‘Mobilising EUR 1 Trillion in Investments’ | North Sea Countries, Industry, TSOs to Ink Offshore Wind Pact
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Government officials from Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway and the UK are set to sign a declaration confirming the ambition to build 300 GW of offshore wind in the North Seas by 2050, and an investment pact with the offshore wind industry and transmission system operators (TSOs) that is said to mobilise EUR 1 trillion in economic activity.
These three paragraphs add a lot of powerful detail.
Under the Offshore Wind Investment Pact for the North Seas, to be signed today (26 January) at the North Sea Summit in Hamburg, governments of the nine North Sea countries will commit to building 15 GW of offshore wind per year from 2031 to 2040.
The heads of state and energy ministers will also vow to de-risk offshore wind investments through a commitment to provide two-sided Contracts for Difference (CfDs) as the standard for offshore wind auction design. The pact also commits governments to remove any regulatory obstacles to power purchase agreements (PPAs), according to WindEurope, which will sign the pact on behalf of the industry.
On the industry’s side, the commitment is to drive down the costs of offshore wind by 30 per cent towards 2040, mobilise EUR 1 trillion of economic activity for Europe, create 91,000 additional jobs and invest EUR 9.5 billion in manufacturing, port infrastructure and vessels.
These two paragraphs say something about cost reductions.
The cost reduction of offshore wind is planned to be achieved through scale effects, lower costs of capital and further industrialisation supported by clarity and visibility on the project pipeline.
The transmission system operators (TSOs) will identify cost-effective cooperation projects in the North Sea, including 20 GW of promising cross-border projects by 2027 for deployment in the 2030s.
I hope there is a project management system, that can step into this frenzy, just as Artemis did in the 1970s with North Sea Oil and Gas.
The BBC has reported the story under a title of UK To Join Major Wind Farm Project With Nine European Countries.
this is the sub-title.
The UK is set to back a vast new fleet of offshore wind projects in the North Sea alongside nine other European countries including Norway, Germany and the Netherlands.
These six paragraphs add more detail.
The government says the deal will strengthen energy security by offering an escape from what it calls the “fossil fuel rollercoaster”.
For the first time, some of the new wind farms will be linked to multiple countries through undersea cables known as interconnectors, which supporters say should lower prices across the region.
But it could prove controversial as wind farm operators would be able to shop around between countries to sell power to the highest bidder – potentially driving up electricity prices when supply is tight.
Energy Secretary Ed Miliband will sign a declaration on Monday at a meeting on the future of the North Sea in the German city of Hamburg, committing to complete the scheme by 2050.
Jane Cooper, deputy CEO of industry body RenewableUK, said the deal would “drive down costs for billpayers” as well as increasing “the energy security of the UK and the whole of the North Sea region significantly”.
But Claire Countinho, shadow energy secretary, warned “we cannot escape the fact that the rush to build wind farms at breakneck speed is pushing up everybody’s energy bills.”
Claire Coutinho, as an outsider at present and a member of a party out of Government had to say something negative, but her negotiations when she was UK Energy Minister with her German opposite number, which I wrote about in UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties, seem very much a precursor to today’s agreement.
Scotland And AquaVentus Partner On North Sea Hydrogen Pipeline Plans
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on H2-View.
These four paragraphs introduce the deal and add some detail.
Hydrogen Scotland has committed to working with the AquaDuctus consortium on cross-border infrastructure concepts to connect Scotland’s offshore wind power to hydrogen production in the North Sea.
Under a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), the two organisations plan to combine Scotland’s offshore wind with AquaVentus’ offshore electrolysis expertise, linking export and import goals across the North Sea.
The AquaDuctus pipeline is a planned offshore hydrogen link designed to carry green hydrogen through the North Sea, using a pipes and wires hybrid approach. The German consortium plans 10GW of offshore electrolysers in the North Sea, producing around one million tonnes of green hydrogen.
The pipeline design allows offshore wind farms to deliver electricity when the grid needs it, or convert power into hydrogen via electrolysis and transport it through pipelines.
Germany is embracing hydrogen in a big way.
- I introduce AquaVentus in AquaVentus, which I suggest you read.
- AquaVentus is being developed by RWE.
- AquaVentus connects to a German hydrogen network called H2ercules to actually distribute the hydrogen.
This video shows the structure of AquaVentus.
I clipped this map from the video.
Note.
- The thick white line running North-West/South-East is the spine of AquaVentus, that will deliver hydrogen to Germany.
- There is a link to Esbjerg in Denmark, that is marked DK.
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Norway, which goes North,
- There appears to be an undeveloped link to Peterhead in Scotland, that is marked UK.
- There appears to be a link to just North of the Humber in England, that is marked UK.
- Just North of the Humber are the two massive gas storage sites of Aldbrough owned by SSE and Rough owned by Centrica.
- Aldbrough and Rough gas storage sites are being converted into two of the largest hydrogen storage sites in the world!
- There appear to be small ships sailing up and down the East Coast of the UK. Are these small coastal tankers, that are distributing the hydrogen to where it is needed?
When it is completed, AquaVentus will be a very comprehensive hydrogen network.
I believe that offshore electrolysers could be built in the area of the Hornsea 4, Dogger Bank South and other wind farms and the hydrogen generated would be taken by AquaVentus to either Germany or the UK.
- Both countries get the hydrogen they need.
- Excess hydrogen would be stored in Aldbrough and Rough.
- British Steel at Scunthorpe gets decarbonised.
- A 1.8 GW hydrogen-fired powerstation at Keadby gets the hydrogen it needs to backup the wind farms.
Germany and the UK get security in the supply of hydrogen.
Conclusion
This should be a massive deal for Germany and the UK.
Centrica Really Can’t Lose At Sizewell
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica’s £1.3 billion investment in Sizewell C guarantees substantial returns, even with cost overruns.
These two-and-a-half paragraphs explain the funding.
Now we know what Ed Miliband means by his “golden age of nuclear” — golden for the companies putting their money into Sizewell C. Yes, reactor projects have a habit of blowing up private investors. But maybe not this one. It looks more like an exercise in transferring risk to consumers and the taxpayer.
Sure, nobody builds a £38 billion nuke on a Suffolk flood plain without a frisson of danger. But the energy secretary and his Treasury chums have done their bit to make things as safe as possible for the companies putting in equity alongside the government’s 44.9 per cent stake: Canada’s La Caisse with 20 per cent, British Gas-owner Centrica (15 per cent), France’s EDF (12.5 per cent) and Amber Infrastructure (7.6 per cent).
For starters, nearly all the debt for the 3.2 gigawatt plant, three-quarters funded by loans, is coming from the state-backed National Wealth Fund. It’s bunging in up to £36.6 billion, with £5 billion more guaranteed by a French export credit agency.
It looks to me that between them the British and French governments are providing £41.5 billion of loans to build the £38 billion nuke.
These are my thoughts.
Hydrogen And Sizewell C
This page on the Sizewell C web site is entitled Hydrogen And Sizewell C.
Under a heading of Hydrogen Buses, this is said.
At Sizewell C, we are exploring how we can produce and use hydrogen in several ways. We are working with Wrightbus on a pilot scheme which, if successful, could see thousands of workers transported to and from site on hydrogen double decker buses. You can read more about the pilot scheme in our press release
Firstly, it could help lower emissions during construction of the power station. Secondly, once Sizewell C is operational, we hope to use some of the heat it generates (alongside electricity) to make hydrogen more efficiently.
This would appear to be a more general statement about hydrogen and that the following is planned.
- Hydrogen-powered buses will be used to bring workers to the site. A press release on the Sizewell C web site, talks about up to 150 buses. That would probably be enough buses for all of Suffolk.
- Hydrogen-powered construction equipment will be used in the building of the power station.
- It also talks about using the excess heat from the power station to make hydrogen more efficiently. I talk about this process in Westinghouse And Bloom Energy To Team Up For Pink Hydrogen.
This is a substantial investment in hydrogen.
Centrica And Electricity From Sizewell C
The article in The Times, also says this.
Even so, there’s a fair bit of protection for the likes of Centrica, which has also agreed a 20-year offtake deal for its share of Sizewell’s electricity. The price of that is not yet known.
Nothing is said in the article about the size of Centrica’s electricity offtake.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell C, that would by 480 MW.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell B + C, that would by 660 MW.
If they use their share to generate hydrogen, Suffolk would have a massive hydrogen hub.
To power the buses and construction of Sizewell C, Sizewell B could be used to provide electricity to create the hydrogen.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Produced?
Centrica, along with other companies, who include Hyundai and Kia, are backers of a company in Hull called HiiROC, who use a process called Thermal Plasma Electrolysis to generate hydrogen.
On their web site, they have this sub-heading.
A Transformational New Process For Affordable Clean Hydrogen
The web site also describes the process as scalable from small modular units up to industrial scale. It also says this about the costs of the system: As cheap as SMR without needing CCUS; a fraction of the energy/cost of water electrolysis.
If HiiROC have achieved their objective of scalability, then Centrica could grow their electrolyser to meet demand.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Distributed?
Consider.
- Currently, the Sizewell site has both road and rail access.
- I can still see in my mind from the 1960s, ICI’s specialist articulated Foden trucks lined up in the yard at Runcorn, taking on their cargoes of hydrogen for delivery all over the country.
- As that factory is still producing hydrogen and I can’t remember any accidents in the last sixty years, I am fairly sure that a range of suitable hydrogen trucks could be developed to deliver hydrogen by road.
- The road network to the Siewell site is being updated to ensure smooth delivery of workers and materials.
- The rail access to the Sizewell site is also being improved, for the delivery of bulk materials.
I believe there will be no problems delivering hydrogen from the Sizewell site.
I also believe that there could be scope for a special-purpose self-propelled hydrogen tanker train, which could both distribute and supply the hydrogen to the vehicles, locomotives and equipment that will be using it.
Where Will The Hydrogen Be Used?
I have lived a large part of my life in Suffolk and know the county well.
In my childhood, there was quite a lot of heavy industry, but now that has all gone and employment is based on agriculture, the Port of Felixstowe and service industries.
I can see hydrogen being used in the following industries.
Transport
Buses and heavy trucks would be powered by hydrogen.
The ports in the East of England support a large number of heavy trucks.
Large Construction Projects
Sizewell C is not the only large construction project in the East of England, that is aiming to use low-carbon construction involving hydrogen. In Gallagher Group Host Hydrogen Fuel Trial At Hermitage Quarry, I talked about a hydrogen fuel trial for the Lower Thames Crossing, that involved JCB and Ryse Hydrogen.
Hydrogen for the Lower Thames Crossing could be delivered from Sizewell by truck, down the A12.
Rail
We may not ever see hydrogen-powered passenger trains in this country, but I do believe that we could see hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
Consider.
- The latest electro-diesel Class 99 locomotives from Stadler have a Cummins diesel engine.
- The diesel engine is used, when there is no electrification.
- Cummins have developed the technology, that allows them to convert their latest diesel engines to hydrogen or natural gas power, by changing the cylinder head and the fuel system.
- Access to the Port of Felixstowe and London Gateway needs a locomotive with a self-powered capability for the last few miles of the route.
A Class 99 locomotive converted to hydrogen would be able to run with out emitting any carbon dioxide from Felixstowe or London Gateway to Glasgow or Edinburgh.
Ports
Ports have three main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for port workers.
- To fuel ships of all sizes from the humblest work-boat to the largest container ships.
- There may need to be fuel for hydrogen-powered rail locomotives in the future.
There are seven ports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth, Harwich, Ipswich, London Gateway, Lowestoft and Tilbury.
The proposed Freeport East is also developing their own green hydrogen hub, which is described on this page on the Freeport East web site.
Airports
Airports have two main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for airport workers.
- In the future, there is likely to be hydrogen-powered aircraft.
There are three airports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Norwich, Southend and Stansted.
Agriculture And The Rural Economy
Agriculture and the rural economy would be difficult to decarbonise.
Consider.
- Currently, most farms would use diesel power for tractors and agricultural equipment, which is delivered by truck.
- Many rural properties are heated by propane or fuel oil, which is delivered by truck.
- Some high-energy rural businesses like blacksmiths rely on propane, which is delivered by truck.
- Electrification could be possible for some applications, but ploughing the heavy land of Suffolk, with the added weight of a battery on the tractor, would probably be a mathematical impossibility.
- JCB are developing hydrogen-powered construction equipment and already make tractors.
- Hydrogen could be delivered by truck to farms and rural properties.
- Many boilers can be converted from propoane to run on hydrogen.
I feel, that hydrogen could be the ideal fuel to decarbonise agriculture and the rural economy.
I cover this application in detail in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Exports
Consider.
- Sizewell B and Sizewell C nuclear powerstations have a combined output of 4.4 GW.
- A rough calculation shows that there is a total of 7.2 GW of wind farms planned off the Suffolk coast.
- The East Anglian Array wind farm alone is said in Wikipedia to be planned to expand to 7.2 GW.
- The Sizewell site has a high capacity connection to the National Grid.
Nuclear plus wind should keep the lights on in the East of England.
Any excess electricity could be converted into hydrogen.
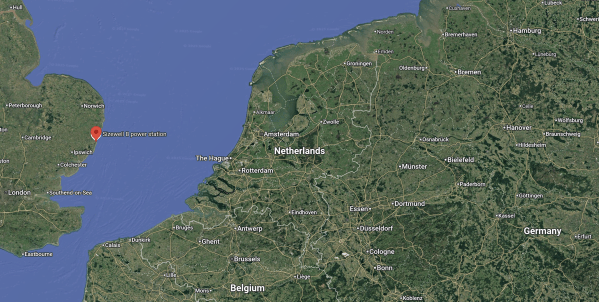
This Google Map shows the location of Sizewell B in relation to Belgium, Germany and The Netherlands.
The Sizewell site is indicated by the red arrow.
The offshore oil and gas industry has used technology like single buoy moorings and coastal tankers to collect offshore natural gas for decades.
I don’t see why coastal hydrogen tankers couldn’t export excess hydrogen to places around the North Sea, who need the fuel.
It should be born in mind, that Centrica have a good reputation in doing natural gas trading. This expertise would surely be useful in hydrogen trading.
Conclusion
I believe that a hydrogen hub developed at Sizewell makes sense and I also believe that Centrica have the skills and technology to make it work.
Offshore Grid For Irish, Celtic and North Seas Closer To Delivery
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Irish Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Joint development can be ‘key step for Europe’s energy future’ and climate neutrality
These paragraphs add detail.
EirGrid and other leading European power transmission system operators (TSOs) have backed moves to develop an offshore electricity grid for the Irish, Celtic and North seas.
The next stage in a collaboration, being undertaken by nine system operators under the Offshore TSO Collaboration (OTC), was announced at the WindEurope annual conference in Copenhagen on Wednesday.
It followed the initial results of a pilot study evaluating how the grid could be established.
The report supports Europe’s goal of establishing a “green power plant” offshore that will play a crucial role in the Continent securing an independent, affordable and climate-neutral energy supply.
If you open the article, there is an excellent map of the various interconnectors, that will be in place by 2040.
Conclusion
This is all good stuff and can only lead to energy security for the participating countries.
Ørsted, Simply Blue, Subsea7 Submit Application For 100 MW Scottish Floating Wind Farm
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Ørsted, Simply Blue Group and Subsea7, through their joint venture partnership in Scotland, have submitted an offshore consent application for the proposed 100 MW Salamander floating offshore wind farm, one of the 13 projects selected in Scotland’s Innovation and Targeted Oil and Gas (INTOG) leasing round.
The article starts with a map that shows the location of the Salamander floating offshore wind farm and it shows how the sea is getting very crowded 35 kilometres off Peterhead.
This map shows the various ScotWind leases, around the North of Scotland.
The numbers are Scotwind’s lease number in their documents.
These are the Scotwind wind farms to the North-East of Scotland.
- 1 – BP Alternative Energy Investments – 859 km² – 2.9 GW – Fixed
- 2 – SSE Renewables – 859 km² – 2.6 GW – Floating
- 3 – Falck Renewables Wind – 280 km² – 1.2 GW – Floating
- 4 – Shell – 860 km² – 2.0 GW – Floating
- 5 – Vattenfall – 200 km² – 0.8 GW – Floating
- 6 – DEME – 187 km² – 1.0 GW – Fixed
- 9 – Ocean Winds – 429 km² – 1.0 GW – Fixed
- 10 – Falck Renewables Wind – 134 km² – 0.5 GW – Floating
- 11 – Scottish Power Renewables – 684 km² – 3.0 GW – Floating
- 12 – BayWa r.e. UK – 330 km² – 1.0 GW – Floating
Note.
- Salamander is located to the South of wind farms 10, 11 and 12 and to the North-West of wind farm 5.
- These windfarms total up to 16 GW.
- 4.9 GW are fixed foundation wind farms.
- 11.1 GW are floating wind farms.
These are my thoughts.
The Salamander Project
In the big scheme of things, the 100 MW Salamander wind farm, is rather a tiddler of a wind farm.
On the Salamander wind farm web site, a section gives the Project Goals.
- Our innovative pre-commercial stepping-stone concept will use novel floating foundations to (i) maximise Scottish content, (ii) enable the Scottish supply chain to gear up for the future floating offshore wind commercial opportunities in ScotWind and (iii) reduce the financial, environmental and technology risks of floating offshore wind.
- The Salamander project will contribute to the Scottish Government and UK Government net-zero targets. The project can contribute to the Scottish government’s target of 11 GW of installed offshore wind by 2030, as well as the UK government’s target of 5 GW of operational floating offshore wind by the same date.
- We are dedicated to developing a sustainable and transformative project, working with the oceans, and enabling communities to benefit from Project Salamander. Therefore, we commit to having a continuous and strong stakeholder and community engagement.
It appears to me, that the Salamander project will be a pathfinder for the 11.1 GW of floating wind farms to be built off Peterhead.
Bringing The Electricity South
National Grid are building four interconnectors between Eastern Scotland and Eastern England.
- Eastern Green Link 1 – Torness and Hawthorn Pit
- Eastern Green Link 2 – Peterhead and Drax
- Eastern Green Link 3 – Westfield and Lincolnshire
- Eastern Green Link 4 – Peterhead and Lincolnshire
Note.
- All interconnectors are 2 GW.
- All interconnectors are offshore for a long part of their route.
- It also appears that National Grid are burying much of the onshore sections.
But the 4 GW of interconnectors will only be able to bring a quarter of the offshore electricity generated in the Peterhead area to the South.
What Will Happen To The Excess Electricity?
Consider.
- There could be 16 GW of planned offshore wind power around Peterhead and North-East Scotland.
- There is only 4 GW of interconnector capacity between Peterhead and Eastern England.
- There is another 6.8 GW of electricity around North-West Scotland.
- There is 2.8 GW of electricity being developed to the East of Shetland.
- The Crown Estate is thinking of increasing the size of some offshore wind farms.
It is likely, that other wind farms will be built in the seas around the North of Scotland.
It appears that the North of Scotland could have at least 20 GW of excess electricity.
Possible solutions would include.
- Developing energy intensive industries like metal refining.
- More interconnectors to Denmark, England, Ireland and Norway.
- Storage of the electricity in giant pumped storage hydroelectric power stations.
- Creation of green hydrogen for export.
Note.
- Aluminium refining has been developed in the North of Scotland before.
- More interconnectors are a possibility, especially as Scotland is developing cable manufacturing capacity.
- Some maps show extra interconnectors between West Scotland and Merseyside.
- At least 70 GWh of pumped storage hydroelectric power stations are being developed along the Great Glen.
- I suspect that the pumped storage hydroelectric power stations could be connected to the wind farms, by cables under the waters of Loch Ness.
But surely, production of green hydrogen for export would be a very good way to go.
- Extra electrolysers could be added as required.
- Because of the interconnectors down both East and West Coasts, electrolysers could be built in England, where there is a large need for hydrogen.
- Hydrogen would be exported initially by tanker ships.
- At some point in the future, it might be viable to build a hydrogen pipeline to connect to the growing European hydrogen network.
The giant pumped storage hydroelectric power stations and the hydrogen electrolysers would be sized to make sure, that no wind power is never wasted.
Conclusion
The 100 MW Salamander floating wind farm may only be small, but it will prove the technology, the manufacturing and the supply chains, so that Scotland can have a second energy boom from the North Sea.
But this boom will certainly last longer than a hundred years.
North Sea, Baltic Sea Countries Enter Pacts To Protect Offshore Energy Infrastructure Amid Concerns Over Russian Sabotage
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Eight Baltic Sea countries signed a joint declaration on collaborating closer to secure critical offshore energy infrastructure in the region on 10 April, only a day after six North Sea countries entered into a similar agreement. Both are a result of security concerns arising from the Russian invasion of Ukraine and reports of possible sabotage of offshore and subsea energy infrastructure in the North and Baltic Seas.
These are the first two paragraphs.
Concerns over Russia sabotaging offshore energy assets came into the spotlight after four gas leaks were found in September 2022 on the twin Nord Stream pipeline system in the Baltic Sea.
Following national investigations into the incident initiated by Germany, Sweden and Denmark, and studies by the Norwegian and Swedish seismic institutes, European authorities said that the incident could have been the result of “deliberate actions”.
Hopefully, mutual defence will see off, the Evil Vlad!
Industry Calls For 10 GW Of Offshore Hydrogen In German National H2 Strategy
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Offshore wind and hydrogen developers and organisations in Germany have called on the federal government to set clear targets for offshore hydrogen in the update of the country’s National Hydrogen Strategy, with an additional 10 GW of offshore electrolysis capacity to be added by 2035.
These two paragraphs add detail the story and name those who are behind it.
On 26 May, several companies and industry organisations signed an appeal sent to the German Federal Government that highlights offshore hydrogen’s advantage of adding large-scale capacities and asks that a target of an additional 10 GW of offshore hydrogen by 2035 be added to both the country’s hydrogen strategy and the area development plan.
The parties that signed the appeal include the German offshore wind-to-hydrogen initiative AquaVentus, offshore wind and hydrogen players BP, Siemens Gamesa, Gasunie, Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP), EnBW, Equinor, and Lhyfe, as well as industry organisations WAB and the Federal Association of Offshore Wind Farm Operators (BWO), among others.
These two paragraphs describe an area to be developed for the first offshore hydrogen production.
As reported in January, in the country’s new area development plan for offshore wind, Germany’s Federal Maritime and Hydrographic Agency (BSH) also outlined the first offshore hydrogen area in the North Sea.
The area, SEN-1, spans over 100 square kilometres in the North Sea and will allow for an electrolysis capacity of up to 1 GW to be tested and connected with a hydrogen pipeline.
Note.
- 1 GW if electricity should create about 435 tonnes of hydrogen per day.
- That amount of hydrogen could be stored as liquid in a sphere with a radius of 11.35 metres.
The Netherlands Chooses Site For World’s Largest Offshore Wind-to-Hydrogen Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The Dutch government has designated an area for what will become the world’s largest offshore hydrogen production project. That area is Ten noorden van de Waddeneilanden (the North of the Wadden Islands), identified earlier for offshore wind development and deemed most suitable for providing 500 MW of electrolysis capacity and for the transport of hydrogen to land.
This Google Map shows the Wadden Islands.
Note.
- Groningen is in the South-East corner of the map.
- I wrote about Eemshaven, which is to the North-East of Groningen in The Train Station At The Northern End Of The Netherlands.
- The Wadden or Frisian Islands are along the coast.
The Wadden Islands of the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark are a World Heritage Site.
In Can The UK Have A Capacity To Create Five GW Of Green Hydrogen?, I said the following.
Ryze Hydrogen are building the Herne Bay electrolyser.
- It will consume 23 MW of solar and wind power.
- It will produce ten tonnes of hydrogen per day.
The electrolyser will consume 552 MWh to produce ten tonnes of hydrogen, so creating one tonne of hydrogen needs 55.2 MWh of electricity.
If the Dutch build a 500 MW electrolyser it will produce 217 tonnes of hydrogen per day.
The Dutch Plan For Hydrogen
This 500 MW electrolyser fits well with the The Dutch Plan For Hydrogen.
Maximising Space In North Sea Essential To Tackling Energy Security And Net Zero Targets
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the Eastern Daily Press.
These two paragraphs introduce the article.
Reviving wells in the Southern North Sea, powering oil and gas platforms with wind turbines, capturing and storing CO2 and hydrogen systems, starting work on world-class offshore wind farms off the coast and consent for Sizewell C nuclear power station – the East of England is ripe with opportunity for companies ready for the challenge.
The industrialised North Sea is becoming supercharged in the name of UK energy security – so much so that a spatial planning exercise is under way to optimise the seabed for energy security and make everything fit for maximum efficiency.
This is an article, that must be read fully.
These are some topics that are discussed.
- Looking at old wells to see if more oil and gas can be extracted.
- Electrification of oil and gas facilities, where economic and possible.
- Powering oil and gas facilities with offshore wind.
This is also said about the Innovation and Targeted Oil and Gas (INTOG) leasing round.
The Innovation and Targeted Oil and Gas (INTOG) leasing round is open for developers to apply for the rights to build offshore wind farms specifically to provide low-carbon electricity to power oil and gas installations in Scotland. It offers the opportunity to enable small scale (less than 100MW) innovation projects, including alternative outputs such as hydrogen.
It looks like mopping up the oil and gas in the North Sea could be promoted as a possible alternative to fracking.
I shall be interested to see how INTOG progresses.
At worst, it will mean that oil and gas installations will be powered by zero-carbon electricity, but in addition it could recover worthwhile amounts of oil and gas.
Germany Has Potential For 82 GW Of Offshore Wind
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Renewables Now.
These are the two introductory paragraphs.
Germany has the potential to raise its offshore wind energy capacity to 81.6 GW which is above the federal government’s target of 70 GW by 2045, a study by research institute Fraunhofer IWES shows.
To exploit all the potential for wind energy in the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, Germany needs to devise a strategy for more efficient use of the available space and use new offshore wind power technologies in additional areas in a way that will not raise concerns and affect nature conservation.
This map shows the German parts of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea.
Note.
- White lines show the borders with The Netherlands, Denmark and Poland.
- Heligoland in the South-East corner of the North Sea. Could this island be used as a giant offshore substation?
- There are plenty of ports to service offshore developments.
- It looks like compared to the UK, a fair proportion of German offshore wind farms will be closer to the land.
Currently, Germany has 7.8 GW of offshore wind in operation, with around seventy percent of the turbines in the North Sea.
According to the Wikipedia entry called Wind Power In The UK, in 2019, the UK had installed 8.4 GW of offshore wind turbines, and there could be a potential to have a total of 120 GW in British waters.
With the Belgians, Danes, Dutch, Irish, Norwegians, Poles and Swedes joining this party, I can see the world’s largest wind power station being developed in the North and Baltic Seas.