Could The Settle And Carlisle Be Used As A More Formal Route?
In June 2021, I wrote Through Settle And Carlisle Service Under Consideration, which starts like this.
The title of this post, is the same as that of an article in the June 2021 Edition of Modern Railways.
This is the first paragraph.
Plans for a new Leeds to Glasgow through service via the Settle and Carlisle line are being developed, with CrossCountry and the Department for Transport starting to look at the possible scheme.
It sounds like a sensible idea to me.
The article also suggests the following.
- CrossCountry is a possible operator.
- CrossCountry are keen to improve services between Leeds and Glasgow
- The trains could be InterCity 125s, freed up, by a the arrival of Class 221 trains from Avanti West Coast, when they receive their new Class 805 trains.
- Maintenance of the trains wouldn’t be a problem, as this could be done at Neville Hill in Leeds or Craigentinny in Edinburgh.
- Services could start in December 2023.
But nothing more has been heard.
However some things have happened.
The Settle And Carlisle Has Become A Popular Charter Route
Google AI gave me this paragraph.
The Settle and Carlisle line is an extremely popular, premier route for heritage rail charters, steam excursions, and luxury rail tours in the UK, often operating at full capacity. Renowned for its scenic 72-mile journey through the Yorkshire Dales and Pennines, it features iconic structures like the Ribblehead Viaduct.
I have also written these posts about charters on the Settle and Carlisle Line.
Scheduled Steam-Hauled Services For the Settle And Carlisle Railway
Rail Operator Crosses Line For First Time In Years
‘Staycation Express’ To Return Along Full Length of S & C
It doesn’t appear that the numbers of charter trains are showing any sign of decrease.
LNER Has Ordered Class 897 Trains
When LNER took over the East Coast Main Line services, they had six main classes of trains.
- Five-car Class 800/1 bi-mode trains
- Nine-car Class 800/2 bi-mode trains
- Five-car Class 801/1 electric trains
- Nine-car Class 801/2 electric trains
- Seven-car InterCity225 trains
- Nine-car InterCity225 trains
Note.
- The five-car trains can run in pairs as ten-car trains.
- The Class 800 and Class 801 trains can run to destinations, that lack full electrification using diesel power where needed.
- Hitachi are developing battery-power for rail routes without electrification.
In 2023 to replace the InterCity225 trains ten ten-car Class 897 tri-mode trains were ordered from CAF, which will soon be in service, over all LNER’s network.
LNER Has Fully Electrified And Unelectrified Destinations
LNER’s current destinations, that are fully electrified to King’s Cross include.
- Bradford Forster Square
- Berwick on Tweed
- Darlington
- Doncaster
- Durham
- Edinburgh Haymarket
- Edinburgh Waverley
- Grantham
- Keithley
- Leeds
- Newark Northgate
- Newcastle
- Peterborough
- Retford
- Shipley
- Skipton
- Stevenage
- Wakefield Westgate
- York
Whilst those are not fully electrified include.
- Aberdeen
- Cleethorpes
- Dundee
- Grimsby Town
- Harrogate
- Huddersfield
- Horsforth
- Hull
- Inverness
- Lincoln
- Middlesbrough
- Sheffield
- Sunderland
- Thornaby
- Worksop
Note.
- Other destinations can be added as required.
- I suspect, that Class 897 trains will be able to approach many stations without electrification on battery power alone.
- Staff and Passengers would probably like underground stations like Sunderland to be worked on batteries alone.
The Class 800 bi-mode, the Class 801 electric and the Class 897 tri-mode trains will give LNER a very flexible fleet.
Onward To Skipton, Carlisle and Glasgow Central And Edinburgh From Bradford Forster Square
I wonder is someone has realised that the Class 897 trains could use their tri-mode capabilities to invade Scotland?
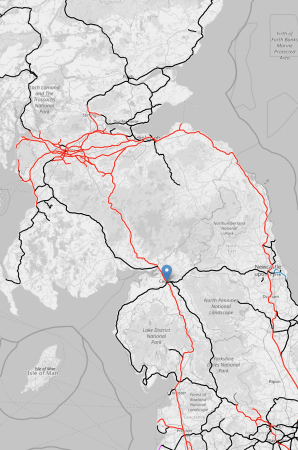
This OpenRailwayMap shows the railways between the Scottish Lowlands and northern England.
Note.
- Red tracks are electrified.
- Black tracks are not.
- The blue arrow in the middle of the map indicates Carlisle.
- The red track going North-South through Carlisle is the West Coast Main Line.
- The black track going South from Carlisle is the Settle and Carlisle Line.
- Where it turns red is at Skipton station and the electrification can power the train to Bradford Foster Square, Doncaster, Leeds or Sheffield stations.
- The West Coast Main Line splits North of Carlisle and electrified trains can reach either Glasgow Central in the West or Edinburgh Haymarket or Waverley in the East.
- The black track going North-South between Carlisle and Glasgow via Dumfries is the Glasgow South Western Line, which can be used as a diversionary route by some trains with a self-powered capability.
The Settle and Carlisle Line certainly makes Anglo-Scottish routes more robust and flexible when there is bad weather, engineering works or overhead wire or signalling failures.
Will Class 897 Trains Be Able To Run On The Settle And Carlisle Line?
I asked Google AI this question and it gave this answer.
Yes LNER’s new Class 897 tri-mode trains (scheduled for introduction from 2027) will be able to run on the Settle and Carlisle line. As tri-mode electro-diesel multiple units, these 10-car trains are designed to operate across the entire LNER network, utilizing electric, diesel, or battery power to manage non-electrified routes like this, providing a modern alternative to older, diesel-only fleets.
Key details regarding Class 897 on the Settle and Carlisle Line:
Tri-mode Capability: These trains can run on electric, diesel, or battery power, making them highly versatile for non-electrified, scenic, or challenging routes.
Operating Strategy: The trains are designed for flexibility and can be used across the LNER network, which includes routes connecting to Scotland via the West Coast Main Line (WCML) or through services from Leeds.Upgrading Service: They will replace the 40-year-old InterCity 225 fleet, offering a more environmentally friendly, modern alternative to current diesel bi-modes, such as the Class 800/802.
The route is a major, yet challenging, rail line featuring 20 viaducts and 14 tunnels, making it suitable for modern, versatile train sets.
I also believe that running Class 897 trains between Yorkshire and Glasgow offers opportunities to run new services, that will appeal to both travellers and rail operators.
Does The UK Need More Passenger Rail Capacity Between Yorkshire And Glasgow?
I asked Google AI this question and it gave this answer.
Yes, the UK requires more passenger rail capacity between Yorkshire and Glasgow due to severe overcrowding and forecasted demand growth. Major routes like the East Coast Main Line (ECML) and West Coast Main Line (WCML) are, or will soon be, at maximum capacity. Key constraints include infrastructure limitations and the need for better Scotland-England connectivity.
Key insights on this need:
Capacity Constraints: The WCML, particularly at its southern end, is already effectively full, with limited capacity for additional, longer trains. Similarly, the ECML is experiencing significant overcrowding.
Growing Demand: Passenger demand for long-distance rail travel continues to rise, with significant increases noted in journeys between Scotland and other regions.
Infrastructure Issues: Constraints include steep inclines, tight curves, and the need to mix passenger and freight traffic, particularly on the West Coast route.
Proposed Solutions: While some improvements are planned, such as Lumo extending services to Glasgow, the Integrated Rail Plan (IRP) focuses on capacity enhancements in the North/Midlands.
Strategic Need: Enhanced, high-speed connections are considered essential for long-term economic integration and to prevent increased air travel/emissions.
The great advantage of the route, is that is already in place.
Can The Settle And Carlisle Line Handle Planned Diversions?
Can The Settle And Carlisle Line Handle The Caledonian Sleeper?
I asked Google AI this question and it gave this answer.
The Settle-Carlisle line is not a standard route for the Caledonian Sleeper, which typically travels via the West Coast Main Line (WCML) to Edinburgh, Glasgow, and beyond. While the line is a scenic, double-track route with significant infrastructure, it is generally used for local services and freight, not long-distance, heavy sleeper trains.
Key Considerations:
Route: The Caledonian Sleeper operates on the West Coast Main Line, serving destinations like Edinburgh, Glasgow, Aberdeen, Inverness, and Fort William.
Capacity & Infrastructure: While the Settle-Carlisle line has major structures like the Ribblehead Viaduct, it is not the primary route for high-speed or overnight sleeper services.
Operational Normal: The sleeper service splits into portions at Edinburgh, and does not regularly operate via the Settle-Carlisle line.
In short, the Settle-Carlisle line is not designed for or used by the Caledonian Sleeper, which operates via the West Coast Main Line.
But it does appear, that in the past some sleeper trains have used it.
How Many Freight Trains Use the Settle And Carlisle Line In A Typical Day?
This article on the BBC is entitled Settle To Carlisle line: Shortage of trains ‘Hampering Growth’, says this about the number of trains.
From only two trains a day in the 1980s the Settle and Carlisle line now sees 14 passenger and 18 freight services a day.
That is progress!
Could Electric Trains Run Between St. Pancras International and Sheffield Stations With No More Electrification?
A reader suggested, that I look at this, so here goes!
- A couple of weeks ago, I took a Class 222 diesel train back from Sheffield to St. Pancras International and it seemed a few minutes quicker.
- Looking at the timetable today, at least one service on the route is now just under two hours and some others are just over.
So the new Class 810 trains may not be fully in service yet, but the trains have already had an effect on the timetable.
How Far North Is The Midland Main Line Being Electrified?
I asked Google AI this question and received this answer.
As of early 2026, the Midland Main Line (MML) is electrified as far north as Wigston, just south of Leicester.
- Northern Limit: The section from Kettering up to Wigston South Junction was energised in July 2024, representing the current northern limit of 25kV overhead line equipment (OLE).
- Pause in Further Electrification: Following a UK government spending review, the further, planned northward extension of electrification to Leicester, Derby, Nottingham, and Sheffield was indefinitely paused in July 2025.
- Current Operations: While electrification has stopped at Wigston, the line is served by new bi-mode (electro-diesel) trains, allowing for electric running from London St Pancras to Wigston before switching to diesel power.
- Previous Work: The line is also fully electrified from London St Pancras to Bedford, including the route to Corby.
Note.
- South Wigston Junction and Sheffield are 69.4 miles apart.
- The Hitachi trains can raise and lower pantographs on the move.
Distances without wires from London St. Pancras International to various destinations are as follows.
- Sheffield – 69.4 miles
- Leicester – 3.7 miles
- Derby – 36.4 miles
- Nottingham – 31.1 miles
As trains will have to go out and back to these destinations distances travelled will be doubled.
- Sheffield – 138.8 miles
- Leicester – 7.4 miles
- Derby – 72.8 miles
- Nottingham – 62.2 miles
It looks to me, that if the new Class 810 trains, can travel 138.8 miles on batteries and diesel engines as a tri-mode train, then the Midland Main Line is electrified.
Could The Sheffield Services Turn Round At Doncaster And Charge Their Batteries There?
Note.
- South Wigston Junction and Doncaster are 79.5 miles apart.
- Doncaster is a fully-electrified station.
- Sheffield and Doncaster would get two extra connecting trains per hour.
- The two services could also call at Meadowhall and/or Rotherham Central.
The Class 810 trains could charge their batteries, whilst passengers to and from Doncaster left and entered the trains.
Could A Simple Cross-Platform Change Be Arranged Between East Coast And Midland Main Line Services?
Doncaster station has two long island platforms, one of which is generally used for Northbound services and one for Southbound services.
Note.
- All electrified tracks are shown in red.
- The two wide island platforms, with Northbound on the West side and Southbound on the East side.
- Each island platform has an electrified platform face on both sides.
- The four platforms faces on the island platforms can hold pairs of five-car Hitachi trains.
- There are two through tracks or avoiding lines between the two island platforms for trains that aren’t stopping.
- There are bay platforms at the ends of the station for local trains.
- The station is fully step-free with a wide pedestrian underpass.
I know the station well and it looks to me, that East Midland Railway’s five-car services for St. Pancras could charge up in the Southern ends of the four faces of the island platforms and the two South-facing bay platforms.
I also believe that a pair of five-car Class 810 trains could be handled and charged, should it become necessary.
It looks to me, that the engineers updating the East Coast Main Line, know that they were caught out badly by High Speed Two, so the redesign for the next fifty or a hundred years will be completely future-proofed.
Doncaster and London could almost be considered to be twin main lines, with two pairs of high speed lines taking different routes, that serve different towns and cities.
How Many Travellers Go Between East Scotland And The North-East of England And The English Midlands?
It must be quite a few, as in the new East Coast Main Line timetable, more Scottish services stop at places like Doncaster and Newark.
But surely, if you could go between say Perth or Aberdeen and Derby or Nottingham in two battery-electric trains, with a relaxed change at Doncaster, you’d take it?
I certainly would!
East Coast And Midland Main Lines Compared
These are times between London and Doncaster.
- Current times between Doncaster and London are typically between 1 hour and 31-40 minutes going via the East Coast Main Line.
- I estimate times between Doncaster and London will be typically 2 hours and 22-27 minutes going via the Midland Main Line.
Note.
- Doncaster and London King’s Cross is 156 miles
- Doncaster and London St. Pancras International is 183.3 miles
- So the Midland Main Line route would appear to to be about 45 minutes slower.
- I suspect, that for passengers between between London and North of York, it will always be quicker to use an East Coast Main Line service.
These are times between London and Sheffield.
- Current times between Sheffield and London are typically between 2 hours and 4-9 minutes going via the Midland Main Line.
- I estimate times between Sheffield and London will be typically between 2 hours and 2 minutes going via the East Coast Main Line.
Note.
- Sheffield and London King’s Cross is via Retford.
- Sheffield and London King’s Cross is 162.1 miles
- Sheffield and London St. Pancras International is 183.3 miles
- Sheffield and Retford is 23.5 miles
- So the Midland Main Line route would appear to to be a few minutes slower.
I would feel that there is scope that under Great British Railways to optimise services between London and Doncaster and Sheffield.
The Master Cutler
The Master Cutler is a named train, that is described in this Wikipedia entry, that was introduced in 1947.
- Over its life it has run into both King’s Cross and St. Pancras.
- I can remember the train in the 1950s, running into King’s Cross.
- It has also been run to and from Leeds.
- It has been run as a Pullman service.
- There are reports of overcrowding in recent years.
It strikes me that the Master Cutler could do with a revamp.
- As St. Pancras can accept pairs of five-car Class 810 trains, ten-car trains could be run into King’s Cross or St. Pancras.
- An alternative would be to use a nine-car Hitachi Class 800/801 train.
- All trains would be battery electric.
- All trains would use the East Coast Main Line for a faster service.
- Services could terminate in the North at Leeds.
- The service could be run as a Pullman service.
- This article on Ian Visits, writes about East Coast Main Line trains using St. Pancras.
I would create a train service, that would attract passengers from all over the world.
Who knows?
If it was conceived in the right way, it might warrant a second service or similar service on other lines like these possibilities.
London and Blackpool via Crewe, Wigan and Preston.
- London and Aberystwyth via Birmingham and Shrewsbury.
- London and Bristol via Bath
- London and Fishguard via Cardiff and Swansea
- London and Holyhead via Birmingham and Chester
- London and Liverpool
- London and Manchester
- London and Newcastle via York and Durham
- London and Norwich via Colchester and Ipswich
- London and Plymouth via Exeter
Note.
- All routes could be run using electric or battery-electric trains.
- The Fishguard and Holyhead services would be zero-carbon routes to Ireland, connecting to appropriate zero-carbon ferries.
- Could services be arranged so that all parts of the country have at least one service in both directions every day?
- In the days of British Rail, London and Norwich had a very high-class service, that could serve a full English breakfast between Colchester and London, which certainly wasn’t like the regular joke.
Get the offering right and it could level-up the UK.
South Yorkshire Now Has Better North-South Connections
The December 14th 2025 timetable change was a big day for South Yorkshire.
Three big changes will transform, public transport in South Yorkshire.
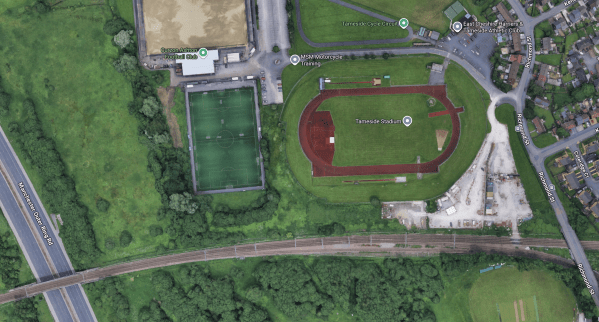
The Opening Of A New Tram-Stop At Magna Science Adventure Centre On The Tram-Train Route Between Sheffield And Rotherham
The Magna Science Adventure Centre is described like this in the first paragraph of its Wikipedia entry.
Magna Science Adventure Centre is an educational visitor attraction in Rotherham, South Yorkshire, England.
This map shows the site and the tram-train track between Sheffield and Rotherham.
Note.
- The tram-train track runs East-West across the top of the map.
- Sheffield is to the West and Rotherham is to the East.
- At the Western end of the site, a label indicates the position of the Magna Platform.
- The position of the tram-train stop is already marked.
- There will be 29 extra Park-and-Ride spaces.
- The Magna Science Adventure Centre is indicated by the purple arrow in the middle of the map.
- Magna Way runs East-West through the site.
- There are four pavilions: Earth, Air, Fire, and Water.
This article on the BBC is entitled Lifts And Bridge Added As Tram Stop Takes Shape.
This picture from the article shows the bridge with lifts.
Note.
It will be an impressive tram stop.
It doesn’t look like it will be long before it opens.
But as yet no information is available.
Google AI gave this answer.
The new Magna Tram Train stop is scheduled to open in early 2026.
Construction of the new £10 million station and Park & Ride facility in Rotherham, part of a wider investment in the South Yorkshire Supertram network, is currently on track.
The new stop will improve access to the Magna Science Adventure Centre, local businesses, and link up with existing walking and cycling routes, aiming to ease congestion in the Lower Don Valley.
I shall be going next week to take photographs of the tram stop.
The Increase In Frequency Of Express Trains Serving Doncaster On The East Coast Main Line
Since the December 14th 2025 timetable change, the Monday to Friday express trains, that stop at Doncaster on the East Coast Main Line have included.
- CrossCountry – 8 trains per day (tpd) in both directions.
- Grand Central – 4 tpd in both directions.
- Hull Trains – 7 tpd in both directions.
- LNER- 3.5 trains per hour (tph) in both directions.
- TransPennineExpress – 1 tph in both directions.
Note.
- This totals to 173 express trains per day stopping at Doncaster
- Or about 7 tph in both directions or a train every 8.5 minutes.
- This is about a thirty percent increase in frequency.
- Doncaster has become the Crewe of South Yorkshire.
I can see this large number of express trains to Doncaster bringing large numbers of visitors to go to the Magna Science Adventure Centre or its tram stop for onward connection to other destinations on the Sheffield Supertram network.
The trouble is, that at present the Magna tram stop is not connected to Doncaster station.
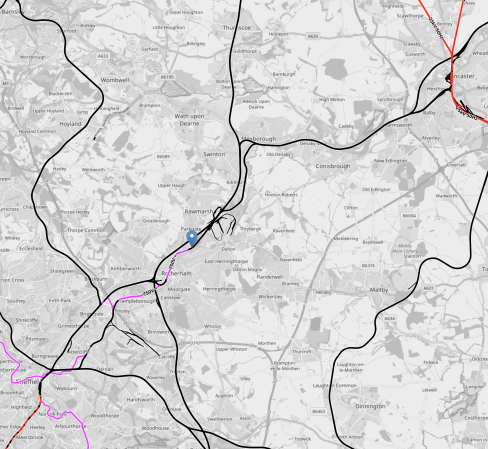
This OpenRailwayMap shows the rail lines between Doncaster and Sheffield stations.
Note.
- The short length of red track in the North-East corner of the map is the East Coast Main Line.
- Doncaster station can be picked out.
- The short length of red track in the South-West corner of the map is the Midland Main Line, which connects Sheffield to London.
- Sheffield station is at the Northern end of the electrification, which will be installed soon.
- The pink tracks are the 750 VDC electrified tracks of the Sheffield Supertram.
- The blue arrow marks Rotherham Parkgate station, which is the limit of the current tram-train route.
The tram-train route needs to be extended so that the tram-trains can go between Rotherham Parkgate tram stop and Doncaster station.
The route seems to have these characteristics.
- It is about 11.8 miles long.
- Stops are Rotherham Central, Swinton (South Yorkshire), Mexborough and Conisborough.
- Diesel trains take about thirty minutes between Rotherham Central and Doncaster.
- All platforms at Doncaster are electrified with 25 KVAC.
- Platform 5 is a convenient bay platform at Doncaster, that could be used by the tram-trains.
- Sheffield’s Class 399 tram-trains can use 25 KVAC for traction.
- South Wales have similar Stadler tram-trains, that are to be fitted with batteries.
I am fairly sure, that a solution can be found so that Sheffield’s tram-trains can be extended to Doncaster station.
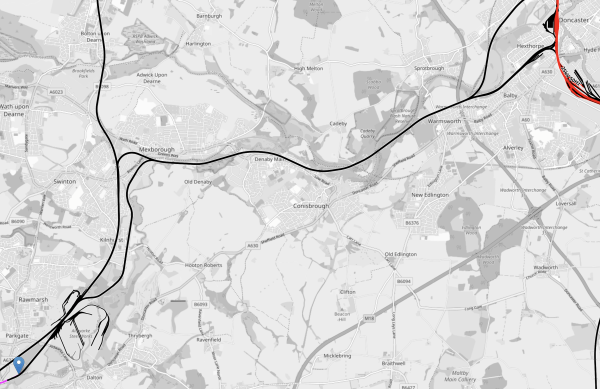
This OpenRailwayMap shows the route between Rotherham Parkgate tram stop and Doncaster station.
Note.
- The short length of red track in the North-East corner of the map is the East Coast Main Line.
- Doncaster station can be picked out.
- The short length of pink tracks are the 750 VDC electrified tracks of the Sheffield Supertram.
- The blue arrow marks Rotherham Parkgate station, which is the limit of the current tram-train route.
- Most of the route is not electrified.
As there is electrification at both ends, I suspect the easiest way of powering the trams would be to use batteries, as has been done in South Wales.
The New Class 810 trains between London St. Pancras And Sheffield On The Midland Main Line
These new Class 810 trains have started running this month and I suspect soe travellers will use these trains to go to Magna or its tram stop.
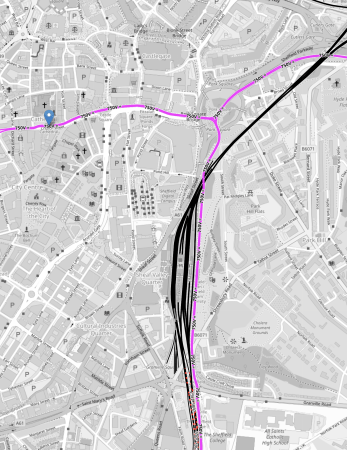
his OpenRailwayMap shows the tram routes in Sheffield city centre.
Note.
- The pink tracks are tram-tracks.
- The black tracks are unelectrified train tracks.
- The short lengths of red-and-black tracks are tracks to be electrified with 25 KVAC overhead, for the Class 810 trains.
- The blue error indicated the Cathedral tram-stop, where tram-trains will be caught to Magna.
- The mass of black tracks in the middle of the map is Sheffield station.
- There is a tram stop on the East side of the train station for the trams.
- Trams going South go to Halfway and Herdings Park.
- Trams going North-East go to Rotherham Parkgate and Meadowhall Interchange, and will go to Magna, when it opens.
- Trams going North-West go to Malin Bridge and Middlewood.
It is a difficult interchange between Cathedral and Sheffield station, if you are catching the tram-train, as it is a hard walk up hill, so it might be better if you are goinging between Sheffield station and the tram-train to change trams at Meadowhall South.
Huddersfield Station – 30th September 2025
This press release on the Network Rail Media Centre is entitled Huddersfield Station Set To Reopen Next Week With New Temporary Layout.
As it is now next week, I went to have a look at the progress today.
I made a mistake and got on a Grand Central Train, which meant, I had to change at York.
Speeding past Drax power station on the Selby Diversion, I took these pictures.
We were only in a 125 mph diesel, so we couldn’t take advantage of the 160 mph running, that the East Coast Main Line’s new signalling might allow on this section. The Wikipedia entry for the Selby Diversion, says this about the possible speeds.
The line was the first purpose-built section of high-speed railway in the UK having a design speed of 125 mph; however, research by British Rail in the 1990s indicated that the route geometry would permit up to 160 mph operation, subject to the necessary overhead line equipment and signalling upgrades. The new line also avoided the speed restriction over the swing bridge at Selby. The former ECML route, the NER’s 1871 York and Doncaster branch line, was closed from Selby northwards.
As the Selby Diversion opened in 1983, I wouldn’t be surprised that the calculations were performed on British Rail Research’s Pace 231-R, which was similar to the one I used at ICI and the pair, that NASA used calculate how to land Apollo on the moon.
When I eventually got to Huddersfield, I took these pictures.
Note.
- In I’ve Just Glimpsed The Future Of Train Travel Across The North Of England And I Like It, there are pictures of Huddersfield station, that were taken on the 21st August, soon after the work started.
- In Huddersfield Station – 15th December 2023, there are pictures of Huddersfield before the work started.
- Much of the work seems to have been done at the Western end of the station to lengthen the platform on the Penistone Line to Sheffield.
- Platform 2 for the Penistone Line has also been renumbered Platform 1.
Work still to be carried out at Huddersfield station, includes refurbishing the roof, installing the electrification and adding a couple of new platforms.
These are my thoughts.
Which Platforms Will Be Electrified?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the proposed electrification in Huddersfield station.
Note.
- The blue arrow in the North-East corner of the map indicates Huddersfield atation.
- The two red-and-black tracks going diagonally across the map are the Hudderfield Line.
- The red-and-black colour, indicates that the two tracks will be electrified.
- South of these two tracks, the Penistone Line sneaks into Platform 1 at Huddersfield station.
- The Penistone Line goes to Sheffield in a South-Westerly direction.
- There appears to be a crossover, so that trains from the Penistone Line can use both Platforms 1 and 2 in Huddersfield station.
- The OpenRailwayMap appears to show planned electrification between Stalybridge and Leeds stations.
- To the East of Leeds planned electrification is shown as far as Micklefield and Church Fenton stations.
Once installed, this electrification will create a complete electrified route across the Pennines from Liverpool Lime Street in the West to the East Coast Main Line in the East.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the planned electrification between Micklefield and Hull stations.
Note.
- Red tracks are electrified.
- Black tracks are not electrified.
- York is in the North-West corner of the map, with the electrified East Coast Main Line going through the station North-South.
- South of York, the East Coast Main Line now splits.
- The Western branch includes an electrified line to Micklefield station, Neville Hill depot and Leeds station.
- The Eastern Branch is the Selby Diversion, which is an electrified 160 mph line, that avoids the Selby coalfield.
- Running West-East across the map is the unlectrified Micklefield and Hull Line, which goes via Selby.
- Hull is in the South-East corner of the map.
- Hull is 42 miles from Micklefield and 36.1 miles from the Temple Hirst junction on the Selby Diversion, so it is within range of battery-electric trains, with charging at Hull station.
- Hitachi’s battery-electric Class 802 trains, used by Hull Trains and TransPennine Express, which are currently on test, should certainly be able to serve Hull.
Hull can become an electrified station, without the expense and disruption of full electrification.
How Long Is Platform 1 At Huddersfield Station?
This OpenRailwayMap shows the new Platform 1 at Huddersfield station.
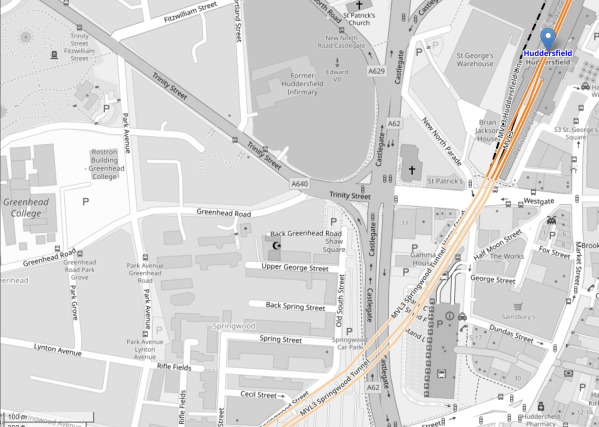
Note.
The blue arrow indicates Huddersfield station.
- The three darker orange lines indicate the two through platforms 2 and 3, and the reconfigured bay platform 1.
- There is a cross-over between platforms 1 and 2, which connects Platform 2 to the Penistone Line.
- In the South-West corner of the map is a hundred metre scale.
- Using the scale, I estimate that the length of the bay platform 1 is around 120 metres.
- In the last two rows of pictures in the gallery of this post, a three car Class 150 train is shown in Platform 1.
- A three car Class 150 train is approximately sixty metres long.
Looking at the pictures, I wouldn’t be surprised if the new platform has been designed to take two three-car Class 150 trains. It would certainly take a pair of two-car Class 150 trains.
Other trains and their lengths that might use the platform include.
- Class 170 – three-car – 70.85 metres
- Class 195 – two-car – 48.05 metres
- Class 195 – three-car – 71.40 metres
- Class 195 – 2 x two-car – 96.10 metres
- Class 810 – five-car – 120 metres
The Class 810 uses 24 metre cars, so that a pair of trains, will fit in St. Pancras. But with perhaps selective door opening could a single Class 810 train run a St. Pancras and Huddersfield service, perhaps with a split and join at Sheffield.
Electrification Across The Pennines
The TransPennine Route will be electrified between Liverpool Lime Street and Micklefield stations, once the current works between Huddersfield and Leeds are complete.
Sections without electrification include.
- Bradford Interchange and Doncaster – 52.1 miles
- Cleethorpes and Doncaster – 52.1 miles
- Harrogate and Leeds – 18.3 miles
- Hazel Grove and Doncaster – 52.6 miles
- Hull and Micklefield – 42 miles
- Hull and Temple Hirst junction – 36.1 miles
- Saltburn and Northallerton – 28.1 miles
- Sunderland and Northallerton – 46.8 miles
- Scarborough and York – 42.1 miles
I expect that Hitachi trains with batteries or CAF’s tri-mode trains will be able to handle these routes in a low-carbon manner.
Electrification Between Stalybridge And Huddersfield
This section is shown as being electrified on OpenRailwayMap.
But as it is only 18 miles and includes the Standedge Tunnels will the route use battery-electric trains?
The Three Baltic Countries Sign The Largest Railway Electrification Agreement In History
The title of this post, is the same as that as this news item on the LTG Group web site.
This is the sub-heading.
Today in Vilnius, the institutions of the three Baltic countries responsible for implementing the Rail Baltica project signed a historic agreement on railway electrification. The contract, valued at €1.77 billion (excluding VAT), has been awarded to COBELEC Rail Baltica – a consortium formed by the Spanish companies Cobra Instalaciones y Servicios S.A. and Elecnor Servicios y Proyectos S.A.U.
These three paragraphs add more detail.
The electrification of the Rail Baltica European railway is considered the largest cross-border railway electrification initiative in Europe, implemented as a single, joint project.
“Rail Baltica is more than just infrastructure – it is an economic and security link to the West. This contract is particularly important for our integration into the European railway network, enabling smooth passenger and freight transport while strengthening the resilience of the Baltic region. It is our strategic pathway to the future,” said Eugenijus Sabutis, Acting Minister of Transport and Communications of Lithuania.
One of the largest contracts in the history of the Baltic States was signed by the institutions responsible for implementing the project: LTG Infra, the infrastructure company of the LTG Group; Eiropas Dzelzceļa Līnijas in Latvia; and Rail Baltic Estonia in Estonia. Representatives from the ministries of transport and communications of all three countries also gathered in Vilnius for the occasion.
Note.
- The electrification will be to the European standard of 25 KVAC overhead.
- There will be a total of 2,400 km. of electrification.
- High-speed passenger and freight trains will operate on the full length of the route.
- It is planned that the electricity used will be generated from renewable energy sources.
- I feel everybody will be pleased except Putin.
The Russian dictator and war-monger won’t like it, as the railway will not be built to Russian standards.
Electrification – The Baldrick Way
Electrification In England
There are two major electrification projects underway in England at the moment; the Midland Main Line to Sheffield and Nottingham and the TransPennine Upgrade between Church Fenton and Stalybridge via Leeds and Huddersfield.
In addition, there are other important routes, that need to be electrified around the UK.
- Edinburgh and Aberdeen
- Crewe and Holyhead
- Newbury and Taunton
- Cardiff and Fishguard
- Bristol and Penzance
- Peterborough and Birmingham
- Peterborough and Doncaster via Lincoln
- Felixstowe and Peterborough
There must be loads of other important routes.
Do We Need Electrification Or A Zero-Carbon Railway?
A zero-carbon Railway is probably sufficient, as that would include traditional electrification.
Are The Electrification On The Midland Main Line And The TransPennine Upgrade Working To Similar Objectives?
The Midland Main Line carries the following services.
- Long distance expresses between London St. Pancras and Derby, Nottingham and Sheffield, which will be run in the future, by Hitachi bi-mode express trains.
- Local suburban electrics between London St. Pancras and Bedford and Corby.
- A variety of heavy freight trains between Chesterfield and London.
- Various regional services run by diesel multiple units.
The Midland Main Line is a typical mixed railway.
It is electrified between London St. Pancras and Wigston Junction, which is a total of 95.3 miles.
Sheffield is a further 69.4 miles from Wigston and Nottingham is just 31.1 miles.
The maximum range needed by a battery-electric train is 69.4 miles.
The TransPennine Route carries the following services.
- Long distance expresses between Liverpool and Newcastle and Hull via Manchester, Huddersfield, Bradford and Leeds, which are run by Hitachi bi-mode express trains and diesel multiple units.
- Local suburban electrics around Liverpool, Manchester and Leeds
- A variety of heavy freight trains along the route.
- Various regional services run by diesel multiple units.
The TransPennine Route is another typical mixed railway and carries a similar traffic mix to the Midland Main Line.
Much of the TransPennine Route is electrified, with these exceptions.
- Cleethorpes and Doncaster 52.1 miles
- Doncaster and Manchester Piccadilly – 61.2 miles
- Manchester United FC and Liverpool South Parkway – 26.2 miles
- Hull and Leeds – 51.8 miles
- Redcar and Northallerton – 28.1 miles
- Scarborough and York – 42.1 miles
- Stalybridge and Church Fenton – 50 miles
The maximum range needed by a battery-electric train is 61.2 miles.
This brief analysis indicates to me, that Hitachi battery-electric bi-modes with a range of eighty miles on batteries and charging at selective stations like Cleethorpes, Hull, Nottingham, Redcar, Scarborough and Sheffield could run electric high speed trains on both the Midland Main Line and the TransPennine Route with very little extra infrastructure.
I asked Google AI what is the range of a Class 802 train on batteries and received this reply.
A Class 802 train converted for a battery-electric trial, known as BEMU, has demonstrated the capability to run up to 60 miles (approximately 97 km) on batteries in a trial setting, with real-world data suggesting potential future trains could achieve a range of 100 to 150 km (62 to 93 miles). This technology is intended to allow these trains to cover non-electrified sections of track, reducing the need for overhead wires and potentially saving on electrification costs for intercity routes.
In What Will Be The Range Of A Hitachi Class 800 Battery Train?, I came to this conclusion.
The first version of the battery-electric train will have a range of around a hundred miles, so that they can handle the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line diversion, which is 93.7 miles, on battery power.
But fairly soon after introduction into service, I will be very surprised if they don’t claim the Guinness world record by running farther than the Stadler FLIRT Akku’s 139 miles.
No-one likes being second!
The 93.7 miles needed for the East Coast Main Line diversion via the Great Northern and Great Eastern Joint Line through Lincoln will be more than enough range for Hitachi’s battery-electric trains to run the full length of both the Midland Main Line and the TransPennine Route.
Electrifying A Route
I think that Network Rail have identified an efficient way to electrify an express route.
You start by doing these actions.
- Get the track layout right, so that trains can use the route at the optimal speed.
- Update the signalling to a high standard. I suspect digital signalling would be a good idea, to maximise the capacity of a route.
- Make sure, that the chosen battery-electric express trains can handle the route.
- Charging stations would be installed as required.
The battery-electric trains would be introduced as soon as the route is ready.
Hopefully with good project management, there would be the following benefits compared to traditional electrification.
- Difficult sections like tunnels could be left without electrification.
- Fewer bridges would need to be demolished and rebuilt.
- There would be less disruption to local residents.
- Siemens have developed a Rail Charging Converter, which connects to the domestic rather than the National Grid, so is easier to install.
But the big benefit is that new electric trains could probably be introduced earlier, which hopefully should increase ridership and revenue.
Once the expresses were working well, the best way to decarbonise the rest of the services on the route can be ascertained and actioned.
Completing Northern Powerhouse Rail
The Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two Connection To Manchester Airport Station
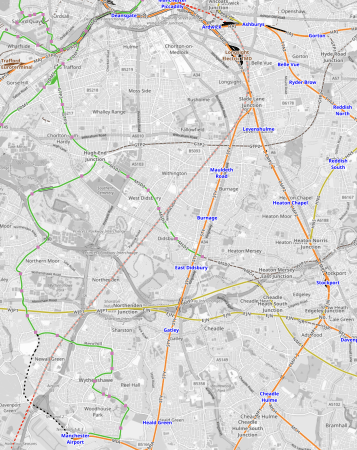
This OpenRailwayMap shows the rail connections that terminate at Manchester Airport station.
Note.
- The two runways are clearly shown.
- Manchester Airport station is indicated by the blue arrow near the top of the map.
- The orange tracks are rail lines.
- The green lines are Manchester Metrolink tracks.
- Rail and tram services approach the airport station from the East.
- The red dotted line is the current proposed path of Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two
- The black dotted line appears to be an extension of the tram line to the airport.
This second OpenRailwayMap shows the lines around the airport station to a larger scale.
Note.
- Manchester Airport station is indicated by the blue arrow at the bottom of the map.
- The orange tracks are rail lines.
- The green lines are Manchester Metrolink tracks.
- The red dotted line is the current proposed path of Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
- The Manchester Metrolink now makes a loop around the Airport.
I think the following will happen.
- A large proportion of passengers and staff travelling between Manchester Airport and Manchester City Centre will use Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
- Passengers and staff, who live locally will use the Manchester Metro loop.
- Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two will replace some of the current train services.
- Some services on the Castlefield Corridor will migrate to Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
There could be as many as twelve trains per hour (tph) between Manchester Airport and Manchester City Centre on Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two. But a new urban line like that, which was mostly in a tunnel could probably handle 20 tph.
Manchester Airport And Crewe
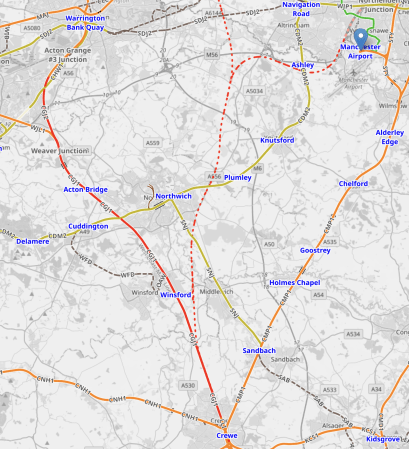
This OpenRailwayMap shows the railways between Manchester Airport and Crewe stations.
Note.
- Manchester Airport station is indicated by the blue arrow at the top of the map.
- The orange tracks are rail lines.
- The red track going down the left hand side of the map is the West Coast Main Line.
- The green lines are Manchester Metrolink tracks.
- The red dotted line is the current proposed path of Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
- Crewe station is at the bottom of the map in the middle.
There could be as many as 12 tph between Manchester Airport and Crewe.
Manchester Airport And Manchester Piccadilly
This OpenRailwayMap shows the railways between Manchester Airport and Manchester Piccadilly stations.
Note.
- Manchester Airport station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The orange tracks are existing rail lines.
- The green lines are Manchester Metrolink tracks.
- The red dotted line going up the middle of the map is the current proposed path of Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
- Manchester Piccadilly station is at the Northern end of Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
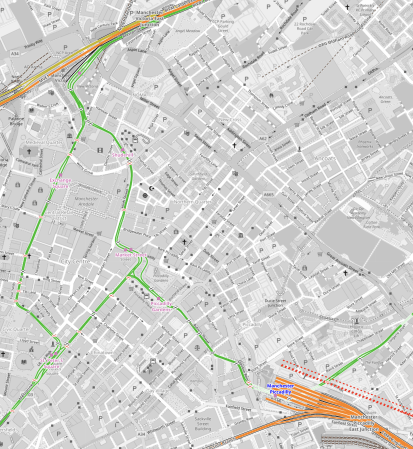
This OpenRailwayMap shows the City Centre between Manchester Piccadilly and Manchester Victoria stations.
Note.
- Manchester Piccadilly station is in the South-East corner of the map.
- The red dotted lines creeping into the map is the current proposed path of Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two.
- All the platforms in Manchester Piccadilly station can be picked out, with the Castlefield Corridor breaking away to the West.
- The current plans will need demolition of buildings to the North of Manchester Piccadilly station.
- Manchester Victoria station is in the North-West corner of the map.
- The green line of the Manchester Metrolink route picks out the walking route between Manchester’s two main stations.
- About halfway between Manchester Piccadilly and Manchester Victoria stations is the open space of Piccadilly Gardens.
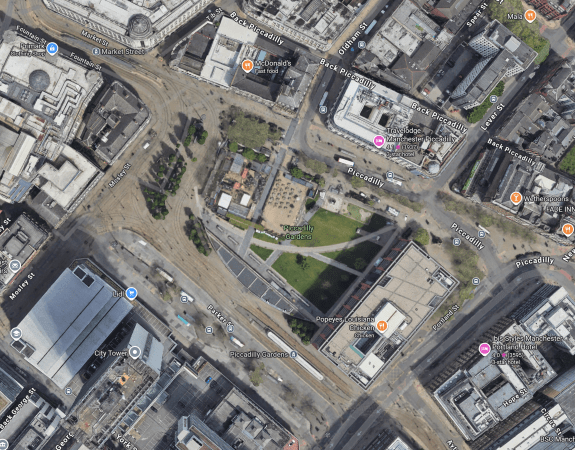
This Google Map shows Piccadilly Gardens.
Note.
- The Manchester Metrolink running through.
- There are two Metrolink stops ; Market Street and Piccadilly Gardens, in the area.
- It appears any stop on the Manchester Metrolink can be reached with no more than a single change from one of these two stops.
Looking at the map showing Victoria and Piccadilly stations, I wonder, if a Lizzie Line of the North could be built under Manchester City Centre.
- There would be underground platforms at Piccadilly station, with two through platforms and two to terminate trains from the South.
- Local services from Piccadilly station could continue as now, although services to Manchester Airport could be simplified.
- There would be an underground station at Piccadilly Gardens with two through platforms , to connect with an expanded Manchester Metrolink, buses and walking routes.
- There would be underground platforms at Victoria station, with two through platforms and two to terminate trains from the East.
- Local services from Victoria could continue as now.
- There could be as many as 12 tph between Manchester Victoria, Piccadilly Gardens, Manchester Piccadilly and Manchester Airport.
Just as the Lizzie Line was slotted into London, with the minimum of disruption, I am fairly certain, a similar but smaller construction process could be carried out in Manchester City Centre.
- Manchester doesn’t have an Underground to avoid.
- The stations could be very similar to each other and like Custom House station on the Lizzie Line, they could be built with giant concrete Lego.
- There would only be four stations to create.
- The tunnel would be about fifteen miles at most.
- The tunnel would not need to be electrified as the trains could run on batteries.
As a Manchester Rail Tunnel has been talked about for decades, I suspect there is a big knowledge base of ground conditions, which would help with the design and construction.
Between Manchester Victoria And Leeds
Consider.
- The electrification between Manchester Victoria and Stalybridge stations has recently been switched on.
- Part of the electrification between Leeds and York stations has been switched on.
- Full electrification is being installed between Leeds and Manchester Victoria stations.
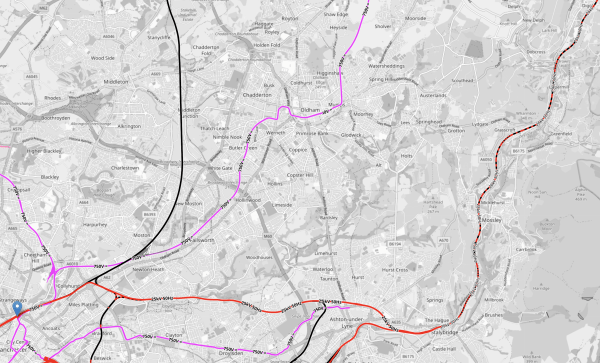
This OpenRailwayMap shows the Huddersfield Line between Manchester Victoria station and a few miles short of Huddersfield station.
Note.
- Manchester Victoria station is indicated by the blue arrow in the South-West corner of the map.
- Huddersfield station is just off the map in the North-East corner.
- Manchester Victoria and Stalybridge stations is fully electrified and shown in red.
- Stalybridge and Huddersfield stations is being electrified and is shown as black and red dotted.
- Electrification between Huddersfield and Leeds is underway under the TransPennine Upgrade.
This section will be completed, when the Manchester City Centre Rail Tunnel is connected to the Huddersfield Line.
Connecting The Manchester City Centre Rail Tunnel To The Huddersfield Line
This Google Map shows where the Huddersfield Line crosses the M60 Motorway to the West of Ashton-under-Lyme.
Note.
- The newly-electrified Huddersfield Line runs across the map.
- The M60 Motorway is on the left.
- There are facilities for athletics, cricket and football.
I wouldn’t be surprised if the Eastern portal of the Manchester City Centre Rail Tunnel was in this area.
But looking at Google Maps between this site and Manchester Victoria, there are other sites.
Conclusion
I now feel that it is possible to create a Northern Powerhouse Rail/High Speed Two route using a tunnel under Manchester.
Obviously, there is more work to be done.
The Problem Of Electrifying Leicester Station
This post is my attempt to try and explain the problem of electrifying the Midland Main Line through Leicester station.
This Google map shows the Southern end of the station.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the station.
Note.
- There appear to be five tunnels under the station buildings and London Road.
- What is the tunnel going underneath the tracks used for?
Leicester station has a Grade II Listed frontage.
Note.
- It is an impressive Victorian station.
- The station building is on a bridge over the tracks.
- The station is also on one of the main roads through Leicester.
- The road layout is very complicated.
This 3D Google Map, shows an aerial view of the station.
Note.
- There four platforms, which are numbered 1-4 from the left.
- The expresses between London and Derby, Nottingham and Sheffield use the two middle tracks.
- Other main line and East-West services use the outside platforms.
- There is an avoiding line for freight services.
- 5. The step-free footbridge is clearly visible.
This second 3D Google Map, shows an enlargement of the frontage of the station.
These pictures show what is inside the building at the front of the station.
The building would appear to be a Grade II Listed taxi rank and free twenty-minute car park.
There are plans to increase the capacity of the station.
- A fifth platform will be added.
- Three miles of quadruple track will be be built South of the station.
- The Midland Main Line was also to be electrified.
Real Time Trains indicates that the distance between Leicester and Wigston North junction is 3.1 miles.
This OpenRailMap shows that section of track.
Note.
- Leiester station is at the top of the map.
- Wigston junction is the triangular junction at the bottom of the map.
- Wigston North Junction is indicated by the blue arrow.
- OpenRailwayMap only shows a 100 mph Northbound track and a 90 mph Southbound track on the route.
It looks to me, that four tracks between Leicester and Wigston North junction would mean that trains could expedite arrivals to and departures from Leicester to and from the South.
South From Wigston Junction
Consider.
- London St. Pancras and Kettering is a four-track railway as far as the Corby Branch.
- North of Luton the slowest maximum speed is 100 mph, with much of the line rated at 110 mph plus.
- Wigston North junction and Luton station is 65.8 miles.
- Current Class 222 diesel trains typically take 40 minutes.
- This is an average speed of 98.7 mph.
- An average speed of 110 mph between Wigston North junction and Luton station would take 36 minutes.
- An average speed of 125 mph between Wigston North junction and Luton station would take 31.6 minutes.
- An average speed of 130 mph between Wigston North junction and Luton station would take 30.4 minutes.
I believe with track improvements and digital signalling, there are time savings to be gained between St. Pancras and Leicester stations.
Ultimately, if the 140 mph design speed of the Class 810 trains under digital signalling could be maintained, this would do the following.
- Push the St. Pancras and Leicester times under an hour.
- Push the St. Pancras and Nottingham times under ninety minutes.
- Push the St. Pancras and Sheffield times under two hours.
Batteries would only be used on the three miles between Wigston North junction and Leicester station.
Could Bi-Mode Trains Be Used?
They could be used initially and to prove if the partial electrification works.
But each train has four diesel engines and sometimes they will be working in pairs through the stations between Leicester and Sheffield.
Passengers will take a dim view of being covered in lots of diesel smoke, when they have been promised clean, zero-carbon electric trains.
But the battery-electric trains will be much quieter and pollution-free.
This page on the Hitachi Rail web site is entitled Intercity Battery Trains.
New Infrastructure Needed
The only infrastructure needed will be that which will support the new trains.
The Class 810 trains will be maintained at Etches Park at Derby.
If they are battery-electric trains, there may be some strategically-placed chargers, which typically would be a short length of overhead wire.
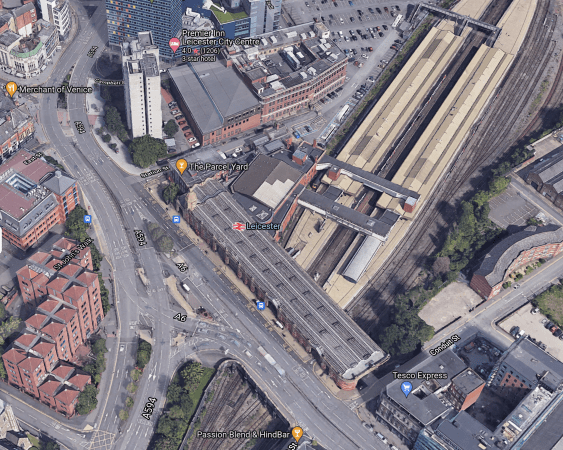
Wigston Junction – 10th July 2025
It now appears that Wigston Junction, is as far North, as electrification will get on the Midland Main Line for some time.
This OpenRailwayMap shows the maximum speeds through the junction.
Note.
- Leicester station is to the North.
- London is to the South.
- Nuneaton is to the West.
- South Wigston station is indicated by a blue arrow.
- The Midland Main Line goes between the North and South points of the junction.
- Trains going North have a maximum speed of 100 mph.
- Trains going South have a maximum speed of 80 mph.
- Trains going along the North-West leg of the junction have a maximum speed of 40 mph.
- Trains going along the South-West leg of the junction have a maximum speed of 30 mph.
It would also appear that trains going North on the Midland Main Line can have a maximum speed of 100 mph or even 110 mph for most of the way between Market Harborough and just before Leicester, whilst going South is perhaps a couple of minutes slower.
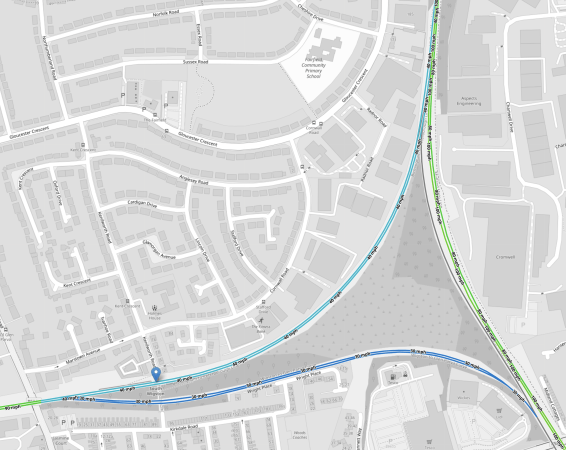
This OpenRailwayMap shows the original plan for electrification through the junction.
Note.
- Red tracks are electrified.
- Black tracks are not electrified.
- Black/red dashed tracked were being electrified, but most are now paused.
- As before South Wigston station is indicated by a blue arrow.
Only the South point of the junction is electrified.
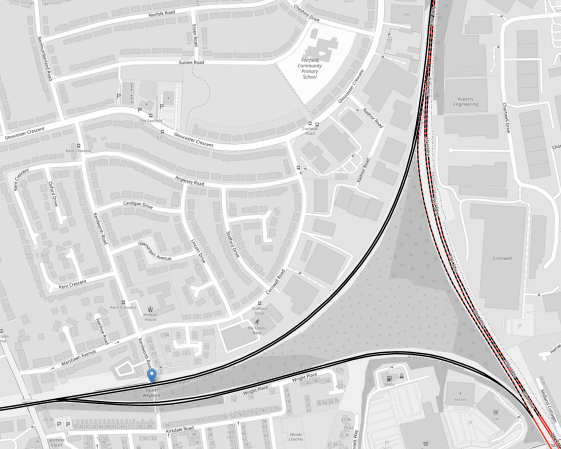
These pictures were taken from the train, as I passed Southwards from the North point of the junction to Market Harborough station.
Note.
- The first three pictures show the chord connecting to South Wigston station and on to Nuneaton.
- The next six pictures show the extra single track on the East side of the junction.
- There is a third track South of Wigston junction, that is about two miles long and electrified.
- All tracks South of Wigston junction are electrified.
It looks like a train could wait in the loop and be passed by a Northbound express.
Could the loop be used to charge trains in an emergency?
Conclusion
It would appear that Wigston junction could be a suitable place for the electrification to be paused.
All services to the North of Wigston junction would be on battery power, unless there is electrification.