arrow in the Theobalds Enterprise Centre.
- The New River can be seen at the West of the map.
- A hedge runs roughly East-West to the North of the Enterprise Centre.
- North of the hedge are a number of football pitches, which appear to belong to the Affinity Academy at Goffs Churchgate.
The hedge could be the Northern boundary of the Google site.
This Google Map shows the area between the South of the Enterprise Centre and the East-West lane I picked out earlier.
A crude measurement indicates it could be around 33 acres or slightly more.
This picture is used in nearly all the news reports about the Data Centre.
Note.
- Could that be the gentle curve of the New River on the left?
- With the high fence, the New River forms an almost-mediaeval defence against trespassers.
- There looks to be a dual-carriageway road running down the other side of the site, which would be the A10.
- Between the A10 and the site, there appears to be loots of dark areas, which I take to be car parks.
- Are the car-parking spaces in the front of the picture marked for those, who are disabled? There certainly appear to be chargers on some spaces.
I have a few thoughts.
The Relative Locations Of Google’s Data Centre And Sunset Studios?
This Google Map shows the two sites to the West of the A10.
Note.
- St. Mary’s High School is in the North-West corner of the map.
- Cheshunt Football Club is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The dual-carriageway A10 runs North-South on the map.
- I believe that Google’s Waltham Cross Data Centre will be located in the field to the West of the A10, at the top of the map.
- The A10 connects to the M25 at Junction 25, which is in the centre at the bottom of the map.
- In The Location Of Sunset Studios In Broxbourne, Sunset Studios are placed to the North West of the Junction 25 roundabout.
- Just as the A10 forms the Eastern boundary of both sites, the New River forms the Western boundary.
The two sites are close together between the A10 and the New River, separated by the dual-carriageway Lieutenant Ellis Way.
Will Google’s Data Centre Be Storing Data For Sunset Studios?
I’ve never worked in the production of films, but these days with digital electronic cameras, CGI, motion capture and other techniques, producing a film must need huge amounts of data storage.
- So have Sunset Studios outsourced their data storage needs to Google?
- Perhaps too, Sunset Studios found the local authority welcoming and this attitude was recommended to Google.
- Both sites will need local services like electricity, gas, sewage and water.
I suspect that there would be cost savings in construction and operation, if the two sites shared the utilities.
Providing Electricity And Heat For Both Sites
Consider.
- I estimate from information given in the Wikipedia entry for Google Data Centres, that a data centre needs between 10 and 12 MW.
- There is no obvious power source like offshore wind or a nuclear power station nearby.
- There is the 715 MW Rye House gas-fired power station, which is a few miles away.
- In Google Buys Scottish Offshore Wind Power, I talked about how Google had signed a Corporate Power Purchase Agreement to buy 100 MW from the Moray West offshore wind farm.
Google and Sunset Studios would also want an electrical and heat supply that is at least 100 % reliable.
Liverpool University had the same problem on their hundred acre campus in the centre of Liverpool.
- The University decided to build their own 4 MW Combined Heat and Power Unit (CHP), which is described in this data sheet.
- It is fired by natural gas.
- On their web site, Liverpool University state that their CHP can be adapted to different fuel blends. I take this includes zero-carbon fuels like hydrogen and carbon-neutral fuels like biomethane.
But given their location in Waltham Cross close to the Lea Valley, CHP units may have a use for their carbon dioxide.
This Google Map shows between Junction 15 of the M25 and Tomworld.
Note.
- Junction 25 of the M25, where it joins the A10 is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The sites of Google’s Data Centre and Sunset Studios can be picked out with reference to the previous map.
- Tomworld is in the North-East corner of the map.
- So why should Tomworld need a lot of carbon-dioxide?
This Google Map shows Tomworld.
Note.
- This web page indicates what Tomworld do.
- They have 44 acres of glass growing tomatoes, about five miles to the North-East of Google’s Data Centre.
- The map has lots of other greenhouses.
I know of a guy, who has a large greenhouse, that grows tomatoes for the supermarkets.
- He heats the greenhouse with a gas-fired Combined Heat and Power Unit (CHP).
- The electricity produced runs his business.
- Any surplus electricity is fed into the grid.
- The carbon dioxide is fed to the plants in the greenhouse, which helps them grow quality tomatoes.
I just wonder, if carbon dioxide from CHP units at Google’s Data Centre and Sunset Studios could be used by the multitude of greenhouses in the Lea Valley.
Could A Carbon Dioxide Pipeline Be Built Along The M25?
This Google Map shows the Northern section of the M25, South of Waltham Cross.
Note.
- The M25 running East-West across the bottom of the map.
- Junction 25 of the M25 in the South-West corner of the map.
- The A10 running North-South at the West of the map.
- Google’s data centre and Sunset Studio are to the West of the A10.
- The River Lee, which has numerous water courses is at the East of the map.
I wonder, if a carbon dioxide pipeline could be built along the M25 to connect the producers to those who could use it?
- It would not be a dangerous pipeline as carbon dioxide is a fire extinguisher.
- It wouldn’t be a huge pipe.
I think it would be possible.
Google’s Commitment To Being Zero-Carbon
This blog post on the Google web site is entitled Our $1 Billion Investment In A New UK Data Centre, has a section, which has a sub-title of 24/7 Carbon-Free Energy By 2030, where this is a paragraph.
Additionally, we’re also exploring new and innovative ways to use the heat generated by data centres, and this new facility will also have provisions for off-site heat recovery. Off-site heat recovery presents an opportunity for energy conservation that benefits the local community, as it allows us to capture the heat generated by the data centre so that it can be used by nearby homes and businesses. The data centre is also set to deploy an air-based cooling system.
If they are using off-site heat recovery, it would be logical to use waste carbon dioxide from CHPs to provide carbon dioxide for the local horticultural businesses.
Will Google Be Building A Vertical Farm Nearby?
In Schneider Electric: Vertical Farming – The Next Yield In Data Centre Sustainability, I noted that some data centres are paired with vertical farms to increase their sustainability.
Could Google be doing that in Waltham Cross?
- They will have a lot of waste heat.
- They will have a fair bit of carbon dioxide, which could be used to help plants grow.
- The local workforce probably contains a lot of experience of market gardening.
I like the idea of pairing a data centre and a vertical farm.
Public Transport Access
Consider.
- Increasingly, the cost of electric vehicles, medical problems and the UK economic situation are causing people to adopt a car-free lifestyle.
- After my stroke, my eyesight deteriorated such, that I am no longer allowed to drive.
- Others may live in one-car families and it may not be their’s to use every day.
- Or your car may just break down on the way to work.
For these and probably lots of other reasons, any large site employing a lot of employees, must have a valid way of getting there by public transport.
The nearest rail station to Google’s Data Centre and Sunset Studios is Theobalds Grove station.
This Google Map shows the roads between the sites and the station.
Note.
- The Sunset Waltham Cross label in the South West corner.
- Google’s Data Centre will be just off the map to the West of the A10.
- Theobalds Grove station is marked by the TfL roundel in the North-East corner of the map.
- There would appear to be no bus stops on Winston Churchill Way or the A10.
I walked South from the station to Winston Churchill Way, where I took these pictures.
Note.
- At that point, I gave up because of the cold and pollution.
- It was also a Saturday morning about midday.
The route I took is certainly not an alternative route to get to Google’s Data Centre or Sunset Studios.
A Possible Station At Park Plaza North
This article on the BBC is entitled Broxbourne: Two New Stations Planned.
This is the sub-heading.
Two new train stations could be built in Hertfordshire if plans to tighten planning policies are adopted.
This is the first paragraph.
Broxbourne Borough Council said stops at Park Plaza North – between Turkey Street and Theobalds Grove London Overground stations – and Turnford on the London to Bishop’s Stortford route would be subject to a consultation.
Later the BBC say that Park Plaza North station will be South of the A121 Winston Churchill Way near Waltham Cross
This Google Map shows the area South-East of the roundabout, where Winston Churchill Way meets the A10.
Note.
- The green patch of land to the South-East of the roundabout where Winston Churchill Way meets the A10 appears to be ripe for development.
- Looking at the green patch with a higher resolution, the land is little more than high class scrub beloved of newts.
- The London Overground line to Cheshunt runs down the East side of the site.
- To the North, the London Overground crosses Winston Churchill Way to get to Theobalds Grove station.
- To the South, the London Overground crosses the M25 to get to Turkey Street station.
- There is a lane running East-West along the South edge of the site, which crosses the railway in a level crossing.
This picture clipped from Google StreetView shows the level crossing.
This is certainly one, that drivers dread.
This GoogleMap shows the level crossing and a stretch of the London Overground.
Note.
- The level crossing is in the South-East corner of the map.
- There isn’t much space to put a London-bound platform on the East side of the tracks, South of the Park Road circle.
- There is plenty of space to put a Cheshunt-bound platform on the West side of the tracks.
- North of the Park Road circle, there would appear to be space for two platforms.
It will need a lot of ingenuity to provide a safe and efficient solution to the problems of the level crossing and fitting a station in this limited space.
The first thing I’d do, would be to dig an underpass for pedestrians and cyclists to connect the two halves of Park Lane.
SSE Thermal Outlines Its Vision For The UK’s Net Zero Transition
The title of this post is the same as that of this news item from SSE Thermal.
This is the opening statement.
SSE Thermal, part of SSE plc, is calling on government to turbocharge the delivery of low-carbon technologies to help deliver a net zero power system by 2035.
Two paragraphs then outline what the company is doing.
The low-carbon developer is bringing forward multiple low-carbon projects across the UK. This includes Keadby 3 Carbon Capture Power Station in the Humber – which is being developed in collaboration with Equinor and recently became the first power CCS project in the country to receive planning permission – and Aldbrough Hydrogen Pathfinder, which would unite hydrogen production, storage and power generation in one location by the middle of this decade.
These projects would form part of SSE’s £24bn investment programme in the UK, and in addition to supporting the decarbonisation of industrial heartlands and powering a low-carbon future, they would also help to secure a just transition for workers and communities.
The news item then talks about the future.
Now, SSE Thermal has published ‘A vision for the UK’s net zero transition’ which outlines the need for these low-carbon technologies and the potential of carbon capture and hydrogen in providing flexible back-up to renewables.
It also outlines the steps Government should take to facilitate this:
- Progress the deployment of carbon capture and storage (CCS) and hydrogen infrastructure in a minimum of four industrial areas by 2030.
- Support first-of-a-kind carbon capture and storage and hydrogen projects to investment decisions before the end of next year.
- Increase its ambition for power CCS to 7-9GW by 2030, with regular auctions for Dispatchable Power Agreements.
- Set out a policy ambition for hydrogen in the power sector and a strategy for delivering at least 8GW of hydrogen-capable power stations by 2030.
- Accelerate the delivery of business models for hydrogen transport and storage infrastructure, to kickstart the hydrogen economy.
These are my thoughts.
Carbon Capture And Use
There is no mention of Carbon Capture And Use, which in my view, should go hand in hand with Carbon Capture And Storage.
- Sensible uses for carbon dioxide include.
- Feeding it to plants like tomatoes, flowers, salad vegetables, soft fruit and herbs in greenhouses.
- Mineral Carbonation International can convert a dirty carbon dioxide stream into building products like blocks and plasterboard.
- Deep Branch, which is a spin-out from Nottingham University, can use the carbon dioxide to make animal feed.
- Companies like CarbonCure add controlled amounts of carbon dioxide to ready-mixed concrete to make better concrete and bury carbon dioxide for ever.
Surely, the more carbon dioxide that can be used, the less that needs to be moved to expensive storage.
Note.
- There is a lot of carbon dioxide produced in Lincolnshire, where there are a lot of greenhouses.
- At least three of these ideas have been developed by quality research in Universities, in the UK, Australia and Canada.
- I believe that in the future more uses for carbon dioxide will be developed.
The Government should do the following.
- Support research on carbon capture.
- Support Research on finding more uses for carbon dioxide.
Should there be a disposal premium or tax credit paid to companies, for every tonne of carbon dioxide used in their processes? It might accelerate some innovative ideas!
Can We Increase Power CCS to 7-9GW by 2030?
That figure of 7-9 GW, means that around a GW of CCS must be added to power stations every year.
Consider.
- It is probably easier to add CCS to a new-build power station, than one that is a couple of decades old.
- Better and more affordable methods of CCS would probably help.
- In Drax To Pilot More Pioneering New Carbon Capture Technology, I wrote about a promising spin-out from Nottingham University
- In Drax Secures £500,000 For Innovative Fuel Cell Carbon Capture Study, I wrote about another system at Drax, that captures carbon dioxide from the flue gases at Drax.
If we develop more ways of using the carbon dioxide, this will at least cut the cost of storage.
Can We Deliver At Least 8GW Of Hydrogen-Capable Power Stations By 2030?
Do SSE Thermal mean that these power stations will always run on hydrogen, or that they are gas-fired power stations, that can run on either natural gas of hydrogen?
In ‘A vision for the UK’s net zero transition’, this is said about the hydrogen power stations.
Using low-carbon hydrogen with zero carbon emissions at point of combustion, or blending hydrogen into existing stations.
So if these power stations were fitted with carbon capture and could run on any blend of fuel composed of hydrogen and/or natural gas, they would satisfy our needs for baseload gas-fired power generation.
Hydrogen Production And Storage
SSE’s vision document says this about Hydrogen Production.
Using excess renewables to create carbon-free hydrogen, alongside other forms of low-carbon hydrogen, which can then be stored and used to provide energy when needed.
SSE’s vision document also says this about Hydrogen Storage.
Converting existing underground salt caverns or creating new purpose-built caverns to store hydrogen and underpin the hydrogen economy.
This page on the SSE Thermal web site is entitled Aldbrough Has Storage, where this is said about storing hydrogen at Aldbrough.
In July 2021, SSE Thermal and Equinor announced plans to develop one of the world’s largest hydrogen storage facilities at the Aldbrough site. The facility could be storing low-carbon hydrogen as early as 2028.
With an initial expected capacity of at least 320GWh, Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage would be significantly larger than any hydrogen storage facility in operation in the world today. The Aldbrough site is ideally located to store the low-carbon hydrogen set to be produced and used in the Humber region.
From my own experience, I know there is a similar salt structure in Cheshire, which has also been used to store gas.
Earlier, I said, that one of the things, that SSE would like the Government to do is.
Progress the deployment of carbon capture and storage (CCS) and hydrogen infrastructure in a minimum of four industrial areas by 2030.
If Cheshire and Humberside are two sites, where are the other two?
Deciding What Fuel To Use
If you take the Humberside site, it can provide electricity to the grid in three ways.
- Direct from the offshore and onshore wind farms.
- Using natural gas in the gas-fired power stations.
- Using hydrogen in the gas-fired power stations.
SSE might even add a battery to give them a fourth source of power.
In the 1970s, I used dynamic programming with Allied Mills to get the flour mix right in their bread, with respect to quality, cost and what flour was available.
Finance For SSE Thermal Plans
The news item says this.
These projects would form part of SSE’s £24bn investment programme in the UK.
£24bn is not the sort of money you can realise solely from profits or in sock drawers or down sofas, but provided the numbers add up, these sorts of sums can be raised from City institutions.
Conclusion
I like SSE Thermal’s plans.
Making Carbon Dioxide Into Protein For Innovative Animal Feed
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Horizon.
These are the first three paragraphs.
It’s common knowledge that proteins, a key component of human nutrition, are also essential for making animal feeds. Less well known is the uncomfortable fact that much of the protein we feed animals in Europe leads to deforestation and overfishing worldwide.
Biotechnology start-up Deep Branch have designed a biochemical transformation process that turns carbon dioxide (CO2) into a protein-rich powder for animals to eat.
The Deep Branch process converts carbon dioxide into a powder, called Proton, which has around 70% protein content. This is much higher than natural soy, which has around 40%.
Note.
- The technology is the brainchild of Peter Rowe, a PhD graduate in molecular biology of Nottingham University in the UK.
- Deep Branch appears to be a well-backed Anglo-Dutch company.
- Their backers are European and British household names and institutions.
- Drax, who have plenty of carbon dioxide, are also backers.
I believe that even if Deep Branch doesn’t succeed, then someone else will, with this technology.