New Chiltern Railways Trains Set To Unlock 10,000 More Seats A Day
The title of this post is the same as that of this press release from Chiltern Railways.
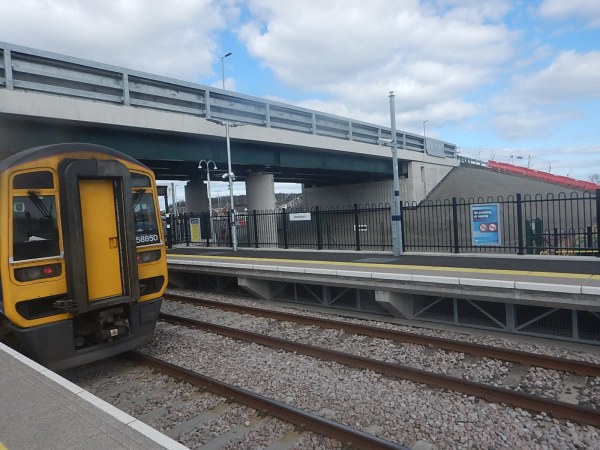
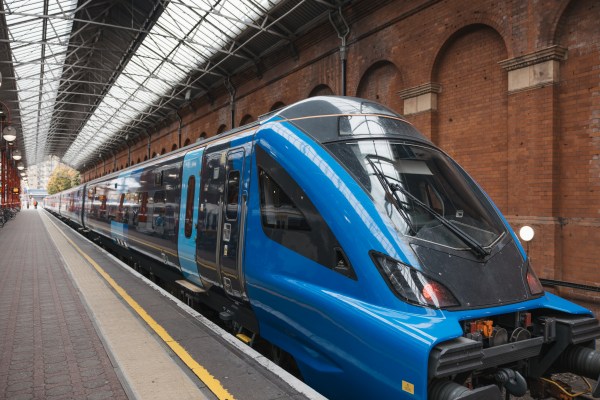
This picture from Chiltern Railways shows the train at Marylebone.

These three paragraphs are from the press release and add more details.
Chiltern Railways today (Tuesday 14 October) showcased for the first time its newest (Mark 5A) trains, set to add 10,000 more seats for customers each weekday from December 2026.
The trains, to be introduced between London to West Midlands from early 2026, will enable Chiltern to deliver more capacity across each of its West Midlands, Aylesbury, and Oxford routes as part of the operator’s efforts to deliver better journeys for customers.
The newest fleet will consist of 13 modern trains set to transform customer journeys during 2026. The trains will replace Chiltern’s oldest carriages, which are nearly 50 years old, with state-of-the-art equivalents, and provide a significant improvement to the on-board experience.
Today, I also received an update from Modern Railways, which was entitled Chiltern Railways Mk 5As To Enter Traffic Early Next Year, and included this delivery schedule.
From December 2026 there will be ten Mk 5A sets in traffic each day, with one ‘hot spare’ and one undergoing maintenance. That leaves one extra set which, CR has suggested, could eventually be pressed into traffic.
I have a few thoughts.
How Do The Trains Compare Physically?
These are basic figures for the two different types of train sets.
- The current Mark 3 are five-car sets of 23 metres coaches, that weigh about 36 tonnes. The driving van trailer is 18.83 metres and 43.7 tonnes
- The future Mark 5A are four-car sets of 22.2 metres coaches, that weigh about 43 tonnes. The driving trailer is 22.37 metres and 43 tonnes.
Lengths and weights of various sets will be as follows.
- Mark 3 – five-car and driving van trailer – 133.83 metres and 223.7 tonnes.
- Mark 5A – four-car and driving trailer – 111.17 metres and 215 tonnes
- Mark 5A – five-car and driving trailer – 155.57 metres and 258 tonnes
Note.
- Chiltern Railways and TransPennine Express use the same Class 68 locomotives.
- The five-car Mark 3 and the four-car Mark 5A sets are quite similar in length and weight
- This could mean that both sets would perform similarly with the same locomotives on the same route.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that the new Platform 4 at Birmingham |Snow Hill station will be able to handle all configurations.
I almost feel that when CAF designed the Mark 5A sets for TransPennine Express, they also had Chiltern in mind as another possible sale.
How Many Trains Would Be Needed To Run Between London Marylebone And Birmingham?
Consider.
- Trains currently run half-hourly on the route between 06:00 to 23:30, which is up to 36 services per day.
- When Platform 4 is operational at Birmingham Snow Hill station, all services could probably stop at both Birmingham Moor Street and Birmingham Snow Hill stations.
- A round trip between London Marylebone and Birmingham Snow Hill stations currently takes about five hours.
I’m fairly certain that to run a half-hourly core service would need ten trains.
Could Chiltern Develop Another Network On The Other Side Of Birmingham?
Consider.
- Trains could run twice an hour from 06:00 to 23:30, which is up to 36 services per day.
- When Platform 4 is operational at Birmingham Snow Hill station, all services could probably stop at both Birmingham Moor Street and Birmingham Snow Hill stations.
- Chiltern Railways already run several services a day to Stourbridge Junction.
- Chiltern Railways have run services to Kidderminster station in the past.
- Wrexham & Shropshire used to run locomotive-hauled Mark 3 four-car sets with driving van trailers, as far as Wrexham via Shrewsbury.
It looks to me, that with the right rolling stock configurations, Chiltern’s network can be developed on the other side of Birmingham.
- Destinations could include Stourbridge Junction, Kidderminster, Shrewsbury, Wolverhampton, Chirk, Ruabon and Wrexham General.
- Some services would need longer trains.
Obviously services would only be run if they were viable.
Would It Help Growth In A Town Or Area, If It Had A Rail Connection To London And/Or The Nearest Major City?
I know Lincoln is on the other side of the country, but I asked Google AI if Lincoln’s rail link to London has brought growth to the city and received this answer.
Yes, Lincoln’s rail link to London has brought significant growth by improving tourism, business travel, and student mobility, and is expected to spur further economic benefits through faster journey times and increased services. The direct link has made Lincoln more accessible for visitors and is a key part of the city’s long-term strategy for economic growth and development.
That was fairly definite.
How would that apply to an extended Chiltern Main Line.
- Politicians are always saying growth is important.
- An extended Chiltern Main Line servicewould improve connections of a lot of places to London and Birmingham.
- Shrewsbury is the easiest connection for West Wales.
- Surely a rail connection to a major city, might tempt someone to open a branch or a new factory.
Would a rail service make people feel more included?
An Interesting Comment From Lord Peter Hendy
This article on Modern Railways is entitled Chiltern FINALLY Signs Mk 5 Deal.
This extract from the article describes the deal.
An agreement for Chiltern Railways to lease the Mk 5A coaches previously operated by TransPennine Express and owned by Beacon Rail Leasing has been signed – and the trains are due to replace the current Mk 3 stock in phases from 2026. A 10-year lease has been agreed for the vehicles.
Chiltern will take on all 13 five-car sets as well as the spare Driving Trailer and the dedicated pool of 14 Class 68 locomotives.
The article also, has this excellent quote from Lord Peter Hendy, who is the Rail Minister at the end.
This government is putting passengers back at the heart of the 21st century railway by investing to make journeys easier, greener, and more comfortable.
“We are continuing to support Chiltern as they develop a plan to introduce additional services into their timetable, giving people more opportunities to work, live, and socialise.
I agree with much of what Lord Peter Hendy says, but could we see some actions to back up the words.
I have a few thoughts.
Lumo To Glasgow
I wrote about this new service in Lumo Will Extend Its King’s Cross And Edinburgh Service To Glasgow.
Given the opposition of the Transport Minister to open access services, I didn’t think this innovative service would be approved.
- But it does add an affordable passenger-friendly service to London and Glasgow routes.
- It will certainly be an easier route to London for some in Scotland.
- It also adds some much-needed direct services between Newcastle and Glasgow.
Did Lord Peter Hendy have words to help Lumo get its approval?
As I wrote in Could London And Central Scotland Air Passengers Be Persuaded To Use The Trains?, I also believe that this new Lumo service could persuade more air passengers to take the train to Scotland.
Lumo To Stirling
I wrote about this service in ORR: Open Access Services Given Green Light Between London And Stirling.
- First Group has taken over Grand Union Trains and the service will now be run by Lumo, who will use diesel Class 222 trains.
- But Lumo will have the option of running their electric Class 803 trains on the route, as it is fully electrified, when their fleet receives more trains.
This was another service, that I didn’t think would be approved, as no other services on the West Coast Main Line were approved, as Network Rail objected.
But it certainly meets the words in Lord Peter Hendy’s statement.
Like Lumo’s service to Glasgow, when the Stirling service gets electric trains, it will surely cut carbon emissions of travellers to Central Scotland.
Chiltern’s Replacement Trains
Chiltern Railways are replacing this fleet of locomotive hauled trains.
- 8 Class 68 locomotives
- 25 Mark 3 coaches
- 6 Driving Van Trailers
As services between London Marylebone and Birmingham Moor Street stations consist of one locomotive, five coaches and one driving van trailer, that means there are two spare locomotives, one spare coach and one spare driving van trailer, if there are five rakes of coaches in service.
The new fleet will be.
- 14 Class 68 locomotives
- 52 Mark 5A coaches
- 14 Driving Van Trailers
If services between London Marylebone and Birmingham Moor Street stations consist of one locomotive, four coaches and one driving van trailer, that means there are one spare locomotive and one spare driving van trailer, which gives a possible thirteen rakes of coaches in service.
There are certainly enough to expand Chiltern’s services. The obvious destination would surely be Oxford. These pictures show the two North-pacing platforms at Oxford station.
The platforms would be shared with East-West Rail, but they are around 160 metres in length.
The Modern Railways article quote Arriva Group Managing Director UK Trains Amanda Furlong as saying this.
Upgrading our fleet is a vital next step in Chiltern’s modernisation plans and an important part of Arriva’s wider ambition to support the transition to more sustainable rail travel across the UK and Europe.
We are proud to support this important milestone for Chiltern Railways, which is a great example of what can be achieved through strong collaboration with Government to deliver practical improvements for passengers. We look forward to seeing these upgraded trains improve journeys and lower emissions across the network.
She certainly would agree on some issues with Lord Peter Hendy.
So will Chiltern Railways do something to reduce the carbon footprint of their fourteen Class 68 locomotives?
- The Class 68 locomotives don’t have too many miles on the clock.
- Chiltern have already run some their Class 68 locomotives on HVO, so this must be a possibility.
- In total there are thirty-four Class 68 locomotives in service all of which have Caterpillar engines, so a conversion to zero-carbon power could be worthwhile.
I asked Google for an AI Overview on How many diesel locomotives have caterpillar engines worldwide? I got this answer.
While a precise worldwide count of diesel locomotives powered by Caterpillar (CAT) engines is difficult to pinpoint, it’s estimated that hundreds, if not thousands, of locomotives are equipped with CAT engines. Caterpillar has a long history of supplying engines to the rail industry, with engines like the 3500 series powering both mainline and switcher locomotives. Additionally, CAT engines are also used in generator sets for Head End Power (HEP) in passenger locomotives.
Note.
- It appears that, Caterpillar might have given up making truck engines because of emission issues.
- London Marylebone and Oxford is 66.8 miles
- London Marylebone and Birmingham Snow Hill is 112.3 miles.
Perhaps one of the consultants like Ricardo could convert these locomotives to run on hydrogen.
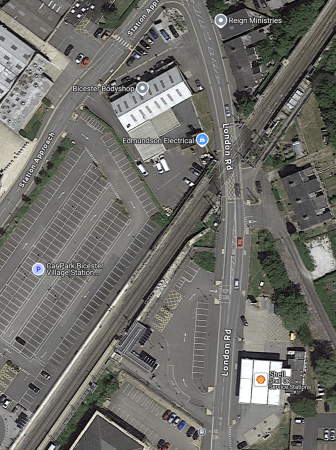
Bicester Village Station – 28th May 2025
I went to Bicester Village station today and took these pictures.
Note.
- The station is fully step-free, with lifts.
- There is a reasonable coffee-shop.
- There is a very large car-park.
There are two trains per hour (tph) in both directions between Marylebone and Oxford stations.
This Google Map shows the station.
Note.
- London is to the North.
- Oxford is to the South.
- The footbridge dates from October 2021 and is not shown on the map.
- The London Road level crossing is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The London Road level crossing is a problem, as I indicated in Bicester MP Calls On Chancellor To Fund London Road Crossing.
- To take the pictures of the level crossing, I crossed the footbridge to the North-West side of the station and walked through the car park to the station entrance on Station Approach. I then walked past the Bicester Bodyshop and Edmundson Electrical to the level crossing.
- The Shell garage can be clearly seen behind the level crossing.
During my walk of about thirty-five minutes three trains passed over the level crossing.
These are my thoughts.
The Long Platforms
The platforms are long.
- The Oxford-bound platform, which is Platform 1, is 240 metres long.
- The London-bound platform, which is Platform 2, is 230 metres long.
Both platforms will take a pair of five-car Hitachi Express Trains.
It looks to me, that East-West Rail are expecting a large number of passengers.
East-West Rail Plans For Powering Trains
I detailed these in Plans For Powering Trains And Details Of Our Upcoming Consultation.This post was based on an East-West Rail news item with the same title.
Distances include.
- London Marylebone and Oxford – 66.8 miles.
- Bletchley and Oxford – 47.2 miles.
Both distances are within range of five-car Hitachi Express Trains, that have been fitted with batteries.
I also suspect other manufacturers could supply suitable trains.
Thoughts On The London Road Level Crossing
This article on the BBC is entitled Level Crossing Petition Supported By Thousands.
This is the sub-heading.
A petition calling for a fully accessible underpass at a town’s level crossing has received more than 3,000 signatures.
These three paragraphs add more detail.
Launched by MP for Bicester and Woodstock Calum Miller, the petition calls on the government to ensure any replacement of the level crossing at London Road in Bicester includes access for cars, not just cyclists and pedestrians.
It is set to be closed on safety grounds when the East West Rail (EWR) line becomes fully operational, which many fear would cut off crucial access to thousands of residents.
Mr Miller will present the petition, which can only be signed in person, in Parliament on 3 June.
The argument is certainly hotting up.
But I believe, that a bridge that meets everybody’s requirements might be possible to be built.
- Suppose that all trains and locomotives passing through the level crossing had to be self-powered. Passenger trains could be battery-electric and freight locomotives could be either hydrogen or battery powered through the location of the level crossing.
- The track could also be lowered through the crossing.
- These actions would reduce the height of any bridge taking the road over the railway.
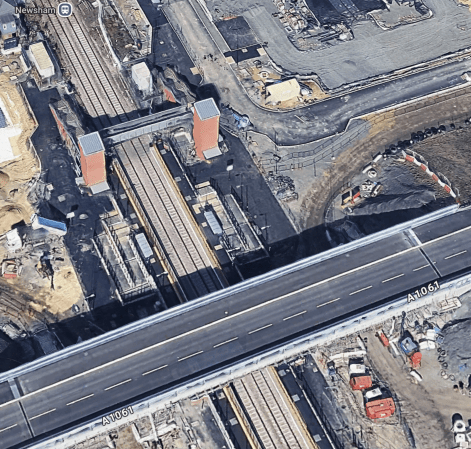
It looks to me that on the Northumberland Railway, which has recently opened, they had a similar problem, but they were able to squeeze a bridge into the space, as this 3D Google Map shows.
Note.
- The bridge looks like it carries a two-lane road and a pedestrian/cycle way.
- There is no electrification.
- I believe that the Northumberland Line could be run by battery-electric trains.
- The road bridge has been built to accept all traffic using the railway.
In Newsham Station – 30th March 2025, there are several pictures of the bridge. This one shows the bridge with a train.
In Trains: £34m For Revival Of 50-Year-Old North-East Railway Line, I said this about battery-electric trains for the Northumberland Line.
I’m drawn inextricably to the conclusion, that the trains should be 100 mph battery-electric trains.
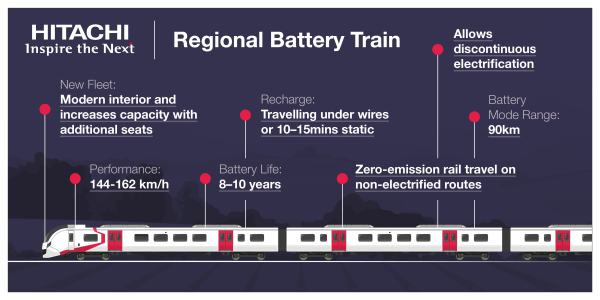
Hitachi, who have a factory in the North-East, have announced their Regional Battery Train in July 2020, which is described in this Hitachi infographic.
These trains can be based on Class 385 trains.
- They are 100 mph trains.
- They come in three- and four-cars lengths.
- The three-car trains have 206 seats.
- They can work in pairs.
- They can use 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- They have a range of 90 kilometres or 56 miles on battery power.
- The batteries would be charged on the ECML between Benton North junction and Newcastle station.
- The battery packs will be designed and manufactured by Hyperdrive Innovation in Sunderland.
- They have big windows for the views.
I’m sure Hitachi and Hyperdrive would like a fleet in service, just up the road from their factories.
Could a similar or even thinner bridge be squeezed in at Bicester Village station to take London Road over the railway?
I think it can, if they use some of the latest 3D modelling.
Plans For Powering Trains And Details Of Our Upcoming Consultation
The title of this post, is the same as that of a news item on the East West Rail web site.
This is the sub heading.
We’re pleased to share plans for how we’ll power trains on East West Rail, as well as information and dates of our public consultation on latest proposals for the project.
These are the first two paragraphs.
As part of our latest proposals, which we’ll be sharing for public consultation from 14 November, we’re providing information on our preference for green traction power in the form of discontinuous electrification with hybrid battery-electric trains, after the Chancellor confirmed government support for the project in yesterday’s budget.
As well as reducing carbon emissions, discontinuous electrification would mean overhead lines would only need to be installed along some sections of the route, which would reduce disruption to existing structures and potentially reduce visual impacts in more sensitive locations on the new railway between Bedford and Cambridge. This option would also cost less than full electrification and would need less land for things such as mast foundations.
There is also a short video, which explains discontinuous electrification.
I feel that to use discontinuous electrification and hybrid battery-electric trains is the way to go on this railway between Oxford and Cambridge.
- It is a zero-carbon solution.
- There is electrification at Reading. Didcot, Bletchley, Milton Keynes, Bedford and Cambridge along the route, so grid connections will be already available.
- Sandy, where East West Rail crosses the East Coast Main Line, is fully electrified and must have a grid connection.
- A small article in the November 2024 Edition of Modern Ralways, says that Hitachi are developing a smaller battery for commuter and suburban trains.
- Didcot to Oxford could be electrified and there is already a grid connection at Didcot.
Discontinuous electrification could be used to extend East West Rail to Norwich, Ipswich and Colchester.
These are my detailed observations and thoughts.
Existing Electrification
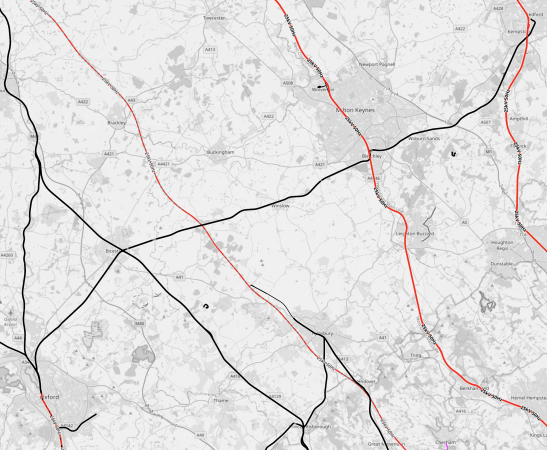
This OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification between Oxford and Bedford.
Note.
- Bold red lines are tracks electrified at 25 KVAC.
- Bold black lines are tracks without electrification.
- Oxford is in the South-West corner of the map.
- Bedford is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The bold black line of the Western section of the East West Rail connects the two cities.
- The lines through Oxford are shown as being electrified. The black stub pointing East to the South of Oxford is the Cowley Branch.
The rail lines crossing East West Rail from West to East are as follows.
- Chiltern Main Line – Not Electrified
- High Speed Two – Will Be Electrified
- West Coast Main Line – Electrified
- Midland Main Line – Electrified
I suspect all lines, except for the Chiltern Main Line, will be able to provide a grid connection for East West Rail.
This second OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification between Bedford and Cambridge.
Note.
- Bold red lines are tracks electrified at 25 KVAC.
- Bold black lines are tracks without electrification.
- Bedford is in the South-West corner of the map.
- Cambridge is in the North-East corner of the map.
- The Eastern section of the East West Rail connects the two cities.
- Both maps are to the same scale
The rail lines crossing East West Rail from West to East are as follows.
- Midland Main Line – Electrified
- East Coast Main Line – Electrified
- West Anglia Main Line – Electrified
I suspect all lines will be able to provide a grid connection for East West Rail.
Distances Without Electrification
These sections are not electrified.
- Oxford and Bletchley – 47.2 miles
- Bletchley and Bedford – 16.5 miles
- Bedford and Cambridge – 29.2 miles
- Ely and Norwich – 53.7 miles
- Norwich and Great Yarmouth – 18.4 miles
- Cambridge and Haughley Junction – 41.3 miles
I am assuming that the East West Rail could extend past Cambridge on these two routes.
- Ely, Thetford, Norwich and Great Yarmouth.
- Newmarket, Bury St. Edmunds, Stowmarket, Ipswich, Manningtree and Colchester.
All sections have electrification at both ends, if Didcot Junction and Oxford is electrified, as is expected to happen.
Train Battery Range Needed
The route layout, I have proposed means that if you go for the battery-electric train with the longest battery range you can afford and it can’t handle Ely and Norwich, the existing electrification can be extended to bridge the gap.
Application Of Discontinuous Electrification To Greater Anglia And Chiltern Railways
If discontinuous electrification can be applied to East West Rail, it can surely be applied to Greater Anglia and Chiltern Railways, given the fact that the route networks of all three companies overlap and share tracks.
Greater Anglia already have a fleet of Class 755 trains, which are designed to be converted to battery-electric operation.
With batteries fitted, I believe that these trains could handle most of the current routes they do now.
The other routes would be handled with selective lengths of overhead electrification in terminal stations to charge the trains before return.
Electrification Between Oxford And Bicester Village Stations
Oxford station has two North-facing bay platforms, that are used by Chiltern and other services terminating at the station from the North.
Note.
- Chiltern Railways already run two trains per hour (tph) between these platforms and Marylebone.
- I would assume the platforms will be used by East West Rail services, that terminate at Oxford station.
- If discontinuous electrification is to be used, then these two platforms could be electrified to charge trains before they return.
- East West Rail have not published their proposed services yet, but it could be one tph to both Milton Keynes Central and Bedford stations.
I can see Chiltern buying battery-electric trains to run services between Marylebone and Oxford, and some other routes.
Marylebone and Oxford is 66.7 miles, which is probably two far for even Stadler’s remarkable battery-electric trains, but if say between Oxford and Bicester Village station were to be electrified, would it make it possible to run battery-electric trains between Marylebone and Oxford with charging at both end of the route.
In Chiltern Sets Out New Fleet Ambitions, I talk about Chiltern’s possible new fleet, as proposed by their MD in September 2023.
Improvements At Marylebone Station – 15th October 2024
I passed through Marylebone station today and took these pictures of the improvements.
Note.
- The Class 165 and Class 168 trains are being refurbished.
- The Chiltern gate line has been improved.
- A wider ticket gate line has been installed in the Underground station.
- The stairs to the Bakerloo Line has been replaced with a third escalator.
- The last picture shows the lack of grab handles in the doors of Bakerloo Line trains.
It certainly looks like Chiltern Railways and its assets are improving.
Chiltern Railways Seeks Fleet Proposals
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Business UK.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Chiltern Railways has invited proposals from established rolling stock owners for the lease and maintenance of between 25 and 70 existing vehicles to operate inter-city and regional services on the Chiltern Main Line between London Marylebone and Birmingham.
The operator is seeking either ‘self-powered’ multiple units or locomotive-hauled coaches, which can operate at 160 km/h in fixed formations of five or six passenger vehicles.
It does appear that only existing vehicles will be allowed.
These are my thoughts.
A Very Tight Timescale
The Rail Business UK article, says this about entry into service.
Requests to participate are required by February 2. Driver training is planned for 2024, and entry to passenger service for early 2025.
This requirement probably means that new trains are not allowed, as I doubt any manufacturer could deliver them by early 2025.
Although, I could envisage a proposal, where a couple of trains are delivered early for driver training and the other trains are delivered, as soon as they are refurbished or perhaps even built.
100 mph Trains With At Least Five Cars
The second paragraph from the Rail Business UK article is very definite about speed and the length of trains.
The operator is seeking either ‘self-powered’ multiple units or locomotive-hauled coaches, which can operate at 160 km/h in fixed formations of five or six passenger vehicles.
It does appear, that this paragraph, rules out multiple units, with less than five coaches. Unless it counts a two-car Class 175 train and a three-car Class 175 train working together as a five-car fixed formation. They would though be 100 mph trains.
Noise Restrictions
This noise restriction must be met according to the Rail Business UK article.
The trains must also offer a reduction in ambient noise compared to Chiltern’s existing MkIII coaches hauled by a Class 68 diesel locomotive.
This could be a difficult condition to meet for some trains and probably rules out diesel locomotives.
What Fuels Can Be Used?
This is the only restriction in the Rail Business UK article.
Any diesel-powered trains should be compatible with use of alternative fuels, such as HVO, from the service introduction date.
Chiltern have experience of this fuel.
‘Self-Powered’ Multiple Units Or Locomotive-Hauled Coaches
i am tending towards the former for the following reasons.
- I was told by someone, that between London and Norwich, ‘self-powered’ multiple units are faster than locomotive-hauled coaches.
- Without the locomotive and the driving van trailer, you may get more passengers in a shorter train. This might avoid some platform lengthening.
- The Chiltern route to Birmingham has around a dozen stops and the lighter ‘self-powered’ multiple units may save time.
- Battery-electric ‘self-powered’ multiple units can be very quiet.
- Chiltern have had complaints about noise from diesel locomotives.
The last two points probably clinch it.
The Operating Speed Of The Chiltern Main Line
I have followed the Chiltern Main Line on OpenRailwayMap and virtually all of it is faster than 75 mph, with several sections of 90-100 mph running.
Hence the need for 100 mph trains!
What Distances Are Involved
The route can be split into sections.
- London Marylebone and High Wycombe – 28.1 miles
- High Wycombe and Banbury – 41 miles
- Banbury and Warwick – 21.8 miles
- Warwick and Birmingham Moor Street – 20.8 miles
Note.
- The total distance is 111.7 miles.
- High Wycombe and Warwick are 62.8 miles apart.
No sections are too challenging.
Could A Battery-Electric Train Handle The Route?
In The Data Sheet For Hitachi Battery Electric Trains, these were my conclusions for the performance.
- The battery pack has a capacity of 750 kWh.
- A five-car train needs three battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- A nine-car train needs five battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- The maximum range of a five-car train with three batteries is 117 miles.
- The maximum range of a nine-car train with five batteries is 121 miles.
It would appear that a five-car train with three batteries could handle the route, but there would need to be some form of charging at both ends of the route. This might not be too easy to arrange, as all three terminal stations are not the most spacious.
Could A Tri-Mode Train Handle The Route?
LNER have taken the tri-mode route with their new trains, which I wrote about in First Tri-Mode Long Distance Trains For The East Coast Main Line.
These trains could be a possibility, especially if they used battery power in stations where there have been complaints of noise.
I suspect CAF’s tri-mode trains could also be run on HVO, as it is likely they’ll have Rolls-Royce mtu engines, which can use the fuel.
As Hitachi’s Class 802 trains also use Rolls-Royce mtu engines and Hitachi are developing a tri-mode version, these trains are also a possibility.
Although tri-mode trains are a possibility, I doubt that delivery would be easy by the beginning of 2025.
Unless, the Government has tipped off CAF and/or Hitachi and they are already building some trains that can be completed as tri-modes.
After all, CrossCountry, Grand Central, South Western Railway and TransPennine may need tri-mode trains for their routes.
What About Hydrogen?
I don’t think, there is a hydrogen train, that would be suitable and could start driver training this year.
So, unless someone like Stadler says they have a train, hydrogen looks to be a non-starter.
An Unusual Solution
As I said on the previous section about hydrogen, the time-scale is tight and this probably cuts out totally new trains.
But we may have an unusual solution, that surprised everyone.
Consider.
- I have stated that I believe that a five-car Class 802 train with three battery packs has a range of 117 miles.
- The range would be enough to go between London Marylebone and Birmingham.
- So why not put in short lengths of overhead electrification at High Wycombe, Banbury and Warwick, where the train can have a quick splash and dash?
I am certain, that a unusual strategy like this can be made to work.
Conclusion
I suspect we’ll see an innovative solution, that gives ISquared what they want.
Chiltern Sets Out New Fleet Ambitions
The title of this post is the same as that of an article in the September 2023 Edition of Modern Railways.
These are the first three paragraphs.
Chiltern Railways deserves to be the next operator to order new trains, its Managing Director Richard Allan has told Modern Railways.
On 7 August the operator published a tender notice seeking proposals for the supply of between 20 and 70 new or converted low-emission trains. This followed the unveiling on 19 July of its ‘RightRoute’ vision setting out the case for investment in new trains, which was presented to stakeholders and parliamentarians in Westminster.
Chiltern is prioritising replacement of its Class 165 DMU fleet, which comprises 89 vehicles. It carried out a pre-market engagement exercise last Autumn, and Mr. Allan said the view is that a battery train would be suitable for the Marylebone to Aylesbury route, either operating solely on battery power or additionally picking up power from the London Underground four-rail system South of Amersham.
These are my thoughts.
Electrification At Amersham
This OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification at Amersham station.
Note.
- Tracks shown in pink are electrified with the London Underground four-rail system.
- Tracks shown in black are not electrified.
- All three platforms are electrified.
The track layout allows both Chiltern and London Underground trains to pass through Amersham station on electrified lines.
Electrification Between Amersham And Harrow-on-the-Hill
This OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification at Northwood station.
Note.
- Tracks shown in pink are electrified with the London Underground four-rail system.
- All four platforms are electrified.
- Some sections are only double-track.
All tracks between Amersham And Harrow-on-the-Hill stations are electrified.
Electrification At Harrow-on-the-Hill
This OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification at Harrow-on-the-Hill station.
Note.
- Tracks shown in pink are electrified with the London Underground four-rail system.
- Tracks shown in black are not electrified.
- All six platforms are electrified.
The track layout allows both Chiltern and London Underground trains to pass through Harrow-on-the-Hill station on electrified lines.
Electrification Between Harrow-on-the-Hill And Finchley Road
Willesden Green station is typical of the stations on this section
This OpenRailwayMap shows the electrification at Willesden Green station
Note.
- Tracks shown in pink are electrified with the London Underground four-rail system.
- Tracks shown in black are not electrified.
- The two tracks South of the station are the Chiltern tracks.
- All Chiltern Trains along this route use these two separate tracks, that are not electrified.
Stations with this layout include Northwick Park, Preston Road, Wembley Park, Neasden, Dollis Hill, Willesden Green, Kilburn and West Hampstead.
The Chiltern Tracks Alongside The Metropolitan Line
I took these pictures as I journeyed from West Hampstead to Harrow-on-the-Hill.
Note.
- The Chiltern Tracks are those farthest from the train without electrification.
- There also seemed a lot of graffiti, where the tracks weren’t electrified.
- Platforms 1 and 2 at Harrow-on-the-Hill station are electrified and used by Chiltern’s diesel trains.
Finding a Jubilee or Metropolitan Line train with clean enough windows for photography was difficult.
Distances Between Stations
These are the distances, times and electrification, between selected stations, between Marylebone and Aylesbury Vale Parkway.
- Marylebone and Harrow-on-the-Hill – 9.2 miles – 13 minutes – Not Electrified
- Harrow-on-the-Hill and Amersham – 14.3 miles – 24 minutes – Electrified
- Amersham and Aylesbury – 15.3 miles – 23 minutes – Not Electrified
- Aylesbury and Aylesbury Vale Parkway – 2.3 miles – 7 minutes – Not Electrified
Note.
- The 24 minutes between Harrow-on-the-Hill and Amersham, should be enough to fully-charge the batteries.
- Harrow-on-the-Hill to Marylebone and return is 18.5 miles.
- Amersham to Aylesbury Vale Parkway and return is 35.2 miles.
As Merseyrail’s Class 777 trains have achieved 83.9 miles on battery power, I am fairly sure that Marylebone and Aylesbury Vale Parkway could be achieved by a battery electric multiple unit, that has been designed for the route.
Rolling Stock
Bombardier built the Class 378 Electrostar train, so that it would run on the London Underground four-rail system to Richmond. so I’m sure that Alstom could build Aventras, that could use the Underground electrification.
I’m also sure that other UK trains manufacturers and suppliers like CAF, Hitachi, Siemens and Stadler have the expertise.
The article mentions between twenty and seventy trains. The number probably depends on the train length.
I think we’ll see some interesting bids.
Train Charging Issues
The main charging will be done between Harrow-on-the-Hill and Amersham using the London Underground four-rail system already installed for the Metropolitan trains between London and Amersham and Chesham.
As the electrification will be powering six trains per hour in both directions between Harrow-on-the-Hill and Amersham and charging the batteries on the Chiltern trains, I wouldn’t be surprised to find, that the power system will be uprated.
I also suspect, that the trains could have the ability to use 25 KVAC overhead electrification, as this could allow short lengths of electrification to be used to charge the trains at terminal stations.
Speed Issues
If you look at the speeds and times, you get the following.
- Current Chiltern Class 165 trains are 75 mph trains.
- Current Underground S Stock trains are 62 mph trains.
- Chiltern take 33 minutes between Amersham and Marylebone.
- Trains in both services run every half hour.
- There is also an every half hour service between Chesham and Aldgate, which means there are six trains per hour between Chalfont & Latimer and Harrow-on-the-Hill.
- I suspect Chiltern set the timetable, by going through first with the slower Amersham and Chesham services following.
- This means that if the new Chiltern trains are 100 mph trains, it shouldn’t make much difference to the operation of the trains.
But the faster Chiltern trains could knock eight minutes off the time between Amersham and Harrow-on-the-Hill stations.
In an ideal world, where TfL had more money, faster Underground trains would allow more services to the area.
Leamington Spa Services
Chiltern Railways run two local services from Leamington Spa station.
- One service goes to Stratford-on-Avon, which is a distance of 15.3 miles.
- The other service goes to Birmingham Moor Street, which is a distance of 22.7 miles.
- Both services are run by Class 165 diesel trains.
- Both services have a frequency of one train per two hours.
I suspect that these services could be run using battery-electric trains with charging at Leamington Spa.
Timescale
This is said about timescale.
Under the plans set out in its ‘RightRoute’ prospectus, Chiltern wants to agree scope and funding for new trains this year and launch the first new trains by 2027 between London and Aylesbury, and upgrade infrastructure and trains on the West Midlands route between 2028 and 2035.
West Midlands Route
This is said about the West Midlands route.
Mr Allan said that after ‘165’ replacement consideration would be given to the best solution for the main line between London and the West Midlands, including whether this would involve partial or full electrification, with a rolling stock solution to succeed the Class 168 DMUs and loco-hauled sets to be devised accordingly. Chiltern’s Interim Engineering & Safety Director Tim Sayer told Modern Railways one potential option the Government and Network Rail are keen on is third party funding of electrification, which could be built into a manufacturer’s contract for new stock.
Note.
- I must admit that I like the idea of bundling rolling stock and electrification in one contract.
- After all, rolling stock and maintenance have been bundled together for some years and it seems to work.
- I disclose some of Hitachi’s thinking in Solving The Electrification Conundrum, which is based on an article in Modern Railways.
I wonder if Hitachi will come up with a solution something like this.
- A number of five-car battery-electric trains.
- High quality interiors.
- They would serve Birmingham Moor Street, Oxford and Stratford-on-Avon.
- Short lengths of electrification in terminals and perhaps at strategic locations in the middle. Banbury?
- Automation as needed.
It could be a service that’s a viable alternative to High Speed Two for some passengers.
Charging At London Marylebone Station
I recently took these pictures at Marylebone station.
Note.
- It is a surprisingly spacious station and I feel that Furrer+Frey or some other specialist company could add some form of charging to the platforms.
- In its simplest form it would be a short length of 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
- Charging would be performed using the train’s pantograph.
It appears that the turnround time in Marylebone is typically twelve minutes or more, which should be adequate to fully charge a train.
Charging At Oxford Station
These pictures show the bay platforms at Oxford station, where Chiltern services terminate.
I wouldn’t be surprised, if these two platforms were designed for future 25 KVAC overhead electrification.
Marylebone And Oxford Services
Marylebone and Oxford are only 66.7 miles apart and I believe that a battery electric train would be able to shuttle between the two terminals, charging as required after each journey.
Charging At Birmingham
These pictures show the bay platforms at Birmingham Moor Street station, where some Chiltern services terminate.
Note.
- Currently, Birmingham Moor Street station has two through platforms and two bay platforms.
- None of the platforms are electrified.
- Some plans include adding two more bay platforms to the station.
- Electrifying the bay platforms 3 and 4, would allow the charging battery electric trains from London.
The two through platforms could also be electrified to help Birmingham’s local trains decarbonise and allow London services to reach Birmingham Snow Hill station.
Marylebone And Birmingham Services
Consider.
- Marylebone and Birmingham Moor Street are only 111.7 miles apart.
- Birmingham Moor Street and Birmingham Snow Hill stations are only 0.6 miles apart.
- Birmingham Moor Street and Birmingham Snow Hill stations could be easily connected by an electrified line.
- Stadler are talking of battery-electric trains having a range of over 125 miles.
- It might be sensible to electrify Banbury to give the batteries a top up.
I believe that a battery electric train would be able to shuttle between Marylebone and Birmingham, charging as required after each journey.
Conclusion
It seems a sound plan!
25kV Battery Train Charging Station Demonstration
This project was one of the winners in the First Of A Kind 2022 competition run by Innovate UK.
In this document, this is said about the project.
Project No: 10037158
Project title: 25kV Battery Train Charging Station Demonstration
Lead organisation: SIEMENS MOBILITY LIMITED
Project grant: £59,910
Public description: The UK rail industry is committed to decarbonisation, including the removal of diesel trains by 2040.
Replacing diesel trains with electric, hydrogen or battery bi-mode rolling stock provides faster, smoother and more reliable journeys, as well as eliminating local pollution and greatly reducing carbon dioxide. To enable clean, green electric bi-mode operation without continuous electrification requires enhancement of the power supply to existing electrification and novel charging facilities to support bi-mode trains. No small, low-cost solution is currently available for charging facilities that are compatible with standard UK trains and locally available power supplies and space.
Siemens Mobility, working with ROSCO, TOCs and Network Rail, will deliver a novel AC charging solution enabling simple installation of small, low-cost rapid charging facilities fed from existing standard local power supply cables. Compatible with all OLE-powered trains, the novel design enables the removal of diesel passenger train operation on non-electrified routes across the UK, while minimising land requirements and modifications required to existing station structures.
My Thoughts And Conclusion
Consider.
- The solution works with all 25 KVAC trains.
- It looks like it is a compact overhead electrification system, which might have originally been designed for a European tram or German S-Bahn system.
- It is claimed to be low-cost.
- Siemens were not asking for a lot of money.
- ROSCO, TOCs and Network Rail are all involved, which must be good.
It looks to me, that someone at Siemens has raided the parts bin and found some small, low-cost overhead electrification, that can be installed in the UK gauge and powered by a fairly standard mains supply.
It strikes me, that this system would be ideal to install in a station like Marylebone, if services to the station were to be run by battery-electric trains.
Could Chiltern Go Battery-Electric?
In the October 2022 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled Chiltern Considers Turbo Future, with a sub-title of Battery Replacement Could Be On The Cards.
These are the first two paragraphs.
In early September Chiltern Railways was preparing to launch a market sounding exercise to consider options for the future of the Class 165 Turbo DMU fleet.
The operator has 28×2-car and 11×3-car ‘165s’. which operate alongside its more modern Class 168 DMUs and its loco-hauled sets. The market sounding exercise will consider two options for the future of the fleet – some sort of hybrid conversion, or outright replacement.
The Class 165 Trains
The Class 165 trains were built in 1990-1991.
- Maximum Speed – 75 mph
- Prime Movers – One per car, Perkins 2006-TWH
- 2-car Trains – 28
- 3-car Trains – 11
One is being converted to a diesel/battery hybrid.
The Class 168 Trains
The Class 168 trains were built in 1998-2004.
- Maximum Speed – 100 mph
- Prime Movers – One per car, MTU 6R 183TD13H
- 2-car Trains – 9
- 3-car Trains – 8
- 4-car Trains – 11
One has been converted to a diesel/battery hybrid.
Conversion To Hybrid Operation
If this proves to be feasible, it will surely be the more affordable of the two options.
But it does leave Chiltern with a mixed fleet with two types of train with different maximum speeds and these lengths.
- 2-car Trains – 37
- 3-car Trains – 19
- 4-car Trains – 11
Would a fleet of similar trains, with perhaps a maximum speed of 100 mph, be better operationally?
Battery-Electric Operation
The Modern Railways article introduces the concept of battery-electric operation with this paragraph.
If a replacement fleet is considered the best option for the Turbo units, the replacements could take the form of a straight battery EMU, taking advantage of recent advances in ‘fast charge’ technology.
The article also says this about battery technology and electrification.
There is optimism that advances in battery technology will provide a smooth pathway to decarbonise Chiltern’s operations – the company serves the only non-electrified London terminus.
In the longer-term, it is hoped electrification from Birmingham to Banbury as part of a strategy to decarbonise CrossCountry and freight services would enable Chiltern to run a battery EMU on London to Birmingham duties, running under battery power as far north as Banbury and switching to overhead wires from there, both powering the unit and enabling the batteries to be recharged.
The Modern Railways article looked at each route and I will do this in more detail.
London Marylebone And Aylesbury via High Wycombe
London Marylebone and Oxford would be under battery operation for 40 miles.
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone and Aylesbury stations.
London Marylebone And Aylesbury Vale Parkway
London Marylebone and Oxford would be under battery operation for 41 miles.
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone and Aylesbury Vale Parkway stations.
It might be better to electrify between Aylesbury and Aylesbury Vale Parkway stations.
London Marylebone And Banbury
London Marylebone and Oxford would be under battery operation for 69 miles.
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone and Banbury stations.
Leamington Spa And Birmingham Moor Street
Assuming the Birmingham and Banbury section of the route is electrified, this route will be electrified.
London Marylebone And Birmingham Moor Street Or Birmingham Snow Hill
Assuming the Birmingham and Banbury section of the route is electrified, this route can be considered to be in two sections.
- London Marylebone and Banbury – Battery operation – 69 miles
- Banbury and Birmingham – Electric operation – 42 miles
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone station and on the electrified section.
London Marylebone And Gerrards Cross
London Marylebone and Oxford would be under battery operation for 19 miles or 38 miles both ways.
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone station.
London Marylebone And High Wycombe
London Marylebone and Oxford would be under battery operation for 28 miles or 56 miles both ways.
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone station.
London Marylebone And Oxford
London Marylebone and Oxford would be under battery operation for 66.8 miles.
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone and Oxford stations.
London Marylebone And Stratford-upon-Avon
Assuming the Birmingham and Banbury section of the route is electrified, this route can be considered to be in two sections.
- London Marylebone and Banbury – Battery operation – 69 miles
- Banbury and Hatton Junction – Electric operation – 26 miles
- Hatton Junction and Stratford-upon-Avon – Battery operation – 9 miles
Trains would be charged at London Marylebone station and on the electrified section.
Chiltern’s Mainline Service
Chiltern’s Mainline service between London and Birmingham is run by either a Class 68 locomotive pulling a rake of six Mark 3 coaches and a driving van trailer or two or three Class 168 trains.
As the locomotive-hauled train is about eight coaches, it could surely be replaced by two four-car multiple units working together.
I believe that if Chiltern obtained a fleet of four-car battery electric trains, this would be the most efficient fleets for all their routes.
Charging At London Marylebone Station
I took these pictures at Marylebone station today.
Note.
- It is a surprisingly spacious station and I feel that Furrer+Frey or some other specialist company could add some form of charging to the platforms.
- Charging would probably performed using the train’s pantograph.
It appears that the turnround time in Marylebone is typically twelve minutes or more, which should be adequate to fully charge a train.
Conclusion
Both solutions will work for Chiltern.
But I prefer the new battery-electric train, which has some crucial advantages.
- Battery-electric trains will be quieter than hybrid trains.
- Marylebone station has a noise problem and battery-electric trains are very quiet.
- Chiltern have ambitions to built new platforms at Old Oak Common and to serve Paddington. This could be easier with a battery electric train.
Rhe only disadvantage is that Banbury and Birmingham would need to be electrified.
A Chiltern Class 68 Locomotive At Marylebone Station
As I was passing through Marylebone station, I took these pictures of a very clean Class 68 locomotive.
If I’m going to Birmingham, I generally use Chiltern, as often you get to travel in one of these well-restored Mark 3 coaches hauled by a Class 68 locomotive.
With the Mark 3 coach, you get a full size table and a large window to enjoy the countryside.
- The Class 68 locomotives were all built by Stadler in Spain, within the last ten years.
- The UK has a fleet of 34 Class 68 locomotives.
- They are powered by a Caterpillar diesel engine.
- The only problem with the trains is that the Class 68 locomotives are diesel.
But is Caterpillar working on a simple solution?
Search the Internet for “Caterpillar Hydrogen” and you find press releases and other items, like this press release, which is entitled Caterpillar to Expand Hydrogen-Powered Solutions to Customers.
I wouldn’t be surprised to find out, that Stadler and Caterpillar were working on a program to provide a solution to convert Class 68 locomotives to hydrogen.