Could Anglia Railways’ London Crosslink Be Recreated As Part Of The London Overground?
This is the first paragraph of the Wikipedia entry for the original London Crosslink.
London Crosslink was a passenger train service operated by Anglia Railways between Norwich and Basingstoke, using the North London Line to bypass central London. Class 170 Turbostar diesel multiple units were used, and the service operated between 22 May 2000 and 28 September 2002, supported by funding from the Strategic Rail Authority through its Rail Passenger Partnership fund.
Note.
- The service called at Diss, Stowmarket, Ipswich, Colchester, Whitham, Chelmsford, Ingatestone, Romford, Stratford, Highbury & Islington, Camden Road, Willesden Junction, West Hampstead Thameslink, Brentford, Feltham, Staines, Woking, and Farnborough (Main)
- It ran six times on Monday to Friday and five times on Sunday.
- Feltham and Woking stations have a coach link to Heathrow.
- Journeys took around 3 hours and 44 minutes.
Over the years, attractions and other rail lines and stations served by the route have changed. improved and been added.
- In 2006, the Arsenal’s Emirates Stadium opened within walking distance of Highbury & Islington station.
- In 2012, the Olympic Stadium opened at Stratford and is now used by West Ham United.
- In 2020, Brentford Stadium opened within walking distance of Brentford station.
- There are long-term plans for a station at Brentford stadium.
- In 2022, Romford and Stratford stations were connected to the Elizabeth Line.
- In 2025, Beaulieu Park station was added to the Greater Anglia Main Line.
- In 2026, both ends of the route came under the control of Great British Railways.
At some point in the future, Old Oak Common Lane station will open to link the route to High Speed Two, the Great Western Main Line and the Elizabeth Line.
In Can The Signalling Of The London Overground Be Improved?, I looked in detail at the signalling of the London Overground and if it could handle more trains.
My conclusion was that on the East and North London Lines, another three trains per hour (tph) could probably be accommodated, which over an average day was probably around sixty trains.
As a restored London Crosslink would need just six paths per day, I would suspect the service could be restored, if it were thought to be a good idea.
I certainly feel that capacity would not be a problem.
These are a few other thoughts.
Will There Be Political Problems?
Providing the London Mayor approves, I can’s see any problem with Labour and I can’t see other parties objecting if passengers like it.
Would It Be Sensible To Use Lumo Branding And Trains?
Consider.
- Lumo is trusted branding.
- A five-car Lumo Class 803 train is 132 metres long and a pair of four-car London Overground Class 710 trains is 166 metres long, so I suspect platform length problems will be minimal.
- I doubt there will be problems on the Greater Anglia network.
- Stratford and Norwich is mainly a 100 mph network.
- Not all parts of the route have 25 KVAC overhead electrification, but batteries can be fitted to the Class 803 trains, that will cover any gaps.
- My calculations show that the modern trains will be twenty-two minutes quicker, than Anglia Railways Class 170 diesel trains.
- At one point Anglia Railways was owned by First Group, so FirstGroup may have knowledge of the problems of the route.
I believe it would be sensible to use Lumo branding and trains.
Could The Route Be Extended?
Consider.
- It could probably be extended to Winchester, Southampton and Bournemouth in the South.
- If offshore hydrogen takes off at Great Yarmouth, it might be worth extending with a reverse to Yarmouth in the North.
- Yarmouth has had a direct service from London in the past.
The service could also develop days out by the sea.
Great Yarmouth Terminal Set For Redevelopment Under Port Of East Anglia Name
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
The UK’s Peel Ports Group has decided to invest a further GBP 10 million (approximately EUR 11.3 million) into its Great Yarmouth site, which is being rebranded as the Port of East Anglia.
These four paragraphs add details to the story.
The newly announced GBP 10 million brings this year’s total investment to GBP 70 million across the site and will be used to redevelop the port’s Northern Terminal, helping to accommodate the next generation of offshore wind projects across the region, according to Peel Ports.
Earlier this year, a substantial investment into its Southern Terminal was announced by the port, which has earmarked GBP 60 million to transform capacity and improve efficiencies.
This involves ensuring the port can support multiple hydrogen, carbon capture, offshore wind, and nuclear projects for decades to come.
Its existing terminals service a variety of construction customers, including infrastructure projects such as Sizewell C and offshore energy projects based in the southern North Sea.
Note.
- In Yarmouth Harbour To Be ‘Completed’ In £60m Project, I talk about the work to be done on the Southern Terminal.
- The work on the Southern Terminal includes a roll-on roll-off (RORO) lift ramp and a large storage area.
- Start on the work on the Southern Terminal will start in 2026.
With all the construction work mentioned in the last two paragraphs, I suspect that the Port of Great Yarmouth will be busy?
These are some further thoughts.
Why Is The Port Of Great Yarmouth Being Renamed?
The article says this.
The new name, which will come into effect in early 2026, also aligns with the creation of a new combined authority for Suffolk and Norfolk, according to Peel Ports.
Peel Ports name change is fairly sensible, but as I was conceived in Suffolk and I’m an Ipswich Town supporter, I don’t feel that the two counties should be merged.
Does The Mention Of Hydrogen Mean That The Port Of Great Yarmouth Will Be Hosting A Hydrogen Electrolyser, To Fuel Trucks And Ships?
I asked Google AI, “If A Hydrogen Electrolyser is To Be Built In The Port Of Great Yarmouth?”, and received this answer.
While there are no current public plans for an immediate construction of a large-scale hydrogen electrolyser within the Port of Great Yarmouth, significant port expansion and infrastructure upgrades are underway to ensure it can support future hydrogen projects and related clean energy initiatives.
Note.
- If technology to handle hydrogen, is copied from North Sea gas, there is certainly a lot of proven technology that can be used again.
- There may even be depleted gas fields, where captured carbon dioxide, hydrogen or North Sea gas can be stored.
I find the most exciting thing, would be to send hydrogen to Germany.
Why Would Anybody Export Hydrogen To Germany?
I asked Google AI, the question in the title of this section and received this answer.
Countries would export hydrogen to Germany because Germany has a large, growing demand for hydrogen to power its heavily industrialised economy and achieve its decarbonisation goals, but lacks sufficient domestic renewable energy capacity to produce the required amounts.
Germany also, uses a lot of bloodstained Russian gas and indigenous polluting coal.
How Could Anybody Export Hydrogen To Germany?
- Wilhelmshaven is one of the main import ports for hydrogen in North West Germany.
- Great Yarmouth is probably the closest larger port to Germany.
- Great Yarmouth and Wilhelmshaven are probably about 300 miles apart, by the shortest route.
- Great Yarmouth would need to build infrastructure to export hydrogen.
The easiest way to transport the hydrogen from Great Yarmouth to Wilhelmshaven, is probably to use a gas tanker built especially for the route.
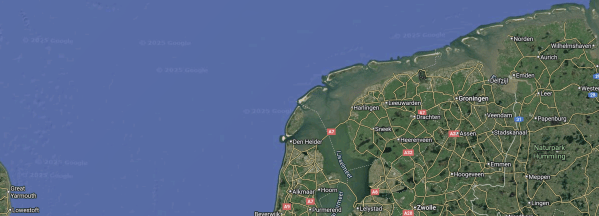
This Google Map shows the route between Great Yarmouth and Wilhelmshaven.
Note.
- The North-East corner of East Anglia with Great Yarmouth to the North of Lowestoft, is in the bottom-left corner of the map.
- Wilhelmshaven is a few miles inland in the top-right corner of the map.
- Could a coastal tanker go along the Dutch and German coasts to Wilhelmshaven?
I have no skills in boats, but would Great Yarmouth to Wilhelmshaven to take hydrogen to Germany?
RWE Are Developing Three Wind Farms To The North-East of Great Yarmouth
RWE are a large German Electricity company and the UK’s largest generator of electricity.
The company is developing three wind farms to the North-East of Great Yarmouth.
- Norfolk Boreas – 1.2 GW – 45 miles offshore
- Norfolk Vanguard West – 1.2 GW – 29 miles offshore
- Norfolk Vanguard East – 1.2 GW – 28 miles offshore
Note.
- The electricity for all three wind farms is to be brought ashore at Happisburgh South, which is about 22 miles North of Great Yarmouth.
- The original plan was to take the electricity halfway across Norfolk to the Necton substation to connect to the grid.
- The natives will not be happy about a 4.2 GW overhead line between Happisburgh and Necton.
- RWE have built offshore electrolysers before in German waters.
- Could an electrical cable or a hydrogen pipe be laid in the sea between Happisburgh South and the Port of Great Yarmouth?
- The electrolyser could either be offshore at Happisburgh or onshore in the Port of Great Yarmouth.
As I don’t suspect these three wind farms will be the last connected to the Port of Great Yarmouth, I would expect that RWE will put the electrolyser offshore at Happisburgh and connect it by a hydrogen pipeline to the Port of Great Yarmouth.
Could There Be A Connection To The Bacton Gas Terminal?
Consider.
The Bacton Gas Terminal, which feeds gas into the UK Gas Network, is only 4.2 miles up the coast from Happisburgh South.
Some climate scientists advocate blending hydrogen into the gas supply to reduce carbon emissions.
In Better Than A Kick In The Teeth – As C Would Say!, I disclosed that I now have a new hydrogen-ready boiler, so I’m not bothered, if I get changed to a hydrogen blend.
So could hydrogen from the Norfolk wind farms be fed into the grid to reduce carbon emissions?
Could The Port Of Great Yarmouth Become A Hydrogen Distribution Centre?
Thinking about it, the port could also become a distribution centre for green hydrogen.
Consider.
- Hydrogen-powered ships, tugs and workboats could be refuelled.
- Hydrogen-powered trucks could also be refuelled.
- Tanker-trucks could distribute hydrogen, to truck and bus operators, farms and factories, that need it for their transport and operations.
- I believe, that construction equipment will be increasingly hydrogen-powered.
In my life, I have lived at times in two country houses, that were heated by propane and there are about 200,000 off-grid houses in the UK, that are heated this way.
The two houses, where I lived would have been a nightmare to convert to heat pumps, but it would have been very easy to convert them to a hydrogen boiler and power it from a tank in the garden.
It should be noted, that the new boiler in my house in London is hydrogen-ready.
So the Port of Great Yarmouth could be the major centre for hydrogen distribution in Norfolk.
In the 1960s, I used to work in ICI’s hydrogen plant at Runcorn. If you ride in a hydrogen bus in England, it is likely that the hydrogen came from the same plant. Handled correctly, hydrogen is no less safe and reliable than natural gas or propane.
Do RWE Have A Comprehensive Hydrogen Plan For Germany?
What is interesting me, is what Germany company; RWE is up to. They are one of the largest UK electricity producers.
In December 2023, they probably paid a low price, for the rights for 3 x 1.4 GW wind farms about 50 km off North-East Norfolk from in-trouble Swedish company; Vattenfall and have signed contracts to build them fairly fast.
In March 2024, wrote about the purchase in RWE And Vattenfall Complete Multi-Gigawatt Offshore Wind Transaction In UK.
Over the last couple of years, I have written several posts about these three wind farms.
March 2023 – Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base
November 2023 – Aker Solutions Gets Vattenfall Nod To Start Norfolk Vanguard West Offshore Platform
December 2023 – SeAH To Deliver Monopiles For Vattenfall’s 2.8 GW Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Project
Then in July 2023, I wrote Vattenfall Stops Developing Major Wind Farm Offshore UK, Will Review Entire 4.2 GW Zone
Note.
- There does appear to be a bit of a mix-up at Vattenfall, judging by the dates of the reports.Only, one wind farm has a Contract for Difference.
- It is expected that the other two will be awarded contracts in Round 6, which should be by Summer 2024.
In December 2023, I then wrote RWE Acquires 4.2-Gigawatt UK Offshore Wind Development Portfolio From Vattenfall.
It appears that RWE paid £963 million for the three wind farms.
I suspect too, they paid for all the work Vattenfall had done.
This transaction will give RWE 4.2 GW of electricity in an area with very bad connections to the National Grid and the Norfolk Nimbies will fight the building of more pylons.
So have the Germans bought a pup?
I don’t think so!
Where Is Wilhemshaven?
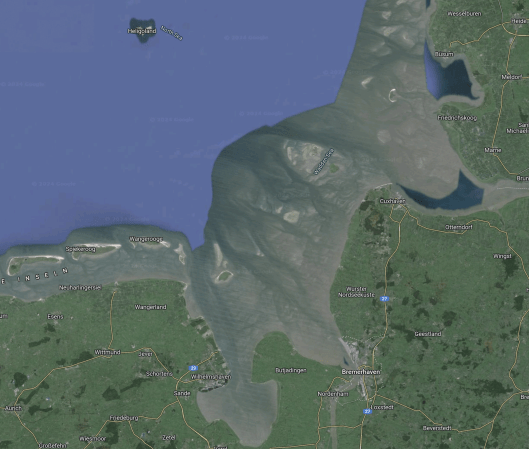
This Google Map shows the location of Wilhemshaven.
Note.
- Heligoland is the island at the top of the map.
- The Germans call this area the Wdden Sea.
- The estuaries lead to Wilhelmshaven and Bremerhaven.
- Cuxhaven is the port for Heligoland, which is connected to Hamburg by hydrogen trains.
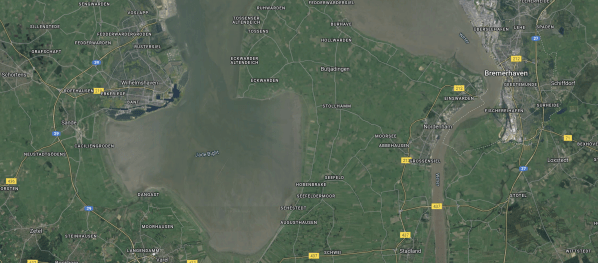
This second map shows between Bremerhaven and Wilhelmshaven.
Note.
- Wilhelmshaven is to the West.
- Bremerhaven is in the East.
- The River Weser runs North-South past Bremerhaven.
I’ve explored the area by both car and train and it is certainly worth a visit.
The Wilhemshaven Hydrogen Import Terminal
German energy company; Uniper is building a hydrogen import terminal at Wilhemshaven to feed German industry with hydrogen from places like Australia, Namibia and the Middle East. I wrote about this hydrogen import terminal in Uniper To Make Wilhelmshaven German Hub For Green Hydrogen; Green Ammonia Import Terminal.
I suspect RWE could build a giant offshore electrolyser close to the Norfolk wind farms and the hydrogen will be exported by tanker or pipeline to Germany or to anybody else who pays the right price.
All this infrastructure will be installed and serviced from Great Yarmouth, so we’re not out of the deal.
Dogger Bank South Wind Farm
To make matters better, RWE have also signed to develop the 3 GW Dogger Bank South wind farm.
This could have another giant electrolyser to feed German companies. The wind farm will not need an electricity connection to the shore.
The Germans appear to be taking the hydrogen route to bringing electricity ashore.
Energy Security
Surely, a short trip across the North Sea, rather than a long trip from Australia will be much more secure and on my many trips between the Haven Ports and The Netherlands, I haven’t yet seen any armed Houthi pirates.
RWE And Hydrogen
On this page on their web site, RWE has a lot on hydrogen.
Very Interesting!
H2ercules
This web site describes H2ercules.
The goal of the H2ercules initiative is to create the heart of a super-sized hydrogen infrastructure for Germany by 2030. To make this happen, RWE, OGE and, prospectively, other partners are working across various steps of the value chain to enable a swift supply of hydrogen from the north of Germany to consumers in the southern and western areas of the country. In addition to producing hydrogen at a gigawatt scale, the plan is also to open up import routes for green hydrogen. The transport process will involve a pipeline network of about 1,500 km, most of which will consist of converted gas pipelines.
Where’s the UK’s H2ercules?
Conclusion
The Germans have got there first and will be buying up all of our hydrogen to feed H2ercules.
RWE Acquires 4.2-Gigawatt UK Offshore Wind Development Portfolio From Vattenfall
The title of this post, is the same as that of this press release from RWE.
These three bullet points, act as sub-headings.
- Highly attractive portfolio of three projects at a late stage of development, with grid connections and permits secured, as well as advanced procurement of key components
- Delivery of the three Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone projects off the UK’s East Anglia coast will be part of RWE’s Growing Green investment and growth plans
- Agreed purchase price corresponds to an enterprise value of £963 million
These two paragraphs outline the deal.
RWE, one of the world’s leading offshore wind companies, will acquire the UK Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone portfolio from Vattenfall. The portfolio comprises three offshore wind development projects off the east coast of England – Norfolk Vanguard West, Norfolk Vanguard East and Norfolk Boreas.
The three projects, each with a planned capacity of 1.4 gigawatts (GW), are located 50 to 80 kilometres off the coast of Norfolk in East Anglia. This area is one of the world’s largest and most attractive areas for offshore wind. After 13 years of development, the three development projects have already secured seabed rights, grid connections, Development Consent Orders and all other key permits. The Norfolk Vanguard West and Norfolk Vanguard East projects are most advanced, having secured the procurement of most key components. The next milestone in the development of these two projects is to secure a Contract for Difference (CfD) in one of the upcoming auction rounds. RWE will resume the development of the Norfolk Boreas project, which was previously halted. All three Norfolk projects are expected to be commissioned in this decade.
There is also this handy map, which shows the location of the wind farms.
Note that there are a series of assets along the East Anglian coast, that will be useful to RWE’s Norfolk Zone development.
- In Vattenfall Selects Norfolk Offshore Wind Zone O&M Base, I talked about how the Port of Great Yarmouth will be the operational base for the Norfolk Zone wind farms.
- Bacton gas terminal has gas interconnectors to Belgium and the Netherlands lies between Cromer and Great Yarmouth.
- The cable to the Norfolk Zone wind farms is planned to make landfall between Bacton and Great Yarmouth.
- Sizewell is South of Lowestoft and has the 1.25 GW Sizewell B nuclear power station, with the 3.2 GW Sizewell C on its way, for more than adequate backup.
- Dotted around the Norfolk and Suffolk coast are 3.3 GW of earlier generations of wind farms, of which 1.2 GW have connections to RWE.
- The LionLink multipurpose 1.8 GW interconnector will make landfall to the North of Southwold
- There is also the East Anglian Array, which currently looks to be about 3.6 GW, that connects to the shore at Bawdsey to the South of Aldeburgh.
- For recreation, there’s Southwold.
- I can also see more wind farms squeezed in along the coast. For example, according to Wikipedia, the East Anglian Array could be increased in size to 7.2 GW.
It appears that a 15.5 GW hybrid wind/nuclear power station is being created on the North-Eastern coast of East Anglia.
The big problem is that East Anglia doesn’t really have any large use for electricity.
But the other large asset in the area is the sea.
- Undersea interconnectors can be built to other locations, like London or Europe, where there is a much greater need for electricity.
- In addition, the UK Government has backed a consortium, who have the idea of storing energy by using pressurised sea-water in 3D-printed concrete hemispheres under the sea. I wrote about this development in UK Cleantech Consortium Awarded Funding For Energy Storage Technology Integrated With Floating Wind.
A proportion of Russian gas in Europe, will have been replaced by Norfolk wind power and hydrogen, which will be given a high level of reliability from Suffolk nuclear power.
I have some other thoughts.
Would Hydrogen Be Easier To Distribute From Norfolk?
A GW-range electrolyser would be feasible but expensive and it would be a substantial piece of infrastructure.
I also feel, that placed next to Bacton or even offshore, there would not be too many objections from the Norfolk Nimbys.
Hydrogen could be distributed from the site in one of these ways.
- By road transport, as ICI did, when I worked in their hydrogen plant at Runcorn.
- I suspect, a rail link could be arranged, if there was a will.
- By tanker from the Port of Great Yarmouth.
- By existing gas interconnectors to Belgium and the Netherlands.
As a last resort it could be blended into the natural gas pipeline at Bacton.
In Major Boost For Hydrogen As UK Unlocks New Investment And Jobs, I talked about using the gas grid as an offtaker of last resort. Any spare hydrogen would be fed into the gas network, provided safety criteria weren’t breached.
I remember a tale from ICI, who from their refinery got a substantial amount of petrol, which was sold to independent petrol retailers around the North of England.
But sometimes they had a problem, in that the refinery produced a lot more 5-star petrol than 2-star. So sometimes if you bought 2-star, you were getting 5-star.
On occasions, it was rumoured that other legal hydrocarbons were disposed of in the petrol. I was once told that it was discussed that used diluent oil from polypropylene plants could be disposed of in this way. But in the end it wasn’t!
If hydrogen were to be used to distribute all or some of the energy, there would be less need for pylons to march across Norfolk.
Could A Rail Connection Be Built To The Bacton Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows the area between North Walsham and the coast.
Note.
- North Walsham is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- North Walsham station on the Bittern Line is indicated by the red icon.
- The Bacton gas terminal is the trapezoidal-shaped area on the coast, at the top of the map.
ThisOpenRailwayMap shows the current and former rail lines in the same area as the previous Google Map.
Note.
- North Walsham station is in the South-West corner of the map.
- The yellow track going through North Walsham station is the Bittern Line to Cromer and Sheringham.
- The Bacton gas terminal is on the coast in the North-East corner of the map.
I believe it would be possible to build a small rail terminal in the area with a short pipeline connection to Bacton, so that hydrogen could be distributed by train.
There used to be a branch line from North Walsham station to Cromer Beach station, that closed in 1953.
Until 1964 it was possible to get trains to Mundesley-on-Sea station.
So would it be possible to build a rail spur to the Bacton gas terminal along the old branch line?
In the Wikipedia entry for the Bittern Line this is said.
The line is also used by freight trains which are operated by GB Railfreight. Some trains carry gas condensate from a terminal at North Walsham to Harwich International Port.
The rail spur could have four main uses.
- Taking passengers to and from Mundesley-on-Sea and Bacton.
- Collecting gas condensate from the Bacton gas terminal.
- Collecting hydrogen from the Bacton gas terminal.
- Bringing in heavy equipment for the Bacton gas terminal.
It looks like another case of one of Dr. Beeching’s closures coming back to take a large chunk out of rail efficiency.
Claire Coutinho And Robert Habeck’s Tete-a-Tete
I wrote about their meeting in Downing Street in UK And Germany Boost Offshore Renewables Ties.
- Did Habeck run the RWE/Vattenfall deal past Coutinho to see it was acceptable to the UK Government?
- Did Coutinho lobby for SeAH to get the contract for the monopile foundations for the Norfolk Zone wind farms?
- Did Coutinho have a word for other British suppliers like iTMPower.
Note.
- I think we’d have heard and/or the deal wouldn’t have happened, if there had been any objections to it from the UK Government.
- In SeAH To Deliver Monopiles For Vattenfall’s 2.8 GW Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Project, I detailed how SeAH have got the important first contract they needed.
So it appears so far so good.
Rackheath Station And Eco-Town
According to the Wikipedia entry for the Bittern Line, there are also plans for a new station at Rackheath to serve a new eco-town.
This is said.
A new station is proposed as part of the Rackheath eco-town. The building of the town may also mean a short freight spur being built to transport fuel to fire an on-site power station. The plans for the settlement received approval from the government in 2009.
The eco-town has a Wikipedia entry, which has a large map and a lot of useful information.
But the development does seem to have been ensnared in the planning process by the Norfolk Nimbys.
The Wikipedia entry for the Rackheath eco-town says this about the rail arrangements for the new development.
The current rail service does not allow room for an extra station to be added to the line, due to the length of single track along the line and the current signalling network. The current service at Salhouse is only hourly during peak hours and two-hourly during off-peak hours, as not all trains are able to stop due to these problems. Fitting additional trains to this very tight network would not be possible without disrupting the entire network, as the length of the service would increase, missing the connections to the mainline services. This would mean that a new 15-minute shuttle service between Norwich and Rackheath would have to be created; however, this would interrupt the main service and cause additional platforming problems. Finding extra trains to run this service and finding extra space on the platforms at Norwich railway station to house these extra trains poses additional problems, as during peak hours all platforms are currently used.
In addition, the plans to the site show that both the existing and the new rail station, which is being built 300m away from the existing station, will remain open.
. As the trains cannot stop at both stations, changing between the two services would be difficult and confusing, as this would involve changing stations.
I feel that this eco-town is unlikely to go ahead.
Did RWE Buy Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone To Create Green Hydrogen For Europe?
Consider.
- Vattenfall’s Norfolk Zone is a 4.2 GW group of wind farms, which have all the requisite permissions and are shovel ready.
- Bacton Gas terminal has gas pipelines to Europe.
- Sizewell’s nuclear power stations will add security of supply.
- Extra wind farms could be added to the Norfolk Zone.
- Europe and especially Germany has a massive need for zero-carbon energy.
The only extra infrastructure needing to be built is the giant electrolyser.
I wouldn’t be surprised if RWE built a large electrolyser to supply Europe with hydrogen.
Vattenfall Stops Developing Major Wind Farm Offshore UK, Will Review Entire 4.2 GW Zone
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on offshoreWIND.biz.
This is the sub-heading.
Vattenfall has stopped the development of the Norfolk Boreas offshore wind power project in the UK and will review the way forward for the entire 4.2 GW Norfolk Zone, the Swedish energy company revealed in its interim report.
This is the first paragraph.
The developer said that the decision to stop the project was made due to ”challenging market conditions”, adding that ”financial frameworks have not adapted to reflect the current market conditions” so far.
Vattenfall are also complaining about inflation and cost increases if up to 40 %.
I have my thoughts.
Great Yarmouth Support Base
In some ways, I find this decision to pull out strange, as it was only in March this year that Vattenfall signed a contract with Peel Ports to build a support base for their Norfolk wind farms at Great Yarmouth.
I don’t think that Peel Ports will be too bothered, as they are a well-funded company and there are plenty of wind farm proposals in the sea around Norfolk, who could use a base at Great Yarmuth.
Cable Routes And Nimbys
These Norfolk wind farms have suffered opposition from Nimbys to the cable route, that will be taking the electricity away from the coast. This may have increased the cost of delivery of the electricity to market.
An Offshore Cable Route
In January 2022, I wrote Is There A Need For A Norfolk-Suffolk Interconnector?, where I analysed the amount of energy, that will be produce in Norfolk and Suffolk.
This was my conclusion.
I believe there are a lot of possibilities, that would meet the three objectives, I stated earlier.
-
- Avoid as much disruption on the land as possible.
- Create the capacity to deliver all the energy generated to customers, either as electricity or hydrogen.
- Create an expandable framework, that would support all the wind farms that could be built in the future.
In addition, simple mathematics says to me, that either there will need to be extra capacity at both Bicker Fen and Bullen Lane substations and onward to the rest of the country, or a large electrolyser to convert several gigawatts of electricity into hydrogen for distribution, through the gas network.
Note.
- An offshore Multiple Purpose Interconnector (MPI) could be built between Bicker Fen in Lincolnshire and the Isle of Grain.
- An electrolyser could be built offshore, joined to the MPI and connected to the Bacton gas terminal.
- There could be local offshore hydrogen storage.
- Bicker Fen is connected to the Viking Link to Denmark.
- An offshore link could have its Southern end at the Isle of Grain, from where the electricity can be exported to Germany, by the NeuConnect interconnector, that is under construction.
There must be sufficient capacity, so that all energy is delivered to customers, as either electricity or hydrogen.
I’ve always favoured delivering electricity from these and other East Anglian wind farms with an offshore cable route away from the coast between perhaps Bicker Fen in Lincolnshire and the the Isle of Grain, from where the electricity can be exported to Germany, by an interconnector, that is being built.
Competition From Scotland
National Grid are improving the offshore grid between Scotland and Humberside, so perhaps Vattenfall might have a competition problem, when it comes to selling their electricity.
If you have no market for a product, then the price drops.
Is East Anglia A Bad Place To Have Surplus Electricity?
Consider.
- It should also be remembered that East Anglia has no heavy electricity users.
- There are also no substantial mountains for building large pumped-storage hydro schemes, as Scotland is proposing to do.
- The construction of Sizewell C will add more electricity to the area.
In my view the best thing to do would be to build a giant electrolyser near the Bacton gas terminal.
Was It A Mistake For Vattenfall To Make A Bid?
Looking at the delivery problems for the Norfolk wind farms, I think that Vattenfall made a bad decision to bid for them.
- The wind farms are too far North to serve London and the South-East and to export the electricity to the Continent.
- They are also too far South to serve the industry in the North around the Humber and the Tees.
It looks an obvious case of wrong Location, Location and Location.
Could Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Viking Work Economically?
I suspect these ideas could help.
- A Multiple Purpose Interconnector (MPI) would be built between Bicker Fen in Lincolnshire and the Isle of Grain.
- The MPI would connect to any wind farms on the route.
- An offshore electrolyser opposite Bacton would be connected to the MPI to use surplus electricity to generate hydrogen, which would be distributed through the gas grid.
The whole network of wind farms, interconnectors, electrolysers and storage needs to be comprehensively designed, so that it provides the South-East corner of England, with enough reliable electricity and hydrogen.
Could Greater Anglia Run A Comprehensive Service For East Anglia?
Consider.
- In the last fifty years, there have been direct trains between London Liverpool Street and Lowestoft stations.
- In the last forty years, there have been direct trains between London Liverpool Street and Peterborough stations.
- Greater Anglia currently run an hourly train between London Liverpool Street and Ipswich stations, with stops at Stratford, Shenfield, Chelmsford, Hatfield Peverel, Witham, Kelvedon, Marks Tey, Colchester and Manningtree
- Frequencies on both routes were not high and less than four trains per day (tpd), but they must have been a demand for these services.
- Greater Anglia promised to run a Lowestoft service, when they successfully reapplied for the franchise.
- Greater Anglia have 38 Class 755 trains, of which 14 are three-cars and 24 are four-cars.
- Class 755 trains can run in twoses and possibly threeses. (Suffolk dialect for twins and triplets!)
Could these elements be assembled to provide a comprehensive East Anglia service?
- A pair of Class 755 trains would leave Liverpool Street for Ipswich.
- They would takeover some of the paths of the hourly Liverpool Street and Ipswich service and run possibly about four or five tpd, according to demand.
- Between Liverpool Street and Ipswich the trains could stop at Stratford, Shenfield, Chelmsford, Hatfield Peverel, Witham, Kelvedon, Marks Tey, Colchester and Manningtree
- The services would splitgoing North and join going South at Ipswich
- One train would go to Peterborough with stops at Needham Market, Stowmarket, Elmswell, Thurston, Bury St. Edmunds, Soham, Ely, Manea, March and Whittlesea.
- The other would go to Lowestoft with stops at Woodbridge, Melton, Wickham Market, Saxmundham, Darsham, Halesworth, Brampton, Beccles and Oulton Broad South.
Note.
- The Class 755 trains would use electricity, where electrification exists.
- They would use diesel on lines without electrification.
- They would be able to hold 100 mph, so wouldn’t delay other trains.
- Seventeen towns would get new direct services to and from London.
- A Class 745 train is 236.6 metres long, whereas a pair of four-car Class 755 trains is only 161.4 metres.
- A three-train formation of Class 755 trains is only 5.5 metres longer than a single Class 745 train.
I am fairly sure no new substantial infrastructure would be required.
I have some further thoughts.
Example Timings
These timings to and from London are based on current timings of the Class 745 and 755 trains.
- Ipswich – 60 mins
- Stowmarket -70 mins
- Bury St. Edmunds – 88 mins
- Soham – 108 mins
- Ely – 117 mins
- March – 136 mins
- Peterborough – 158 mins
- Woodbridge – 75 mins
- Melton – 80 mins
- Wickham Market – 86 mins
- Saxmundham – 97 mins
- Darsham – 104 mins
- Halesworth – 113 mins
- Brampton – 119 mins
- Beccles – 128 mins
- Oulton Broad South – 138 mins
- Lowestoft – 146 mins
Notes.
- Times to and from Ipswich are based on typical services at the current time.
- I have assumed that there are no stops South of Ipswich.
- Saxmundham is the closest station to Sizewell and could be important in bringing in construction workers for Sizewell C.
I think some of the times like those to and from Bury St. Edmunds, Ipswich, Lowestoft, Saxmundham and Woodbridge could create popular routes.
Battery-Electric Trains
Consider.
- I wrote about Stadler’s expertise with battery-electric trains in Stadler FLIRT Akku Battery Train Demonstrates 185km Range.
- 185 km. is 115 miles.
- The Class 756 trains for Transport for Wales are similar trains to the Class 755 trains fitted with batteries.
- In Battery Power Lined Up For ‘755s’, I wrote about plans to put batteries in the Class 755 trains.
These sections of lines are not electrified on the routes I have talked about.
- Haughley Junction and Ely – 38 miles
- Ely and Peterborough – 30.5 miles
- Westerfield and Lowestoft – 38 miles
As there is electrification at Ely, Haughley, Peterborough and Westerfield and South to London, I am fairly certain the route could be run by battery-electric trains.
Electrification To Sizewell C
In the January 2023 Edition of Modern Railways, there is an article, which is entitled Rail Set To Support Sizewell C Construction.
It details how sidings will be built to support the construction, with up to four trains per day (tpd), but the electrification word is not mentioned.
This is surprising to me, as increasingly, big construction projects are being managed to emit as small an amount of carbon as possible. High Speed Two is being built this way and I suspect Rolls-Royce’s SMR design will minimise carbon emissions during manufacture and construction. It will be very surprising if Sizewell C doesn’t follow High Speed Two’s example. After all, it may be an isolated site, but in Sizewell B, it’s got one of the UK’s biggest carbon-free electricity generators a couple of hundred metres away.
The writer of the Modern Railways article, thinks an opportunity is being missed.
I feel the following should be done.
- Improve and electrify the East Suffolk Line between Ipswich and Saxmundham Junction.
- Electrify the Aldeburgh Branch Line and the sidings to support the construction or agree to use battery-electric or hydrogen zero-carbon locomotives.
One of the collateral benefits of electrifying from Ipswich to Saxmundham Junction, is that it will make it easier for battery-electric Class 755 trains to work Ipswich and Lowestoft services.
- If the trains were to leave Saxmundham Junction going North with a full battery, they should be able to travel to Lowestoft and return.
- Battery-electric Class 755 trains could bring in workers from Ipswich or Lowestoft and further afield.
- It could even leave behind a zero-carbon branch line to Sizewell, Leiston and Aldeburgh, with two tph to Ipswich.
Sizewell C could be a superb demonstration project for low-carbon construction!
The Lowestoft-Great Yarmouth Conurbation
The Wikipedia entry for Lowestoft says this about the town.
The estimated population in the built-up area exceeds 70,000. Its development grew with the fishing industry and as a seaside resort with wide sandy beaches. As fishing declined, oil and gas exploitation in the North Sea in the 1960s took over. While these too have declined, Lowestoft is becoming a regional centre of the renewable energy industry.
Whilst the Wikipedia entry for Great Yarmouth says this about the town.
Great Yarmouth, often called Yarmouth, is a seaside town and unparished area in, and the main administrative centre of, the Borough of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England; it straddles the River Yare and is located 20 miles (30 km) east of Norwich. A population of 38,693 in the 2011 Census made it Norfolk’s third most populous. Its fishing industry, mainly for herring, shrank after the mid-20th century and has all but ended.[3] North Sea oil from the 1960s supplied an oil-rig industry that services offshore natural gas rigs; more recently, offshore wind power and other renewable energy industries have ensued.
Wikipedia also said this about the population of the wider Great Yarmouth.
The wider Great Yarmouth borough had a population of around 92,500, which increased to 97,277 at the 2011 census.
Taken together they are one of the largest conurbations in East Anglia.
The main means of transport between the two towns is by road.
Surely, two towns of over 70,000 people, who are only a few miles apart need a rail connection.
Onward From Lowestoft To Great Yarmouth
If the comprehensive East Anglia service, I’m discussing is to be truly comprehensive, it must serve the Norfolk Broads and Great Yarmouth.
This would also improve the connectivity between two of the largest coastal towns in East Anglia, that I indicated in the last section.
This OpenRailwayMap shows a cunning plan proposed by Network Rail to connect Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth.
Note.
- Great Yarmouth is in the North East corner of the map.
- Two lines lead West from Great Yarmouth station, with the more Northerly route going direct to Norwich and the more Southerly one going to Norwich via Berney Arms and Reedham.
- Lowestoft is in the South East corner of the map.
- Two lines lead West from Lowestoft station, with the Northern route going to Norwich via Reedham and the Southern one going to Ipswich via Oulton Broad South.
- The route of a coastal railway connecting the two towns is also shown.
Network Rail’s cunning plan is indicated on this second nap from OpenRailwayMap.
Note.
- Reedham station is in the North-West corner of the map on the line to Norwich.
- To the East of the station is a triangular junction.
- The track from the North-East corner of the junction is the line to Great Yarmouth.
- The track from the Southern corner of the junction is the line to Lowestoft.
- Unfortunately, the South-Eastern leg of the junction was removed in 1880.
In Norfolk Rail Line To Remain Closed As £68m Upgrade Project Overruns, I said this.
Network Rail are talking about reinstating the Reedham Chord to create a more direct route between East Anglia’s largest North-Eastern towns. This is said about the Reedham Chord in Direct Yarmouth Services in the Wikipedia entry for Lowestoft station.
In January 2015, a Network Rail study proposed the reintroduction of direct services between Lowestoft and Yarmouth by reinstating a spur at Reedham. Services could once again travel between two East Coast towns, with an estimated journey time of 33 minutes, via a reconstructed 34-chain (680 m) north-to-south arm of the former triangular junction at Reedham, which had been removed in c. 1880. The plans also involve relocating Reedham station nearer the junction, an idea which attracted criticism.
This sounds a good plan to me.
- It would allow direct services between Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth.
- It would allow direct services between Ipswich and Great Yarmouth with a reverse at Lowestoft in about two hours.
- With possible charging at Lowestoft and/or Great Yarmouth, a scenic route could be created between Ipswich and Norwich for battery-electric Class 755 trains. If that doesn’t get people out of their cars then nothing will!
- Various leisure, tourism and work-related opportunities would be created.
Never in the field of railway engineering would such a small chord have given so much.
Sizewell C Issues
Sizewell C will be a massive project and I also suspect that like High Speed Two, it will be built in a manner that will be zero-carbon where possible.
We already know from the Modern Railways article, that four tpd will shuttle material to a number of sidings close to the site. This is a good start.
Since Sizewell A opened, trains have regularly served the Sizewell site to bring in and take out nuclear material. These occasional trains go via Ipswich and in the last couple of years have generally been hauled by Class 88 electro-diesel locomotives.
It would be reasonable to assume that the Sizewell C sidings will be served in the same manner.
But the route between Westerfield Junction and Ipswich station is becoming increasingly busy with the following services.
- Greater Anglia’s London and Norwich services
- Greater Anglia’s Ipswich and Cambridge services
- Greater Anglia’s Ipswich and Felixstowe services
- Greater Anglia’s Ipswich and Lowestoft services
- Greater Anglia’s Ipswich and Peterborough services
- Freight services serving the Port of Felixstowe, which are expected to increase significantly in forthcoming years.
But the Modern Railways article says this about Saxmundham junction.
Saxmundham junction, where the branch meets the main line, will be relaid on a slightly revised alignment, retaining the existing layout but with full signalling giving three routes from the junction protecting signal on the Down East Suffolk line and two in the Down direction on the bidirectional Up East Suffolk line. Trap points will be installed on the branch to protect the main line, with the exit signal having routes to both running lines.
Does the comprehensive signalling mean that a freight train can enter or leave the Sizewell sidings to or from either the busy Ipswich or the quieter Lowestoft direction in a very safe manner?
I’m no expert on signalling, but I think it does.
- A train coming from the Lowestoft direction needing to enter the sidings would go past Saxmundham junction on the Up line. Once clear of the junction, it would stop and reverse into the branch.
- A train coming from the Ipswich direction needing to enter the sidings would approach in the wrong direction on the Up line and go straight into the branch.
- A train leaving the sidings in the Lowestoft direction would exit from the branch and take the Up line until it became single track. The train would then stop and reverse on to the Down line and take this all the way to Lowestoft.
- A train leaving the sidings in the Ipswich direction would exit from the branch and take the Up line all the way to Ipswich.
There would need to be ability to move the locomotive from one end to the other inside the Sizewell site or perhaps these trains could be run with a locomotive on both ends.
The advantage of being able to run freight trains between Sizewell and Lowestoft becomes obvious, when you look at this Google Map, which shows the Port of Lowestoft.
Note.
- The Inner Harbour of the Port of Lowestoft.
- The East Suffolk Line running East-West to the North of the Inner Harbour.
- Lowestoft station at the East side of the map.
I doubt it would be the most difficult or expensive of projects to build a small freight terminal on the North side of the Inner Harbour.
I suspect that the easiest way to bring the material needed to build the power station to Sizewell would be to do the following.
- Deliver it to the Port of Lowestoft by ship.
- Tranship to a suitable shuttle train for the journey to the Sizewell sidings.
- I estimate that the distance is only about 25 miles and a battery or hydrogen locomotive will surely be available in the UK in the next few years, that will be able to provide the motive power for the return journey.
In The TruckTrain, I wrote about a revolutionary freight concept, that could be ideal for the Sizewell freight shuttle.
Great Yarmouth Racecourse
Great Yarmouth Racecourse is one of my favourite racecourses and I believe it is one of the attractions in Great Yarmouth, that would benefit from an improved rail service between Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth, as it would almost double those with efficient public transport access to the racecourse.
The walking distance between Great Yarmouth station and the racecourse is walkable for many and I remember doing it since C died.
With the train connection to Lowestoft and perhaps a courtesy bus from the station, I wouldn’t be surprised to see that a Lowestoft-Yarmouth rail connection being very good for the racecourse. Especially as road traffic between the two towns can be not the best.
Finishing At Norwich
There are operational reasons to carry on to Norwich, where Crown Point, is the home base for the Class 755 trains.
But it would also link a lot of places that are dependant on tourism and are also heavily involved in East Anglia’s energy industry.
Onward From Peterborough To Lincoln
If the Lowestoft service can extend to Great Yarmouth, an extension of the Peterborough service to Lincoln via Spalding and Sleaford might be possible.
But with LNER also serving Lincoln from Kings Cross, I doubt the route would carry many passengers to and from London.
Conclusion
A service from London, that splits into two trains at Ipswich for Lowestoft and Peterborough has possibilities.
Norfolk Wind Farms Offer ‘Significant Benefit’ For Local Economy
The title of this post, is the same as that of this article on the BBC.
This is a comprehensive article, which looks at the benefits of the huge Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard wind farms will have to the economy of Norfolk.
The last section is devoted to Norfolk Nimby; Raymond Pearce.
This is the section.
Following the re-approval of the decision by the government, Mr Pearce says he is considering a new appeal over what he calls “a very poor decision”.
He is also sceptical of claims the two new wind farms will bring the economic gains promised by Vattenfall.
“It’s renewable energy at any cost and the cost here is to the environment in Norfolk,” he says.
“I don’t blame them for being positive about it, it’s their industry but they’re not looking at it holistically.”
He says he is not against renewable energy but thinks a better plan is needed to connect the offshore windfarms and minimise the number of cables and substations onshore.
It’s his money if he appeals, but we do need more wind, solar and other zero-carbon energy to combat global warming and its effects like the encroachment of the sea around Norfolk.
I believe, that building wind farms off the coast of Essex, Suffolk and Norfolk is a good move, as in the future, if we have spare electricity, it will be easy to export energy to Europe, through existing interconnectors.
But I do agree with him, that a better plan is needed to connect the offshore windfarms and minimise the number of cables and substations onshore.
A Norfolk Powerhouse
This map from Vattenfall, the developer of the two wind farms, shows the position of the farms and the route of the cable to the shore.
Note.
- The purple line appears to be the UK’s ten mile limit.
- Norfolk Boreas is outlined in blue.
- Norfolk Vanguard is outlined in orange.
- Cables will be run in the grey areas.
- Both wind farms are planned to have a capacity of 1.8 GW
Landfall will be just a few miles to the South of the Bacton gas terminal.
Bacton Gas Terminal
Bacton gas terminal is much more than a simple gas terminal.
- It is a complex of six gas terminals on four sites.
- There is a National Grid terminal, that odourises and blends the gas before distributing it into the National Transmission System via five outgoing 36-inch feeders to much of Southern England.
- There is a gas interconnector to Belgium.
- There is a gas interconnector to The Netherlands.
- There is coastal erosion in the area.
With the need to decarbonise, I can’t help feeling that the Bacton gas terminal is very much on the decline and the site will need to be repurposed in the next few years.
Blending Hydrogen With Natural Gas
If you blend a proportion of hydrogen into natural gas, this has two beneficial effects.
- Gas used in domestic and industrial situations will emit less carbon dioxide.
- In the near future we will be replacing imported natural gas with hydrogen.
The hydrogen could be produced by a giant electrolyser at Bacton powered by the electricity from the two Norfolk wind farms.
At the present time, a research project call HyDeploy is underway, which is investigating the blending of hydrogen into the natural gas supply.
- Partners include Cadent, Northern Gas Networks, the Health and Safety Executive, Keele University and ITM Power and Progessive Energy.
- A first trial at Keele University has been hailed as a success.
- It showed up to twenty percent of hydrogen by volume can be added to the gas network without the need to change any appliances or boilers.
Larger trials are now underway.
A Giant Electrolyser At Bacton
If hydrogen were to be produced at Bacton by a giant electrolyser, it could be used or distributed in one of the following ways.
- Blended with natural gas for gas customers in Southern England.
- Stored in a depleted gas field off the coast at Bacton. Both Baird and Deborah gas fields have been or are being converted to gas storage facilities, connected to Bacton.
- Distributed by truck to hydrogen filling stations and bus and truck garages.
- Greater Anglia might like a hydrogen feed to convert their Class 755 trains to hydrogen power.
- Sent by a short pipeline to the Port of Great Yarmouth and possibly the Port of Lowestoft.
- Exported to Europe, through one of the interconnectors.
Note.
- If the electrolyser were to be able to handle the 3.6 GW of the two wind farms, it would be the largest in the world.
- The size of the electrolyser could be increased over a few years to match the output of the wind farms as more turbines are installed offshore.
- There is no reason, why the electrical connection between Bacton and the landfall of the wind farm cable couldn’t be offshore.
If ITM Power were to supply the electrolyser, it would be built in the largest electrolyser factory in the World, which is in Sheffield in Yorkshire.
A Rail Connection To The Bacton Gas Terminal
This Google Map shows the area between North Walsham and the coast.
Note.
- North Walsham is in the South-Western corner of the map.
- North Walsham station on the Bittern Line is indicated by the red icon.
- The Bacton gas terminal is the trapezoidal-shaped area on the coast, at the top of the map.
I believe it would be possible to build a small rail terminal in the area with a short pipeline connection to Bacton, so that hydrogen could be distributed by train.
How Much Hydrogen Could Be Created By The Norfolk Wind Farms?
In The Mathematics Of Blending Twenty Percent Of Hydrogen Into The UK Gas Grid, I said the following.
Ryze Hydrogen are building the Herne Bay electrolyser.
- It will consume 23 MW of solar and wind power.
- It will produce ten tonnes of hydrogen per day.
The electrolyser will consume 552 MWh to produce ten tonnes of hydrogen, so creating one tonne of hydrogen needs 55.2 MWh of electricity.
Each of the Norfolk wind farms, if they were working flat out would produce 43.2 GWh of electricity in a day.
Dividing the two figures gives a daily production rate of 782.6 tonnes of hydrogen per day.
But what happens if the wind doesn’t blow?
This is where the gas storage in the Baird, Deborah and other depleted gas fields comes in.In times of maximum wind, hydrogen is stored for use when the wind doesn’t blow.
Conclusion
I believe a plan like this, would be much better for Norfolk, the UK and the whole planet.
Using the existing gas network to carry the energy away from Norfolk, could mean that the electricity connection across Norfolk could be scaled back.
Is There A Need For A Norfolk-Suffolk Interconnector?
The coast of East Anglia from the Wash to the Haven Ports of Felixstowe, Harwich and Ipswich is becoming the Energy Coast of England.
Starting at the Wash and going East and then South, the following energy-related sites or large energy users are passed.
Bicker Fen Substation
Bicker may only be a small hamlet in Lincolnshire, but it is becoming increasingly important in supplying energy to the UK.
Nearby is Bicker Fen substation, which connects or will connect the following to the National Grid.
- The 26 MW Bicker Fen onshore windfarm.
- The 1,400 MW interconnector from Denmark called Viking Link.
- The proposed 857 MW offshore wind farm Triton Knoll.
This Google Map shows the location of Bicker Fen with respect to The Wash.
Bicker Fen is marked by the red arrow.
The Google Map shows the substation.
It must be sized to handle over 2 GW, but is it large enough?
Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm
The Dudgeon offshore wind farm is a 402 MW wind farm, which is twenty miles off the North Norfolk coast.
- It has 67 turbines and an offshore substation.
- It is connected to the shore at Weybourne on the coast from where an underground cable is connected to the National Grid at Necton.
- It became operational in Oct 2017.
- Equinor and Statkraft are part owners of the windfarm and this is the home page of the wind farm’s web site.
- Equinor is the operator of the wind farm.
This Google Map shows the location of Weybourne on the coast.
Note.
- Weybourne is in the middle on the coast.
- Sheringham is on the coast in the East.
- Holt is on the Southern edge of the map almost South of Weybourne.
This second map shows the location of the onshore substation at Necton, with respect to the coast.
Note.
- The Necton substation is marked by a red arrow.
- Holt and Sheringham can be picked out by the coast in the middle.
- Weybourne is to the West of Sheringham.
- Necton and Weybourne are 35 miles apart.
Digging in the underground cable between Necton and Weybourne might have caused some disruption.
Looking at Weybourne in detail, I can’t find anything that looks like a substation. So is the Necton substation connected directly to Dudgeon’s offshore substation?
Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm
The Sheringham Shoal offshore wind farm is a 316.8 MW wind farm, which is eleven miles off the North Norfolk coast.
- It has 88 turbines and two offshore substations.
- As with Dudgeon, it is connected to the shore at Weybourne on the coast.
- But the underground cable is connected to an onshore substation at Salle and that is connected to the National Grid at Norwich.
- It became operational in Sept 2012.
- Equinor and Statkraft are part owners of the windfarm and this is the home page of the wind farm’s web site.
- Equinor is the operator of the wind farm.
This second map shows the location of the onshore substation at Salle, with respect to the coast.
Note.
- The Salle substation is marked by a red arrow.
- Holt, Weybourne and Sheringham can be picked out by the coast in the middle.
- Weybourne is to the West of Sheringham.
- Salle and Weybourne are 13.5 miles apart.
Could the following two statements be true?
- As the Sheringham Shoal wind farm was built first, that wind farm was able to use the shorter route.
- It wasn’t built large enough to be able to handle the Dudgeon wind farm.
The statements would certainly explain, why Dudgeon used a second cable.
Extending The Dudgeon And Sheringham Shoal Wind Farms
Both the Dudgeon And Sheringham Shoal web sites have details of the proposed join extension of both wind farms.
This is the main statement on the Overview page.
Equinor has been awarded an Agreement for Lease by the Crown Estate, the intention being to seek consents to increase the generating capacity of both the Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm and the Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm.
They then make three points about the development.
- Equinor is proposing a joint development of the two projects with a common transmission infrastructure.
- As part of the common DCO application, the Extension Projects have a shared point of connection at the National Grid Norwich Main substation.
- These extension projects will have a combined generating capacity of 719MW which will make an important contribution to the UK’s target of 30GW of electricity generated by offshore wind by 2030.
This statement on the Offshore Location page, describes the layout of the wind farms.
The Sheringham Shoal Offshore Wind Farm extension is to the north and the east of the existing wind farm, while its Dudgeon counterpart is to the north and south east of the existing Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm site. The proposed extension areas share the boundaries with its existing wind farm site.
They then make these two important points about the development.
- Equinor is seeking to develop the extension project with a joint transmission infrastructure. A common offshore substation infrastructure is planned to be located in the Sheringham Shoal wind farm site.
- The seabed export cable which will transmit the power generated by both wind farm extensions will make landfall at Weybourne.
There is also this map.
Note.
- The purple line appears to be the UK’s ten mile limit.
- The Sheringham Shoal Extension is outlined in red.
- The Dudgeon Extension is outlined in blue.
- The black lines appear to be the power cables.
I suspect the dotted blue lines are shipping routes sneaking their way through the turbines.
This statement on the Onshore Location page, describes the layout of the offshore and onshore cables.
A new seabed export cable will bring the electricity generated by both the Sheringham Shoal and Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm extensions to shore at Weybourne, on the coast of Norfolk.
They then make these two important points about the development.
- From there a new underground cable will be installed to transmit that power to a new purpose built onshore substation, which will be located within a 3km radius of the existing Norwich main substation, south of Norwich. This will be the National Grid network connection point for the electricity from both wind farm extensions.
- The power will be transmitted from landfall to the substation using an HVAC system which eliminates the need for any relay stations along the onshore cable route.
There is also this map.
It will be a substantial undertaking to build the underground cable between Weybourne and South of Norwich.
Bacton Gas Terminal
The Bacton gas terminal is a complex of six gas terminals about ten miles East of Cromer.
- It lands and processes gas from a number of fields in the North Sea.
- It hosts the UK end of the BBL pipeline to The Netherlands.
- It hosts the UK end of the Interconnector to Zeebrugge in Belgium.
- The Baird and Deborah fields, which have been developed as gas storage, are connected to the gas terminal. They are both mothballed.
This Google Map shows the location of the terminal.
Note.
- The Bacton gas terminal is marked by a red arrow.
- Sheringham is in the North West corner of the map.
- Cromer, Overstrand, Trimingham and Mundesley are resort towns and villages along the coast North of Bacton.
This second map shows the Bacton gas terminal in more detail.
Would you want to have a seaside holiday, by a gas terminal?
Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Vanguard
Norfolk Boreas and Norfolk Vanguard are two wind farms under development by Vattenfall.
- Norfolk Boreas is a proposed 1.8 GW wind farm, that will be 45 miles offshore.
- Norfolk Vanguard is a proposed 1.8 GW wind farm, that will be 29 miles offshore.
This map shows the two fields in relation to the coast.
Note.
- The purple line appears to be the UK’s ten mile limit.
- Norfolk Boreas is outlined in blue.
- Norfolk Vsnguard is outlined in orange.
- Cables will be run in the grey areas.
This second map shows the onshore cable.
Note.
- The cables are planned to come ashore between Happisburgh and Eccles-on-Sea.
- Bacton gas terminal is only a short distance up the coast.
- The onshore cable is planned to go from here across Norfolk to the Necton substation.
But all of this has been overturned by a legal ruling.
This article on the BBC is entitled Norfolk Vanguard: Ministers Wrong Over Wind Farm Go-Ahead, Says Judge.
These are the first four paragraphs.
A High Court judge has quashed permission for one of the world’s largest offshore wind farms to be built off the east coast of England.
The Norfolk Vanguard Offshore Wind Farm was granted development consent in July by the Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS).
But Mr Justice Holgate overturned the decision following legal action from a man living near a planned cable route.
A Department for BEIS spokeswoman said it was “disappointed by the outcome”.
I bet the spokeswoman was disappointed.
Vattenfall and the BEIS will go back to the drawing board.
But seriously, is it a good idea to dig an underground cable all the way across Norfolk or in these times build a massive overhead cable either?
Perhaps the solution is to connect the Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Vanguard wind farms to a giant electrolyser at Bacton, which creates hydrogen.
- The underground electricity cable across Norfolk would not be needed.
- Bacton gas terminal is only a few miles up the coast from the cable’s landfall.
- The UK gets another supply of gas.
- The hydrogen is blended with natural gas for consumption in the UK or Europe.
- A pure hydrogen feed can be used to supply hydrogen buses, trucks and other vehicles, either by tanker or pipeline.
- Excess hydrogen could be stored in depleted gas fields.
The main benefit though, would be that it would transform Bacton gas terminal from a declining asset into Norfolk’s Hydrogen Powerhouse.
Great Yarmouth And Lowestoft
Great Yarmouth Outer Harbour and the Port of Lowestoft have not been the most successful of ports in recent years, but with the building of large numbers of wind farms, they are both likely to receive collateral benefits.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see the support ships for the wind farms switching to zero-carbon power, which would require good electrical connections to the ports to either charge batteries or power electrolysers to generate hydrogen.
Sizewell
Sizewell has only one nuclear power station at present; Sizewell B, but it could be joined by Sizewell C or a fleet of Small Modular Reactors (SMR).
The Sizewell Overhead Transmission Line
Sizewell also has a very high capacity overhead power line to Ipswich and the West.
I doubt, it would be possible to build an overhead transmission line like this today.
Sizewell And Hydrogen
EdF, who own the site are involved with Freeport East and may choose to build a large electrolyser in the area to create hydrogen for the Freeport.
East Anglia Array
The East Anglia Array will be an enormous wind farm., comprising up to six separate projects.
It will be thirty miles offshore.
It could generate up to 7.2 GW.
The first project East Anglia One is in operation and delivers 714 MW to a substation in the Deben Estuary, which connects to the Sizewell high-capacity overhead power line.
Most projects will be in operation by 2026.
Freeport East
As the Freeport develops, it will surely be a massive user of both electricity and hydrogen.
Problems With The Current Electricity Network
I don’t believe that the current electricity network, that serves the wind farms and the large energy users has been designed with the number of wind farms we are seeing in the North Sea in mind.
Every new windfarm seems to need a new connection across Norfolk or Suffolk and in Norfolk, where no high-capacity cables exist, this is stirring up the locals.
There is also no energy storage in the current electricity network, so at times, the network must be less than efficient and wind turbines have to be shut down.
Objections To The Current Policies
It is not difficult to find stories on the Internet about objections to the current policies of building large numbers of wind farms and the Sizewell C nuclear power station.
This article on the East Anglia Daily Times, which is entitled Campaigners Unite In Calling For A Pause Before ‘Onslaught’ Of Energy Projects ‘Devastates’ Region is typical.
This is the first paragraph.
Campaigners and politicians have called on the Government to pause the expansion of the energy industry in Suffolk, which they fear will turn the countryside into an “industrial wasteland” and hit tourism.
The group also appear to be against the construction of Sizewell C.
I feel they have a point about too much development onshore, but I feel that if the UK is to thrive in the future we need an independent zero carbon energy source.
I also believe that thousands of wind farms in the seas around the UK and Ireland are the best way to obtain that energy.
Blending Hydrogen With Natural Gas
Blending green hydrogen produced in an electrolyser with natural gas is an interesting possibility.
- HyDeploy is a project to investigate blending up to 20 % of green hydrogen in the natural gas supply to industrial and domestic users.
- Partners include Cadent, ITM Power, Keele University and the Health and Safety Executive.
- Natural gas naturally contains a small amount of hydrogen anyway.
- The hydrogen gas would be distributed to users in the existing gas delivery network.
I wrote about HyDeploy in a post called HyDeploy.
Thje only loser, if hydrogen were to be blended with natural gas would be Vlad the Poisoner, as he’d sell less of his tainted gas.
An Interconnector Between Bicker Fen And Freeport East
I believe that an electricity interconnector between at least Bicker Fen and Freeport East could solve some of the problems.
My objectives would be.
- Avoid as much disruption on the land as possible.
- Create the capacity to deliver all the energy generated to customers, either as electricity or hydrogen.
- Create an expandable framework, that would support all the wind farms that could be built in the future.
The interconnector would be a few miles offshore and run along the sea-bed.
- This method of construction is well proven.
- It was used for the Western HVDC Link between Hunterston in Scotland and Connah’s Quay in Wales.
- Most wind farms seem to have existing substations and these would be upgraded to host the interconnector.
Connections en route would include.
Dudgeon Offshore Wind Farm
The interconnector would connect to the existing offshore substation.
Sheringham Shoal Wind Farm
The interconnector would connect to the existing offshore substation.
Dudgeon and Sheringham Shoal Extension Offshore Wind Farms
These two wind farms could be connected directly to the interconnector, if as planned, they shared an offshore substation in the Sheringham Shoal Extension offshore wind farm.
Bacton Gas Terminal
I would connect to the Bacton Gas Terminal, so that a large electrolyser could be installed at the terminal.
The hydrogen produced could be.
- Stored in depleted gas fields connected to the terminal.
- Blended with natural gas.
- Exported to Europe through an interconnector.
- Supplied to local users by truck or pipeline.
After all, the terminal has been handling gas for over fifty years, so they have a lot of experience of safe gas handling.
Norfolk Boreas And Norfolk Vanguard
These two wind farms could be connected directly to the interconnector, if they shared an offshore substation.
It would also help to appease and silence the objectors, if there was no need to dig up half of Norfolk.
Great Yarmouth And Lowestoft
It might be better, if these ports were supplied from the interconnector.
- Either port could have its own electrolyser to generate hydrogen, which could be.
- Used to power ships, trucks and port equipment.
- Liquefied and exported in tankers.
- Used to supply local gas users.
- Hydrogen could be supplied to a converted Great Yarmouth power station.
Both Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft could become hydrogen hub towns.
Sizewell
This site has a high-capacity connection to the National Grid. This connection is a big eyesore, but it needs to run at full capacity to take electricity from the Energy Coast to the interior of England.
That electricity can come from Sizewell B and/or Sizewell C nuclear power stations or the offshore wind farms.
East Anglia Array
There would probably need to be a joint offshore substation to control the massive amounts of electricity generated by the array.
Currently, the only wind farm in operation of this group is East Anglia One, which uses an underground cable connection to the Sizewell high-capacity connection to the Bullen Lane substation at Bramford.
Freeport East, Ipswich And Bullen Lane Substation
This Google Map shows the area between Ipswich and the coast.
Note.
- Sizewell is in the North-East corner of the map.
- Felixstowe, Harwich and Freeport East are at the mouth of the rivers Orwell and Stour.
- The Bullen Lane substation is to the West of Ipswich and shown by the red arrow.
I would certainly investigate the possibility of running an underwater cable up the River Orwell to connect the Southern end of the interconnector Between Bicker Fen And Freeport East.
This Google Map shows the Bullen Lane Substation.
It looks impressive, but is it big enough to handle all the electricity coming ashore from the offshore wind farms to the East of Suffolk and the electricity from the power stations at Sizewell?
Conclusion
I believe there are a lot of possibilities, that would meet the threeobjectives, I stated earlier.
- Avoid as much disruption on the land as possible.
- Create the capacity to deliver all the energy generated to customers, either as electricity or hydrogen.
- Create an expandable framework, that would support all the wind farms that could be built in the future.
In addition, simple mathematics says to me, that either there will need to be extra capacity at both Bicker Fen and Bullen Lane substations and onward to the rest of the country, or a large electrolyser to convert several gigawatts of electricity into hydrogen for distribution, through the gas network.
A Trip On The East Suffolk Line In A New Stadler Class 755 Train
Today, I took a round trip between Ipswich and Lowestoft stations, along the East Suffolk Line, in one of Greater Anglia’s new Class 755 trains.
These are my observations and comments.
Stations
The stations vary between the very good and the very basic.
- I don’t think that any station has a step-free bridge to cross the line.
- Many stations are just a single platform.
- Crossing the line often involves a nearby level crossing.
- Westerfield, Woodbridge, Saxmundham, Darsham, Halesworth and Beccles have two platforms.
- Lowestoft and Ipswich are both step-free from the street to the platforms.
- There also appears to be step-free access between the new trains and the platforms.
Overall, from what I could see from the train, each stop was fairly efficient, although I do think that when the drivers and train staff, fully get to grips with the trains, that there is time to be saved on each of the ten stops.
Consider.
- These trains have much better acceleration and deceleration, than the trains for which the timetable was written.
- The trains have level access between train and platform. At Lowestoft, I saw an electric wheelchair roll out of the train at a smart speed.
- These trains set the Gold Standard for step-free access.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see at least a minute and possibly two minutes saved at each station.
That would reduce the current journey time of one hour and thirty minutes between Lowestoft and Ipswich by perhaps ten minutes.
Level Crossings
Consider.
- Over the years, Greater Anglia and its predecessors right back teyond British Rail have been plagued by accidents at level crossings.
- Network Rail would like to close them all,
- But there are always a lot of local objections especially in rural counties like Suffolk.
- Removal is often expensive, as a new toad of several miles needs to be constructed.
I noticed perhaps ten crossings on my trip.
A big problem is that at many stations on the East Suffolk Line, there is a level crossing and it is often the only way to cross the line.
This Google Map shows Saxmundham station.
This is typical of the line. But here at Saxmundham, there is probably enough space to squeeze in a step-free bridge like this one, that won the Network Rail/RIBA Footbridge Design Competition.
There are lots of rural stations like Saxmundham in the country, so why should suburban stations get all the investment?
How long will it be before one of the new Class 755 trains hits a vehicle on an East Anglian level crossing?
Other Traffic
The only other trains that I saw on the route were Greater Anglia trains going the other way, which we passed in stations like Beccles and Saxmundham.
Checking on realtrimetrains.co.uk, there appears to have been no trains other than the Lowestoft and Ipswich service all day.
It appears that although parts of the route are only single track, that a well-designed timetable operated by well-trained and well-performing staff can provide a reliable hourly service.
Line Speed
I brought my personal dynamometer car with me and the train trundled along at a very easy and leisurely 55-60 mph, which is around the operating speed of the line of 55 mph.
Consider.
- The train gave me the impression, that all those 2,920 kW in the diesel engines could go a bit faster.
- The timetable was probably designed around a Class 156 train, which has just 425 kW per car, as opposed to the 730 kW per car of the Stadler train.
- I estimate that the Stadler train is about sixty percent heavier per car, but it does have a lot of electrical gubbins to carry around.
- The weight of the Stadler train does appear to be lighter per car than a Class 170 train.
I would expect that a well-driven Class 755 train has the power and speed to skip from station to station along the East Suffolk Line at several minutes faster than the timetable.
The line is 49 miles long and trains typically take 90 minutes between Lowestoft and Ipswich. That is an average speed of just under 33 mph.
The leg between Saxmundham and Darsham is just over four miles long and it takes nine minutes. This is an average speed of 27 mph.
Consider
- The acceleration of a Class 755 train is 0.9 m/s², which means to get up to a line speed of 60 mph takes thirty seconds.
- Four miles at 60 mph takes four minutes.
- Driver assistance software can tell the driver exactly where to start slowing for the next station.
It might be possible to do the Saxmundham and Darsham leg in perhaps three or four minutes less than the current timetable.
How much time could be saved on the whole route between Lowestoft and Ipswich?
Trains Needed
Look at a typical Off Peak pattern.
- An Off Peak train is the 1007 from Lowestoft, which arrives at Ipswich at 1136.
- This train returns from Ipswich at 1217, which arrives in Lowestoft at 1343.
- It then leaves Lowestoft for Ipswich at 1407.
The train takes four hours to do a round trip on the route, with forty-one minutes wait at Ipswich and twenty-four minutes wait at Lowestoft.
As trains are scheduled from Lowestoft at 1107, 1207 and 1307, four trains will be needed to provide the service.
This is very inefficient.
I feel that it is totally possible for the new trains to run between Lowestoft and Ipswich in around an hour and fifteen minutes, which would mean a saving of between one-two minutes on each leg of the journey.
Suppose though the trains could achieve this time, with an allowance of fifteen minutes to turn the trains at the two end stations.
This would mean that the round trip is now three hours and only three trains will be needed to provide the service.
The Possibility Of A Half-Hourly Service
The current timetable waits for awkward times in each of the end stations.
But my proposed hour and fifteen minute journey with a fifteen minute turnround could offer the possibility of a half-hourly service.
- Suppose two trains left Ipswich and Lowestoft at identical times on the hour.
- They would arrive at their destination an hour and fifteen minutes later at a quarter past the hour.
- By the half-hour, they would be ready to return to the other station.
- They would arrive back at the start at a quarter to the hour and fifteen minutes they would be ready to repeat the cycle.
The only problem would be to make sure all trains met each other at a place, where they could pass.
The half-hourly service would need six trains. or two more than the current service.
I don’t think that any major engineering works will be needed, although , there might be a need to adjust a passing loop or the signalling.
This is probably only one of many possibilities to provide a half-hourly services.
A Service Between Ipswich And Leiston And Aldeburgh
As I passed this branch the orange army was clearing the track of years of tree and other plant growth.
I’ve always thought that this would be a good idea and I wrote about it in A Station For Leiston.
- A half-hourly service would need two trains.
- It would add extra capacity between Ipswich and Saxmundham.
- It would certainly be needed if Sizewell C is built.
- Much of the route is double-track between Saxmundham and Ipswich.
It should also be noted that Sizewell has a high-capacity electricity grid connection and with the growtyh of offshore wind, Sizewell might be the ideal place for a large energy storage facility,
Cambridge And Lowestoft?
I took a train recently between Cambridge and Norwich and I noticed it went on to Cromer and Sheringham.
This was just Greater Anglia’s way of scheduling the trains for their convenience.
But could the same joining be done between these two services.
- Lowestoft and Ipswich
- Ipswich and Cambridge
It would do the following.
- Make better use of Platform 1 at Ipswich.
- Improve train utilisation.
- It might encourage day trippers to the coast to use the trains.
- It would improve the link from East Suffolk to Stabsted Airport.
- Create a comprehensive service, that connects all the major towns in Suffolk.
- It would connect these Suffolk towns; Lowestoft, Beccles, Saxmundham, Woodbridge, Ipswich, Needham Market, Stowmarket, Bury St. Edmund’s and Newnarket.
- It would serve the proposed A14 Parkway station.
- It would be an excellent feeder sewrvice for the East-West Rail Link.
It would be a true TransSuffolk railway.
Could There Be A Lowestoft And Great Yarmouth Service?
There has been talk of a new service between Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth stations.
There are two options to provide a service.
- Reinstatement of the Reedham Curve that was closed in 1880.
- By reversing the train in Reedham station.
I describe these options in Norfolk Rail Line To Remain Closed As £68m Upgrade Project Overruns.
As the second option does not need any extra infrastructure, I think it is more likely.
This was my conclusion about the route with a reverse.
Typical timings appear to be.
- Between Reedham and Yarmouth – 14-16 minutes
- Between Reedham and Lowestoft – 24-26 minutes
Given that the Class 755 trains have the following characteristics.
- They are 100 mph trains.
- They are optimised for fast stops.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see a sub-forty minute time between Lowestoft and Yarmouth.
It would appear that one train could run an hourly shuttle between Lowestoft and Great Yarmouth.
A Scenic Route Between Norwich And Ipswich
Using the current times between Ipswich and Lowestoft and Norwich and Yarmouth, it also looks like a sub-three hour scenic route is possible between Ipswich and Norwich.
It could be East Anglia’s version of the Cumbrian Coast Line.
Onboard Catering
The East Suffolk Line service currently takes ninety minutes.
I feel that this service is one that could benefit from a coffee service from a trolley.
The service could be provided by Greater Anglia or as on the Settle & Carlisle Line, by the local Community Rail Partnership.
Conclusion
The arrival of Class 755 trains on the East Suffolk Line could be the start of something special!