Carew Castle Express Unveiled In Carmarthen
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail UK.
These are the first two paragraphs.
The ‘Carew Castle Express’ has been unveiled to mark the introduction of brand-new Transport for Wales (TfW) trains between Swansea and Carmarthen.
Named as part of TfW’s Magnificent Train Journey competition, the name ‘Carew Castle Express’ was chosen by year 5 pupil Rhys Protheroe from Johnstown Primary School in Carmarthen.
But perhaps, this extract is the most significant statement in the article.
Soon every service west of Carmarthen will be on one of the brand-new trains.
Alexia Course, chief commercial officer for TfW, said: “We’re excited to be running our brand-new trains in West Wales and we’re adding more to our network every few weeks.
CAF and TfW don’t seem to be hanging about in getting these new trains into service.
But then, I suspect some of the trains they replace, will be going to the scrapyard in Newport.
How Will These Trains Be Decarbonised?
My one worry is that these Class 197 trains and the similar Class 195 trains at Northern and the Class 196 trains at West Midlands Trains are diesel powered.
Nothing has been said about how these 141 trains will be decarbonised.
But all three fleets have the same Rolls-Royce mtu 6H 1800 R85L engines, so at least one solution will fit all!
A Thought About LNER’s New Trains
These trains appear to have been delivered quickly.
Did this influence the decision of LNER to buy CAF trains for their fleet expansion?
The Data Sheet For Hitachi Battery Electric Trains
Was I just slow to spot this data sheet or has it only just been released?
You can download a copy from this page on the Hitachi web site.
In a section on the page, which is entitled Intercity Battery Trains, this is said.
A quick and easy application of battery technology is to install it on existing or future Hitachi intercity trains. Adding just one battery reduces emissions by more than 20% and offers cost savings of 20-30%.
Our intercity battery powered trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same or increased performance. Hitachi Rail’s modular design means this can be done without the need to re-engineer or rebuild the train and return them to service as quickly as possible for passengers.
These are my initial thoughts.
Plug-and-Play
It looks like the train is plug-and-play.
A diesel engine will be swapped for a battery-pack and the train’s computer controls the power sources accordingly.
Hitachi’s Battery Philosophy Explained
This is said on the data sheet.
Battery technology has the potential to play a significant role in the future of sustainable rail mobility, setting
the rail industry on the path to full intercity decarbonisation by 2050.
Installing batteries on intercity trains can complement electrification and provide a low emission alternative
to domestic air travel.Our retrofit solution for intercity trains offers phased replacement of diesel engines at the time that they would
have been due for their regular heavy maintenance overhaul, replacing each engine in turn until trains are fully battery electric. The solution delivers fuel cost savings and lowers CO2 emissions by at least 20% for every engine replaced, and a 20% reduction in whole life maintenance costs – well within the battery’s life span of 8-10 years.
Performance On Battery Power
The data sheet gives these bullet points.
- 750kW peak power
- Weight neutral.
- At least 20% lower CO2 emissions
- 70km on non-electrified routes
- 20% reduction in whole life maintenance costs
- Up to 30% fuel cost savings
- Zero emissions in and out of stations
- Charge on the move
- 10 year life span
Note.
- 750 kW peak power, is around the power of the diesel-engine, that will be replaced.
- I wouldn’t be surprised that powerwise, the battery pack looks like a diesel engine.
- Weight neutral means that acceleration, performance and handling will be unchanged.
- Batteries are easier to maintain than diesels.
- It is stated that a train can be fully-decarbonised.
I have a feeling these trains are no ordinary battery-electric trains.
Seventy Kilometre Range On Battery
Seventy kilometres is 43.5 miles.
This may not seem much, but the data sheet says this.
Our battery hybrid trains can cover 70km on non-electrified routes, operating at intercity speeds at the same
or increased performance. By identifying the routes with short non-electrified sections of 70km or less, we could
see the replacement of existing diesel trains with fully battery-operated trains on those routes within a year.
And, using battery power to avoid electrifying the hardest and most expensive areas, such as tunnels and bridges,
enables flexibility on electrification, minimising passenger disruption during upgrades.
Note.
- It looks like the trains can operate at 125 mph on battery power, where the track allows it. But then the rolling restistance of steel wheel on steel rail, is much lower, than that of rubber tyres on tarmac.
- Hitachi seem to have developed a philosophy on how the trains will be used.
- Hitachi’s pantographs, go up and down with all the alacrity of a whore’s drawers. They will be ideal for a short length of electrification.
I think these LNER routes could be immediately decarbonised.
- LNER – London and Harrogate , where only 18.3 miles is unelectrified. Trains may not need charging, as a full battery could handle both ways.
- LNER – London and Hull, where 36.1 miles is unelectrified. A short length of electrification to charge trains would be needed at Hull.
- LNER – London and Lincoln, where only 16.7 miles is unelectrified. Trains would not need charging, as a full battery could handle both ways.
- LNER – London and Middlesbrough, where only 20.3 miles is unelectrified. Trains would not need charging, as a full battery could handle both ways.
Note.
- It looks like some services could start fairly soon, once batteries are available.
- Hull Trains could use the 70 km batteries and charging at Hull, as it passed through. This would decarbonise Hull Trains passenger operations.
- Services to Aberdeen, Cleethorpes and Inverness would be out of range of the initial Hitachi trains.
Could the last point, partially explain the purchase of the CAF tri-mode trains, which I wrote about in First Tri-Mode Long Distance Trains For The East Coast Main Line?
We shall see what we shall see.
But having a choice of battery-electric or tri-mode trains will enable route development and decarbonisation.
What Is The Size Of The Battery Pack?
In How Much Power Is Needed To Run A Train At 125 Or 100 mph?, I estimated that to maintain 125 mph, a Class 801 train has a usage figure of 3.42 kWh per vehicle mile.
If a five-car Class 800 can run 70 km or 43.5 miles at 125 mph, as indicated by Hitachi, then the battery size can be calculated.
3.42 * 5 * 43.5 = 743.85 kWh
As the battery pack can supply 750 kW according to the data sheet, this looks like this will run the train for an hour.
Is that coincidence or a design criteria?
What Battery Capacity Would Be Needed For A Hundred Miles?
For a five-car train, this is the energy needed for a hundred miles.
3.42 *5 * 100 = 1710 kWh or three batteries.
For a nine-car train, this is the energy needed for a hundred miles.
3.42 *9 * 100 = 3078 kWh or five batteries.
It looks like all diesel engines will be replaced by batteries.
Will Class 801 Trains Swap Their Single Diesel Engine For a Battery Power Pack?
Consider.
- Class 801 trains have a single diesel engine for emergency power.
- Lumo’s Class 803 trains, are all-electric with a battery-pack for emergency hotel power only.
- Hitachi must have full details on the performance of Lumo’s trains.
- The East Coast Main Line is notorious for the wires to come tumbling down.
- The diesel engine and the battery pack appear to weigh the same.
- Batteries cost less to maintain than diesels.
I can’t see why the single diesel engine can’t be replaced by a standard battery pack, without loosing any functionality.
What Would Be The Range Of A Fully Battery-Electric Train?
This is a paragraph from a data sheet.
Our retrofit solution for intercity trains offers phased replacement of diesel engines at the time that they would
have been due for their regular heavy maintenance overhaul, replacing each engine in turn until trains are fully battery electric. The solution delivers fuel cost savings and lowers CO2 emissions by at least 20% for every engine replaced, and a 20% reduction in whole life maintenance costs – well within the battery’s life span of 8-10 years.
Note.
- It looks like Hitachi are expecting operators to replace engines in turn.
- Replacing engines with batteries saves the operators money.
As a five-car Class 800 train has three diesel engines and a nine-car train has five engines, does this mean that the range of fully-batteried Class 800 train is 70 km or 210 km?
- A fully-batteried Class 800 train will weigh the same as the current diesel.
- One battery can drive the train for 70 km at 125 mph according to Hitachi.
- There are no branches of electrified lines that are 125 mph lines without electrification.
- I would assume that the train can use regenerative braking to recharge the batteries.
- 210 kilometres is 130 miles.
I don’t know much about the electrical systems of Hitachi’s trains, but it is likely that there will be an electrical bus to distribute power from one end of the train to the other.
So a five-car Class 800 train with three fully-charged battery packs could have over 2 MWh of electricity on board, that could be used for traction.
- Applying the usage figure of 3.42 kWh per vehicle mile, gives a range for the five-car train of at least 117 miles.
- The equivalent figure for a nine-car train will be at least 121 miles.
These distances would open up routes like these on the East Coast Main Line.
- LNER – London King’s Cross and Aberdeen – 91.4 miles – Charge before return.
- LNER/Hull Trains – London King’s Cross and Beverley via Temple Hirst junction – 44.3 miles – No Charging needed before return.
- Grand Central – London King’s Cross and Bradford Interchange via Shaftholme junction – 47.8 miles – No Charging needed before return.
- LNER – London King’s Cross and Cleethorpes via Newark and Lincoln – 63.9 miles – Charge before return.
- LNER – London King’s Cross and Harrogate via Leeds – 18.3 miles – No Charging needed before return.
- LNER – London King’s Cross and Inverness– 146.2 miles – Charge before return.
- LNER/Hull Trains – London King’s Cross and Hull via Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles – No Charging needed before return.
- LNER – London King’s Cross and Middlesbrough via Northallerton – 20.3 miles – No Charging needed before return.
- LNER – London King’s Cross and Scarborough via York – 42.1 miles – No Charging needed before return.
- LNER/Grand Central – London King’s Cross and Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles – No Charging needed before return.
Note.
- The miles are the longest continuous distance without electrification.
- Only Aberdeen, Cleethorpes and Inverness would need to charge trains before return.
- Inverness may be too far. But is it in range of LNER’s new CAF tri-mode trains?
The battery range would also allow LNER to use the Lincoln diversion on the Joint Line.
Why Didn’t LNER Buy More Azumas?
This puzzles me and I suspect it puzzles other people too.
Surely, an all Azuma fleet will be easier to manage.
But in this article on Modern Railways, which is entitled LNER Orders CAF Tri-mode Sets, this is said.
Modern Railways understands the new fleet will be maintained at Neville Hill depot in Leeds and, like the ‘225’ sets, will be used predominantly on services between London and Yorkshire, although unlike the ‘225s’ the tri-modes, with their self-power capability, will be able to serve destinations away from the electrified network such as Harrogate and Hull.
Note.
- Hull would possibly need work to provide some form of charging for battery-electric Azumas, but Harrogate is close enough to be served by a one-battery Azuma.
- The CAF Tri-mode sets would certainly handle routes like Cleethorpes, Middlesbrough and Sunderland, but would they really need a ten-car train.
- Ten-car trains would also be busy on the Leeds route.
- The UK is going to need more 125 mph trains for Cross Country, Grand Central, Grand Union, TransPennine Express and possibly other train companies.
- Has Hitachi got the capacity to build the trains in the UK?
So has the Government given the order to CAF to create a level of competition?
Conclusions
These are my conclusions about Hitachi’s battery packs for Class 80x trains, which were written in November 2023.
- The battery pack has a capacity of 750 kWh.
- A five-car train needs three battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- A nine-car train needs five battery-packs to travel 100 miles.
- The maximum range of a five-car train with three batteries is 117 miles.
- The maximum range of a nine-car train with five batteries is 121 miles.
As battery technology gets better, these distances will increase.
Hitachi have seen my figures.
They also told me, that they were in line with their figures, but new and better batteries would increase range.
In July 2025, I wrote Batteries Ordered For Grand Central Inter-City Trains, which mentions the following.
- Grand Central’s trains will be electric-diesel-battery hybrid inter-city trainsets.
- The trains will have lithium ion phosphate batteries.
- The trains will be delivered in 2028.
- The batteries will be smaller and more powerful, than current batteries.
This is also said about safety, hazards and cybersecurity.
The Safety Integrity Level 2 and IEC 61508 compliant battery management system will detect and mitigate hazards and meet the IEC 62243 cybersecurity standard.
These batteries would appear to give Hitachi and Grand Central Trains everything they want and need.
It looks like the new battery chemistry, will give Hitachi extra range.
First Tri-Mode Long Distance Trains For The East Coast Main Line
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from LNER.
This is the sub-heading.
London North Eastern Railway (LNER) is pleased to confirm that CAF has been named as the successful bidder to deliver a fleet of 10 new tri-mode trains for LNER. Porterbrook has been chosen as the financier of the new fleet. The trains will be able to operate in electric, battery or diesel mode.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Benefits of tri-mode trains range from a reduction in emissions, particulates, noise and vibration pollution, lower maintenance and operating costs and upgradeable technology, with an expected increase in range and performance as technology develops further. Battery power reduces the need to use diesel traction in areas where overhead powerlines are not available.
Complementing the modern Azuma fleet of 65 trains, the new ten-coach trains will help LNER achieve its vision of becoming the most loved, progressive and trusted train operator in the UK, delivering an exceptional service for the customers and communities served along its 956-mile network.
I have a few thoughts.
Will The Trains Have Rolls-Royce mtu Diesel Engines?
Consider.
- CAF’s Class 195, 196 and 197 Civity trains for the UK all have Rolls-Royce mtu diesel engines.
- Porterbrook are headquartered in Derby.
- Rolls-Royce are headquartered in Derby.
- In Rolls-Royce And Porterbrook Agreement Will Drive Rail Decarbonisation, I talked about how the two companies were planning to decarbonise trains using techniques like mtu Hybrid PowerPacks and hydrogen fuel cells.
I would think it very likely that the new trains will have Rolls-Royce mtu engines.
Will The Trains Have Rolls-Royce mtu Hybrid PowerPacks?
It was in 2018, that I first wrote about mtu Hybrid PowerPacks in Rolls-Royce And Porterbrook Launch First Hybrid Rail Project In The UK With MTU Hybrid PowerPacks.
- Examples of these power packs are now running in Germany, Ireland and the UK.
- The mtu Hybrid PowerPack how has its own web site.
- There is also this YouTube video.
- If CAF use off-the-shelf mtu Hybrid PowerPacks in their Civity trains, there is one big massive plus – They don’t have to develop the complicated control software to get a combination of diesel engines and batteries to perform as immaculately as Busby Berkeley’s dancers or a Brigade of Guards.
- The mtu Hybrid PowerPacks also have a big plus for operators – The batteries don’t need separate charging infrastructure.
- In Rolls-Royce Releases mtu Rail Engines For Sustainable Fuels, I talk about how mtu engines can run on sustainable fuels, such as biodiesel or HVO.
I think it is extremely likely that CAF’s new trains for LNER will be powered by mtu Hybrid PowerPacks.
Class 800 And Class 397 Trains Compared
The Class 800 train is LNER’s workhorse to Scotland from London.
The Class 397 train used by TransPennine Express, is a 125 mph Civity train.
Differences include.
- The Class 800 train can run at 140 mph, where the signalling allows, but is the Class 397 train only capable of 125 mph?
- The Class 397 train accelerate at 0.92 m/s², whereas the Class 800 train can only manage 0.7 m/s².
- The Hitachi train has 14 % more seats, 36 First and 290 Standard as opposed to 22 First and 264 Standard in five-car trains.
I will add to this list.
Will The New Trains Be Capable Of 140 mph Running?
As the East Coast Main Line is being fully digitally signalled to allow 140 mph running of the numerous Hitachi expresses on the route, I wouldn’t be surprised to see, that the new CAF trains will be capable of 140 mph.
In this article on Modern Railways, which is entitled LNER Orders CAF Tri-mode Sets, this is said.
The new fleet will be equipped with CAF Signalling’s European Rail Traffic Management System digital signalling. This will align with the East Coast Digital Programme, which aims to introduce European Train Control System (ETCS) on the southern stretch of the East Coast main line from King’s Cross to Stoke Tunnel by 2029.
Later in the article this is said.
LNER has retained 12 ‘91s’ hauling eight rakes of Mk 4s, and the rollout of ETCS is another reason the operator has sought to order the replacement fleet. LNER’s passenger numbers have rebounded more quickly than other operators post-Covid, which has helped make the case for confirming the order.
This does seem sensible.
What Will Be The Range Of The CAF Trains Without Electrification?
The longest LNER route without electrification is the Northern section of the Inverness service between Inverness and Dunblane, which is 146.1 miles. There are also eight stops and some hills.
In Edinburgh to Inverness in the Cab of an HST, there’s a video of the route.
I’m sure that even, if they don’t normally run the new trains to Inverness, being able to do so, could be useful at some point.
It should be noted that the Guinness World Record for battery-electric trains is 139 miles, which is held by a Stadler Akku.
I am left with the conclusion that London and Inverness needs a tri-mode train or lots of electrification. Did this rule out Hitachi?
The Number Of Trains Ordered
The Modern Railways article says this about the number of trains.
The contract includes an eight-year maintenance services agreement with an option to extend; CAF says the order value, including maintenance, exceeds €500 million. When the tender was published the intention was to include an option for five additional sets; LNER confirmed to Modern Railways there is an option to purchase additional sets on top of the base order of 10.
Can we assume this means that other trains will be ordered, if the trains are a success?
Can These New CAF Trains Be Made Net Zero?
This is a paragraph, in the LNER press release.
This new fleet of trains will keep LNER on track to reduce its emissions by 67 per cent by 2035 and be net zero by 2045. LNER has already reduced carbon emissions by 50 per cent compared with 2018/19. Per mile, LNER trains produce 15 times less carbon emissions than a domestic flight.
As the new CAF trains will probably have a service life of at least forty years, there must be some way, that these new trains can be made net zero.
Consider.
- I am absolutely certain, that the new CAF trains will have Rolls-Royce mtu diesel engines.
- LNER’s existing Class 800 and 801 trains have Rolls-Royce mtu diesel engines.
Rolls-Royce mtu according to some of Rolls-Royce’s press releases appear to be developing net zero solutions based on hydrogen or net zero fuels.
This press release from Rolls-Royce is entitled Rolls-Royce Successfully Tests mtu Engines With Pure Hydrogen, suggests that Rolls-Royce mtu are working on a solution.
Routes They Will Serve
The Modern Railways article says this about the routes to be served.
Modern Railways understands the new fleet will be maintained at Neville Hill depot in Leeds and, like the ‘225’ sets, will be used predominantly on services between London and Yorkshire, although unlike the ‘225s’ the tri-modes, with their self-power capability, will be able to serve destinations away from the electrified network such as Harrogate and Hull.
Note.
- This surprised me, as I’d always expected the Yorkshire routes will be served by Hitachi battery-electric trains.
- But it does look that both Harrogate and Hull stations, have long enough platforms to hold a ten-car train.
- With their tri-mode technology, it also looks like the CAF trains won’t be needed to be charged before returning to London.
The last point would enable them to try out new routes.
These are distances from the electrification of the East Coast Main Line of the destinations that LNER served, where there is not full electrification.
- Aberdeen via Ladybank – 91.4 miles
- Carlisle via Skipton – 86.8 miles
- Cleethorpes via Newark and Lincoln – 63.9 miles
- Harrogate via Leeds – 18.3 miles
- Huddersfield via Leeds – 17.2 miles
- Hull via Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- Inverness via Dunblane – 146.1 miles
- Lincoln via Newark – 16.7 miles
- Middlesbrough via Northallerton – 22.2 miles
- Scarborough via York – 42.1 miles
- Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Carlisle could be a possibility during High Speed Two upgrading of the West Coast Main Line or for an enthusiasts’ special or tourist train.
- Cleethorpes is a possible new service for LNER. I wrote about this in LNER To Serve Cleethorpes.
- Scarborough must be a possible new service for LNER.
- All stations can take ten-car trains, with the possible exception of Middlesbrough, which is currently being upgraded.
- Huddersfield and Leeds is being electrified under the TransPennine Upgrade.
This would appear to show that LNER need enough bi-mode or tri-mode trains to run services to Aberdeen, Cleethorpes, Harrogate, Hull, Inverness, Lincoln, Middlesbrough and Sunderland.
But.
- It would appear that the initial batch of trains, will not be serving the North of Scotland.
- Aberdeen and Inverness could be served, when there is enough electrification at the Southern end.
I am also fairly sure, that no significant infrastructure is required.
Do Hitachi Have A Problem?
I am starting to wonder, if Hitachi are having trouble with the designing and building of their battery packs.
- It’s not like Hitachi to allow someone to run off with a €500 million contract from under their nose.
- Are they short of capacity to build the trains at Newton Aycliffe?
But then they’re probably up to their elbows in work on the High Speed Two Classic-Compatible trains.
Are There Any Other Routes, Where The New CAF Trains Could Be Employed?
The trains would certainly be suitable for these routes.
- Chiltern – InterCity services.
- CrossCountry Trains – Fleet replacement
- Grand Central Trains – Fleet replacement
- Grand Union Trains – For Carmarthen and Stirling open access services.
- Great Western Railway – Replacing Castles in the South West.
- ScotRail – Replacing Inter7City trains.
- South Western Railway – Basingstoke and Exeter St. Davids and other routes.
Note.
- CAF could sell a lot of trains.
- I estimate that fleet replacement for Grand Central Trans would cost around €350 million
- The specification would vary according to the route.
Could CAF have got the LNER order, because they have the capacity in the Newport factory?
Conclusion
It looks like CAF have done a good job in designing the trains.
I’m also fairly sure that CAF are using Rolls-Royce mtu PowerPacks.
May The Maths Be With You!
It was a bit of a surprise, when in the November 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, in an article, which was entitled Extra Luggage Racks For Lumo, I read this closing paragraph.
Lumo celebrated its second birthday in late October and was also set to mark the carriage of its two-millionth passenger. It is understood Lumo is interested in augmenting its fleet, such has been the success of the service; while many operators favour bi-mode units, Lumo is proud of its all-electric credentials so straight EMUs are still preferred, although the possibilities of including batteries which could power the trains may be pursued (the ‘803s’ have on-board batteries, but only to provide power to on-board systems if the electricity supply fails).
I find this development very interesting.
Surely the obvious way to increase capacity would be to acquire some extra identical trains and run the busiest services as ten-car trains. I talked about Hull Trains running ten-car trains in Ten-Car Hull Trains. Both companies have five trains, so I suspect that this number would allow for occasional ten-car trains.
If not, then add a few identical trains to the fleet, so capacity can be matched to the demand.
- Some services would be ten-car instead of five-car.
- Platforms at Edinburgh, King’s Cross and Newcastle already handle nine and ten-car trains, so infrastructure costs would be minimal.
- No extra paths would be needed, as a ten-car train can run in a path, that normally has five-car trains, as Hull Trains have shown.
A simple spreadsheet should probably predict, when and how many extra trains need to be added to the fleet.
Lumo And Traction Batteries
But why does the Modern Railways’s article talk about traction batteries?
In the two years since Lumo started their service, there have been days, when the East Coast Main Line has been closed for engineering works, bad weather or an incident. I wrote about an incident in Azumas Everywhere!.
Some of these engineering works have been able to be by-passed by using diversions. But not all of these diversion routes are fully-electrified, so are not available for Lumo.
There would appear to be three viable diversions for the East Coast Main Line.
- Werrington Junction and Doncaster via Lincoln – Not Electrified – 85.4 miles
- Doncaster and York via Leeds – Being Electrified – 55.5 miles
- Northallerton and Newcastle – Not Electrified – 56.8 miles
If all or some of Lumo’s five-car trains had a battery-range of a hundred miles, they would be able to divert around some blockades.
Note.
- A traction battery could also provide power to on-board systems if the electricity supply fails.
- A traction battery would allow the train to skip past some catenary problems.
- I would be interested to know how much diversions, bad weather and incidents have cost Lumo in lost sales and refunds.
As an electrical engineer, I believe, that the emergency-only and the traction batteries could be the same design, but with different software and capacity.
The extra cost of the larger capacity traction battery, might deliver a better service and also pay for itself in the long term.
Extending Lumo’s Route
Lumo will want to maximise revenue and profits, so would it be possible to extend the route North of Edinburgh?
Consider.
- Edinburgh and Aberdeen is 131.4 miles
- Ladybank is a station to the North of the Forth Bridge, which is under 40 miles from Edinburgh.
- The line between Edinburgh and Ladybank is being electrified.
- Ladybank is just 91.4 miles South of Aberdeen.
At some point in the next few years, I believe that one of Lumo’s trains fitted with a hundred mile traction battery could reach Aberdeen on electric power.
The train would need to be charged at Aberdeen before returning South.
How would Aberdonians like that?
Unfortunately, Inverness is 146.1 miles from the nearest electrification at Dunblane, so it is probably too far for a hundred mile traction battery.
It does appear to me that if Lumo’s trains were fitted with a hundred mile traction battery, this would enable them to take some non-electrified diversions and provide a service to Aberdeen.
How Useful Would A Hundred Mile Range Battery-Electric Train Be To Other Operators?
I take each operator in turn.
Hull Trains
Consider.
- It appears that Hull Trains change between diesel and electric power at Temple Hirst junction, which is between Doncaster and Selby, on their route between King’s Cross and Hull/Beverley.
- The distance between Temple Hirst junction and Beverley is 44.3 miles.
- It would appear that an out-and-return journey could be possible on a hundred mile traction battery.
- The hundred mile traction battery would also allow Hull Trains to use the Lincoln diversion, either when necessary or by design.
To ensure enough range, a short length of overhead electrification could be erected at Hull station to combat range anxiety.
The Modern Railways article also says this.
The co-operation between sister East Coast Main Line open access operators Lumo and Hull Trains continues, with one recent move being the use of Hull Trains ‘802’ on Lumo services to cover for a shortage of the dedicated ‘803s’ while one was out of action for repairs following a fatality. although the two types are similar, there are notable differences, most obviously that the Hull Trains units are bi-modes while the Lumo sets are straight EMUs, and a training conversion course is required for Lumo drivers on the ‘802s’. There are also challenges from a passenger-facing perspective – the Hull trains units have around 20 % fewer seats and a First Class area.
If Hull Trains used traction batteries rather than diesel engines could the trains be identical to Lumo’s trains from the driver’s perspective?
This would surely appeal to First Group, who are the owner of both Hull Trains and Lumo.
TransPennine Express
These are TransPennine Express services.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Newcastle – Fully Electrified
- Liverpool Lime Street and Hull – Part Electrified – Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- Manchester Airport and Saltburn – Part Electrified – Saltburn and Northallerton – 33.6 miles
- Manchester Piccadilly and Newcastle – Fully Electrified
- Manchester Piccadilly and Scarborough – Part Electrified – York and Scarborough – 42.1 miles
- York and Scarborough – Not Electrified – 42.1 miles
- Manchester Piccadilly and Huddersfield – Fully Electrified
- Huddersfield and Leeds – Fully Electrified
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes – Part Electrified – Hazel Grove and Cleethorpes – 104.6 miles
Note.
- I am assuming that the TransPennine Upgrade has been completed and Manchester and Leeds is electrified.
- Liverpool Lime Street and Cleethorpes will need some form of charging at Cleethorpes and a slightly larger battery.
All of these TransPennine Rxpress routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
LNER
These are distances from the electrification of the East Coast Main Line.
- Aberdeen via Ladybank – 91.4 miles – Charge before return
- Bradford Forster Square – Electrified
- Carlisle via Skipton – 86.8 miles – Charge before return
- Cleethorpes via Newark and Lincoln – 63.9 miles – Charge before return
- Harrogate via Leeds – 18.3 miles
- Huddersfield via Leeds – 17.2 miles
- Hull via Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- Lincoln via Newark – 16.7 miles
- Middlesbrough via Northallerton – 22.2 miles
- Scarborough via York – 42.1 miles
- Skipton – Electrified
- Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Carlisle could be a possibility during High Speed Two upgrading of the West Coast Main Line or for an enthusiasts’ special or tourist train.
- Cleethorpes is a possible new service for LNER. I wrote about this in LNER To Serve Cleethorpes.
- Scarborough must be a possible new service for LNER.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return. Carlisle is electrified, but Cleethorpes is not.
- The only new infrastructure would be the charging at Cleethorpes.
All of these LNER routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
The hundred mile traction battery would also allow LNER to use the Lincoln diversion.
Grand Central
These are distances from the electrification of the East Coast Main Line for Grand Central’s services.
- Bradford Interchange via Shaftholme junction – 47.8 miles
- Cleethorpes via Doncaster – 52.1 miles – Charge before return
- Sunderland via Northallerton – 47.4 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Cleethorpes is a possible new service for Grand Central.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return.
All of these routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
The hundred mile traction battery would also allow Grand Central to use the Lincoln diversion.
Avanti West Coast
These are distances from the electrification of the West Coast Main Line for Avanti West Coast’s services.
- Chester via Crewe – 21.1 miles
- Gobowen via Wolverhampton – 47.7 miles
- Holyhead via Crewe – 105.5 miles – Charge before return
- Shrewsbury via Wolverhampton – 29.7 miles
- Wrexham via Crewe – 33.3 miles
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- Gobowen is a possible new service for Avanti West Coast.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return.
All of these routes would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
Great Western Railway
These are distances from the electrification of the Great Western Main Line for Great Western Railway’s services.
- Bristol Temple Meads via Chippenham – 24.4 miles
- Carmarthen via Cardiff Central – 77.4 miles – Charge before return
- Cheltenham Spa via Swindon – 43.2 miles
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – 120.4 miles – Charge before return
- Great Malvern via Didcot East junction – 76.1 miles – Charge before return
- Hereford via Didcot East junction – 96.9 miles – Charge before return
- Oxford via Didcot Parkway – 10.3 miles
- Paignton via Newbury – 148.7 miles – Charge before return
- Pembroke Dock via Cardiff Central – 121.6 miles – Charge before return
- Penzance via Newbury – 172.6 miles – Charge before return
- Plymouth via Newbury – 120.4 miles – Charge before return
- Swansea via Cardiff Central – 53 miles – Charge before return
- Weston-super-Mare via Chippenham – 43.8 miles
- Worcester Foregate Street via Didcot East junction – 68.2 miles – Charge before return
- Worcester Shrub Hill via Didcot East junction – 67.6 miles – Charge before return
Note.
- The first place after the ‘via’ is where the electrification ends.
- ‘Charge before return’ means the train must be charged before return.
- Partial electrification through Hereford, Great Malvern, Worcester Foregate Street and Worcester Shrub Hill, could possibly be used to charge services from Hereford and Worcester.
- Partial electrification through Penzance, Plymouth and Exeter St. Davids, could possibly be used to charge services from the South West.
- Partial electrification West of Swansea, could possibly be used to charge services from West Wales.
All routes, except for Hereford and Worcester, the South-West and West Wales, would be possible with a battery-electric train with a hundred mile traction battery.
I’ll now look at the three groups of services in more detail.
Services To Hereford And Worcester
These are distances from the electrification of the Great Western Main Line for Great Western Railway’s Hereford and Worcester services.
- Great Malvern via Didcot East junction – 76.1 miles
- Hereford via Didcot East junction – 96.9 miles
- Worcester Foregate Street via Didcot East junction – 68.2 miles
- Worcester Shrub Hill via Didcot East junction – 67.6 miles
Note.
- All services join the Great Western Main Line at Didcot East junction.
- Some services will be probably need to have, their batteries charged at the Hereford and Worcester end.
At the present time, the electrification finishes at Didcot East junction, but if it were to be extended to Charlbury station, these would be the distances without electrification.
- Great Malvern via Charlbury – 52.3 miles
- Hereford via Charlbury – 73.1 miles
- Worcester Foregate Street via Charlbury – 44.4 miles
- Worcester Shrub Hill via Charlbury – 43.8 miles
Note.
- Some of the track between Oxford and Charlbury is only single track, which may give advantages, when it is electrified.
- It might be possible with a hundred mile traction battery for all Worcester services to charge their batteries between Charlbury and London Paddington and not need a charge at Worcester to return.
- A larger traction battery or extending the electrification to perhaps Morton-in-Marsh could see Great Malvern in range of battery-electric trains from London Paddington without a charge.
- Hereford would probably be too far to get away without charging at Hereford.
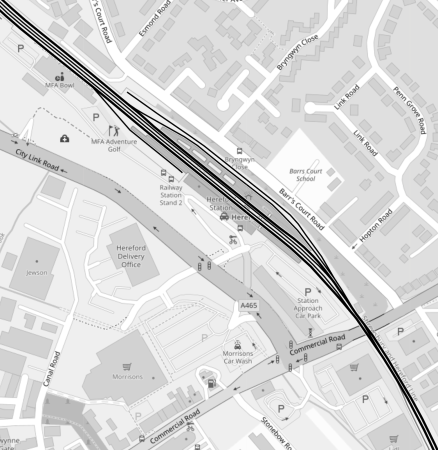
This OpenRailwayMap shows the layout of Hereford station.
I’m certain that a platform can be found, where there is space for a charger, which could also be used for other trains serving the station.
Services To The South West
In the August 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled GWR Seeks Opportunities To Grow.
This is the sub-heading.
Managing Director Mark Hopwood tells Philip Sherratt there is plenty of potential to increase rail’s economic contribution.
This is two paragraphs.
The desire to provide electrification to support aggregates traffic from the Mendip quarries could also benefit GWR , says Mr. Hopwood. ‘Having an electric loco would massively help with pathing heavy freight trains through the Thames Valley. If you could electrify from Newbury to East Somerset Junction, a big chunk of the Berks and Hants route would be wired.
Then you can ask how much further you could get on battery power on an IET without running out of juice.’
Newbury to East Somerset Junction would be 53.5 miles of electrification, so I can build this table of services to the South-West
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – 120.4 miles – 66.9 miles
- Paignton via Newbury – 148.7 miles – 95.2 miles
- Penzance via Newbury – 251.9 miles – 198.5 miles
- Plymouth via Newbury – 172.6 miles – 119 miles
Note.
- The distance between Penzance and Plymouth is 79.5 miles.
- The first figure in the table is the distance to Newbury.
- The second figure in the table is the distance to East Somerset junction.
A possible way of running these four services to London on battery power is emerging.
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – Charge before return – Run on battery for 66.9 miles to East Somerset junction.
- Paignton via Newbury – Charge before return – Run on battery for 95.2 miles to East Somerset junction.
- Penzance via Newbury- Charge before return – Run on battery for 79.5 miles to Plymouth – Charge at Plymouth – Run on battery for 119 miles to East Somerset junction.
- Plymouth via Newbury – Charge before return – Run on battery for 119 miles to East Somerset junction.
Once at East Somerset junction, it’s electrification all the way to Paddington.
This is the corresponding way to run services from London.
- Exeter St. Davids via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 66.9 miles to Exeter St. Davids.
- Paignton via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 95.2 miles to Paignton.
- Penzance via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 119 miles to Plymouth – Charge at Plymouth – Run on battery for 79.5 miles to Penzance.
- Plymouth via Newbury – Run on electrification to East Somerset junction, charging the battery on the way – Run on battery for 119 miles to Plymouth.
More electrification or a larger than a hundred mile traction battery would be needed, as Plymouth and East Somerset junction is 119 miles.
But if a Stadler Akku can do 139 miles on a charge, why shouldn’t a Hitachi battery-electric train?
Services To West Wales
It seems that the current timetable is already setup for battery-electric trains to run to and beyond Swansea.
- Carmarthen and Swansea is almost exactly 32 miles.
- Pembroke Dock and Swansea is 73.4 miles.
- Swansea and Cardiff Central is 45.7 miles.
Note
- All these sections could be run by a battery-electric train, with a fully-charged hundred mile traction battery.
- All trains going to or from Carmarthen or Pembroke Dock reverse at Swansea, where a generous time of more than eleven minutes is allowed for the manoeuvre.
- During the reverse at Swansea, there is sufficient time to charge the batteries, if overhead wires were present.
Battery-electric services could serve Wales Wales with overhead electrification at Carmarthen, Pembroke Dock and Swansea.
Conclusion
We will go a long way, if we embrace battery-electric trains.
Most routes can be handled with a train with a traction battery range of 100 miles.
Exceptions are.
- Hazel Grove and Cleethorpes – 104.6 miles
- Plymouth and East Somerset junction – 119 miles
But if a Stadler Akku can do 139 miles on a charge, why shouldn’t a Hitachi battery-electric train?
Lumo Carbon Data Shows Its Trains Are 22 Times Greener Than Flying
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail Advent.
These paragraphs detail how the figures were obtained.
To mark the second anniversary of its branding as ‘Lumo’, the operator commissioned consultancy firm Arup to provide an independent report about all direct emissions from its operations; emissions from the grid-supplied energy it uses; and other emissions in its supply chain.
Scope 1: Direct emissions from operations that are owned and controlled by Lumo;
Scope 2: Emissions from the use of grid-supplied electricity, heat, steam and/or cooling by Lumo;
Scope 3: All other emissions that occur in the value chain of Lumo.In the last two years, Lumo has carried over two million passengers. The figures reveal that, per passenger, emissions from a London-to-Edinburgh journey are twenty-two times the level for flying (149 kgCO2e) than for using Lumo (6.8kgCO2e).
I have a few thoughts.
Carbon Savings With LNER
LNER’s Class 801 trains are similar to Lumo’s Class 803 trains.
The main difference, is that the LNER have emergency diesel engines, whereas Lumo have emergency batteries to run the trains systems, if the catenary goes down.
So LNER on balance will generate a bit more carbon than Lumo.
But the difference will be marginal.
Carbon Savings With Avanti West Coast
Avanti’s Class 390 trains to Scotland, are all-electric, so there will be a carbon-saving.
Probably about the same as with LNER.
Avanti West Coast’s New Class 807 Trains
If the Class 807 trains were cars, they would be Lotuses.
- They are electric only and have no heavy diesel engines or traction batteries.
- They don’t even have emergency batteries for when the catenary fails.
- They have a redesigned nose. Is it more aerodynamic?
- The heavy tilt mechanism is history.
- As with all the other Hitachi high speed trains, they are capable of 125 mph, or 140 mph if the signalling permits.
These trains will undoubtedly have faster acceleration and deceleration and could probably knock minutes off the timings at all the stops.
Tucked away beside the Grand Union Sets Out Stirling Ambitions article in the December 2022 Edition of Modern Railways is a report on Avanti West Coast’s application for a second service between Euston and Liverpool.
This is said.
Avanti West Coast has applied for access rights for its second hourly Euston to Liverpool service, starting from December 2023, although a phased introduction of the new service is likely. This would make use of Avanti’s new fleet of 10×7-car Class 807 Hitachi EMUs, which are expected to enter service from Autumn 2023. The ‘807s’ would be deployed on the current hourly Liverpool service, on which a call at Liverpool South Parkway would be added. (provision is made for this in the December 2022 timetable.).
Pendolinos would then operate the second service each hour, calling at Lichfield Trent Valley and Tamworth.
A linespeed project is in progress to raise the permissible speed for non-tilting trains on the West Coast Main Line, and Avanti’s new Hitachi trains will take advantage of this.
I can’t wait to go to Liverpool in one of these trains.
Their carbon emissions should be in line with Lumo.
Avanti West Coast’s New Class 805 Trains
These are equivalent to the Class 802 trains, but with probably Class 807 train interiors and looks.
I wonder how long these trains will keep their diesel engines before battery power is the most affordable option.
Once they go battery-electric, their carbon emissions should be in line with Lumo.
Conclusion
I can’t see any other mantra than.
Electric good, diesel bad
Especially, if like most computers, it’s just plug and play.
Rolls-Royce Completes Next Step On Its Journey To Decarbonising Business Aviation
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from Rolls-Royce.
This is the sub-heading.
Rolls-Royce today announces the successful completion of a series of tests with 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) on its latest generation of business aviation engines, the Pearl 15 and the Pearl 10X. The Pearl 15, the first member of the Pearl engine family, powers Bombardier’s Global 5500 and 6500 aircraft, while the Pearl 10X will power Dassault’s ultra-long-range flagship aircraft, the Falcon 10X.
These are the websites for the three aircraft, with number of passengers, typical cruise speed and range.
- Bombardier Global 5500 – 16 pax – Mach 0.85 – 5900 nm
- Bombardier Global 6500 – 17 pax – Mach 0.85 – 6600 nm
- Dassault Falcon 10X – 19 pax – Mach 0.925 – 7500 nm
This screenshot from the Dassault Falcon 10X web site shows the range from London.
Note that Buenos Aires, the Falkland Islands, Seattle, Seoul and Tokyo are all within range.
I have a few thoughts and observations.
Jet A-1 And 100% SAF
This paragraph from the press release describes how Rolls-Royce are testing the compatibility of Jet A-1 and 100% SAF.
As well as proving compatibility with 100% SAF another target of the test campaign was to run a back-to-back engine test with both Jet A-1 and SAF on the same Pearl 10X engine. The aim was to confirm further improvements in the environmental footprint when switching to SAF. The results from this first back-to-back engine emission test under standard certification conditions provides important correlations for the evaluation of future SAF within our environmental strategy.
Compatibility and back-to-back running is surely very important, as it could be many years before all airports can supply 100 % SAF for visiting jet aircraft.
The Fuels Used In The Tests And The Benefits
These two paragraphs from the press release describes the fuels used and the benefits..
The HEFA (Hydro-processed Esters and Fatty Acids) SAF was produced from waste-based sustainable feedstocks such as used cooking oils and waste fat. This fuel has the potential to significantly reduce net CO2 lifecycle emissions by about 80% compared to conventional jet fuel.
The back-to-back tests conducted with conventional fossil-based fuel and subsequently SAF also confirmed a cleaner combustion of the sustainable fuel, with significantly lower levels of non-volatile particulate matter (nvPM). In combination with the low NOx combustor technology of the Pearl 10X and its additive manufactured combustor tiles a reduction of all emissions was achieved.
Note.
- An eighty percent reduction in lifecycle emissions is not to be sneezed at.
- Cleaner combustion and low NOx emissions are very much bonuses.
- Additive manufacture is better known as 3D-printing and I’m not surprised that Rolls-Royce have embraced the technology.
As an engineer and retired light aircraft pilot, I suspect the tests have met Rolls-Royce’s objectives.
Moving To 100 % SAF
This is the final paragraph of the press release.
The tests demonstrated once again that Rolls-Royce’s current engine portfolio for large civil and business jet applications can operate with 100% SAF, laying the groundwork for moving this type of fuel towards certification. At present, SAF is only certified for blends of up to 50% with conventional jet fuel. By the end of 2023 Rolls-Royce will have proven that all its in-production Trent and business aviation engines are compatible with 100% SAF.
It must be a good selling point for aircraft equipped with Rolls-Royce engines, that the buyer knows that the aircraft can run on 100% SAF.
100 % SAF As An Airline Marketing Tool
It will be interesting to see how airlines use 100% SAF to sell tickets.
As an example, I can see routes like London and Scotland becoming very competitive.
- Avanti West Coast, LNER and Lumo already run all-electric trains to Edinburgh and Glasgow.
- The technology exists to decarbonise trains to Aberdeen and Inverness..
- Other open access operators could well move in to a lucrative market.
- The only way, that the airlines will be able to compete on emissions, would be to move to 100 % SAF.
There must be hundreds of routes like London and Scotland around the world.
100 % SAF And Business Jets
In A Class 319 Train, But Not As We Know It!, I told this tale.
I am reminded of a tale, that I heard from a former GEC manager.
He was involved in selling one of GEC’s Air Traffic Control radars to a Middle Eastern country.
The only working installation of the radar was at Prestwick in Scotland, so he arranged that the dignitaries and the sales team would be flown to Prestwick in GEC’s HS 125 business jet.
As they disembarked at Prestwick and walked to the terminal, the pilot called the GEC Manager over.
The pilot told him “The Scottish Highlands at this time of the year, are one of the most beautiful places in the world! Would you and your guests like a low-level tour on the way back? I can arrange it, if you say so!”
Despite knowing GEC’s draconian attitude to cost control he said yes.
The sale was clinched!
I also remember an article in Flight International about how JCB sold diggers.
- Dealers in a country like Greece would put together a party of prospective customers.
- The customers would then be flown to East Midlands Airport in JCB’s business jet, which is close to the JCB factory at Rocester.
- After a sales demonstration and a tour of the factory they would be flown home.
I once met a lady who had been one of JCB’s cabin staff and she told me it was a very successful sales technique.
I suspect that a business jet running on 100 % SAF would be an even better sales aid.
There are also increasing protests from the greens about business jets, which are seen as producing pollution and are only the toys of the rich and powerful.
Surely, if they were running on 100 % SAF, this would make business jets more acceptable.
100 % SAF And Niche Airlines
In the web site for the Falcon 10X, there is a section called Mission Flexibility, where this is said.
As large as it is, the Falcon 10X can still access typical airports serving business aviation as well as others with challenging approaches. The Falcon 10X will be London City-capable so that it can fly you straight into the heart of global finance. When you’re ready for rest and relaxation, the 10X can whisk you to out-of-the-way corners of the world.
British Airways used to run a service between London City Airport and New York.
- The route used 32-seat Airbus A-318 airliners.
- The flight stopped at Shannon for refuelling.
- It was business class only.
I suspect someone will think about running a similar London City Airport and New York service using a Falcon 10X.
- It has nineteen seats.
- It could do it in one hop.
- It could run on 100 % SAF.
- British Airways must have all the passenger data from the discontinued service.
- A Falcon 10X flies higher than a Boeing 767, Boeing 787 or an Airbus A350.
I have a feeling that flight time would be comparable or better to a flight between Heathrow and New York.
Conclusion
Rolls-Royce would appear to have the right strategy.
If I was going to New York in business class, I’d use it.
Yorkshire To See More LNER Services And Longer Trains
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Rail UK.
These are the two introductory paragraphs.
London North Eastern Railway (LNER) is meeting an increase in demand from leisure travellers by adding more services and thousands more seats on trains between Yorkshire and London every Sunday.
Sundays are now one of the most popular days for journeys with 30% more customers travelling across the 956-mile LNER network than in 2019.
From December 2023, three new services and longer trains will be introduced on Sundays between London and Yorkshire.
Improving Trains Between London And Bradford
Current Services Between London And Bradford
LNER services run between Kings Cross and Bradford Forster Square stations.
- Two trains per day (tpd) run between Bradford and London in the early morning.
- Two tpd run between London and Bradford in the evening.
- Trains take two and three-quarter hours.
- Stops are at Shipley, Leeds, Wakefield Westgate, Doncaster, Retford Grantham and Stevenage.
- Trains seem to be generally a pair of five-car Class 801 trains.
Note.
- Trains reverse at Leeds.
- The timetable seems a bit lopsided, as there is no early morning train to Bradford or an evening one to London.
- Harrogate gets a one train per two hours (tp2h) service to and from London.
The timetable could do with an improvement.
Grand Central services run between Kings Cross and Bradford Interchange stations.
- Four tpd run between Bradford and London.
- Four tpd run between London and Bradford.
- Trains take three and a quarter hours.
- Stops are at Pontefract Monkhill, Wakefield Kirkgate, Mirfield, Brighouse, Halifax and Low Moor
- Trains are five-car Class 180 trains, which have seen better days.
Note.
- The timetable seems a bit lopsided, as there is no early morning train to Bradford or an evening one to London.
The timetable and the trains could do with an improvement.
LNER’s New Ticketing And Nine-Ten Car Trains
LNER have introduced the selling of Advanced Tickets from machines or the Booking Office as late as five minutes before the train leaves.
- My last three trips from Leeds to London cost me £33.55, £33.75 and £33.55 with my Senior Railcard.
- All were bought less than ten minutes before the train left.
- In two of the journeys, I spread out in two seats
- Trains were either a pair of five-car Class 801 trains or a nine-car InterCity 225.
I took these pictures after my last return from Leeds on Tuesday.
Note.
- Two of the three trains I’ve taken lately have arrived 3-4 minutes early.
- Not a great increase, but I do wonder if LNER are seeing what is possible with the new digital signalling.
- The British Rail era; InterCity 225 seems to hold its own against the new Hitachi train.
I wouldn’t be surprised that LNER intend to both run high-capacity trains between London and Leeds and fill them by competitive pricing.
A Grand Central Train Failure On Tuesday
This was my journey to Bradford on Tuesday,
- I was supposed to take the 1057 Grand Central service to Bradford Interchange, where it was timed to arrive at 1400.
- But the train didn’t run and we were all advised to get on the 1103 to Leeds and change at Doncaster.
- We arrived at Doncaster in Platform 4, a minute late at 1240 and got straight on a Grand Central train in the opposite Platform 6.
- We left Doncaster at 1251, which was sixteen minutes late.
- But we arrived in Bradford Interchange more or less on time at 1401.
Despite leaving six minutes late from Kings Cross and changing trains at Doncaster, we arrived at Bradford on time.
Battery-Electric Trains Between London and Bradford Interchange
I feel that my journey on Tuesday indicated.
- Electric trains between London and Doncaster can easily meet the current timetable.
- The Grand Central train went between Doncaster and Bradford Interchange was sixteen minutes faster than the timetable.
I wouldn’t be surprised that London and Bradford Interchange could be a few minutes under three hours.
Consider.
- It has been said that between Bradford Interchange and Leeds will be electrified.
- Bradford Interchange and Doncaster does not have electrification, but is only 52 miles.
- Electrification of Bradford Interchange station, will allow battery-electric trains to be charged in around 10-12 minutes.
- Most inter-city battery-electric trains have a battery range of at least eighty miles.
- Digital signalling is being installed between London and Doncaster to allow 140 mph running and more trains in the timetable.
I believe that a battery-electric train with sufficient range, charging South of Doncaster and at Bradford Interchange could go between London and Bradford Interchange in 5-10 minutes under three hours.
Bradford Interchange and all the other stations North of Doncaster on the route could probably also have a one tp2h service to and from London and the South.
Splitting And Joining Of Trains
Consider.
- Pairs of the Hitachi Class 801 trains have the ability to split and join en route, during a station stop extended by a few minutes.
- Platforms are long enough to handle splitting and joining at Doncaster, Leeds and York.
- Currently, three services to and from London go past Leeds; Bradford Forster Square, Harrogate and Skipton. All these services reverse in Leeds station, when they pass through.
- The reversing in Leeds station takes about 8-9 minutes.
- The track between Leeds and Bradford Forster Square is electrified.
- Leeds and Harrogate is not electrified and is 19.3 miles.
- The track between Leeds and Skipton is electrified.
- Bradford Forster Square has a service of two tpd.
- Harrogate has a service of one tp2h.
- Skipton has a service of one tpd.
In the Wikipedia entry for LNER, this is said.
From December 2019, LNER introduced a Harrogate to London service six times a day. LNER expected to introduce two-hourly services to Bradford and a daily service to Huddersfield by May 2020 when more Azuma trains had been introduced, however the latter has not yet been introduced.
Note.
- The Huddersfield service would have to reverse in Leeds station, like those to Bradford Forster Square, Harrogate and Skipton.
- Leeds and Huddersfield is not electrified and is 17.1 miles.
- Leeds and Huddersfield is being electrified.
Could LNER’s plan be to give Bradford Forster Square, Harrogate, Huddersfield and Skipton stations a two-hourly service , as the Wikipedia extract indicated, they intend to do for Bradford?
- All trains enter and leave Leeds to and from the West.
- Pairs of five-car trains would split and join at Leeds.
- Bradford Forster Square and Skipton services would be served by electric trains.
- Harrogate and Huddersfield services would be served by bi-mode or battery-electric trains.
- Horsforth, Keighley and Shipley could also get a one tp2h service to London.
It looks like services via Leeds could be much improved.
In a two-hour period the Leeds area will have the following trains to and from London Kings Cross.
- Two trains between London and Leeds via Peterborough, Doncaster and Wakefield Westgate
- One train between London and Bradford Forster Square via Stevenage, Grantham, Retford (Bradford-bound only), Doncaster, Wakefield Westgate, Leeds and Shipley.
- One train between London and Harrogate via Stevenage, Grantham, Doncaster, Wakefield Westgate, Leeds and Horsforth
- One train between London and Huddersfield via Stevenage, Grantham, Doncaster, Wakefield Westgate and Leeds
- One train between London and Skipton via Peterborough, Newark Northgate, Doncaster, Wakefield Westgate, Leeds, Shipley (London-bound only) and Keighley.
Note.
- Stops between London and Leeds would be adjusted to satisfy passenger numbers.
- Currently, there are a total of four trains in a two hour period.
- Six trains will be fitted in by having two London and Leeds trains and two pairs of five-car trains, that joined and split at Leeds.
There is still only four train paths needed in a two hour period between London and Leeds.
Digital Signalling Between London And Doncaster
The East Coast Digital Programme has its own web site, which gives this introduction to the programme.
The East Coast Digital Programme is delivering the next generation of train travel – creating a better performing East Coast Main Line for passengers and everyone else who uses and depends on it.
As part of the programme, traditional lineside signals will be removed and replaced with state-of the art digital signalling to improve the reliability of the train service.
The new technology continuously communicates with each train, providing signalling information directly to a computer screen in the driver’s cab. It boosts reliability, reduces carbon emissions and provides a more punctual service for customers.
In the first stage, digital signalling will be introduced on the Northern City Line, between Finsbury Park and Moorgate. It will then be progressively rolled out on the southern section of the East Coast Main Line (between London King’s Cross and the Stoke Tunnels, near Grantham).
It is expected that the first trains to operate on the East Coast Main Line using digital signalling technology will run in 2025, with all improvements expected to be completed by the end of the decade.
As a result of this programme, the East Coast Main Line will be GB’s first intercity mainline to be upgraded to digital. It lays the foundation for further improvements across the network, creating a more efficient railway fit for the future.
There is also a video.
Benefits of digital signalling will include.
- 140 mph running instead of 125 mph.
- An increase in the number of train paths.
- Trains will be able to be run closer together.
As a Graduate Control Engineer, I also believe that digital signalling will enable better control of trains through bottlenecks.
- Could ERTMS And ETCS Solve The Newark Crossing Problem?
- Is There An ERTMS-based Solution To The Digswell Viaduct?
A computer solution would surely be more affordable than some massive civil engineering.
What Will Be The Fastest Times Possible Between London King’s Cross And Leeds?
I put my thoughts in What Will Be The Fastest Times Possible Between London King’s Cross And Leeds?.
Conclusion
The original High Speed Two specification gave a time of one hour and twenty-one minutes between Euston and Leeds.
I suspect that time will be approached before 2040.
New Livery On An InterCity 225
I took these pictures of an InterCity 225 at Doncaster station.
They scrub up well for a train that entered service in 1989.
Thoughts On Rail Capacity Between London And The North
This is just a rough calculation to see how many trains can be run between London and the North.
I shall do the calculation by station.
Euston
Trains are.
- Avanti – Birmingham – 1 tph (trains per hour)
- Avanti – Blackpool North – 1 tpd (trains per day)
- Avanti – Blackpool North via Birmingham – 2 tpd
- Avanti – Edinburgh via Birmingham – 1 tp2h – (trains per two hours)
- Avanti – Glasgow – 1 tph
- Avanti – Glasgow via Birmingham – 5 tpd
- Avanti – Holyhead – 8 tpd
- Avanti – Liverpool – 1 tph
- Avanti – Manchester – 3 tph
- WMT – Birmingham – 2 tph
- WMT – Crewe – 1 tph
This gives totals of 9 tph, 1 tp2h and 16 tpd
King’s Cross
Trains are.
- Grand Central – Bradford – 4 tpd
- Grand Central – Sunderland – 6 tpd
- Hull Trains – Beverley – 2 tpd
- Hull Trains – Hull – 5 tpd
- LNER – Bradford- 2 tpd
- LNER – Edinburgh – 3 tp2h
- LNER – Harrogate – 1 tp2h
- LNER – Hull – 1 tpd
- LNER – Leeds – 3 tp2h
- LNER – Lincoln – 1 tp2h
- LNER – Middlesbrough – 1 tpd
- LNER – Skipton – 1 tpd
- LNER – Sunderland – 1 tpd
- LNER – York- 1 tp2h
- Lumo – Edinburgh – 5 tpd
This gives totals of 9 tp2h and 28 tpd
Marylebone
Trains are.
- Chiltern – Birmingham – 2 tph
This gives totals of 2 tph
St. Pancras
Trains are.
- EMR – Corby – two tph
- EMR – Nottingham – two tph
- EMR – Sheffield- two tph
This gives totals of 6 tph
Grand Totals
Grand totals are 17 tph, 10 tp2h and 44 tpd
I will assume.
- 10 tp2h is equivalent to 5 tph.
- 44 tpd is equivalent to 3 tph if trains start journeys between 0600 and 2100.
This means that currently, there is the equivalent of 25 tph between London and the North.
The Effect Of High Speed Two
The capacity of High Speed Two is 17 tph, so, that appears to be a 68 % increase in paths to the North.
Consider.
- Assume we need 25 tph between London and the North.
- 17 tph will be on High Speed Two.
- 8 tph will be on classic routes like the East Coast Main Line, Midland Main Line and West Coast Main Line.
- High Speed Two trains are 400 metres long.
- Current trains are about 240 metres long.
I have done a weighted calculation, which shows that passenger capacity between London and the North, will increase by around 45 %.
High Speed Two will surely release paths between London and the North on the classic routes, that could accommodate somewhere around 17 tph.
These could be used for.
- Services not suitable for High Speed Two
- New services
- Freight services
- Open access services
There is a lot of capacity that can be reused.
What Will Happen To Classic Routes Between London And The North?
Consider.
- The East Coast Main Line between London and Doncaster, is being upgraded with full digital signalling to allow running at up to 140 mph and increased train frequencies.
- Similar upgrades will be surely be applied to the other classic routes between London and the North.
- Important destinations, that will not be served by High Speed Two, like Coventry, Derby, Leicester, Luton, Milton Keynes and Peterborough could be given high speed connections, to Birmingham, London and Manchester.
- The East Coast Main Line, Midland Main Line and West Coast Main Line will all be electrified with some sections of quadruple track in a few years.
- Currently, the East Coast Main Line, Midland Main Line and West Coast Main Line are mainly 125 mph lines and these could be upgraded to 140 mph with digital signalling.
I could envisage the East Coast Main Line, Midland Main Line and West Coast Main Line being developed into a secondary 140 mph network based on the existing stations lines and services.
Conclusion
High Speed Two is going to have a lot of collateral benefits in Middle England.