Huddersfield Station – 30th September 2025
This press release on the Network Rail Media Centre is entitled Huddersfield Station Set To Reopen Next Week With New Temporary Layout.
As it is now next week, I went to have a look at the progress today.
I made a mistake and got on a Grand Central Train, which meant, I had to change at York.
Speeding past Drax power station on the Selby Diversion, I took these pictures.
We were only in a 125 mph diesel, so we couldn’t take advantage of the 160 mph running, that the East Coast Main Line’s new signalling might allow on this section. The Wikipedia entry for the Selby Diversion, says this about the possible speeds.
The line was the first purpose-built section of high-speed railway in the UK having a design speed of 125 mph; however, research by British Rail in the 1990s indicated that the route geometry would permit up to 160 mph operation, subject to the necessary overhead line equipment and signalling upgrades. The new line also avoided the speed restriction over the swing bridge at Selby. The former ECML route, the NER’s 1871 York and Doncaster branch line, was closed from Selby northwards.
As the Selby Diversion opened in 1983, I wouldn’t be surprised that the calculations were performed on British Rail Research’s Pace 231-R, which was similar to the one I used at ICI and the pair, that NASA used calculate how to land Apollo on the moon.
When I eventually got to Huddersfield, I took these pictures.
Note.
- In I’ve Just Glimpsed The Future Of Train Travel Across The North Of England And I Like It, there are pictures of Huddersfield station, that were taken on the 21st August, soon after the work started.
- In Huddersfield Station – 15th December 2023, there are pictures of Huddersfield before the work started.
- Much of the work seems to have been done at the Western end of the station to lengthen the platform on the Penistone Line to Sheffield.
- Platform 2 for the Penistone Line has also been renumbered Platform 1.
Work still to be carried out at Huddersfield station, includes refurbishing the roof, installing the electrification and adding a couple of new platforms.
These are my thoughts.
Which Platforms Will Be Electrified?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the proposed electrification in Huddersfield station.
Note.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map indicates Huddersfield atation.
- The two red-and-black tracks going diagonally across the map are the Hudderfield Line.
- The red-and-black colour, indicates that the two tracks will be electrified.
- South of these two tracks, the Penistone Line sneaks into Platform 1 at Huddersfield station.
- The Penistone Line goes to Sheffield in a South-Westerly direction.
- There appears to be a crossover, so that trains from the Penistone Line can use both Platforms 1 and 2 in Huddersfield station.
- The OpenRailwayMap appears to show planned electrification between Stalybridge and Leeds stations.
- To the East of Leeds planned electrification is shown as far as Micklefield and Church Fenton stations.
Once installed, this electrification will create a complete electrified route across the Pennines from Liverpool Lime Street in the West to the East Coast Main Line in the East.
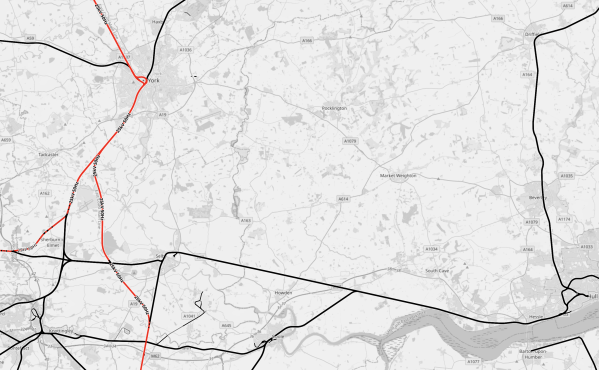
This OpenRailwayMap shows the planned electrification between Micklefield and Hull stations.
Note.
- Red tracks are electrified.
- Black tracks are not electrified.
- York is in the North-West corner of the map, with the electrified East Coast Main Line going through the station North-South.
- South of York, the East Coast Main Line now splits.
- The Western branch includes an electrified line to Micklefield station, Neville Hill depot and Leeds station.
- The Eastern Branch is the Selby Diversion, which is an electrified 160 mph line, that avoids the Selby coalfield.
- Running West-East across the map is the unlectrified Micklefield and Hull Line, which goes via Selby.
- Hull is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Hull is 42 miles from Micklefield and 36.1 miles from the Temple Hirst junction on the Selby Diversion, so it is within range of battery-electric trains, with charging at Hull station.
- Hitachi’s battery-electric Class 802 trains, used by Hull Trains and TransPennine Express, which are currently on test, should certainly be able to serve Hull.
Hull can become an electrified station, without the expense and disruption of full electrification.
How Long Is Platform 1 At Huddersfield Station?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the new Platform 1 at Huddersfield station.
Note.
The blue arrow indicates Huddersfield station.
- The three darker orange lines indicate the two through platforms 2 and 3, and the reconfigured bay platform 1.
- There is a cross-over between platforms 1 and 2, which connects Platform 2 to the Penistone Line.
- In the South-West corner of the map is a hundred metre scale.
- Using the scale, I estimate that the length of the bay platform 1 is around 120 metres.
- In the last two rows of pictures in the gallery of this post, a three car Class 150 train is shown in Platform 1.
- A three car Class 150 train is approximately sixty metres long.
Looking at the pictures, I wouldn’t be surprised if the new platform has been designed to take two three-car Class 150 trains. It would certainly take a pair of two-car Class 150 trains.
Other trains and their lengths that might use the platform include.
- Class 170 – three-car – 70.85 metres
- Class 195 – two-car – 48.05 metres
- Class 195 – three-car – 71.40 metres
- Class 195 – 2 x two-car – 96.10 metres
- Class 810 – five-car – 120 metres
The Class 810 uses 24 metre cars, so that a pair of trains, will fit in St. Pancras. But with perhaps selective door opening could a single Class 810 train run a St. Pancras and Huddersfield service, perhaps with a split and join at Sheffield.
Electrification Across The Pennines
The TransPennine Route will be electrified between Liverpool Lime Street and Micklefield stations, once the current works between Huddersfield and Leeds are complete.
Sections without electrification include.
- Bradford Interchange and Doncaster – 52.1 miles
- Cleethorpes and Doncaster – 52.1 miles
- Harrogate and Leeds – 18.3 miles
- Hazel Grove and Doncaster – 52.6 miles
- Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- Hull and Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- Saltburn and Northallerton – 28.1 miles
- Sunderland and Northallerton – 46.8 miles
- Scarborough and York – 42.1 miles
I expect that Hitachi trains with batteries or CAF’s tri-mode trains will be able to handle these routes in a low-carbon manner.
Electrification Between Stalybridge And Huddersfield
This section is shown as being electrified on OpenRailwayMap.
But as it is only 18 miles and includes the Standedge Tunnels will the route use battery-electric trains?
Government Approval For Large Solar Farm
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
A large solar farm in East Yorkshire has been given the go ahead by the government.
These two introductory paragraphs add more detail.
The 3,155 acre (1,277 hectares) site will be built on land around Gribthorpe, Spaldington and Wressle and Howden.
Its developers said it would produce 400 megawatts of electricity – enough to power 100,000 homes.
Note.
- This solar farm is five square miles or a 2.2 mile square.
- Due to the size of the scheme the planning application was handled by the Planning Inspectorate as it was classed as national infrastructure.
- Ed Miliband may have been involved in the final decision.
- The solar farm would connect to the National Grid at the Drax substation in North Yorkshire.
But the solar farm is not without opposition, as these last three paragraphs indicate.
George McManus, spokesman for East Riding Against Solar Expansion (ERASE), said the approval “brings us a step closer to enormous swathes of agricultural land being blanketed in a million, Chinese manufactured, solar panels.”
He added: “Other projects in the pipeline will see another 20,000 acres disappear under glass.
“The East Riding is being industrialised and people need to wake up to that.”
Nothing is said about where Reform UK’s Mayor for Hull and East Yorkshire sits.
Arriving In Liverpool Lime Street Station – 10th May 2025
Liverpool Lime Street station has one of the more spectacular approaches of British railway stations, as these pictures show.
These sections describe the approach.
Crossing The Mersey
You cross the Mersey at Runcorn on the Ethelfreda or Britannia Bridge, which is described in this Wikipedia entry.
It was completed in 1868 and hopefully in a few years, it will be carrying High Speed Two trains between London and Liverpool.
On your right as you cross the Mersey to Liverpool is the Silver Jubilee road bridge, which is a through arch bridge that opened in 1961 to replace a historic transporter bridge. I am just a little bit too young to have seen the transporter bridge.
Further to your right, you can see the Mersey Gateway Bridge, which is a cable-stayed bridge, that opened in 2017 and is described in this Wikipedia entry.
Drax’s Biomass
As you approach Lime Street station, you pass through Edge Hill, where there are the GB Railfreight sidings, where the biomass trains for Drax power station are marshalled for their journey across the Pennines. These Drax trains seem to be one of the few freight trains in the UK, that carry advertising. Tesco trains also do, but their’s is just big letters.
In Do Cummins And Stadler Have a Cunning Plan?, I talked about the possible conversion at some date in the future of GB Railfreight’s new electro-diesel Class 99 locomotives to electro-hydrogen locomotives. These locomotives will surely be ideal for hauling Drax’s biomass trains across the Pennines.
I do believe that these Class 99 locomotives are the future of heavy freight trains in the UK. In Iarnród Éireann Looks At Diesel Loco Replacement Options, I write about speculation, that Stadler may build a version for the Irish.
Through The Edge Hill Cutting
From Edge Hill a deep cutting through the sandstone takes you into Lime Street station.
It looked good in the sun, but the first time I arrived in the city to start my studies at Liverpool University, it was chucking it down and the cutting was very dark and wet.
It was a very different welcome to that, which I got yesterday.
My Train Arrived In Platform 10
Liverpool Lime Street has two cast iron train sheds.
- The Western shed has platform 1 to 5 and generally handles trains from the East.
- The Eastern shed has platform 6 to 10 and generally handles trains from the South.
Note.
- Changing between trains is just a step-free walk across the station concourse.
- Both sections have their own taxi rank and full-size clock.
- The Ticket Office is in the Western train shed.
I just walked from my train to the Ticket Office, bought a Lancashire Day Ranger ticket and then walked fifty metres to my next train.
How many stations have such an easy change of trains?
Is Liverpool Lime Street Station Ready For High Speed Two?
Consider.
- I travelled North in an 11-car Class 390 train, which is 265.3 metres long and can carry 607 passengers.
- As the last pictures show, the train fitted easily into platform 10.
- High Speed Two plans to send 200 metre classic-compatible trains to Liverpool Lime Street, with each having a capacity of up to 528.
It looks to me, that these High Speed Two classic-compatible trains will fit into Liverpool Lime Street station, at any platform that currently accepts an eleven-car Class 390 train.
Looking on Real Time trains over the last few days, I’ve found eleven-car Class 390 trains using platforms 9, 10 and 6.
It seems that Network Rail’s engineers have done a superb job to turn the Grade II Listed station, into one of the best operationally.
Eastern Green Link 2 Moves Up A Gear Using Low Carbon Fuel For Material Handling Trucks
The title of this post is the same, as that of this press release from National Grid.
These three bullet points act as sub-headings.
- Eastern Green Link 2 (EGL2), a high voltage direct current (HVDC) 436km subsea transmission cable connecting Scotland and England, is being delivered as a joint venture by National Grid Electricity Transmission and SSEN Transmission.
- Project sustainability efforts are accelerating by adopting Hydrogenated Vegetable Oil (HVO) fuelled trucks to move materials in Yorkshire.
- The introduction of HVO fuel will deliver up to 90% reduction in direct CO2 emissions.
The use of HVO fuel is good and the carbon dioxide emission savings are to be welcomed, but there is only so much of this HVO fuel available.
If hydrogen-fueled trucks were available, then this would deliver up to 100% reduction in direct CO2 emissions.
This paragraph from the press release talks about where the HVO fuel will be used.
HVO, a low-carbon biofuel made from waste vegetable oils, will be used at the Wren Hall converter station site in North Yorkshire, where 20-tonne construction trucks will transport approximately 370,000 tonnes of quarry stone from a quarry 27 miles away. This switch from conventional diesel to HVO is expected to deliver up to a 90% reduction in direct CO2 emissions and an 80% reduction in other harmful emissions such as particulate matter.
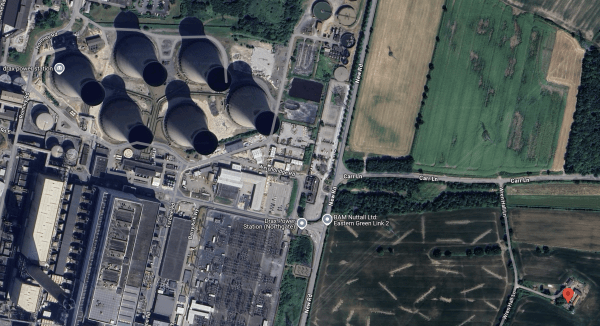
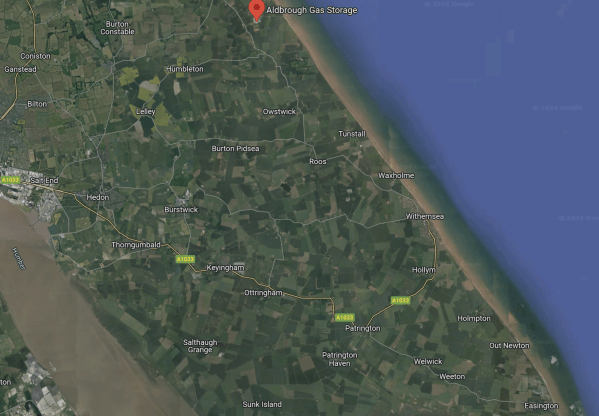
This Google Map shows the location of Wren Hall with respect to Drax power station.
Note.
- The six large cooling towers of the Drax power station are in the North-West corner of the map.
- Google Maps indicate, where they think Wren Hall is, with a red arrow.The lane running North-South to the West of the red arrow is called Wren Hall Lane.
- There is a legend saying BAM Nuttall Ltd Eastern Green Link 2 on the opposite side of the square of lanes to the red arrow.
Click the map to show it to a larger scale.
It looks to me, that if hydrogen could be provided on the Drax site, then the 370,000 tonnes of quarry stone from a quarry 27 miles away could be brought to the site by hydrogen-powered 20-tonne construction trucks.
So how could hydrogen be provided on the Drax site?
- Drax is a 2.6 GW biomass power station, so I’m sure that some electricity could be used to generate hydrogen.
- Drax is a rail-connected site, so hydrogen could be brought in by rail.
- Depending on the amount of hydrogen needed, hydrogen could surely be brought in by road.
I feel that if hydrogen-powered 20-tonne construction trucks were available, this transfer of quarry stone could be performed carbon-free.
Conclusion
This project illustrates a problem with large infrastructure projects all over the UK.
Moving the large amounts of stone, concrete, sand and rubble into and out of construction sites generates a lot of carbon dioxide and pollution from the 20-tonne trucks employed.
If I were to be given Ed Miliband’s job of Secretary of State for Energy Security and Net Zero, one of my first actions, would be to say that all new 20 tonne construction and cement trucks would have to be zero carbon.
I suspect, that zero-carbon with trucks this size, will mean hydrogen, as the weight of the battery would destroy the mathematics of the truck.
This would obviously reduce carbon emissions, but more importantly, what would it do for the health of those working on large construction sites?
In MAN Expands Its Zero-Emission Portfolio, I show MAN’s heavy hydrogen trucks.
This is an articulated heavy hydrogen truck.
I’m sure that MAN could build a hydrogen-powered 20-tonne construction truck.
In Cummins Agrees To Integrate Its Hydrogen ICE Technology Into Terex® Advance Trucks, I talk about the solution to the cement truck problem.
This is a side view of the top-of-the-range monster.
Note.
- Front is to the right.
- I suspect the driver doesn’t have to get out of the cab to discharge the concrete.
- The engine is at the rear with vertical exhausts.
- All axles are driven.
You’d certainly notice one of these if they were to be used in the City of London.
And this is the baby of the range.
Three axles is normal for the UK. so I wonder if this machine will ever make it across the pond.
This last paragraph in the original article describes the X15H hydrogen internal combustion engine.
The X15H was showcased at the Advanced Clean Transportation (ACT) Expo in May (2023), along with its hydrogen ICE-powered concept truck. The X15H features a 700-bar pressure 80kg capacity hydrogen storage system and a range of more than 500 miles, with up to 500 horsepower.
Could one of these trucks really deliver ready-mix concrete from London to Manchester and return?
The trucks would appear to be available, so let’s get a few over and try them out.
Incidentally, if someone had told me ten years ago, there would be rear-wheel drive trucks like Volkswagen Beetles, I’d have said they were wrong in no uncertain terms.
The Wren Hall substation would appear to be an ideal trial project for hydrogen-powered construction trucks and cement trucks.
Ministers Will Relax Rules To Build Small Nuclear Reactors
The title of this post is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Britain’s five nuclear power stations, which generate about 6GW in total, powering 13 million homes, are all nearing the end of their lives
These first three paragraphs indicate the reasons why, the government wants to relax the rules.
Ministers are preparing to relax planning rules to make it easier to build mini nuclear power plants in more parts of the country in order to hit green energy targets and boost the industry.
They are also examining whether it is possible to streamline the process for approving the safety of new nuclear power plants as a way to reduce construction delays.
At present rules state that only the government may designate sites for potential nuclear power stations, of which there are eight, severely limiting where they can be built.
The article includes a vote and surprisingly to me, the vote embedded in the article, shows 92 % in favour of relaxing the rules and only 8 % against.
I must admit these figures surprise me, as I’d have thought more would have been against.
Certain Words Frighten The Public
It is because nuclear is one of those words, that I felt that the vote in favour would have been much lower.
Regular readers of this blog will know, that in the 1960s,, I worked for ICI doing itinerant computing and instrumentation tasks, in my first job after leaving Liverpool University with a degree in Control Engineering.
I can now classify the experience as a superb apprenticeship, where I learned a lot that has been useful to me in later life.
For a time, I was working on nuclear magnefic resonance or NMR scans. ICI Mond Division in Runcorn had one of the best installations for analysing chemicals using this technique, which is described in this Wikipedia entry, which starts with these sentences.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a frequency characteristic of the magnetic field at the nucleus. This process occurs near resonance, when the oscillation frequency matches the intrinsic frequency of the nuclei, which depends on the strength of the static magnetic field, the chemical environment, and the magnetic properties of the isotope involved; in practical applications with static magnetic fields up to ca. 20 tesla, the frequency is similar to VHF and UHF television broadcasts (60–1000 MHz).
One day, the Senior Scientist, who ran the machine came in to work and announced that the property of nuclear magnetic resonance would be replacing X-rays, as the technology had just been used to give a three-dimensional image of something like the tail of a mouse.
Now fifty-five years later, many if not most of us have had MRi scans.
The Wikipedia entry for Magnetic Resonance Imaging or MRi, explains, what happened to the dreaded N-word.
MRI was originally called NMRI (nuclear magnetic resonance imaging), but “nuclear” was dropped to avoid negative associations.
Perhaps, it would be easier to build nuclear power stations, if the level of science teaching in the UK was better.
The Three Paragraphs In Detail
Earlier, I copied three paragraphs from The Times, into this post.
I shall now look at each in detail.
Paragraph 1
Ministers are preparing to relax planning rules to make it easier to build mini nuclear power plants in more parts of the country in order to hit green energy targets and boost the industry.
I was in Suffolk, when the planning of Sizewell B was undertaken.
There appeared to be little strong opposition, but the general feeling was what there was from second home owners, who were worried that the value of their holiday home would decline.
Employment and commerce created by Sizewell B was certainly good for the area in lots of ways.
At the time, my late wife; C was practicing as a family barrister in chambers in Ipswich. She believed that the building of Sizewell B had had a good effect on the area, as it had injected work and money, which had created the finance to allow a couple to end a marriage, that had long since died. She stated a couple of times, that Sizewell B was good for her practice.
Paragraph 2
They are also examining whether it is possible to streamline the process for approving the safety of new nuclear power plants as a way to reduce construction delays.
My worry about streamlining the process for approving safety, is that we approve nuclear power stations so rarely, do we have the qualified personnel to replace elapsed time with people. I would suggest that we don’t.
But we could have.
- We have some excellent universities, where Nuclear Engineering can be studied.
- How many personnel leave the Royal Navy each year, who could be trained as nuclear safety inspectors?
- If say Rolls-Royce and/or Hitachi are building several small modular nuclear reactors a year in the UK, then nuclear engineering will become fashionable, as electronics was for my generation of engineers and it will attract the brightest students.
Perhaps an established university, with access to the needed skills should be funded to set up a Nuclear Safety Institute
Paragraph 3
At present rules state that only the government may designate sites for potential nuclear power stations, of which there are eight, severely limiting where they can be built.
I can envisage new small modular nuclear reactors being built in the UK, where there is a need for lots of electricity to support developments like.
- Offshore wind farms
- Data centres
- Green steelmaking
- Metal refining
- Hydrogen production.
Rolls-Royce have said that their small reactors will be around 470 MW, so I could imagine power stations of this size being placed on disused coal-fired power station sites to boost power in an area. I have already suggested building some on Drax in The Future Of Drax Power Station.
In some locations, the choice could be between a small modular nuclear reactor and some form of energy storage.
Powering Germany
But there is one controversial area, where we can take advantage.
- The Germans are very short of electricity because of their reliance on coal and Russian gas that needs to be replaced.
- The 1.4 GW NeuConnect interconnector is being built by European and Japanese money between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven.
- The AquaVentus hydrogen system could be extended to Humberside to link with UK hydrogen production and storage.
- A couple of small modular nuclear reactors could be built on Humberside to back up hydrogen production, when the wind isn’t blowing.
But Rolls-Royce and other companies have been putting small nuclear reactors close to the sea bed safely for decades, so why no design an offshore reactor that can be placed at a safe distance offshore?
We would need to solve the Putin and friends problem first, but I can see the UK exporting a lot of electricity and hydrogen produced by nuclear energy.
The Future Of Drax Power Station
Drax power station is not liked by a lot of environmentalists.
I have been thinking about the future of the power station and the public company that owns it.
Drax power station has a nameplate capacity of around 2.5 GW running on biomass.
It also will be the Southern end of EGL2, which will be an undersea electricity 2 GW superhighway distributing Scottish wind power from Peterhead in Scotland. So the dreaded biomass hated by certain groups will be relegated from the Premier League of electricity generation and replaced by Scottish wind.
As reported in various publications, Drax has signed a deal in the US, so that the biomass can be used for the production of sustainable aviation fuel (SAF)
To my mind, the Drax site could be an ideal one for one or more small modular nuclear reactors.
- The large Drax site has been producing electricity for 52 years.
- In 1986, the site produced nearly 4 GW of electricity.
- I would suspect that the substations on the site could be enlarged to distribute 4 GW of electricity.
- EGL2 will bring in 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity.
- The site has excellent rail connections.
- The site has twelve cooling towers and is encircled by the River Ouse.
- Could all this water be used for cooling the small modular nuclear reactors.
I believe that perhaps three small modular nuclear reactors could be built on the Drax site to backup EGL2 and bring a reliable source of sustainable power to Yorkshire.
Drax is also only about forty miles from the vast hydrogen stores at Aldbrough and Rough, so if Drax needed, if could use excess electricity to create hydrogen for storage.
SSE is consulting on a 1+ GW hydrogen power station at Keadby, so perhaps Drax should have a similar hydrogen power station on its site?
Lakeside Facility Connects To Grid And Becomes UK’s Largest Transmission Connected Battery
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- National Grid plugs TagEnergy’s 100MW battery project in at its Drax substation.
- Following energisation, the facility in North Yorkshire is the UK’s largest transmission connected battery energy storage system (BESS).
- The facility is supporting Britain’s clean energy transition, and helping to ensure secure operation of the electricity system.
This paragraph introduces the project.
A battery storage project developed by TagEnergy is now connected and energised on the electricity transmission network, following work by National Grid to plug the facility into its 132kV Drax substation in North Yorkshire.
- Lakeside Energy Park’s 100MW/200MWh facility is now the largest transmission connected BESS project in the UK following energisation.
- The new facility will boost the capacity and flexibility of the network, helping to balance the system by soaking up surplus clean electricity and discharging it back when the grid needs it.
- To ensure a safe connection, National Grid, working with its contractor Omexom, upgraded its Drax 132kV substation to accommodate the additional clean power.
- Works included extending the busbars – which enable power flows from generation source on to power lines – upgrading busbar protection and substation control systems, and installing an operational tripping scheme, all of which helps keep the network stable and operating securely.
Owned and operated by TagEnergy – with Tesla, Habitat Energy and RES as project partners – the newly-connected battery will help exploit the clean electricity potential of renewable projects in the region, storing and releasing green energy to power homes and businesses and also helping to relieve any system constraints.
National Grid’s adjacent Drax 400kV substation already hosts the connection for Drax power station – the UK’s largest biomass facility – and will also connect the Eastern Green Link 2 electrical superhighway when it starts importing clean energy from Scotland in 2029.
Drax power station seems to be growing into a large node with several gigawatts of electricity, the UK’s largest BESS, a large biomass power station and the Eastern Green Link 2 electrical superhighway which will import clean energy from Scotland from 2029.
Drax appears to be transforming from the dirty man of the UK into a Jolly Green Giant.
I can see further power stations and sources, storage devices and technology joining the party at Drax.
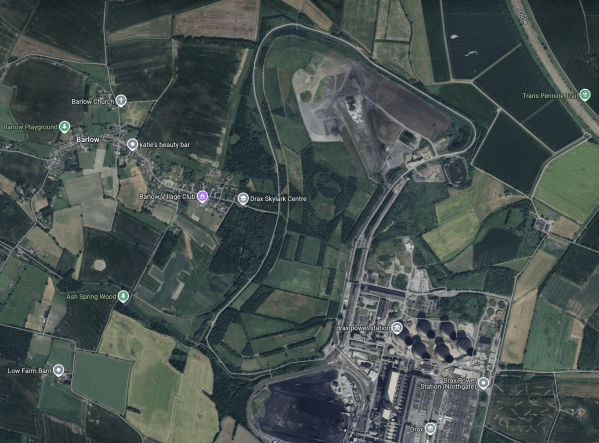
This Google Map shows the Drax site.
Note.
- The cooling towers can be picked out in the South-East quarter of the map.
- The site is rail and road connected, with the River Ouse nearby.
- There is a lot of space.
Surely, Drax would have a big enough space, with a high quality and high capacity electrical connection for Ørsted and Highview Power to put one of their three 200 MW/2.5 GWh batteries, that I talked about in Centrica Business Solutions And Highview Power.
Race For Clean Power Surges Ahead As New Electricity Superhighway Greenlit
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Ofgem.
These three paragraphs, explain the infrastructure.
Flagged by the National Energy System Operator (NESO) as an essential element in achieving the Government’s Clean Power 2030 ambition, Eastern Green Link 1 (EGL1As part of its mission to rapidly upgrade the energy system with a minimum cost to customers, Ofgem has identified over £43m of savings which have been cut from the project costs without impacting delivery or quality. Communities that host the infrastructure in Scotland and North-East England are also set to benefit from a £7.9m social value and community benefit fund.) is a high voltage electricity superhighway able to transport 2 gigawatts of homegrown wind generated electricity between Torness, East Lothian and Hawthorn Pit, County Durham. A gigawatt (GW) is equivalent to one billion watts, and one gigawatt hour (GWh) of electricity is enough to power one million homes for one hour. Most of the 196km cable will be under the North Sea, with the remaining 20km of cables underground linking the cable to substations and converter stations in Scotland and England.
The project will reduce Great Britain’s reliance on volatile international gas markets by further harnessing the power of homegrown North Sea wind. NESO’s recent Clean Power 2030 Report has also shown that the project will deliver annual saving of over £870m by reducing the need to compensate British wind generators who are currently asked to turn off production during times of high wind due to lack of grid capacity. This in turn will help drive down consumer bills.
Note.
- Eastern Green Link 1 (EGL1) is a high voltage electricity superhighway able to transport 2 gigawatts of homegrown wind generated electricity between Torness, East Lothian and Hawthorn Pit, County Durham.
- This is the second down the eastern side of the UK.
- In Contracts Signed For Eastern Green Link 2 Cable And Converter Stations, I described how contracts were signed for EGL2 from Peterhead in Scotland to Drax in England .
- Most of the 196km cable will be under the North Sea, with the remaining 20km of cables underground linking the cable to substations and converter stations in Scotland and England.
There are another two 2 GW cables to follow in the current plan!
Energy In – Hydrogen And Carbon Dioxide Out
This article was inspired by this article in the Sunday Times, which is entitled ‘It’s A Slog’: Life Inside Britain’s Last Coal Power Station.
The article is about Ratcliffe-on-Soar power station, which is next to East Midlands Parkway station.
This is the first paragraph of the station’s Wikipedia entry.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar Power Station is a coal-fired power station owned and operated by Uniper at Ratcliffe-on-Soar in Nottinghamshire, England. Commissioned in 1968 by the Central Electricity Generating Board, the station has a capacity of 2,000 MW. It is the last remaining operational coal-fired power station in the UK, and is scheduled to close in September 2024.
I took these pictures of the power station in 2019.
Ratcliffe-on-Soar is the last of a number of large coal-fired power stations, that were built in the area, mainly along the River Trent.
- Rugeley – 600 MW – 1961
- Drakelow – 1630 MW – 1964
- Willington – 800 MW – 1962
- Castle Donington – 600 MW – 1958
- Ratcliffe-on-Soar – 2000 MW – 1968
- High Marnham – 1000 MW – 1959
- Cottam – 2000 MW – 1968
- West Burton – 2000 MW – 1968
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 10,630 MW of electricity.
- There are also a few large gas-fired power stations along the river, that are still operating.
- Both coal and gas-fired stations use the water from the River Trent for cooling.
At the mouth of the river, there is the Keadby cluster of gas-fired power stations.
- Keadby 1 – 734 MW – 1996
- Keadby 2 – 849 MW – 2023
- Keadby 3 – 910 MW – 2027
- Keadby Hydrogen – 900 MW – 2030
Note.
- The date is the commissioning date.
- That is 3,393 MW of electricity.
- Keadby 2 is the most efficient CCGT in the world.
- Keadby 3 will be fitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby 2 has been designed to be retrofitted with carbon capture.
- Keadby Hydrogen will be fuelled by zero-carbon hydrogen.
As the years progress, I can see the Keadby cluster of power stations becoming a large zero-carbon power station to back-up wind farms in the North Sea.
- Hydrogen power stations will emit no carbon dioxide.
- Carbon dioxide from all gas-fired stations will be captured.
- Some carbon dioxide will be sold on, to companies who can use it, in industries like construction, agriculture and chemical manufacture.
- The remaining carbon dioxide will be stored in depleted gas fields.
As technology improves, more carbon dioxide will be used rather than stored.
Other Power Sources In The Humberside Area
In the next few sub-sections, I will list the other major power sources in the Humberside area.
Drax Power Station
Drax power station is a shadow of its former self, when it was one of the power stations fed by the newly discovered Selby coalfield.
These days it is a 2,595 MW biomass-fired power station.
Eastern Green Link 2
Eastern Green Link 2 will be a 2 GW interconnector between Peterhead in Scotland and Drax.
It is shown in this map.
Note.
- Most of the route is underwater.
- It is funded by National Grid.
- Contracts have been signed, as I talk about in Contracts Signed For Eastern Green Link 2 Cable And Converter Stations.
- It is scheduled to be completed by 2029.
This interconnector will bring up to 2 GW of Scottish wind-generated electricity to Drax and Humberside.
Drax has the substations and other electrical gubbins to distribute the electricity efficiently to where it is needed.
2 GW could also reduce the amount of biomass used at Drax.
In the long term, if the concept of the four Eastern Green Links is successful, I could see another Eastern Green Link to Drax to replace imported biomass at Drax.
I also, don’t see why a smaller Drax can’t be run on locally-sourced biomass.
Solar Farms And Batteries Along The River Trent
As the coal-fired power stations along the River Trent are demolished, solar farm developers have moved in to develop large solar farms.
Salt End Power Station And Chemical Works
These two paragraphs from the Wikipedia entry for Salt End describes the hamlet and its power station and chemical works.
Salt End or Saltend is a hamlet in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, in an area known as Holderness. It is situated on the north bank of the Humber Estuary just outside the Hull eastern boundary on the A1033 road. It forms part of the civil parish of Preston.
Salt End is dominated by a chemical park owned by PX group, and a gas-fired power station owned by Triton Power. Chemicals produced at Salt End include acetic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonia, bio-butanol, bio-ethanol, ethyl acetate (ETAC) and ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) with animal feed also being produced on site.
I wonder, if running the complex on hydrogen would give cost and marketing advantages.
Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage Facility
This page on the SSE Thermal web site is entitled Plans For World-Leading Hydrogen Storage Facility At Aldbrough.
This is the most significant paragraph of the page, that is definitely a must-read.
With an initial expected capacity of at least 320GWh, Aldbrough Hydrogen Storage would be significantly larger than any hydrogen storage facility in operation in the world today. The Aldbrough site is ideally located to store the low-carbon hydrogen set to be produced and used in the Humber region.
This is a hydrogen storage facility for a much wider area than Humberside.
Rough Gas Storage Facility
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Rough Gas Storage Facility.
Rough is a natural gas storage facility under the North Sea off the east coast of England. It is capable of storing 100 billion cubic feet of gas, nearly double the storage capacities in operation in Great Britain in 2021.
In Wood To Optimise Hydrogen Storage For Centrica’s Rough Field, I describe Centrica’s plans to convert the Rough gas storage into a massive hydrogen storage.
The Location Of Aldbrough Gas Storage, Rough Gas Storage, Salt End And Easington Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows between Salt End and the coast.
Note.
- The river crossing the South-West corner of the map is the Humber.
- Salt End with its power station and chemical works is on the North Bank of the Humber, where the river leaves the map.
- Aldbrough Gas Storage is marked by the red arrow at the top of the map.
- Easington Gas Terminal is in the South-East corner of the map.
- According to Wikipedia, gas flows into and out of the Rough Gas Storage are managed from Easington.
Looking at the map, I feel that the following should be possible.
- The two gas storage sites could be run together.
- Salt End power station and the related chemical works could run on hydrogen.
- Salt End will always have a reliable source of hydrogen.
- This hydrogen could be green if required.
All the chemical works at Salt End, could be run on a zero-carbon basis. Would this mean premium product prices? Just like organic does?
Enter The Germans
The Germans have a huge decarbonisation problem, with all their coal-fired power stations and other industry.
Three massive projects will convert much of the country and industry to hydrogen.
- H2ercules, which is a project of OGE and RWE, will create a hydrogen network to bring hydrogen, to where it is needed.
- In Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal, I describe how Uniper are going to build a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhelmshaven.
- AquaVentus is an RWE project that will use 10.3 GW of offshore wind power in German territorial waters to create a million tonnes per year of green hydrogen.
These would appear to be three of Europe’s largest hydrogen projects, that few have ever heard of.
AquaVentus And The UK
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that delivers hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Denmark.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Brough owned by Centrica.
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
In the last century, the oil industry, built a substantial oil and gas network in the North Sea.
It appears now the Germans are leading the building of a substantial hydrogen network in the North Sea.
These are my thoughts about development of the AquaVentus network.
Hydrogen Production And AquaVentus
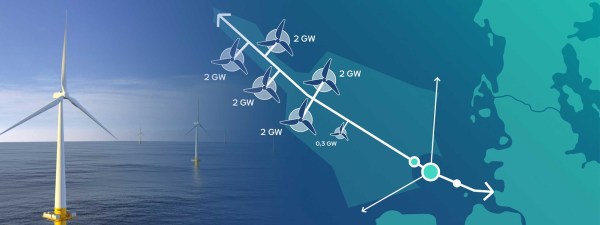
This RWE graphic shows the layout of the wind farms feeding AquaVentus.
Note.
- There is a total of 10.3 GW.
- Is one of the 2 GW web sites on the UK-side of AquaVentus, the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm, which is being developed by RWE?
- Is the 0.3 GW wind farm, RWE’s Norfolk wind farm cluster, which is also being developed by RWE?
Connecting wind farms using hydrogen pipelines to Europe, must surely mitigate the pylon opposition problem from Nimbys in the East of England.
As the AquaVentus spine pipeline could eventually connect to Peterhead, there will be other opportunities to add more hydrogen to AquaVentus.
Hydrogen Storage And AquaVentus
For AquaVentus to work efficiently and supply a large continuous flow of hydrogen to all users, there would need to be storage built into the system.
As AquaVentus is around 200 kilometres in length and natural gas pipelines can be up to 150 centimetres in diameter, don’t underestimate how much hydrogen can be stored in the pipeline system itself.
This page on the Uniper web site is entitled Green Wilhelmshaven: To New Horizons.
This is a sentence on the page.
Access to local hydrogen underground storage at the Etzel salt cavern site.
An Internet search gives the information, that Etzel gas storage could be developed to hold 1 TWh of hydrogen.
That would be enough hydrogen to supply 10 GW for a hundred hours.
Note that the UK branch of AquaVentus reaches the UK, just to the South of the massive hydrogen storage facilities at Aldbrough and Rough.
It would appear that both Germany and the UK are connected to AquaVentus through substantial storage.
I am certain, that all country connections to AquaVentus will have substantial storage at the country’s hydrogen terminal.
AquaDuctus
This would appear to be the first part of the AquaVentus network and has its own web site.
The web site is entitled Nucleus Of A Offshore Hydrogen Backbone.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The project partners are focusing on a scalable, demand-driven infrastructure: By 2030, AquaDuctus will connect the first large hydrogen wind farm site, SEN-1, with a generation capacity of approximately one gigawatt. SEN-1 is located in the German EEZ in the northwest of Helgoland. The pipeline will transport at a length of approx. 200 km green hydrogen produced from offshore wind to the German mainland and from there to European consumers via the onshore hydrogen infrastructure.
In the next project stage, AquaDuctus will be extended to the remote areas of the German exclusive economic zone towards the tip of the so-called duck’s bill. By that, additional future hydrogen wind farm sites will be connected. Along its way AquaDuctus will provide interconnection points with the opportunity for linking of adjacent national offshore hydrogen infrastructures originating from Denmark, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium and United Kingdom which opens the door for Europe-wide offshore hydrogen transport by pipeline.
There is also an interactive map, that gives more details.
This paragraph explains, why the Germans have chosen to bring the energy ashore using hydrogen, rather than traditional cables.
Recent studies show that offshore hydrogen production and transport via pipelines is faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly than onshore electrolysis with a corresponding connection of offshore wind turbines via power cables. The German federal government has also recognized this advantage and has clearly expressed its intention to promote offshore hydrogen production in the North Sea.
I suspect, that some UK offshore wind farms will use the same techniques.
Hydrogen Production For The UK
Electrolysers will probably be built along the East Coast between Peterhead and Humberside and these will feed hydrogen into the network.
- Some electrolysers will be offshore and others onshore.
- Turning off windfarms will become a thing of the past, as all surplus electricity will be used to make hydrogen for the UK or export to Europe.
- Until needed the hydrogen will be stored in Albrough and Rough.
Backup for wind farms, will be provided using hydrogen-fired power stations like Keadby Hydrogen power station.
Financial Implications
I reported on Rishi Sunak’s Manifesto Speech, which he made on June 11th. This is an extract
This document on the Policy Mogul web site is entitled Rishi Sunak – Conservative Party Manifesto Speech – Jun 11.
These are three paragraphs from the speech.
We don’t just need military and border security. As Putin’s invasion of Ukraine has shown, we need energy security too. It is only by having reliable, home-grown sources of energy that we can deny dictators the ability to send our bills soaring. So, in our approach to energy policy we will put security and your family finances ahead of unaffordable eco zealotry.
Unlike Labour we don’t believe that we will achieve that energy security via a state-controlled energy company that doesn’t in fact produce any energy. That will only increase costs, and as Penny said on Friday there’s only one thing that GB in Starmer and Miliband’s GB Energy stands for, and that’s giant bills.
Our clear plan is to achieve energy security through new gas-powered stations, trebling our offshore wind capacity and by having new fleets of small modular reactors. These will make the UK a net exporter of electricity, giving us greater energy independence and security from the aggressive actions of dictators . Now let me just reiterate that, with our plan, we will produce enough electricity to both meet our domestic needs and export to our neighbours. Look at that. A clear, Conservative plan not only generating security, but also prosperity for our country.
I can’t remember any reports about an energy security policy, which he outlined in the last paragraph of my extract from his speech.
He also said we would have sufficient electricity to export to our neighbours. As I said earlier some of this energy will be in the form of hydrogen, which has been created by offshore electrolysers.
If we are exporting electricity and hydrogen to Europe, this is likely to have three effects.
- An improvement in Europe’s energy security.
- H2ercules will improve and decarbonise German industry, using UK hydrogen.
- The finances of UK plc will improve.
It looks like there would be winners all round.
Rishi Sunak had the cards and he played them very badly.
It is now up to Keir Starmer, Great British Energy and Jürgen Maier to play those cards to link the energy systems of the UK and Germany to ensure security and prosperity for Europe.
C-Capture Launches Innovative Carbon Capture Trial For Cement Industry
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from C-Capture.
This is the sub-heading.
C-Capture, developers of next generation technology for carbon dioxide removal, has launched a new carbon capture trial in the cement manufacturing sector in partnership with Heidelberg Materials.
This is the first paragraph.
The trial, which utilises C-Capture’s innovative solution for industrial decarbonisation, is taking place at Heidelberg Material’s cement manufacturing plant in Ketton. It forms part of C-Capture’s national project, ‘XLR8 CCS – Accelerating the Deployment of a Low-Cost Carbon Capture Solution for Hard-to-Abate Industries’. Working with project partners across the UK, C-Capture’s XLR8 CCS project will demonstrate that a low-cost carbon capture solution is a reality for difficult-to-decarbonise industries in the race to net zero.
I wrote about C-Capture’s technology in Could Drax Power Station Solve The Carbon Dioxide Shortage?
The technology appears to have been spun out of Leeds University.
BP and Drax are investors.
This page on the C-Capture web site is called Technology and has a very neat interactive guide to how the technology works.
Conclusion
I have high hopes for this company and its technology.