Lower Thames Crossing Tunnelling ‘To Begin In 2028’
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
The tunnelling process for the Lower Thames Crossing is due to begin in 2028.
These three paragraphs add more detail to the story.
National Highways said negotiations to buy one of the world’s largest tunnelling machines were now under way.
It would be capable of digging 60 metres below the Thames, creating a new road link between Essex and Kent, and now enables the project to secure private sector investment to deliver the remainder of the construction.
Next summer, work on the northern tunnel entrance where the tunnel machine will begin its journey will get under way.
Hopefully, it’ll all be complete by the early 2030s.
The Elephant In The Garden Of England
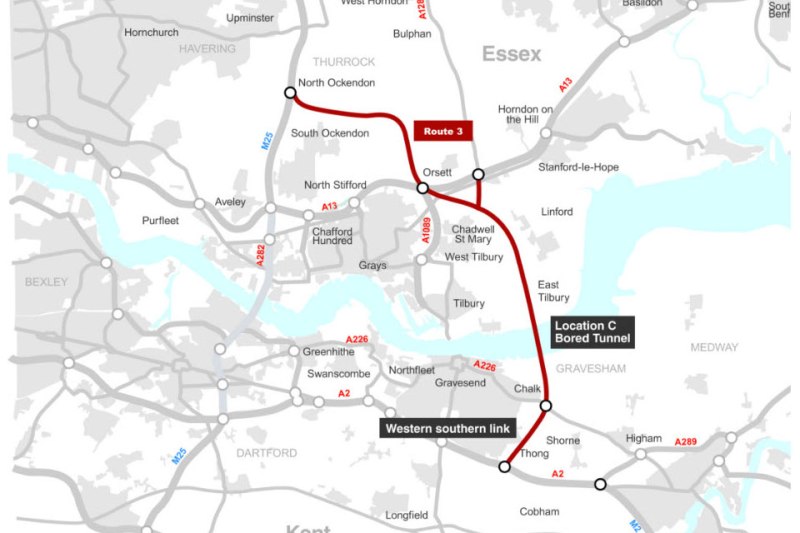
This section shows the proposed route of the Lower Thames Crossing.
It as an extract of a previous post called Elizabeth Line To Ebbsfleet Extension Could Cost £3.2 Billion.
It is proposed that the new Lower Thames Crossing is built to the East of Gravesend.
This map from the Department of Transport, shows the route.
Note.
- The new crossing, which is shown in red, bypasses the Dartford Crossing on the M25.
- The A226 runs between Gravesend and Higham via a junction with the new crossing at Chalk.
- Northfleet is to the West of Gravesend.
This Google Map shows the area between Chalk and Higham.
£1.5 billion Enables UK-US Pair To Get Their Hands On Europe’s Giant LNG Terminal
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Offshore Energy.
This is the sub-heading.
UK-based energy player Centrica and U.S. investment firm Energy Capital Partners (ECP), part of Bridgeport Group, have brought into their fold a liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminal in Kent County, United Kingdom.
This paragraph gives Centrica’s view of the Grain LNG Terminal.
The UK firm portrays the terminal as Europe’s largest LNG regasification facility, with a capacity of 15 million tonnes of LNG a year. Located on the UK’s Isle of Grain, the terminal features unloading infrastructure, regasification equipment, and truck-loading facilities.
In a press release, which is entitled Investment in Grain LNG, that was published in August 2025, Centrica said this.
Opportunities for efficiencies to create additional near-term value, and future development options including a combined heat and power plant, bunkering, hydrogen and ammonia.
The tone of the article in Offshore Energy and the press release is unmistakable. – Centrica intend to make good use of their investment.
I suggest you read both documents fully.
- Europe’s largest LNG regasification facility, with a capacity of 15 million tonnes of LNG a year, will certainly need a large combined heat and power plant.
- Will any spare power from the CHP plant, be sent to Germany, through the 1.4 GW NeuConnect interconnector, which should be commissioned by 2028?
- Hydrogen, ammonia and LNG are the three low-carbon fuels used by modern ships, so I suspect hydrogen and ammonia will be produced on the island.
- Centrica are investors in the efficient hydrogen-generation process ; HiiROC.
- Hydrogen and nitrogen are the two feedstocks for ammonia.
Centrica certainly have big plans for the Grain LNG Terminal.
I shall be following Centrica closely.
Investment in Grain LNG
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Centrica.
This sub-heading outlines the deal.
Centrica plc (the “Company”, “Centrica”) is pleased to announce the acquisition of the Isle of Grain liquified natural gas terminal (“Grain LNG”) in partnership1 with Energy Capital Partners LLP (“ECP”) from National Grid group (“National Grid”) for an enterprise value of £1.5 billion. After taking into account approximately £1.1 billion of new non-recourse project finance debt, Centrica’s 50% share of the equity investment is approximately £200 million.
The press release lists these key points.
- Grain LNG delivers vital energy security for the UK, providing critical LNG import/export, regasification and rapid response gas storage capacity to balance the energy system.
- Aligned with Centrica’s strategy of investing in regulated and contracted assets supporting the energy transition, delivering predictable long-term, inflation-linked cash flows, with 100% of capacity contracted until 2029, >70% until 2038 and >50% until 2045.
- Opportunities for efficiencies to create additional near-term value, and future development options including a combined heat and power plant, bunkering, hydrogen and ammonia.
- Highly efficient funding structure, with Centrica’s equity investment of approximately £200 million alongside non-recourse project financing.
- Strong life of asset returns aligned with Centrica’s financial framework, with an expected unlevered IRR2 of around 9% and an equity IRR2 of around 14%+
Underpins delivery of £1.6 billion end-2028 EBITDA target3 – Centrica’s share of EBITDA expected to be approximately £100 million per annum and cash distributions expected to be around £20 million on average per annum for 2026-2028, representing an attractive yield on Centrica’s equity investment - Partnership with ECP (part of Bridgepoint Group plc), one of the largest private owners of natural gas generation and infrastructure assets in the U.S. with direct experience in supporting grid reliability.
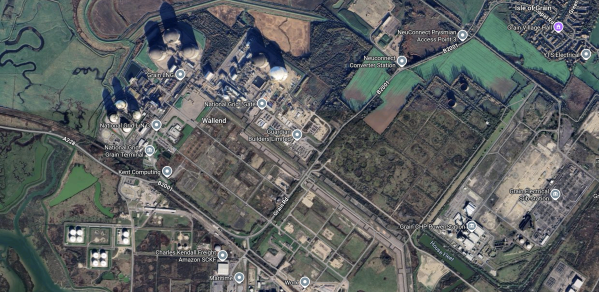
This Google Map shows the various energy assets on the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- It appears that works for the 1, 400 MW NeuConnect interconnector to Wilhelmshaven in Germany, are taking place in the North-East corner of the map.
- Grain CHP powerstation is a 1,275MW CCGT power station, which is owned by German company; Uniper, that is in the South-East corner of the map, which can also supply up to 340MW of heat energy recovered from the steam condensation to run the vapourisers in the nearby liquefied natural gas terminal.
- The Grain LNG terminal is at the Western side of the map.
- In the Thames Estuary to the East of the Isle of Grain, I estimate that there are about 1,500 MW of wind turbines.
I find it interesting that two of the assets are German owned.
I have some thoughts.
It Is A Large Site With Space For Expansion
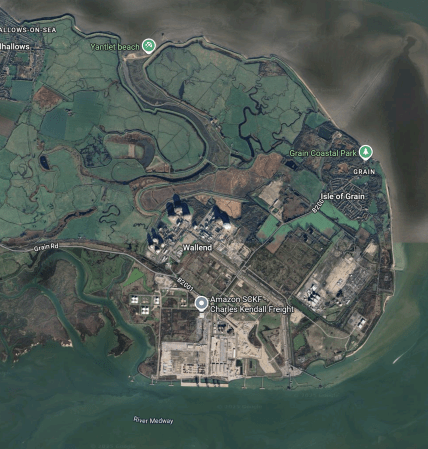
This Google Map shows the whole of the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- The Grain LNG terminal is around the label Wallend.
- The River Medway runs East-West at the bottom of the map.
- Gas tankers deliver and take on gas at jetties on the North Bank of the Medway.
There could be space to expand the terminal, if the RSPB would allow it.
As an example, I asked Google AI, if peregrine falcons nest on chemical plants and got this reply.
Yes, peregrine falcons do nest on chemical plants. They have adapted to using various urban and industrial structures, including chemical plants, for nesting. This is particularly true in areas where natural cliff habitats are scarce.
Peregrine falcons are known for their adaptability, and their population has seen a resurgence in recent decades, partly due to their ability to utilize man-made structures. These structures often mimic their natural cliffside nesting
Cliffs do seem scarce on the Isle of Grain. I also asked Google AI, if peregrine falcons ate small rodents, as several chemical and other plants, where I’ve worked, had a rodent problem. One plant had a cat problem, as there had been so many rats. This was the reply.
Yes, peregrine falcons do eat small rodents, though they primarily consume birds. While their diet mainly consists of other birds like pigeons, doves, and waterfowl, they will also hunt and eat small mammals, including rodents such as mice, rats, and voles. They are opportunistic hunters and will take advantage of readily available prey, including insects, amphibians, and even fish.
I’m sure if Centrica wanted to expand, they’d employ the best experts.
Who Are ECP?
One of the key points of the press release is that this deal is a partnership with ECP (part of Bridgepoint Group plc), one of the largest private owners of natural gas generation and infrastructure assets in the U.S. with direct experience in supporting grid reliability.
The Wikipedia entry for ECP or Energy Capital Partners has this first section.
Energy Capital Partners Management, LP (ECP) is an American investment firm headquartered in Summit, New Jersey. It focuses on investments in the energy sector. The firm has additional offices in New York City, Houston, San Diego, Fort Lauderdale and Seoul.
In August 2024, ECP merged with Bridgepoint Group to form a private assets investment platform.
The Wikipedia entry for the Bridgepoint Group has this first paragraph.
Bridgepoint Group plc is a British private investment company listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.
The company had started as part of NatWest.
Are The Germans Going To Take Away Some Of Our Electricity?
Consider.
- Germany has a big need to replace Russian gas and indigenous coal, and to decarbonise.
- Neuconnect is a 1.4 GW interconnector between the Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven in Germany. It is scheduled to be completed in 2028.
- The Grain CHP powerstation is a 1,275MW CCGT power station, which is owned by German company; Uniper, could almost keep NeuConnect working at full power on its own.
- I said earlier, in the Thames Estuary to the East of the Isle of Grain, I estimate that there are about 1,500 MW of wind turbines. One of which is part German-owned.
The Germans are also building a large electrolyser at Wilhelshaven, which is described by Google AI like this.
The Wilhelmshaven Green Energy Hub will initially feature a 500MW electrolyzer, with plans to potentially expand to 1GW, according to Energy Monitor. The hub, a joint project between Tree Energy Solutions (TES) and EWE, aims to produce green hydrogen using renewable energy sources like offshore wind. The 500MW electrolyzer is scheduled to be operational by 2028.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see that the Wilhelmshaven electrolyser were to be powered by British-generated electricity flowing down NeuConnect.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include A Combined Heat And Power Plant
This objective was set in one of the key points.
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Grain LNG Terminal.
Grain LNG Terminal is a Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) terminal on the Isle of Grain, 37 miles (60 km) east of London. It has facilities for the offloading and reloading of LNG from ships at two jetties on the River Medway; for storing and blending LNG; for truck loading; and regasifying and blending natural gas to meet UK specifications. The terminal can handle up to 15 million tonnes per annum of LNG, has a storage capacity for one million cubic metres of LNG, and is able to regasify up to 645 GWh per day (58 million cubic metres per day) for delivery into the high pressure gas National Transmission System (NTS). The facility is owned and operated by National Grid Grain LNG Ltd, a wholly owned subsidiary of National Grid.
Note.
- This paragraph was written before the Centrica takeover.
- The terminal also converts liquid natural gas into gas to be distributed around the UK.
The heat needed to convert the liquid natural gas to gas is provided by the Grain CHP power station.
- Currently 340 MW of heat is provided.
- If the Grain LNG terminal is expanded, it will probably need more heat.
I can see Centrica building a combined heat and power (CHP) power station, that can be expanded to meet the current and future needs of gasification at the Grain LNG terminal.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see the CHP power station fitted with carbon capture, as Kent is surely one county, where carbon dioxide can be used in food production, so we can generate our carbon dioxide and eat it.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Hydrogen
This objective was set in one of the key points.
Consider.
- Centrica are an investor in HiiROC, who have a unique method of generating affordable zero-carbon hydrogen called thermal plasma electrolysis, which uses a fifth of the electricity, that traditional electrolysis does.
- HiiROC can use natural gas as a feedstock. Centrica won’t be short of that at Grain.
- There is space to build a large HiiROC system at the Isle of Grain site.
- The hydrogen could be taken away by tanker ships.
Like the electricity , which will use the 450 mile NeuConnect interconnector, the hydrogen could even be exported to Wilhelmshaven in Germany by pipeline.
Wilhelmshaven is being setup to be a major German hub to both generate, import and distribute hydrogen.
I asked Google AI, how much hydrogen a GWh would produce and received this answer.
A GWh of electricity can produce approximately 20-22 tonnes of hydrogen through electrolysis, depending on the efficiency of the electrolyzer. Modern commercial electrolyzers operate at an efficiency of roughly 70-80%, meaning they require about 50-55 kWh of electricity to produce 1 kg of hydrogen. A GWh (1 gigawatt-hour) is equal to 1,000,000 kWh, and 1 tonne of hydrogen contains roughly 33.33 MWh of energy.
As it is claimed on the web that HiiROC is five times more efficient than traditional electrolysis, it could need around 10-11 kWh to produce one kg. of hydrogen.
1 GWh would produce between 90-100 tonnes of hydrogen.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Ammonia
This objective was set in one of the key points.
I asked Google AI if ammonia can be produced from hydrogen and received this answer.
Yes, ammonia (NH3) can be produced from hydrogen (H2) through a process called the Haber-Bosch process. This process involves combining hydrogen with nitrogen (N2) from the air, under high temperature and pressure, in the presence of a catalyst.
Ammonia has a large number of uses, including making fertiliser and the powering of large ships.
I asked Google AI, if there are small Haber-Bosch processes to make ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen and received this answer.
Yes, there are efforts to develop smaller-scale Haber-Bosch processes for ammonia production. While the traditional Haber-Bosch process is typically associated with large industrial plants, research and development are exploring ways to adapt it for smaller, distributed production, particularly for localized fertilizer or fuel applications.
I wondered if Centrica are involved in the efforts to develop smaller-scale Haber-Bosch processes for ammonia production.
Google AI gave me this quick answer.
Centrica is involved in research related to the Haber-Bosch process, particularly in the context of transitioning to a low-carbon energy future. They are exploring how to adapt the Haber-Bosch process, which is crucial for fertilizer production but also a significant source of CO2 emissions, to utilize renewable energy sources. This includes investigating the use of green hydrogen produced from water electrolysis and renewable electricity. Centrica is also involved in research related to using ammonia as a fuel, including potentially for power generation
That looks to be a very positive answer. Especially, as local low-carbon fertiliser production could be a very powerful concept.
Centrica Says Their Future Development Options Include Bunkering
This objective was set in one of the key points.
Bunkering is the process of refuelling ships.
I didn’t know much about bunkering, when I started to read Centrica’s press release, but the Wikipedia entry, was a good way to get some information.
This section in the Wikipedia entry is entitled Two Types Of Bunkering, where this is said.
The two most common types of bunkering procedure at sea are “ship to ship bunkering” (STSB), in which one ship acts as a terminal, while the other moors. The second type is “stern line bunkering” (SLB), which is the easiest method of transferring oil but can be risky during bad weather.
Over the years, I have found, that two zero-carbon fuels are under development, for powering ships; hydrogen and ammonia. Others are developing ships powered by naturalo gas.
I asked Google AI if hydrogen can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, hydrogen can power ships. It can be used as a fuel for fuel cells, which generate electricity to power the ship’s propulsion and other systems, or it can be burned in modified combustion engines. Hydrogen offers a zero-emission solution for shipping, with water vapor being the only byproduct when used in fuel cells.
Google AI also told me this.
The world’s first hydrogen-powered cruise ship, the “Viking Libra”, is currently under construction and is scheduled for delivery in late 2026. This innovative vessel, a collaboration between Viking Cruises and Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri, will utilize hydrogen for both propulsion and electricity generation, aiming for zero-emission operation.
I also asked Google AI if ammonia can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, ammonia can be used to power ships and is considered a promising alternative fuel for the maritime industry. Several companies and organizations are actively developing ammonia-powered ship designs and technologies. While challenges remain, particularly around safety and infrastructure, ammonia is seen as a key potential fuel for decarbonizing shipping.
Finally, I asked I asked Google AI if natural gas can power ships and received this answer.
Yes, ships can be powered by natural gas, specifically in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG). LNG is increasingly used as a marine fuel, offering environmental benefits over traditional fuels like diesel.
It would seem to be a case of you pays your money and makes a choice between one of four technologies; ammonia, hydrogen fuel-cell, hydrogen-ICE and LNG.
I looks to me, that if Centrica provide bunkering services for ships, they have the means to cover most of the market by providing hydrogen and ammonia, in addition to natural gas.
Although, I don’t know much about bunkering, I do feel that the two current methods, that work for oil, could be made to work for these fuels.
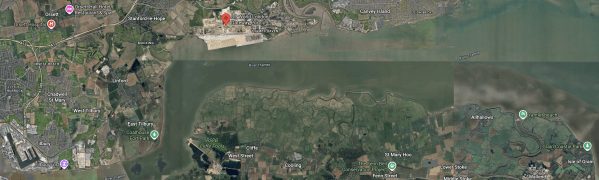
This Google Map shows the Thames Estuary.
Note.
- The Port of Tilbury is in the South-West corner of the map.
- London Gateway is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Isle of Grain is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Other ports between Tilbury and the Isle of Grain include Barking, Dagenham, Dartford, Erith, Greenwich, Northfleet, Purfleet, Silvertown and Thurrock.
There was never a more true phrase than – “Location, Location and Location”. And the Isle of Grain would appear to be in the right place to send out a bunkering tanker to a passing ship, that was calling at a port in London or just passing through the Strait of Dover.
This Google Map shows the Thames between London Gateway and the Isle of Grain.
Note.
- London Gateway is indicated by the red arrow.
- The Isle of Grain is in the South-East corner of the map.
It seems to me, that a refuelling philosophy could easily be worked out.
How Large is The Bunkering Market?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
The world bunker fuel market is a multi-billion dollar industry, with the market size valued at USD 150.93 billion in 2023. It is projected to reach USD 242.29 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% according to SkyQuest Technology. In terms of volume, the global bunker demand was estimated at 233.1 million metric tons in 2023 according to the IMO.
The market is not small!
KCC Leader Writes To The Minister For Future Of Roads About The Increase In Dartford Crossing Charges
The title of this post, is the same as that of this news item from Kent County Council.
Although it is a long letter, it would be wrong to publish only part of it in this post.
As the newly elected Leader of Kent County Council, I would welcome dialogue about the increase in the charge for the Dartford Crossing due to come into effect from September.
The increase is capped at £1, but this represents a 40% uplift on the current £2.50 charge in each direction for those without a pre-pay account. This is the only crossing option east of London until the Lower Thames Crossing is open (in 2032 at the earliest) and so Kent residents and businesses have no viable alternative when using this important route. The alternative is to drive into Greater London, potentially incurring a further charge for the Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ), and the paying even more (£4 each way) to use the Blackwall or Silvertown tunnels.
Whilst most local residents in Dartford benefit from unlimited crossings for a fixed £25 annual fee, this ignores the fact that there is no reasonable alternative route for anyone in Kent making the journey to the Midlands, North and beyond. This is a constraint on the local and national economy.
The Crossing’s accounts for 2023-24 show that cash receipts were £221.6m with operating costs of £134.9m, leaving a net profit of £86.7m. Clearly the crossing is not on the cusp of losing money.
For the increase to be intended to manage demand, without an alternative route there is no way of managing routing, so it will only suppress the journeys for the very poorest in our society. This is hardly equitable. It will also increase costs to the supply chain which will be passed onto customers – furthering the cost-of-living pressures for so many hard-working people.
Our residents still remember that the toll was meant to end when the infrastructure was paid for, but changes in policy mean the charge has continued indefinitely. Effectively another tax for making journeys to work, visiting friends and family, and spending hardearned money at local resorts and attractions.
Given the impact on Kent is so great, there is a strong argument that KCC, as the Highways authority for Kent, should be passported a proportion of this money each year to aid the upkeep of the road network. When one considers the amount of foreign traffic that transverses Kent’s roads, alongside the amount of traffic from other counties within the UK, it is fair to say Kent is the Gateway County. And with that in mind we feel that lack of any financial benefit KCC receives from the Dart Charge needs to be considered as we struggle to maintain our road networks. This new funding stream would enable us to make a tangible difference to the condition of our Local Road Network or help fund major improvement schemes on the Strategic Road Network, including funding towards the new Lower Thames Crossing – unlocking growth and opportunities, and helping to offset the detrimental impact of the increased crossing charge. Kent occupies a strategic position between the UK and Europe, and its transport network is vital for UK supply chains and British businesses, therefore investment in Kent is an investment in the national economy.
I hope you carefully consider this possibility if you move forward with the toll increase.
Yours sincerely
Linden Kemkaran
Linden Kemkaran was elected to Kent County Council as a Reform UK Councillor.
This article on the HuffPost is entitled New Reform UK Council Leader Calls Ukraine War ‘A Distraction’.
This is the sub-heading.
Linden Kemkaran promised to take the Ukraine flag down in Kent’s county council chamber.
These are the first three paragraphs of the article.
A new Reform UK council leader has called the Ukraine war a “distraction”.
Linden Kemkaran, named leader of Kent County Council a week after Reform UK’s sweeping victories in the local elections, appeared to downplay the impact of the largest conflict in Europe since World War 2.
Speaking after she was named as council leader on Thursday evening, she promised to remove the Ukrainian flag from the chamber.
She may have a point about the Dartford Crossing, but her dismissal of Ukraine as a distraction, marks her out in my book as one of Putin’s friends.
Also published today, is this article on the BBC, which is entitled Three men found guilty of Wagner-linked arson attack in London.
As the arson attack took place in Bexley, just over the Kent border with London, I wonder what her view will be on the undoubtedly long sentences these terrorists working for Russia will receive. Are they just a distraction?
Project Fortress
Project Fortress is described like this in its Wikipedia entry.
Project Fortress (formerly Cleve Hill Solar Farm) is a photovoltaic power station under construction on the Graveney marshes between Faversham and Whitstable, Kent in the UK.
Once operational, it will be the largest solar farm in the UK, generating 373 MW of electricity from 900 acres (360 ha) of vertical solar panels and will also include 700 MWh of battery storage. Because of its size, it is a nationally significant infrastructure project so outside the standard local planning procedure.
Electricity will be exported from the project via the 400 kV National Grid substation at Cleve Hill, constructed to serve the London Array offshore wind farm that lies to the north. Here, a battery array will be placed, that will charge from the sunlight during the day and release the energy at night when it is needed.
It is one of the very few co-located solar farms and lithium ion batteries that are co-located with a wind farm in the UK.
We need more of these to balance our power supplies and improve their quality.
Could An Open Access Operator Develop A Train Service Along The South Coast of The UK Between Kent and Fishguard?
Before I go into detail, I will answer a question that explains the terminology and the why’s and wherefores’ of the title of this post.
What Is An Open Access Operator?
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry of an Open Access Operator.
In rail transport, an open-access operator is an operator that takes full commercial risk, running on infrastructure owned by a third party and buying paths on a chosen route and, in countries where rail services run under franchises, are not subject to franchising.
In the UK, these are all open access operators, that are running services.
Note.
- Other groups are developing services.
- Regional, High Speed, International, Local and Sleeper services seem to be offered by various open access operators.
- Grand Central is a subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn,
- Hull Trains and Lumo are both subsidiaries of FirstGroup.
Open Access operators seem to operate in most European Union countries.
Why Run Between Kent and Fishguard?
- The main purpose of the train service would be to provide a low-cost rail connection between the island of Ireland and particularly the Republic of Ireland, with the Southern part of England and the European Union.
- At both ends of the route the train service would connect to ferries.
- At the Eastern end, the train service would also connect to Eurostar services through the Channel Tunnel.
- The Port of Dover could be efficiently connected to Dover Priory Station.
- Dover Priory Station could be the Eastern terminus.
- The service could stop at Folkestone Central station, if ferries call at the Port of Folkestone in the future.
- The service could stop at Ashford International station for Eurostar services.
- Fishguard Harbour station has been built as a train terminus for the Port of Fishguard.
- Fishguard Harbour station could be the Western terminus.
This could be a busy service.
Where Would The Trains Call?
Intermediate stations would depend on passenger umbers, but could start as Folkestone Central, Ashford International, Hastings, Eastbourne, Brighton, Portsmouth & Southsea, Southampton Central, Romsey, Salisbury, Warminster, Westbury, Trowbridge, Bradford-on-Avon, Bath Spa, Bristol Temple Meads, Bristol Parkway, Newport, Cardiff Central, Gowerton, Llanelli and Carmarthen.
How Long Would The Journey Be?
The journey would be around 377 miles and I suspect could take about three and a half hours with modern digital signalling.
Surprisingly, the route is fully-electrified except for the following.
- Ashford International and Ore – 27.9 miles
- Southampton Central and Bristol Parkway – 82 miles
- Cardiff Central and Fishguard Harbour – 115.6 miles
All gaps should be able to be bridged using battery power.
I suspect trains would be Hitachi high speed battery-electric trains.
Would Any European Funding Be Available?
This is an interesting question, as the service does join up two separate sections of the European Union.
Council’s Concerns Over Suggested Tunnel Charges
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
Concerns have been raised by a county council over suggested charges at the Silvertown and Blackwall tunnels in London.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Kent County Council (KCC) said the proposed charges could impact on the county’s traffic, including at the Dartford Crossing.
The council said although it supported TfL’s ambition to improve journey reliability and reduce air pollution, it believed the proposed changes could “significantly affect” drivers from Kent.
I can’t see that the charges on the two tunnels won’t affect drivers habits.
Thirty years ago, before satellite-navigation had been invented, when my family and myself lived in East Suffolk, if I was returning from Brighton or Gatwick, I would make a choice about, whether to use the Dartford Crossing or the Blackwall Tunnel. Sometimes traffic was so bad, that I had to take the longer Western route using the M11 and the A14.
I didn’t really bother about the toll on the Dartford Tunnel, as it was then, but often the free Blackwall route was quicker.
In those days, I was relying on radio reports, but now with satellite-navigation, drivers will be taking more intelligent decisions, that take account of tolls.
The BBC article also says this.
The council says Kent drivers make up 10% of the Blackwall Tunnel’s users.
So it looks like the drivers of Kent will be paying tolls to London.
These are my thoughts.
How Can The Tolls Be Avoided?
There will still be two free crossings, to the East of Tower Bridge; the Rotherhithe Tunnel and the Woolwich Ferry, but how long will they remain free, if they drain money from the tolled tunnels?
What About The Trains?
Trains from somewhere like Ebbsfleet international station can be used.
Ebbsfleet international station has a lot of parking, but at some stations parking is distinctly limited.
I doubt though, that Transport for London have done a professional survey of the amount of parking that is needed.
They tend to believe if people live out of London, that parking for trips to London is not a Transport for London problem.
Are there any plans to increase the train frequencies, if more people use them?
Note that Off Peak Day Return tickets can be purchased with a Railcard, from Dartford to London for under a tenner, and from Ebbsfleet international to London for under fifteen pounds.
If Built, Will The Lower Thames Crossing Help?
The first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the Lower Thames Crossing, describes it like this.
The Lower Thames Crossing is a proposed road crossing of the Thames estuary downstream of the Dartford Crossing that links the counties of Kent and Essex, and its proposed approaches. If built it would pass through the districts of Thurrock and Gravesham, supplementing the Dartford route. The approximately 14.3-mile (23.0 km) route is being assessed by the Planning Inspectorate.
As it is likely to cost nine billion pounds and take six years to build, I can’t see the current Government building it.
But it would certainly make it easier for traffic to go between the Channel Tunnel and North of London.
Conclusion
I can see the UK muddling through, when we should be bold and create the transport infrastructure for the Twenty-First Century.
For instance, I would extend the Elizabeth Line in the North-East to Southend and in the South-East to Ebbsfleet and Gravesend. With the existing cross-platform interchange at Whitechapel, I believe, it could pick up much of the cross-river passenger traffic close to London.
I also feel that there will need to be improved connections between the fast-expanding London Gateway freight port and the Channel Tunnel.
UK Confirms £205 Million Budget To Power More Of Britain From Britain
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from the Department of Energy Security And NetZero.
This is the sub title.
UK government confirms budget for this year’s Contracts for Difference scheme as it enters its first annual auction, boosting energy security.
These are the three bullet points.
- Government announces significant financial backing for first annual flagship renewables auction, boosting Britain’s energy security
- £170 million pledged for established technologies to ensure Britain remains a front runner in renewables and £10 million ring-fenced budget for tidal
- Scheme will bolster investment into the sector every year, delivering clean, homegrown energy as well as green growth and jobs
These are my thoughts.
First And Annual
The scheme is flagged as both first and annual!
Does this mean, that each Budget will bring forward a pot of money for renewables every year?
My father, who being a letterpress printer and a Cockney poet would say it did and I’ll follow his lead.
Two Pots
In Contracts for Difference Round 4, there were three pots.
- Pot 1 – Onshore Wind and Solar
- Pot 2 – Floating Offshore Wind, Remote Island Wind and Tidal Stream
- Pot 3 – Fixed Foundation Offshore Wind
This document on the government web site lists all the results.
For Contracts for Difference Round 5, there will be two pots, which is described in this paragraph of the press release.
Arranged across 2 ‘pots’, this year’s fifth Allocation Round (AR5) includes an allocation of £170 million to Pot 1 for established technologies, which for the first time includes offshore wind and remote island wind – and confirms an allocation of £35 million for Pot 2 which covers emerging technologies such as geothermal and floating offshore wind, as well as a £10 million ring-fenced budget available for tidal stream technologies.
It could be described as a two-pot structure with a smaller ring-fenced pot for tidal stream technologies.
Contract for Difference
There is a Wikipedia entry for Contract for Difference and I’m putting in an extract, which describes how they work with renewable electricity generation.
To support new low carbon electricity generation in the United Kingdom, both nuclear and renewable, contracts for difference were introduced by the Energy Act 2013, progressively replacing the previous Renewables Obligation scheme. A House of Commons Library report explained the scheme as:
Contracts for Difference (CfD) are a system of reverse auctions intended to give investors the confidence and certainty they need to invest in low carbon electricity generation. CfDs have also been agreed on a bilateral basis, such as the agreement struck for the Hinkley Point C nuclear plant.
CfDs work by fixing the prices received by low carbon generation, reducing the risks they face, and ensuring that eligible technology receives a price for generated power that supports investment. CfDs also reduce costs by fixing the price consumers pay for low carbon electricity. This requires generators to pay money back when wholesale electricity prices are higher than the strike price, and provides financial support when the wholesale electricity prices are lower.
The costs of the CfD scheme are funded by a statutory levy on all UK-based licensed electricity suppliers (known as the ‘Supplier Obligation’), which is passed on to consumers.
In some countries, such as Turkey, the price may be fixed by the government rather than an auction.
Note.
- I would trust the House of Commons Library to write up CfDs properly.
- As a Control Engineer, I find a CfD an interesting idea.
- If a generator has more electricity than expected, they will make more money than they expected. So this should drop the wholesale price, so they would get less. Get the parameters right and the generator and the electricity distributor would probably end up in a stable equilibrium. This should be fairly close to the strike price.
I would expect in Turkey with Erdogan as President, there are also other factors involved.
Renewable Generation With Energy Storage
I do wonder, if wind, solar or tidal energy, is paired with energy storage, this would allow optimisation of the system around the Contract for Difference.
If it did, it would probably mean that the generator settled into a state of equilibrium, where it supplied a constant amount of electricity.
Remote Island Wind
Remote Island Wind was introduced in Round 4 and I wrote about it in The Concept Of Remote Island Wind.
This was my conclusion in that post.
I must admit that I like the concept. Especially, when like some of the schemes, when it is linked to community involvement and improvement.
Only time will tell, if the concept of Remote Island Wind works well.
There are possibilities, although England and Wales compared to Scotland and Ireland, would appear to be short of islands.
This map shows the islands of the Thames Estuary.
Note.
- In Kent, there is the Isle of Sheppey and the Isle of Grain.
- Between the two islands is a large gas terminal , a gas-fired power station and an electricity sub-station connecting to Germany.
- In Essex, there is Canvey, Foulness and Potton Islands.
- There is also the site at Bradwell, where there used to be a nuclear power station.
If we assume that each island could support 200 MW, there could be a GW of onshore wind for London and perhaps a couple of SMRs to add another GW.
This map shows the islands around Portsmouth.
Note.
- Hayling Island is to the East of Portsmouth.
- Further East is Thorney Island with an airfield.
The Isle of Wight could be the sort of island, that wouldn’t welcome wind farms, although they do make the blades for turbines. Perhaps they should have a wind farm to make the blades even more green.
But going round England and Wales there doesn’t seem to be many suitable places for Remote Island Wind.
I do think though, that Scotland could make up the difference.
Geothermal Energy
This is directly mentioned as going into the emerging technologies pot, which is numbered 2.
I think we could see a surprise here, as how many commentators predicted that geothermal heat from the London Underground could be used to heat buildings in Islington, as I wrote about in ‘World-First’ As Bunhill 2 Launches Using Tube Heat To Warm 1,350 Homes.
Perhaps, Charlotte Adams and her team at Durham University, will capitalise on some of their work with a abandoned coal mine, that I wrote about in Exciting Renewable Energy Project for Spennymoor.
Timescale
This paragraph gives the timescale.
The publication of these notices mean that AR5 is set to open to applications on 30 March with results to be announced in late summer/early autumn 2023, with the goal of building upon the already paramount success of the scheme.
It does look like the Government intends this round to progress at a fast pace.
Conclusion
If this is going to be an annual auction, this could turn out to be a big spur to the development of renewable energy.
Supposing you have a really off-beat idea to generate electricity and the idea place in the world is off the coast of Anglesey.
You will certainly be able to make a bid and know like Eurovision, one auction will come along each year.
Extending The Elizabeth Line – Connection To Southeastern High Speed One Services
The Two Stratford Stations
In this post, Stratford station is the station handling Greater Anglia and London Overground, Underground and Docklands Light Railway services, with Stratford International station handles High Speed services.
The Elizabeth Line And The Great Western Railway Services
One of the most important stations on the Elizabeth Line is Paddington, where it connects to the London terminus of the Great Western Railway.
I would expect that quite a few passengers going to the West and Wales on the Great Western Railway, will be transported to Paddington by the Elizabeth Line.
The Elizabeth Line And Greater Anglia Services
Another of the important stations on the Elizabeth Line is Liverpool Street, where the station is the London terminus of the Greater Anglia.
I would expect that quite a few passengers going to East Anglia on the Greater Anglia, will be transported to Liverpool Street by the Elizabeth Line.
Southeastern High Speed One Services
Southeastern runs some High Speed services on High Speed One to provide Kent with an improved service to London.
Current services are
- London St Pancras International to Ramsgate via Faversham.
- London St Pancras International to Ramsgate via Dover Priory.
- London St Pancras International to Margate via Canterbury West.
Note
- All trains are one train per hour (tph).
- All trains stop at Stratford International and Ebbsfleet International.
- All trains are run by 140 mph Class 395 trains.
There has also been talk of running a fourth service to Hastings and Eastbourne via Stratford International, Ebbsfleet International and Ashford International.
St. Pancras Station
All of these trains terminate in three platforms; 11 to 13 at St. Pancras International station.
St. Pancras is not the ideal terminal for the Southeastern High Speed services.
- St. Pancras is not on the Elizabeth Line.
- St.Pancras doesn’t have good connections to Heathrow.
- All connections to the Underground are a long walk.
- Eurostar services are a longer walk.
- East Midland services are also a longer route, with stairs and escalators for good measure.
St. Pancras station was designed by a committee, as a museum to Victorian architecture, rather than as a working station.
Ebbsfleet International Station Must Be The Largest Parkway Station In The UK
It holds nearly five thousand cars and it is served by Southeastern High Speed Services.
Thanet Parkway Station Will Open This Year
Thanet Parkway station is under construction.
- It will have nearly three hundred parking spaces.
- It will be served by Southeastern High Speed Services.
- It should open in May 2023.
This station will need a good connection to London.
Could An Interchange Between The Elizabeth Line And Southeastern High Speed Services Be Provided At Stratford?
Such an alternative interchange would be popular with passengers.
- The Elizabeth Line from Stratford currently serves the West End, the Northern section of the City of London, East London, Liverpool Street, Paddington and the West End directly.
- The Elizabeth Line from Stratford currently serves Canary Wharf, Cannon Street, Charing Cross, Euston, Heathrow, King’s Cross. Reading, St. Pancras and Victoria with a change at Whitechapel.
- The Central Line, which shares platforms with the Elizabeth Line serves Bank and the West End directly.
- The Overground is easily accessed for travel across North London to Richmond.
- The Jubilee Line is easily accessed for travel to London Bridge, Waterloo and Westminster.
It would be connected to two large parkway stations and lots of parking all over Kent.
I believe that Stratford must be promoted as an alternative terminus for Southeastern High Speed Services.
Today, I walked both ways between two Stratford stations.
These pictures show the route I took between Stratford and Stratford International stations, through the Eastfield Shopping Centre.
Note.
- I went through the Shopping Centre.
- I passed Marks & Spencer’s large food hall, excellent toilets and a Food Court.
- By the Food Court is an exit that leads to an entrance to Stratford International station.
- The walk took about 10 minutes.
- It was vaguely level.
- Lifts by-passed the escalators.
- One thing that makes the journey to London easier, is to travel in the Eastern end of the train, as the lifts and escalators at Stratford International station, are at that end.
It does need some better signage, but they were doing a bit of refurbishment, so that may already be underway.
It could be a very high quality interchange and it is already better than St. Pancras.
Coming back I took the longer route outside the Shopping Centre.
Note.
- I just turned left out of the entrance, walked along the road and turned right past the bus station.
- If the weather had been colder or wetter, I’d have gone back via the Shopping Centre.
- The walk took about 12 minutes.
I think normally, I’d go back through the Shopping Centre, as there’s a Marks and Spencer Food Hall on the route and it’s slightly quicker and often warmer.
Could Stratford Station Be A London Superhub Station?
When you consider the stations connected to Stratford in London, East Anglia and Kent, it has an excellent collection.
- Airports – Gatwick, Heathrow, Luton, Southend and Stansted
- Cities – Cambridge, Canterbury, Chelmsford, Colchester, Ipswich, Norwich and Southend-on-Sea
- London Main and Terminal Stations – Cannon Street, Charing Cross, Clapham Junction, Euston, Farringdon, King’s Cross, London Bridge, Liverpool Street, Marylebone, Moorgate, Paddington, Victoria and Waterloo
- Major Areas – Canary Wharf, City of London, Hampstead, Olympic Park and West End
- Ports – Dover, Felixstowe, Folkestone and Harwich
You can even get a train to Slough, with a change at Whitechapel.
I would think it already is a London Superhub Station.
Extending The Elizabeth Line – Serving South-East London
The Inadequacies Of Abbey Wood Station
Abbey Wood station is the Elizabeth Line’s main terminus in South-East London.
The architecture is impressive, as the pictures taken before the station was finished show.
But other things are less than impressive.
- There is no station parking.
- Central London rail terminals served by Elizabeth Line services are only Liverpool Street/Moorgate and Paddington.
- Central London rail terminals served by National Rail services are Cannon Street, London Bridge, King’s Cross and St. Pancras.
In my view, Abbey Wood is a lost cause, as a commuter station, unless substantial parking is built at the station.
Parking At Stations In West Kent
This list shows the number of car parking spaces at stations in West Kent and South East London.
- Barnehurst – 162 *
- Belvedere – None *
- Bexleyheath – 83 *
- Chatham – 276 *
- Dartford – 186 *
- Ebbsfleet International – 4945 #
- Erith – None *
- Eynsford – 15
- Farningham Road – None
- Gillingham – 152 *
- Gravesend – 94 *
- Greenhithe – 8 *
- Longfield – 88
- Meopham – 167
- Northfleet – None *
- Plumstead – None *
- Rochester – None *
- St. Mary Cray – 31
- Slade Green – 25
- Sole Street – 61
- Stone Crossing – None *
- Strood – 112 *
- Swanley – 106
- Swanscombe – None *
- Welling – 117
Note.
- An asterisk (*) indicates direct trains to and from Abbey Wood station for the Elizabeth Line.
- An hash(#) indicates direct trains to and from Stratford International for the Elizabeth Line.
These figures are according to the National Rail web site.
It looks like unless you can walk to your nearest station and that has an easy connection to Abbey Wood, you’re probably better off going to Ebbsfleet and parking there.
Travelling Between Ebbsfleet International And The Elizabeth Line At Stratford International
Consider.
- Southeastern’s Highspeed service between Ebbsfleet International and Stratford International has a frequency of three trains per hour (tph)
- It takes less than twelve minutes between the two stations.
- It takes ten minutes to walk between Stratford International and Stratford Station for the Elizabeth Line and Greater Anglia services.
- There are eight Elizabeth Line tph to Paddington, calling at all stations. For Heathrow change at Whitechapel station.
Note.
- From these points, it should be possible to estimate the time you should park at Ebbsfleet to get to an event in London or East Anglia, if you live in Kent and are parking at Ebbsfleet International.
- I think four tph between Ebbsfleet International and Stratford International would make the route more attractive.
- If you’re going to Norwich or Ipswich be careful, as only one of the two tph stop at Stratford.
I catch the 12:30 from Liverpool Street for matches at Ipswich on Saturdays. This is the 12:38 from Stratford, so I suspect if you parked at parked at Ebbsfleet before 12:00, you’d make it.
Who’d have thought, that when they built the massive car parks at Ebbsfleet international, that they would be a Park-and-Ride for football at Ipswich. And Norwich too!
Changing Trains At Stratford
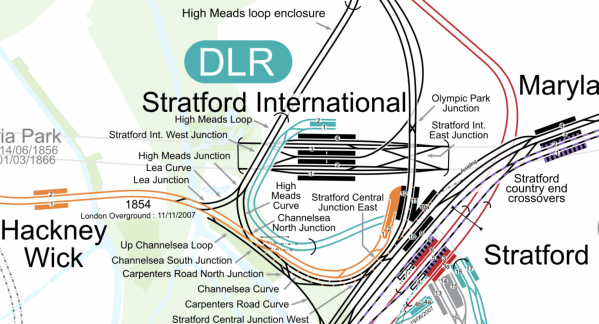
This map from Cartometro shows the two Stratford stations.
Note.
- The Elizabeth Line is shown in purple.
- The Central Line is shown in red.
- The Jubilee Line is shown in silver.
- The Overground is shown in orange.
- Lifts and escalators take passengers to and from the surface from between platforms 2 and 3 at Stratford International station.
Two pedestrian tunnels connect all the platforms in Stratford station.
- Elizabeth Line trains use platforms 5 and 8.
- Central Line trains use platforms 3, 3a and 6.
- Great Eastern Main Line trains use platforms 9, 9a and 10.
- Overground trains use platforms 1 and 2.
All platforms have lifts.
I suspect, that when you get to know the Stratford complex well, it’s easier than it looks.
But it does need better signage.
Full Step-Free Route Between Ebbsfleet And Heathrow Central
I have just used Transport for London’s Journey Planner, as if I was in a wheelchair and need full step-free access to go from Ebbsfleet to Heathrow Central.
This was the route.
- Southeastern to Stratford International station – 10 mins
- Walk to Stratford station – 21 mins
- Jubilee Line to Bond Street – 24 mins
- Bond Street to Heathrow Central – 32 mins
Note.
- The times are slower than say myself.
- I think it is possible to pick up the Elizabeth Line at Stratford.
But the route is certainly possible in a wheel-chair.
The Penge Interchange
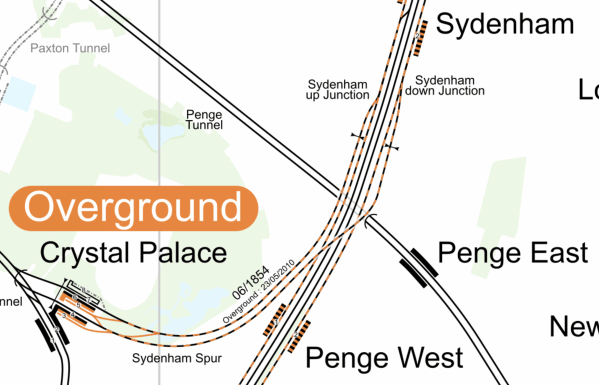
This map from Cartometro shows where the East London Line of the London Overground and the Chatham Main Line between Victoria and Chatham cross in Penge.
Note.
- The East London Line runs North-South through Sydenham and Penge West stations.
- The Chatham Main Line runs through Penge East station.
There is a plan by Transport for London to create a Penge Interchange station on railway land, where the two lines cross.
- The station could replace Penge West and Penge East stations.
- It would be fully step-free.
- Interchange would be allowed between the East London Line and the Chatham Main Line.
This would increase connectivity for those travelling to and from South-East London and West Kent.
I brlieve that this one interchange could help level-up a large area of South-East London.