Legal Challenge Against Gatwick Airport’s Second Runway To Begin
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on ITVX.
These four paragraphs add more details.
Plans to challenge a second runway at Gatwick Airport will be heard in the High Court next week.
The campaign and environmental group Communities Against Gatwick Noise Emissions (CAGNE) opposes Transport Secretary Heidi Alexander’s decision to grant development consent for the project.
In the hearing, which will run from 20 to 23 January 2026, CAGNE’s argues that the climate change impacts of the extra runway have not been properly assessed.
The planned expansion would see the repurposing of Gatwick Airport’s emergency runway for use as a second operational runway. The extra capacity is expected to lead to more than 100,000 more flights per year.
These two paragraphs give CAGNE’s case.
CAGNE says that this decision was flawed, arguing that there are numerous gaps in the environmental assessment of the airport expansion. These include a failure to adequately assess inbound flight emissions, the climate impact of non-carbon dioxide emissions, the handling of additional sewage, and noise pollution.
The group also argues that the second runway plans rely too heavily on the UK’s Jet Zero Strategy (JZS), which assumes ambitious improvements in the aviation industry in areas such as fuel efficiency.
My feelings are as follows.
- We need more runway capacity.
- Eventually all aircraft will be powered by electricity, hydrogen or sustainable aviation fuel (SAF).
- Because of the need for large amounts of renewable electricity to make hydrogen and SAF, the runway will need to be near offshore wind farms.
Only Doncaster Sheffield, Gatwick, Liverpool, Stansted and some Scottish airports are near the sea or could be connected to the coast by an easy-to-build cable or pipeline.
CAGNE may well win their case, but I fell Nimbys will also stop Heathrow getting a third runway.
Could Doncaster Sheffield Airport Become A Hydrogen Airport?
I asked Google AI, what is the current status of Doncaster Sheffield Airport and received this reply.
Doncaster Sheffield Airport (DSA) is currently in a state of active, public-funded redevelopment after closing in late 2022 due to financial issues, with plans to reopen for passenger flights by late 2027 or 2028, following significant funding (around £160m) secured by the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority (SYMCA) for the City of Doncaster Council to take over operations and rebuild commercial viability, with freight and general aviation potentially returning sooner.
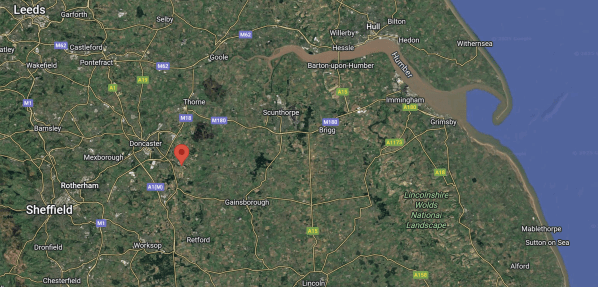
This Google Map shows the location of the airport.
Note.
- The distinctive mouth of the River Humber can be picked out towards the North-East corner of the map.
- Hull and Grimsby sit in the mouth of the Humber.
- The red arrow indicates Doncaster Sheffield Airport.
- Leeds is in the North-West corner of the map.
- The towns and city of Doncaster, Rotherham and Sheffield can be picked out to the West of the airport.
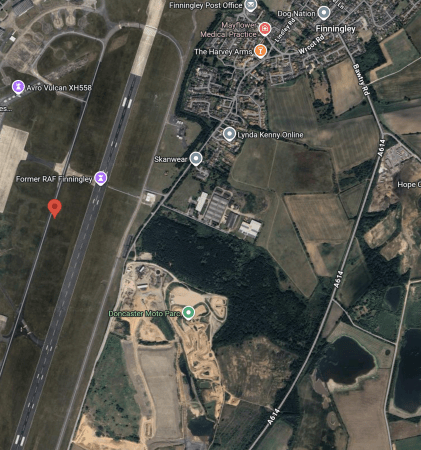
This second Google Map shows a close-up of the airport.
On my visit to NASA in the 1980s, where an Artemis system was used to project manage the turnround of the Space Shuttle, I was asked questions by one of NASA’s support people about RAF Finningley. Nothing too technical, but things like what is Doncaster like.
When I asked why, they said there’s a high chance that a Space Shuttle could land at RAF Finningley, as it has one of the best runways for a very heavy aircraft in Europe.
Looking at the runway, it is a long and wide runway that was built for heavy RAF nuclear bombers like Valiants, Victors and Vulcans.
I believe that we will eventually see hydrogen- and/or nuclear-powered airliners flying very long routes across the globe, just as a nuclear-powered example, attempted to do in the first episode of the TV series Thunderbirds, which was called Trapped in the Sky and has this Wikipedia entry.
Just as the Space Shuttle did, these airliners and their air-cargo siblings will need a large runway.
Doncaster Sheffield Airport already has such a runway.
These hydrogen- and nuclear-powered aircraft will make Airbus A 380s look small and will need runways like the one at Finningley.
But I don’t think we’ll ever see nuclear-powered aircraft in the near future, so the aircraft will likely be hydrogen.
Other things in favour of making Doncaster Sheffield Airport, an airport for long range hydrogen aircraft include.
- The airport is close to the massive hydrogen production and storage facilities being developed on Humberside at Aldbrough and Rough.
- The airport could be connected to the Sheffield Supertram.
- The airport could be connected to the trains at Doncaster station, which has 173 express trains per day to all over the country.
- The airport would fit well with my thoughts on hydrogen-powered coaches, that I wrote about inFirstGroup Adds Leeds-based J&B Travel To Growing Coach Portfolio
- The airport might even be able to accept the next generation of supersonic aircraft.
- The airport could certainly accept the largest hydrogen-powered cargo aircraft.
- The Airport isn’t far from Doncaster iPort railfreight terminal.
Did I read too much science fiction?
I have some further thoughts.
Do Electric Aircraft Have A Future?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
Yes, electric aircraft absolutely have a future, especially for short-haul, regional, and urban air mobility (UAM), promising quieter, zero-emission flights, but battery limitations mean long-haul flights will rely more on hydrogen-electric or Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAF) for the foreseeable future. Expect to see battery-electric planes for shorter trips by the late 2020s, while hybrid or hydrogen solutions tackle longer distances, with a significant shift towards alternative propulsion by 2050.
That doesn’t seem very promising, so I asked Google AI what range can be elected from electric aircraft by 2035 and received this answer.
By 2035, fully electric aircraft ranges are expected to be around 200-400 km (125-250 miles) for small commuter planes, while hybrid-electric models could reach 800-1,000 km (500-620 miles), focusing on short-haul routes due to battery limitations; larger, long-range electric flight remains decades away, with hydrogen propulsion targeting 1,000-2,000 km ranges for that timeframe.
Note.
- I doubt that many prospective passengers would want to use small commuter planes for up to 250 miles from Doncaster Sheffield airport with hundreds of express trains per day going all over the UK mainland from Doncaster station.
- But Belfast City (212 miles), Dublin (215 miles) and Ostend (227 miles), Ronaldsway on the Isle of Man (154 miles) and Rotterdam(251 miles) and Schipol 340 miles) may be another matter, as there is water to cross.
It looks like it will be after 2035 before zero-carbon aircraft will be travelling further than 620 miles.
My bets would be on these aircraft being hydrogen hybrid aircraft.
What Will The Range Of Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft In 2040?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
By 2040, hydrogen-powered commercial aircraft are projected to have a range that covers short- to medium-haul flights, likely up to 7,000 kilometers (approximately 3,780 nautical miles), with some models potentially achieving longer ranges as technology and infrastructure mature.
The range of these aircraft will vary depending on the specific technology used (hydrogen fuel cells versus hydrogen combustion in modified gas turbines) and aircraft size.
It looks like we’ll be getting there.
This Wikipedia entry is a list of large aircraft and there are some very large aircraft, like the Antonov An-225, which was destroyed in the Ukraine War.
A future long-range hydrogen-powered airline must be able to match the range of current aircraft that will need to be replaced.
I asked Google AI what airliner has the longest range and received this reply.
The longest-range airliner in service is the Airbus A350-900ULR (Ultra Long Range), specifically configured for airlines like Singapore Airlines to fly extremely long distances, reaching around 9,700 nautical miles (18,000 km) for routes like Singapore to New York. While the A350-900ULR holds records for current operations, the upcoming Boeing 777-8X aims to compete, and the Boeing 777-200LR was previously known for its exceptional range.
I believe that based on the technology of current successful aircraft, that an aircraft could be built, that would be able to have the required range and payload to be economic, with the first version probably being a high-capacity cargo version.
What Would An Ultra Long Range Hydrogen-Powered Airliner Look Like?
Whatever the aircraft looks like it will need to be powered. Rolls-Royce, appear to be destining a future turbofan for aircraft called the Ultrafan, which has this Wikipedia entry.
I asked Google AI, if Rolls-Royce will produce an Ultrafan for hydrogen and received this answer.
Rolls-Royce is actively developing the UltraFan architecture to be compatible with hydrogen fuel in the future, but the current UltraFan demonstrator runs on Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF). The company has a research program dedicated to developing hydrogen-powered engines for future aircraft, aiming for entry into service in the mid-2030s.
I asked Google AI, if Rolls-Royce have had major difficulties converting engines to hydrogen and received this answer.
Rolls-Royce has not encountered insurmountable difficulties but faces significant engineering and logistical challenges in converting engines to run on hydrogen. The company has made substantial progress in testing both stationary and aero engines using pure hydrogen, confirming its technical feasibility.
Given the company’s success in developing engines in the past, like the R Type, Merlin, RB 211, Pegasus, Trent, mtu 4000 and others, I suspect there’s a high chance of a successful hydrogen-powered Ultrafan.
If you look at a history of large passenger and cargo aircraft over the last sixty years, there has been a lot of the following.
- Conversion of one type of aircraft to a totally different type.
- Fitting new engines to a particular type.
- Fitting new avionics to a particular type.
Examples include.
- Fitting new CFM-56 engines to DC-8s.
- The first two Nimrods were converted from unsold Comet 4Cs.
- Converting Victor bombers to RAF tanker aircraft.
- Converting BA Tristars to RAF tanker aircraft.
- Converting DC-8s to cargo aircraft.
- Airbus converted five Airbus A 300-600 into Belugas, which have this Wikipedia entry.
- Airbus converted six Airbus A 330-200F into BelugaXLs, which have this Wikipedia entry.
- Converting two Boeing-747s to carry Space Shuttles ; one from American Airlines and one from Japan Airlines, which have this Wikipedia entry.
Note.
- Most of these examples have been successful.
- The last three examples have been very successful.
- Most of these applications do not have a human cargo.
This picture shows an Emirates Air Lines’s Airbus A 380 on finals at Heathrow.
Note.
- The aircraft was landing on Runway 27 L.
- The four engines and the vertical oval cross-section of the fuselage are clearly visible.
- The Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 380 shows two floors across the fuselage; the upper floor with eight seats in 2-4-2 and the lower floor with ten seats in 3-4-3, and a pair of LD3 cargo containers in the basement.
I’d be interested to know, how much hydrogen could be put in the basement and how far it could take the plane with a full load of passengers!
This link to the Wikipedia entry, shows the cross section in detail.
Note
I wouldn’t be surprised that the first application of large hydrogen aircraft will be for cargo and it could be an Airbus Beluga or perhaps an Airbus A 380 freighter?
CO2 to SAF: A One-Step Solution
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on the Chemical Engineer.
This is the sub-heading,
Oxford spinout OXCCU has launched a demonstration plant at London Oxford Airport to trial its one-step process of turning CO2 into sustainable aviation fuel (SAF). Aniqah Majid visited the plant to investigate the benefits of its “novel” catalyst
One word in this sub-heading caught my eye.
When I was a young engineer in the Computer Techniques section in the Engineering Department at ICI Plastics Division, I did a small mathematical modelling project for this chemical engineer, using the section’s PACE 231-R analogue computer.

He was impressed and gave the 23-year-old self some advice. “You should apply that beast to catalysts.”
I have never had the chance to do any mathematically modelling of catalysts either at ICI Plastics or since, but I have invested small amounts of my own money in companies working with advanced catalysts.
So when OXCCU was picked up by one of my Google Alerts, I investigated.
I like what I found.
The three raw ingredients are.
- Green Hydrogen
- Carbon dioxide perhaps captured from a large gas-fired powerstation like those in the cluster at Keadby.
- OXCCU’s ‘novel’ catalyst, which appears to be an iron-based catalyst containing manganese, potassium, and organic fuel compounds.
I also suspect, that the process needs a fair bit of energy. These processes always seem to, in my experience.
This paragraph outlines how sustainable aviation fuel or (SAF) is created directly.
This catalyst reduces CO2 and H2 into CO and H2 via a reverse water gas shift (RWGS) process, and then subsequently turns it into jet fuel and water via Fischer-Tropsch (FT).
The Wikipedia entry for Fischer-Tropsch process has this first paragraph.
The Fischer–Tropsch process (FT) is a collection of chemical reactions that converts a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, known as syngas, into liquid hydrocarbons. These reactions occur in the presence of metal catalysts, typically at temperatures of 150–300 °C (302–572 °F) and pressures of one to several tens of atmospheres. The Fischer–Tropsch process is an important reaction in both coal liquefaction and gas to liquids technology for producing liquid hydrocarbons.
Note.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that to obtain the carbon monoxide and hydrogen or syngas for the Fischer-Tropsch process, excess hydrogen is used, so the OXCCU process may need a lot of affordable hydrogen, some of which will be converted to water in the RWGS process.
- The high temperatures and pressures for the Fischer-Tropsch process will need a lot of energy, as I predicted earlier.
But I don’t see why it won’t work with the right catalyst.
The Wikipedia entry for the Fischer-Tropsch process also says this.
Fischer–Tropsch process is discussed as a step of producing carbon-neutral liquid hydrocarbon fuels from CO2 and hydrogen.
Three references are given, but none seem to relate to OXCCU.
OXCCU have a web site, with this title.
Jet Fuel From Waste Carbon
And this mission statement underneath.
OXCCU’s mission is to develop the world’s lowest cost, lowest emission pathways to make SAF from waste carbon, enabling people to continue to fly and use hydrocarbon products but with a reduced climate impact.
It looks like they intend to boldly go.
Conclusion
My 23-year-old self may have been given some good advice.
Thoughts On The Airbus A 390
Ask Google what she knows about the Airbus A 390 and you get this AI Summary.
The Airbus A390 is a three-deck, six-engine aircraft that can carry around 1,000 passengers. It’s based on the A380, but with a third deck and extra engines. The A390 was custom-built for Qantas to fly between Melbourne and New York.
Google got their summary from this page on steemit.
Search for images of the Airbus A 390 and you get several images of this unusual three-deck aircraft, that looks like a widened Airbus A 380 with six engines.
These are some of my thoughts.
Wikipedia Entries
There is no Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 390.
But.
- There is a Wikipedia entry for the Airbus A 380.
- There is also a Wikipedia entry for the six unusual Airbus Beluga XLs, which are used to transport two pairs of Airbus A 350 wings between factories.
The A 390 is supposedly based on the A 380 and the Beluga XL appears to have a fuselage that is a bit like the Airbus A 390.
Will The Airbus A 390 Fly?
After reading the two Wikipedia entries, I am fairly sure that an Airbus A 390 airliner, as shown in the pictures would be able to fly.
Although, I must say, that I was surprised, at seeing an Airbus Beluga XL on video. This is a Beluga XL landing at Heathrow.
So I think we can say, that Airbus know more than a bit about the aerodynamics of three-deck fuselages.
The Antonov An-225 Mriya
This aircraft designed and built in the Soviet Union , does have a Wikipedia entry.
These three paragraphs from the start of the entry, give some details of this unusual and very large aircraft.
The Antonov An-225 Mriya (Ukrainian: Антонов Ан-225 Мрія, lit. ’dream’ or ‘inspiration’) was a strategic airlift cargo aircraft designed and produced by the Antonov Design Bureau in the Soviet Union.
It was originally developed during the 1980s as an enlarged derivative of the Antonov An-124 airlifter for transporting Buran spacecraft. On 21 December 1988, the An-225 performed its maiden flight; only one aircraft was ever completed, although a second airframe with a slightly different configuration was partially built. After a brief period of use in the Soviet space programme, the aircraft was mothballed during the early 1990s. Towards the turn of the century, it was decided to refurbish the An-225 and reintroduce it for commercial operations, carrying oversized payloads for the operator Antonov Airlines. Multiple announcements were made regarding the potential completion of the second airframe, though its construction largely remained on hold due to a lack of funding. By 2009, it had reportedly been brought up to 60–70% completion.
With a maximum takeoff weight of 640 tonnes (705 short tons), the An-225 held several records, including heaviest aircraft ever built and largest wingspan of any operational aircraft. It was commonly used to transport objects once thought impossible to move by air, such as 130-ton generators, wind turbine blades, and diesel locomotives.
This further paragraph described the destruction of the aircraft.
The only completed An-225 was destroyed in the Battle of Antonov Airport in 2022 during the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy announced plans to complete the second An-225 to replace the destroyed aircraft.
I feel that the Mriya is significant for the Airbus A 390 for three reasons.
- Mriya was a six-engine heavy-lift cargo aircraft developed from a certified four-engine transport.
- Mriya was starting to make a name for being able to move over-sized cargo around the world.
- Given the parlous state of parts of the world and the ambitions of some of its so-called leaders, I believe, as I suspect others do, that a heavy-lift cargo aircraft is needed for disaster relief.
So are Airbus looking at the possibilities of converting some unwanted A 380 airliners into the heavy-lift aircraft, that they believe the world needs?
- They may even want some for their own purposes.
- Jeff Bezos or Elon Musk may need a heavy-lift aircraft for their space programs.
Converting some unwanted Airbus A 380s into heavy-lift cargo aircraft could be a more affordable route, than designing and building new aircraft from scratch.
Redundant Coal Wagons To Be Converted For Construction Traffic
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Railway Gazette.
These three paragraphs describe the project.
WH Davis is to convert coal wagons owned by leasing company Porterbrook for use by Freightliner to transport aggregates.
’This is a fantastic opportunity to demonstrate what can be achieved by giving redundant fleets a purpose for the next 30-plus years’, said WH Davis Managing Director Andy Houghton on December 19. ‘It’s a truly sustainable option that also gives UK manufacturing a boost to enable the creation of UK jobs in the industry. I really can’t wait to see our latest box wagon design in traffic for Freightliner in 2025.’
Mark Wyborn, Head of Freight at Porterbrook, said freight volumes in the construction sector were expected to continue growing, and the deal ’highlights our commitment to investing in the long-term growth of rail freight while providing affordable, innovative and sustainable rolling stock for the UK railway’.
We need more recycling projects like these.
In the article, there is a picture of a Class 66 locomotive like this one.
Except this one, which is named after Benjamin Gimbert GC, is different in that it is running on Hydrotreated Vegetable Oil (HVO). which is a more sustainable fuel.
Unfortunately, there is only so much second-hand vegetable oil from the likes of McDonalds and Burger King and it is also a component of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF).
But in the UK, we have engineers at Cummins, JCB, Ricardo and a number of other companies, research organisations and universities, who could create a conversion for the American two-stroke diesels of the Class 66 locomotive so they could run on hydrogen.
These posts detail attempts to create a zero-carbon or dual-fuel locomotive in the UK and some of my thoughts.
- Dual-Fuel Class 37 And 66 Locomotive Concepts Unveiled
- Could Class 66 Locomotives Be Converted Into Battery-Electric Locomotives?
- Freightliner Secures Government Funding For Dual-Fuel Project
- Grants To Support Low-Carbon Technology Demonstrators
- Thoughts On A Battery/Electric Replacement For A Class 66 Locomotive
- A Hydrogen-Powered Locomotive
- Our Sustainability Journey
The Bi-Mode Class 99 locomotive is coming, but we need action now.
I estimate it would probably cost up to £2million to convert a Class 66 locomotive to hydrogen.
So why not have a competition with a prize of perhaps £10million to see who, can produce the best Class 66 or Class 68 locomotive conversion by the end of 2025?
Conclusion
We need urgent action to cut pollution, noise and emissions from heavy freight locomotives and market forces and government grants don’t seem to have produced a solution, so perhaps a competition with a big prize might do it.
It could even be televised,
Airport Of The Future
I am fairly sure, that in ten years, there will be a lot of zero-carbon aircraft flying short haul routes. I have been particularly impressed by some of the ideas from Airbus, although Boeing seem to be very quiet on the subject. Perhaps it’s the difference between visionaries and engineers, and accountants.
But you rarely read anything about how airports are preparing for even a low-carbon future.
- Some long-stay car-parks could be made electric vehicles only, so they would become massive grid batteries, whilst owners are travelling.
- Airside vehicles can all be made zero-carbon.
- Sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) shouldn’t be a problem, as it would be handled like jet fuel.
- Do airports have a large enough grid connection for all the electrification of vehicles and some planes?
- Do airports have a plan for hydrogen?
The last two points, probably mean we should have built Maplin.
- It could have a cable and a hydrogen pipeline from wind farms and co-located hydrogen electrolysers in the Thames Estuary.
- The Elizabeth Line or a new line could easily be extended or built to the airport, to give a 125 mph connection.
But that enemy of the planet; Harold Wilson cancelled it.
Rolls-Royce Announces Successful Run Of UltraFan Technology Demonstrator To Maximum Power
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
This is the sub-heading.
Rolls-Royce today announces it has successfully run its UltraFan® technology demonstrator to maximum power at its facility in Derby, UK. The initial stage of the test was conducted using 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF).
These are the first four paragraphs.
This is an important milestone for the UltraFan demonstrator, which was successfully tested for the first time earlier this year. Since then, the UltraFan team has been gradually increasing the power as part of the rigorous testing regime and the demonstrator has performed in line with our expectations. The results of the test will provide us with valuable learning and data, which our teams will now take away and continue to analyse.
This achievement reinforces our confidence in the suite of technologies that has been developed as part of the UltraFan programme. Confirming this capability is a big step towards improving the efficiency of current and future aero-engines as UltraFan delivers a 10% efficiency improvement over our Trent XWB, which is already the world’s most efficient large aero-engine in service. In total that’s a 25% efficiency gain since the launch of the first Trent engine.
UltraFan’s scalable technology from ~25,000-110,000lb thrust also offers the potential to power the new narrowbody and widebody aircraft anticipated in the 2030s.
As part of the UltraFan development programme we have identified a number of technologies that are potentially transferable to our current Trent engines, which will provide our customers with even greater availability, reliability and efficiency.
These are my thoughts.
What Is UltraFan?
UltraFan has a section in the Wikipedia entry for the Rolls-Royce Trent engine, where these are the two opening paragraphs.
After the Advance comes the UltraFan, initially aimed to be ready for service from 2025. A geared turbofan with a variable pitch fan system that promises at least 25% improvement in fuel burn, the UltraFan aims for a 15:1 bypass ratio and 70:1 overall pressure ratio.
The Ultrafan keeps the Advance core, but also contains a geared turbofan architecture with variable-pitch fan blades. As the fan will vary pitch to be optimised for each flight phase, it won’t need a thrust reverser. Rolls-Royce will use carbon composite fan blades instead of its usual hollow titanium blades, and along with new material adoption will save 340 kg (750 lb) per engine.
This is a bit different from previous engines.
Variable-Pitch Fan Blades
Variable Pitch Fan has its own Wikipedia entry, where these are the two opening paragraphs.
A variable pitch fan is similar in concept to that of a variable-pitch propeller and involves progressively reducing the pitch (or blade angle) of the fan on a turbofan as the engine is throttled. Although variable pitch fans are used in some industrial applications, the focus of this article is on their use in turbofan engines. No production engine uses such a feature; however, it will likely be required on at least some of the next generation of high bypass ratio turbofans.
One of the methods used to reduce Thrust-specific fuel consumption is to improve Propulsive Efficiency. This involves reducing the effective jet velocity of the engine by reducing specific thrust. This, in turn, reduces the optimum fan pressure ratio required and consequently the cold nozzle pressure ratio. At cruise flight speeds the nozzle is choked and the fan working line is fairly steep and linear. However, at low flight speeds the ram pressure rise in the air intake is so low the nozzle is well un-choked. Consequently, the fan working line is highly curved and well to the left of the cruise flight speed working line, potentially reducing the fan surge margin to a dangerous level, particularly at lower throttle settings. Readers unfamiliar with surge lines, working lines, etc. should read the Wikipedia article on Compressor map.
The extract says that no production engine uses this feature. So will UltraFan be the first?
Variable pitch fan blades seem to offer two advantages; better efficiency and lower weight. If the reliability is acceptable, then that must be a winner.
No Thrust Reverser
This sentence is also in the Wikipedia entry for Variable Pitch Fan.
One advantage of the variable fan option is that varying the fan pitch offers the possibility of reversing engine thrust without the need for heavy blocker doors, cascades, etc.
It does look like the UltraFan will be a lighter engine, than its predecessor.
Composite Fan Blades
Composite Fan Blades were tried in the 1960s for the Rolls-Royce RB211 engine.
But they failed and were replaced by titanium blades.
At the time, I was at Liverpool University and John Wilkinson was a fellow student.
John’s father was the manager of a Tesco store in Derby.
That Tesco store had a nice line in selling out-of-date chickens and turkeys to Rolls-Royce to test the engines for bird strikes.
Improving The Engine’s Efficiency
This is the second paragraph of the press release.
This achievement reinforces our confidence in the suite of technologies that has been developed as part of the UltraFan programme. Confirming this capability is a big step towards improving the efficiency of current and future aero-engines as UltraFan delivers a 10% efficiency improvement over our Trent XWB, which is already the world’s most efficient large aero-engine in service. In total that’s a 25% efficiency gain since the launch of the first Trent engine.
Note.
- The Trent engine was first run in 1990 and has improved 25 % since.
- The Trent XWB engine was first run in 2010 and has improved 10 % since.
The increase in efficiency appears to be linear.
A Saleable Design
This is the third paragraph of the press release.
UltraFan’s scalable technology from ~25,000-110,000lb thrust also offers the potential to power the new narrowbody and widebody aircraft anticipated in the 2030s.
If that means that an UltraFan can power an aircraft as small as an A320, then that is sensational, as it will give Rolls-Royce access to the A320/Boeing 737 market, where they have virtually no sales.
UltraFan Is About A Suite Of Technologies
This is from the second paragraph of the extract.
This achievement reinforces our confidence in the suite of technologies that has been developed as part of the UltraFan programme.
And this is the fourth paragraph.
As part of the UltraFan development programme we have identified a number of technologies that are potentially transferable to our current Trent engines, which will provide our customers with even greater availability, reliability and efficiency.
As you learn more about your future project, why not apply that knowledge to current projects.
Running On SAF Is Part Of The Testing
I’m reassured that testing of the technology using Sustainable Aviation Fuel has started early in the program.
This is surely going to be the fuel, that aircraft will use until hydrogen becomes available.
Conclusion
It looks like Rolls-Royce are redefining, what a standard aero engine looks like.
- It will give a 10 % fuel saving over their latest engines launched thirteen years ago.
- The UltraFan engines will save weight and hopefully more fuel.
- It will allow Rolls-Royce to compete in the A320/737 market, where they have no engine at present.
I would watch the share price
Rolls-Royce Successfully Completes 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel Test Programme
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
This is the sub-heading.
Rolls-Royce today announces that it has successfully completed compatibility testing of 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) on all its in-production civil aero engine types.
These are the first three paragraphs.
This fulfils a commitment, made in 2021, to demonstrate there are no engine technology barriers to the use of 100% SAF.
A ground test on a BR710 business jet engine at the company’s facility in Canada, completed the test regime. Other engines tested as part of the programme were: Trent 700, Trent 800, Trent 900, Trent 1000, Trent XWB-84, Trent XWB-97, Trent 7000, BR725, Pearl 700, Pearl 15 and Pearl 10X.
Testing has involved a variety of ground and flight tests to replicate in-service conditions. All the tests confirmed the use of 100% SAF does not affect engine performance.
That would appear to be very comprehensive.
Conclusion
Rolls-Royce look like they are prepared for sustainable aviation fuel!
But are operators, airlines, airports and aircraft manufacturers?
Virgin Atlantic Granted Permit For Historic 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel Flight
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Virgin Atlantic.
These two paragraphs outline the proposed flight.
Virgin Atlantic’s historic 100% sustainable aviation fuel flight has been granted a permit to fly by the Civil Aviation Authority.
Virgin Atlantic plans to fly across the Atlantic from London Heathrow to New York JFK on 28 November 2023 to test and showcase the feasibility of flying on 100% SAF.
Note.
- Strangely, I’ve never flown Virgin, although I did once book then to go to Kenya, but as the flight was cancelled at the last minute, I swapped to Kenya Airways.
- Virgin have seventeen Rolls-Royce-powered Boeing 787s.
As Branson is involved, I do wonder, if this is more about PR than anything else.
This paragraph talks about sustainable aviation fuel (SAF).
SAF is fuel derived from non-petroleum based renewable sources that is capable of being used as a replacement for, or blended with, kerosene. SAF can currently be used in jet engines to a maximum blend of 50% with traditional kerosene without the need for any modifications. There are several processes to produce SAF, including algae, synthesised fuels from hydrogen waste, or from directly capturing carbon dioxide. When fully replacing kerosene, SAF could reduce lifecycle carbon emissions by over 70% compared to conventional fossil jet fuel.
There is nothing specifically said about the fuel, that Virgin Atlantic will use.
I first mentioned this flight in a post in December 2022, which is entitled World’s First Net Zero Transatlantic Flight To Fly From London in 2023, Powered By The Rolls-Royce Trent 1000.
The press release from Rolls-Royce, said that the flight would be this year. So, that appears to be happening.
In fact, it does appear that Rolls-Royce are being thorough with their testing of sustainable aviation fuel, as these posts include both Rolls-Royce and sustainable aviation fuel.
- Rolls-Royce Completes Next Step On Its Journey To Decarbonising Business Aviation
- New Rolls-Royce Small Engine Set To Begin Tests To Advance Hybrid-Electric Flight
- Rolls-Royce And Gulfstream Give Wings To Sustainable Business Aviation
- News Of The Day From Rolls-Royce
- First In-flight 100% Sustainable-Fuels Emissions Study Of Passenger Jet Shows Early Promise
- Rolls-Royce Joins Boeing And World Energy For Successful 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel Flight
Several are based on Rolls-Royce press releases.
Rolls-Royce Completes Next Step On Its Journey To Decarbonising Business Aviation
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
This is the sub-heading.
Rolls-Royce today announces the successful completion of a series of tests with 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) on its latest generation of business aviation engines, the Pearl 15 and the Pearl 10X. The Pearl 15, the first member of the Pearl engine family, powers Bombardier’s Global 5500 and 6500 aircraft, while the Pearl 10X will power Dassault’s ultra-long-range flagship aircraft, the Falcon 10X.
These are the websites for the three aircraft, with number of passengers, typical cruise speed and range.
- Bombardier Global 5500 – 16 pax – Mach 0.85 – 5900 nm
- Bombardier Global 6500 – 17 pax – Mach 0.85 – 6600 nm
- Dassault Falcon 10X – 19 pax – Mach 0.925 – 7500 nm
This screenshot from the Dassault Falcon 10X web site shows the range from London.
Note that Buenos Aires, the Falkland Islands, Seattle, Seoul and Tokyo are all within range.
I have a few thoughts and observations.
Jet A-1 And 100% SAF
This paragraph from the press release describes how Rolls-Royce are testing the compatibility of Jet A-1 and 100% SAF.
As well as proving compatibility with 100% SAF another target of the test campaign was to run a back-to-back engine test with both Jet A-1 and SAF on the same Pearl 10X engine. The aim was to confirm further improvements in the environmental footprint when switching to SAF. The results from this first back-to-back engine emission test under standard certification conditions provides important correlations for the evaluation of future SAF within our environmental strategy.
Compatibility and back-to-back running is surely very important, as it could be many years before all airports can supply 100 % SAF for visiting jet aircraft.
The Fuels Used In The Tests And The Benefits
These two paragraphs from the press release describes the fuels used and the benefits..
The HEFA (Hydro-processed Esters and Fatty Acids) SAF was produced from waste-based sustainable feedstocks such as used cooking oils and waste fat. This fuel has the potential to significantly reduce net CO2 lifecycle emissions by about 80% compared to conventional jet fuel.
The back-to-back tests conducted with conventional fossil-based fuel and subsequently SAF also confirmed a cleaner combustion of the sustainable fuel, with significantly lower levels of non-volatile particulate matter (nvPM). In combination with the low NOx combustor technology of the Pearl 10X and its additive manufactured combustor tiles a reduction of all emissions was achieved.
Note.
- An eighty percent reduction in lifecycle emissions is not to be sneezed at.
- Cleaner combustion and low NOx emissions are very much bonuses.
- Additive manufacture is better known as 3D-printing and I’m not surprised that Rolls-Royce have embraced the technology.
As an engineer and retired light aircraft pilot, I suspect the tests have met Rolls-Royce’s objectives.
Moving To 100 % SAF
This is the final paragraph of the press release.
The tests demonstrated once again that Rolls-Royce’s current engine portfolio for large civil and business jet applications can operate with 100% SAF, laying the groundwork for moving this type of fuel towards certification. At present, SAF is only certified for blends of up to 50% with conventional jet fuel. By the end of 2023 Rolls-Royce will have proven that all its in-production Trent and business aviation engines are compatible with 100% SAF.
It must be a good selling point for aircraft equipped with Rolls-Royce engines, that the buyer knows that the aircraft can run on 100% SAF.
100 % SAF As An Airline Marketing Tool
It will be interesting to see how airlines use 100% SAF to sell tickets.
As an example, I can see routes like London and Scotland becoming very competitive.
- Avanti West Coast, LNER and Lumo already run all-electric trains to Edinburgh and Glasgow.
- The technology exists to decarbonise trains to Aberdeen and Inverness..
- Other open access operators could well move in to a lucrative market.
- The only way, that the airlines will be able to compete on emissions, would be to move to 100 % SAF.
There must be hundreds of routes like London and Scotland around the world.
100 % SAF And Business Jets
In A Class 319 Train, But Not As We Know It!, I told this tale.
I am reminded of a tale, that I heard from a former GEC manager.
He was involved in selling one of GEC’s Air Traffic Control radars to a Middle Eastern country.
The only working installation of the radar was at Prestwick in Scotland, so he arranged that the dignitaries and the sales team would be flown to Prestwick in GEC’s HS 125 business jet.
As they disembarked at Prestwick and walked to the terminal, the pilot called the GEC Manager over.
The pilot told him “The Scottish Highlands at this time of the year, are one of the most beautiful places in the world! Would you and your guests like a low-level tour on the way back? I can arrange it, if you say so!”
Despite knowing GEC’s draconian attitude to cost control he said yes.
The sale was clinched!
I also remember an article in Flight International about how JCB sold diggers.
- Dealers in a country like Greece would put together a party of prospective customers.
- The customers would then be flown to East Midlands Airport in JCB’s business jet, which is close to the JCB factory at Rocester.
- After a sales demonstration and a tour of the factory they would be flown home.
I once met a lady who had been one of JCB’s cabin staff and she told me it was a very successful sales technique.
I suspect that a business jet running on 100 % SAF would be an even better sales aid.
There are also increasing protests from the greens about business jets, which are seen as producing pollution and are only the toys of the rich and powerful.
Surely, if they were running on 100 % SAF, this would make business jets more acceptable.
100 % SAF And Niche Airlines
In the web site for the Falcon 10X, there is a section called Mission Flexibility, where this is said.
As large as it is, the Falcon 10X can still access typical airports serving business aviation as well as others with challenging approaches. The Falcon 10X will be London City-capable so that it can fly you straight into the heart of global finance. When you’re ready for rest and relaxation, the 10X can whisk you to out-of-the-way corners of the world.
British Airways used to run a service between London City Airport and New York.
- The route used 32-seat Airbus A-318 airliners.
- The flight stopped at Shannon for refuelling.
- It was business class only.
I suspect someone will think about running a similar London City Airport and New York service using a Falcon 10X.
- It has nineteen seats.
- It could do it in one hop.
- It could run on 100 % SAF.
- British Airways must have all the passenger data from the discontinued service.
- A Falcon 10X flies higher than a Boeing 767, Boeing 787 or an Airbus A350.
I have a feeling that flight time would be comparable or better to a flight between Heathrow and New York.
Conclusion
Rolls-Royce would appear to have the right strategy.
If I was going to New York in business class, I’d use it.