Trump Administration’s Legal Setbacks Are Good News For Offshore Wind — And The Grid
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Tech Crunch.
These two paragraphs give more details.
The Trump administration suffered a series of legal setbacks this week after judges allowed work to restart on several offshore wind farms under construction on the East Coast.
The Department of the Interior had ordered a stop to five projects totaling 6 gigawatts of generating capacity in December, citing national security concerns. The judicial orders will allow three projects to resume construction: Revolution Wind off Rhode Island, Empire Wind off New York, and Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind off — you guessed it — Virginia.
The developers each filed lawsuits shortly after the Trump administration issued the stop work order, which had been effective for 90 days.
Trump is now learning you don’t win them all.
I would suggest that you read the full article, as there is a lot of good stuff there.
This is the concluding paragraph.
he potential is even bigger when viewed on a national scale. Offshore wind could generate 13,500 terawatt-hours of electricity per year, which is three times more than the U.S. currently consumes.
If the US, were to use all the fossil fuels, that Trump would like, there would be no point in buying Greenland as the Trump proportion of the resulting Global Warming would probably melt the country.
Legal Challenge Against Gatwick Airport’s Second Runway To Begin
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on ITVX.
These four paragraphs add more details.
Plans to challenge a second runway at Gatwick Airport will be heard in the High Court next week.
The campaign and environmental group Communities Against Gatwick Noise Emissions (CAGNE) opposes Transport Secretary Heidi Alexander’s decision to grant development consent for the project.
In the hearing, which will run from 20 to 23 January 2026, CAGNE’s argues that the climate change impacts of the extra runway have not been properly assessed.
The planned expansion would see the repurposing of Gatwick Airport’s emergency runway for use as a second operational runway. The extra capacity is expected to lead to more than 100,000 more flights per year.
These two paragraphs give CAGNE’s case.
CAGNE says that this decision was flawed, arguing that there are numerous gaps in the environmental assessment of the airport expansion. These include a failure to adequately assess inbound flight emissions, the climate impact of non-carbon dioxide emissions, the handling of additional sewage, and noise pollution.
The group also argues that the second runway plans rely too heavily on the UK’s Jet Zero Strategy (JZS), which assumes ambitious improvements in the aviation industry in areas such as fuel efficiency.
My feelings are as follows.
- We need more runway capacity.
- Eventually all aircraft will be powered by electricity, hydrogen or sustainable aviation fuel (SAF).
- Because of the need for large amounts of renewable electricity to make hydrogen and SAF, the runway will need to be near offshore wind farms.
Only Doncaster Sheffield, Gatwick, Liverpool, Stansted and some Scottish airports are near the sea or could be connected to the coast by an easy-to-build cable or pipeline.
CAGNE may well win their case, but I fell Nimbys will also stop Heathrow getting a third runway.
US Federal Court Clears Revolution Wind To Resume Construction As Ørsted, Skyborn’s Lawsuit Against Stop-Work Orders Progresses
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The US District Court for the District of Columbia has granted the preliminary injunction sought by the joint venture between Ørsted and Skyborn Renewables for the Revolution Wind project, which was ordered to pause construction by the US government. When the stop-work order was issued on 22 December 2025, the 704 MW project had seven wind turbines left to install.
This paragraph adds more detail.
The underlying lawsuit that the Revolution Wind joint venture filed against the first stop-work order issued for the offshore wind farm on 22 August 2025, which was supplemented to also challenge the 22 December 2025 order, continues to progress in the court, while the preliminary injunction will allow the construction activities to restart immediately.
Note.
- Ørsted said on the 12th January 2026, that they would resume work as soon as practically possible.
- Ørsted have also said that the project is approximately 87 per cent complete and was expected to begin generating power this month.
- In New York Attorney General Files Lawsuits Against Trump Admin’s Stop-Work Orders For Empire Wind, Sunrise Wind, Trump is also facing a second legal action over offshore wind.
It does seem that we are seeing what happens, when the irresistible force that is Trump meets the immovable force, that is United States law.
New York Attorney General Files Lawsuits Against Trump Admin’s Stop-Work Orders For Empire Wind, Sunrise Wind
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
New York Attorney General (AG) Letitia James has filed two lawsuits against what the AG says is “the Trump administration’s unlawful attempt to halt construction” on Empire Wind 1 and Sunrise Wind, two large-scale offshore wind projects being built in the US federal waters off New York.
These three paragraphs add more detail.
In the lawsuits, filed simultaneously for the two projects in the US District Court for the District of Columbia on 9 January, Attorney General James argues that the stop-work orders fail to explain the federal government’s change in position and to provide a genuine justification for the suspension. This makes the orders “arbitrary and capricious, in violation of the Administrative Procedure Act”, says the New York AG, whose lawsuit is asking the court to declare the stop-work orders unlawful and block their enforcement.
Pointing out that the two offshore wind farms are expected to power more than one million New York homes, the Attorney General says pausing them could threaten the state’s economy and energy grid, as well as the jobs created by the projects, which currently employ thousands of workers and have already invested billions of US dollars.
Furthermore, the New York AG emphasised that both Empire Wind 1 and Sunrise Wind had undergone more than a decade of extensive review by federal, state, and local authorities, including environmental impact analysis, public comment periods, and coordination with numerous federal agencies, including the US Department of Defense.
I’m no lawyer, but I do think that the New York Attorney General has a good case.
Development Consent Decision On 3 GW Dogger Bank South Project Postponed
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK Secretary of State for Energy Security and Net Zero has set a new deadline for the decision on the Development Consent Order (DCO) for Dogger Bank South, a 3 GW offshore wind project developed by RWE, which the company owns in partnership with Masdar.
These two paragraphs add more detail to the project.
The statutory deadline for the decision on the project was 10 January 2026. This has now been moved to 30 April.
According to a statement from the Minister for Energy Consumers, Martin McCluskey, the extension will allow time to request further information that was not provided for consideration during the examination period and to give all interested parties the opportunity to review and comment on such information.
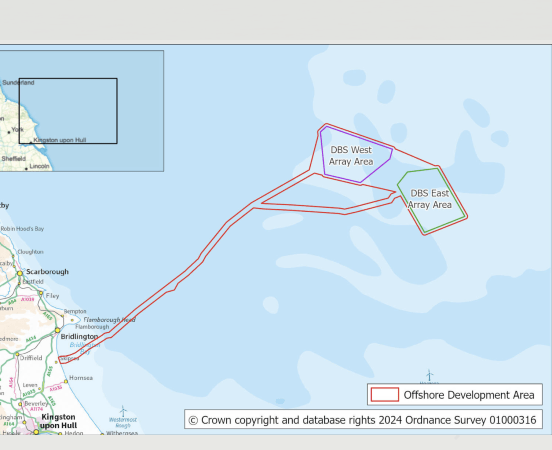
I clipped this map from the Dogger Bank South web site.
Note.
- Bridlington, Kingston-Upon-Hull and Scarborough can be picked out on the coast of East Yorkshire.
- The two wind farms and the route of the cables to the shore can be clearly seen.
I just wonder, whether the nature of the project is changing.
Consider.
- Three GW is a lot of power to move across Yorkshire to where it can be connected to the grid.
- In Consultation On Offshore Wind Reform: Hydrogen Sector Calls For Hybrid Connection Concepts And Warns Of Compensation Risks, German companies involved in the AquaVentus project are calling for more hydrogen to be produced offshore and piped to the shore.
- Could hydrogen produced in the Dogger Bank Wind farms be piped to the Northern end of the AquaVentus pipeline on the German sector of the Dogger Bank?
- A pipeline or cable could still bring energy to Yorkshire.
- The hydrogen could go to the hydrogen stores at Aldbrough and Rough.
- SSE and Centrica could play hydrogen-bankers to the Germans, as Germany is short of hydrogen storage.
- East Yorkshire is building two hydrogen power stations at Keadby and Ferrybridge.
- Support for the Dogger Bank South wind farms will probably be from RWE’S Grimsby hub.
Is this the Anglo-German co-operation, I talked about in UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties at work?
I can see benefits for this arrangement for the UK.
- Hydrogen production is offshore.
- A lot of the onshore employment is in the UK.
- There will be a hydrogen pipeline between Germany and the vast hydrogen storage of Humberside via the German Dogger Bank and Dogger Bank South wind farms.
- Will there be a hydrogen pipeline between the North of Scotland and Humberside via the AquaVentus pipeline?
- There will also be a substantial cash flow to the UK Treasury because of all the hydrogen production in UK waters.
RWE may also be able to use a standard hydrogen production platform in German and UK waters.
This is the sort of plan, that the money men will like.
German Wind Tender Awards 3.46 GW Amid Record Demand, Lower Prices
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Renewables Now.
These are the first three paragraphs.
Germany’s Federal Network Agency (BNetzA) selected 415 projects with a combined capacity of 3,456 MW in the last onshore wind tender round for 2025, seeing record interest in the procedure and falling prices.
Until the deadline of November 1, as many as 905 bids totalling 8,155 MW were submitted, while the target was 3,450 MW. As many as 37 projects had to be excluded from the competition, the agency said on Thursday.
The value of the successful bids ranged between EUR 0.058 (USD 0.068) per kWh and EUR 0.0612 per kWh. The average volume-weighted award price stood at EUR 0.0606 per kWh, which is below the value of EUR 0.0657 per kWh in the previous round and significantly lower than the maximum possible amount of EUR 0.0735 per kWh.
Note.
- These figures show that the German onshore wind market is healthy and the price of the electricity is falling.
- The procedure marks the fourth onshore wind tender round for 2025. In the previous three rounds, the Federal Network Agency allocated capacities of 3,448 MW, 3,447 MW and 4,094 MW, respectively, so with this round’s 3,456 MW, that makes 14.445 GW or about four-and-a-half Hinckley Point Cs.
- Germany is 45 % larger than the UK in terms of land area.
If we were installing wind turbines at the same rate as the Germans, we’d have installed a few megawatts short of ten gigawatts onshore in the same period of time.
I have some thoughts on these figures.
Does More Onshore Wind Mean Lower Electricity Prices?
If we were installing onshore wind turbines at the same rate as the Germans, our energy prices might be lower.
More research needs to be done.
Do The Germans Have A Pricing Structure That Encourages The Take-Up Of Onshore Wind?
If they do, then we should think of using it in certain locations.
Ørsted-Skyborn JV Takes Legal Action Against US Gov’t Over Stop-Work Order; Seven Turbines Left To Install On Revolution Wind
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
On New Year’s Day, Revolution Wind LLC, the 50/50 joint venture between Ørsted and Skyborn Renewables, filed a supplemental complaint in the US District Court for the District of Columbia and plans to move for a preliminary injunction to block the lease suspension order recently imposed by the US government that stopped construction on its 704 MW project, which is now approximately 87 per cent complete and was expected to start generating power in January 2026.
These five paragraphs give more details of the story.
The lease suspension order, issued by the US Department of the Interior’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) on 22 December 2025, directed all major offshore wind projects under construction to pause pending a review of alleged national security risks.
The developer asserts the suspension is unlawful and would cause substantial harm to the project, similar to the August 2025 stop-work order.
The project partners say Revolution Wind secured all required federal and state permits in 2023 after extensive reviews and engaged in multi-year consultations with defence authorities, resulting in formal mitigation agreements.
The project is approximately 87 per cent complete, with all foundations, offshore substations and export cables – and 58 of the total 65 wind turbines – installed, and was expected to begin generating power this month.
The developer also noted that the project will supply affordable power to over 350,000 homes under long-term power purchase agreements and support grid reliability in the Northeast.
A Verdict From Google AI
Pending any final result from my learned friends, I asked Google AI, if Revolution Wind will win their case and received this answer.
The question of whether Revolution Wind will ultimately win its case against the federal government’s Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM) has no final answer yet, as the litigation is ongoing. However, a federal judge has so far ruled in favor of Revolution Wind in a key preliminary step.
Key Developments in the Case
Initial Ruling: In September 2025, a U.S. District Court judge in D.C., Royce Lamberth, granted a preliminary injunction that allowed construction on the nearly-complete project to resume. The judge stated that Revolution Wind was likely to succeed on the merits of its claims and that the project would face “substantial harm” otherwise. The judge called the government’s initial “stop-work order” the “height of arbitrary and capricious action” because it failed to provide a factual basis for the cited national security concerns.
Outcome Uncertainty: The preliminary injunction allows work to continue while the full case proceeds, which could take years. The final outcome of the case depends on the court’s ultimate decision on the merits of the lawsuit
There is going to be some interesting reporting of this case, when the judges give their verdict.
The most interesting case, will probably be the one surrounding Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind as that is a 2.6 GW wind farm, which will generate a lot of fees for lawyers.
Britain’s Biggest Clean Power Projects Among 2.4GW Of Transmission Connections National Grid Delivers In 2025
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from National Grid.
This is the sub-heading.
Record-breaking renewable power projects are among the 2.4GW of new generation connections we plugged into our transmission network during 2025, in another key step in the UK’s clean energy transition.
This first paragraph adds some detail to the headlines.
This year’s works build on the 3GW of connections we delivered in 2024 – which included a new interconnector between Wales and Ireland – and is part of 12.6GW of generation capacity we’ve connected in England and Wales over the past five years.
The rate of connections appear to have been fairly steady over the last five years, at about 2.5 GW/year.
Three projects are highlighted.
- In April the 373MW Cleve Hill Solar Park, Britain’s largest solar array, began exporting power across the network following work to connect it at our Cleve Hill substation in Kent.
- Over summer Statera Energy’s Thurrock Storage project, the country’s biggest battery energy storage system (BESS), connected at our Tilbury substation in Essex to add 300MW of flexible capacity across London and the south east.
- And in September we completed upgrades and commissioning activity at our Lackenby substation in North Yorkshire in readiness for RWE’s Sofia offshore wind farm – one of the world’s biggest – to complete construction.
They also completed works for more than 400MW of additional BESS connections during the year, including a 150MW scheme connecting at Ferrybridge substation in West Yorkshire, a 100MW facility plugging in at Thornton substation in North Yorkshire, and further projects at our substations in Enderby (Leicestershire), Rainhill (Merseyside) and Bredbury (Greater Manchester).
I think that adds up to ten projects in total.
It looks like National Grid had a good year.
Consultation On Offshore Wind Reform: Hydrogen Sector Calls For Hybrid Connection Concepts And Warns Of Compensation Risks
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the AquaVentus web site.
There is this statement on the home page.
Berlin, January 02 2026. In the context of the consultation launched by the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWE) on the reform of the Wind Energy at Sea Act (WindSeeG), the hydrogen initiative AquaVentus is calling for clear legislative action to enable a cost-efficient and system-friendly development of offshore wind energy. At the heart of its position is the timely legal establishment of hybrid connection concepts, allowing offshore wind farms to be connected via both electricity cables and hydrogen pipelines.
Note.
- I’ve always felt that copying proven technologies from the offshore oil and gas industry is good practice.
- It may be easier to recycle infrastructure like pipelines, platforms and storage by creating the hydrogen offshore.
- In the UK, Centrica and SSE are already re-purposing natural gas storage for hydrogen.
It may feel safer to some for the hydrogen to be produced a distance offshore.
Offshore Wind Turbines In 2025: China Continues Leading In Single-Unit Capacity, Vestas’s 15 MW Turbine Installed At Offshore Wind Farms
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
In offshoreWIND.biz‘s 2024 annual wind turbine overview, you could have read about the first 16 MW floating wind platform installed offshore and a 26 MW prototype under construction, both in China, and a 21 MW prototype being assembled in Europe. Wind turbine generator (WTG) technology did not stop progressing in 2025, with Chinese OEMs still leading capacity-wise, while in Europe, first offshore wind farms are now featuring 15 MW turbines and a 21+ MW model was installed onshore for testing.
The article is very much a must-read and there is a lot of innovation going on.
As a comparison, between 2020 and 2026 we commissioned or are building these offshore wind farms in the UK.
- East Anglia One – 2000 – 714 MW – 102 x 7 MW
- Hornsea One – 2020 – 1218 MW – 174 x 7 MW
- Kincardine – 2021 – 49.5 MW – 6 x floating
- Hornsea Two – 2022 – 1386 MW – 165 x 8 MW
- Moray East – 2022 – 950 MW – 100 x 9.5 MW
- Triton Knoll – 2022 – 857 MW – 90 x 9.5 MW
- Seagreen Phase 1 – 2023 – 1400 MW – 114 x 10 MW
- Dogger Bank A – 2025 – 1235 MW – 95 x 13 MW
- Moray West – 2025 – 882 MW – 60 x 14 MW
- Neart Na Gaoithe – 2025 – 450 MW – 54 x 8 MW
- Dogger Bank B – 2026 – 1235 MW – 95 x 13 MW
- East Anglia 3 – 2026 – 1372 – 95 x 14 MW
- Sofia – 2026 – 1400 MW – 100 x 14 MW
Average sizes for the various years are as follows.
- 2020 – 7 MW
- 2021 – floating
- 2022 – 8-9.5 MW
- 2023 – 10 MW
- 2025 – 8-14 MW
- 2026 – 13-14 MW
It can clearly be seen that in the last few years, turbines have been getting bigger.
I have some thoughts on the article.
2025 Saw Some Plans For And Installations Of Some Very Large Turbines
These four monsters were mentioned at the start of the article.
- 26 MW – Prototype installed for testing (China)
- 21.5 MW – Prototype installed for testing (Europe)
- 15 MW Installed at offshore wind farms (Europe)
- 50 MW Twin-turbine platform; Announced (China)
- MingYang Turbines to Spin on Hexicon’s Floating Offshore Wind Project
- World’s First Offshore Wind Farm Using 16 MW Turbines Enters Construction In China
- The Secret Of The TwinHub
- Hexicon Wins UK’s First Ever CfD Auction For Floating Offshore Wind
- The Chinese seem to be providing turbines for both manufacturers.
- The TwinHub is the Swedish design, being built for trial in Cornwall.
- This new design is a 50 MW design, whereas these two are 32 MW.