Centrica Really Can’t Lose At Sizewell
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica’s £1.3 billion investment in Sizewell C guarantees substantial returns, even with cost overruns.
These two-and-a-half paragraphs explain the funding.
Now we know what Ed Miliband means by his “golden age of nuclear” — golden for the companies putting their money into Sizewell C. Yes, reactor projects have a habit of blowing up private investors. But maybe not this one. It looks more like an exercise in transferring risk to consumers and the taxpayer.
Sure, nobody builds a £38 billion nuke on a Suffolk flood plain without a frisson of danger. But the energy secretary and his Treasury chums have done their bit to make things as safe as possible for the companies putting in equity alongside the government’s 44.9 per cent stake: Canada’s La Caisse with 20 per cent, British Gas-owner Centrica (15 per cent), France’s EDF (12.5 per cent) and Amber Infrastructure (7.6 per cent).
For starters, nearly all the debt for the 3.2 gigawatt plant, three-quarters funded by loans, is coming from the state-backed National Wealth Fund. It’s bunging in up to £36.6 billion, with £5 billion more guaranteed by a French export credit agency.
It looks to me that between them the British and French governments are providing £41.5 billion of loans to build the £38 billion nuke.
These are my thoughts.
Hydrogen And Sizewell C
This page on the Sizewell C web site is entitled Hydrogen And Sizewell C.
Under a heading of Hydrogen Buses, this is said.
At Sizewell C, we are exploring how we can produce and use hydrogen in several ways. We are working with Wrightbus on a pilot scheme which, if successful, could see thousands of workers transported to and from site on hydrogen double decker buses. You can read more about the pilot scheme in our press release
Firstly, it could help lower emissions during construction of the power station. Secondly, once Sizewell C is operational, we hope to use some of the heat it generates (alongside electricity) to make hydrogen more efficiently.
This would appear to be a more general statement about hydrogen and that the following is planned.
- Hydrogen-powered buses will be used to bring workers to the site. A press release on the Sizewell C web site, talks about up to 150 buses. That would probably be enough buses for all of Suffolk.
- Hydrogen-powered construction equipment will be used in the building of the power station.
- It also talks about using the excess heat from the power station to make hydrogen more efficiently. I talk about this process in Westinghouse And Bloom Energy To Team Up For Pink Hydrogen.
This is a substantial investment in hydrogen.
Centrica And Electricity From Sizewell C
The article in The Times, also says this.
Even so, there’s a fair bit of protection for the likes of Centrica, which has also agreed a 20-year offtake deal for its share of Sizewell’s electricity. The price of that is not yet known.
Nothing is said in the article about the size of Centrica’s electricity offtake.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell C, that would by 480 MW.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell B + C, that would by 660 MW.
If they use their share to generate hydrogen, Suffolk would have a massive hydrogen hub.
To power the buses and construction of Sizewell C, Sizewell B could be used to provide electricity to create the hydrogen.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Produced?
Centrica, along with other companies, who include Hyundai and Kia, are backers of a company in Hull called HiiROC, who use a process called Thermal Plasma Electrolysis to generate hydrogen.
On their web site, they have this sub-heading.
A Transformational New Process For Affordable Clean Hydrogen
The web site also describes the process as scalable from small modular units up to industrial scale. It also says this about the costs of the system: As cheap as SMR without needing CCUS; a fraction of the energy/cost of water electrolysis.
If HiiROC have achieved their objective of scalability, then Centrica could grow their electrolyser to meet demand.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Distributed?
Consider.
- Currently, the Sizewell site has both road and rail access.
- I can still see in my mind from the 1960s, ICI’s specialist articulated Foden trucks lined up in the yard at Runcorn, taking on their cargoes of hydrogen for delivery all over the country.
- As that factory is still producing hydrogen and I can’t remember any accidents in the last sixty years, I am fairly sure that a range of suitable hydrogen trucks could be developed to deliver hydrogen by road.
- The road network to the Siewell site is being updated to ensure smooth delivery of workers and materials.
- The rail access to the Sizewell site is also being improved, for the delivery of bulk materials.
I believe there will be no problems delivering hydrogen from the Sizewell site.
I also believe that there could be scope for a special-purpose self-propelled hydrogen tanker train, which could both distribute and supply the hydrogen to the vehicles, locomotives and equipment that will be using it.
Where Will The Hydrogen Be Used?
I have lived a large part of my life in Suffolk and know the county well.
In my childhood, there was quite a lot of heavy industry, but now that has all gone and employment is based on agriculture, the Port of Felixstowe and service industries.
I can see hydrogen being used in the following industries.
Transport
Buses and heavy trucks would be powered by hydrogen.
The ports in the East of England support a large number of heavy trucks.
Large Construction Projects
Sizewell C is not the only large construction project in the East of England, that is aiming to use low-carbon construction involving hydrogen. In Gallagher Group Host Hydrogen Fuel Trial At Hermitage Quarry, I talked about a hydrogen fuel trial for the Lower Thames Crossing, that involved JCB and Ryse Hydrogen.
Hydrogen for the Lower Thames Crossing could be delivered from Sizewell by truck, down the A12.
Rail
We may not ever see hydrogen-powered passenger trains in this country, but I do believe that we could see hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
Consider.
- The latest electro-diesel Class 99 locomotives from Stadler have a Cummins diesel engine.
- The diesel engine is used, when there is no electrification.
- Cummins have developed the technology, that allows them to convert their latest diesel engines to hydrogen or natural gas power, by changing the cylinder head and the fuel system.
- Access to the Port of Felixstowe and London Gateway needs a locomotive with a self-powered capability for the last few miles of the route.
A Class 99 locomotive converted to hydrogen would be able to run with out emitting any carbon dioxide from Felixstowe or London Gateway to Glasgow or Edinburgh.
Ports
Ports have three main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for port workers.
- To fuel ships of all sizes from the humblest work-boat to the largest container ships.
- There may need to be fuel for hydrogen-powered rail locomotives in the future.
There are seven ports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth, Harwich, Ipswich, London Gateway, Lowestoft and Tilbury.
The proposed Freeport East is also developing their own green hydrogen hub, which is described on this page on the Freeport East web site.
Airports
Airports have two main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for airport workers.
- In the future, there is likely to be hydrogen-powered aircraft.
There are three airports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Norwich, Southend and Stansted.
Agriculture And The Rural Economy
Agriculture and the rural economy would be difficult to decarbonise.
Consider.
- Currently, most farms would use diesel power for tractors and agricultural equipment, which is delivered by truck.
- Many rural properties are heated by propane or fuel oil, which is delivered by truck.
- Some high-energy rural businesses like blacksmiths rely on propane, which is delivered by truck.
- Electrification could be possible for some applications, but ploughing the heavy land of Suffolk, with the added weight of a battery on the tractor, would probably be a mathematical impossibility.
- JCB are developing hydrogen-powered construction equipment and already make tractors.
- Hydrogen could be delivered by truck to farms and rural properties.
- Many boilers can be converted from propoane to run on hydrogen.
I feel, that hydrogen could be the ideal fuel to decarbonise agriculture and the rural economy.
I cover this application in detail in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Exports
Consider.
- Sizewell B and Sizewell C nuclear powerstations have a combined output of 4.4 GW.
- A rough calculation shows that there is a total of 7.2 GW of wind farms planned off the Suffolk coast.
- The East Anglian Array wind farm alone is said in Wikipedia to be planned to expand to 7.2 GW.
- The Sizewell site has a high capacity connection to the National Grid.
Nuclear plus wind should keep the lights on in the East of England.
Any excess electricity could be converted into hydrogen.
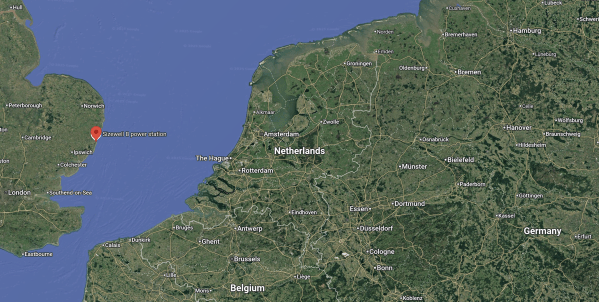
This Google Map shows the location of Sizewell B in relation to Belgium, Germany and The Netherlands.
The Sizewell site is indicated by the red arrow.
The offshore oil and gas industry has used technology like single buoy moorings and coastal tankers to collect offshore natural gas for decades.
I don’t see why coastal hydrogen tankers couldn’t export excess hydrogen to places around the North Sea, who need the fuel.
It should be born in mind, that Centrica have a good reputation in doing natural gas trading. This expertise would surely be useful in hydrogen trading.
Conclusion
I believe that a hydrogen hub developed at Sizewell makes sense and I also believe that Centrica have the skills and technology to make it work.
London Gatwick Implementing Time-Based Separation On Single Mixed-Mode Runway
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on Flight Global.
These four paragraphs introduce the technique.
UK air navigation service NATS has applied its intelligent arrival separation system to a mixed-mode single runway for the first time, with implementation at London Gatwick.
The system uses dynamic time-based – rather than distance-based – approach spacing in order to maintain sufficient arrival rates in strong headwind conditions.
Headwinds reduce the groundspeed of inbound aircraft flying at a set airspeed. This means a longer interval between two arrivals spaced a fixed distance apart.
“Having to maintain set separation distances in those conditions reduces the landing rate and can have a significant knock-on effect to the airport operation,” says NATS.
I have flown light aircraft onto main runways at major airports several times, including Cardiff, Dublin, Edinburgh, Hamburg, Leeds, Liverpool, Manchester, Naples, Nice, Southend and Stansted.
In one approach I made to Dublin airport, this type of approach may well have been of assistance.
I was flying into Dublin in my Piper Arrow; G-JMTT.
- I had crossed over Anglesey to leave Wales and I was talking to RAF Valley, whilst I crossed the Irish Sea in more of a direct line for Dublin Airport.
- The RAF handed me over to Dublin Approach, who gave me a series of vectors to point me at the main runway at Dublin Airport.
- Dublin Tower, then gave me the instruction. “Tango-Tango Can you speed it up a bit! There’s a Jumbo on your tail!”
- I replied. “Affirmative! Tango-Tango!” I then lowered the nose and pointed it at the runway to speed things up a bit.
- Dublin Tower, then asked. “Tango-Tango On landing, can you expedite clearing the runway?”
- There was then a brief exchange, where I negotiated my route off the runway, by taking the first taxiway on the left and then stopping.
- After a safe landing and a stop on the taxiway, Dublin Tower called. “Tango-Tango! We’ll give you ten out of ten for that!”
- After which the Jumbo rushed past on the runway, with the pilot giving a quick laugh over the radio.
- Dublin Tower called. “Welcome to Dublin!”
The Irish have different ways of doing things!
But, seriously, NATS are probably just implimenting a computerised form of what good air traffic controllers have done for years.
In that arrival at Dublin, the controllers had stretched the time and distance between my small Piper and the Jumbo, so everything was safe.
There alternative would have been to delay one of the planes.
Conclusion
It looks to me that the application of a new algorithm by NATS, will squeeze a few more aircraft into Gatwick’s single runway.
UK Investment Summit Latest: Starmer Announces £1.1bn Expansion Of Stansted Airport
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on The Times.
The Times has this sub-heading about Stansted
Analysis: Stansted Deal Prioritises Growth Over Climate
There are four paragraphs of analysis.
Over the weekend, Sir Keir Starmer made clear that his commitments to boost workers’ rights would not get in the way of his desire to bring in cash from the owners of P&O. As ministers now trumpet a deal to upgrade Stansted airport, it seems that growth and jobs also trump concerns about emissions.
Louise Haigh, the transport secretary who prompted the row with DP World by calling P&O a “rogue operator”, praised the Stansted deal as a “clear signal that Britain is open for business”. She argued that Stansted could be upgraded “while also meeting our existing environment obligations”, with the airport promising a new solar farm to generate electricity. But environmentalists will be dismayed by the prospect of more plane journeys and associated emissions.
The deal also raises fresh questions about a third runway at Heathrow after years of dithering under the Conservatives. No 10 has previously said it is “not opposed” to expansion if it can meet tests on emissions, climate change, noise pollution — and growth.
Starmer has said he will not duck decisions because they are “too difficult”. A decision on Heathrow offers a very clear test of that promise.
Is Hydrogen The Reason For The Choice Of Stansted?
I wonder if the choice of Stansted for expansion is down to the likelihood, that East Anglia will be a big centre for the generation of zero-carbon green and pink hydrogen, with gigawatts of offshore wind farms for the green and nuclear at Sizewell for the pink.
Aircraft of the future will surely need hydrogen for flying to their destinations.
Already, the massive construction of Sizewell C is going to be performed using zero-construction methods involving electricity and hydrogen, as far as is possible.
Large construction at Stansted Airport could be done in a similar manner, using perhaps a hydrogen pipeline between Sizewell and Stansted running along the A 14. This would probably be built anyway, so that East Anglia’s large numbers of heavy trucks could be converted to hydrogen.
Already the hydrogen buses to bring workers to the Sizewell C site have been ordered from Wrightbus in Ballymena.
Airbus, are planning to have their hydrogen-powered Boeing 737/A 320-size airliner in service by the mid-2030s. From visualisations released by Airbus, the Zeroe hydrogen Turbofan looks very much like a redesigned version of the current A320 neo, with two hydrogen turbofans (hopefully with RR on the side!) Converting an existing proven airliner, only means that the new parts need to be certified, so this would bring the plane into service quicker.
Airbus’s infographic shows the Zeroe hydrogen Turbofan will seat up to 200 passengers and have a range of 2,000 nautical miles or 3,700 km.

Discover the three zero-emission concept aircraft known as ZEROe in this infographic. These turbofan, turboprop, and blended-wing-body configurations are all hydrogen hybrid aircraft.
A typical A 320 neo will fly 165 passengers up to 3,500 nautical miles or 6.500 km.
A few distances from Stansted include.
- Athens – 2,400 km.
- Berlin – 905 km.
- Cairo – 3514 km.
- Copenhagen 913 km.
- Dublin – 470 km.
- Edinburgh – 509 km.
- Gander 3,800 km
- Geneva – 760 km.
- Glasgow – 540 km.
- Istanbul – 2480 km.
- Madrid – 1300 km.
- Milan – 960 km.
- Munich – 909 km.
- Palma de Mallorca – 1,400 km.
- Reykjavík – 1870 km.
- Rome – 1,442 km.
- Stockholm – 1,400 km.
- Tel-Aviv – 3,564 km.
- Tenerife North – 2944 km.
- Tenerife South – 2999 km.
- Warsaw 1,412 km.
These distances would mean, a lot of current European destinations could be reached, if the plane were filled at both airports, but a surprising number of popular places could be reached by only refuelling at Stansted.
It also appears to me, that with refuelling in Iceland and perhaps a stopover, in that delightful and different country, zero-carbon flights across the Atlantic would be possible.
If a hydrogen-powered aircraft has the 3,700 km. range that Airbus are promising, it will be an aircraft with a lot of possibilities!
Short Flights
- Amsterdam – 541 km.
- Cardiff – 253 km.
- Exeter – 284 km.
- Jersey – 344 km.
- Liverpool – 264 km.
- Newcastle – 373 km.
- Newquay – 399 km.
- Ronaldsway – 408 km.
- Southampton – 151 km.
Some of these flights would be competing with trains.
Flights Around The British Isles
One of the longest flights around the British Isles would be between Stansted and Sumburgh Airport in the Shetland Isles.
But this is only 894 kilometres, so a return trip would be possible.
I also feel that arranging hydrogen refuelling on Shetland will not be a difficult task, as the islands are likely to have copious supplies of green hydrogen.
Flights From Stansted To Europe
Applying a ten percent reserve probably means a safe one-way range of around 1,700 km.
This would mean that.
- Amsterdam – 541 km.
- Berlin – 905 km.
- Copenhagen – 913 km.
- Madrid – 1300 km.
- Milan – 960 km.
- Munich – 909 km.
- Palma de Mallorca – 1,400 km.
- Rome – 1,442 km.
- Stockholm – 1,400 km.
- Warsaw 1,412 km.
Should all be in range. of an out-and-back flight, after fully fuelling the plane at Stansted Airport.
Others like.
- Athens – 2,400 km.
- Bucharest – 2070 km.
- Cairo – 3514 km.
- Istanbul – 2480 km.
- Lisbon – 1630 km.
- Malta – 2107 km.
- Marrakech – 2350. km.
- Sofia – 2010 km.
- Tel-Aviv – 3,564 km.
- Tenerife North – 2944 km.
- Tenerife South – 2999 km.
Could be handled by refuelling at the destination.
Hopping Across The Atlantic
Consider.
- My great aunt Beatrice used to fly the Atlantic in the 1950s, although it was usually a succession of small hops between Heathrow Shannon and Gander Airports. I think she regularly used ships like the Queen Mary and Elizabeth, as she found them less stressful.
- Icelandair offer short stopovers in Reykjavik and I suspect they will offer this with hydrogen-fuelled aircraft.
- British Airways used to offer a London City Airport to New York flight via Shannon using an Airbus A 318.
I would certainly be interested to hop across from Stansted to New York in a hydrogen-powered aircraft, and I suspect others would do it for the environmental brownie points.
Legs could be.
- Stansted and Reykjavík – 1870 km.
- Reykjavík and Gander – 2568 km
- Gander and New York – 1767 km.
A stop could possibly be squeezed in at Boston.
It could be an interesting way to cross the Atlantic.
Hydrogen Production In East Anglia
I said earlier that East Anglia could produce a lot of zero-carbon green and prink hydrogen from wind and nuclear and this would be used for the following.
- Aviation out of Stansted and Southend Airports.
- Shipping out of the Port of Felixstowe, London Gateway and other smaller ports.
- Providing energy for heavy transport in East Anglia.
- Providing energy for Freeport East at Felixstowe and Harwich.
- Refuelling passing shipping.
- Supplying off-grid energy to rural properties and businesses in the East of England, which I wrote about in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Any spare hydrogen could always be sold to the Germans.
Decarbonisation Of The Railways In East Anglia
Undoubtedly, some hydrogen will be used to decarbonise some parts of East Anglia’s railways.
Many passenger trains are electrified, but some rural and cross-country services still use diesel. However, the Class 745 trains, that were built by Stadler for these services could be converted to hydrogen or battery-electric.
Similarly, locomotives that haul the freight trains out of the ports of East Anglia will be replaced with hydrogen or battery-electric locomotives.
I am fairly certain, that by 2040, all railways in East Anglia will be zero-carbon.
The East-West Rail Link
It is not known yet, whether the current government will continue to build the East West Rail Link, but it could be invaluable in connecting Stansted Airport to the West of England.
Connecting Stansted Airport To The North Of England and Scotland By Rail
If Stansted is developed as a zero-carbon airport, based on the new hydrogen-powered aircraft, travellers between say the North of England and Scotland, will surely want to travel to Stansted in a carbon-free manner.
So would it be sensible to run rail electric services between the North and Stansted?
Conclusion
Stansted could develop into the UK’s zero-carbon airport.
No Shortcuts In Evia Aero’s Path To Being Europe’s First Green Regional Airline
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on FutureFlight.
This is the first paragraph.
The closer you examine the task of establishing a green airline, the clearer it becomes that it does not begin and end with sourcing net zero carbon aircraft. Evia Aero is a case in point in that while the German start-up has made provisional commitments to a pair of electric aircraft developers, for now, it is more preoccupied with getting a somewhat daunting operational ecosystem in place.
The article is an interesting read and certainly follows this old joke about aviation.
If you want to make a small fortune in aviation, start with a large fortune.
The article is mainly drawn from an interview with the founder of Evia Aero; Florian Kruse and these are some of his thoughts.
On Sustainability
This paragraph talks about a truly sustainable aviation company.
First you have to be sure that you can operate as a truly sustainable aviation company,” Evia Aero founder Florian Kruse told FutureFlight. The Bremen-based venture plans to invest in photovoltaic (PV) solar energy plants at the airports it intends to serve to fulfill its commitment to being self-sufficient in green energy, which could include electricity and hydrogen fuel. The next step will be installing the required refueling and recharging facilities.
I’ll agree with that objective, but is it an affordable commitment?
On An Air Operator Certificate
This paragraph talks about an Air Operator Certificate.
Only when these tasks are well advanced, probably in 2024, will Evia Aero secure the air operator certificate it needs to launch commercial scheduled services in Europe. The company has yet to determine whether it will establish an operation from scratch or acquire an existing AOC holder.
Having seen a friend struggle to get an airline going, I wonder, if existing AOC holders will have an advantage in getting fully certified.
Why Not Start A Traditional Airline And Transition To A Green One?
This was Florian Kruse’s answer.
Some people ask us why we don’t just start operating normal [fossil-fuel-burning] aircraft today and then make a transition [to net zero],But we don’t think that works. The only way to be successful in this is to be green with everything from the start.
But by his choice of the Britten-Norman Islander, Florian is taking a conservative route with a proven small airliner, that has been flown into hundreds, if not thousands, of airfields all over Europe and the wider world.
I suspect too, that a lot of experienced Islander pilots from all over the world, will want to add these aircraft to their log book. So recruitment of top quality pilots will not be a problem!
Refuelling And Maintenance
This is said about refuelling and maintenance.
In this regard, Evia Aero’s strategy isn’t based purely on a sustainability agenda. It views the plans for refueling and maintenance as key parts of its revenue stream.
Does this mean, it will be supplying support services to other operators of zero-carbon aircraft?
It should be remembered that the business model of some companies is based heavily on a business aircraft. Will these companies change their philosophy or change the aircraft?
One company that used business jets to sell construction equipment in the past was JCB. Prospective customers would be flown to the UK for demonstrations at their test site near the factory. GEC also used to use their business jet creatively.
The Eviation Alice, which Evia Aero intend to fly, will also be available in a six-seat business configuration.
I can imagine many companies using zero-carbon business aircraft creatively and to send the right message to customers and green activists, who haven’t been friendly in the past.
Thinking about this, as I type, I think that zero-carbon business aircraft could be a significant sector of the zero-carbon aircraft market. It would also appeal to many politicians, royalty, innovative business me and women and the very rich.
In the case of King Charles, I suspect a six-seat Eviation Alice or similar based at Northolt Airport would cost less to run than the Royal Train.
Pricing
This is said on pricing.
It believes (passengers) will pay a premium to access airfields in locations across northern Europe that are not well served by road and rail links.
I’ll go with that, as many years ago, I needed to go to Stavanger for a day or so from Ipswich. So I flew Air Anglia from Norwich in a Bandeirante, rather than go from Heathrow with a change at Oslo.
Backing And Expertise
This is a paragraph from the FutureFlight article.
Evia Aero is not without expertise as it seeks to put these building blocks in place. One of its backers, Energiequelle, is involved in a business that owns and operates PV plants in Finland and Germany. Its leadership team also includes Gerd Weber, CEO of regional airline OLT, and the chair of its advisory board is Axel Trampnau, who previously ran the carrier Germania.
That seems reasonably strong.
If Energiequelle live up the mission statement on their web site, they could be particularly useful.
Hydrogen-Powered Islanders
This is said about their purchase of conversion kits for Islanders to be converted to hydrogen power.
Under current plans, the first aircraft in the Evia Aero flight will be nine-passenger Britten-Norman Islanders under a plan being advanced by Cranfield Aerospace Solutions (CAeS) to convert the piston-powered models to hydrogen propulsion. Evia Aero expects these aircraft to be ready to enter service in 2026 and has agreed to buy 15 of the conversion kits.
The Islander may have flown nearly sixty years ago, but nearly 1300 have been built and they are still being manufactured, so there should be plenty available from conversion and spare parts shouldn’t be a problem.
Cranfield Aerospace Solutions, is a spin-out of Cranfield University and the article says this about an ongoing project between CAeS and Evia Aero.
In 2022, the new airline signed a wider agreement with CAeS covering a provisional order for 10 hydrogen-powered 19-seat aircraft. The companies have not yet determined whether these would be conversions of existing aircraft or a clean-sheet design. Under the UK’s Project Fresson, CAeS is working on plans for new 19- and 75-seat zero-emissions regional airliners.
CAeS look like another serious contender in the zero-carbon airliner market.
Eviation Alice
This is said about the Eviation Alice.
Evia Aero has signed a memorandum of understanding covering provisional orders for 25 of Eviation’s nine-passenger, all-electric Alice aircraft. It expects to add the first of these to its fleet in 2028, a year after the U.S.-based manufacturer now says it aims to complete type certification, initially with the FAA.
Note.
- Alice is running two years behind the Islander.
- Certifying the Islander should be easier as it is an existing airliner.
I could see the earlier delivery and entry into service of the Islander, being used to develop the business.
Range And Routes
This is said about range and routes.
With either of these aircraft, Evia Aero will be launching its services with the equipment providing a modest payload and range. The Cranfield Islanders will be able to fly up to around 200 kilometers (109 nm), while Eviation last year reduced its range projections from 440 to 250 nm, citing the limitations of current battery technology.
Kruse accepts these limitations, while already laying plans to add subsequent 19-seat aircraft to his fleet. He showed FutureFlight route maps for both aircraft including planned destinations extending along the North Sea and Channel coasts from Denmark through Germany and the Benelux countries and into France and the UK.
- The range isn’t that long.
- It is 629 kilometres between Evia Aero’s base at Bremen and Southend.
- Schiphol is closer at 89 kilometres with Groningen at 147 kilometres.
But the interesting one is Heligoland at 139 kilometres.
Heligoland
This Google Map shows the archipelago.
Note.
- Heligoland is the island in the West.
- Düne is the island in the East.
- You can just pick out the characteristic pattern of Heligoland Airport‘s three concrete runways.
Why would anybody want to go to a rock in the North Sea?
This article on the Guardian, which is entitled Heligoland: Germany’s Hidden Gem In The North Sea, gives lots of reasons, including.
- History.
- It is a regular day trip from the German coast by ship.
- It used to be British.
- It could be at the heart of offshore wind developments.
But for German day-trippers, it’s probably the attraction of the island being duty-free.
It could be a nice little earner for an airline based in Bremen and it would be within the range of the Islanders.
A Pattern Of German Islands
This Google Map shows the German corner of the North Sea.
Note.
- The island of Heligoland at the top of the map.
- Bremen in the South-East corner of the map.
- The string of islands along the German and Dutch coasts.
- The red area marks out the most-Easterly island of Wangerooge.
This Google Map shows Wangerooge in detail.
Flugplatz Wangerooge is in the South-East corner of the map.
- It has an 850 metre asphalt runway.
- The island appears to have a sizeable beach.
- The island has a population of around 1200.
The Wikipedia entry for Wangerooge says this about the character of the island.
In order to guarantee a relaxed atmosphere, cars are prohibited on the island. The island can be reached by ship from Harlesiel, or it can be reached by plane via its airfield, regular service being offered from Harlesiel, Bremen, or Hamburg. The ferries leave at different times every day according to the tide. As on most East Frisian Islands, a small narrow gauge railway line, the Wangerooge Island Railway, connects the harbor to the main village.
The Wikipedia entry, for the Wangerooge Island Railway gives a lot of detail about what looks to be a fascinating railway, including this opening paragraph.
The single track Wangerooge Island Railway (Wangerooger Inselbahn) is an unelectrified narrow gauge railway with a track gauge of 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) located on the East Frisian island of Wangerooge off the northwestern coast of Germany. It is the most important means of transport on the island and is the only narrow gauge railway operated today by the Deutsche Bahn.
I must visit next time, I go to Hamburg.
Working towards the West the next airfield, I can find is on Langeoog, which is shown in this Google Map.
Flugplatz Langeoog is marked by the blue arrow towards the South-East corner of the map.
Working towards the West the next airfield, I can find is on Nordeney, which is shown on this Google Map.
Flughaven Nordeney is at the bottom of the map.
It has a 1000 metre runway and judging by the planes on the map, it is very busy.
Continuing West brings me to the Eastern end of the island of Juist, which is shown on this Google Map.
Flugplatz Juist is indicated the rightmost blue arrow. This extract from the Wikipedia entry, illustrates the importance of this airfield.
As of 2013, the airfield had up to 500 takeoffs and landings on weekends, the second most aircraft movements in the state of Lower Saxony, after Hannover Airport. The airfield is a critical piece of infrastructure for the island, due to ferry traffic being dependent on the tides.
The airfield was also the first on the East Frisian Islands to have a paved runway
Continuing West brings me to Borkum, which is shown on this Google Map.
Note.
Borkum Airport is in the Eastern half of the map.
- It has a 1000 metre asphalt runway.
- Borkum has a population of around 5000.
On this brief exploration of the German East Frisian Islands, I have been surprised to find five airfields; Borkum, Juist, Langeoog, Nordeney and Wangerooge.
- All seem to have asphalt or concrete runways.
- Were these runways built as part of a plan to improve transport to the islands, as it appears the tides make the ferries a bit variable?
It also appears that the islands are totally or at least partially car-free.
On one island I noticed that the taxis are horse-drawn carriages.
So does this all fit well with the philosophy of Evia Aero of flying zero-carbon aircraft?
I suspect it does.
I also think, that Evia Aero’s thinking has been influenced by recent events in the area, which I talked about in From Groningen To Leer By Train.
- To put it simply, a freighter called the Emsmoon, demolished the Freisenbrücke, which carries the Groningen and Bremen railway over the River Ems.
- Zero-carbon aircraft flying between Groningen and Bremen would be a viable and quicker and more comfortable alternative to the bus I took.
I wonder if Evia Aero are planning a service between Groningen and Bremen.
- Groningen and Bremen is 147 kilometres.
- Islanders can cruise at 240 kph.
- The service could call at the five intermediate airports.
- I would reckon, that the service would take about an hour between Groningen and Bremen.
- The aircraft would be refuelled at Groningen and Bremen.
- I am fairly certain that two planes could run an hourly service.
I also suspect that the ticketing could be run by an app and if there were no passengers wanting to get on or off at an intermediate stop, then the plane would continue to the next stop, which would save fuel. If a passenger missed a plane, there would be only a wait of an hour until the next one.
Get this right and if it proves successful, then extra services could be added, to create a true Turn-Up-And-Go air service.
Landing And Take-Off Performance
This is a paragraph from the FutureFlight article.
Both the Islander and the Alice offer short takeoff and landing performance that will allow them to get in and out via limited runways in small communities. In the case of the Islander, which has been in service for several decades, it will even be able to operate from grass landing strips.
Every little helps.
Islanders can also use sand runways, as they do at Barra.
Refueling The Islanders
This image of the hydrogen-powered Islander was clipped from the Cranfield Aerospace Solutions’ home page.
Consider.
- Many years ago, I had fun with a farmer friend moving a lot of apples in boxes, that were destined for Aspall Cyder with his forklift. The machine was powered by gas in a cylinder strapped horizontally behind the driver.
- We ran out of gas halfway through and it was a simple matter of disconnecting the bottle and connecting another.
- Drop tanks have been used in military aircraft for almost a hundred years.
- Universal Hydrogen refuels its hydrogen-powered aircraft by changing a fuel capsule.
Look at the above picture and note the two green cylinders under the wings.
- Could they be two hydrogen tanks for the aircraft?
- They appear to have some aerodynamic features. Could this reduce drag, but increase lift?
- Could they be cylinders for the hydrogen fuel?
- If they are fuel cylinders, is it possible for one or two people and/or possibly a special truck to easily swap an empty one for a full one?
Fast refuelling would allow the aircraft to work hard.
Connecting To Major Hubs
My proposed East Frisian Islands service, only connects to Groningen and Bremen on the mainland.
- Schiphol and Groningen Airports are only 93 kilometres apart.
- Bremen and Hamburg Airports are only 103 kilometres apart.
After refuelling, flying on without a change of plane to a major hub would be possible.
Channel Hops
This is said about range.
With either of these aircraft, Evia Aero will be launching its services with the equipment providing a modest payload and range. The Cranfield Islanders will be able to fly up to around 200 kilometers (109 nm), while Eviation last year reduced its range projections from 440 to 250 nm, citing the limitations of current battery technology.
The only hops, I can find less than two hundred kilometres are.
- Calais and Manston – 61 kilometres
- Calais and Lydd – 71 kilometres
- Calais and Southend – 111 kilometres
- Le Touquet and Lydd – 69 kilometres
- Le Touquet and Manston – 94 kilometres
- Le Touquet and Southend – 134 kilometres
- Ostend and Manston – 107 kilometres
- Ostend and Lydd – 138 kilometres
- Ostend and Southend – 210 kilometres
- Cherbourg and Southampton – 147 kilometres
Note.
- Manston and Southend are probably the two best British airports, as they have or will have a rail connection.
- Only Le Touquet has a railway station close to the airport on the European side.
I do suspect, that Eurostar could kill channel-hopping, by adding extra services.
Possible Markets
The methodology developed at Bremen, could probably be applied to other services around Europe and the wider world.
This is a paragraph from the FutureFlight article.
Evia Aero, which Kruse said is already in talks with as many as 30 regional airports about possible air services, is also eyeing the Nordic countries, the UK’s islands, and parts of southern Germany as target markets. Norway with its mountainous coastline seems a promising early adopter for short flights in net zero aircraft, not least because the country’s government plans to ban conventional aircraft on domestic routes from 2030.
The low noise of the electric aircraft might make them acceptable, where other aircraft have been rejected in the past.
Conclusion
T think Evia Aero plans are sound, but I do wonder whether the freighter trashing the railway got Florian Kruse and his friends thinking.
Extending The Elizabeth Line – Toilets On A Service Between Heathrow And Southend Airports
The Wikipedia entry for Crossrail, has a section about an extension to Southend Airport, where this is said.
Stobart Aviation, the company that operates Southend Airport in Essex, has proposed that Crossrail should be extended beyond Shenfield along the Shenfield–Southend line to serve Southend Airport and Southend Victoria. The company has suggested that a direct Heathrow-Southend link could alleviate capacity problems at Heathrow. The extension proposal has been supported by Southend-on-Sea City Council.
I think there could be a big problem, in that I estimate the journey will take a few minutes short of two hours. Surely, this will mean toilets will need to be fitted.
Extending The Elizabeth Line – An Extension To Southend Airport
The Wikipedia entry for Crossrail, has a section for an extension to Southend Airport, where this is said.
Stobart Aviation, the company that operates Southend Airport in Essex, has proposed that Crossrail should be extended beyond Shenfield along the Shenfield–Southend line to serve Southend Airport and Southend Victoria. The company has suggested that a direct Heathrow-Southend link could alleviate capacity problems at Heathrow. The extension proposal has been supported by Southend-on-Sea City Council.
I have written about extending Crossrail to Southend before in Council Launches Campaign To Extend Crossrail To Southend-on-Sea.
In that post, I gave these reasons.
- Extra capacity between London and Southend
- A more intensive service to Southend Airport
- A twenty-four hour service to Southend Airport
- Enabling housing
- Taking pressure from Liverpool Street
I came to the conclusion, that extending the Elizabeth Line to Southend could have a lot going for it.
Times Change
But that post was written nearly four years ago and times change and they will change more in the next few years.
The Elizabeth Line Trains Are Shorter Than The Liverpool Street And Southend Victoria Trains
This has also happened and the pair of five-car Class 720 trains, that Greater Anglia use for Southend Victoria services are over thirty metres longer than the Elizabeth Line’s nine-car Class 345 trains.
This would mean that there would be no need for platform lengthening along the route to Southend Victoria.
Zero-Carbon Aircraft Are Under Development
Zero-carbon aircraft like the Heart Aerospace ES-19 could be in service by 2027. These aircraft will probably have a limited range of around 400 km and a charge time of 40 minutes.
- Southend Airport’s position on the East side of London would enable the creation of zero-carbon flights to places like Amsterdam, Brussels, Lille, Paris and Rotterdam.
- A quick estimate indicates that aircraft like the ES-19 could fly from Southend to Amsterdam and recharge in around two hours.
- Intensively scheduled, these electric aircraft could make several round trips per day.
- Would almost silent electric aircraft be able to fly twenty-four hours per day?
These flights could seriously increase the number of passengers to Southend Airport before the end of the decade.
More Housing
I think more housing will be built between Shenfield and Southend, which will increase the need for more services past Shenfield.
The Great Eastern Main Line Will Have Full Digital Signalling
More and more trains will be running on the Great Eastern Main Line and like other main lines in the UK, it will receive full digital signalling, which would probably be applied to the Shenfield and Southend Line.
This would give the extra capacity to Southend Victoria, that running the Elizabeth Line to Southend Airport and Southend Victoria would need.
Possible Services
I think there are two main possible options, but there may be others.
- A long Elizabeth Line extension all the way to Southend Victoria.
- A short Elizabeth Line extension only as far as Southend Airport.
My feelings are as follows.
- The Greater Anglia service should remain as it is with three trains per hour (tph) calling at all stations to Shenfield, Stratford and Liverpool Street.
- Perhaps three or four Elizabeth Line tph would extend to Southend Victoria, calling at all stations.
- All Elizabeth Line trains would call at all stations to and from London, as they do now!
Full digital signalling would handle the extra trains.
Conclusion
I think it will be unlikely that the Elizabeth Line will be extended to Southend in the next few years, but before the end of the decade, I can certainly see limited Elizabeth Line services going all the way to Southend Victoria.
Opinion: Why Aviation Needs to Go Green, and How
The title of this post is the same as that of this article on Aeronautics Online.
Read the article and especially what it says about the Wright Electric Jet.
This is a paragraph from Wikipedia, talking about co-operation between Wright Electric and easyJet.
In September 2017, UK budget carrier EasyJet announced it was developing an electric 180-seater for 2027 with Wright Electric. Wright Electric built a two-seat proof-of-concept with 272kg (600lb) of batteries, and believes that batteries can be scaled up with substantially lighter new battery chemistries: a 291 nautical mile (540km) range would suffice for 20% of Easyjet passengers. Wright Electric plans to develop a 10-seater and eventually an at least 120 passengers single-aisle, short-haul airliner and targets 50% lower noise and 10% lower costs.
I would assume, that the plane also emits a lot less CO2 and other pollutants.
I would assume that the plane will be built by using the best of these technologies.
- Aerodynamics
- Lightweight structures
- Electric Motors
- Batteries
- Electronics and avionics.
But I also believe that designing an electric aircraft could be a very different process to a conventional one.
There Is No Fuel
Consider.
- Fuel is a high proportion of the weight of an airliner on take-off.
- There are a lot of complicated systems to pump fuel to the engines and also from tank to tank to trim or balance the aircraft
- When a conventional airliner takes off, it is much heavier than when it lands, as fuel has been burned.
- Fuel is dangerous in a heavy landing or crash.
On the other hand, I’m fairly certain, that empty batteries and full ones weigh the same.
This would mean, that the plane aerodynamics and structure, would be designed to be optimal in the various phases of flight.
- Taxiing out to the runway.
- Taking off.
- The climb to the cruising altitude.
- The cruise
- The descent to the destination airport.
- The landing
- Taxiing in to the terminal or stand.
In the climb, cruise and descent phases power would be set and the trim adjusted, by the autopilot to attain the right speed and rate of climb or descent.
Aerodynamics
As the weight of the aircraft would be the same in all three phases and would need more or less the same lift, with clever aerodynamics, I think we will see a very simple wing. In fact, probably more like that of a sailplane than an airliner.
Wikipedia says this about the design.
The aircraft is to run on batteries and handle flights of under 300 miles. It will feature high aspect-ratio wings for energy efficient flight, distributed electric propulsion and swappable battery packs with advanced cell chemistry.
Note that sailplanes have high aspect ratio wings.
Compared to say a small jet airliner like an Airbus A318, I suspect that the wings will be longer, but possibly simpler.
The Wright Electric Jet will probably have various aerodynamic aids, like flaps and winglets. In fact the picture on Wikipedia shows the latter, which reduce drag.
A Simple Flight Profile
The fastest way to fly between A and B is probably to take off and climb as fast as possible to the optimum cruising altitude, where an optimum cruise is maintained, until the time comes to descend into the destination airport. Much of the descent would be straight in to the runway.
I have flown in an easyJet Airbus 320 from Schipol to Southend in much this manner and the plane arrived ahead of schedule.
I suspect that easyJet like to fly like this, as it saves fuel, but Air Traffic Control probably doesn’t allow it that often.
But simple efficient profiles like this would be ideal for electric aircraft.
If as I suspect their aerodynamics would allow a better glide ratio than a jet powered airliner. So to get a longer range, an electric aircraft might do a long approach.
A Low Noise Aircraft
As I said earlier, Wright are talking about fifty percent less noise.
This could be a game-changer for a smaller airport like Luton or Southend, where the approach can be over residential areas.
Especially for Southend, where planes from the East could do a long descent over the sea and come straight in on Runway 23.
Could Southend become London’s short-haul airport for electric aircraft?
- easyJet and Ryanair are already there.
- There’s plenty of wind power in the area
- It has a good rail connection to London and could be served by Crossrail.
Essex is a county that likes to be different.
Airbus
The original article also mentions Airbus.
Airbus has the skills to design the required light and strong airframe, the aerodynamic knowledge.and a large support network.
They also have a lot to lose, if someone else takes away, the smaller part of their masrket.
Ignore Airbus at your peril.
Conclusion
The more I think about it, the more that I think a 120 passenger electric airliner with a range of 540 km, could be a very handy plane.