Great Yarmouth Terminal Set For Redevelopment Under Port Of East Anglia Name
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s Peel Ports Group has decided to invest a further GBP 10 million (approximately EUR 11.3 million) into its Great Yarmouth site, which is being rebranded as the Port of East Anglia.
These four paragraphs add details to the story.
The newly announced GBP 10 million brings this year’s total investment to GBP 70 million across the site and will be used to redevelop the port’s Northern Terminal, helping to accommodate the next generation of offshore wind projects across the region, according to Peel Ports.
Earlier this year, a substantial investment into its Southern Terminal was announced by the port, which has earmarked GBP 60 million to transform capacity and improve efficiencies.
This involves ensuring the port can support multiple hydrogen, carbon capture, offshore wind, and nuclear projects for decades to come.
Its existing terminals service a variety of construction customers, including infrastructure projects such as Sizewell C and offshore energy projects based in the southern North Sea.
Note.
- In Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project, I talk about the work to be done on the Southern Terminal.
- The work on the Southern Terminal includes a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
- Start on the work on the Southern Terminal will start in 2026.
With all the construction work mentioned in the last two paragraphs, I suspect that the Port of Great Yarmouth will be busy?
These are some further thoughts.
Why Is The Port Of Great Yarmouth Being Renamed?
The article says this.
The new name, which will come into effect in early 2026, also aligns with the creation of a new combined authority for Suffolk and Norfolk, according to Peel Ports.
Peel Ports name change is fairly sensible, but as I was conceived in Suffolk and I’m an Ipswich Town supporter, I don’t feel that the two counties should be merged.
Does The Mention Of Hydrogen Mean That The Port Of Great Yarmouth Will Be Hosting A Hydrogen Electrolyser, To Fuel Trucks And Ships?
I asked Google AI, “If A Hydrogen Electrolyser is To Be Built In The Port Of Great Yarmouth?”, and received this answer.
While there are no current public plans for an immediate construction of a large-scale hydrogen electrolyser within the Port of Great Yarmouth, significant port expansion and infrastructure upgrades are underway to ensure it can support future hydrogen projects and related clean energy initiatives.
Note.
- If technology to handle hydrogen, is copied from North Sea gas, there is certainly a lot of proven technology that can be used again.
- There may even be depleted gas fields, where captured carbon dioxide, hydrogen or North Sea gas can be stored.
I find the most exciting thing, would be to send hydrogen to Germany.
Why Would Anybody Export Hydrogen To Germany?
I asked Google AI, the question in the title of this section and received this answer.
Countries would export hydrogen to Germany because Germany has a large, growing demand for hydrogen to power its heavily industrialised economy and achieve its decarbonisation goals, but lacks sufficient domestic renewable energy capacity to produce the required amounts.
Germany also, uses a lot of bloodstained Russian gas and indigenous polluting coal.
How Could Anybody Export Hydrogen To Germany?
- Wilhelmshaven is one of the main import ports for hydrogen in North West Germany.
- Great Yarmouth is probably the closest larger port to Germany.
- Great Yarmouth and Wilhelmshaven are probably about 300 miles apart, by the shortest route.
- Great Yarmouth would need to build infrastructure to export hydrogen.
The easiest way to transport the hydrogen from Great Yarmouth to Wilhelmshaven, is probably to use a gas tanker built especially for the route.
This Google Map shows the route between Great Yarmouth and Wilhelmshaven.
Note.
- The North-East corner of East Anglia with Great Yarmouth to the North of Lowestoft, is in the bottom-left corner of the map.
- Wilhelmshaven is a few miles inland in the top-right corner of the map.
- Could a coastal tanker go along the Dutch and German coasts to Wilhelmshaven?
I have no skills in boats, but would Great Yarmouth to Wilhelmshaven to take hydrogen to Germany?
RWE Are Developing Three Wind Farms To The North-East of Great Yarmouth
RWE are a large German Electricity company and the UK’s largest generator of electricity.
The company is developing three wind farms to the North-East of Great Yarmouth.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1.2 GW – 45 miles offshore
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1.2 GW – 29 miles offshore
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1.2 GW – 28 miles offshore
Note.
- The electricity for all three wind farms is to be brought ashore at Happisburgh South, which is about 22 miles North of Great Yarmouth.
- The original plan was to take the electricity halfway across Norfolk to the Necton substation to connect to the grid.
- The natives will not be happy about a 4.2 GW overhead line between Happisburgh and Necton.
- RWE have built offshore electrolysers before in German waters.
- Could an electrical cable or a hydrogen pipe be laid in the sea between Happisburgh South and the Port of Great Yarmouth?
- The electrolyser could either be offshore at Happisburgh or onshore in the Port of Great Yarmouth.
As I don’t suspect these three wind farms will be the last connected to the Port of Great Yarmouth, I would expect that RWE will put the electrolyser offshore at Happisburgh and connect it by a hydrogen pipeline to the Port of Great Yarmouth.
Could There Be A Connection To The Bacton Gas Terminal?
Consider.
The Bacton Gas Terminal, which feeds gas into the UK Gas Network, is only 4.2 miles up the coast from Happisburgh South.
Some climate scientists advocate blending hydrogen into the gas supply to reduce carbon emissions.
In Better Than A Kick In The Teeth – As C Would Say!, I disclosed that I now have a new hydrogen-ready boiler, so I’m not bothered, if I get changed to a hydrogen blend.
So could hydrogen from the Norfolk wind farms be fed into the grid to reduce carbon emissions?
Could The Port Of Great Yarmouth Become A Hydrogen Distribution Centre?
Thinking about it, the port could also become a distribution centre for green hydrogen.
Consider.
- Hydrogen-powered ships, tugs and workboats could be refuelled.
- Hydrogen-powered trucks could also be refuelled.
- Tanker-trucks could distribute hydrogen, to truck and bus operators, farms and factories, that need it for their transport and operations.
- I believe, that construction equipment will be increasingly hydrogen-powered.
In my life, I have lived at times in two country houses, that were heated by propane and there are about 200,000 off-grid houses in the UK, that are heated this way.
The two houses, where I lived would have been a nightmare to convert to heat pumps, but it would have been very easy to convert them to a hydrogen boiler and power it from a tank in the garden.
It should be noted, that the new boiler in my house in London is hydrogen-ready.
So the Port of Great Yarmouth could be the major centre for hydrogen distribution in Norfolk.
In the 1960s, I used to work in ICI’s hydrogen plant at Runcorn. If you ride in a hydrogen bus in England, it is likely that the hydrogen came from the same plant. Handled correctly, hydrogen is no less safe and reliable than natural gas or propane.
US Floating Wind Platform Developer Issues RFI To Fabricators Worldwide
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Aikido Technologies, which recently secured a spot at a Norwegian offshore demo site, has released an RFI for its 15 MW ‘AO60’ floating wind platform to offshore wind fabricators.
These are the first four paragraphs which add more details.
The California-based floating wind foundation developer said on social media that it had issued the RFI to more than ten “top-tier offshore wind fabricators from around the world”.
The RFI has been released in three separate packages, each tailored to a specific type of facility: one for standard offshore steel shops, one for tubular/jacket yards, and one for monopile/tower facilities.
“This is how we can build 1, 50 or 100 of these units with existing fabrication capabilities, with components that can be easily transported around the world for final assembly at a local port. No need for custom yards, custom vessels or custom ports”, Aikido Technologies said.
In May 2025, the company was allocated a slot for its AO60 platform at the Marine Energy Test Centre (METCentre) in Norway, where Aikido will deploy what it says is a first-of-its-kind 15 MW demonstration project.
As someone, who wrote project management computer systems for thirty years, I like Aikido’s plans and feel they would be well suited to the UK, where we have quite a few local ports, that would appear suitable for final assembly of the A060 platforms.
In Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project, I describe the expansion of the Port of Great Yarmouth.
These two paragraphs describe the work to be done.
Peel Ports said it would invest between £50m and £60m in Great Yarmouth’s Outer Harbour by developing the southern terminal, creating a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
Port director Richard Goffin said the construction work, which is set to begin in 2026, would “complete” the port as laid out in a business case in the early 2000s.
This image from Peel Ports Group shows how the Port of Great Yarmouth will look after the the proposed development.
As the Port of Great Yarmouth has a depth of ten metres it could be an ideal base for the assembly and maintenance of floating wind turbines.
Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is the sub-heading.
A major port is set to expand to prepare for construction work linked to several national infrastructure projects.
These first two paragraphs, which give more details.
Peel Ports said it would invest between £50m and £60m in Great Yarmouth’s Outer Harbour by developing the southern terminal, creating a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
Port director Richard Goffin said the construction work, which is set to begin in 2026, would “complete” the port as laid out in a business case in the early 2000s.
This image from Peel Ports Group shows how the Port of Great Yarmouth will look after the the proposed development.
And this Google Map shows the port as it is today.
Note.
- The large triple shed, with the cross-wise middle section can be picked out in both the image and the map.
- The label by the shed says Origin Fertilisers, so I suspect the three objects on the quayside, which are visible in both the image and the map could be conveyors for loading and unloading ships with fertiliser.
- The two breakwaters are visible in both the image and the map.
It looks like the development would mainly involve filling in the Southern part of the current harbour.
With only a quick look and scant details, it looks to me, that it is a development that could be easily realised.
I have some thoughts.
Rail Access To The Port
There is no rail access to the port and I couldn’t see how it could be provided, without demolishing half of the town.
But there are carriage sidings at Great Yarmouth station, which are described in this Wikipedia entry like this.
New sidings were provided at the western end of the station to cope with the additional services operating into the station, following the closure of the M&GN system. It is a crescent-shaped site between the A47 road and Wherryman’s Way at the northernmost point of the River Yare, about 1⁄4 mi (400 m) north-west of the station. It had fallen out of use in the 1980s when Norwich Crown Point depot was built.
In 2010, the unused sidings were purchased by Great Yarmouth Borough Council; they were intended for use as a freight terminal, despite the lack of rail connection to the town’s port. It was hoped that 10,000 tonnes of sugar cane per week would be carried from Yarmouth to Cantley. The need to use a lorry shuttle between the docks and the rail yard, along with a £3.2 million quote for replacing the sidings at Cantley, saw the plan dropped.[19]
In May 2020, Eastern Rail Services commenced a lease with Norfolk County Council and Network Rail for Yarmouth Vauxhall sidings. Managing director James Steward said the siding “matched ERS’s requirement for an East Anglian site to base its rolling stock.” Following extensive de-vegetation works, Direct Rail Services 37402 became the first locomotive in 19 years to run into the sidings on 26 May 2020, followed the next day by it delivering five former Greater Anglia Mark 3 coaches for storage. On 6 July 2020, ERS was authorised a licence exemption permitting them to operate trains within the site
The Port of Great Yarmouth appears to be keen to do its part in the construction of Sizewell C. Could components for the power station, be brought into the port through the new roll-on/roll-off berth and then transferred to rail in the former carriage sidings?
This 3D Google Map shows the carriage sidings.
Most of the rolling stock appears to be retired Mark 2 and M3 coaches.
Road Access To The Port
This Google Map shows Great Yarmouth and the Port and roads in the area.
Note.
- The red arrow indicates Great Yarmouth station.
- The Port of Great Yarmouth is in the South-East corner of the map.
- The A 47 runs down the West side of the town.
- The River Yare runs from the railway station to the sea, just below the port.
There is a road on the East bank of the River Yare, that connects to the A 47 and could easily connect to a rail cargo terminal to the North-West of the station in the derelict carriage sidings.
I can certainly see Nimbies not liking the new roll-on/roll-off ferry creating traffic in the town.
The Construction Of Sizewell C
Sizewell C is very similar to Hinckley Point C and this extract from the Wikipedia entry for Hinckley Point C describes some of that power station’s construction.
In March 2017, EDF, after the Office for Nuclear Regulation (ONR) gave approval to start building, the building of the first parts of the plant proper began with a network of tunnels to carry cabling and piping. Work was also under way on a jetty to land building materials, a seawall, and accommodation blocks.
In January 2018, EDF said that they were on track to start generating electricity by 2025 and that they planned to start constructing above-ground structures for the power station by June 2019.
The approximate 2,000 cubic metres (71,000 cu ft) concrete pour for the first reactor started on 11 December 2018. It was completed over a 30-hour period, creating the first part of the unit one 4,500 tonne base, a platform 3.2 metres (10 ft 6 in) thick. The reactor building will be built on the (to be completed) platform. This construction start marks the first new reactor build in the UK after a 30-year break, and the second PWR in the UK, after Sizewell B.
Completion of the base for the first reactor, the final 8,954 cubic metres (316,200 cu ft) of concrete, was achieved in June 2019. Completion of the base for the second reactor, 8,991 cubic metres (317,500 cu ft) of concrete, was achieved in June 2020.
Construction utilises the world’s largest crane, the Sarens SGC-250 double ring crane, which is responsible for lifting Hinkley Point C’s heaviest components. More than 600 heavy fabrications, including the five major parts of each unit’s steel containment liner and dome, are positioned by the SGC-250. The crane, named Big Carl, was delivered in modular form, consisting of over 400 deliveries.
In February 2023, the first nuclear reactor pressure vessel was delivered to site via the Bristol Channel Hinkley-dedicated wharf at Combwich. The pressure vessel was built in France in 2022 by Framatome.
In May 2024, the first of the 520 tonne steam generators was delivered to site in the same manner as the reactor pressure vessel.
Note.
- A good proportion of the power station and the materials to build it were brought in by sea.
- The size of everything is huge.
- Big Carl seems to make appearances in all big projects.
- According to the BBC, Peel Ports are spending £60million on a new roll-on/roll-off terminal, 350 metres of quay and ten hectares of high quality storage space.
I wouldn’t be surprised, if they have the contract for Sizewell C’s logistics, that Peel Ports will be laughing all the way to the bank.
If nothing else, after Sizewell C is completed, they will have a high-class port facility at the end of the A 47 from Birmingham, Leicester, Peterborough and Norwich, which could open up possible ferry routes to Europe.
Between Great Yarmouth And Sizewell
If the components come in to Great Yarmouth on trailers on the RORO ferries from France, they could be taken to Sizewell on the A 12 road.
Smaller components may be taken by road, but I wouldn’t rule out a transfer to rail in the carriage sidings at Great Yarmough, as I indicated earlier.
Centrica Really Can’t Lose At Sizewell
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article in The Times.
This is the sub-heading.
Centrica’s £1.3 billion investment in Sizewell C guarantees substantial returns, even with cost overruns.
These two-and-a-half paragraphs explain the funding.
Now we know what Ed Miliband means by his “golden age of nuclear” — golden for the companies putting their money into Sizewell C. Yes, reactor projects have a habit of blowing up private investors. But maybe not this one. It looks more like an exercise in transferring risk to consumers and the taxpayer.
Sure, nobody builds a £38 billion nuke on a Suffolk flood plain without a frisson of danger. But the energy secretary and his Treasury chums have done their bit to make things as safe as possible for the companies putting in equity alongside the government’s 44.9 per cent stake: Canada’s La Caisse with 20 per cent, British Gas-owner Centrica (15 per cent), France’s EDF (12.5 per cent) and Amber Infrastructure (7.6 per cent).
For starters, nearly all the debt for the 3.2 gigawatt plant, three-quarters funded by loans, is coming from the state-backed National Wealth Fund. It’s bunging in up to £36.6 billion, with £5 billion more guaranteed by a French export credit agency.
It looks to me that between them the British and French governments are providing £41.5 billion of loans to build the £38 billion nuke.
These are my thoughts.
Hydrogen And Sizewell C
This page on the Sizewell C web site is entitled Hydrogen And Sizewell C.
Under a heading of Hydrogen Buses, this is said.
At Sizewell C, we are exploring how we can produce and use hydrogen in several ways. We are working with Wrightbus on a pilot scheme which, if successful, could see thousands of workers transported to and from site on hydrogen double decker buses. You can read more about the pilot scheme in our press release
Firstly, it could help lower emissions during construction of the power station. Secondly, once Sizewell C is operational, we hope to use some of the heat it generates (alongside electricity) to make hydrogen more efficiently.
This would appear to be a more general statement about hydrogen and that the following is planned.
- Hydrogen-powered buses will be used to bring workers to the site. A press release on the Sizewell C web site, talks about up to 150 buses. That would probably be enough buses for all of Suffolk.
- Hydrogen-powered construction equipment will be used in the building of the power station.
- It also talks about using the excess heat from the power station to make hydrogen more efficiently. I talk about this process in Westinghouse And Bloom Energy To Team Up For Pink Hydrogen.
This is a substantial investment in hydrogen.
Centrica And Electricity From Sizewell C
The article in The Times, also says this.
Even so, there’s a fair bit of protection for the likes of Centrica, which has also agreed a 20-year offtake deal for its share of Sizewell’s electricity. The price of that is not yet known.
Nothing is said in the article about the size of Centrica’s electricity offtake.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell C, that would by 480 MW.
- If they get 15 % of Sizewell B + C, that would by 660 MW.
If they use their share to generate hydrogen, Suffolk would have a massive hydrogen hub.
To power the buses and construction of Sizewell C, Sizewell B could be used to provide electricity to create the hydrogen.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Produced?
Centrica, along with other companies, who include Hyundai and Kia, are backers of a company in Hull called HiiROC, who use a process called Thermal Plasma Electrolysis to generate hydrogen.
On their web site, they have this sub-heading.
A Transformational New Process For Affordable Clean Hydrogen
The web site also describes the process as scalable from small modular units up to industrial scale. It also says this about the costs of the system: As cheap as SMR without needing CCUS; a fraction of the energy/cost of water electrolysis.
If HiiROC have achieved their objective of scalability, then Centrica could grow their electrolyser to meet demand.
How Would The Hydrogen Be Distributed?
Consider.
- Currently, the Sizewell site has both road and rail access.
- I can still see in my mind from the 1960s, ICI’s specialist articulated Foden trucks lined up in the yard at Runcorn, taking on their cargoes of hydrogen for delivery all over the country.
- As that factory is still producing hydrogen and I can’t remember any accidents in the last sixty years, I am fairly sure that a range of suitable hydrogen trucks could be developed to deliver hydrogen by road.
- The road network to the Siewell site is being updated to ensure smooth delivery of workers and materials.
- The rail access to the Sizewell site is also being improved, for the delivery of bulk materials.
I believe there will be no problems delivering hydrogen from the Sizewell site.
I also believe that there could be scope for a special-purpose self-propelled hydrogen tanker train, which could both distribute and supply the hydrogen to the vehicles, locomotives and equipment that will be using it.
Where Will The Hydrogen Be Used?
I have lived a large part of my life in Suffolk and know the county well.
In my childhood, there was quite a lot of heavy industry, but now that has all gone and employment is based on agriculture, the Port of Felixstowe and service industries.
I can see hydrogen being used in the following industries.
Transport
Buses and heavy trucks would be powered by hydrogen.
The ports in the East of England support a large number of heavy trucks.
Large Construction Projects
Sizewell C is not the only large construction project in the East of England, that is aiming to use low-carbon construction involving hydrogen. In Gallagher Group Host Hydrogen Fuel Trial At Hermitage Quarry, I talked about a hydrogen fuel trial for the Lower Thames Crossing, that involved JCB and Ryse Hydrogen.
Hydrogen for the Lower Thames Crossing could be delivered from Sizewell by truck, down the A12.
Rail
We may not ever see hydrogen-powered passenger trains in this country, but I do believe that we could see hydrogen-powered freight locomotives.
Consider.
- The latest electro-diesel Class 99 locomotives from Stadler have a Cummins diesel engine.
- The diesel engine is used, when there is no electrification.
- Cummins have developed the technology, that allows them to convert their latest diesel engines to hydrogen or natural gas power, by changing the cylinder head and the fuel system.
- Access to the Port of Felixstowe and London Gateway needs a locomotive with a self-powered capability for the last few miles of the route.
A Class 99 locomotive converted to hydrogen would be able to run with out emitting any carbon dioxide from Felixstowe or London Gateway to Glasgow or Edinburgh.
Ports
Ports have three main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for port workers.
- To fuel ships of all sizes from the humblest work-boat to the largest container ships.
- There may need to be fuel for hydrogen-powered rail locomotives in the future.
There are seven ports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth, Harwich, Ipswich, London Gateway, Lowestoft and Tilbury.
The proposed Freeport East is also developing their own green hydrogen hub, which is described on this page on the Freeport East web site.
Airports
Airports have two main uses for hydrogen.
- To power ground-handing equipment, to create a pollution-free atmosphere for airport workers.
- In the future, there is likely to be hydrogen-powered aircraft.
There are three airports with excellent road and/or rail connections to the Sizewell site; Norwich, Southend and Stansted.
Agriculture And The Rural Economy
Agriculture and the rural economy would be difficult to decarbonise.
Consider.
- Currently, most farms would use diesel power for tractors and agricultural equipment, which is delivered by truck.
- Many rural properties are heated by propane or fuel oil, which is delivered by truck.
- Some high-energy rural businesses like blacksmiths rely on propane, which is delivered by truck.
- Electrification could be possible for some applications, but ploughing the heavy land of Suffolk, with the added weight of a battery on the tractor, would probably be a mathematical impossibility.
- JCB are developing hydrogen-powered construction equipment and already make tractors.
- Hydrogen could be delivered by truck to farms and rural properties.
- Many boilers can be converted from propoane to run on hydrogen.
I feel, that hydrogen could be the ideal fuel to decarbonise agriculture and the rural economy.
I cover this application in detail in Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network.
Exports
Consider.
- Sizewell B and Sizewell C nuclear powerstations have a combined output of 4.4 GW.
- A rough calculation shows that there is a total of 7.2 GW of wind farms planned off the Suffolk coast.
- The East Anglian Array wind farm alone is said in Wikipedia to be planned to expand to 7.2 GW.
- The Sizewell site has a high capacity connection to the National Grid.
Nuclear plus wind should keep the lights on in the East of England.
Any excess electricity could be converted into hydrogen.
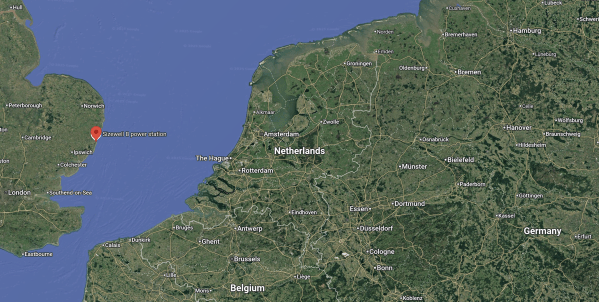
This Google Map shows the location of Sizewell B in relation to Belgium, Germany and The Netherlands.
The Sizewell site is indicated by the red arrow.
The offshore oil and gas industry has used technology like single buoy moorings and coastal tankers to collect offshore natural gas for decades.
I don’t see why coastal hydrogen tankers couldn’t export excess hydrogen to places around the North Sea, who need the fuel.
It should be born in mind, that Centrica have a good reputation in doing natural gas trading. This expertise would surely be useful in hydrogen trading.
Conclusion
I believe that a hydrogen hub developed at Sizewell makes sense and I also believe that Centrica have the skills and technology to make it work.
ScottishPower Renewables Picks Port For East Anglia Two Pre-Assembly
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
ScottishPower Renewables, Iberdrola’s UK arm, has selected Peel Ports Great Yarmouth as the staging ground for pre-assembly works for its 960 MW East Anglia Two offshore wind project.
This is the introductory paragraph.
The companies have signed a reservation agreement that will see the Siemens Gamesa turbine components and sections come together for assembly at the Norfolk site before installation in the southern North Sea in 2028.
Note.
- The Port of Great Yarmouth was used for this task with East Anglia One.
- The turbine blades will be manufactured at Siemens Gamesa’s offshore wind blade factory in Hull.
- The monopiles will come from Sif in Rotterdam.
This is the first sentence of the Wikipedia entry for the East5 Anglia Array.
The East Anglia Array is a proposed series of offshore wind farms located around 30 miles off the east coast of East Anglia, in the North Sea, England. It has begun with the currently operational East Anglia ONE, that has been developed in partnership by ScottishPower Renewables and Vattenfall. Up to six individual projects could be set up in the area with a maximum capacity of up to 7.2 GW.
These articles on offshoreWIND.biz indicate that ScottishPower Renewables has been busy signing contracts for East Anglia Two.
- December 4th, 2024 – Nexans Lands Export Cable Contract For East Anglia Two Offshore Wind Farm.
- November 28th, 2024 – Hitachi Energy to Integrate 960 MW East Anglia Two Wind Farm into UK Grid.
- November 12th, 2024 – Siemens Gamesa Bags GBP 1 Billion Turbine Contract For East Anglia Two.
- November 6th, 2024 – Seaway7 Wins East Anglia Two Inter-Array Cable Contract.
- October 31st, 2024 – Sif, Smulders to Deliver Monopiles and TPs For ScottishPower’s East Anglia Two Offshore Wind Farm.
They must have employed lawyers on roller skates to get five contracts signed in just over a month.
Conclusion
East Anglia Two appears to be definitely under way and the Wikipedia extract says there could be a lot more, if all the other wind farms are developed in the same way using the Port of Great Yarmouth.
A total capacity in the East Anglia Array of 7.2 GW will surely be good for both East Anglia and the UK as a whole, but will the natives be happy with all the onshore infrastructure?
I wouldn’t be surprised to see further wind farm developed to generate hydrogen offshore, which will be either brought ashore to the Bacton gas terminal, using existing or new pipelines or distributed using tanker ships to where it is needed.
RWE And the Norfolk Wind Farms
In March 2024, I wrote RWE And Vattenfall Complete Multi-Gigawatt Offshore Wind Transaction In UK, which described how Vattenfall had sold 4.2 GW of offshore wind farms, situated off North-East Norfolk to RWE.
This map from RWE shows the wind farms.
Note.
- The Norfolk Zone consists of three wind farms; Norfolk Vanguard West, Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard East.
- The three wind farms are 1.4 GW fixed-foundation wind farms.
- In Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base, I describe how the Port of Great Yarmouth had been selected as the O & M base.
- Great Yarmouth and nearby Lowestoft are both ports, with a long history of supporting shipbuilding and offshore engineering.
The wind farms and the operational port are all close together, which probably makes things convenient.
So why did Vattenfall sell the development rights of the three wind farms to RWE?
Too Much Wind?
East Anglia is fringed with wind farms all the way between the Wash and the Thames Estuary.
- Lincs – 270 MW
- Lynn and Inner Dowsing – 194 MW
- Race Bank – 580 MW
- Triton Knoll – 857 MW
- Sheringham Shoal – 317 MW
- Dudgeon – 402 MW
- Hornsea 3 – 2852 MW *
- Scroby Sands – 60 MW
- East Anglia One North – 800 MW *
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW *
- East Anglia Three – 1372 MW *
- Greater Gabbard – 504 MW
- Galloper – 353 MW
- Five Estuaries – 353 MW *
- North Falls – 504 MW *
- Gunfleet Sands – 172 MW
- London Array – 630 MW
Note.
- Wind farms marked with an * are under development or under construction.
- There is 4339 MW of operational wind farms between the Wash and the Thames Estuary.
- An extra 6781 MW is also under development.
If all goes well, East Anglia will have over 11 GW of operational wind farms or over 15 GW, if the three Norfolk wind farms are built.
East Anglia is noted more for its agriculture and not for its heavy industries consuming large amounts of electricity, so did Vattenfall decide, that there would be difficulties selling the electricity?
East Anglia’s Nimbies
East Anglia’s Nimbies seem to have started a campaign against new overground cables and all these new wind farms will need a large capacity increase between the main substations of the National Grid and the coast.
So did the extra costs of burying the cable make Vattenfall think twice about developing these wind farms?
East Anglia and Kent’s Interconnectors
East Anglia and Kent already has several interconnectors to Europe
- Viking Link – Bicker Fen and Jutland – 1.4 GW
- LionLink – Suffolk and the Netherlands – 1.8 GW – In Planning
- Nautilus – Suffolk or Isle of Grain and Belgium – 1.4 GW – In Planning
- BritNed – Isle of Grain and Maasvlakte – 1.0 GW
- NeuConnect – Isle of Grain and Wilhelmshaven – 1.4 GW – Under Construction
- GridLink Interconnector – Kingsnorth and Warande – 1.4 GW – Proposed
- HVDC Cross-Channel – Sellinge and Bonningues-lès-Calais – 2.0 GW
- ElecLink – Folkestone and Peuplingues – 1.0 GW
- Nemo Link – Richborough and Zeebrugge – 1.0 GW
Note.
- Five interconnectors with a capacity of 6.4 GW.
- A further four interconnectors with a capacity of 6 GW are on their way.
At 12.4 GW, the future capacity of the interconnectors between South-East England and Europe, is nor far short of South-East English wind power.
There are also two gas pipelines from the Bacton gas terminal between Cromer and Great Yarmouth to Europe.
The Wikipedia entry for the Bacton gas terminal gives these descriptions of the two gas pipelines.
Interconnector UK – This can import gas from, or export gas to, Zeebrugge, Belgium via a 235 km pipeline operating at up to 147 bar. There is a 30-inch direct access line from the SEAL pipeline. The Interconnector was commissioned in 1998.
BBL (Bacton–Balgzand line) – This receives gas from the compressor station in Anna Paulowna in the Netherlands. The BBL Pipeline is 235 km long and was commissioned in December 2006.
It would appear that East Anglia and Kent are well connected to the Benelux countries, with both electricity and gas links, but with the exception of the Viking Link, there is no connection to the Scandinavian countries.
Did this lack of connection to Sweden make convincing the Swedish government, reluctant to support Vattenfall in their plans?
Bringing The Energy From The Norfolk Wind Farms To Market
It looks to me, that distributing up to 4.2 GW from the Norfolk wind farms will not be a simple exercise.
- Other wind farms like the 2852 MW Hornsea 3 wind farm, may need a grid connection on the North Norfolk coast.
- The Nimbies will not like a South-Western route to the National Grid at the West of Norwich.
- An interconnector to Denmark or Germany from North Norfolk would probably help.
But at least there are two gas pipelines to Belgium and the Netherlands.
RWE, who now own the rights to the Norfolk wind farms, have a large amount of interests in the UK.
- RWE are the largest power producer in the UK.
- They supply 15 % of UK electricity.
- They have interest in twelve offshore wind farms in the UK. When fully-developed, they will have a capacity of almost 12 GW.
- RWE are developing the Pembroke Net Zero Centre, which includes a hydrogen electrolyser.
RWE expects to invest up to £15 billion in the UK by 2030 in new and existing green technologies and infrastructure as part of this.
Could this be RWE’s plan?
As the Norfolk wind farms are badly placed to provide electricity to the UK grid could RWE have decided to use the three Norfolk wind farms to produce hydrogen instead.
- The electrolyser could be placed onshore or offshore.
- If placed onshore, it could be placed near to the Bacton gas terminal.
- There are even depleted gas fields, where hydrogen could be stored.
How will the hydrogen be distributed and/or used?
It could be delivered by tanker ship or tanker truck to anyone who needs it.
In Developing A Rural Hydrogen Network, I describe how a rural hydrogen network could be developed, that decarbonises the countryside.
There are three major gas pipelines leading away from the Bacton gas terminal.
- The connection to the UK gas network.
- Interconnector UK to Belgium.
- BBL to The Netherlands.
These pipelines could be used to distribute hydrogen as a hydrogen blend with natural gas.
In UK – Hydrogen To Be Added To Britain’s Gas Supply By 2025, I describe the effects of adding hydrogen to the UK’s natural gas network.
Iberdrola Preparing Two East Anglia Offshore Wind Projects For UK’s Sixth CfD Round
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
ScottishPower Renewables, Iberdrola’s company in the UK, is getting the East Anglia One North and East Anglia Two offshore wind projects ready for the upcoming auction round for Contracts for Difference (CfD).
These three paragraphs give more details.
This is according to project updates Iberdrola published as part of its financial results for 2023.
Iberdrola says “good progress is being made in the key engineering and design work” for the two projects and, while they were not presented in the UK’s fifth CfD Allocation Round (AR5), preparations are being made to take part in Allocation Round 6 (AR6).
The two offshore wind farms are part of the GBP 6.5 billion (around EUR 7.6 billion) East Anglia Hub project, which also includes East Anglia Three, currently in construction and expected to start delivering electricity in 2026. The 1.4 GW East Anglia Three was awarded Contract for Difference in July 2022.
It is now possible to build a table of Iberdrola’s East Anglian Hub.
- East Anglia One – 714 MW – Commissioned in 2020.
- East Anglia One North – 800 MW – To be commissioned in 2026.
- East Anglia Two – 900 MW – To be commissioned in 2026.
- East Anglia Three – 1372 MW – To be commissioned in 2026.
Note.
- East Anglia One is the largest windfarm in Iberdrola’s history
- These four wind farms are connected to the shore at Bawdsey on the River Deben.
These wind farms are a total of 3786 MW.
In addition there are RWE’s three Norfolk wind farms.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1386 MW – To be commissioned in 2027.
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1380 MW – To be commissioned before 2030.
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1380 MW – To be commissioned before 2030.
These wind farms are a total of 4146 MW, with a grand total of 7932 MW.
What Will Happen To The Electricity?
Consider.
- It is a lot of electricity.
- The good people of Norfolk are already protesting about the cables and pylons, that will connect the electricity to the National Grid.
- The good people of Suffolk will probably follow, their Northern neighbours.
- The wind farms are owned by Spanish company; Iberdrola and German company; RWE.
I wonder, if someone will build a giant electrolyser at a convenient place on the coast and export the hydrogen to Europe by pipeline or tanker.
- The ports of Felixstowe, Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft could probably handle a gas tanker.
- The Bacton gas terminal has gas pipelines to Belgium and The Netherlands.
In addition, there are various electricity interconnectors in use or under construction, that could send electricity to Europe.
- National Grid’s Lion Link to the Netherlands.
- NeuConnect to Germany from the Isle of Grain.
Whoever is the UK’s Prime Minister in 2030 will reap the benefits of these East Anglian and Norfolk wind farms.
In addition.
- The Hornsea wind farm will have tripled in size from 2604 MW to 8000 MW.
- The Dogger Bank wind farm will have grown from 1235 MW to 8000 MW.
- There is 4200 MW of wind farms in Morecambe Bay and around England.
They would be so lucky.
RWE Acquires 4.2-Gigawatt UK Offshore Wind Development Portfolio From Vattenfall
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from RWE.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- Highly attractive portfolio of three projects at a late stage of development, with grid connections and permits secured, as well as advanced procurement of key components
- Delivery of the three Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone projects off the UK’s East Anglia coast will be part of RWE’s Growing Green investment and growth plans
- Agreed purchase price corresponds to an enterprise value of £963 million
These two paragraphs outline the deal.
RWE, one of the world’s leading offshore wind companies, will acquire the UK Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone portfolio from Vattenfall. The portfolio comprises three offshore wind development projects off the east coast of England – Norfolk Vanguard West, Norfolk Vanguard East and Norfolk Boreas.
The three projects, each with a planned capacity of 1.4 gigawatts (GW), are located 50 to 80 kilometres off the coast of Norfolk in East Anglia. This area is one of the world’s largest and most attractive areas for offshore wind. After 13 years of development, the three development projects have already secured seabed rights, grid connections, Development Consent Orders and all other key permits. The Norfolk Vanguard West and Norfolk Vanguard East projects are most advanced, having secured the procurement of most key components. The next milestone in the development of these two projects is to secure a Contract for Difference (CfD) in one of the upcoming auction rounds. RWE will resume the development of the Norfolk Boreas project, which was previously halted. All three Norfolk projects are expected to be commissioned in this decade.
There is also this handy map, which shows the location of the wind farms.
Note that there are a series of assets along the East Anglian coast, that will be useful to RWE’s Norfolk Zone development.
- In Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base, I talked about how the Port of Great Yarmouth will be the operational base for the Norfolk Zone wind farms.
- Bacton gas terminal has gas interconnectors to Belgium and the Netherlands lies between Cromer and Great Yarmouth.
- The cable to the Norfolk Zone wind farms is planned to make landfall between Bacton and Great Yarmouth.
- Sizewell is South of Lowestoft and has the 1.25 GW Sizewell B nuclear power station, with the 3.2 GW Sizewell C on its way, for more than adequate backup.
- Dotted around the Norfolk and Suffolk coast are 3.3 GW of earlier generations of wind farms, of which 1.2 GW have connections to RWE.
- The LionLink multipurpose 1.8 GW interconnector will make landfall to the North of Southwold
- There is also the East Anglian Array, which currently looks to be about 3.6 GW, that connects to the shore at Bawdsey to the South of Aldeburgh.
- For recreation, there’s Southwold.
- I can also see more wind farms squeezed in along the coast. For example, according to Wikipedia, the East Anglian Array could be increased in size to 7.2 GW.
It appears that a 15.5 GW hybrid wind/nuclear power station is being created on the North-Eastern coast of East Anglia.
The big problem is that East Anglia doesn’t really have any large use for electricity.
But the other large asset in the area is the sea.
- Undersea interconnectors can be built to other locations, like London or Europe, where there is a much greater need for electricity.
- In addition, the UK Government has backed a consortium, who have the idea of storing energy by using pressurised sea-water in 3D-printed concrete hemispheres under the sea. I wrote about this development in UK Cleantech Consortium Awarded Funding For Energy Storage Technology Integrated With Floating Wind.
A proportion of Russian gas in Europe, will have been replaced by Norfolk wind power and hydrogen, which will be given a high level of reliability from Suffolk nuclear power.
I have some other thoughts.
Would Hydrogen Be Easier To Distribute From Norfolk?
A GW-range electrolyser would be feasible but expensive and it would be a substantial piece of infrastructure.
I also feel, that placed next to Bacton or even offshore, there would not be too many objections from the Norfolk Nimbys.
Hydrogen could be distributed from the site in one of these ways.
- By road transport, as ICI did, when I worked in their hydrogen plant at Runcorn.
- I suspect, a rail link could be arranged, if there was a will.
- By tanker from the Port of Great Yarmouth.
- By existing gas interconnectors to Belgium and the Netherlands.
As a last resort it could be blended into the natural gas pipeline at Bacton.
In Major Boost For Hydrogen As UK Unlocks New Investment And Jobs, I talked about using the gas grid as an offtaker of last resort. Any spare hydrogen would be fed into the gas network, provided safety criteria weren’t breached.
I remember a tale from ICI, who from their refinery got a substantial amount of petrol, which was sold to independent petrol retailers around the North of England.
But sometimes they had a problem, in that the refinery produced a lot more 5-star petrol than 2-star. So sometimes if you bought 2-star, you were getting 5-star.
On occasions, it was rumoured that other legal hydrocarbons were disposed of in the petrol. I was once told that it was discussed that used diluent oil from polypropylene plants could be disposed of in this way. But in the end it wasn’t!
If hydrogen were to be used to distribute all or some of the energy, there would be less need for pylons to march across Norfolk.
Could A Rail Connection Be Built To The Bacton Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows the area between North Walsham and the coast.
Note.
- North Walsham is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- North Walsham station on the Bittern Line is indicated by the red icon.
- The Bacton gas terminal is the trapezoidal-shaped area on the coast, at the top of the map.
ThisOpenRailwayMap shows the current and former rail lines in the same area as the previous Google Map.
Note.
- North Walsham station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The yellow track going through North Walsham station is the Bittern Line to Cromer and Sheringham.
- The Bacton gas terminal is on the coast in the North-East corner of the map.
I believe it would be possible to build a small rail terminal in the area with a short pipeline connection to Bacton, so that hydrogen could be distributed by train.
There used to be a branch line from North Walsham station to Cromer Beach station, that closed in 1953.
Until 1964 it was possible to get trains to Mundesley-on-Sea station.
So would it be possible to build a rail spur to the Bacton gas terminal along the old branch line?
In the Wikipedia entry for the Bittern Line this is said.
The line is also used by freight trains which are operated by GB Railfreight. Some trains carry gas condensate from a terminal at North Walsham to Harwich International Port.
The rail spur could have four main uses.
- Taking passengers to and from Mundesley-on-Sea and Bacton.
- Collecting gas condensate from the Bacton gas terminal.
- Collecting hydrogen from the Bacton gas terminal.
- Bringing in heavy equipment for the Bacton gas terminal.
It looks like another case of one of Dr. Beeching’s closures coming back to take a large chunk out of rail efficiency.
Claire Coutinho And Robert Habeck’s Tete-a-Tete
I wrote about their meeting in Downing Street in UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties.
- Did Habeck run the RWE/Vattenfall deal past Coutinho to see it was acceptable to the UK Government?
- Did Coutinho lobby for SeAH to get the contract for the monopile foundations for the Norfolk Zone wind farms?
- Did Coutinho have a word for other British suppliers like iTMPower.
Note.
- I think we’d have heard and/or the deal wouldn’t have happened, if there had been any objections to it from the UK Government.
- In SeAH To Deliver Monopiles For Vattenfall’s 2.8 GW Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Project, I detailed how SeAH have got the important first contract they needed.
So it appears so far so good.
Rackheath Station And Eco-Town
According to the Wikipedia entry for the Bittern Line, there are also plans for a new station at Rackheath to serve a new eco-town.
This is said.
A new station is proposed as part of the Rackheath eco-town. The building of the town may also mean a short freight spur being built to transport fuel to fire an on-site power station. The plans for the settlement received approval from the government in 2009.
The eco-town has a Wikipedia entry, which has a large map and a lot of useful information.
But the development does seem to have been ensnared in the planning process by the Norfolk Nimbys.
The Wikipedia entry for the Rackheath eco-town says this about the rail arrangements for the new development.
The current rail service does not allow room for an extra station to be added to the line, due to the length of single track along the line and the current signalling network. The current service at Salhouse is only hourly during peak hours and two-hourly during off-peak hours, as not all trains are able to stop due to these problems. Fitting additional trains to this very tight network would not be possible without disrupting the entire network, as the length of the service would increase, missing the connections to the mainline services. This would mean that a new 15-minute shuttle service between Norwich and Rackheath would have to be created; however, this would interrupt the main service and cause additional platforming problems. Finding extra trains to run this service and finding extra space on the platforms at Norwich railway station to house these extra trains poses additional problems, as during peak hours all platforms are currently used.
In addition, the plans to the site show that both the existing and the new rail station, which is being built 300m away from the existing station, will remain open.
. As the trains cannot stop at both stations, changing between the two services would be difficult and confusing, as this would involve changing stations.
I feel that this eco-town is unlikely to go ahead.
Did RWE Buy Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone To Create Green Hydrogen For Europe?
Consider.
- Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone is a 4.2 GW group of wind farms, which have all the requisite permissions and are shovel ready.
- Bacton Gas terminal has gas pipelines to Europe.
- Sizewell’s nuclear power stations will add security of supply.
- Extra wind farms could be added to the Norfolk Zone.
- Europe and especially Germany has a massive need for zero-carbon energy.
The only extra infrastructure needing to be built is the giant electrolyser.
I wouldn’t be surprised if RWE built a large electrolyser to supply Europe with hydrogen.
Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Vattenfall has selected Peel Ports as the preferred bidder, and its port at Great Yarmouth as the location for the operations and maintenance base of the Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone in the UK.
This was said about the competition to host the facility.
Vattenfall said that the competition was fierce to secure the agreement with an excellent bid from Lowestoft and Associated British Ports. With both ports offering excellent services it is clear that East Anglia’s potential as a superpower of offshore wind is secure.
I have a few thoughts.
Lowestoft In Suffolk And Great Yarmouth In Norfolk Must Work Together
This Google Map shows the coast between the two ports.
Note.
- Great Yarmouth is at the top of the map.
- Lowestoft is at the bottom of the map.
- The two towns are less than twelve miles apart.
- The Great Yarmouth Outer Harbour, is towards the top of the map.
The Google Map shows the port in more detail.
Note.
- Great Yarmouth Outer Harbour only opened in 2009.
- It has an average depth of 10 metres.
- It was planned as a container port, but the ships didn’t materialise.
- Some consider it to be a bit of a white elephant.
Could the Outer Harbour be used to assemble floating wind turbines?
I think it could but at present, there are no plans to use floating wind turbines off the coast of Norfolk.
I suspect though, if someone decided to build floating wind farms to the East of the Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone fields, that Great Yarmouth Outer Harbour could be used to assemble the floating wind turbines.
This Google Map shows the Port of Lowestoft.
Note.
- There is over a kilometre of quays.
- It doesn’t have the water depth of Great Yarmouth.
- There is a lot of brownfield sites along the River Waveney.
- The East Anglia One wind farm is managed from Lowestoft.
Both harbours have their good and bad points.
- Both have good rail connections to Norwich.
- Lowestoft has a rail connection to Ipswich and has been promised a London service.
- Road connections to Ipswich and Norwich need improvement.
I suspect that it was a close contest, as to the port that got the Vattenfall contract.
A Lowestoft And Great Yarmouth Rail Connection
This map from Open RailwayMap between the two towns.
Note.
- The existing railways are shown in yellow.
- Former railways are shown in black dotted lines.
- There was even a railway along the coast.
The only rail connection between the ports is via Reedham, where the track layout is shown on this second OpenRailwayMap.
Note.
- Reedham station is in the North West corner on the line to Norwich.
- The line going North-East goes to Great Yarmouth.
- The line going South goes to Lowestoft.
There used to be a chord connecting Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft, but it was cancelled by Beeching’s grandfather.
There is certainly scope to improve the rail connection between the two ports.
- There could be a convenient change at Reedham, if the timetables were adjusted.
- Trains could reverse at Reedham.
- The chord could be reopened to allow direct trains.
It wouldn’t be the most challenging rail project to have an hourly rail service between the two ports.
A Lowestoft And London Rail Service
This was promised with a frequency of something like four trains per day (tpd)
I think it should run between London and Yarmouth with a reverse at Lowestoft.